many patients seen on secondary referral as normal results in the presence of what had been considered
|
|
|
- Hilary Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1983, 58, Articular hypermobility simulating chronic rheumatic disease R M LEWKONIA AND B M ANSELL Division of Rheumatology, Medical Research Council Clinical Research Centre, Northwick Park Hospital, Harrow SUMMARY A retrospective survey of 54 children with symptoms associated with articular hypermobility showed only occasional recognition of the syndrome before referral; some patients had been treated for inflammatory arthritis. Of the patients, 78 % were girls; their mean age at onset of symptoms (11 years) was 3 years older than the mean age of the boys. Hypermobility was localised rather than generalised in most patients, and this may be an important reason for the apparent under recognition of the syndrome. Articular hypermobility is a cardinal feature of many heritable disorders of connective tissues' and is associated with developmental orthopaedic disorders, most notably congenital dislocation of the hip.2 Kirk et al. drew attention to a syndrome of musculoskeletal complaints associated with hypermobile joints in otherwise normal subjects.3 Of that series of 24 patients, 75 % showed symptoms before the age of 16 years. Symptoms included arthralgia, joint swelling, and muscle cramps. Our retrospective survey of children with symptoms associated with hypermobility paid particular attention to features of the syndrome specific to childhood and reviewed the extent to which the syndrome had been recognised before referral. Patients and methods We reviewed the records of 42 girls and 12 boys aged 2 to 16 years who had been seen and examined by one of us (BMA) over a period of 6 years. They had all been referred to the Medical Research Council's Juvenile Rheumatism Unit at Taplow or the Division of Rheumatology at the Medical Research Council's Clinical Research Centre, Northwick Park. Patients with hypermobility and coincident inflammatory joint disease were not included. Articular mobility was assessed with the procedures described by Carter and Wilkinson.4 Features sought included hyperextension of the fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joints, apposition of the thumbs to the forearms, hyperextension of the elbows or knees beyond 100, and excessive mobility of the ankles (Figure). Unusual mobility of other joints found in the course of routine rheumatological examination was also noted. Height and weight were recorded on standard growth centile charts. Laboratory assays for indices of inflammatory joint disease were performed only if there were signs of possible synovitis. Laboratory tests were not necessary in many patients seen on secondary referral as normal results in the presence of what had been considered to be inflammatory joint disease were often the reason for referral. Results Sixty of our patients had Caucasian parents, one boy was Chinese, one boy had an Iranian father, and one girl had an Asian mother and a Caucasian father who had craniocleidodysostosis. Features of heritable disorders of connective tissue were sought, but only two patients had definite features of such diseases. The Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type III was diagnosed in a girl who developed dislocated shoulders at 3 months, dislocated hips at 4 years and had a striking family history of articular hypermobility. A 15 year old girl was considered to have the marfanoid hypermobility syndrome5 because she had arachnodactyly and other features of Marfan's phenotype; her height was at the 75th centile and her weight at the 3rd centile. Two girls were training in gymnastics, one spending as much as 30 hours a week in training for competitive gymnastics. A further two girls were attending ballet school. Several of the older children dated the onset of their symptoms to minor sports injuries. Referrals came from a variety of medical 988
2 Articular hypermobility simulating chronic rheumatic disease 989 Figure Procedures for showing articular hypermobility.4 (From Wynne-Davies,2 by kind permission of the author and the editor of The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery.) sources including 12 from paediatrics departments, 7 from rheumatology and rehabilitation departments, 5 from orthopaedic departments, and 30 from general practice. Hypermobility had been suggested as a diagnosis in only six of these cases. Three patients had already undergone arthroscopy of the knee, and another had undergone patellar shaving for presumed chondromalacia patellae. Many patients had received prescriptions for aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and, of the patients previously seen by rheumatologists, two had been treated with systemic steroids and one with penicillamine after simpler antirheumatic agents had proved ineffective. The mean age at onset of symptoms in boys was 7-71 years, which was significantly younger than the mean age at onset of symptoms in girls (10.98) (P=0.047). Table 1 shows the distribution of heights and weights with the mean height and weight centiles for boys lower than those for girls. Regression analysis of height and weight centiles for individual patients showed the lines for boys and girls to be parallel, but the regression line for girls was significantly higher than that for boys (P=0.043). Ranking of the distribution of affected joints showed the knees to be most commonly affected by both symptoms and signs (Table 2). The mean age at onset of symptoms of back pain was
3 990 Lewkonia and Ansell Table 1 Age and stature ofpatients with articular hypermobility Boys Girls Age at onset of symptoms: 1-5 years years years 5 Total 12 Mean age (SD) at onset (years) 7-71 (4-83) Mean centile height (SD) when (21-99) examined Mean centile weight (SD) when (22-78) examined *Excludes patient with Marfan's syndrome. Symptoms Knee 5 (41) (with swelling) 1 (8*3) Back 1 (8-3) Elbow 2 (16*6) Hip Fingers (with swelling) Wrist Shoulder Ankle Limb pain 4 (33) Knee Back Elbow Hip Fingers (MCP joints) Ankle Wrist Generalised hypermobility Hypermobile joints 7 (58 * 3) 4 (33*3) 1 (8-3) 3 (25) 1 (8-3) 28 ( 10 ( 10( '23) 5 (1 5 (1 '1.9) 11 (.'26) 3 (7 7 (1 7 (1 5 (1 24 ( 19 ( 6 (1 13 ( 2 (4 8 (1 may lead to unnecessary investigation or treatment for inflammatory joint disease.7 The apparent tendency to mistake hypermobility for inflammatory - joint disease in these patients may reflect lack of 4 awareness of the syndrome but may also be a 12 consequence of the difficulties of assessing abnormal 26 joint mobility in childhood. Criteria for diagnosis of (3.41) generalised hypermobility were developed by Carter and Wilkinson, who reported abnormality in 7 % of 285 normal school children aged 6 to 11 years (27-78)* Articular mobility declines progressively throughout and after childhood,2 89 and the criteria have been found to be both sensitive'0 and insensitive" at different ages in population surveys. In the Scottish survey of Wynne-Davies 65% of subjects had Table 2 Articular distribution of symptom. s and hypermobile wrists at 2 years old, falling to only 5% abnormal joint mobility in boys and girls wi, ~th at 7, and 30 % had hypermobile knees at 18 months, articular hypermobility falling to 5% at 31 years.'2 In addition to variation Symptoms No (%) boys No (%)girls with age and anatomical site,13 joint mobility also (n =12) (n= 42) tends to be greater in females than males in all age groups.8 Thus the well known criteria of Carter and 66) Wilkinson4 for generalised articular hypermobility 23) must be applied in the context of the age and sex of 1.9) the patient and may not be fulfilled in many who, nevertheless, have localised hypermobility. It follows from previous population surveys that, 6.6) hypermobility being common, inflammatory arthritis 1.9) may precede or coexist with both symptomatic and.5) non-symptomatic hypermobility, and this is a potential source of diagnostic confusion that merits (57) special consideration. Clinical features that would 045) suggest 'benign hypermobility' rather than inflam- A42) matory joint disease include the absence of systemic (30.9).-7) illness or rash, absent or limited joint swelling, large. * 5) and medium sized joints predominantly affected 9) rather than small joints, and absence of synovial or soft tissue thickening despite chronicity of symptoms. Muscle cramps and limb pain that are not localised 13-2 (SD 1-59) years, and all but o0 ne of the 11 to joints and occur after strenuous exertion are patients with back pain were girls. T'he boy with unusual in inflammatory joint diseases but common back pain and one of the girls were later found in this syndrome. A family history of 'loose jointedon x ray examination to have Sc:heuermann's ness' in childhood is also useful as circumstantial osteochondritis. evidence in differential diagnosis. Negative or normal laboratory results will sustain the diagnosis of Discussion hypermobility, which is essentially one of exclusion. If there is persistent synovial effusion, even with The presence of articular hypermob)ility as the normal laboratory results for inflammatory and basis of presenting complaints had bee,n recognised infective disease, it is diagnostically helpful to show occasionally in our series of patients referred by the absence of pleocytosis in the joint fluid to be paediatricians and other specialists ass well as by confident that a hypermobile child does not also general practitioners. Patients in whom hyper- have arthritis. mobility had been recognised would prc)bably not be Bruising or wide scars should prompt examination referred, and our series is therefore likelly to show an of skin elasticity and consideration of the Ehlersascertainment bias. Nevertheless, the hlypermobility Danlos syndrome. Only two of our patients had syndrome seems to be under recognis4 ed,8 and this definite features of heritable syndromes of abnormal
4 connective tissue. In this regard our findings do not concur with those of a recent report'4 that described 9 patients from five families with the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes types I, II, and III who were referred to a paediatric rheumatology clinic over a period of 6 months. The relation of the commonly occurring hypermobility of childhood to the classical Ehlers- Danlos syndrome, especially the mild type III variety, is likely to remain uncertain until a specific biochemical abnormality is shown in the Ehlers- Danlos syndrome types I, II, and III. The prevalence of symptomatic hypermobility cannot be assessed from this retrospective survey because of the selected nature of the referred patients, but it is clear that only a minority of children with hypermobility develop symptoms. The mechanism of symptoms in those who do manifest the hypermobility syndrome are unknown, and the syndrome does not appear to correlate with the extent of hypermobility. Indeed, children with gross hypermobility associated with various types of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome may have symptoms due to instability of weight bearing joints but they rarely develop joint effusions or the musculoskeletal complaints of the hypermobility syndrome (R M Lewkonia and F M Pope, unpublished observations). The onset of symptoms in some of our older patients followed excessive or unaccustomed activities in physical education or sports. The preponderance of girls in this series and their tendency to be slightly taller than expected for their age are also of interest. These observations suggest that symptoms arise when ligaments and connective tissues are subjected to mechanical stress inappropriate to the stage of maturity that the individual has reached; this progressively constrains joint mobility. It remains difficult to explain the pathogenesis of joint swelling, the persistence of symptoms, or the non-articular limb pains noted in our patients or in the original series of Kirk et al.3 Psychological problems appeared to be important in perpetuating symptoms in some of our patients, but it was difficult to establish that such factors were not more common than would be expected in a suitably matched control population. Several of our patients had family histories of either juvenile chronic or adult arthritis, and, not unexpectedly, the development of joint or limb pains in another member of the family generated considerable anxiety. Back pain was predominantly a symptom of older girls, a group also especially susceptible to psychogenic limb pain.15 Failure to recognise the hypermobility syndrome was an important factor in perpetuating symptoms, which, in a few patients, had led to counterproductive invasive orthopaedic Articular hypermobility simulating chronic rheumatic disease 991 investigation or the use of potent antirheumatic drugs. The most important factor in management was often careful explanation of the nature of symptoms associated with hypermobility together with reassurance that the symptoms were not a prelude to juvenile chronic arthritis. In most of the patients available to us for follow up symptoms had resolved within a year or two of the diagnosis being established and explained. Persistence of symptoms necessitates reinvestigation with consideration of both psychosocial circumstances and the possibility of slowly evolving disease processes. The long term prognosis of this syndrome requires elucidation, and this can only be achieved with very lengthy longitudinal studies. The important question of whether the hypermobility syndrome predisposes a subject to premature osteoarthritis3 has to be considered in the context that articular hypermobility is not a homogeneous entity. The long term consequences of hypermobility were not addressed in the present study, but our observations in other patients suggested that individuals with a childhood history of articular hypermobility may present in middle age with osteoarthritis developing at distinctive sites, namely the carpometacarpal of the thumb, patellofemoral joint, and joints of the midcervical spine. We thank Stephen Duffy, Division of Computing and Statistics, Clinical Research Centre, for help in statistical interpretation. RML was in receipt of an Associateship of the Canadian Arthritis Society. References Hollister DW, Byers PH, Holbrook KA. Genetic disorders of collagen metabolism. Adv Hum Genet 1982;12: Wynne-Davies R. Acetabular dysplasia and familial joint laxity: two etiological factors in congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1970;52B: Kirk JA, Ansell BM, Bywaters EGL. The hypermobility syndrome. Musculoskeletal complaints associated with generalized joint hypermobility. Ann Rheum Dis 1967; 26: Carter CO, Wilkinson J. Persistent joint laxity and congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1964;46R: Walker BA, Beighton PH, Murdoch JL. The marfanoid hypermobility syndrome. Ann Intern Med 1969 ;71: Biro F, Gewanter HL, Baum J. The benign hypermobility syndrome in pediatrics. (Abstract) Arthritis Rheum 1982;25(Supplement, April) :S144. Bird HA, Wright V. Joint hypermobility mimicking pauci-articular Juvenile polyarthritis. Br Med J 1978;ii: Beighton P, Solomon L, Soskolone CL. Articular mobility in an African population. Ann Rheum Dis 1973; 32:413-8.
5 992 Lewkonia and Ansell 9Moran HM, Hall MA, Barr A, Ansell BM. Spinal mobility in the adolescent. Rheumatol Rehab 1976;18: Bird HA, Brodie DA, Wright V. Quantification of joint laxity. Rheumatol Rehab 1979;18: Silverman S, Constine L, Harvey W, Grahame R. Survey of joint mobility and in vivo skin elasticity in London school children. Ann Rheum Dis 1975 ;34: Wynne-Davies R. Familial joint laxity. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine 1971 ;64: Wood PHN. Is hypermobility a discrete entity? Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine 1971;64: British Paediatric Association Annual meetings April York University April York University April York University April York University 14 Osborn TG, Lichtenstein JR, Moore TL, Weiss T, Zuckner J. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome presenting as rheumatic manifestations in the child. J Rheumatol 1981; 8: Apley J. Limb pain with no organic disease. Clin Rheum Dis 1976;2: Correspondence to Dr B M Ansell, Division of Rheumatology, Clinical Research Centre, Northwick Park Hospital, Watford Road, Harrow, Middlesex HAI 3UJ. Received 15 August 1983 Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 December Downloaded from on 20 January 2019 by guest. Protected by
Dr. K. Brindha, M.D PG ESI PGIMSR, K.K Nagar, Chennai
 Dr. K. Brindha, M.D PG ESI PGIMSR, K.K Nagar, Chennai Case History 9 year old boy presented with a 3 week history of: Swelling of major lower limb joints Progression was additive (right ankle followed
Dr. K. Brindha, M.D PG ESI PGIMSR, K.K Nagar, Chennai Case History 9 year old boy presented with a 3 week history of: Swelling of major lower limb joints Progression was additive (right ankle followed
IJPMR ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 IJPMR ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10066-0019 Benign Joint Hypermobility Syndrome Study of the Comparative Efficacy of Strengthening Exercise between Extensor Group of Muscles and Both Flexor and
IJPMR ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10066-0019 Benign Joint Hypermobility Syndrome Study of the Comparative Efficacy of Strengthening Exercise between Extensor Group of Muscles and Both Flexor and
Joint hypermobility is a liability for the performing artist
 International Symposium on Performance Science ISBN 978-90-9022484-8 The Author 2007, Published by the AEC All rights reserved Joint hypermobility is a liability for the performing artist Rodney Grahame
International Symposium on Performance Science ISBN 978-90-9022484-8 The Author 2007, Published by the AEC All rights reserved Joint hypermobility is a liability for the performing artist Rodney Grahame
DIAGNOSTIC ASSOCIATIONS WITH HYPERMOBUJTY IN RHEUMATOLOGY PATIENTS
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1995;34:1157-1161 DIAGNOSTIC ASSOCIATIONS WITH HYPERMOBUJTY IN RHEUMATOLOGY PATIENTS N. HUDSON, M. R. STARR, J. M. ESDAILE and M.-A. FTTZCHARLES Rheumatic Disease Unit,
British Journal of Rheumatology 1995;34:1157-1161 DIAGNOSTIC ASSOCIATIONS WITH HYPERMOBUJTY IN RHEUMATOLOGY PATIENTS N. HUDSON, M. R. STARR, J. M. ESDAILE and M.-A. FTTZCHARLES Rheumatic Disease Unit,
HYPERLAXITY SYNDROME Symptoms Questions to the patient Signs Acute or Traumatic Chronic or Nontraumatic
 A 30 year old project manager, who is new to your general practice, presents with right anterior knee pain after slipping and landing on his knee three months ago. Imaging shows no abnormality, but he
A 30 year old project manager, who is new to your general practice, presents with right anterior knee pain after slipping and landing on his knee three months ago. Imaging shows no abnormality, but he
Alison Middleditch MCSP MMACP Director of Surrey Physiotherapy and is based in Coulsdon, Surrey
 Alison Middleditch MCSP MMACP Director of Surrey Physiotherapy and is based in Coulsdon, Surrey Alison qualified from Kings College Hospital and has worked in both the NHS and Private Practice. She held
Alison Middleditch MCSP MMACP Director of Surrey Physiotherapy and is based in Coulsdon, Surrey Alison qualified from Kings College Hospital and has worked in both the NHS and Private Practice. She held
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (heds) vs. Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD): What s the Difference?
 Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (heds) vs. Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD): What s the Difference? There has been a major revision in the approach to joint hypermobility (JH) as a whole. To recognize
Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (heds) vs. Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD): What s the Difference? There has been a major revision in the approach to joint hypermobility (JH) as a whole. To recognize
Lower Extremity Sports Injuries
 Lower Extremity Sports Injuries AAP Musculoskeletal Boot Camp Sigrid F. Wolf, MD Pediatric Sports Medicine Fellow Northwestern University Lurie Children s Hospital Disclosure I have no relevant financial
Lower Extremity Sports Injuries AAP Musculoskeletal Boot Camp Sigrid F. Wolf, MD Pediatric Sports Medicine Fellow Northwestern University Lurie Children s Hospital Disclosure I have no relevant financial
Instability due to disorders of collagen metabolism and inflammation
 Instability due to disorders of collagen metabolism and inflammation Chris Holroyd Consultant Rheumatologist University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust Outline Overview of hypermobility Genetic
Instability due to disorders of collagen metabolism and inflammation Chris Holroyd Consultant Rheumatologist University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust Outline Overview of hypermobility Genetic
All rights reserved.
 RODNEY GRAHAME UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON SCHOOL OF MEDICINE, U. WASHINGTON HMS 1967 EDS III 1968 (KIRK et al) (BEIGHTON) RHEUMATOLOGY GENETICS ERIC BYWATERS VICTOR McKUSICK HMS 1967 EDS III 1968 (KIRK
RODNEY GRAHAME UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON SCHOOL OF MEDICINE, U. WASHINGTON HMS 1967 EDS III 1968 (KIRK et al) (BEIGHTON) RHEUMATOLOGY GENETICS ERIC BYWATERS VICTOR McKUSICK HMS 1967 EDS III 1968 (KIRK
PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF AGE OF ONSET IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
EDS my first 50 years!
 EDS my first 50 years! Rodney Grahame Honorary Professor UCL Unit for Rheumatology & Connective Tissue Disease, University College London and the London International Hypermobility Clinic MARS AND VENUS
EDS my first 50 years! Rodney Grahame Honorary Professor UCL Unit for Rheumatology & Connective Tissue Disease, University College London and the London International Hypermobility Clinic MARS AND VENUS
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Hypermobility of Joints
 Hypermobility of Joints Peter Beighton Rodney Grahame Howard Bird Hypermobility of Joints Fourth Edition Peter Beighton, OMB, MD, PhD FRCP, FRSSA Department of Human Genetics University of Cape Town Cape
Hypermobility of Joints Peter Beighton Rodney Grahame Howard Bird Hypermobility of Joints Fourth Edition Peter Beighton, OMB, MD, PhD FRCP, FRSSA Department of Human Genetics University of Cape Town Cape
PROFESSOR RODNEY GRAHAME THE HYPERMOBILITY UNIT, LONDON & UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON
 PROFESSOR RODNEY GRAHAME THE HYPERMOBILITY UNIT, LONDON & UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON EDS EDS 1 FREDERICK PARKES-WEBER (1863-1962) 1200 medical articles + 23 books over 50 years; 7 eponymous diseases including
PROFESSOR RODNEY GRAHAME THE HYPERMOBILITY UNIT, LONDON & UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON EDS EDS 1 FREDERICK PARKES-WEBER (1863-1962) 1200 medical articles + 23 books over 50 years; 7 eponymous diseases including
Postural Tachycardia Syndrome and Hypermobility Syndrome
 Postural Tachycardia Syndrome and Hypermobility Syndrome Blair P. Grubb MD FACC Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics Health Science Campus University of Toledo Toledo, Ohio USA Over the years it became
Postural Tachycardia Syndrome and Hypermobility Syndrome Blair P. Grubb MD FACC Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics Health Science Campus University of Toledo Toledo, Ohio USA Over the years it became
General appearance examination
 Childhood athletic participation has dramatically increased over the past twenty years. Children are being introduced to organised sports at increasingly immature stages of physical development. It is
Childhood athletic participation has dramatically increased over the past twenty years. Children are being introduced to organised sports at increasingly immature stages of physical development. It is
Adult Reconstruction Hip Education Tracks
 Adult Reconstruction Hip Education Tracks Adult Reconstruction Hip Track for the Specialist - HIP1 ICL 281 A Case-based Approach to High Risk Total Hip - When Do I Do Something Differently? ICL 241 The
Adult Reconstruction Hip Education Tracks Adult Reconstruction Hip Track for the Specialist - HIP1 ICL 281 A Case-based Approach to High Risk Total Hip - When Do I Do Something Differently? ICL 241 The
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF DYSPLASIA
 PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
Benign joint hypermobility syndrome (BJHS) is the occurrence
 Benign Joint Hypermobility Syndrome: Evaluation, Diagnosis, and Management MAJ Michael R. Simpson, DO, MC, USA Benign joint hypermobility syndrome (BJHS) is a connective tissue disorder with hypermobility
Benign Joint Hypermobility Syndrome: Evaluation, Diagnosis, and Management MAJ Michael R. Simpson, DO, MC, USA Benign joint hypermobility syndrome (BJHS) is a connective tissue disorder with hypermobility
Learning Objectives. Epidemiology 7/22/2016. What are the Medical Concerns for the Adolescent Female Athlete? Krystle Farmer, MD July 21, 2016
 What are the Medical Concerns for the Adolescent Female Athlete? Krystle Farmer, MD July 21, 2016 Learning Objectives Discuss why females are different than males in sports- the historical perspective.
What are the Medical Concerns for the Adolescent Female Athlete? Krystle Farmer, MD July 21, 2016 Learning Objectives Discuss why females are different than males in sports- the historical perspective.
Prevalence of generalised joint hypermobility in school-aged children from east-central European region
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 75, No. 1, pp. 48 52 DOI: 10.5603/FM.a2015.0065 Copyright 2016 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Prevalence of generalised joint hypermobility
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 75, No. 1, pp. 48 52 DOI: 10.5603/FM.a2015.0065 Copyright 2016 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Prevalence of generalised joint hypermobility
Basics of Soft- Tissue Examination
 Basics of Soft- Tissue Examination Basics of Soft Tissue Exam For practitioners who primarily use their hands to treat the human structure: Examination must include functional tests to determine the type
Basics of Soft- Tissue Examination Basics of Soft Tissue Exam For practitioners who primarily use their hands to treat the human structure: Examination must include functional tests to determine the type
Hip Arthroscopy Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Hip Arthroscopy Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives 1. INTRODUCTION AND SCOPE NHS DORSET CLINICAL COMMISSIONING GROUP
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Hip Arthroscopy Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives 1. INTRODUCTION AND SCOPE NHS DORSET CLINICAL COMMISSIONING GROUP
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
major trauma such as rupture of the Achilles tendon injuries (Kirk et al, 1967; Carter and Sweetnam, ^.
 Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 8, No., September 984, pp. 4-48 P. Klemp I. D. Learmonth HYPERMOBILITY AND INJURIES IN A PROFESSIONAL BALLET COMPANY P. KLEMP, MD, FCP(SA), and. D. LEARMONTH, FRCS, FCS(SA)
Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 8, No., September 984, pp. 4-48 P. Klemp I. D. Learmonth HYPERMOBILITY AND INJURIES IN A PROFESSIONAL BALLET COMPANY P. KLEMP, MD, FCP(SA), and. D. LEARMONTH, FRCS, FCS(SA)
Forthomme B, Croisier JL, Crielaard JM. Departement of physical medicine and rehabilitation ULg.
 Contribution to an adapted physiotherapy in the hyperlaxity syndromes. Kaux JF, Foidart-Dessalle M, Toussaint G, Forthomme B, Croisier JL, Crielaard JM. Departement of physical medicine and rehabilitation
Contribution to an adapted physiotherapy in the hyperlaxity syndromes. Kaux JF, Foidart-Dessalle M, Toussaint G, Forthomme B, Croisier JL, Crielaard JM. Departement of physical medicine and rehabilitation
Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for patellar instability in patients with hypermobility
 N. R. Howells, J. D. Eldridge From Bristol Royal Infirmary, Bristol, United Kingdom KNEE Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for patellar instability in patients with hypermobility A CASE CONTROL
N. R. Howells, J. D. Eldridge From Bristol Royal Infirmary, Bristol, United Kingdom KNEE Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for patellar instability in patients with hypermobility A CASE CONTROL
Wrist Ganglion. Did not notice Suddenly. Over several hours Over several days Over several weeks Over several months
 Onset, Duration and Frequency Are you left handed or right handed? Left Right Both Which side of your body is affected? Left Right Both If both, which side is more severe? Left Right Varies About the same
Onset, Duration and Frequency Are you left handed or right handed? Left Right Both Which side of your body is affected? Left Right Both If both, which side is more severe? Left Right Varies About the same
Biochemical marker changes benign hypermobility syndrome (BHMS)
 Original Research Article Biochemical marker changes benign hypermobility syndrome (BHMS) T. N. Tamilselvam 1*, Malarvizhi 2 1 Senior Assistant Professor, Institute of Rheumatology, Madras Medical College
Original Research Article Biochemical marker changes benign hypermobility syndrome (BHMS) T. N. Tamilselvam 1*, Malarvizhi 2 1 Senior Assistant Professor, Institute of Rheumatology, Madras Medical College
Inheritable Connective Tissue Diseases: Or It s Probably Not Marfan s. RJ Willes 4/23/2018
 Inheritable Connective Tissue Diseases: Or It s Probably Not Marfan s RJ Willes 4/23/2018 This pretty much sums it up. Inheritable Connective tissues diseases A homogenous collection of varied syndromes
Inheritable Connective Tissue Diseases: Or It s Probably Not Marfan s RJ Willes 4/23/2018 This pretty much sums it up. Inheritable Connective tissues diseases A homogenous collection of varied syndromes
Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions
 Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions Orthopaedic Opinion Online is a website designed to provide information to patients who have
Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions Orthopaedic Opinion Online is a website designed to provide information to patients who have
and eyes and have also looked at histocompatibility and 1980 were identified as having had either rate (ESR) and all ANA results were noted. ANA.
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 168-172 Antinuclear antibody studies in juvenile chronic arthritis A M LEAK, B M ANSELL, AND S J BURMAN Division of Rheumatology, Canadian Red Cross Memorial
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 168-172 Antinuclear antibody studies in juvenile chronic arthritis A M LEAK, B M ANSELL, AND S J BURMAN Division of Rheumatology, Canadian Red Cross Memorial
Currently at Cincinnati Children s Hospital As of 9/1/12, will be at Lutheran General Hospital in Chicago
 EDS and TOMORROW NO financial disclosures Currently at Cincinnati Children s Hospital As of 9/1/12, will be at Lutheran General Hospital in Chicago Also serve on the Board of Directors of the Ehlers-Danlos
EDS and TOMORROW NO financial disclosures Currently at Cincinnati Children s Hospital As of 9/1/12, will be at Lutheran General Hospital in Chicago Also serve on the Board of Directors of the Ehlers-Danlos
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
Joint involment in orthopedic diseases
 Joint involment in orthopedic diseases PReS Latin America Basic Pediatric Rheumatology Course 2015 Aguas de São Pedro, São Paulo, Brazil Carmen L. De Cunto carmen.decunto@hospitalitaliano.org.ar Sección
Joint involment in orthopedic diseases PReS Latin America Basic Pediatric Rheumatology Course 2015 Aguas de São Pedro, São Paulo, Brazil Carmen L. De Cunto carmen.decunto@hospitalitaliano.org.ar Sección
development of erosive osteoarthritis?
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Ankle Arthroscopy.
 Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Definitions of joint hypermobility: o Joint hypermobility (JH): Capability for a joint to move beyond normal physiological limits.
 Definitions of joint hypermobility: o Joint hypermobility (JH): Capability for a joint to move beyond normal physiological limits. Descriptor, not diagnosis Also known as joint laxity, double-jointedness,
Definitions of joint hypermobility: o Joint hypermobility (JH): Capability for a joint to move beyond normal physiological limits. Descriptor, not diagnosis Also known as joint laxity, double-jointedness,
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
EHLERS DANLOS SYNDROME. Fransiska Malfait, MD PhD Centre for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium
 EHLERS DANLOS SYNDROME Fransiska Malfait, MD PhD Centre for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium EDS is a heritable collagen disorder Heterogeneous group of diseases with: - Multi-systemic
EHLERS DANLOS SYNDROME Fransiska Malfait, MD PhD Centre for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium EDS is a heritable collagen disorder Heterogeneous group of diseases with: - Multi-systemic
THE SUPPORT YOU NEED.
 PROFESSIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC RANGE THE SUPPORT YOU NEED. Introductory Offer ends 30 JUNE 2018 BACK Introductory Special Offer 20% OFF. VLK-2262 Sacro Belt Provides support and compression to the sacroiliac
PROFESSIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC RANGE THE SUPPORT YOU NEED. Introductory Offer ends 30 JUNE 2018 BACK Introductory Special Offer 20% OFF. VLK-2262 Sacro Belt Provides support and compression to the sacroiliac
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging
 Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
NORTH BAY SYMPOSIUM SATURDAY JANUARY 20 TH 2018
 NORTH BAY SYMPOSIUM SATURDAY JANUARY 20 TH 2018 ROBERT HAIMSON, M.D. ORTHOPEDIC SURGEON SMGR FELLOW IN AAOS DIPLOMATE IN ABOS COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS: WHAT
NORTH BAY SYMPOSIUM SATURDAY JANUARY 20 TH 2018 ROBERT HAIMSON, M.D. ORTHOPEDIC SURGEON SMGR FELLOW IN AAOS DIPLOMATE IN ABOS COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS: WHAT
The role of orthopedic surgery in the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes
 The Ehlers-Danlos Society P.O. Box 87463 Montgomery Village, MD 20886 USA Phone: +1 410-670-7577 The Ehlers-Danlos Society - Europe Office 7 35-37 Ludgate Hill London EC4M 7JN UK Phone: +44 203 887 6132
The Ehlers-Danlos Society P.O. Box 87463 Montgomery Village, MD 20886 USA Phone: +1 410-670-7577 The Ehlers-Danlos Society - Europe Office 7 35-37 Ludgate Hill London EC4M 7JN UK Phone: +44 203 887 6132
Subpopulations within juvenile psoriatic arthritis: A review of the literature
 Clinical & Developmental Immunology, June December 2006; 13(2 4): 377 380 Subpopulations within juvenile psoriatic arthritis: A review of the literature MATTHEW L STOLL 1 & PETER A NIGROVIC 1,2, 1 Division
Clinical & Developmental Immunology, June December 2006; 13(2 4): 377 380 Subpopulations within juvenile psoriatic arthritis: A review of the literature MATTHEW L STOLL 1 & PETER A NIGROVIC 1,2, 1 Division
Arthroscopy. Turnberg Building Orthopaedics
 Arthroscopy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Introduction An arthroscopy is a type of keyhole surgery used both to diagnose and treat
Arthroscopy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Introduction An arthroscopy is a type of keyhole surgery used both to diagnose and treat
Patellofemoral Pathology
 Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
Valgus Knee Deformities in Children with Juvenile Chronic Polyarthritis Treated by Epiphysial Stapling
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 388. Valgus Knee Deformities in Children with Juvenile Chronic Polyarthritis Treated by Epiphysial Stapling B. M. ANSELL, G. P. ARDEN, and I. McLENNAN* From
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1970, 45, 388. Valgus Knee Deformities in Children with Juvenile Chronic Polyarthritis Treated by Epiphysial Stapling B. M. ANSELL, G. P. ARDEN, and I. McLENNAN* From
Inter-examiner reproducibility of tests and criteria for generalized joint hypermobility and benign joint hypermobility syndrome
 Rheumatology 2007;46:1835 1841 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kem290 Inter-examiner reproducibility of tests and criteria for generalized joint hypermobility and benign joint hypermobility syndrome B. Juul-Kristensen
Rheumatology 2007;46:1835 1841 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kem290 Inter-examiner reproducibility of tests and criteria for generalized joint hypermobility and benign joint hypermobility syndrome B. Juul-Kristensen
The Hip from Cradle to Grave. Haemish Crawford Ascot Hospital Starship Children s Hospital
 The Hip from Cradle to Grave Haemish Crawford Ascot Hospital Starship Children s Hospital Developmental dysplasia hip DDH Irritable vs. septic hip Perthes disease Slipped Upper Femoral Epiphysis (SUFE)
The Hip from Cradle to Grave Haemish Crawford Ascot Hospital Starship Children s Hospital Developmental dysplasia hip DDH Irritable vs. septic hip Perthes disease Slipped Upper Femoral Epiphysis (SUFE)
Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 327-331 The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists C. F. MURRAY-LESLIE, D. J. LINTOTT, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 327-331 The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists C. F. MURRAY-LESLIE, D. J. LINTOTT, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Management of Chronic Elbow Pain
 Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
Insurance Guideline Summary
 Insurance Guideline Summary Foot/Ankle: Soft Goods- Ankle lace-up, Velocity, PTTD $83.00 Had an injury, surgery, or chronic instability (will not be covered for osteoarthritis unless you document instability
Insurance Guideline Summary Foot/Ankle: Soft Goods- Ankle lace-up, Velocity, PTTD $83.00 Had an injury, surgery, or chronic instability (will not be covered for osteoarthritis unless you document instability
EDNF Center for Clinical Care & Research at GBMC PHYSICIANS CONFERENCE September 15, 2014
 EDNF Center for Clinical Care & Research at GBMC 2014 PHYSICIANS CONFERENCE September 15, 2014 Pain in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Clair A. Francomano, M.D. Director, EDNF Center for Clinical Care and Research
EDNF Center for Clinical Care & Research at GBMC 2014 PHYSICIANS CONFERENCE September 15, 2014 Pain in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Clair A. Francomano, M.D. Director, EDNF Center for Clinical Care and Research
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM
 ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
The New Science of Osteoarthritis
 The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
Aortic regurgitation in seropositive juvenile arthritis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 229-234 Aortic regurgitation in seropositive juvenile arthritis A. M. LEAK,' M. W. MILLAR-CRAIG,2 AND BARBARA M. ANSELL1 From the 'Juvenile Rheumatism Unit,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 229-234 Aortic regurgitation in seropositive juvenile arthritis A. M. LEAK,' M. W. MILLAR-CRAIG,2 AND BARBARA M. ANSELL1 From the 'Juvenile Rheumatism Unit,
PAIN SYNDROMES
 www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it PAIN SYNDROMES 1) Fibromyalgia Syndrome Synonyms Fibromyalgia is a diffuse idiopathic musculoskeletal pain syndrome. Fibromyalgia is a disease causing widespread musculoskeletal
www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it PAIN SYNDROMES 1) Fibromyalgia Syndrome Synonyms Fibromyalgia is a diffuse idiopathic musculoskeletal pain syndrome. Fibromyalgia is a disease causing widespread musculoskeletal
Regions Hospital Delineation of Privileges Orthopaedic Surgery
 Regions Hospital Delineation of Orthopaedic Surgery Applicant s Last First M. Instructions: Place a check-mark where indicated for each core group you are requesting. Review education and basic formal
Regions Hospital Delineation of Orthopaedic Surgery Applicant s Last First M. Instructions: Place a check-mark where indicated for each core group you are requesting. Review education and basic formal
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Kineto. Orthopaedics & Rehabilitation Products
 Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited Kineto Orthopaedics & Rehabilitation Products Our orthopaedic and rehabilitation products comprise of a variety of adjustable rehabilitation braces for support,
Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited Kineto Orthopaedics & Rehabilitation Products Our orthopaedic and rehabilitation products comprise of a variety of adjustable rehabilitation braces for support,
Hypermobility of Joints
 Peter Beighton. Rodney Grahame. Howard Bird Hypermobility of Joints Second Edition With 71 Figures Foreword by Professor Eric Bywaters Co-ordinating Editor (Second Edition): Rodney Grahame Springer-Verlag
Peter Beighton. Rodney Grahame. Howard Bird Hypermobility of Joints Second Edition With 71 Figures Foreword by Professor Eric Bywaters Co-ordinating Editor (Second Edition): Rodney Grahame Springer-Verlag
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY
 All patients referred to specialist clinics are assigned to a priority category based on their clinical need and related psychosocial factors. The examples given are indicative only and the clinician reviewing
All patients referred to specialist clinics are assigned to a priority category based on their clinical need and related psychosocial factors. The examples given are indicative only and the clinician reviewing
9/6/2012. Less risk of injury Fewer back & posture problems Function more efficiently
 Unit 4 Ability to use your joints fully through a wide range of motion Having long muscles that allow your joints to be free enough to allow adequate movement. People who are flexible are often involved
Unit 4 Ability to use your joints fully through a wide range of motion Having long muscles that allow your joints to be free enough to allow adequate movement. People who are flexible are often involved
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis
 Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Dupuytrens contracture
 OA Wrist Ganglion/Cysts Dupuytrens contracture Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel pathway For advice on management of CTS please follow link to Map of Medicine Trigger Finger Trigger finger pathway For
OA Wrist Ganglion/Cysts Dupuytrens contracture Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel pathway For advice on management of CTS please follow link to Map of Medicine Trigger Finger Trigger finger pathway For
A Patient s Guide to Patellofemoral Problems
 A Patient s Guide to Patellofemoral Problems 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Patellofemoral Problems 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Bilateral Hip & Sacroiliac Support. Devin Laing Eloy Ramos
 Bilateral Hip & Sacroiliac Support Devin Laing Eloy Ramos BACKGROUND INFORMATION Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a connective tissue disorder characterized by varying degrees of skin hyperextensibility,
Bilateral Hip & Sacroiliac Support Devin Laing Eloy Ramos BACKGROUND INFORMATION Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a connective tissue disorder characterized by varying degrees of skin hyperextensibility,
EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME TYPE III: HYPERMOBILITY TYPE 1
 EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME TYPE III: HYPERMOBILITY TYPE 1 Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Type III: Hypermobility Type Rachel Conley Bellingham Technical College Anatomy and Physiology 241 EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME TYPE
EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME TYPE III: HYPERMOBILITY TYPE 1 Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Type III: Hypermobility Type Rachel Conley Bellingham Technical College Anatomy and Physiology 241 EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME TYPE
PASIG MONTHLY CITATION BLAST: No.90 January 2014
 PASIGMONTHLYCITATIONBLAST:No.90 January2014 DearPerformingArtsSIGmembers: CSM2014isFebruary3 6.Ihopetoseeyouthere!Conferenceinformationand handoutsareup,takealook: http://www.apta.org/csm/ CSM2014PASIGprogramminginLasVegas:Wednesday,February5th
PASIGMONTHLYCITATIONBLAST:No.90 January2014 DearPerformingArtsSIGmembers: CSM2014isFebruary3 6.Ihopetoseeyouthere!Conferenceinformationand handoutsareup,takealook: http://www.apta.org/csm/ CSM2014PASIGprogramminginLasVegas:Wednesday,February5th
Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes Overview for primary care providers
 Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes Overview for primary care providers Roberto Mendoza-Londono MD, MSc, FCCMG, FRCPC Medical Director-EDS service, Hospital for Sick Children/UHN Interim Division Head, Genetics, HSC
Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes Overview for primary care providers Roberto Mendoza-Londono MD, MSc, FCCMG, FRCPC Medical Director-EDS service, Hospital for Sick Children/UHN Interim Division Head, Genetics, HSC
SERVICES. Contact us. Rapid Assessment, Intervention and Treatment
 Contact us For more information about Orthopaedic Services, please visit our website at www.londonbridgehospital.com or contact: GP Liaison Department Tel: +44 (0)20 7234 2009 Fax: +44 (0)20 7234 2019
Contact us For more information about Orthopaedic Services, please visit our website at www.londonbridgehospital.com or contact: GP Liaison Department Tel: +44 (0)20 7234 2009 Fax: +44 (0)20 7234 2019
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Pain in Osteoarthritis
 Pain in Osteoarthritis By Edward L. Treadwell, MD Professor of Medicine- Rheumatology/Immunology Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University School of Medicine Greenville, NC 27834 E-mail: treadwelle@ecu.edu
Pain in Osteoarthritis By Edward L. Treadwell, MD Professor of Medicine- Rheumatology/Immunology Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University School of Medicine Greenville, NC 27834 E-mail: treadwelle@ecu.edu
Patellar Instability. OrthoInfo Patella Instability Page 1 of 5
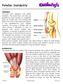 Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
Institute for Bone, Joint Replacement, Orthopaedics Spine and Sports Medicine
 24-Hour Helpline: 011-30403040 BLK Super Speciality Hospital Pusa Road, New Delhi - 110005 (India). www.blkhospital.com Institute for Bone, Joint Replacement, Orthopaedics Spine and Sports Medicine Introduction
24-Hour Helpline: 011-30403040 BLK Super Speciality Hospital Pusa Road, New Delhi - 110005 (India). www.blkhospital.com Institute for Bone, Joint Replacement, Orthopaedics Spine and Sports Medicine Introduction
GPSTR ST1/ST2 Specialty Guide TRAUMA & ORTHOPAEDICS
 Derby GP Specialty Training Programmes Derby GP Level Specialty 3, Education Training Centre Programmes Level Royal 3, Education Derby Hospital Centre Royal Uttoxeter Derby Road Hospital Uttoxeter Derby
Derby GP Specialty Training Programmes Derby GP Level Specialty 3, Education Training Centre Programmes Level Royal 3, Education Derby Hospital Centre Royal Uttoxeter Derby Road Hospital Uttoxeter Derby
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics)
 Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Ankle Arthritis PATIENT INFORMATION. The ankle joint. What is ankle arthritis?
 PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
2011 Armed Conflict Injuries to the Extremities 2011 Ankylosing Spondylitis In Clinical Practice 2010 Vitamin D Physiology,Molecular Biology, and
 Orthopedics 2013 Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics Volume 4 2013 Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics Volume 3 2013 Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics Volume 2 2013 Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics Volume
Orthopedics 2013 Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics Volume 4 2013 Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics Volume 3 2013 Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics Volume 2 2013 Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics Volume
Patellofemoral Joint. Question? ANATOMY
 Doug Elenz is a paid Consultant/Advisor for the Biomet Manufacturing Corporation. Doug Elenz, MD Team Orthopaedic Surgeon The University of Texas Men s Athletic Department Question? Patellofemoral Joint
Doug Elenz is a paid Consultant/Advisor for the Biomet Manufacturing Corporation. Doug Elenz, MD Team Orthopaedic Surgeon The University of Texas Men s Athletic Department Question? Patellofemoral Joint
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus
 Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Symptom and joint mobility progression in the joint hypermobility syndrome (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, hypermobility type)
 Symptom and joint mobility progression in the joint hypermobility syndrome (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, hypermobility type) M. Castori 1, I. Sperduti 2, C. Celletti 3, F. Camerota 3, P. Grammatico 1 1 Medical
Symptom and joint mobility progression in the joint hypermobility syndrome (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, hypermobility type) M. Castori 1, I. Sperduti 2, C. Celletti 3, F. Camerota 3, P. Grammatico 1 1 Medical
Chapter 10: Flexibility
 Chapter 10: Flexibility Lesson 10.1: Flexibility Facts Self-Assessment 10: Arm, Leg, and Trunk Flexibility Lesson Objectives: Describe the characteristics of flexibility. Explain how you benefit from good
Chapter 10: Flexibility Lesson 10.1: Flexibility Facts Self-Assessment 10: Arm, Leg, and Trunk Flexibility Lesson Objectives: Describe the characteristics of flexibility. Explain how you benefit from good
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
 OFFICE OF MEDICAL CANNABIS Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome SEPTEMBER 2016 Introduction Briefings such as this one are prepared in response to petitions to add new conditions to the list of qualifying conditions
OFFICE OF MEDICAL CANNABIS Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome SEPTEMBER 2016 Introduction Briefings such as this one are prepared in response to petitions to add new conditions to the list of qualifying conditions
Your Orthotics service is changing
 Your Orthotics service is changing Important for referrers on changes effective from January 2015 Why is the service changing? As demand for the orthotics service increases and budgets remain relatively
Your Orthotics service is changing Important for referrers on changes effective from January 2015 Why is the service changing? As demand for the orthotics service increases and budgets remain relatively
Clinical Practice & Referral Guideline - Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
 Clinical Practice & Referral Guideline - Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip *This guideline was developed from the American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline: Early Detection of Developmental
Clinical Practice & Referral Guideline - Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip *This guideline was developed from the American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline: Early Detection of Developmental
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Familial Mediterranean Fever
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Familial Mediterranean Fever Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS FMF 1.1 What is it? Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a genetically transmitted disease. Patients
