NonMalignant Granulocyte & Monocyte Disorders. M.Farhadi Tehran,1390
|
|
|
- Tobias Turner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 بنام خداوند بخشنده مھربان
2 NonMalignant Granulocyte & Monocyte Disorders M.Farhadi Tehran,1390
3 Overview In this lecture we discuss " Benign Changes in Granulocytes & Monocytes as a response to various nonmalignant disease states and toxic challenges". These changes include both "Quantitative & Qualitative variations that can be detected by Laboratory tests. So it divided to changes in quantity & morphology of Neutophils,Eosinophils,Basophils i & Monocytes in Acquired & Inherited states.
4
5 Introduction * it well recognized that: "Changes in leukocyte concentration & morphology are the Body's Normal Responses". *most often One cell Type affected than others and provide important clue to Diagnosis. *the cell type affected depends largely on it's Function(e.g. Bacterial infection----neutrophils) *thus absolute determination of cell type count aids in differential diagnosis,especially when Total Leukocyte Count is Abnormal.
6 Leukocytosis refer to a condition in which the total leukocyte count tis more than 11.0x10^9/L 10^9/L in an adult. * reference range vary significantly among different sources and laboratories. **the absolute concentration of each cell type of leukocyte can be calculated l from: Absolute cells/l=total Leukocyte Count/L x Percent of cell type from differential count
7 Leukopenia Refers to a decrease in leukocytes below 4.5x10^9/L usually due to decrease in Neutrophils but lymphocytes and other cell types rarely can be contribute Morphologic or Qualitative variations of WBCs are noted by Stained Blood Smear Examination. Some of them affect cell Function while others-
8 NEUTROPHIL DISORDERS Neutrophils are most numerous white blood cells within peripheral blood. Neutrophilia is more common than neutropenia. Qualitative changes requires careful microscopic examination. Qualitative changes provide important diagnostic information.
9
10 QUANTITATIVE DISORDERS 1- Caused by Malignant or Benign disorders. 2-Benign disorders are usually ACQUIRED and may cause an increase ( NEUTROPHILIA) or decrease (NEUTROPENIA). 3- Neutrophilia is more common. 4-Three main mechanisms affecting neutrophil concentration in peripheral blood.
11 Factors Affecting Neutrophil Concentration in PB *Bone marrow production & release *Rate of Neutrophil egress to tissue or survival time in blood *R t f i ti t i l ti *Rate of marginating to circulating pool
12 Neutrophilia 1-Neutrophil count varies with Age & Race 2-In adults exceeds 7.0x10^9 / L 3-Benign neutrophilia mostly as a result of reaction to physiologic or pathologic process and is called Reactive Neutrophilia & divided to: Immediate, Acute, Chronic Neutrophilia
13
14 Immediate Neutrophilia -Can Occure without Pathologic stimulus -Probably a simple redistribution of marginated granulocyte pool(mgp) to circulating granulocyte pool(cgp). - 50% of neutrophils are freely circulating & other 50% are loosely attached to vessels endothelial cells.lab count only CGP.
15 Immediate Neutrophilia - Neutrophil increase is immediate but transient,lasting about minutes - Appear to be independent of bone marrow input and tissue egress. - Also called PSEUDONEUTROPHILIA or SHIFT NEUTROPHILIA, because no real change in number within vasculature occurs. -Neutrophils are Mature &Normal. -Due to Active Exercise,Epinephrine,Anxiety,Anesthesia
16 ACUTE NEUTROPHILIA -Occurs within 4-5 hr of a pathologic stimulus -Results from increase in the flow of neutrophils from BM storage pool to PB -More pronounced than immediate neutrophilia -The immature neutrophils may increase,more bands & if demand continues release of metamyelocyte & myelocyte seen. -As BM production increase & storage pool replenished the WBC differential return Normal
17
18 CHRONIC NEUTROPHILIA -Follows Acute Neutrophilia -If stimulus continues beyond a few days,the storage pool depleted,& BM shows increaed numbers of early neutrophil precursors including Myeloblasts,Promyelocytes & Myelocytes. -PB show increased Bands,Metamyelocyte,Myelocyte& Myelocyte& rarely Promyelocyte so named=shift TO THE LEFT
19
20 Conditions Associated with Neutrophilia 1- Acute Bacterial & Fungal Infections 2-Inflammatory Processes 3-Metabilic alterations;uremia,eclampsia,gout eclampsia 4-Neoplasms 5-Acute Hemorrhage or Hemolysis 6-Rebound from BMT or CSF treatment 7-Certain chemicals,toxins,drugs 8-Chronic Myeloproliferative Disorders
21 Reactive Chronic Neutrophilia - caused by benign or toxic conditions -total WBC count less than 50x10^9/L -the immature cells seen in PB are Bands & Metamyelocytes -toxic changes(toxic granulation,dohle bodies & cytoplasmic vacuoles) seen even after WBC count return to normal. -LAP score may elevated.
22
23 Bacterial Infection -most common cause of neutrophilia(pyogenic ones as satph & strep) -depend on bacterial;virulence,extend of infection & Response of host WBC count may range from 7.0x10^9/L to 70x10^9/L but usually it is around 10-25x10^9/L. -in sever infections BM exhausted & Neutropenia developed with poor prognosis
24
25 Other Considerations * Chronic bacterial infection leads to chronic stimulation on BM & new steady state of increase Neutrophil production develop. *Other organisms(fungal,rickettsia,spirochete,parasites *Certain bacteria are with Neutropenia. *Whooping cough is with Lymphocytosis. *Early course of viral infections Neutrophilia.
26
27 Tissue Destruction/Injury,Inflammatory, Metabolic Disorders Etiology; By increasing Neutrophil input from BM in response to increased egress to the tissue. Damaged tissue release cytokines act as chemotactin(wbc granules,o3-,crystalsua,... Disease States such as;tissue necrosis & Infarction,Burns,Neoplasms,Trauma,Uremia,Rheu matoid arthritis,gout,drug intoxication,...
28 Leukemoid Reaction Pathophysiology;extreme neutrophilic reactions to sever infections or necrotizing tissue. Definition;a benign leukocyte proliferation by a total WBC count usually greater than 50,000/ql with many circulating immature WBC precursor In Neutrophilic Leukomoid Rx, PB contain many Bands,Metamyelocytes,increased Myelocytes & Promyelocytes and rarely Blasts
29 Leukemoid Reaction... * PB picture may indistinguishable from CML. ** D.Dx ; Genetic studies,molecular analysis, Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP) score,... ***Contrary to Leukemia,the leukemoid reaction is Transient,fade after inciting stimulus. ****Can be seen in;chronic infections(tb), Ca of Lung,Stomach,Breast,Liver Liver & others
30
31 Leukoerythroblastic Reaction is characterized by the presence of nucleated erythrocytes & a neutrophilic shift to the left PB. The Total Neutrophil count may; Increase,Decrease,or Normal. The erythrocytes often exhibit poikilocytosiswith teardrop shapes & anisocytosis.mostly often in Chronic Myeloproliferative states(myelofibrosis myelophthisis&sever hemolytic anemia(hdfn)
32 Stimulated Bone Marrow States *when BM is stimulated to produce RBCs(in response to hemorrhage/hemolysis) neutrophils may also share in process lead to neutrophilia. *Hematopoietic Growth Factors(GM-CSF) can rapidly increase total WBC count & it's precursor including Blasts(used in BMT,High dose Chemotherapy,Stem cell donate *Drugs(Corticosteroid) I output, D migration
33 Physiologic Leukocytosis - at birth & for first few days of life,with a slight shift to the left. -Physiologic stress including ; exposure to extreme temperture,emotional stimuli,exercise and labor during delivery could cause neutrophilia generally without a shift to the left.
34 NEUTROPENIA Occurs when Neutrophil Count falls below; x10^9/L(varies with ethnic group). Agranulocytosis, when neutrophil count is below 0.5x10^9/L. mostly associated with high probablity of infection.basophils & Eosinophils also commonly depleted in sever neutropenia.
35 Causes of Neutropenia 1-Decrease bone marrow production 2-Increase cell loss(due to immune destruction or increase neutrophil egress to tissue) 3-Pseudoneutropenia(increase neutrophil margination) 4-Spurious or False neutropenia result from neutrophil agglutination,disintegration&lab instrumental problem or error
36 Decrease Bone Marrow Production Bone marrow show myeloid hypoplasia,and and M:E ratio is decreased. With decrease production BM storage pool is depleted,neutrophil egress to tissue also decrease and both circulating & marginal pools decrease. Immature cells may enter the PB in attempt to alleviate to neutrophil shortage.cells younger than Band are less efficient in phagocytosis
37 Stem Cell Disorders - Stem cell failure such as aplastic anemia, radiotherapy or chemotherapy or infiltration of hematopoietic tissue by malignant cells(myelophthisis). -Of new leukemia cases 40% present with total leukocyte count less than 10x10^9/L,because normal precursor cells in BM replaced but malignant cells havenot egressed to PB yet.
38 Megaloblastic Anemia -Neutropenia is a charactristic findings in megaloblastic anemia & myelodysplastic syndroms(mds). -Marrow is usually hyperplastic. -Neutropenia result from abnormal myeloid cells being destroyed before release to peripheral blood(ineffective granulopoiesis).
39 Congenital Neutropenia Disorders of Production cyclic neutropenia,familial ili l neutropenia,fnconi i pancytopenia,reticular dysgenesis,sever congenital neutropenia,wiskott-aldrich syndrom Disorderd of RNA synthesis& processing cartilage-hair hypoplasia,dyskeratosis congenital,shwachman-diamond syndrome Disorders of Metabolism( Barth syndrome,glycogen storage disease,type 1b) Disorders of vesicular transport(chediak- Higashi,Cohen,Griscelli,Hermansky-pudlak
40 Immune Neutropenia *Antibodies directed against neutrophil-specific antigens(na)may cause decrease in number. *Leukocytes destroyed similar to RBCs(IHA) *Immune mechanisms;1-direct cell lysis or 2-Sensitization & subsequent sequestration in spleen.two types present;alloimmune and Autoimmune neutropenia
41 Alloimmune Neonatal Neutropenia Occurs when transplacental transfer of maternal alloantibodies directed against infant's neutrophil antigens(infant Ags are paternal origin). Affected infants may develop infections,until neutropenia resolved usually in few weeks,same same as Rh HDN except first child can affected. Alloimmune Neutropenia can result : transfusion
42 Autoimmune Neutropenia Two forms recognized:primary & Secondary Primary AIN ;antibody-coated neutrophils are sequestered&destroyed by spleen.unknown etiology, Young children with fever & infection,spontaneous remission after month.secondary AIN in older patients with other autoimmune disorders(sle,ra),antineutrophil Abs arenot only cause & actual target of Abs not known.
43 Hypersplenism May result in a selective culling of neutrophils producing mild neutropenia. The Bone Marrow exhibits neutrophilic hyperplasia. Thrombocytopenia and occasionally Anemia may also accompany hypersplenism.
44 Spurious,or False Neutropenia 1- EDTA induced neutrophil adherence to RBCs 2-Disintegration of Neutrophils over time prior to testing 3-Disruption of abnormally fragil leukocytes during preparation of the blood for testing 4-Neutrophil aggregation(some paraproteins) Psudoneutropeniashift of CGP to MGP in some endotoxin bacteria & hypersensitivity(transient)
45 Qualitative or Morphologic Neutrophil Abnormalities Nuclear Abnormalities Pelger-Huet,Hypersegmentation,Pyknotic nuclei Cytoplasmic Abnormalities Dohle bodies,toxic granules,cytoplasmic Vacuoles,intracellular organism(fungi,bacteria) Inherited Functional Abnormalities Alder-Reilly anomaly,chediak-higashi,may- Hegglin anomaly,chronic Granulomatous Disease,Myeloperoxidase id &AdhesionDeficiency, i
46 Pelger-Huet Anomaly A benign anomaly,autosomal autosomal dominant fashion occuring 1 in 5000 individuals. Nucleus doesnot segment beyond two-lobed stage & may appear round with no segmentation Coarse chromatin clumping aid to DDx to Band. "pince-nez" shape:dumbbell shape with two lobes connected by a thin strand of chromatin. Acquired/pseudo Pelger-Huet in CMD/MDS
47
48 Hypersegmentation larger than normal neutrophils with six or more nuclear segments are a common & early indicator of Megaloblastic Anemia.These cells with pancytopenia & Macro ovalocytes typically accompany vit B12 defeciency. Rarely hereditary hypersegmentation reported without clinical significance.
49
50 Pyknotic Nucleus Pyknotic or degenerating nuclei found in dying neutrophils in PB & other body fluids. The nuclear chromatin condenses & the segments disappear becoming smooth,dark-staining spheres. If nucleus round these necrotic cells may be confused with nucleated erythrocytes(nrbc).
51
52 Dohle Bodies Dohle bodies are light gray-blue oval inclusions in cytoplasm of neutrophils & eosinophils. Found near the periphery of cell. Composed of aggregates of rough endoplasmic reticulum(rer). May seen in sever infections,burns,cancer,drugs. Looked for other toxic granulation & reactive morphologic changes.same in May-Hegglin.
53
54 Toxic Granules Are large,deep,blue-black primary granules in cytoplasm of segmented Neutrophils & sometimes in bands &meta myelocytes. Toxic granules retain their basophilia in the mature neutrophils Toxic-like granules/inclusions can seen: -as artifact with increased staining/low ph
55
56 Cytoplasmic Vacuoles Appear as clear,unstained areas. Represent the end stage of phagocytosis. Seen in Same conditions of Toxic Granulation & Dohle bodies. As artifact in stored EDTA blood but smaller &uniformly dispersed
57
58 Inherited Functional Abnormality Alder-Reilly Anomaly -Inherited condition i by presence of fl arge purplish granules in all le ukocyte cytoplasm in lysosomal storage disorders(hueler &Hunter s yndromes )mucopolysaccharide stained metachromatically with toluidine blue
59
60 Chediak-Higashi Syndrome A rare autosomal recessive disorder,with death in infancy or childhood due to recurrent rrent bacterial infections. Giant gray-green peroxidase positive i bodies & Giant Lysosomes in WBC & other granule-contai ning cells of other tissues. Result as fusion of primary & secondary neutrophilic granules. Neutropenia & thrombocytopenia seen
61 May-Hegglin Anomaly Rare inherited autosomal dominant trait in which granulocytes contain inclusions similar To Dohle bodies consisting mainly of RNA from rough endoplasmic reticulum. Larger & more round vs Dohle bodies. Variable thrombocytopenia & giant platlets may seen.abnormal bleeding due to low platlets may exhibit.
62
63
64
65 EOSINOPHIL DISORDERS Reactive(secondary)Eosinophilia Primary Eosinophilia
66 Reactive (secondary)eosinophilia Increase above 0.4x10^9/L be induced due to T-lymphokines secretion: 1-Tissue invasive parasites 2-Allergic conditions 3-Respiratory tract disorders 4-Gasterointestinal diseases 5-Skin & Connective tissue disorders d /
67
68 Primary Eosinophilia Collectively known as Hypereosinophilic syndrome(hes) persistent blood eosinophils Above 1.5x10^9/L with tissue infiltration. 1-Idiopathic HES 2-clonal eosinophilia: -eosinophilic leukemia -chronic eosinophilia
69
70 Basophil & Mast cell Disorders Both cells are important in inflammatory & allergic reactions,release inflammatory mediators.immune mechanisms maybe: IgE-dependent & IgE-independent Basophilia=increase above 0.2x10^9/L associated with immediate hypersensitivity R xs & chronic myeloproliferative disorder Basophilic Leukemia very rare>80% basohi l Basopenia inflammation&immune Rxs
71
72
73 Quantitative Monocyte Changes Neoplastic MDS/MPD chronic myelomonocytic y leukemia juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia chronic myelogenous leukemia Acute monocytic,myelomonocytic& myelocytic y leukemia Reactive inflammation/collagen/immune disorders/certain infections Monocytopenia stem cell disorders such as aplastic anemia
74
75 Qualitative Monocyte Disorders Lysosomal storage disorders d Gaucher Disease Niemann-Pick kdisease Miscellaneous (Tay-sachs,Sandhoff & W olman disease) Inherited defeciency in one or more enzymes in lipid metabolism Sea-Blue Histiocytosis Syndrome
76
77
78
Leukocyte Disorders. Dr Alauldeen Mudhafar Zubair
 Leukocyte Disorders Dr Alauldeen Mudhafar Zubair Composition of blood Specialized connective tissue Blood cells (formed elements) suspended in plasma Blood volume: 5-6 liters (approx 1.5 gal) in males
Leukocyte Disorders Dr Alauldeen Mudhafar Zubair Composition of blood Specialized connective tissue Blood cells (formed elements) suspended in plasma Blood volume: 5-6 liters (approx 1.5 gal) in males
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE
 Log Out Help current login :lcytryn@montefiore.org HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE Lawrence Cytryn, M.D. - Course Director 1998 Edward Burns, M.D. Images used by permission within AECOM
Log Out Help current login :lcytryn@montefiore.org HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE Lawrence Cytryn, M.D. - Course Director 1998 Edward Burns, M.D. Images used by permission within AECOM
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML)
 Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم WBCs disorders *Slide 2: - we will focus on the disorders that are related to the # of WBCs - in children the # of lymphocyte is more than it in adults,sometimes more than neutrophils
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم WBCs disorders *Slide 2: - we will focus on the disorders that are related to the # of WBCs - in children the # of lymphocyte is more than it in adults,sometimes more than neutrophils
Notes for the 2 nd histology lab
 Notes for the 2 nd histology lab Note : Please refer to the slides and see the morphological characteristics of each cell, as the practical exam will be in the form of figures. SLIDE #2 Erythropoiesis
Notes for the 2 nd histology lab Note : Please refer to the slides and see the morphological characteristics of each cell, as the practical exam will be in the form of figures. SLIDE #2 Erythropoiesis
Leukocytosis - Some Learning Points
 Leukocytosis - Some Learning Points Koh Liang Piu Department of Hematology-Oncology National University Cancer Institute National University Health System Objectives of this talk: 1. To provide some useful
Leukocytosis - Some Learning Points Koh Liang Piu Department of Hematology-Oncology National University Cancer Institute National University Health System Objectives of this talk: 1. To provide some useful
٢٨/٠١/١٤٣٧. Prof. M. Rushdi.
 ١ PARAMETERS OF LEUCOCYTES PICTURE TtlWBC Total WBCs count Differential LC Hemocytometer Blood film Blood Cell Counter Blood Cell Counter INTERPRETATION OF LEUCOCYTES PICTURE 1.Leucocytosis. 2. Leucopenia.
١ PARAMETERS OF LEUCOCYTES PICTURE TtlWBC Total WBCs count Differential LC Hemocytometer Blood film Blood Cell Counter Blood Cell Counter INTERPRETATION OF LEUCOCYTES PICTURE 1.Leucocytosis. 2. Leucopenia.
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and
 Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
Proceeding of the LAVC Latin American Veterinary Conference Oct , 2009 Lima, Peru
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceeding of the LAVC Latin American Veterinary Conference Oct. 16-19, 2009 Lima, Peru Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the LAVC http://www.ivis.org/
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceeding of the LAVC Latin American Veterinary Conference Oct. 16-19, 2009 Lima, Peru Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the LAVC http://www.ivis.org/
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89
 Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Faculty of Medicine Dr. Tariq Aladily
 Iron deficiency anemia The most common anemia worldwide Only 10% of ingested iron is absorbed Most dietary iron occurs in meat products Absorbed in duodenum Hepcidin By inhibiting ferroportin, hepcidin
Iron deficiency anemia The most common anemia worldwide Only 10% of ingested iron is absorbed Most dietary iron occurs in meat products Absorbed in duodenum Hepcidin By inhibiting ferroportin, hepcidin
Hemopoiesis and Blood
 Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
The Complete Blood Count
 The Complete Blood Count (Cartesian Thinking at Its Best) A SEM Image of Normal Human Blood Laurie Larsson February 22, 2010 Anatomy and Philology II Dr. Danil Hammoudi Introduction A complete blood count
The Complete Blood Count (Cartesian Thinking at Its Best) A SEM Image of Normal Human Blood Laurie Larsson February 22, 2010 Anatomy and Philology II Dr. Danil Hammoudi Introduction A complete blood count
Contents. Section Editor David Blomberg, MD
 Contents A Closer Look At Discussions...viii Heme CAPsules Video...ix Foreword...x Preface to First Edition...xii Preface to Second Edition...xiii Contributors...xiv Current and Past HCMRC Members...xv
Contents A Closer Look At Discussions...viii Heme CAPsules Video...ix Foreword...x Preface to First Edition...xii Preface to Second Edition...xiii Contributors...xiv Current and Past HCMRC Members...xv
Outline: Objectives RED BLOOD CELL. Pathology of RBC and WBC. Morphology and normal value of red blood cell
 SCBM343: Clinical Pathology Pathology of RBC and WBC RED BLOOD CELL Niwat Kangwanrangsan, Ph.D. [niwat.kan@mahidol.ac.th] Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University 272 Rama VI
SCBM343: Clinical Pathology Pathology of RBC and WBC RED BLOOD CELL Niwat Kangwanrangsan, Ph.D. [niwat.kan@mahidol.ac.th] Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University 272 Rama VI
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228
 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD. Part 1
 HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 1 NONNEOPLASTIC DISEASES OF THE WHITE BLOOD CELLS There are five major types of WBCs in the blood: neutrophils,
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 1 NONNEOPLASTIC DISEASES OF THE WHITE BLOOD CELLS There are five major types of WBCs in the blood: neutrophils,
Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue
 CONTENTS Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue White blood cells and lymph nodes Quantitative disorder of white blood cells Reactive lymphadenopathies Infectious lymphadenitis Tumor metastasis
CONTENTS Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue White blood cells and lymph nodes Quantitative disorder of white blood cells Reactive lymphadenopathies Infectious lymphadenitis Tumor metastasis
Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue
 Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul, M.D. Department of Pathology and Forensic Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Naresuan University CONTENTS White blood cells and lymph
Pathology of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid tissue Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul, M.D. Department of Pathology and Forensic Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Naresuan University CONTENTS White blood cells and lymph
Myeloproliferative Disorders - D Savage - 9 Jan 2002
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Leukocytopenias. -lymphocytopenia. -neutropenia. -monocytopenia. BHS seminar 8Nov2014
 Leukocytopenias -lymphocytopenia -monocytopenia -neutropenia BHS seminar 8Nov2014 2010 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent Prof.dr.Lucien Noens, Hematology and Bloodbank, Ghent University hospital Neutrophil
Leukocytopenias -lymphocytopenia -monocytopenia -neutropenia BHS seminar 8Nov2014 2010 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent Prof.dr.Lucien Noens, Hematology and Bloodbank, Ghent University hospital Neutrophil
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
WBCs Disorders 1. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TEST PROGRAM Glass Slide - November 2016
 NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TEST PROGRAM Glass Slide - November 2016 Results from this proficiency test event are available at: http://www.wadsworth.org/regulatory/clep/pt/summaries SLIDE
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TEST PROGRAM Glass Slide - November 2016 Results from this proficiency test event are available at: http://www.wadsworth.org/regulatory/clep/pt/summaries SLIDE
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/
 Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Formation of Blood Cells
 Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 QUESTION 65 A 36-year-old man presents in a post-ictal state after an observed generalised seizure. Full blood investigation shows: haemoglobin 0 g/l [128-175] mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 106 fl [80-7]
QUESTION 65 A 36-year-old man presents in a post-ictal state after an observed generalised seizure. Full blood investigation shows: haemoglobin 0 g/l [128-175] mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 106 fl [80-7]
MORPHOLOGY OF BONE MARROW ASPIRATES. Dr.Prasanna N Kumar Head Department of Pathology, Oman Medical College, Oman
 MORPHOLOGY OF BONE MARROW ASPIRATES Dr.Prasanna N Kumar Head Department of Pathology, Oman Medical College, Oman BONE MARROW ASPIRATION Sites Sternum Anterior or posterior iliac spines Aspiration from
MORPHOLOGY OF BONE MARROW ASPIRATES Dr.Prasanna N Kumar Head Department of Pathology, Oman Medical College, Oman BONE MARROW ASPIRATION Sites Sternum Anterior or posterior iliac spines Aspiration from
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood: Functions. Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation. 2. Regulation. 3. Protection
 Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Introduction to Haematology. Prof Roger Pool Department of Haematology University of Pretoria
 Introduction to Haematology Prof Roger Pool Department of Haematology University of Pretoria Suggested reading Haematology at a Glance Atul Mehta & Victor Hoffbrand Second Edition Published by Blackwell
Introduction to Haematology Prof Roger Pool Department of Haematology University of Pretoria Suggested reading Haematology at a Glance Atul Mehta & Victor Hoffbrand Second Edition Published by Blackwell
12 Dynamic Interactions between Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells and the Bone Marrow: Current Biology of Stem Cell Homing and Mobilization
 Table of Contents: PART I: Molecular and Cellular Basis of Hematology 1 Anatomy and Pathophysiology of the Gene 2 Genomic Approaches to Hematology 3 Regulation of Gene Expression, Transcription, Splicing,
Table of Contents: PART I: Molecular and Cellular Basis of Hematology 1 Anatomy and Pathophysiology of the Gene 2 Genomic Approaches to Hematology 3 Regulation of Gene Expression, Transcription, Splicing,
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History An 11-year-old girl presented to the emergency room with wheezing and was diagnosed as having asthma. Her CBC showed WBC = 12.5 x 10 9 /L; Hgb = 12.4g/dL;
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History An 11-year-old girl presented to the emergency room with wheezing and was diagnosed as having asthma. Her CBC showed WBC = 12.5 x 10 9 /L; Hgb = 12.4g/dL;
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Diseases Of The Blood
 Diseases Of The Blood DR. Associate Professor Of Pathology Faculty Of Medicine Ain Shams University Red Blood Cells and Anemia RBC=4-6 million/mm 2 Hb=12-18 g/dl Oxygen Carrying Molecule Hemoglobin Tetramer:
Diseases Of The Blood DR. Associate Professor Of Pathology Faculty Of Medicine Ain Shams University Red Blood Cells and Anemia RBC=4-6 million/mm 2 Hb=12-18 g/dl Oxygen Carrying Molecule Hemoglobin Tetramer:
CHAPTER:4 LEUKEMIA. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY 8/12/2009
 LEUKEMIA CHAPTER:4 1 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Leukemia A group of malignant disorders affecting the blood and blood-forming tissues of
LEUKEMIA CHAPTER:4 1 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Leukemia A group of malignant disorders affecting the blood and blood-forming tissues of
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES
 MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra university hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences Key Features ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Cytopenias
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra university hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences Key Features ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Cytopenias
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD. Part 4 MYELOID NEOPLASMS
 HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 4 MYELOID NEOPLASMS Introduction: o Myeloid neoplasms are divided into three major categories: o Acute
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 4 MYELOID NEOPLASMS Introduction: o Myeloid neoplasms are divided into three major categories: o Acute
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) & Myeloproliferative neoplasms
 Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) & Myeloproliferative neoplasms Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) A multipotent stem cell that can differentiate into any of the myeloid lineage cells (RBCs, granulocytes, megakaryocytes)
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) & Myeloproliferative neoplasms Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) A multipotent stem cell that can differentiate into any of the myeloid lineage cells (RBCs, granulocytes, megakaryocytes)
r). SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION PAPER nnmlbih UNIVERSITY Sophia Blaauw INSTRUCTIONS FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES
 r). nnmlbih UNIVERSITY OF SCIEFICE nnd TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
r). nnmlbih UNIVERSITY OF SCIEFICE nnd TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
Hematology 101. Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD
 Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR. Dr. Tamara Alqudah
 Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR Dr. Tamara Alqudah Differential Leukocyte Count (DLC) There are 5 main types of WBCs: 1. Neutrophils: 40-80% 2. Eosinophils: 1-6 % 3. Basophils: < 1-2% 4. Lymphocytes:
Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR Dr. Tamara Alqudah Differential Leukocyte Count (DLC) There are 5 main types of WBCs: 1. Neutrophils: 40-80% 2. Eosinophils: 1-6 % 3. Basophils: < 1-2% 4. Lymphocytes:
Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material
 Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis
 Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Objectives are to: Identify the developmental cells of erythropoiesis
Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Objectives are to: Identify the developmental cells of erythropoiesis
Kathleen Finnegan MS MT(ASCP)SHCM
 Kathleen Finnegan MS MT(ASCP)SHCM Discuss the history of hematology automation and digital differentials. Discuss the HemoFAXS Hematology Analysis System by Tissue Gnostics. Review automated microscopy
Kathleen Finnegan MS MT(ASCP)SHCM Discuss the history of hematology automation and digital differentials. Discuss the HemoFAXS Hematology Analysis System by Tissue Gnostics. Review automated microscopy
Differential Blood Smear H3
 Verein für Association pour le Associazione per il medizinische Qualitätskontrolle contrôle de qualité médical controllo di qualità medico Report Differential Blood Smear H3 MQ 2015-4 MQ, Institut für
Verein für Association pour le Associazione per il medizinische Qualitätskontrolle contrôle de qualité médical controllo di qualità medico Report Differential Blood Smear H3 MQ 2015-4 MQ, Institut für
Approaching Neutropenia in Children. SW Florida Osteopathic Medical Society: 39 th Annual Seminars in Family Practice
 Approaching Neutropenia in Children SW Florida Osteopathic Medical Society: 39 th Annual Seminars in Family Practice Approaching Neutropenia in Children Emad Salman M.D Golisano Children s Hospital of
Approaching Neutropenia in Children SW Florida Osteopathic Medical Society: 39 th Annual Seminars in Family Practice Approaching Neutropenia in Children Emad Salman M.D Golisano Children s Hospital of
ADx Bone Marrow Report. Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information
 ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Everyday Challenges and Pitfalls
 Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Everyday Challenges and Pitfalls Kathryn Foucar, MD kfoucar@salud.unm.edu Henry Moon lecture May 2007 Outline Definition Conceptual overview; pathophysiologic mechanisms Incidence,
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Everyday Challenges and Pitfalls Kathryn Foucar, MD kfoucar@salud.unm.edu Henry Moon lecture May 2007 Outline Definition Conceptual overview; pathophysiologic mechanisms Incidence,
Haematology Team431 3/4. White Blood Cells. Abdulrahman Alkadhaib & Alaa Alanazi. Mohammed Page 1 Al-Dhaheri
 3/4 White Blood Cells Abdulrahman Alkadhaib & Alaa Alanazi Mohammed Page 1 Al-Dhaheri Red color = Important information Blue color = Additional notes Objectives: Identify the types of white blood cells
3/4 White Blood Cells Abdulrahman Alkadhaib & Alaa Alanazi Mohammed Page 1 Al-Dhaheri Red color = Important information Blue color = Additional notes Objectives: Identify the types of white blood cells
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa
 Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
Blood & Blood Formation
 Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Chapter 14. Blood. Blood Volume. Blood Composition. Blood
 Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
4. TEXTBOOK: ABUL K. ABBAS. ANDREW H. LICHTMAN. CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY. 5 TH EDITION. Chapter 2. pg
 LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
QUESTIONS OF HEMATOLOGY AND THEIR ANSWERS
 QUESTIONS OF HEMATOLOGY AND THEIR ANSWERS WHAT IS TRUE AND WHAT IS FALSE? Questions 1 Iron deficiency anemia a) Is usually associated with a raised MCV. b) The MCH is usually low. c) Is most commonly due
QUESTIONS OF HEMATOLOGY AND THEIR ANSWERS WHAT IS TRUE AND WHAT IS FALSE? Questions 1 Iron deficiency anemia a) Is usually associated with a raised MCV. b) The MCH is usually low. c) Is most commonly due
Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
Peripheral Blood Smear: Diagnostic Clues and Algorithms
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Evaluation of Bone Marrow Biopsies and Aspirates ANNA PORWIT DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, LUND UNIVERSITY
 Evaluation of Bone Marrow Biopsies and Aspirates ANNA PORWIT DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, LUND UNIVERSITY DISCLOSURES NONE Learning objectives To review the rules of BMA evaluation To review the main issues
Evaluation of Bone Marrow Biopsies and Aspirates ANNA PORWIT DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, LUND UNIVERSITY DISCLOSURES NONE Learning objectives To review the rules of BMA evaluation To review the main issues
EHE1-16 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation
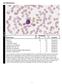 Cell Identification EHE1-16 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Blast cell 154 90.1 Educational Lymphocyte 4 2.3 Educational Lymphocyte, reactive 1 0.6 Educational Lymphoma cell (malignant) 1
Cell Identification EHE1-16 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Blast cell 154 90.1 Educational Lymphocyte 4 2.3 Educational Lymphocyte, reactive 1 0.6 Educational Lymphoma cell (malignant) 1
MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASE. Dr Mere Kende MBBS (UPNG), MMED (Path),MAACB, MACTM, MACRRM (Aus) Lecturer-SMHS UPNG
 MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASE Dr Mere Kende MBBS (UPNG), MMED (Path),MAACB, MACTM, MACRRM (Aus) Lecturer-SMHS UPNG Myeloproliferative Diseases Essential to diagnosis Acquired clonal abnormalities of the hematopoietic
MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASE Dr Mere Kende MBBS (UPNG), MMED (Path),MAACB, MACTM, MACRRM (Aus) Lecturer-SMHS UPNG Myeloproliferative Diseases Essential to diagnosis Acquired clonal abnormalities of the hematopoietic
Blood Cells. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 20-year-old female with sickle cell disease who presents with bilateral leg pain for 3 days. She is scheduled to have bilateral hip and leg
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 20-year-old female with sickle cell disease who presents with bilateral leg pain for 3 days. She is scheduled to have bilateral hip and leg
SH A CASE OF PERSISTANT NEUTROPHILIA: BCR-ABL
 SH2017-0124 A CASE OF PERSISTANT NEUTROPHILIA: BCR-ABL NEGATIVE John R Goodlad 1, Pedro Martin-Cabrera 2, Catherine Cargo 2 1. Department of Pathology, NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde, QEUH, Glasgow 2. Haematological
SH2017-0124 A CASE OF PERSISTANT NEUTROPHILIA: BCR-ABL NEGATIVE John R Goodlad 1, Pedro Martin-Cabrera 2, Catherine Cargo 2 1. Department of Pathology, NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde, QEUH, Glasgow 2. Haematological
Supervisor: Prof. Dr. P Vandenberghe Dr. C Brusselmans
 Contribution of molecular diagnosis in eosinophilia/hypereosinophilia Eosinophilia Hypereosinophilia Hypereosinophilic syndrome Immune mediated hypereosinophilia Chronic eosinophilic leukemia (NOS)/ Idiopathic
Contribution of molecular diagnosis in eosinophilia/hypereosinophilia Eosinophilia Hypereosinophilia Hypereosinophilic syndrome Immune mediated hypereosinophilia Chronic eosinophilic leukemia (NOS)/ Idiopathic
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells)
 Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) As we, leukocytes ( white blood cells ) are of two types : 1- Granulocytes :have granules in the cytoplasm and include neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. 2- Agranulocytes:
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) As we, leukocytes ( white blood cells ) are of two types : 1- Granulocytes :have granules in the cytoplasm and include neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. 2- Agranulocytes:
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
A Practical Approach to Leukopenia/Neutropenia in Children. Vandy Black, M.D., M.Sc., FAAP OLOL Children s Hospital August 24, 2014
 A Practical Approach to Leukopenia/Neutropenia in Children Vandy Black, M.D., M.Sc., FAAP OLOL Children s Hospital August 24, 2014 Disclosures EPIC trial MAST Therapeutics SUSTAIN trial Selexys Pharmaceuticals
A Practical Approach to Leukopenia/Neutropenia in Children Vandy Black, M.D., M.Sc., FAAP OLOL Children s Hospital August 24, 2014 Disclosures EPIC trial MAST Therapeutics SUSTAIN trial Selexys Pharmaceuticals
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD. MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
Chapter 13 The Blood
 Chapter 13 The Blood Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms agglutination erythrocyte lymphocyte albumin fibrin megakaryocyte anemia hematocrit monocyte antigen
Chapter 13 The Blood Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms agglutination erythrocyte lymphocyte albumin fibrin megakaryocyte anemia hematocrit monocyte antigen
Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms
 Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms The minimum number of blasts to diagnose acute myeloid leukemia is 5% 10% 20% 50% 80% AML with the best prognosis is AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormality AML with myelodysplasia
Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms The minimum number of blasts to diagnose acute myeloid leukemia is 5% 10% 20% 50% 80% AML with the best prognosis is AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormality AML with myelodysplasia
Materials and Methods
 Peripheral Blood Morphologic Changes after High-Dose Antineoplastic Chemotherapy and Recombinant Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Administration DANIEL P. KERRIGAN, M.D., ANNIE CASTILLO, M.D.,
Peripheral Blood Morphologic Changes after High-Dose Antineoplastic Chemotherapy and Recombinant Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Administration DANIEL P. KERRIGAN, M.D., ANNIE CASTILLO, M.D.,
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY BLOOD AND BODY FLUID PHYSIOLOGY LECTURER: MR A.O. AKINOLA OBJECTIVES Leukopoiesis Thrombopoiesis Leukopoiesis and Lymphopoiesis White blood
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY BLOOD AND BODY FLUID PHYSIOLOGY LECTURER: MR A.O. AKINOLA OBJECTIVES Leukopoiesis Thrombopoiesis Leukopoiesis and Lymphopoiesis White blood
A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC. A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters
 A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters 2. 45% cells by volume called hematocrit (HCT) a. red blood cells (RBC) mostly
A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters 2. 45% cells by volume called hematocrit (HCT) a. red blood cells (RBC) mostly
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA. April 16, 2008
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Multiple Choice Part I Questions
 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood 10.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by. A) Label A
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood 10.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by. A) Label A
Laboratory Diagnosis for WBC Pathology
 CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Dr. Araceli Jacoba WBC Parameters WBC Count Differential count Absolute count Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP) Special stains of WBC Cluster designation Types of WBC Counts WBC Count
CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Dr. Araceli Jacoba WBC Parameters WBC Count Differential count Absolute count Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP) Special stains of WBC Cluster designation Types of WBC Counts WBC Count
Proper Slide Preparation
 Hematology Essentials: A Foundation for WBC Review Using Case Studies Christine Hinz, MS, MLS(ASCP) CM Proper Slide Preparation smooth, homogenous film 1/2 to 3/4 the slide length straight feather edge
Hematology Essentials: A Foundation for WBC Review Using Case Studies Christine Hinz, MS, MLS(ASCP) CM Proper Slide Preparation smooth, homogenous film 1/2 to 3/4 the slide length straight feather edge
Collect and label sample according to standard protocols. Gently invert tube 8-10 times immediately after draw. DO NOT SHAKE. Do not centrifuge.
 Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Hematopathology Lab. Third year medical students
 Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
PNH Glossary of Terms
 AA Absolute neutrophil count Alendronate Allergen ALT Anemia Antibodies Anticoagulant Anticoagulation Antigen Antithymocyte globulin (ATG) Aplastic Aplastic anemia Band Bilirubin Blast cells Bone marrow
AA Absolute neutrophil count Alendronate Allergen ALT Anemia Antibodies Anticoagulant Anticoagulation Antigen Antithymocyte globulin (ATG) Aplastic Aplastic anemia Band Bilirubin Blast cells Bone marrow
Morfologia normale e patologica
 Morfologia normale e patologica Gina Zini Centro di Ricerca ReCAMH Dpt. Ematologia Università Cattolica S. Cuore - Roma EMATOLOGIA DI LABORATORIO: percorsi diagnostici e obiettivi clinici. Milano 11-12
Morfologia normale e patologica Gina Zini Centro di Ricerca ReCAMH Dpt. Ematologia Università Cattolica S. Cuore - Roma EMATOLOGIA DI LABORATORIO: percorsi diagnostici e obiettivi clinici. Milano 11-12
Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study
 Original Research Article Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study Priyanka Poonam 1*, N.K. Bariar 2 1 Tutor, Department of Pathology, Patna Medical
Original Research Article Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study Priyanka Poonam 1*, N.K. Bariar 2 1 Tutor, Department of Pathology, Patna Medical
Polycthemia Vera (Rubra)
 Polycthemia Vera (Rubra) Polycthemia Vera (Rubra) Increased red cells Clonal Myeloid lineages also increased 2-13 cases per million Mean age: 60 years Sites of Involvement Bone marrow Peripheral blood
Polycthemia Vera (Rubra) Polycthemia Vera (Rubra) Increased red cells Clonal Myeloid lineages also increased 2-13 cases per million Mean age: 60 years Sites of Involvement Bone marrow Peripheral blood
Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material
 Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material - 2018 Objectives Laboratory instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material - 2018 Objectives Laboratory instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II PLATELETS. Mature Stage: No nucleus. Only 2-3 µm in diameter: significantly smaller than RBCs
 1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LAB BLOOD PLATES EOSINOPHIL Contains large red-staining granules Usually 2 lobes 12-17 µm: about the size of neutrophils (2X erythrocytes) regulation/reduction of Histamine.
1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LAB BLOOD PLATES EOSINOPHIL Contains large red-staining granules Usually 2 lobes 12-17 µm: about the size of neutrophils (2X erythrocytes) regulation/reduction of Histamine.
Megakaryocyte or Precursor, Normal
 Precursor, Normal SYNONYMS none VITAL STATISTICS size...20-160 µm in diameter N:C ratio...varible, depending on maturation of cell; early forms have a high N:C rato which decreases as cell matures and
Precursor, Normal SYNONYMS none VITAL STATISTICS size...20-160 µm in diameter N:C ratio...varible, depending on maturation of cell; early forms have a high N:C rato which decreases as cell matures and
Leukocytes and Platelets
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The leukocyte, commonly known as a white blood cell (or WBC), is a major component of the body s defenses against disease. Leukocytes protect the body against invading microorganisms
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The leukocyte, commonly known as a white blood cell (or WBC), is a major component of the body s defenses against disease. Leukocytes protect the body against invading microorganisms
Hematopathology Case Study
 www.medfusionservices.com Hematopathology Case Study CV3515-14 JUNE Clinical Presentation: Clinical Information: A 42 year old male with history of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) presents with an elevated
www.medfusionservices.com Hematopathology Case Study CV3515-14 JUNE Clinical Presentation: Clinical Information: A 42 year old male with history of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) presents with an elevated
Disclosures. Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Case-Based Approach. Objectives. Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
 Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Case-Based Approach Disclosures No conflicts of interests regarding the topic being presented Adam M. Miller, MD PGY-4 Resident Physician Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Case-Based Approach Disclosures No conflicts of interests regarding the topic being presented Adam M. Miller, MD PGY-4 Resident Physician Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Hematology Page 1 of 8
 Hematology Page 1 of 8 Hematology Major Category Code Headings Revised 12/17 1 Basic methodology and test armamentarium 20000 2 Normal hematopoiesis & hemostasis 20100 3 RBC disorders, non-neoplastic 20340
Hematology Page 1 of 8 Hematology Major Category Code Headings Revised 12/17 1 Basic methodology and test armamentarium 20000 2 Normal hematopoiesis & hemostasis 20100 3 RBC disorders, non-neoplastic 20340
