PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS*
|
|
|
- Hilary Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
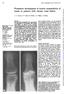
1 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 24, 522. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY B. A. CASTILLO, R. A. EL SALLAB, AND J. T. SCOTT Department of Medicine, Postgraduate Medical School, London It was noted by Bywaters (1964) that cystic changes in rheumatoid joints occur especially "in people who have little pain, strong muscles, and heavy jobs, so that they continue at work despite their rheumatoid arthritis, and the intermittently increased intraarticular pressure due to work drives synovial fluid into the bone marrow spaces in a similar way to that seen in degenerative joint disease, especially of the hip. Patients with many and large cysts usually give a history of never having lost a day's work." These patients retain a fair degree of bone calcification. Those whose limbs fall into disuse because of pain develop relatively shallow erosions and severe osteoporosis. The present study attempts to test this impression by examining the relation between these factors. * Presented at a meeting of the Heberden Society on February Methods Hand radiographs from 204 unselected hospital patients with rheumatoid arthritis were inspected; 51 were discarded because the radiological severity of the disease was not sufficient for the purpose of the study, and the 153 films finally examined and graded were all frompatientswhohadbeenfoundclinicallytohaveclassical or definite rheumatoid arthritis (A.R.A. criteria, Ropes, Bennett, Cobb, Jacox, and Jessar, 1959), the films themselves showing erosive changes of moderate or severe degree (Grades 3 and 4 as defined in "The Epidemiology of Chronic Rheumatism", C.l.O.M.S., 1963). Without knowledge of the patient's identity, all films were graded for degree of depth or cystic change shown by the erosions, the grades being I = slight, II = moderate, III = severe. Examples of each grade are shown in Fig. 1. As will be shown later, more advanced degrees of cystic change were seen in some radiographs than are present in Fig. 1 (c), but these three films are reproduced here because they were used as standards when assessing the others. Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 November Downloaded from Fig. 1.-Degrees of cystic change in rheumatoid erosions. (a) Grade I (Mild); (b) Grade 11 (Moderate); (c) Grade IIt (Severe). 522 on 7 October 2018 by guest. Protected by
2 OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS 523 The 153 radiographs were assessed separately for degree of cystic change and that of porosis (x2 = degree of osteoporosis, the same three grades (I = slight, 44 3; P = <0 001), i.e. films showing most evidence II = moderate, and III = severe) being used. of deep cystic erosions showed least porosis and The patients' hospital records were examined without knowledge of the radiological vice versa. It is true that the 32 films assessment and each showing only patient was graded for degree of physical activity: Grade I porosis were equally distributed among the three grades of cystic change; but, of the 39 showing Grade I: Incapacitated with very little use of hands. Grade II: Leading moderately active life but without Grade III porosis, 35 fell in Grade I of cystic change, strenuous use of hands. 4 in Grade II, and none in Grade III. Grade III: Leading very active life and using hands for hard manual work. (2) Cystic Changes and Physical Activity (Table This grading was made without difficulty in most 1).-This shows a significant positive relation cases. Details of each patient's D.A.T. (differential between the degrees of cystic change and physical agglutination titre: Rose, Ragan, Pearce, and Lipman, activity 1948) were abstracted at the same time, together with (X2 = 61 * 5; P = <0 001). Of the twenty information whether treatment with corticosteroid patients showing Grade III cystic erosions, fourteen hormones was being given were or not. performing Grade III physical activity, six The gradings for cystic change and for osteoporosis Grade II, and none Grade I. were compared with each other, and the gradings for each were compared with those for physical activity, sex, D.A.T., and steroid treatment. Results (1) Cystic Changes and Osteoporosis (Table 1). This shows a significant inverse relation between TABLE I RELATIONSHIP OF CYSTIC CHANGE TO OSTEOPOROSIS (3) Osteoporosis and Physical Activity (Table III).-There is a significant inverse relation between the grades of osteoporosis and physical activity (x2 = 68-0; P = <0 001), i.e. films showing most porosis tended to be those of patients undertaking least physical activity and vice versa.. (Mild) (Moderate) (Severe) Total I (Mild) II (Moderate) III (Severe) Total TABLE II RELATIONSHIP OF CYSTIC CHANGE TO ACTIVITY OF PATIENT Grade of Physical Activity (Low) (Moderate) (High) Total I (Mild) II (Moderate) III (Severe) Total TABLE III RELATIONSHIP OF OSTEOPOROSIS TO ACTIVITY OF PATIENT Grade of Physical Activity I II (Low) (Moderate) (High) IIIToa Total I (Mild) li (Moderate) III (Severe) Total
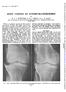
3 524 (4) Physical Activity, Cystic Erosions, Osteoporosis, and Sex (Tables IV, V, and VI).-In the lowest grade of physical activity (Grade I) there was a preponderence of women, and in the highest grade (Grade III) a preponderance of men (Table IV: 2 = 23 96; P = <0001). TABLE IV RELATIONSHIP OF SEX TO PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Grade of Physical Activity ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES Sex Male Female Total I (Low) II (Moderate) III (High) Total There was a corresponding majority of men in those showing Grade III cystic changes (Table V: x= 32-29; P = <0001). TABLE V RELATIONSHIP OF SEX TO GRADE OF CYSTIC CHANGE Sex Male Female Total I (Mild) II (Moderate) III (Severe) Total There was a majority of women in all three grades of osteoporosis, but this was much greater in Grade III than in Grades I and II (Table VI: X2 = 9 95; 0-01> P >0-001). TABLE VI RELATIONSHIP OF SEX TO GRADE OF OSTEOPOROSIS Sex Male Female Total I (Mild) II (Moderate) III (Severe) Total (5) Cystic Erosions and Corticosteroid Treatment (Table VII).-Corticosteroid treatment usually consisted of prednisolone in a dosage of between 5 and 10 mg. daily. Of the twenty patients with Grade III cystic changes, four were taking steroids and sixteen were not, a lower ratio than in Grades I and II. These numbers, however, are not statistically significant (X2 = 217; 0O5> P >0O3). TABLE VII RELATIONSHIP OF CYSTIC CHANGE TO STEROID TREATMENT Treatment With Without Total Steroids Steroids I (Mild) (Moderate) III (Severe) Total (6) Osteoporosis and Corticosteroid Treatment (Table VIII).-Although again the figures do not achieve statistical significance (X2 = 4-15; 0-2> P >0 1), the proportions of patients found to be on steroid treatment rose with increasing severity of osteoporosis. TABLE VIII RELATIONSHIP OF OSTEOPOROSIS TO STEROID TREATMENT Treatment With Without Tot Steroids Steroids I (Mild) II (Moderate) III (Severe) Total (7) Cystic Erosions, Osteoporosis, and D.A.T. D.A.T. results were taken from only 149 patients because they were discrepant in the other four. There was no relation between D.A.T. and cystic erosions (X2 = 2-3; 0-5> P >0<3) or osteoporosis (X2 = 1*46; 0 5> P >03). Discussion It is clear that large cystic erosions of the hands in rheumatoid arthritis are related to the individual's physical activity. They probably occur as a result of raised intra-articular pressure forcing synovial fluid or granulation tissue deeply into the substance of medullary bone. Erosions of this sort can form in any of the joints of the hands or wrist. They are seen most often in the metacarpophalangeal joints, especially the second and third, the metacarpal head being involved more frequently than the base of the proximal phalanx (Fig. 2). Similar but smaller erosions occur in the interphalangeal joints. They are also seen in the carpus and wrist, especially at the carpal surfaces of the radius and ulna, and at the inferior radio-ulnar articulation (Fig. 3).
4 OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS 4 (b) Fig. 2.-Metacarpophalangeal joints from (a) a school teacher and (b) a railway porter, who had persisted at their work over many years despite severe rheumatoid disease. Fig. 3.-Carpal and wrist joints from (a) the railway porter seen in Fig. 2b, and (b) a truck driver, showing cystic erosions in the carpal bones and in the lower end of the radius and ulna. Large cystic erosions are seen in joints other than the hands and wrists, particularly in the knees. Fig. 4 shows, for example, a radiograph of the right knee from a man aged 50, whose job as a television engineer involved a good deal of kneeling, in which he persisted, despite severe rheumatoid arthritis. Caughey and Bywaters (1963) showed that, in kneejoints containing small quantities of fluid, the mean pressures at rest lie between 6 and 33 mm. Hg, rising with muscle contraction and weight-bearing. Dixon and Grant (1964) obtained pressures of over 1,000 mm. Hg during weight-bearing flexion of the knees. Comparable studies in the joints of the hand and wrist have not been carried out, but one must suppose that intra-articular pressure in these joints during active hand movements such as Fig. 4.-Lateral radiograph of the knee of a television engineer with gripping and grasping rises in a similar way. rheumatoid arthritis, showing very large cystic erosions. 525
5 526 The inverse relationship between osteoporosis and physical activity observed in this study requires little comment. Disuse osteoporosis is well known to occur in many local and general situations: mechanical strain appears to be a normal stimulus to osteoblastic activity. The fact that most subjects performing the highest grade of manual activity were men accords with the finding that large cystic erosions are a mainly male characteristic and severe osteoporosis a mainly female one. There was some association of corticosteroid therapy with less pronounced cystic changes and with greater osteoporosis in the hands. Even if this is a valid relationship (and the figures obtained were not statistically significant) the association is probably one of incapacitating disease and consequent corticosteroid therapy rather than one of immediate cause and effect of steroids themselves; although the direct action of these drugs in producing osteoporosis may have played some part. Summary ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES An analysis of the hand radiographs from 153 patients with rheumatoid arthritis led to the conclusion that there is a close relationship between the degree of physical activity and the development of large cystic erosions. These two factors are inversely related to osteoporosis. Cystic erosions are seen more often in men, who perform higher grades of manual activity than women. REFERENCES Bywaters, E. G. L. (1964). "The Hand", In "Radiological Aspects of Rheumatoid Arthritis", edited by M. E. Carter [Int. Congr. Ser. No. 61], p. 43. Excerpta Medica Foundation, Amsterdam. Caughey, D. E., and Bywaters, E. G. L. (1963). Ann. rheum. Dis., 22, 106. Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences (1963). "The Epidemiology of Chronic Rheumatism", vol. 2, "Atlas of Standard Radiographs of Arthritis", prepared by the Department of Rheumatology and Medical Illustration, University of Manchester, and Manchester Royal Infirmary, and the Empire Rheumatism Council's Field Unit. Blackwell, Oxford. Dixon, A. St. J., and Grant, C. (1964). Lancet, 1, 742. Ropes, M. W., Bennett, G. A., Cobb, S., Jacox, R., and Jessar, R. A. (1959). Ann. rheum. Dis., 18, 49. Rose, H. M., Ragan, C., Pearce, E., and Lipman, H. 0. (1948). Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.), 68, 1. Discussion DR. J. LAWRENCE (Manchester): In our population surveys we found that a good many x rays showed bone cysts, though most of them were smaller than those shown by Dr. Scott. They were mostly in the metacarpophalangeal joints and in the region of the wrist joint, and there was some doubt regarding their significance. They were obviously quite often present in joints showing evidence of osteo-arthrosis or rheumatoid arthritis, but the great majority were found in the region of joints which showed no evidence of disease at all. We tried to correlate their presence with clinical rheumatoid arthritis but found no relationship whatsoever. They were more common in males and were found most often in heavy manual workers such as miners. It does seem that in those without arthritis there is the same relationship to heavy manual work. DR. ScorT: That is interesting. One would suppose that in rheumatoid arthritis the development of these deep erosions depends on articular cartilage no longer being intact, so that fluid and granulation tissue is driven into the bone. It is rather difficult to understand why they should be found in patients without joint disease. DR. LAWRENCE: Yes, unless minor injury has caused a small lesion. DR. J. J. R. DUTHIE (Edinburgh): Were any biopsies carried out on these joints? Dr. Cruickshank did some and found them full of granulation tissue. DR. ScoTr: No, but Professor Bywaters once examined some autopsy specimens and I think found both fluid and granulation tissue in these cysts. In our arteriographic studies we have seen them fill with a hyperaemic blush, confirming that they may contain granulation tissue. DR. A. ST. J. DIXON (London): I should very much like to see the French word geode used for these cysts. This term can be applied to osteo-arthritis, gout, and rheumatoid arthritis. When joint pressure rises the hypertrophic synovial tissue which is part of the contents of the joint is subjected to the same pressures. The geode acts as a kind of filter and cells and debris are left behind. DR. D. A. H. YAmS (London): Should we advise our patients to use their rheumatoid hands as actively as possible? DR. SCOTr: I feel sure that this whole question is related to the patient's pain threshold. In general, patients with these large cystic erosions do better than the others and manage to continue with their activities. This is because of their own attitude and not because of any particular treatment they are receiving. DR. G. D. KERSLEY (Bath): In our study of tomograms we found that there was often quite a large opening from these cysts into the joint surface, although on plain x ray they appeared entirely cystic.
6 OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS 527 L'activitk physique, les erosions cystiques et l'ost6oporose La actividad fisica, las erosiones cisticas y la osteoporosis en la artritis reumatoide dans I'arthrite rhumatismale RISUMit SUMARIO Une analyse des radiographies des mains de 153 Un analisis de radiografias de las manos de 153 malades atteints d'arthrite rhumatismale mene a la enfermos con artritis reumatoide ileva a la conclusi6n conclusion qu'il existe un rapport etroit entre l'intensite de de que existe una relaci6n estrecha entre la intensidad de l'activit6 physique et le developpement de grandes la actividad fisica y el desarrollo de grandes erosiones erosions cystiques. Ces deux facteurs se trouvent en cisticas. Estos dos factores estan inversamente relacionrapport inverse de l'osteoporose. Des erosions cystiques ados con la osteoporosis. Las erosiones cisticas se ven se voient plus souvent chez des hommes dont l'activite mas frecuentemente en los hombres cuya actividad manuelle est plus grande que celle des femmes. manual es mas intensa que la de las mujeres. Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 November Downloaded from on 7 October 2018 by guest. Protected by
PREVALENCE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961),, 11. PREVALENCE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. S. LAWRENCE From the Empire Rheumatism Council Field Unit, based on the University of Manchester In 1956, a committee of the American
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961),, 11. PREVALENCE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. S. LAWRENCE From the Empire Rheumatism Council Field Unit, based on the University of Manchester In 1956, a committee of the American
development of erosive osteoarthritis?
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
SYNOVIAL RUPTURE OF THE ELBOW JOINT
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1968), 27, 604 SYNOVIAL RUPTURE OF THE ELBOW JOINT J. D. GOODE Rheumatism Research Wing, Department of Experimental Pathology, Acute synovial rupture in rheumatoid arthritis was first
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1968), 27, 604 SYNOVIAL RUPTURE OF THE ELBOW JOINT J. D. GOODE Rheumatism Research Wing, Department of Experimental Pathology, Acute synovial rupture in rheumatoid arthritis was first
CAPILLARY RESISTANCE AND SKIN-FOLD THICKNESS IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS EFFECT OF CORTICOSTEROID THERAPY
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1966), 25, 272. CAPILLARY RESISTANCE AND SKIN-FOLD THICKNESS IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS EFFECT OF CORTICOSTEROID THERAPY BY B. M. GREENWOOD Postgraduate Medical School, London
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1966), 25, 272. CAPILLARY RESISTANCE AND SKIN-FOLD THICKNESS IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS EFFECT OF CORTICOSTEROID THERAPY BY B. M. GREENWOOD Postgraduate Medical School, London
Straingauge plethysmography in the
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 194 Straingauge plethysmography in the assessment of joint inflammation I. VADASZ Department of Physical Medicine and Rheumatology, Guy's Hospital, London The quantitation of
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 194 Straingauge plethysmography in the assessment of joint inflammation I. VADASZ Department of Physical Medicine and Rheumatology, Guy's Hospital, London The quantitation of
taken at narrower intervals. Some subjects were unable
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 401 Intra-articular pressure in arthritis of the knee Ill. Pressure changes during joint use rheumatoid M. I. V. JAYSON*L AND A. ST. J. DIXON* From the Royal National Hospital
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 401 Intra-articular pressure in arthritis of the knee Ill. Pressure changes during joint use rheumatoid M. I. V. JAYSON*L AND A. ST. J. DIXON* From the Royal National Hospital
Rheumatoid factor tests in the diagnosis and prediction of rheumatoid arthritis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 684-69 Rheumatoid factor tests in the diagnosis and prediction of rheumatoid arthritis D J WALKER,' J D POUND,2 I D GRIFFITHS,' AND R J POWELL2 From the 'Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 684-69 Rheumatoid factor tests in the diagnosis and prediction of rheumatoid arthritis D J WALKER,' J D POUND,2 I D GRIFFITHS,' AND R J POWELL2 From the 'Department
FAMILIAL INCIDENCE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1959), 18, 279. FAMILIAL INCIDENCE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY JOAN M. BREMNER, W. R. M. ALEXANDER, AND J. J. R. DUTHIE Rheumatic Diseases Unit, Northern General Hospital, Edinburgh Several
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1959), 18, 279. FAMILIAL INCIDENCE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY JOAN M. BREMNER, W. R. M. ALEXANDER, AND J. J. R. DUTHIE Rheumatic Diseases Unit, Northern General Hospital, Edinburgh Several
ARTHRITIS* x rays of the cervical spine from patients with. with similar films from a control population.
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 50. CERVICAL SPINE IN PSORIASIS AND IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS* BY DAVID KAPLAN, CHARLES M. PLOTZ, LOUIS NATHANSON, AND LAWRENCE FRANK From the Downstate Medical Center, State
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 50. CERVICAL SPINE IN PSORIASIS AND IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS* BY DAVID KAPLAN, CHARLES M. PLOTZ, LOUIS NATHANSON, AND LAWRENCE FRANK From the Downstate Medical Center, State
INDICATIONS FOR SURGICAL INTERVENTION IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE WRIST AND HAND
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1959), 18, 29. INDICATIONS FOR SURGICAL INTERVENTION IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE WRIST AND HAND The problems of prolonged disability and pain in the wrist and hand resulting from rheumatoid
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1959), 18, 29. INDICATIONS FOR SURGICAL INTERVENTION IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE WRIST AND HAND The problems of prolonged disability and pain in the wrist and hand resulting from rheumatoid
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE FEVER OF STILL'S DISEASE AND THAT OF RHEUMATIC FEVER
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1959), 18, 293. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE FEVER OF STILL'S DISEASE AND THAT OF RHEUMATIC FEVER BY F. J. McMINN AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Rheumatism Research Unit (M.R.C.), Canadian
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1959), 18, 293. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE FEVER OF STILL'S DISEASE AND THAT OF RHEUMATIC FEVER BY F. J. McMINN AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Rheumatism Research Unit (M.R.C.), Canadian
At least one slide latex test was performed on all 65. of them. there were more male cases but after 30 years the. female cases predominated (Fig. 1).
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
ACUTE SYNOVIAL RUPTURE
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 25, 273. ACUTE SYNOVIAL RUPTURE FURTHER OBSERVATIONS BY G. B. W. TAIT, F. BACH, AND A. ST. J. DIXON From St. Stephen's Hospital, Chelsea, and St. Mary Abbot's Hospital, Kensington
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 25, 273. ACUTE SYNOVIAL RUPTURE FURTHER OBSERVATIONS BY G. B. W. TAIT, F. BACH, AND A. ST. J. DIXON From St. Stephen's Hospital, Chelsea, and St. Mary Abbot's Hospital, Kensington
Wrist cysts and fistulae
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 388 Wrist cysts and fistulae An arthrographic study of the rheumatoid wrist* J. M. I. IVESON, A. G. S. HILL, AND V. WRIGHT From the Department of Rheumatology, General Infirmary
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 388 Wrist cysts and fistulae An arthrographic study of the rheumatoid wrist* J. M. I. IVESON, A. G. S. HILL, AND V. WRIGHT From the Department of Rheumatology, General Infirmary
HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE
 ORIGINAL PAPER HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE A CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL BY J. A. KIRK AND G. D. KERSLEY Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Bath
ORIGINAL PAPER HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE A CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL BY J. A. KIRK AND G. D. KERSLEY Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Bath
CREATINE METABOLISM IN ARTHRITIS
 CREATINE METABOLISM IN ARTHRITIS BY J. EUAN DAWSON and HAROLD B. SALT Highfield Hospital, Droitwich, and the Biochemical Laboratory, Royal Infirmary, Worcester (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER 28, 195
CREATINE METABOLISM IN ARTHRITIS BY J. EUAN DAWSON and HAROLD B. SALT Highfield Hospital, Droitwich, and the Biochemical Laboratory, Royal Infirmary, Worcester (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER 28, 195
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
SERUM AND SYNOVIAL FLUID PROTEINS IN ARTHRITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 51. SERUM AND SYNOVIAL FLUID PROTEINS IN ARTHRITIS BY MATTHEW WILKINSON AND BRIAN S. JONES From the Clinical Research Department, Charing Cross Hospital, and the Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 51. SERUM AND SYNOVIAL FLUID PROTEINS IN ARTHRITIS BY MATTHEW WILKINSON AND BRIAN S. JONES From the Clinical Research Department, Charing Cross Hospital, and the Department
INTRA-CUTANEOUS CONGO RED IN RHEUMATOID
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1957), 16, 225. INTRA-CUTANEOUS CONGO RED IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY F. T. SHANNON, W. J. FESSEL, AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Special Unit for the Study and Care ofjuvenile Rheumatism,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1957), 16, 225. INTRA-CUTANEOUS CONGO RED IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY F. T. SHANNON, W. J. FESSEL, AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Special Unit for the Study and Care ofjuvenile Rheumatism,
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB FINGERS (2nd 5th) - PA Projection Patient Position: Seated; hand ; elbow on IR table top Part Position: Fingers centered to IR unless protocol is Central Ray: Perpendicular
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE HAND, FINGERS & THUMB FINGERS (2nd 5th) - PA Projection Patient Position: Seated; hand ; elbow on IR table top Part Position: Fingers centered to IR unless protocol is Central Ray: Perpendicular
in the 77 adults suffering from rheumatoid arthritis ranged from 22 to 79 years (mean 52) and in the 23 with juvenile
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (972), 3, 364 Cervical spine involvement in patients with chronic undergoing orthopaedic surgery E. ORNILLA, B. M. ANSELL, AND A. J. SWANNELL MRC Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red
Ann. rheum. Dis. (972), 3, 364 Cervical spine involvement in patients with chronic undergoing orthopaedic surgery E. ORNILLA, B. M. ANSELL, AND A. J. SWANNELL MRC Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red
SACRO-ILIAC JOINT IN ADULT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND PSORIATIC ARTHROPATHY*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961),, 47. SACRO-LAC JONT N ADULT RHEUMATOD ARTHRTS AND PSORATC ARTHROPATHY* BY A. ST. J. DXON AND E. LENCE Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital, London Sacro-iliitis is
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961),, 47. SACRO-LAC JONT N ADULT RHEUMATOD ARTHRTS AND PSORATC ARTHROPATHY* BY A. ST. J. DXON AND E. LENCE Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital, London Sacro-iliitis is
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
CONCOMITANT INVOLVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER JOINTS BY PROLIFERATIVE AND DEGENERATIVE ARTHRITIS
 CONCOMITANT INVOLVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER JOINTS BY PROLIFERATIVE AND DEGENERATIVE ARTHRITIS BY ROBERT H. RAMSEY From the Departments of Surgery and Surgical Pathology (Dr. Lauren V. Ackerman), Washington
CONCOMITANT INVOLVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER JOINTS BY PROLIFERATIVE AND DEGENERATIVE ARTHRITIS BY ROBERT H. RAMSEY From the Departments of Surgery and Surgical Pathology (Dr. Lauren V. Ackerman), Washington
OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT
 375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
TOMOGRAPHY OF THE SACRO-ILIAC JOINTS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1966), 25, 433 TOMOGRAPHY OF THE SACRO-ILIAC JOINTS BY M. WILKINSON AND J. A. K. MEIKLE From the Bridge ofearn Hospital, Perthshire Because of their situation the sacro-iliac joints have
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1966), 25, 433 TOMOGRAPHY OF THE SACRO-ILIAC JOINTS BY M. WILKINSON AND J. A. K. MEIKLE From the Bridge ofearn Hospital, Perthshire Because of their situation the sacro-iliac joints have
The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint
 i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
i23 The EULAR OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint B Ejbjerg, F McQueen, M Lassere, E Haavardsholm, P Conaghan, P O Connor, P Bird, C Peterfy, J Edmonds, M Szkudlarek,
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Arthritis and Crohn's disease
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 479 Arthritis and Crohn's disease A family study IAN HASLOCK* From the Rheumatism Research Unit, Department ofmedicine, University ofleeds, and the General Infirmary at Leeds
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 479 Arthritis and Crohn's disease A family study IAN HASLOCK* From the Rheumatism Research Unit, Department ofmedicine, University ofleeds, and the General Infirmary at Leeds
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
hands in patients with chronic renal failure
 378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
THE RELATIONSHIP OF RHEUMATOID SERUM FACTOR TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1963), 22, 311. THE RELATIONSHIP OF RHEUMATOID SERUM FACTOR TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS A 5-YEAR FOLLOW UP OF A POPULATION SAMPLE BY J. BALL AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Rheumatism Research
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1963), 22, 311. THE RELATIONSHIP OF RHEUMATOID SERUM FACTOR TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS A 5-YEAR FOLLOW UP OF A POPULATION SAMPLE BY J. BALL AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Rheumatism Research
Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
PARAFFIN-WAX BATHS IN THE TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1955), 14, 278. PARAFFIN-WAX BATHS IN THE TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY R. HARRIS AND J. B. MILLARD From the Department ofphysical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Devonshire Royal
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1955), 14, 278. PARAFFIN-WAX BATHS IN THE TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY R. HARRIS AND J. B. MILLARD From the Department ofphysical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Devonshire Royal
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE LUMBAR SPINE
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 205. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE LUMBAR SPINE BY J. S. LAWRENCE, J. SHARP*, J. BALL, AND FRIDA BIER From the Rheumatism Research Centre and the Empire Rheumatism Council Field
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 205. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE LUMBAR SPINE BY J. S. LAWRENCE, J. SHARP*, J. BALL, AND FRIDA BIER From the Rheumatism Research Centre and the Empire Rheumatism Council Field
Rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 403 Rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow Pattern of joint involvement, and results of synovectomy with excision of the radial head H. STEIN, R. A. DICKSON, AND G. BENTLEY From
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 403 Rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow Pattern of joint involvement, and results of synovectomy with excision of the radial head H. STEIN, R. A. DICKSON, AND G. BENTLEY From
Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
The New Science of Osteoarthritis
 The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
Dynamic Splinting of the
 Dynamic Splinting of the Rheumatoid Hand BY F. RICHARD CONVERY, M.D.,* J. PIERCE CONATY, M.D.** AND VERNON L. NICKEL, M.D.** Rancho Los Amigos Hospital, Downey, California (University of Southern California
Dynamic Splinting of the Rheumatoid Hand BY F. RICHARD CONVERY, M.D.,* J. PIERCE CONATY, M.D.** AND VERNON L. NICKEL, M.D.** Rancho Los Amigos Hospital, Downey, California (University of Southern California
Carpal instability in rheumatoid arthritis and
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 311-318 Carpal instability in rheumatoid arthritis and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease Pathogenesis and roentgen appearance D. RESNICK AND G. NIWAYAMA
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 311-318 Carpal instability in rheumatoid arthritis and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease Pathogenesis and roentgen appearance D. RESNICK AND G. NIWAYAMA
Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Hughes, Jordan, and Hill, 1949) was designed to introduce substances under pressure either subcutaneously
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1956), 15, 227. USE OF THE HYPOSPRAY JET INJECTOR FOR THE INTRA-ARTICULAR AND LOCAL ADMINISTRATION OF HYDROCORTISONE ACETATE* MORRIS ZIFFt, VINCENT CONTRERAS, AND FRANK R. BY From the
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1956), 15, 227. USE OF THE HYPOSPRAY JET INJECTOR FOR THE INTRA-ARTICULAR AND LOCAL ADMINISTRATION OF HYDROCORTISONE ACETATE* MORRIS ZIFFt, VINCENT CONTRERAS, AND FRANK R. BY From the
Inflammatory joint disease: a comparison of liposome
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 485-491 Inflammatory joint disease: a comparison of liposome scanning, bone scanning, and radiography M M O'SULLIVAN,' N POWELL,- A P FRENCH, K E WILLIAMS,4
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 485-491 Inflammatory joint disease: a comparison of liposome scanning, bone scanning, and radiography M M O'SULLIVAN,' N POWELL,- A P FRENCH, K E WILLIAMS,4
FEMORAL HEAD DESTRUCTION IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND OSTEO-ARTHRITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 23. FEMORAL HEAD DESTRUCTION IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND OSTEO-ARTHRITIS A CLINICAL REVIEFW OF 27 CASES Since 1951, intra-articular hydrocortisone has been used in the treatment
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 23. FEMORAL HEAD DESTRUCTION IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND OSTEO-ARTHRITIS A CLINICAL REVIEFW OF 27 CASES Since 1951, intra-articular hydrocortisone has been used in the treatment
Chapter 09 Articulations Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
CARPAL ANKYLOSIS IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 125 1 CARPAL ANKYLOSIS IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS JOSE A. MALDONADO-COCCO, OSVALDO GARCIA-MORTEO, ALBERT0 J. SPINDLER, OSVALDO HUBSCHER. and SUSANA GAGLIARDI Forty-seven of 100 consecutive juvenile
125 1 CARPAL ANKYLOSIS IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS JOSE A. MALDONADO-COCCO, OSVALDO GARCIA-MORTEO, ALBERT0 J. SPINDLER, OSVALDO HUBSCHER. and SUSANA GAGLIARDI Forty-seven of 100 consecutive juvenile
HEMIPLEGIA. 15 months after the operation (in June, 1950) the patient. one of us at the Hammersmith Hospital in September,
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 370. UNILATERAL RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS FOLLOWING HEMIPLEGIA BY MALCOLM THOMPSON AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle-on-Tyne, and the Postgraduate
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 370. UNILATERAL RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS FOLLOWING HEMIPLEGIA BY MALCOLM THOMPSON AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle-on-Tyne, and the Postgraduate
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
SMOKING HABITS RELATED TO INJURY AND
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (196), 14, 57 SMOKING HABITS RELATED TO INJURY AND ABSENTEEISM IN INDUSTRY BY C. R. LOWE From the Department of Social Medicine, University of Birmingham In February, 1957, a mass
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (196), 14, 57 SMOKING HABITS RELATED TO INJURY AND ABSENTEEISM IN INDUSTRY BY C. R. LOWE From the Department of Social Medicine, University of Birmingham In February, 1957, a mass
JOINT LESIONS OF HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1963), 22, 171. JOINT LESIONS O HYPERPARATHYROIDISM BY E. G. L. BYWATERS, A. ST. J. DIXON, AND J. T. SCOTT rom the Postgraduate Medical School of London and the M.R.C. Rheumatism Research
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1963), 22, 171. JOINT LESIONS O HYPERPARATHYROIDISM BY E. G. L. BYWATERS, A. ST. J. DIXON, AND J. T. SCOTT rom the Postgraduate Medical School of London and the M.R.C. Rheumatism Research
HYPERTROPHIC OSTEO-ARTHROPATHY IN POLYARTERITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1956), 15, 46. HYPERTROPHIC OSTEO-ARTHROPATHY IN POLYARTERITIS BY R. R. H. LOVELL AND G. B. D. SCOTT From the Medical Unit and Department of Morbid Anatomy, St. Mary's Hospital, Paddington
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1956), 15, 46. HYPERTROPHIC OSTEO-ARTHROPATHY IN POLYARTERITIS BY R. R. H. LOVELL AND G. B. D. SCOTT From the Medical Unit and Department of Morbid Anatomy, St. Mary's Hospital, Paddington
VISCOSITY OF HYALURONIC ACID IN SYNOVIAL FLUIDS OF PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATIC DISEASES*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 152. STUDIES ON THE CONCENTRATION AND INTRINSIC VISCOSITY OF HYALURONIC ACID IN SYNOVIAL FLUIDS OF PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATIC DISEASES* BY CHESTER T. STAFFORD, WILLIAM NIEDERMEIER,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 152. STUDIES ON THE CONCENTRATION AND INTRINSIC VISCOSITY OF HYALURONIC ACID IN SYNOVIAL FLUIDS OF PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATIC DISEASES* BY CHESTER T. STAFFORD, WILLIAM NIEDERMEIER,
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE. Opinion. 29 November 2006
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 29 November 2006 HEXATRIONE 2% suspension for injection (intra-articular) Box containing one 2-ml vial - CIP code:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 29 November 2006 HEXATRIONE 2% suspension for injection (intra-articular) Box containing one 2-ml vial - CIP code:
Synovial giant cells in rheumatoid arthritis
 Aniii. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 94 Synovial giant cells in rheumatoid arthritis and other joint diseases A. K. BHAN AND S. ROY Department of Pathology, All-India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Dellhi-
Aniii. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 94 Synovial giant cells in rheumatoid arthritis and other joint diseases A. K. BHAN AND S. ROY Department of Pathology, All-India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Dellhi-
I-A-1) Non-specific thickening of synovial membrane
 I-A-1) Non-specific thickening of synovial membrane Grayscale Metatarsal Power Doppler Dorsal aspect of metatarsophalangeal joint in right 1 st toe, longitudinal view Asterisks indicate non-specific thickening
I-A-1) Non-specific thickening of synovial membrane Grayscale Metatarsal Power Doppler Dorsal aspect of metatarsophalangeal joint in right 1 st toe, longitudinal view Asterisks indicate non-specific thickening
Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers. Workbook 11 The articular system
 NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 11 The articular system Contents Workbook 11 The articular system 1 11.1 Aim 3 11.2 Learning outcomes 3 11.3 The articular system 4 11.4 Individual
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 11 The articular system Contents Workbook 11 The articular system 1 11.1 Aim 3 11.2 Learning outcomes 3 11.3 The articular system 4 11.4 Individual
ULNAR DEVIATION OF THE FINGERS
 ULNAR DEVIATION OF THE FINGERS GEORGE R. BY New York, FEARNLEY Ulnar deviation of the fingers at their metacarpophalangeal joints is perhaps the most characteristic deformity of rheumatoid arthritis. Nineteenth-century
ULNAR DEVIATION OF THE FINGERS GEORGE R. BY New York, FEARNLEY Ulnar deviation of the fingers at their metacarpophalangeal joints is perhaps the most characteristic deformity of rheumatoid arthritis. Nineteenth-century
Department of Orthopaedics, Glasgow Royal Infirmary.
 Brit J. Sports Med. - Vol. 14, Nos. 2 & 3, August 1980, pp. 97-101 DEGENERATIVE DISEASE IN WEIGHT-LIFTERS FACTOR FICTION? B. FITZGERALD, FRCS (G). and G. R. MOLATCHIE, FRCS (G)., Department of Orthopaedics,
Brit J. Sports Med. - Vol. 14, Nos. 2 & 3, August 1980, pp. 97-101 DEGENERATIVE DISEASE IN WEIGHT-LIFTERS FACTOR FICTION? B. FITZGERALD, FRCS (G). and G. R. MOLATCHIE, FRCS (G)., Department of Orthopaedics,
ARTHRITIS RADIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC SKELETAL HYPEROSTOSTS
 ARTHRITIS 82 RHEUMATISM OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCiA I ION SECTION OF THE ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION 1 RADIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC
ARTHRITIS 82 RHEUMATISM OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCiA I ION SECTION OF THE ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION 1 RADIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC
EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF ARTHRITIS OF THE HAND CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF SWOLLEN PAINFUL HANDS IN WOMEN OVER 40 YEARS OF AGE
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1960), 19, 229. EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF ARTHRITIS OF THE HAND CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF SWOLLEN PAINFUL HANDS IN WOMEN OVER 40 YEARS OF AGE BY E. A. KAUFFMANN* AND R. FINLAYSONt From the
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1960), 19, 229. EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF ARTHRITIS OF THE HAND CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF SWOLLEN PAINFUL HANDS IN WOMEN OVER 40 YEARS OF AGE BY E. A. KAUFFMANN* AND R. FINLAYSONt From the
NAIL STUDIES IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1960), 19, 167. NAIL STUDIES IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY E. B. D. HAMILTON Rheumatism Research Unit, Medical Research Council, Canadian Red Cross Memorial Hospital, Taplow, Bucks Nail
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1960), 19, 167. NAIL STUDIES IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY E. B. D. HAMILTON Rheumatism Research Unit, Medical Research Council, Canadian Red Cross Memorial Hospital, Taplow, Bucks Nail
Department of Plastic Surgery, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Australia
 ARTICULAR CARTILAGE LOSS IN LONG-STANDING IMMOBILISATION OF INTERPHALANGEAL JOINTS By P. L. FIELD, F.R.C.S., and J. T. HUESTON,/Vi.S., F.R.C.S., F.R.A.C.S. Department of Plastic Surgery, Royal Melbourne
ARTICULAR CARTILAGE LOSS IN LONG-STANDING IMMOBILISATION OF INTERPHALANGEAL JOINTS By P. L. FIELD, F.R.C.S., and J. T. HUESTON,/Vi.S., F.R.C.S., F.R.A.C.S. Department of Plastic Surgery, Royal Melbourne
TREATMENT OF THE POPLITEAL CYST IN THE RHEUMATOID KNEE. A recent report on the surgical treatment of a popliteal cyst in a patient with rheumatoid
 TREATMENT OF THE POPLITEAL CYST IN THE RHEUMATOID KNEE I. M. PINDER, BATH, SOMERSET From the Bath and Wessex Orthopaedic Hospital, Bath A recent report on the surgical treatment of a popliteal cyst in
TREATMENT OF THE POPLITEAL CYST IN THE RHEUMATOID KNEE I. M. PINDER, BATH, SOMERSET From the Bath and Wessex Orthopaedic Hospital, Bath A recent report on the surgical treatment of a popliteal cyst in
Extensor expansion of the rheumatoid hand
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31,112 Extensor expansion of the rheumatoid hand K. M. BACKHOUSE From the Royal College ofsurgeons ofengland, the Chielsea and Kensington Rheumatology Unit, and the Royal London
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31,112 Extensor expansion of the rheumatoid hand K. M. BACKHOUSE From the Royal College ofsurgeons ofengland, the Chielsea and Kensington Rheumatology Unit, and the Royal London
Joints. Vi Michelle Austin
 Joints Vi Michelle Austin Joints Overview A joint, otherwise known as an articulation, is a point at which points connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull bones) and provide mechanical
Joints Vi Michelle Austin Joints Overview A joint, otherwise known as an articulation, is a point at which points connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull bones) and provide mechanical
predicts radiographic change
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE CERVICAL SPINE IN THE ADULT
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1958), 17,. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE CERVICAL SPINE IN THE ADULT BY J. SHARP, D. W. PURSER, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Departments ofrheumatism Research and Orthopaedic Surgery and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1958), 17,. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE CERVICAL SPINE IN THE ADULT BY J. SHARP, D. W. PURSER, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Departments ofrheumatism Research and Orthopaedic Surgery and
The hand radiograph as a diagnostic discriminant between seropositive and seronegative 'rheumatoid
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1983, 42, 605-612 The hand radiograph as a diagnostic discriminant between seropositive and seronegative 'rheumatoid arthritis': a controlled study THOMAS M. BURNS AND
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1983, 42, 605-612 The hand radiograph as a diagnostic discriminant between seropositive and seronegative 'rheumatoid arthritis': a controlled study THOMAS M. BURNS AND
V. WRIGHT. reflected by the recent publication of single cases. and small series (Carrier, 1958; Meaney and Hays,
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961), 20, 123. PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS A COMPARATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC STUDY OF RHEUMATOID ARTHR S AND ARTHRIS ASSOCIATED WITH PSORIASIS BY V. WRIGHT University Department of Clinical Medicine,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961), 20, 123. PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS A COMPARATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC STUDY OF RHEUMATOID ARTHR S AND ARTHRIS ASSOCIATED WITH PSORIASIS BY V. WRIGHT University Department of Clinical Medicine,
Synovial fluid Waaler-Rose and latex tests
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 67 Synovial fluid Waaler-Rose and latex tests E. C. HUSKISSON, F. DUDLEY HART, AND B. W. LACEY Westminster Hospital, London Positive serum Waaler-Rose and Latex tests provide
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 3, 67 Synovial fluid Waaler-Rose and latex tests E. C. HUSKISSON, F. DUDLEY HART, AND B. W. LACEY Westminster Hospital, London Positive serum Waaler-Rose and Latex tests provide
The Prevalence of Gout in Three English Towns
 International Journal of Epidemiology Oxford University Press 82 Vol. 11, No. 1 Printed in Great Britain The Prevalence of Gout in Three English Towns M J GARDNER*. C POWER". D J P BARKER* and R PADDAY*
International Journal of Epidemiology Oxford University Press 82 Vol. 11, No. 1 Printed in Great Britain The Prevalence of Gout in Three English Towns M J GARDNER*. C POWER". D J P BARKER* and R PADDAY*
Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement
 \>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
\>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
"EXPERIMENTAL ERROR " OF THERAPEUTIC TRIALS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 "EXPERIMENTAL ERROR " OF THERAPEUTIC TRIALS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY P. D. BEDFORD From Cowley Road Hospital, Oxford In trials of substances alleged to cause rapid improvement, or to have a cortisoneor
"EXPERIMENTAL ERROR " OF THERAPEUTIC TRIALS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY P. D. BEDFORD From Cowley Road Hospital, Oxford In trials of substances alleged to cause rapid improvement, or to have a cortisoneor
Osteoporosis. World Health Organisation
 Osteoporosis A systemic skeletal disease characterised by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue with subsequent increased risk of fracture. World Health Organisation Epidemiology
Osteoporosis A systemic skeletal disease characterised by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue with subsequent increased risk of fracture. World Health Organisation Epidemiology
IDIOPATHIC OSTEO-ARTHRITIS OF THE HIP
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 31. IDIOPATHIC OSTEO-ARTHRITIS OF THE HIP BY J. R. PEARSON AND D. M. RIDDELL The Robert Jones and Agnes Hunt Orthopaedic Hospital, Oswestry, Shropshire Recent work has been
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1962), 21, 31. IDIOPATHIC OSTEO-ARTHRITIS OF THE HIP BY J. R. PEARSON AND D. M. RIDDELL The Robert Jones and Agnes Hunt Orthopaedic Hospital, Oswestry, Shropshire Recent work has been
CHRONIC ABSORPTIVE ARTHRITIS OR OPERA-GLASS HAND:
 CHRONIC ABSORPTIVE ARTHRITIS OR OPERA-GLASS HAND: REPORT OF EIGHT CASES BY WALTER M. SOLOMON and ROBERT M. STECHER From the Department of Medicine, Western Reserve University City Hospital, Cleveland,
CHRONIC ABSORPTIVE ARTHRITIS OR OPERA-GLASS HAND: REPORT OF EIGHT CASES BY WALTER M. SOLOMON and ROBERT M. STECHER From the Department of Medicine, Western Reserve University City Hospital, Cleveland,
Relation between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A study of 40 patients
 2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
HEREDITARY FACTORS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961), 20, 215. HEREDITARY FACTORS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS BY J. J. DE BLECOURT, THE LATE A. POLMAN, AND T. DE BLJtCOURT-MEINDERSMA From the Department of Rheumatic
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1961), 20, 215. HEREDITARY FACTORS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS BY J. J. DE BLECOURT, THE LATE A. POLMAN, AND T. DE BLJtCOURT-MEINDERSMA From the Department of Rheumatic
CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. BONES AND JOINTS Structure and function of bone(skeleton): Bone is a strong and durable type of connective tissue. It consists
CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. BONES AND JOINTS Structure and function of bone(skeleton): Bone is a strong and durable type of connective tissue. It consists
Radioactive colloidal gold
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 159 Radioactive colloidal gold In chronic knee effusions with Baker's cyst formation R. GRAHAME,* N. W. RAMSEY, AND J. T. SCOTT From the Charing Cross Group of Hospitals and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 159 Radioactive colloidal gold In chronic knee effusions with Baker's cyst formation R. GRAHAME,* N. W. RAMSEY, AND J. T. SCOTT From the Charing Cross Group of Hospitals and
EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID ON RHEUMATOID SYNOVIAL FLUID*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 295. EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID ON RHEUMATOID SYNOVIAL FLUID* BY EMANUEL ABRAMS AND JOHN SANDSONt From the Department of Medicine, Albert Finstein College of Medicine, Bronx Municipal
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 295. EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID ON RHEUMATOID SYNOVIAL FLUID* BY EMANUEL ABRAMS AND JOHN SANDSONt From the Department of Medicine, Albert Finstein College of Medicine, Bronx Municipal
CLINICAL EXPERIENCE WITH IBUPROFEN IN THE
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1969), 28, 513 CLINICAL EXPERIENCE WITH IBUPROFEN IN THE TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY T. M. CHALMERS* Rheumatic Diseases Unit, Northern General Hospital, Edinburgh The search
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1969), 28, 513 CLINICAL EXPERIENCE WITH IBUPROFEN IN THE TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY T. M. CHALMERS* Rheumatic Diseases Unit, Northern General Hospital, Edinburgh The search
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 RA202 positioning class three- EXM Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following hand projections would be used
RA202 positioning class three- EXM Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following hand projections would be used
Types of Body Movements
 Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS
 INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS BY PAUL DIEPPE SUMMARY Osteoarthritis is usually regarded as a non-inflammatory disease. However, several authors have stressed the importance of an inflammatory phase early
INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS BY PAUL DIEPPE SUMMARY Osteoarthritis is usually regarded as a non-inflammatory disease. However, several authors have stressed the importance of an inflammatory phase early
Quantitative study of stiffness in the knee
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 286 Quantitative study of stiffness in the knee joint C. H. SUCH, A. UNSWORTH, V. WRGHT, AND D. DOWSON From the Bioengineering Group for the Study ofjoints, Leeds University
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 286 Quantitative study of stiffness in the knee joint C. H. SUCH, A. UNSWORTH, V. WRGHT, AND D. DOWSON From the Bioengineering Group for the Study ofjoints, Leeds University
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL
 LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
Know all the bones of the skull, lateral view and frontal view. From the worksheets, one of the earlier ones in this unit.
 Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
