ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS
|
|
|
- Helen Lyons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1963, 38, 492. ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS BY PHILIP JACOBS From the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital, Birmingham (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 28, 1963) Ankylosing spondylitis is a disease that usually affects young men, though older men and both young and middle-aged women may suffer from the condition. Close questioning of patients will often elicit a previous history of fleeting joint pains, 'growing pains' and pains low in the back and down the thighs-such symptoms may have been of several years' duration. To Scott (1942) is due the credit for this observation. He recorded cases whose symptoms could be traced back to childhood and he named this stage of the illness 'the prespondylitic syndrome'. He further stated that on account of the wandering nature of the pains, most of such patients have been erroneously treated for months or years for such conditions as recurrent fibrositis, muscular rheumatism or even just growing pains. More recently other authors have confirmed Scott's (1942) observations. Hart (1955) reported that 18 out of 166 male and two out of 18 female patients suffering from established ankylosing spondylitis complained of symptoms beginning between the ages of 10 and 15 years. Edstrom, Thune and Wittbom-Cigen (1960) recorded three boys in whom ankylosing spondylitis started at the ages of 5, 8 and 12 years. Ansell and Bywaters (1962) followed up 43 children who were regarded initially as probably but not definitely suffering from Still's disease. Two of these children developed ankylosing spondylitis, their ages at the onset of symptoms were 10 and 12 years; their sex was not recorded. Though it is true that the possibility of such an early onset of ankylosing spondylitis is becoming increasingly recognized, it is felt that this is not widely known. Due to the indefinite symptomatology and particular age incidence, these patients may seek help from a wide variety of practitioners such as general physicians, paediatricians, rheumatologists and orthopaedic surgeons. Others may 492 remain for years under the care of their general practitioners. In this paper, three cases are presented whose initial symptoms dated from the ages of 10, 11 and 15 years, and over the years the development of the classical picture of ankylosing spondylitis was observed. Problems of the diagnosis are discussed with special reference to radiological findings. Case Histories Case 1. A girl, who was born on January 26, 1944, attended hospital on March 15, 1955, complaining of pain in the right hip. The pain was of four months' duration; thus she dated her symptoms to the age of 103 years. The pain prevented her from running fast and from skipping. On examination, movements of the right hip were painful and restricted. No other abnormal clinical finding was discovered. From a radiograph, March 15, 1955 (Fig. 1), anteroposterior view of the hips, it was thought that there was some acetabular protrusion on both sides. No further lesion was noted, but in retrospect one sees some sclerosis round the right sacro-iliac joint and also slight similar changes on the left side. Having experienced alternating remissions and exacerbations of symptoms for the following nine months, she was admitted to hospital with a tentative diagnosis of protrusio acetabuli. She was treated on traction for three months. Her erythrocyte sedimentation rate (Westergren) was raised at one time to 23 mm./hr., but it subsequently became normal. She became asymptomatic after three months and remained well for the next three years apart from minor exacerbations of low back pain and pain in both hips. A radiograph on February 25, 1958 (Fig. 2) showed irregularity of margins of the right sacro-iliac joint and some peri-articular sclerosis. On December 13, 1960, she complained that exacerbations of pains had become more severe. At this time, though still attending school, she worked on Saturdays filling self-service trays in a supermarket. She complained of pains in both hips after doing this work.
2 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN CHILDREN 493 FIG. 1.-Case 1, March 15, 1955, antero-posterior view of the hips. The sacro-iliac joints were considered to be normal at the time. However, some sclerosis is seen round the right sacro-iliac joint and there is minimal sclerosis round the left sacro-iliac joint. FIG. 2.-Case 1, February 25, 1958, antero-posterior view of sacro-iliac joints showing development of ankylosing spondylitis. The patient is now 14IA years. Irregularity of the right sacro-iliac joint margins and reduction of joint space on the left side are shown.
3 494 ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD FIG. 3.-Case 1, January 4, 1961, postero-anterior view of sacro-iliac joints. Marginal erosions and peri-articular sclerosis are seen on both sides and there is reduction of joint space on the left side. Considerable stiffness in the lumbar spine was noted though movements of the hip joints were full. Her erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 36 mm./hr. She was considered clinically to be suffering from ankylosing spondylitis. A radiograph on January 4, 1961 (Fig. 3) showed definite erosions of both sacro-iliac joints and also some peri-articular sclerosis. No radiological abnormality was found in the hips or in the spine. The lesion progressed for a while, her erythrocyte sedimentation rate remained high and general stiffness of the spine developed. A radiograph on October 13, 1962 (Fig. 4) revealed that the left sacro-iliac joint was completely ankylosed and the right one almost so. Comments. (a) The history of pains, first involving one side then the other with remissions, is typical of the pre-spondylitic stage of ankylosing spondylitis. (b) The disease in this girl started at the age of 10 years and was fully developed before the age of 17 years. FIG. 4.-Case 1, October 13, 1962, the left sacro-iliac joint is now completely ankylosed and the right one almost so.
4 ANKYLOSING SPOND YLITIS IN CHILDREN FIG. 5.-Case 2, August 23, 1957, antero-posterior view of the pelvis. Left-sided sacralization of L5 is noted. Sclerosis is seen round both sacro-iliac joints, more pronounced on the right side. The sclerosis was thought, incorrectly, to be associated with the sacralized 5th lumbar vertebra. (c) Some sclerosis round the right sacro-iliac joint and a little round the left one was seen on the initial and all subsequent radiographs. Though this appearance is not in itself pathognomonic of ankylosing spondylitis, it is felt that one should have paid more attention to it. Case 2. A boy, whose date of birth was September 15, 1944, first attended hospital on August 23, 1957, on account of intermittent pain and limp in the right hip and discomfort in the region of the right sacro-iliac joint. He dated his symptoms to an injury at physical training 18 months previously; ever since that time he had suffered from intermittent attacks of pain. Limited abduction of the right hip was found on examination, but there was no other abnormal physical sign. A radiograph on August 23, 1957 (Fig. 5), showed a left-sided sacralization of L5. Some sclerosis was seen round the right sacro-iliac joint and a little round the left sacro-iliac joint. It was thought that the sclerosis round the sacro-iliac joints was secondary to the anomaly of the lumbo-sacral region. He became symptom free after three months, and no abnormal physical signs were found. He attended hospital next on January 26, 1962, complaining of pain and stiffness, which was now more severe, in the left hip and in the left knee. In the intervening years he had experienced only transient pains which had not inconvenienced him. Now the pains had become sufficiently troublesome to interfere with his work as a butcher. Definite clinical signs of ankylosing spondylitis were present now; his back was flat due to muscle spasm, movements of the spine and hips were 495 restricted. His erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 40 mm./hr. and his Rose-Waaler test was negative. A radiograph on January 26, 1962 (Fig. 6) showed now much dense sclerosis round both sacro-iliac joints with sub-articular erosions. No radiographic evidence of spinal lesions was demonstrable. Comments. (a) Earliest symptoms in this boy were noted at the age of 11 years, and he attended hospital before his 13th birthday. (b) A very similar history to that of Case 1 was given, including asymmetrical development of the lesion. (c) Early sclerosis round sacro-iliac joints was incorrectly attributed to the presence of an anomaly of the lumbo-sacral spine. Case 3. A girl, who was born on August 16, 1936, was first seen on July 17, 1952, with a history of pain in the lower part of the back, over the right sacro-iliac joint and down the right leg. She dated her symptoms to a fall some three months previously, but it seemed that pains in the back caused her to fall. Fleeting pains in the lower part of the back had been noted for some months previously. There was definite pain on compression of the right sacro-iliac joint and some pain and restricted movement in the right hip. A clinical diagnosis of tuberculosis of the right sacro-iliac joint was made. At the time, there was considered to be supporting radiographic evidence for the diagnosis, but on later scrutiny no definite radiological abnormality could be found. She was treated in a plaster spica for three months and then discharged home wearing a spinal support. It was considered that
5 496 ARCIHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD FIG. 6.-Case 2, January 26, There is now much dense sclerosis round both sacro-iliac joints, reduction of joint spaces and periarticular erosions. no definite clinical or radiographic evidence of a tuberculous lesion had been substantiated and a final diagnosis of sacro-iliac strain was suggested. She remained in good general health for the next two and a half years, merely complaining of fleeting pains in the lower part of the back and in the right sacro-iliac region. No disability was caused and she started nursing. Soon after her 18th birthday, she complained of severe pain in the right sacro-iliac joint and also of pain in the left sacro-iliac joint, in both hips and in the spine. Her erythrocyte sedimentation rate was now 40 mm./hr. A radiograph on February 17, 1956 (Fig. 7) showed dense peri-articular sclerosis round both sacro-iliac joints and sub-articular erosions. No spinal lesions were found at this stage. In view of the rather nebulous previous history of a possible tuberculous sacro-iliitis, a biopsy of bone round the right sacro-iliac joint was performed. This procedure ruled out the possibility of a tuberculous lesion. Symptoms progressed rapidly and severe pains and very restricted movements of the hips and spine were experienced. Her erythrocyte sedimentation rate was FIG. 7.-Case 3, February 17, 1956, postero-anterior view of the sacro-iliac joints. There are fully-developed changes of ankylosing spondylitis manifested by dense peri-articular sclerosis and marginal erosions.
6 ANKYLOSING SPOND YLITIS IN CHILDREN FIG. 8.-Case 3, October 4, 1956, antero-posterior view of the pelvis. Marked progression of the lesion is seen. The sacro-iliac joints are almos fused and considerable loss of cartilage in both hips has now resulted. constantly raised. There was no doubt now of the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis. A radiograph on October 4, 1956 (Fig. 8) revealed deterioration. The sacro-iliac joints were almost completely fused and considerable loss of joint cartilage was seen in both hips. Comments. (a) This girl's initial history of fleeting pains first on one side and then on both was very similar to that of Cases 1 and 2. (b) Difficulties in diagnosis arose even when both sacro-iliac joints were affected. In retrospect, my error was due first to being misled by the previous history of a possible tuberculous lesion and, more important, due to unfamiliarity with the possibility of a pre-spondylitic stage of ankylosing spondylitis in a 15-year-old girl. Discussion The diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis in its fully developed form is usually obvious at first sight, both clinically and radiologically. In the early stages of the disease, however, the converse often applies and a definitive diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis may be impossible to reach either clinically or radiologically, even though the condition may be strongly suspected. 497 Factors of importance in considering the diagnosis are: (a) Sex incidence: ankylosing spondylitis occurs more frequently in male subjects. The sex incidence is variously stated but is usually of the order of 10 men to one woman. Consideration of the sex incidence is not likely to be of help in a difficult case, indeed two of the present cases reported were female. (b) Natural history of the disease: West (1949) has described three phases of the disease. (I) repeated attacks of pain and stiffness-this phase corresponds with the pre-spondylitic syndrome of Scott (1942); (2) florid phase of continuous symptoms and general illness; (3) a stage of declining activity and minor relapses. The three cases described fit in well with the first two phases. Only Case 3 has been followed to the third phase. Childhood cases will, of course, be in the first phase. It seems that a relatively latent period of several years may elapse before the second phase is reached. Then the disease pursues a rapid course clinically and radiologically. 6
7 498 ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD (c) Symmetry of the sacro-iliac joint changes: detection of early spinal changes. Erosions of usually in ankylosing spondylitis the sacro-iliac intervertebral, costo-vertebral and costo-transverse joint changes are bilateral and symmetrical. In the joints may appear relatively early in the disease, first phase one side only may be involved or both but their radiographic demonstration may prove sides at different times may be stiff and painful. impossible. In practice not until changes in the The established lesion is not necessarily symmetrical, however. Scott (1942) recognized that ligamentous ossification, will it be possible to be shape of vertebral bodies occur, i.e. squaring and ankylosing spondylitis may manifest itself radiologically as a unilateral sacro-iliitis. Grainger The most useful early sign of ankylosing spondyl- certain that the spine is involved. (1957) recorded and illustrated two further examples. itis in a young patient is the presence of periarticular sclerosis. Unfortunately sclerosis round In these cases, the opposite sacro-iliac joint will eventually be affected but the asymmetrical pattern sacro-iliac joints may be found in conditions other may persist throughout the course of the disease. than ankylosing spondylitis. Not infrequently it is (d) Radiology: in the absence of a specific seen for no apparent cause and there is a tendency biochemical test, the radiological diagnosis of to overlook it, as in Case 1. Anomalies of the ankylosing spondylitis is of prime importance. lumbo-sacral spine may be associated with sclerosis Before considering pathological changes, it is round one or both sacro-iliac joints, due presumably important to understand the normal structural difference between the sacro-iliac joints of adolescence and had a partially sacralized 5th lumbar vertebra, and to reaction to abnormal stresses and strains. Case 2 and adult life. The sacro-iliac joint in childhood the sclerosis round the sacro-iliac joints was originally incorrectly regarded as being secondary to the and adolescence is wider, its margins are naturally serrated and lack articular cortex. Features of the lumbo-sacral anomaly. adult type of joint generally appear between the Adolescent osteochondritis provides a further ages of 17 and 20 years. Then the joint space will be less wide, its margins will lose their serrations and an articular cortex will appear manifested radiographically by a white line. Ankylosing spondylitis or, for that matter, any inflammatory lesion of an adult sacro-iliac joint will cause loss of articular cortex and marginal erosions. Thus the pathological adult sacro-iliac joint will resemble the healthy adolescent joint. Rolleston (1947) has described early changes of ankylosing spondylitis as 'a patchy persistence of the adolescent features of the normal joint, seen in adult life when such appearances would not normally be expected'. Useful as is this concept of the changes of early ankylosing spondylitis in the adult, it is obviously of no help in the diagnosis of early changes in the child or adolescent. It is thus clear that it will be necessary for more advanced changes to be reached before a radiological diagnosis is possible under such circumstances. These later changes would take the form of larger subcortical erosions causing a definite widening of joint space and patchy, mottled amorphous peri-articular sclerosis. It should be mentioned that local osteoporosis round involved joints does occur. However, it is impossible to be certain of this sign since its radiographic appearances are so indefinite. West (1949) emphasized that such terms as 'lack of definition, haziness and ground glass appearance of the sacro-iliac joints' are of no diagnostic aid and indeed such features may be apparent in the healthy subject. The same difficulties apply to the differential diagnosis. This condition may be associated with the presence of sclerosis round the sacro-iliac joints. In this lesion, however, clinical and radiological findings in the spine, usually in the mid- and lower-dorsal regions, are characteristic, and diagnostic difficulties are not to be expected. The rare type of ankylosing spondylitis presenting as a unilateral sacro-iliitis will need to be differentiated from pyogenic and tuberculous lesions. These latter conditions pursue a more rapid clinical and radiological course and confusion should not occur. Admittedly, Case 3 was incorrectly diagnosed as tuberculosis of a sacro-iliac joint originally. The error was attributable to unawareness at the time that ankylosing spondylitis could present itself unilaterally and in a girl of only 15 years. Conclusions Many children complain of fleeting pains in the lower part of the back and in the hips. Potential causes of such symptoms are many and varied; only a very few of such children eventually develop ankylosing spondylitis. Thus the possibility of the onset of the disease must be kept in perspective. The fact that a few of these children may develop ankylosing spondylitis is important. It is suggested that a prolonged follow-up is indicated in a child giving such a history. The natural tendency is to discharge the patient as cured when the latent period is reached. Furthermore, it is suggested that a radiograph of the sacro-iliac joints should be taken before the
8 Summary Three cases of ankylosing spondylitis are reported in whom symptoms began at the ages of 10, 11 and 15 years. Two of these patients were girls. The importance of recognition of the 'pre- ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN CHILDREN 499 child begins training for a career. All three patients spondylitic syndrome' of ankylosing spondylitis is reported began in jobs unsuitable for a sufferer from stressed. ankylosing spondylitis. One was a nurse, another Difficulties in diagnosis of the condition in its a shop assistant and the third a butcher. early stages are discussed. Difficulties in making the early diagnosis of early It is suggested that if the possibility of the condition is borne in mind and heed is taken of the ankylosing spondylitis have been discussed. It is felt that the condition can be diagnosed in some cases slightest radiological changes in the sacro-iliac if it is suspected. Full appreciation of the possibility of the pre-spondylitic phase of the disease is essential. Likewise the radiologist should consider the diagnosis when he sees slightest departures from normal in the sacro-iliac joints. A definitive diagnosis in some will be impossible since no abnormal radiographic changes may be present. joints, the diagnosis will be made more frequently in childhood. It is a pleasure to thank my surgical colleagues, Mr. F. G. Allan and Mr. T. S. Donovan, for kindly allowing me access to their case records. REFERENCES Ansell, B. M. and Bywaters, E. G. L. (1962). Diagnosis of 'probable' Still's disease and its outcome. Ann. rheum. Dis., 21, 253. Edstrom, G., Thune, S. and Wittbom-Cig6n, G. (1960). Juvenile ankylosing spondylitis. Acta rheum. scand., 6, 161. Grainger, R. G. (1957). Radiological aspects of sacro-iliac arthritis. Proc. roy. Soc. Med., 50, 854. Hart, F. D. (1955). Ankylosing spondylitis: A review of 184 cases. Ann. rheum. Dis., 14, 77. Rolleston, G. L. (1947). The early radiological diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis. Brit. J. Radiol., 20, 288. Scott, S. G. (1942). Adolescent Spondylitis or Ankylosing Spondylitis. Oxford University Press, London. West, H. F. (1949). The aetiology of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. rheum. Dis., 8, 143. Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 October Downloaded from on 19 June 2018 by guest. Protected by
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS
 HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
in the 77 adults suffering from rheumatoid arthritis ranged from 22 to 79 years (mean 52) and in the 23 with juvenile
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (972), 3, 364 Cervical spine involvement in patients with chronic undergoing orthopaedic surgery E. ORNILLA, B. M. ANSELL, AND A. J. SWANNELL MRC Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red
Ann. rheum. Dis. (972), 3, 364 Cervical spine involvement in patients with chronic undergoing orthopaedic surgery E. ORNILLA, B. M. ANSELL, AND A. J. SWANNELL MRC Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review
 Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF DYSPLASIA
 PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF CONGENITAL DISLOCATION OF THE HIP*
 A LONGTERM FOLLOWUP OF CONGENITAL DISLOCATION OF THE HIP* E. W. SOMERVILLE From The Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford Drawing upon a total experience of 450 hips affected by established congenital dislocation
A LONGTERM FOLLOWUP OF CONGENITAL DISLOCATION OF THE HIP* E. W. SOMERVILLE From The Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford Drawing upon a total experience of 450 hips affected by established congenital dislocation
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
THE RELAPSE IN SCARLET FEVER
 THE RELAPSE IN SCARLET FEVER BY JAMES S. ANDERSON, M.A., M.D., D.P.H., Medical Superintendent, Leeds City Hospitals, and Lecturer in Infectious Diseases, University of Leeds. In this country during the
THE RELAPSE IN SCARLET FEVER BY JAMES S. ANDERSON, M.A., M.D., D.P.H., Medical Superintendent, Leeds City Hospitals, and Lecturer in Infectious Diseases, University of Leeds. In this country during the
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
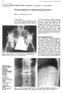 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
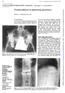 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
SPINA BIFIDA OCCULTA WITH ENGAGEMENT OF THE FIFTH LUMBAR SPINOUS PROCESS. A Cause of Low Back Pain and Sciatica
 SPINA BIFIDA OCCULTA WITH ENGAGEMENT OF THE FIFTH LUMBAR SPINOUS PROCESS A Cause of Low Back Pain and Sciatica CARLOS E. DE ANQUIN, CORDOBA, ARGENTINA Fro,n the Orthopaedic Department, Military Hospital,
SPINA BIFIDA OCCULTA WITH ENGAGEMENT OF THE FIFTH LUMBAR SPINOUS PROCESS A Cause of Low Back Pain and Sciatica CARLOS E. DE ANQUIN, CORDOBA, ARGENTINA Fro,n the Orthopaedic Department, Military Hospital,
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
At least one slide latex test was performed on all 65. of them. there were more male cases but after 30 years the. female cases predominated (Fig. 1).
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY OF THE
 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY OF THE ERECTOR SPNAE N LOW BACK PAN BY J. S. R. GOLDNG From the Orthopaedic Department, The Middlesex Hospital The ligaments of the lower back and of the ankle are injured more often than
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY OF THE ERECTOR SPNAE N LOW BACK PAN BY J. S. R. GOLDNG From the Orthopaedic Department, The Middlesex Hospital The ligaments of the lower back and of the ankle are injured more often than
MEMORANDUM 377/87. DATE: April 5, 1988 TO: ALL WCAT STAFF SUBJECT: DECISION NO. 377/87
 MEMORANDUM 377/87 DATE: April 5, 1988 TYPE: A TO: ALL WCAT STAFF SUBJECT: DECISION NO. 377/87 Aggravation (preexisting condition) (degenerative disc disease) - Disc, herniated (L4-5). - Bricklayer not
MEMORANDUM 377/87 DATE: April 5, 1988 TYPE: A TO: ALL WCAT STAFF SUBJECT: DECISION NO. 377/87 Aggravation (preexisting condition) (degenerative disc disease) - Disc, herniated (L4-5). - Bricklayer not
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging
 Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Unstable fractures of the pelvis treated with a trapezoid compression frame
 Acta Orthop Scand 55, 325-329, 1984 Unstable fractures of the pelvis treated with a trapezoid compression frame Sixteen patients with unstable pelvic fractures were treated by early reduction and fixation
Acta Orthop Scand 55, 325-329, 1984 Unstable fractures of the pelvis treated with a trapezoid compression frame Sixteen patients with unstable pelvic fractures were treated by early reduction and fixation
Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT
 TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
PROFFESOR THAMER AHMED HAMDAN M.B.CH.B, F.R.C.S(ED), F.R.C.P(ED), F.A.C.S,F.I.C.S CHANCELLOR OF BASRA UNIVERSITY SICOT VICE PRESEDENT
 PROFFESOR THAMER AHMED HAMDAN M.B.CH.B, F.R.C.S(ED), F.R.C.P(ED), F.A.C.S,F.I.C.S CHANCELLOR OF BASRA UNIVERSITY SICOT VICE PRESEDENT DR.RAFID A. ALADAB M.B.CH.B,F.I.C.M.S(ORTHO),SICOT DIPLOMA ORTHOPEDIC
PROFFESOR THAMER AHMED HAMDAN M.B.CH.B, F.R.C.S(ED), F.R.C.P(ED), F.A.C.S,F.I.C.S CHANCELLOR OF BASRA UNIVERSITY SICOT VICE PRESEDENT DR.RAFID A. ALADAB M.B.CH.B,F.I.C.M.S(ORTHO),SICOT DIPLOMA ORTHOPEDIC
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
Evaluation of low back pain and assessment of lumbar corsets with and without back supports
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 11, 0, -5 Evaluation of low back pain and assessment of lumbar corsets with and without back supports R. MILLION,' K. HAAVIK NILSEN, M. I. V. JAYSON, AND R. D. BAKER From
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 11, 0, -5 Evaluation of low back pain and assessment of lumbar corsets with and without back supports R. MILLION,' K. HAAVIK NILSEN, M. I. V. JAYSON, AND R. D. BAKER From
HEAD CIRCUMFERENCE OF INFANTS RELATED TO BODY WEIGHT
 Arch Dis Childh 1965 40 672 HEAD CRCUMFERENCE OF NFANTS RELATED TO BODY WEGHT BY R S LLNGWORTH and W LUTZ From the Department of Child Health and the Department of Statistics the University of Sheffield
Arch Dis Childh 1965 40 672 HEAD CRCUMFERENCE OF NFANTS RELATED TO BODY WEGHT BY R S LLNGWORTH and W LUTZ From the Department of Child Health and the Department of Statistics the University of Sheffield
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum.
 The os coxae The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum. The ilium extends from the acetabulum upwards forming the lateral
The os coxae The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum. The ilium extends from the acetabulum upwards forming the lateral
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
A family with primary protrusio acetabuli
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 53-57 A family with primary protrusio acetabuli K. D'ARCY, B. M. ANSELL, AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Juvenile Rheumatism Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 53-57 A family with primary protrusio acetabuli K. D'ARCY, B. M. ANSELL, AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Juvenile Rheumatism Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial
Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 529/97. Recurrences (compensable injury).
 SUMMARY DECISION NO. 529/97 Recurrences (compensable injury). The worker suffered a low back injury in 1984. The worker appealed a decision of the Appeals Officer denying entitlement for recurrences in
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 529/97 Recurrences (compensable injury). The worker suffered a low back injury in 1984. The worker appealed a decision of the Appeals Officer denying entitlement for recurrences in
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 73/09
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 73/09 BEFORE: N. Jugnundan: Vice-Chair HEARING: January 12, 2009 at Toronto Oral DATE OF DECISION: January 20, 2009 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2009 ONWSIAT
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 73/09 BEFORE: N. Jugnundan: Vice-Chair HEARING: January 12, 2009 at Toronto Oral DATE OF DECISION: January 20, 2009 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2009 ONWSIAT
Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors. Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA
 Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA Use AT modifier which means active treatment. Claims submitted for Chiropractic manipulative treatment
Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA Use AT modifier which means active treatment. Claims submitted for Chiropractic manipulative treatment
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
SCOLIOSIS. From the In.stitute of Orthopaedics and the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, London and Stanmore
 THE ILIAC APOPHYSIS AND THE EVOLUTION OF CURVES IN SCOLIOSIS ALEXANDER L. ZAou&sIS, ATHENS, GREECE, and J. I. P. JAMES, EDINBURGH, SCOTLAND From the In.stitute of Orthopaedics and the Royal National Orthopaedic
THE ILIAC APOPHYSIS AND THE EVOLUTION OF CURVES IN SCOLIOSIS ALEXANDER L. ZAou&sIS, ATHENS, GREECE, and J. I. P. JAMES, EDINBURGH, SCOTLAND From the In.stitute of Orthopaedics and the Royal National Orthopaedic
Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예
 대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
given shows signs of careful investigation by all the methods normally available,
 October, 1934 DISEASES & INJURIES TO LOWER SPINE 355 DISEASES AND INJURIES OF THE LOWER SPINE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO COMPENSATION CASES.* By C. W. BUCKLEY, M.D., F.R.C.P. (Physician to the Devonshire
October, 1934 DISEASES & INJURIES TO LOWER SPINE 355 DISEASES AND INJURIES OF THE LOWER SPINE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO COMPENSATION CASES.* By C. W. BUCKLEY, M.D., F.R.C.P. (Physician to the Devonshire
A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint
 J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:189 193 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0082-y CASE REPORT A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint Kei Shinohara Shigeru Soshi
J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:189 193 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0082-y CASE REPORT A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint Kei Shinohara Shigeru Soshi
Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis
 Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Th e experience of the Cattaraugus County Bureau
 P R A C T I C A L A D M IN IS T R A T IV E P O L IC IE S FO R S U P E R V IS IO N O F C H IL D H O O D -T Y P E T U B E R C U L O S I S BASED UPON EXPERIENCE IN CATTARAUGUS COUNTY by J o h n H. K o r n
P R A C T I C A L A D M IN IS T R A T IV E P O L IC IE S FO R S U P E R V IS IO N O F C H IL D H O O D -T Y P E T U B E R C U L O S I S BASED UPON EXPERIENCE IN CATTARAUGUS COUNTY by J o h n H. K o r n
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape
 To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
Focus on... arthrosis. focus health
 Focus on... arthrosis focus health Arthrosis is the most common pathology in the second half of life 2 LET S DO SOME CLARITY Arthrosis (or osteoarthrosis) and arthritis are terms often considered synonymous,
Focus on... arthrosis focus health Arthrosis is the most common pathology in the second half of life 2 LET S DO SOME CLARITY Arthrosis (or osteoarthrosis) and arthritis are terms often considered synonymous,
Evaluation of whiplash injuries by technetium 99m isotope scanning
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1993, 10, 197-202 Evaluation of whiplash injuries by technetium 99m isotope scanning D. BARTON, M. ALLEN, D. FINLAY & I. BELTON Accident & Emergency Department, Leicester
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1993, 10, 197-202 Evaluation of whiplash injuries by technetium 99m isotope scanning D. BARTON, M. ALLEN, D. FINLAY & I. BELTON Accident & Emergency Department, Leicester
RESERVED JUDGMENT OF JUDGE M J BEATTIE
 IN THE DISTRICT COURT HELD AT DUNEDIN Decision No. l e7 /2009 IN THE MATTER AND IN THE MATTER BETWEEN of Injury Prevention, Rehabilitation, and Compensation Act 2001 of an appeal pursuant to Section 149
IN THE DISTRICT COURT HELD AT DUNEDIN Decision No. l e7 /2009 IN THE MATTER AND IN THE MATTER BETWEEN of Injury Prevention, Rehabilitation, and Compensation Act 2001 of an appeal pursuant to Section 149
The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of orthopaedic conditions must be made in conjunction with
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of orthopaedic conditions must be made in conjunction with
SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE*
 SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE* THE INCIDENCE AND DEVELOPMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, University
SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE* THE INCIDENCE AND DEVELOPMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, University
8/4/2012. Causes and Cures. Nucleus pulposus. Annulus fibrosis. Vertebral end plate % water. Deforms under pressure
 Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization
 Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 1015/01. Psychotraumatic disability. DECIDED BY: McIntosh-Janis DATE: 05/04/2001 NUMBER OF PAGES: 8 pages ACT: WCA
 SUMMARY DECISION NO. 1015/01 Psychotraumatic disability. DECIDED BY: McIntosh-Janis DATE: 05/04/2001 NUMBER OF PAGES: 8 pages ACT: WCA 2001 ONWSIAT 1207 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 1015/01 Psychotraumatic disability. DECIDED BY: McIntosh-Janis DATE: 05/04/2001 NUMBER OF PAGES: 8 pages ACT: WCA 2001 ONWSIAT 1207 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL
Neuropathic bladder and spinal dysraphism
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 176-180 Neuropathic bladder and spinal dysraphism MALGORZATA BORZYSKOWSKI AND B G R NEVILLE Evelina Children's Department, Guy's Hospital, London SUMMARY The
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 176-180 Neuropathic bladder and spinal dysraphism MALGORZATA BORZYSKOWSKI AND B G R NEVILLE Evelina Children's Department, Guy's Hospital, London SUMMARY The
Chioma Okechukwu. Course: Biology 205. Instructor: Dr Danil Hammoudi. Topic Scoliosis
 Course: Biology 205 Instructor: Dr Danil Hammoudi Topic Scoliosis 1 Definition Scoliosis is a medical condition with no particular causative agent. It occurs when the spinal cord is curved and it curves
Course: Biology 205 Instructor: Dr Danil Hammoudi Topic Scoliosis 1 Definition Scoliosis is a medical condition with no particular causative agent. It occurs when the spinal cord is curved and it curves
Chapter IV: Percutaneous Puncture of Spinal Cord Cysts
 Acta Radiologica: Diagnosis ISSN: 0567-8056 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard19 Chapter IV: Percutaneous Puncture of Spinal Cord Cysts To cite this article: (1966)
Acta Radiologica: Diagnosis ISSN: 0567-8056 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard19 Chapter IV: Percutaneous Puncture of Spinal Cord Cysts To cite this article: (1966)
Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
Sacroiliac joint infection
 Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
Rib erosions in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 16 Rib erosions in rheumatoid arthritis I. F. ANDERSON, A. B. CORRIGAN, AND G. D. CHAMPION North Shore Hospital, St. Leonards, New South Wales 2065, Australia Defects in the
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 16 Rib erosions in rheumatoid arthritis I. F. ANDERSON, A. B. CORRIGAN, AND G. D. CHAMPION North Shore Hospital, St. Leonards, New South Wales 2065, Australia Defects in the
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Vertebral sclerosis in adults
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
BACK PAIN. Disclaimer. Integrated web marketing. Multimedia Health Education
 BACK PAIN Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or a licensed healthcare
BACK PAIN Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or a licensed healthcare
The problem of making an early diagnosis between resolving and progressive forms of
 THE RIB-VERTEBRA ANGLE IN THE EARLY DIAGNOSIS BETWEEN RESOLVING AND PROGRESSIVE INFANTILE SCOLIOSIS M. H. MEHTA, CALCUTTA, INDIA From the Institute of Orthopaedics amid Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital,
THE RIB-VERTEBRA ANGLE IN THE EARLY DIAGNOSIS BETWEEN RESOLVING AND PROGRESSIVE INFANTILE SCOLIOSIS M. H. MEHTA, CALCUTTA, INDIA From the Institute of Orthopaedics amid Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital,
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
405 Firemans Ave LaVale, Maryland 21502
 Dec 19, 2016 CHIEF COMPLAINT: Iris presents with a chief complaint involving her lower lumbar and sacral region, left sacroiliac region and left anterior hip and groin. ONSET OF SYMPTOMS Iris states this
Dec 19, 2016 CHIEF COMPLAINT: Iris presents with a chief complaint involving her lower lumbar and sacral region, left sacroiliac region and left anterior hip and groin. ONSET OF SYMPTOMS Iris states this
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Facts about Scoliosis
 Facts about Scoliosis Have you or someone in your family recently been diagnosed with scoliosis? Or do you suspect somebody you know has the condition? That is when we usually start googling to learn all
Facts about Scoliosis Have you or someone in your family recently been diagnosed with scoliosis? Or do you suspect somebody you know has the condition? That is when we usually start googling to learn all
The Chailey Levels of Ability Assessment Charts
 The Chailey Levels of Ability Assessment Charts Assessment details NAME D.O.B. DIAGNOSIS DATE OF ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT CENTRE NAME OF ASSESSOR Notes CHAILEY HERITAGE CLINICAL SERVICES Beggars Wood Road
The Chailey Levels of Ability Assessment Charts Assessment details NAME D.O.B. DIAGNOSIS DATE OF ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT CENTRE NAME OF ASSESSOR Notes CHAILEY HERITAGE CLINICAL SERVICES Beggars Wood Road
Request for Specialist Report
 ACCIDEJIT COMPENSATION CORPORATION Claim number: 82737342 Te Klqloroihana "whine Hunp Whirl 18June 2007 ProfessorJ C Theis Orthopaedic Surgeon Otago District Health Board Private Bag 1921 Dunedin Ouno
ACCIDEJIT COMPENSATION CORPORATION Claim number: 82737342 Te Klqloroihana "whine Hunp Whirl 18June 2007 ProfessorJ C Theis Orthopaedic Surgeon Otago District Health Board Private Bag 1921 Dunedin Ouno
WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955), 39, 374. HEREDITARY POSTERIOR POLAR CATARACT WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE* BY C. G. TULLOH London K HEREDITARY, developmental, posterior polar cataract has been encountered in a
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955), 39, 374. HEREDITARY POSTERIOR POLAR CATARACT WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE* BY C. G. TULLOH London K HEREDITARY, developmental, posterior polar cataract has been encountered in a
Idiopathic scoliosis Scoliosis Deformities I 06
 What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
Kyphosis & Scheuermann s Kyphosis
 Kyphosis & Scheuermann s Kyphosis Patient Information Spinal Service Trauma and theatres centre 2 What is kyphosis? Kyphosis is when the upper spine curves outward more than is normal, making the back
Kyphosis & Scheuermann s Kyphosis Patient Information Spinal Service Trauma and theatres centre 2 What is kyphosis? Kyphosis is when the upper spine curves outward more than is normal, making the back
Spondyloperipheral dysplasia
 JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
