TRANSPORT OF URIC ACID BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF RHODNIUS PROLIXUS AND OTHER INSECTS
|
|
|
- Valentine Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7- exp. Biol. 103, (1983) printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 TRANSPORT OF URIC ACID BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF RHODNIUS PROLIXUS AND OTHER INSECTS BY M. J. O'DONNELL, S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER Agricultural Research Council Unit of Invertebrate Chemistry and Physiology, Department of Zoology, Downing Street, Cambridge CB2 3EJ {Received 20 May 1982 Accepted 14 October 1982) SUMMARY Urate is transported against an electrochemical gradient into the lumen of the lower Malpighian tubule oirhodnius. In vivo, higher urate transport rates are induced by the increase in haemolymph urate concentration that follows feeding. The induced rate of transport is sufficient to account for the amount of urate eliminated. In vitro experiments with the tsetseflyglossina suggest a possible induction of transport as a direct response of the tubule cells to an increase in urate concentration in the surrounding fluid. Urate transport has been shown for Malpighian tubules of insects from several different orders, suggesting that the mechanism is widespread. Insect urate transport differs from that of vertebrates; it is ouabain-insensitive and results in the precipitation of free uric acid instead of urate salts. INTRODUCTION Uric acid has long been recognized as the major nitrogenous excretory product of insects (Wigglesworth, 1965; Bursell, 1967). Two properties suit it for this purpose: it contains 33 % nitrogen and, under the acid conditions which prevail in the terminal section of the excretory system (Phillips, 1977), its solubility is quite low (11 nui at ph5-5). Its elimination thus leads to the excretion of large amounts of nitrogen without incurring much loss of water. In several insects, however, uric acid is retained internally where it may serve a variety of functions (Corbet & Rotheram, 1965; Mullins & Cochran, 1974; Berridge, 1965; Harmsen, 1966; Tucker, 1977). For insects with a low nitrogen diet, the usefulness of such retained uric acid, its low toxicity, and the expense of its synthesis (see Gilmour, 1961) may have reduced selection pressure for its elimination. There are limits to the amounts of uric acid or urate that can be accommodated within the body, and insects with a protein-rich diet have mechanisms for uric acid elimination. The tsetse fly, Glossina morsitans Westw., needs to excrete nearly 50% of the dry weight of the ingested blood in the form of nitrogen-containing compounds (mainly uric acid, but also arginine and histidine) merely to dispose of surplus nitrogen (Bursell, 1965). words: Uric acid transport, insects, Malpighian tubules.
2 170 M. J. O'DONNELL, S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. 0. C. GARDINER The blood-sucking bug, Rhodnius prolixus Still, also rapidly eliminates uric acil after one of its large blood meals (Wigglesworth, 1931a). Wigglesworth (19316) proposed a widely accepted model (Chapman, 1971; Roeder, 1953) for excretion of uric acid by the Malpighian tubules of adult Rhodnius, in which urate is first transported into the lumen of the upper fluid secreting region of the tubule. It is then carried in the fluid flow into the lower tubule, where, by reabsorption of water and acidification, uric acid crystals precipitate. However, at least in 5th instar larvae of Rhodnius, no evidence has been found that urate crosses the wall of the upper tubule by any other process than passive diffusion (Maddrell & Gardiner, 1974). The present experiments were undertaken to resolve this anomaly, to characterize more fully the mechanisms involved in uric acid elimination by Rhodnius, and to survey the Malpighian tubules of a range of other insects to see if similar processes occur in them. MATERIALS AND METHODS Fifth instar and adult Rhodnius pmlixus were taken from a laboratory culture maintained on rabbits and sheep and kept at 28 C. Pupae of Glossina morsitans were obtained from the Tsetse Research Laboratory, Langford, Bristol and adults for use were allowed to emerge at 28 C. Other insects, Pieris brassicae L., Schistocerca gregaria Forsk., Tenodora sinensis Saussure, and Calliphora erythrocephala Meigen were taken from laboratory cultures. Malpighian tubules were isolated in drops of saline under liquid paraffin as previously described (Maddrell, 1969) and were stimulated to secrete fluid using l(t 6 M5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) (Maddrell, Pilcher & Gardiner, 1969). To perfuse the lumina of tubules, they were cannulated with fine glass pipettes and fluid was driven through them from a motor driven syringe (Maddrell, Gardiner, Pilcher & Reynolds, 1974). Radioactive [ 14 C]-uric acid was obtained from Amersham International (formerly the Radiochemical Centre, Amersham) and samples were counted with conventional scintillation techniques using a Packard 3255 liquid scintillation spectrometer. The standard saline used tor Rhodnius and the mantid Tenodora sinensis contained (HIM) : NaCl, 129; KC1, 8-6; CaCl 2, 2; MgCl 2, 8-5; NaHCO 3, 10-2; NaH 2 PO 4, 43; and glucose, 34; giving a solution of ph6-8 and 342 mosmol I" 1. A K-free and Nafree saline was prepared by substituting choline chloride for NaCl and KC1 and buffering with Tris. Other salines were according to Nicolson (1976) for Pieris brassicae; Gee (1975) for Glossina morsitans; and Maddrell & Klunsuwan (1973) for Schistocerca gregaria. Chromatography of uric acid samples was carried out using the three systems suggested by Amersham International: (a) paper chromatography using t-butanol: ethyl methyl ketone: formic acid: water (40: 30:15:15), RF = 0-20, (b) thin layer chromatography on cellulose in n-butanol: pyridine: water (1:1:1), RF = 039, and (c) thin layer chromatography on PE1 cellulose using 0-15M-sodium chloride: 95% ethanol (4:1), 7^ = 0-28.
3 Uric acid transport in insects 171 The nature of uric acid/urate in physiological solutions The pk of uric acid is variously given in the literature as lying within the range 3*89 (Weast, 1979) to 5-7 (Spector, 1956). However, even taking the higher value, it follows from the Henderson-Hasselbalch relationship, ph = pk + logio urate/uric acid, that under the conditions of our experiments, ph6-8, more than 90% of uric acid in solution is present as its anionic form. We therefore refer to the substance in solution as urate in the description that follows. Composition of urate in lower Malpighian tubules The levels of sodium, potassium, and urate in the large accumulations of white granules in the lower tubules were measured to determine if uric acid was present as the free acid or if it was complexed with a conjugate base. Selected lower tubules containing large amounts of such granules were dissected in normal saline, rinsed in a large volume of sodium-free and potassium-free choline saline and then placed in 2 ml of distilled water. One ml of this was analysed for its content of sodium and potassium by flame photometry using a Unicam SP90A Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer. The remainder was added to 2 ml of saturated L12CO3 and its urate content determined by measuring absorbance at 292 nm using a Unicam SP500 spectrophotometer. Concentration of urate in haemolymph and urine Haemolymph and urine urate concentrations were also determined spectrophotometrically as described above. However, because there is significant absorbance at 292 nm by substances other than urate, samples were incubated at 20 C for 15 min with 0-25 units ml" 1 uricase (Type IV, Sigma Chemical Co.) in a borate buffer (0-02M, ph85), and any remaining absorbance subtracted. Measurement of intracellular potential differences Glass microelectrodes filled with 3 M KC1 were used in conjunction with a unitygain, high-impedance operational amplifier to measure the intracellular/bath potential difference in lower Malpighian tubules stimulated with 5-HT. Where a set of measurements are averaged they are shown as mean ± S.E.M. (N). RESULTS Permeability of upper Malpighian tubules The dense precipitates containing uric acid, which occur along virtually the whole length of the lower Malpighian tubules of Rhodnius, could, in principle, arise either from a process of concentration of urate-containing fluid passing down from the upper tubule or by inward transport of urate across the walls of the lower tubule leading to saturation of the luminal fluid. This was investigated by measuring urate levels in the fluid secreted by the upper tubules. Ten adult tubules were isolated into standard saline containing 100/iM radioactive uric acid and were stimulated to secrete by the Edition of 10 M 5-HT. The fluid collected from them contained uric acid at a
4 172 M. J. O'DONNELL, S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER concentration of only 19±2/iM (TV = 10), i.e. 17% of that in the bathing fluid. Th^ rate of fluid secretion was nl min" 1 from which it can be calculated* that the average apparent permeability to urate of the walls of the upper Malpighian tubules of adultrhodnius is 1-94 X 10~ 6 cms~ 1 (l-^nlmin" 1 mm ); this compares with an average value of 1-82 X lo^cms" 1 (l-09nlmin~ 1 mm" 2 ) from similar experiments using six upper tubules from 5th instar Rhodnius. It follows from these results that the uric acid deposits in the lumina of the lower tubules are very unlikely to be derived from urate present in the fluid secreted by the upper tubules. Even if the haemolymph were saturated with uric acid (presumably no more than 2 mm at the ph of the haemolymph) it can be calculated* that urate would only enter each upper tubule at a rate of about 5 pmolmin" 1 (assuming each tubule to secrete fluid at 3 nl min" 1 ). The calculated rate of uric acid transport is affected by what value is taken as the rate of fluid secretion by the tubules*. Even if this were as high as 10 nl min" 1 tubule" 1 (which is unlikely as this would sweep uric acid crystals well downstream from the junction of upper and lower tubules where they can be seen to lie in vivo), urate would enter each upper tubule at a rate of only 11-8 pmol min" 1. It follows that the four upper tubules together might then eliminate a maximum of 68-2 nmol day" 1 of uric acid. This, however, is still only 2-3 % of the 3 ^mol (0-5 mg) which Wigglesworth (1931a) found to be the actual amount eliminated each day. It is clear, therefore, that passive movements of urate into the upper tubules are insufficient to meet the insect's needs. Urate transport in the lower Malpighian tubule To test whether the lower tubules can transport urate into the lumen, lower tubules were cannulated and standard saline perfused through them at rates of up to SOnlmin" 1, while they were bathed in saline containing radioactive urate at concentrations ranging from JIM. The fluid emerging from the lumen of such tubules was found in every case to contain a high concentration of tracer, usually 2 10 times that of the bathing medium. Samples of such fluid were subjected to the three chromatographic separation techniques described in Materials and Methods. This showed that virtually all the radioactivity in the samples could be attributed to unchanged urate; no other measurable spots were observed. It is clear that the lower tubules can transport urate from the bathing fluid into the lumen at high rates. Characteristics of urate transport by the lower Malpighian tubules To determine the capacity of lower tubules to transport urate, rates of urate transport were measured with different concentrations of urate in the bathing medium. The highest concentration used was 2-3 mm to ensure that all the urate was in The basis for these calculations is the formula, derived by Ramsay (1958), S/M == b/a+b, where S/M is the ratio of the concentration in the secreted fluid to that in the bathing fluid, b is the permeability of the tubule wall in nl min" 1 mm" 2 and a is the rate of fluid secretion in nl min" 1 mm 2 of tubule wall. The areas of upper tubule wall are 7 mm 2 and 12'S mm 2 for 5th instar larvae and adults respectively. 1 nlmin" 1 mm" 2 is 1-67 X 10~* cms" 1. For example, in the case described of an adult insect with its tubules secreting fluid at 3 nl min" 1, bathed in haemolymph containing 2mn-urate, and each having a permeability to urate of l-16nlmin~' mm" 2, then S/ 2 = l'16/[(3/12'5) , whence S = l'66mm, and the rate of urate elimination by each tubule is 3 nlminjj X l'66mm = 5 pmolmin.
5 Uric acid transport in insects 173 ution. The insects were taken not more than 7 days since their previous moults. In experiments with urate made up in standard salines, it was found that the transport rate fell away rapidly with time (Fig. 1). The urate content of the bathing drops was in all cases large enough to ensure that this was not due to depletion of urate from the bathing medium. Transport rate was better maintained in the saline of Maddrell & Gardiner (1980), which contains amino acids. Urate transport rates in this saline declined relatively little over the course of the experiment (Fig. 2), but significantly higher rates of transport occur with tubules within the first few minutes of isolation. The concentration/transport curves for urate transport at various times after isolation {Fig. 3) show that, at least for a short while, Rhodnius lower Malpighian tubules in vitro can eliminate urate at a rate of SSOpmolmin" 1 when the bathing medium contains about 2 mm-urate. The rate of secretion varies linearly with urate concentration; there is no evidence that the pumping mechanism becomes saturated at the higher concentrations. Some tubules transported urate at such high rates that the apparently clear secreted fluid contained very high concentrations of urate, often around rrim and, exceptionally, as high as 19 mm. The solutions were apparently true solutions. Four 0-2 [A samples of fluid secreted by Malpighian tubules in saline containing 2 mm urate plus radioactive urate as tracer were examined under dark field illumination at 400 X. None showed any traces of crystalline deposits though their urate concentrations were 8-5, 7-6, 8-9, and 9-7 mm. ph in the lower tubule To investigate whether high urate concentrations could be explained by the ph of the lumen of the lower tubule, 5th stage insects fed 24 h previously were injected with 10^1 of saline containing 0-38mM-chlorophenol red (3',3"-dichlorophenol sulphonphthalein, an indicator which is yellow at ph 5 0 and red at ph 6 6). After 2-3 h the dye had appeared in the lumina of the lower tubules and showed there as an orange-yellow I o I I I Time (min) Fig. 1. Declining rates of transport of urate by Malpighian tubules isolated from 5th stage Rkodnius Jinto standard saline. > 103
6 174 M. J. O'DONNELL, S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. 0. C. GARDINER 200 s 'c o Q. 140 O '2 60 a 20 <2 o Time (min) Fig. 2. Rates of urate transport by individual Malpighian tubules of 5th instar Rhodnius isolated into an amino acid-containing saline. The figures by each line indicate the urate concentration in the bath. 400 f after 5 min. 15 o a. 200 I a i! loo o Concentration of urate in bath (mol) Fig. 3. Rates of urate transport by isolated Malpighian tubules of Rhodnius at various concentrations of urate in the bath. The determinations were made either after 5 min (upper line, solid triangles) or after 8 min (lower line, solid circles). The vertical lines attached to the points represent ±s.e.
7 Uric acid transport in insects 175 lour, indicating a ph of 6-2 as judged by comparison with indicator in solutions of known ph. Solubility ofurate /uric acid in solutions of different ph To gain some insight into the solubility of uric acid/urate, the following procedure was carried out. Two mmol of either uric acid or its sodium salt was dissolved in 15 ml af N NaOH (giving a clear solution containing 133 mm urate at ph 12-75). 1-5 mmol of Tris was added as buffer, a trace of phenol red as indicator, and 70 ml of distilled water. A little N HC1 was then slowly run in while the mixture was stirred continuously and its ph monitored (with a Pye PW 9409 digital ph meter). 12ml aliquots were removed when the ph reached 7-50, 7-00, 6-50 and 6 > 00 respectively. 5 [A samples of the clear supernatant were taken at intervals and the urate concentration determined spectrophotometrically. These results (Fig. 4) clearly show that concentrated urate solutions in the ph range 6*0 to 7-5 are not stable but precipitate slowly and somewhat erratically over a long period. However, at times less than 1 h, concentrations of urate in solution up to at least 20 mm can readily be obtained. To check that the urate was in solution and not a colloidal suspension of uric acid, we centrifuged portions of the supernatant from those samples of a solution initially containing 20 mm urate (plus radioactive urate as a marker) at ph 12-5, but brought to ph 7, 6-5 and 6 in the three different samples. In each case considerable amounts of uric acid had precipitated before the samples were taken and the supernatants from the three contained 3-5, 6-8 and 5-6mM urate respectively before being centrifuged. Each sample was then subjected to g for 1 h when the supernatant was assayed for its urate content. The three samples now contained 2-7, 5-5 and 5-3 mm urate. After leaving them to stand for a further 18 h aliquots taken from the surface contained 1-8, 3*6 and 2-OmM urate. These results suggest that centrifugation even at looooog j oco 1-5 h + centrifuged I 5 c Fig. 4. Concentrations of urate and ph of solutions, initially with 20 DIM urate and ph 7'5, 7'0, 6-5 and 6-0. The upper lines indicate the results of two experiments in which the solutions were left 1 h (open circles) or 1-5 h and were centrifuged (solid circles). The solutions from the first experiment were left for 2 days and gave the results shown by the bottom line (open circles); the solutions from the second experiment were left overnight and give the results shown (solid circles, lower line).
8 176 M. J. O'DONNELL, S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER did not have a marked effect on the rate of precipitation of uric acid from solutions. As a further test, we examined under dark field illumination at 400X, samples of fluid made up so as to contain 10 mm urate at ph7-0. Five such samples showed no evidence of light scattering, suggesting that there were no suspended small crystals of uric acid in the fluid. The results of both these sets of experiments suggest that uric acid can exist in apparently true solution at concentrations of up to 10 mm. The above results indicate that fluid produced by stimulated whole Malpighian tubules when they are bathed in a saline containing 1-2 mm urate could well contain as much as mm in solution and that this would only relatively slowly precipitate out at the slightly alkaline ph involved. The significance of changes in fluid secretion rate In the in vivo situation, it is likely that high rates of urate transport (such as occur after feeding - see below) into the lumen, containing slowly moving fluid at ph of about 6, would lead to a relatively much more rapid precipitation of uric acid. In an insect eliminating 7/imol of uric acid day" 1 (see below) it follows that each tubule transports urate at a rate sufficient to deposit 0-3 mg of uric acid day" 1 in the lumen. The specific gravity of uric acid is 1 '86, so this would occupy a volume of 160 nl, more than twice the volume of the lumen of the lower tubule which is 76 nl. In unfed insects the upper tubule may secrete fluid at only 01 nlmin" 1 or 145 nl day" 1, which might not be sufficient to flush the precipitated uric acid out of the lower tubule into the rectum. However, the rate of fluid secretion increases after feeding and reaches 2-3nlmin~' in tubules a few days after the meal (S. H. P. Maddrell, unpublished results). Part of the function of this increase may thus be to prevent the choking of the lower tubules with precipitated uric acid. Effect of feeding upon transport rate Malpighian tubules from 5th instar Rhodnius showed a dramatic increase in in vitro urate secretion within 2-3 days of feeding (Fig. 5). Peak levels of secretion in 0-5 mm urate, pmol min" 1 tubule" 1, were seven times those of unfed control animals of the same age. In 2mM urate, peak rates of secretion 5-6 days after feeding were 814±70pmolmin~ 1 tubule" 1 (N= 17) after 5min in vitro and 726 ±77 pmol min" 1 tubule" 1 after lomin. Urate transport by all four tubules at these rates would be sufficient to account for close to 5 /imol day" 1. To determine how far the urate transport rate measured in vitro could account for in vivo urate excretion the rate at which 5th instar Rhodnius eliminate uric acid and the concentration of urate in the haemolymph were measured. The rate of elimination of uric acid was measured in 5th instar Rhodnius fed about a month after their previous moult. After diuresis (5 h), each insect was placed in an individual 60 ml cylindrical plastic specimen container. At intervals, when the insects were seen to have excreted, they were moved to fresh containers. The used containers were washed out with saturated Li 2 CO 3 solution and the fluid assayed spectrophotometrically to determine its content of urate. From the urate content of an insect's excreta and a knowledge of the time at which its previous excretion had taken place, the daily rate of its uric tf
9 Uric acid transport in insects 111 rination during the intervening period was calculated. The rate of urate eliminaincreased considerably during the first few days after a meal to reach a peak of about 6-7 ^mol day" 1 (Fig. 6). Thereafter the rate declined steadily until a few days after ecdysis when the rate reached a near-negligible value. The fall in uric acid elimination that occurs after the first 2 days probably does not represent a fall in the rate of urate transport. Water elimination after the meal goes on at a slow rate for a day or so then virtually ceases. The rectum then fills with a thick suspension of uric acid crystals rather than a more watery urine and there is consequently a longer delay before urate transported through the Malpighian tubules is actually eliminated from the body. The area under the curve shown in Fig. 6 represents the total amount of uric acid eliminated after the meal. Evaluation of this showed that, on average, each fed insect eliminated 83 /imol of uric acid by 25 days after its meal. To interpret the rates of elimination in terms of active transport, the urate concentration in the haemolymph was determined after feeding. The spectrophotometric absorbance of haemolymph samples from fed animals at 292 nm was measured before and after addition of uricase to the cuvettes. Only 38 ± 5 % (N= 12) of the initial absorbance was due to uric acid, whose concentration in the haemolymph was 2-0±0-3mM (N = 12). Haemolymph urate concentrations were also measured at intervals after feeding. The concentration was 1-2 ± 0-2 miw (N= 14) within the first - 6 c as Days post-feeding 24 Fig. 5. Daily rates (mean ± s.e.) of excretion of uric acid by 5th instar Rhodnius after feeding. Number of animals indicated adjacent to each point.
10 178 M. J. O'DONNELL, S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER 250 r c E o. 3 3 I 'o 12 l Time (days) Fig. 6. Induction of urate secretion in 5th insur Rhodmus Malpighian tubules in response to feeding. Urate secretion rates were measured in vitro in enriched saline containing 0-5 mm urate. 12 h, 1-8 ± 0-2 mm (N = 29) after h, and 1-3 ±0-1 nrn (N = 11) after h. The initial decrease is probably the result of the increase in haemolymph volume which follows feeding (Maddrell & Gardiner, 1980). The change between 24 and 48 h is more likely to be due to an increase in the rate of urate elimination by the lower tubules (see Fig. 6). In vivo, then, uric acid is eliminated at a peak rate of 6-7/imol day" 1, when the haemolymph contains about 2 mm of urate. As we have seen, tubules from insects at this stage when isolated into saline containing 2 mm urate, can transport urate fast enough to account for the elimination of 5 fimo\ day" 1, suggesting that in vivo they could well eliminate urate at the required rate. Induction of urate transport after feeding The results suggest an induction of urate transport in response to feeding. To test whether there was a direct effect of urate concentration upon the tubules, we followed the response in unfed insects to an injection of 10 /il of saline containing 18 mm urate and at a ph of 70. After 24 h, 26 Malpighian tubules from 12 insects transported urate at a rate of 52-1 ± 2-7 pmol min" 1, when isolated in saline containing 0-5 mm urate. Eleven tubules from six unfed insects which had been injected with 10 /il of saline alone transported urate at a rate of 23-8 ±1-7 pmol min" 1. Evidently the injection of 180nmol of urate, although this is only equivalent to the amount eliminated in 2h, is sufficient to induce a doubling of the urate transport rate by the Malpighian tubules. This result suggests that induction is a direct response of the tubules to an increase in haemolymph urate concentration after feeding. It is difficult to test the
11 Uric acid transport in insects 179 kssibility directly using in vitro preparations of Rhodnius tubules because the time required for the induction is longer than it is feasible to maintain in vitro tubules showing secretion of urate at significant rates. However, in vitro experiments with Malpighian tubules of the tsetse fly, Glossina morsitans (Fig. 7) showed a fairly steady rate of urate secretion for periods of more than an hour. These tubules therefore appeared suitable for direct in vitro measurements of the effects of an increase in bathing fluid urate concentration upon the rate of urate transport. In vitro induction of urate transport in Malpighian tubules of Glossina Tubules bathed in saline containing 0-1 mm urate showed a steady transport rate after 10 min (Fig. 8). In response to a step change in bath urate concentration from 0*1 mm urate to either 017mM or 0-3 miw urate after 60 min, all tubules from unfed animals, or animals fed the previous day, increased their urate transport rates for min after the change. For unfed animals (Fig. 8A, B) the mean increase in transport rate from t = 70 min to t = 90 min was 26 % in 0-17 mm urate and 35 % in 0-3 mm urate. For fed animals (Fig. 8C), the mean increase between t = 70 min and t = 90 min was 25 %. For both fed and unfed animals, paired <-tests showed that the differences were significant at the 5 % level. These delayed increases are unlikely to reflect simply the time required for the establishment of a new steady state, because steady state transport rates in low (0-1 mm) urate concentrations are established in about 10 min (Fig. 8). This is partly because fluid secretion rates were sufficient to flush the luminal contents in less than a minute. The delayed response seems more likely to be due to an induction of urate transport following exposure of tubules to an increase in urate concentration. The apparent induction is a rapid effect; higher rates of transport are established within min of the concentration increase. Fig. 8 also suggests that induction in vivo in response to feeding decays rapidly; animals fed the previous day do not show higher rates of urate transport in 01 mm urate. Effects of obstructing the Malpighian tubules Wigglesworth (1931c) studied the function of different segments of the Malpighian tubules by obstructing the tubules at different positions. After 12 h, uratic granules 40 Mr k U if Time (min) 120 ISO Fig. 7. In xjitro urate secretion rates of Glossina Malpighian tubules, bathed in 0-55 mm urate. Secretion rates increase or are stable for longer periods of time than in Rhodnius tubules. N = 9.
12 180 M. J. O'DONNELL, S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER r A Unfed > O I 20 a. C f 4 ^OlmM» 1 «0-3mM o Time (min) \, 0 ISO mm 017mM r c Fed / / ) *, / *"' ' - 0-1mM -»4-«0-3mM Time (min) Fig. 8. In vitro rates of urate transport by Glossina Malpighian tubules in response to a change in bath urate concentration at t = 60 min. Bath urate concentrations are indicated above the time axis. In (A) values for individual tubules are presented. In (B) and (C), mean values (± s.e.) are given. Animals in (C) were fed the previous day. were formed below a single ligature oi> the lower tubule, but not between two ligatures. The latter result is incompatible with secretion of urate by the lower tubules; the following experiments were therefore done to determine the cause of this discrepancy. Within 3-5 h of feeding lower tubules were ligated with silk threads at either one or two positions along their length. The opening in the body cavity was covered with a thin sheet of polyethylene, which was held in place by the surface tension of the haemolymph between the sheet and the cuticle. The animals were dissected and examined h later. For tubules with one ligature, the results were similar to those of Wigglesworth (1931c). For 12 tubules from eight animals, uratic granules were present between the ligature and the hindgut in 11 cases; granules were present above the ligature in four cases, but in relatively small amounts. For tubules ligated at two positions along their lower segment, a precipitate was found between the ligatures in 12 out of 18 animals. This result could only occur if the cells of the lower tubule secreted urate into the lumen, and differs from the results of Wigglesworth's (1931c) study, in which no precipitate was found between the ligatures. It is unlikely that disruption of tracheal supplies during dissection could prevent precipitation of urate between the ligatures. For four animals in which the posterior three spiracles on one side were blocked with wax 1-2 h after feeding, precipitate was observed in normal quantities in "all tubules when dissected h after feeding. A further possibility is that the ligatures in Wigglesworth's experiments may have been too close together. In our experiments, uric acid precipitation was found between ligatures which were, on average, 7-7 mm apart (range m^
13 Uric acid transport in insects 181 Hit such precipitation was not found between ligatures which were only 3*2 mm apart (range 1* 6-8 mm). Effects of varying ph on urate transport The transport of an acidic species such as uric acid might be affected by the ph of the surrounding medium. In fact, urate secretion was not markedly dependent upon ph. When bathed in mi* urate at ph6-3, tubules secreted 14-2 ± 1-4 (N = 9) pmolmin" 1 tubule" 1. At ph7, and in the same concentration of urate, 9pmolmin~ 1 tubule" 1 was secreted. At a ph of 8-3, 7*9 ± 1-4 (N 9) pmolmin" 1 tubule" 1 was secreted from a bath containing miw urate; the corresponding rate at ph 7 was 6-3pmolmin~ 1 tubule" 1. Comparisons with vertebrate urate transport Composition of uratic granules in lower Malpighian tubules The mean sodium/urate ratio was ±0-015 (N = 10), and the mean potassium/urate ratio was ± (N = 10). These values suggest that the majority of the urate is present as uric acid, because each molecule of a urate salt would contain two cations, in which case the sodium/urate ratio and/or potassium/urate ratio would be much higher. Effects ofouabain Mean secretion rate was 41-5 ± 4-6pmolmin~ 1 tubule" 1 (N= 6), when the tubules were bathed in enriched saline containing 0-11 mm urate and 10~ 4 M ouabain. For six control tubules from the same animals, the corresponding rate was 37-9 ± 4-9 pmol min" 1 tubule" 1. A f-test indicated that the differences were not significant, and that ouabain did not, therefore, inhibit urate transport. Site of the urate pump If urate is actively transported across the basal membrane of the lower Malpighian tubule, and subsequently diffuses passively into the lumen, intracellular urate concentrations should be higher than expected from the electrochemical potential between the cell and the bathing medium. Estimation of intracellular urate concentration required a measurement of the volume of the cells of the lower Malpighian tubules. For this purpose, the lower tubules were bathed in saline containing a penetrant solute, [C]-labelled thiourea, and were also cannulated so that they could be perfused with the same solution. After 10 min, the solution in the cannula was replaced with thiourea-free saline, which was used to flush the luminal contents for 1 2 s. The tubule was then quickly pulled through three washes of complex saline (Maddrell & Gardiner, 1980) to remove any thiourea adhering to the external surfaces, and placed in a drop of distilled water. Radioactivity in the drop was determined by liquid scintillation spectrometry. By assuming equilibration of intracellular thiourea concentration with the bathing solution, lower tubule volume was calculated as 34-2 ± 5-1 nl (JV =6). Using this volume estimate, the ratio of urate concentration in the lower tubule to that the bathing medium was determined. Cannulated tubules secreting [ 14 C]-urate
14 182 M. J. O'DONNELL, S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER were flushed with urate-free saline and washed, as for thiourea. Concentrations intracellular urate were 088 ± 0-18 (N=9) times those of the bath, which contained mm-urate. The S/M ratio for tubules which had been secreting urate for 7-12min in a comparable concentration was 5-4 ± 1*2 (N= 8). These results indicated that intracellular urate concentrations were below those in the secretion, but not much less than the bath concentration. However, microelectrode potential measurements showed that the interior of the cells was negative with respect to the bathing medium, so that entry of the negatively charged urate ion into the cells is against an electrical gradient. In the lowermost one-third of the lower tubule, the intracellular potential was 14 ± 1 mv (N = 9). Potentials varied with position along the upper two-thirds of the lower tubule, so that the results were more variable; here the intracellular potential averaged 32±9mV negative, with respect to the bath. If the electrochemical potential difference between the bath and the cell interior were zero, the intracellular urate concentration should be in the range % of that in the surrounding medium. Since the intracellular concentration is higher than this, it seems that urate ions must be transported actively into the cell with pumping sites on the basal cell membranes of the lower Malpighian tubules. Passive movement of urate from within the cell into the lumen is down an electrical gradient. Measurements of the transepithelial potential difference showed that the lumen was negative with respect to the bathing medium by an average of 17*2 ± 3 4 m V (JV = 10). The potential step at the luminal face is thus between 0 and 15 mv, cell negative, which could account for a doubling of the luminal concentration above that of the cell. However, since luminal urate concentrations are 2-10 times those of the bath, there are likely to be additional pumping sites for urate on the luminal surfaces. Urate secretion by other insects To determine if active urate secretion is a common physiological mechanism in insects, S/M ratios for several other species were determined in bathing fluids containing 30-70/imol I" 1 radiolabelled urate. The mean values were: for larvae of a lepidopteran, the large cabbage white butterfly, Pieris brassicae, 1-33 ± 0-13 (N = 6); for an orthopteran, the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria, 2-8 ± 0-5 (N = 10); for a dipteran, a tsetse fly, Glossina morsitans, 6-4±2-6 (N=6); and for a carnivorous dictyopteran, a Chinese praying mantis, Tenodora sinensis, 15-8 ±0-8 (N = 14). Thin layer chromatography indicated that the secretion contained unchanged uric acid in all these animals. These results show that the Malpighian tubules of these insects can transport urate into the lumen against a concentration gradient. However, since in most insect Malpighian tubules the lumen is at a potential positive to the bathing medium (Ramsay, 1953; Gee, 1976), such transport is not necessarily active. However, the passive permeability of Malpighian tubule to substances of similar molecular size to uric acid is not high (Maddrell & Gardiner, 1974). It is likely, therefore, that urate transport in these insects is active as it is in Rhodnius. For another dipteran, the blowfly, Calliphora erythrocephala, thin layer chromatography indicated that uric acid was converted to allantoin (as earlier discovered by Dr M. J. Berridge; personal communication). The ratio of the concentration
15 Uric acid transport in insects 183 Mlantoin in the secreted fluid to the bath concentration of urate was 28-2 ± 3-8 (N ^=71). DISCUSSION This study has shown active urate secretion by the lower Malpighian tubules of Rhodntus. In recently fed animals, in vitro, the rates of secretion are sufficient to account for the observed levels of urate excretion in vivo. Experiments with insects from other orders suggest that active secretion of urate by Malpighian tubules is a widespread phenomenon. In Calliphora, Malpighian tubules convert uric acid to a related nitrogenous compound, allantoin, which is then excreted. Previous proposals for the mechanism of urate excretion in Rhodntus (Wigglesworth, I93la,b,c) involved transport into the upper tubule, and subsequent precipitation in the lower tubule as a result of acidification and water removal. However, our results indicate that transport through the upper tubules is sufficient to account for, at most, only 1-5 % of the total urate excretion. Wigglesworth's proposal was based partly on the results of ligation experiments, which showed that uratic granules did not appear between two ligatures on a lower tubule. The discrepancy between these results and those described above may partly be accounted for by differences in the time between ligation and dissection; Wigglesworth dissected the tubules 12 h after ligation, whereas our results suggest that precipitation does not begin until 5 h after feeding, and therefore we allowed at least 20 h to elapse before dissection. As discussed above, a further possibility is that the ligatures in Wigglesworth's experiments may have been too close together. An important advantage of active urate pumping by the lower tubules may be that urate elimination can be increased when necessary with little effect on the movements of other metabolites. If excretion involved passive movement into the tubule and subsequent precipitation, an increase in excretion would demand an increase in fluid secretion rate and/or an increase in the permeability of the tubule to urate. However, such an increase would produce accelerated movement of other molecules of similar size and charge; the animal would either lose these or be forced to reabsorb them actively. lnrhodnius, the rate of urate transport increases after feeding, presumably because the early stages of digestion of the blood meal produce large amounts of nitrogenous waste. In Glossina, there appears to be a direct induction of the tubules in response to an increase in ambient urate concentration. The rapid onset and decay of induction in Glossina may be necessary in an animal which feeds at frequent intervals. Similar induction effects for the secretion of -aminohippuric acid have been observed in Rhodntus (Maddrell & Gardiner, 1975). Whilst both vertebrates (Dantzler & Braun, 1980) and insects actively secrete urate, the observed lack of effect of ouabain suggests that there are differences in the mechanism of urate transport in the two groups. Urate secretion by mammalian renal tubules is irreversibly inhibited by ouabain (Chonko, 1980). Another difference is that large quantities of sodium and potassium are present in the urate precipitate excreted by reptiles, whereas the precipitate in Rhodnius lower tubules appears to be ^ee uric acid.
16 184 M. J. O'DONNELL, S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER REFERENCES BERKIDGE, M. J. (1965). The physiology of excretion in the cotton stainer, Dysdercus fasciatus Signoret. III. Nitrogen excretion and excretory metabolism. J. exp. Biol. 43, BURSELL, E. (1965). Nitrogenous waste products of the tsetse fly, Glossina morsitans. J. Insect Physiol. 11, BURSELL, E. (1967). Excretion of nitrogen in insects. Adv. Insect Physiol. 4, CHONKO, A. M. (1980). Urate secretion in isolated rabbit renal tubules. Am. J. Physiol. 239, F545-F559. CHAPMAN, R. F. (1971). The Insects: Structure and Function. London: English University Press. CORBET, S. A. & ROTHERAM, S. (1965). The life history of the ichneumonid Nemeritis (Devorgilla) canescens (Gravenhorst) as a parasite of Anagasta kuehmella Zeller, under laboratory conditions. Proc. R. ent. Soc. Land. (A) 40, DANTZLER, W. H. & BRAUN, E. J. (1980). Comparative nephron function in reptiles, birds and mammals. An. J. Physiol. 239, GEE, J. D. (1975). The control of diuresis in the tsetse fly Glossina austeni, a preliminary investigation of the diuretic hormone. J. exp. Biol. 63, GEE, J. D. (1976). Active transport of sodium by the Malpighian tubules of the tsetse fly Glossina morsitans. J. exp. Biol. 64, GILMOUR, D. (1961). The Biochemistry of Insects. New York: Academic Press. HARMSEN, R. (1966). The excretory role of pteridines in Insects. J. exp. Biol. 45, MADDRELL, S. H. P. (1969). Secretion by the Malpighian tubules olrhodnius. The movements of ions and water. J. exp. Biol. 51, MADDRELL, S. H. P. & GARDINER, B. O. C. (1974). The passive permeability of insect Malpighian tubules to organic solutes. J. exp. Biol. 60, MADDRELL, S. H. P. & GARDINER, B. O. C. (1975). Induction of transport of organic anions in Malpighian tubules olrhodnius. J. exp. Biol. 63, MADDRELL, S. H. P. & GARDINER, B. O. C. (1980). The retention of amino acids in the haemolymph during diuresis in Rhodnius prolixus. J. exp. Biol. 87, MADDRELL, S. H. P., GARDINER, B. O. C, PILCHER, D. E. M. & REYNOLDS, S. E. (1974). Active transport by insect Malpighian tubules of acidic dyes and acylamidcs. J. exp. Biol. 61, MADDRELL, S. H. P. & KLUNSUWAN, S. (1973). Fluid secretion by in vitro preparations of the Malpighian tubules of the desert locust, SMstocerca gregaria. J' Insect Physiol. 19, MADDRELL, S. H. P., PILCHER, D. E. M. tc GARDINER, B. O. C. (1969). Stimulatory effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) on secretion by Malpighian tubules of insects. Nature, Land. 222, MULLJNS, D. E. & COCHRAN, D. G. (1974). Nitrogen metabolism in the American cockroach: an examination of whole body and fat body regulation of cations in response to nitrogen balance. J. exp. Biol. 61, NICOLSON, S. W. (1976). Diuresis of the Cabbage white butterfly, Pieris brassicae; fluid secretion by the Malpighian tubules. J. Insect Physiol. 22, PHILLIPS, J. E. (1977). Excretion in insects: function of gut and rectum in concentrating and diluting the urine. Fedn Proc. Fedn Am. Socs exp. Biol. 36, RAMSAY, J. A. (1953). Active transport of potassium by the Malpighian tubules of insects. J. exp. Biol. 30, RAMSAY, J. A. (1958). Excretion by the Malpighian tubules of the stick insect Dixippus morosus (Orthoptera, Phasmidae): amino acids, sugars and urea. J. exp. Biol. 35, ROEDER, K. D. (1953). Insect Physiology. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc. SPECTOR, W. S. (1956). Handbook of Biological Data. Philadelphia & London: W. B. Saunders Company. TUCKER, L. E. (1977). Effect of dehydration and rehydration on the water content and Na + and K + balance in adult male Periplaneta americana. J. exp. Biol. 71, WEAST, R. C. (1979). CRC Handbook of Chemistry & Physics. Florida: CRC Press. WIGCLESWORTH, V. B. (1931a). The physiology of excretion in a blood-sucking insect, Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). I. Composition of the urine. J. exp. Biol. 8, WIGGLESWORTH, V. B. (19316). The physiology of excretion in a blood-sucking insect, Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). II. Anatomy and histology of the excretory system. J. exp. Biol. 8, WIGGLESWORTH, V. B. (1931c). The physiology of excretion in a blood-sucking insect, Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). III. The mechanism of uric acid excretion. J. exp. Biol. 8, WIGGLESWORTH, V. B. (1965). The Principles of Insect Physiology. 6th edition. London: Methuen.
Maintenance of function in single epithelial cells spatially isolated from similar cells
 J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 90, 409-414 (1985) 409 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1985 Maintenance of function in single epithelial cells spatially isolated from similar cells S.
J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 90, 409-414 (1985) 409 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1985 Maintenance of function in single epithelial cells spatially isolated from similar cells S.
PHYSIOLOGICAL DISCONTINUITY IN AN EPITHELIUM WITH AN APPARENTLY UNIFORM STRUCTURE
 J. exp. Biol. (1978), 75. 133-145 133 With 7 figures frinted in Great Britain PHYSIOLOGICAL DISCONTINUITY IN AN EPITHELIUM WITH AN APPARENTLY UNIFORM STRUCTURE BY S. H. P. MADDRELL Agricultural Research
J. exp. Biol. (1978), 75. 133-145 133 With 7 figures frinted in Great Britain PHYSIOLOGICAL DISCONTINUITY IN AN EPITHELIUM WITH AN APPARENTLY UNIFORM STRUCTURE BY S. H. P. MADDRELL Agricultural Research
THE RETENTION OF AMINO ACIDS IN THE HAEMOLYMPH DURING DIURESIS IN RHODNIUS
 J. exp. Biol. (1980), 87, 315-329 315 With ^figuret in Great Britain THE RETENTION OF AMINO ACIDS IN THE HAEMOLYMPH DURING DIURESIS IN RHODNIUS A.R.C. BY S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER Unit of
J. exp. Biol. (1980), 87, 315-329 315 With ^figuret in Great Britain THE RETENTION OF AMINO ACIDS IN THE HAEMOLYMPH DURING DIURESIS IN RHODNIUS A.R.C. BY S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER Unit of
DIURESIS IN THE TSETSE FLY GLOSSINA AUSTENI
 f. exp. Biol. (1975). 63, 381-390 381 ^t*a 6 figures Printed in Great Britain DIURESIS IN THE TSETSE FLY GLOSSINA AUSTENI BY J. D. GEE* University of Cambridge, Department of Zoology, Downing Street, Cambridge
f. exp. Biol. (1975). 63, 381-390 381 ^t*a 6 figures Printed in Great Britain DIURESIS IN THE TSETSE FLY GLOSSINA AUSTENI BY J. D. GEE* University of Cambridge, Department of Zoology, Downing Street, Cambridge
THE ACTION OF THE EXCRETORY APPARATUS OF CALLIPHORA VOMITORIA IN HANDLING INJECTED SUGAR SOLUTION
 J. exp. Biol. (1976), 64, 131-140 With 8 figures Printed in Great Britain THE ACTION OF THE EXCRETORY APPARATUS OF CALLIPHORA VOMITORIA IN HANDLING INJECTED SUGAR SOLUTION BY G. KNOWLES* Department of
J. exp. Biol. (1976), 64, 131-140 With 8 figures Printed in Great Britain THE ACTION OF THE EXCRETORY APPARATUS OF CALLIPHORA VOMITORIA IN HANDLING INJECTED SUGAR SOLUTION BY G. KNOWLES* Department of
THE PASSIVE PERMEABILITY OF INSECT MALPIGHIAN TUBULES TO ORGANIC SOLUTES
 y. Exp. Biol. (1974), 60, 641-651 64.! With 5 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE PASSIVE PERMEABILITY OF INSECT MALPIGHIAN TUBULES TO ORGANIC SOLUTES BY S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER A.R.C.
y. Exp. Biol. (1974), 60, 641-651 64.! With 5 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE PASSIVE PERMEABILITY OF INSECT MALPIGHIAN TUBULES TO ORGANIC SOLUTES BY S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER A.R.C.
Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water
 Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
THE PERMEABILITY OF THE CUTICULAR LINING OF THE INSECT ALIMENTARY CANAL
 J. exp. Biol. (1980), 85, 237-237 227 With 3 figures Printed in Great Britain THE PERMEABILITY OF THE CUTICULAR LINING OF THE INSECT ALIMENTARY CANAL BY S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER A.R.C. Unit
J. exp. Biol. (1980), 85, 237-237 227 With 3 figures Printed in Great Britain THE PERMEABILITY OF THE CUTICULAR LINING OF THE INSECT ALIMENTARY CANAL BY S. H. P. MADDRELL AND B. O. C. GARDINER A.R.C. Unit
ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SODIUM BY THE ISOLATED MIDGUT OF HYALOPHORA CECROPIA
 J. Exp. Biol. (1971). 54. 269-374 269 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SODIUM BY THE ISOLATED MIDGUT OF HYALOPHORA CECROPIA BY W. R. HARVEY AND K. ZERAHN* Department of Biology,
J. Exp. Biol. (1971). 54. 269-374 269 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SODIUM BY THE ISOLATED MIDGUT OF HYALOPHORA CECROPIA BY W. R. HARVEY AND K. ZERAHN* Department of Biology,
HORMONAL CONTROL OF EXCRETION IN THE AMERICAN COCKROACH
 J. Exp. Biol. (197), 4, 35-* 1 35 With 2 text-figures Printed in Great Britain HORMONAL CONTROL OF EXCRETION IN THE AMERICAN COCKROACH I. RELEASE OF A DIURETIC HORMONE FROM THE TERMINAL ABDOMINAL GANGLION
J. Exp. Biol. (197), 4, 35-* 1 35 With 2 text-figures Printed in Great Britain HORMONAL CONTROL OF EXCRETION IN THE AMERICAN COCKROACH I. RELEASE OF A DIURETIC HORMONE FROM THE TERMINAL ABDOMINAL GANGLION
Amino acids modulate ion transport and fluid secretion by insect Malpighian tubules
 The Journal of Experimental Biology 26, 79-91 23 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/jeb.58 79 Amino acids modulate ion transport and fluid secretion by insect Malpighian tubules Matthew H. Hazel
The Journal of Experimental Biology 26, 79-91 23 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/jeb.58 79 Amino acids modulate ion transport and fluid secretion by insect Malpighian tubules Matthew H. Hazel
Chapter 44. Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Water Balance and Waste Disposal osmoregulation managing water content and solute composition based on movements of solutes excretion
Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Water Balance and Waste Disposal osmoregulation managing water content and solute composition based on movements of solutes excretion
Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretion
 Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE: A SECOND DIURETIC HORMONE IN RHODNIUS PROUXUS. Accepted 26 October 1990
 J. exp. Biol. 156, 557-566 (1991) 557 Primed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1991 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE: A SECOND DIURETIC HORMONE IN RHODNIUS PROUXUS BY S. H. P. MADDRELL 1, W. S. HERMAN
J. exp. Biol. 156, 557-566 (1991) 557 Primed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1991 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE: A SECOND DIURETIC HORMONE IN RHODNIUS PROUXUS BY S. H. P. MADDRELL 1, W. S. HERMAN
AP Biology. Homeostasis. Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. Homeostasis
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment omeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment omeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION
 1 2 3 4 5 6 OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION OSMOREGULATION Process by which animals control their solute concentrations and balance water gain and loss Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water
1 2 3 4 5 6 OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION OSMOREGULATION Process by which animals control their solute concentrations and balance water gain and loss Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
[697] Zoological Laboratory, University of Cambridge. (Received 14 June 1956)
![[697] Zoological Laboratory, University of Cambridge. (Received 14 June 1956) [697] Zoological Laboratory, University of Cambridge. (Received 14 June 1956)](/thumbs/89/100955348.jpg) [697] EXCRETION BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF THE STICK INSECT, DIXIPPUS MOROSUS (ORTHOPTERA, PHASMIDAE): CALCIUM, MAGNESIUM, CHLORIDE, PHOSPHATE AND HYDROGEN IONS BY J. A. RAMSAY Zoological Laboratory,
[697] EXCRETION BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF THE STICK INSECT, DIXIPPUS MOROSUS (ORTHOPTERA, PHASMIDAE): CALCIUM, MAGNESIUM, CHLORIDE, PHOSPHATE AND HYDROGEN IONS BY J. A. RAMSAY Zoological Laboratory,
Aspects of the control of diuresis in the blood gorging insect, Rhodnius prolixus
 Aspects of the control of diuresis in the blood gorging insect, Rhodnius prolixus 17 Pestycydy, 2008, (1-2), 17-26. ISSN 0208-8703 Aspects of the control of diuresis in the blood gorging insect, Rhodnius
Aspects of the control of diuresis in the blood gorging insect, Rhodnius prolixus 17 Pestycydy, 2008, (1-2), 17-26. ISSN 0208-8703 Aspects of the control of diuresis in the blood gorging insect, Rhodnius
THE CONTROL OF DIURESIS IN THE TSETSE FLY GLOSSINA AUSTENI: A PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION OF THE DIURETIC HORMONE BY J. D. GEE*
 J. exp. Biol. (1975), 63, 391-401 301 ^With 5 figures Printed in Great Britain THE CONTROL OF DIURESIS IN THE TSETSE FLY GLOSSINA AUSTENI: A PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION OF THE DIURETIC HORMONE BY J. D. GEE*
J. exp. Biol. (1975), 63, 391-401 301 ^With 5 figures Printed in Great Britain THE CONTROL OF DIURESIS IN THE TSETSE FLY GLOSSINA AUSTENI: A PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION OF THE DIURETIC HORMONE BY J. D. GEE*
K. A. COLLIER AND M. J. O DONNELL* McMaster University, Department of Biology, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada L8S 4K1
 The Journal of Experimental Biology 200, 7 13 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 JEB01 7 ANALYSIS OF EPITHELIAL TRANSPORT BY MEASUREMENT OF K +, Cl AND ph GRADIENTS
The Journal of Experimental Biology 200, 7 13 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 JEB01 7 ANALYSIS OF EPITHELIAL TRANSPORT BY MEASUREMENT OF K +, Cl AND ph GRADIENTS
Physiology of Excretory Systems
 Physiology of Excretory Systems Fig 12-2 (a) Urea is formed by the ornithine-urea cycle in most vertebrates. Because ATP is required for the first step, nitrogen excretion in ureotelic animals is more
Physiology of Excretory Systems Fig 12-2 (a) Urea is formed by the ornithine-urea cycle in most vertebrates. Because ATP is required for the first step, nitrogen excretion in ureotelic animals is more
Chapter 10 EXCRETION
 Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
ACTIVE TRANSPORT BY INSECT MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF ACIDIC DYES AND OF ACYLAMIDES
 J. Exp. Biol. (i974). 61, 357-377 357 *Vth 21 figures in Great Britain ACTIVE TRANSPORT BY INSECT MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF ACIDIC DYES AND OF ACYLAMIDES BY S. H. P. MADDRELL, B. O. C. GARDINER, D. E. M. PILCHER*
J. Exp. Biol. (i974). 61, 357-377 357 *Vth 21 figures in Great Britain ACTIVE TRANSPORT BY INSECT MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF ACIDIC DYES AND OF ACYLAMIDES BY S. H. P. MADDRELL, B. O. C. GARDINER, D. E. M. PILCHER*
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste:
 I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Homeostasis. Thermoregulation. Osmoregulation. Excretion. how organisms regulate their body temperature
 Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF WATER BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF THE STICK INSECT, DIXIPPUS MOROSUS (ORTHOPTERA, PHASMIDAE)
 [ 104 ] ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF WATER BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF THE STICK INSECT, DIXIPPUS MOROSUS (ORTHOPTERA, PHASMIDAE) BY J. A. RAMSAY Zoological Laboratory, University of Cambridge {Received 8 July
[ 104 ] ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF WATER BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF THE STICK INSECT, DIXIPPUS MOROSUS (ORTHOPTERA, PHASMIDAE) BY J. A. RAMSAY Zoological Laboratory, University of Cambridge {Received 8 July
A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* Previous studies (1, 2) have shown that after the ingestion of caffeine
 A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* BY HERBERT H. CORNISH AND A. A. CHRISTMAN (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan,
A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* BY HERBERT H. CORNISH AND A. A. CHRISTMAN (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan,
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment
 Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
THE HORMONAL CONTROL OF DIURESIS IN THE CABBAGE WHITE BUTTERFLY PIERIS BRASSICAE
 J. exp. Biol. (1976). 65, 56S-S75 565 fvith 5 figures Printed in Great Britain THE HORMONAL CONTROL OF DIURESIS IN THE CABBAGE WHITE BUTTERFLY PIERIS BRASSICAE BY SUSAN W. NICOLSON Department of Zoology,
J. exp. Biol. (1976). 65, 56S-S75 565 fvith 5 figures Printed in Great Britain THE HORMONAL CONTROL OF DIURESIS IN THE CABBAGE WHITE BUTTERFLY PIERIS BRASSICAE BY SUSAN W. NICOLSON Department of Zoology,
College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.)
 GLUCOSE ABSORPTION IN THE RENAL TUBULES OF THE FROG. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory of the University of Durham College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.) OPINION is divided on the
GLUCOSE ABSORPTION IN THE RENAL TUBULES OF THE FROG. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory of the University of Durham College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.) OPINION is divided on the
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
[386] THE EXCHANGE OF LABELLED SODIUM IN THE LARVA OF AEDES AEGYPTI L.
![[386] THE EXCHANGE OF LABELLED SODIUM IN THE LARVA OF AEDES AEGYPTI L. [386] THE EXCHANGE OF LABELLED SODIUM IN THE LARVA OF AEDES AEGYPTI L.](/thumbs/94/119893800.jpg) [386] THE EXCHANGE OF LABELLED SODIUM IN THE LARVA OF AEDES AEGYPTI L. BY JOHN E. TREHERNE Department of Zoology, University of Bristol (Received 19 October 1953) INTRODUCTION The osmotic and ionic regulation
[386] THE EXCHANGE OF LABELLED SODIUM IN THE LARVA OF AEDES AEGYPTI L. BY JOHN E. TREHERNE Department of Zoology, University of Bristol (Received 19 October 1953) INTRODUCTION The osmotic and ionic regulation
Complete the table below to compare the processes of excretion and secretion.
 1. Excretion and secretion are two processes that take place in the body of a mammal. Complete the table below to compare the processes of excretion and secretion. excretion secretion one difference one
1. Excretion and secretion are two processes that take place in the body of a mammal. Complete the table below to compare the processes of excretion and secretion. excretion secretion one difference one
LITHIUM ADMINISTRATION TO PATIENTS
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1976), 57, 323-327 AN IRREVERSIBLE EFFECT OF LITHIUM ADMINISTRATION TO PATIENTS C. LINGSCH & K. MARTIN Department of Pharmacology, University of Cambridge, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QD
Br. J. Pharmac. (1976), 57, 323-327 AN IRREVERSIBLE EFFECT OF LITHIUM ADMINISTRATION TO PATIENTS C. LINGSCH & K. MARTIN Department of Pharmacology, University of Cambridge, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QD
[485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS
![[485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS [485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS](/thumbs/90/101209894.jpg) [485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS BY V. B. WIGGLESWORTH Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received 3 November 1954) The thoracic or ' prothoracic'
[485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS BY V. B. WIGGLESWORTH Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received 3 November 1954) The thoracic or ' prothoracic'
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Basic mechanisms of Kidney function
 Excretion Basic mechanisms of Kidney function Urine formation in Amphibians Urine formation in Mammals Urine formation in Insects Nitrogen balance Kidneys The most fundamental function of kidneys) is to
Excretion Basic mechanisms of Kidney function Urine formation in Amphibians Urine formation in Mammals Urine formation in Insects Nitrogen balance Kidneys The most fundamental function of kidneys) is to
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (2) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 TUBULAR FUNCTIONS (Learning objectives 54-57) 1 Tubular Transport About 99% of filtrated water and more than 90% of the filtrated
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (2) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 TUBULAR FUNCTIONS (Learning objectives 54-57) 1 Tubular Transport About 99% of filtrated water and more than 90% of the filtrated
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
Your Goal. Animal s Urinary and Osmoregulatory systems. Paragraph 1: Introduction Goal introduce the paper. Paragraph 1: Introduction
 Your Goal Animal s Urinary and Osmoregulatory systems l Be able to tell the story of kidney evolution as an essay. Maintenance Introduction Goal introduce the paper l Homeostasis is the of Maintenance
Your Goal Animal s Urinary and Osmoregulatory systems l Be able to tell the story of kidney evolution as an essay. Maintenance Introduction Goal introduce the paper l Homeostasis is the of Maintenance
Chapter 16. Urinary System and Thermoregulation THERMOREGULATION. Homeostasis
 Homeostasis Chapter 16 Urinary System and Thermoregulation! Homeostasis Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite fluctuations in the external environment! Examples of homeostasis Thermoregulation
Homeostasis Chapter 16 Urinary System and Thermoregulation! Homeostasis Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite fluctuations in the external environment! Examples of homeostasis Thermoregulation
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
FLUID UPTAKE AND THE MAINTENANCE OF BLOOD VOLUME IN OCTOPUS
 J. exp. Biol. 175, 211 218 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 211 FLUID UPTAKE AND THE MAINTENANCE OF BLOOD VOLUME IN OCTOPUS M. J. WELLS and J. WELLS Department of
J. exp. Biol. 175, 211 218 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 211 FLUID UPTAKE AND THE MAINTENANCE OF BLOOD VOLUME IN OCTOPUS M. J. WELLS and J. WELLS Department of
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
Experiment 1. Isolation of Glycogen from rat Liver
 Experiment 1 Isolation of Glycogen from rat Liver Figure 35: FIG-2, Liver, PAS, 100x. Note the presence of a few scattered glycogen granules (GG). Objective To illustrate the method for isolating glycogen.
Experiment 1 Isolation of Glycogen from rat Liver Figure 35: FIG-2, Liver, PAS, 100x. Note the presence of a few scattered glycogen granules (GG). Objective To illustrate the method for isolating glycogen.
ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SALICYLATE BY RAT JEJUNUM
 Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology (1981) 66, 91-98 91 Printed in Great Britain ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SALICYLATE BY RAT JEJUNUM R. B. FISHER University Laboratory of Physiology, Oxford (RECEIVED
Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology (1981) 66, 91-98 91 Printed in Great Britain ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SALICYLATE BY RAT JEJUNUM R. B. FISHER University Laboratory of Physiology, Oxford (RECEIVED
Renal Pharmacology. Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics BIMM118
 Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
[ 533 ] AMINO ACID ABSORPTION IN THE LOCUST (SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA FORSK.)
![[ 533 ] AMINO ACID ABSORPTION IN THE LOCUST (SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA FORSK.) [ 533 ] AMINO ACID ABSORPTION IN THE LOCUST (SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA FORSK.)](/thumbs/87/95280787.jpg) [ 533 ] AMINO ACID ABSORPTION IN THE LOCUST (SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA FORSK.) BY J. E. TREHERNE A.R.C. Unit of Insect Physiology, Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received 23 March 1959) INTRODUCTION
[ 533 ] AMINO ACID ABSORPTION IN THE LOCUST (SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA FORSK.) BY J. E. TREHERNE A.R.C. Unit of Insect Physiology, Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received 23 March 1959) INTRODUCTION
Homeostatic Regulation
 Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Body Fluid Regulation and Excretion. Chapter 36
 Body Fluid Regulation and Excretion Chapter 36 Excretion The excretory system monitors the concentration of body fluids and removes harmful or waste substances from the body Water, nutrients and minerals
Body Fluid Regulation and Excretion Chapter 36 Excretion The excretory system monitors the concentration of body fluids and removes harmful or waste substances from the body Water, nutrients and minerals
Keywords (reading p ) Ammonia toxicity Urea Uric acid Osmoconformer Osmoregulator Passive transport Facilitated diffusion Active transport
 Controlling the Internal Environment II: Salt and water balance Keywords (reading p. 936-949) Ammonia toxicity Urea Uric acid Osmoconformer Osmoregulator Passive transport Facilitated diffusion Active
Controlling the Internal Environment II: Salt and water balance Keywords (reading p. 936-949) Ammonia toxicity Urea Uric acid Osmoconformer Osmoregulator Passive transport Facilitated diffusion Active
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
THE EXCRETION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF RHODNIUS
 [ no] THE EXCRETION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF RHODNIUS BY J. A. RAMSAY From the Zoological Laboratory, University of Cambridge {Received 18 June 1951) (With Four Text-figures)
[ no] THE EXCRETION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF RHODNIUS BY J. A. RAMSAY From the Zoological Laboratory, University of Cambridge {Received 18 June 1951) (With Four Text-figures)
Metabolism of echitamine and plumbagin in rats
 J. Biosci., Vol. 3, Number 4, December 1981, pp. 395-400. Printed in India. Metabolism of echitamine and plumbagin in rats B. CHANDRASEKARAN and B. NAGARAJAN Microbiology Division, Cancer Institute, Madras
J. Biosci., Vol. 3, Number 4, December 1981, pp. 395-400. Printed in India. Metabolism of echitamine and plumbagin in rats B. CHANDRASEKARAN and B. NAGARAJAN Microbiology Division, Cancer Institute, Madras
[689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY
![[689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY [689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY](/thumbs/91/107443416.jpg) [689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY E. BURSELL Department of Zoology, University College of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia {Received 7 March i960) INTRODUCTION
[689] LOSS OF WATER BY EXCRETION AND DEFAECATION IN THE TSETSE FLY E. BURSELL Department of Zoology, University College of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia {Received 7 March i960) INTRODUCTION
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
THE INFLUENCE OF THE DIURETIC HORMONE ON THE PROCESS OF URINE SECRETION BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF CARAUSIUS MOROSUS
 J. Exp. Biol. (1970), 53, 46S-484 465 With 1 plate and 10 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE INFLUENCE OF THE DIURETIC HORMONE ON THE PROCESS OF URINE SECRETION BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF CARAUSIUS
J. Exp. Biol. (1970), 53, 46S-484 465 With 1 plate and 10 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE INFLUENCE OF THE DIURETIC HORMONE ON THE PROCESS OF URINE SECRETION BY THE MALPIGHIAN TUBULES OF CARAUSIUS
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Osmoregulation_and_Excretion_p2.notebook June 01, 2017
 What water balance problems face organisms? Animals balance water gain and loss in one of two ways: 1. Osmoconformers are isotonic to their surroundings so they do not lose or gain water they usually live
What water balance problems face organisms? Animals balance water gain and loss in one of two ways: 1. Osmoconformers are isotonic to their surroundings so they do not lose or gain water they usually live
BIOL 347L Laboratory Three
 Introduction BIOL 347L Laboratory Three Osmosis in potato and carrot samples Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration,
Introduction BIOL 347L Laboratory Three Osmosis in potato and carrot samples Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration,
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Chapter 32 Excretion
 Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
COPULATION AND EGG-PRODUCTION IN RHODNIUS PROLIXUS: THE ROLE OF THE SPERMATHECAE
 J. Exp. BM. (1965), 4*. 373-378 3-73 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain COPULATION AND EGG-PRODUCTION IN RHODNIUS PROLIXUS: THE ROLE OF THE SPERMATHECAE BY K. G. DAVEY Institute of Parasitology,
J. Exp. BM. (1965), 4*. 373-378 3-73 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain COPULATION AND EGG-PRODUCTION IN RHODNIUS PROLIXUS: THE ROLE OF THE SPERMATHECAE BY K. G. DAVEY Institute of Parasitology,
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Chapter MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
THE PHYSIOLOGY OF CARBON DIOXIDE TRANSPORT IN INSECT BLOOD
 THE PHYSIOLOGY OF CARBON DIOXIDE TRANSPORT IN INSECT BLOOD PART III. THE BUFFER CAPACITY OF GASTROPHILUS BLOOD BY L. LEVENBOOK, Molteno Institute, University of Cambridge (Received 23 November 1949) (With
THE PHYSIOLOGY OF CARBON DIOXIDE TRANSPORT IN INSECT BLOOD PART III. THE BUFFER CAPACITY OF GASTROPHILUS BLOOD BY L. LEVENBOOK, Molteno Institute, University of Cambridge (Received 23 November 1949) (With
WJEC. BY4 Kidney Questions
 NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
The incorporation of labeled amino acids into lens protein. Abraham Speclor and Jin H. Kinoshita
 The incorporation of labeled amino acids into lens protein Abraham Speclor and Jin H. Kinoshita Calf and rabbit lenses cultured in a medium containing a radioactive amino acid incorporate some labeled
The incorporation of labeled amino acids into lens protein Abraham Speclor and Jin H. Kinoshita Calf and rabbit lenses cultured in a medium containing a radioactive amino acid incorporate some labeled
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
ION CONCENTRATION AND ACTIVITY IN THE HAEMOLYMPH OF AEDES AEGYPTI LARVAE
 J. exp. Biol. (1982), IOI, 143-151- ^ith & figures in Great Britain ION CONCENTRATION AND ACTIVITY IN THE HAEMOLYMPH OF AEDES AEGYPTI LARVAE BY H. A. EDWARDS Department of Zoology, South Parks Road, Oxford
J. exp. Biol. (1982), IOI, 143-151- ^ith & figures in Great Britain ION CONCENTRATION AND ACTIVITY IN THE HAEMOLYMPH OF AEDES AEGYPTI LARVAE BY H. A. EDWARDS Department of Zoology, South Parks Road, Oxford
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).
![Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside). Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).](/thumbs/80/80478709.jpg) 1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
(ethanol) suggests that it is similar to the diuresis following ingestion of water.
 435 J. Physiol. (I946) I04, 435-442 6I2.464.I THE EFFECT OF ETHYL ALCOHOL AND SOME OTHER DIURETICS ON CHLORIDE EXCRETION IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON AND ISABEL G. SMITH, From the Physiology Department,
435 J. Physiol. (I946) I04, 435-442 6I2.464.I THE EFFECT OF ETHYL ALCOHOL AND SOME OTHER DIURETICS ON CHLORIDE EXCRETION IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON AND ISABEL G. SMITH, From the Physiology Department,
Acid Base Balance. Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih. Clinical Chemistry Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih
 Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Organic Molecule Composition of Milk: Lab Investigation
 Name: Organic Molecule Composition of Milk: Lab Investigation Introduction & Background Milk & milk products have been a major food source from earliest recorded history. Milk is a natural, nutritionally
Name: Organic Molecule Composition of Milk: Lab Investigation Introduction & Background Milk & milk products have been a major food source from earliest recorded history. Milk is a natural, nutritionally
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP
 CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Accepted
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Accepted
After studying this lecture, you should be able to...
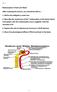 Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
water balance water nitrogen chapter 42
 water balance chapter 42 water osmoregulation water and dissolved solutes adjusting the composition of internal body fluids in arthropods -- hemolymph in vertebrates -- interstitial fluid transport epithelia
water balance chapter 42 water osmoregulation water and dissolved solutes adjusting the composition of internal body fluids in arthropods -- hemolymph in vertebrates -- interstitial fluid transport epithelia
Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Sansom & Manston, 1963) and rats (Payne & Sansom, 1963). It appeared
 J. Physiol. (1964), 170, pp. 613-620 613 Printed in Great Britain THE RELATIVE TOXICITY IN RATS OF DISODIUM ETHYLENE DIAMINE TETRA-ACETATE, SODIUM OXALATE AND SODIUM CITRATE BY J. M. PAYNE AND B. F. SANSOM
J. Physiol. (1964), 170, pp. 613-620 613 Printed in Great Britain THE RELATIVE TOXICITY IN RATS OF DISODIUM ETHYLENE DIAMINE TETRA-ACETATE, SODIUM OXALATE AND SODIUM CITRATE BY J. M. PAYNE AND B. F. SANSOM
Chapter 7: Membranes
 Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
[6n ] THE ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF SOME SUGARS IN THE LOCUST, SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA (FORSK.)
![[6n ] THE ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF SOME SUGARS IN THE LOCUST, SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA (FORSK.) [6n ] THE ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF SOME SUGARS IN THE LOCUST, SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA (FORSK.)](/thumbs/95/125550838.jpg) [6n ] THE ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF SOME SUGARS IN THE LOCUST, SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA (FORSK.) A.R.C. BY J. E. TREHERNE Unit of Insect Physiology, Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received
[6n ] THE ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF SOME SUGARS IN THE LOCUST, SCHISTOCERCA GREGARIA (FORSK.) A.R.C. BY J. E. TREHERNE Unit of Insect Physiology, Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Osmoregulation and Excretion 1. There are two basic solutions to the problem of balancing water gain with water loss. a. The first, available only to marine animals, is to be an osmoconformer. The concentration
Osmoregulation and Excretion 1. There are two basic solutions to the problem of balancing water gain with water loss. a. The first, available only to marine animals, is to be an osmoconformer. The concentration
reciprocal of the rate of deiodination being proportional to the reciprocal
 J. Phy&iol. (1972), 222, pp. 475-485 475 With 6 text-figuree Printed in Great Britain DEIODINATION OF THYROID HORMONES BY THE PERFUSED RAT LIVER BY A. P. HILLIER From the Physiological Laboratory, University
J. Phy&iol. (1972), 222, pp. 475-485 475 With 6 text-figuree Printed in Great Britain DEIODINATION OF THYROID HORMONES BY THE PERFUSED RAT LIVER BY A. P. HILLIER From the Physiological Laboratory, University
Diagram of the inner portions of the kidney
 Excretory and Endocrine functions of the kidney The kidneys are the main excretory organs which eliminate in the urine, most metabolites primarily those containing nitrogen such as ammonia, urea and creatinine.
Excretory and Endocrine functions of the kidney The kidneys are the main excretory organs which eliminate in the urine, most metabolites primarily those containing nitrogen such as ammonia, urea and creatinine.
I. Chemical Properties of Phospholipids. Figure 1: Phospholipid Molecule. Amphiphatic:
 I. Chemical Properties of Phospholipids Figure 1: Phospholipid Molecule Amphiphatic: a) The amphiphatic nature & cylindrical shape of phospholipids contributes to their ability to assume bilayers in an
I. Chemical Properties of Phospholipids Figure 1: Phospholipid Molecule Amphiphatic: a) The amphiphatic nature & cylindrical shape of phospholipids contributes to their ability to assume bilayers in an
Overton,1 who has worked exhaustively at the subject, looked upon. considered by some to be due to the state of the fluid originally in the
 THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
substance excreted protein-deficient diet protein-rich diet. urea uric acid ammonium ions creatinine
 1. Define the term excretion....... [Total 2 marks] 2. The table below shows the mass of different substances excreted by a volunteer during two 24 hour periods. During the first 24 hour period, the volunteer
1. Define the term excretion....... [Total 2 marks] 2. The table below shows the mass of different substances excreted by a volunteer during two 24 hour periods. During the first 24 hour period, the volunteer
