Correction of prominent ears: techniques and complications
|
|
|
- Damon Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2): pissn , eissn Correction of prominent ears: techniques and complications Jiyun Choi, MD, PhD Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Rep. of Korea Prominent ears are present in approximately 5% of the Caucasian population. It is characterized by autosomal dominant inheritance and commonly caused by 2 developmental defects: underdevelopment of the antihelical fold and overdevelopment of the conchal wall. A thorough preoperative evaluation includes examination of ear symmetry, size, shape, and projection. Mustarde first described a technique for creating an antihelical fold by utilizing permanent conchoscaphal mattress sutures. Furnas popularized a technique of conchal setback using permanent cochomastoidal suturing. Keywords: prominent ears; mustard technique; furnas technique; complications Introduction Prominent ears are present in approximately 5% of the Caucasian population [1]. They are characterized by autosomal dominant inheritance and commonly caused by two developmental defects: underdevelopment of the antihelical fold and overdevelopment of the conchal wall [1]. The ear is a complex structure of cartilage and skin with many intricate involutions and folds. It includes five critical elements: the concha, helix, antihelix, tragus, and lobule. Parts of lesser importance include the antitragus, intertragic notch, and Darwin s tubercle [2]. The anatomical divisions of the ear are based in embryology, and the ear s origins are from the first (mandibular) and second (hyoid) branchial arches. These hillocks begin to fuse and form the external ear. Assigning a specific anatomic location on the ear to any given hillock is more speculative, but it is generally thought that the tragus helical crus and part of the helix develop from the mandibular arch, and the remainder of the external ear develops from the hillocks of the hyoid arch [2]. The ear attains approximately 85% of its adult size by 3 years of age [3]. Ear width matures in boys at 7 years and in girls at 6; ear length matures in boys at 13 years of age and in girls at 12 [4]. This implies that children 5 6 years of age may safely undergo otoplasty without compromising external ear growth. The average height of an adult pinna is cm, with a width of cm. The helix is elevated 1 2 cm from the mastoid. The ideal auriculocephalic angle is degrees; the conchocephalic and conchomastoid angles are 90 degrees [5]. The upper pole of the ear should fall at the level of the brow, whereas the inferior aspect of the lobe should fall at the level of the nasal ala. From the scalp, the helical rim of the ear commonly projects laterally mm at the superior pole, mm at the midpoint, and mm at the lobule [3]. The superficial temporal and postauricular branches of the external carotid system provide excellent blood supply to the pinna. The innervation to the external ear follows its embryologic branchial arch origins. It consists of the anterior and posterior branches of the great auricular nerve, which innervates the first branchial arch structures (tragus and helical crus), and the auriculotemporal nerve, which innervates the second Received February , Revised May , Accepted May Corresponding author: Jiyun Choi, Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Chosun University College of Medicine, 365 Pilmundaero, Dong-gu, Gwangju 61452, Rep. of Korea Tel: , Fax: , happyent@naver.com This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Copyright c Korean Society of Korean Cosmetic Surgery (KSKCS) Korean College of Cosmetic Surgery (KCCS).
2 Correction of prominent ears branchial arch structures (helix, scapha, antihelix, concha, antitragus, external acoustic meatus, and lobule). The external auditory meatus also receives innervation from branches of the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves (Fig. 1) [6]. Preoperative evaluation A preoperative evaluation includes an examination of ear symmetry, size, shape, and projection. The physical exam of each auricle should be documented, with special attention to the status of the antihelix, and the depth and projection of the conchal bowl, as these two deformities most often coexist in a protruding ear. During preoperative evaluation, one should assess the following in a patient with prominent ears: (1) degree of antihelical folding; (2) depth of the conchal bowl; (3) plane of the lobule and deformity, if present; (4) angle between the helical rim and the mastoid plane; (5) quality and spring of the auricular cartilage [7]. The optimal timing of surgical correction depends on a rational approach based on auricular growth and the age of school matriculation. As the ear is nearly fully developed by the 6 7 years of age, correction may be performed at this time [8]. Existing deformities, postoperative course, realistic outcomes, and complications may be discussed with the patient and parents at that time. Helix - Helical crus - Superior crus -Triangularis fossa - Inferior crus Antihelix Otoplasty procedures Mustard technique In 1963, Mustarde [9] first described the creation of an antihelical fold using permanent conchoscaphal mattress sutures. Several subtle refinements of this technique have been described since that time, but the fundamentals of the procedure remain unchanged. Pediatric patients most commonly undergo this procedure under general anesthesia, and perioperative broad-spectrum antibiotics are administered. The face is prepped as a sterile field so that both ears can be visualized simultaneously. After infiltration with lidocaine 1% with epinephrine 1/100,000, an elliptical or dumbbell-shaped skin excision is made that tapers at both ends for ease of closure. Typically, more skin is excised from the postauricular surface than from the mastoid to camouflage the resulting scar into the postauricular sulcus following setback. Wide undermining is performed in the supraperichondrial plane almost up to the helical rim. The area of intended neoantihelix may be demarcated by placing 25-gauge needles through the anterior auricular skin at the intended site of antihelix creation and bringing the needle out the posterior side. The cartilage is then marked with methylene blue. The Mustarde procedure consists of inserting three to four horizontal placement sutures (4-0 nylon) to permanently recreate the antihelix. The suture is placed through the cartilage and anterior perichondrium, but not the anterior skin. Outer cartilage bites of 1 cm are separated by 2 mm. The distance between the outer and inner cartilage bites is 16 mm. The ear dressing is removed on the first postoperative day to check for hematomas, and then replaced for 3 4 additional days. Subsequently, a headband is worn continuously for 2 weeks and at night for an additional 4 6 weeks (Fig. 2) [9]. External meatus Tragus - Intertragal notch Fig. 1. Normal auricular anatomy. Lobule Scapha Anti tragus Concha - Cymba - Cavum Furnas technique In 1968, Furnas [10] popularized a conchal setback technique using permanent cochomastoidal suturing. This procedure is often used in conjunction with techniques to correct an absent antihelical fold, as described above. The patient is prepped and draped in a manner similar to that described for antihelical fold correction. After infiltration of lidocaine 1% with epinephrine 1/100,000, a fusiform incision is made in the postauricular region. The width of the incision is estimated by manually pushing the concha towards the mastoid. Care is taken to avoid excessive skin excision, as tension on 91
3 Jiyun Choi Fig. 2. Mustarde technique. the wound predisposes to hypertrophic scar formation. Little to no skin excision is required inferior to the level of the antitragus. After skin excision, the soft tissue and postauricular muscle are excised from the postauricular sulcus. Sufficient soft tissue is excised to produce a pocket to receive the concha during suture placement. The skin over the helix, antihelix, and concha is undermined with scissors, and permanent horizontal mattress sutures (e.g., 4-0 nylon) are placed at the lateral third of the concha cavum and concha cymba, parallel to the natural curve of the auricular cartilage. The sutures are placed through the cartilage and lateral perichondrium, but not the lateral auricular skin. At least three sutures are placed for adequate setback. The sutures are placed on what was the ascending wall of the concha. When tightened, they convert the wall into a longer floor of the concha. For long-term successful conchal reduction, suture bites of mastoid periosteum must be removed. Extremely thick cartilage frequently seen in older individuals may be weakened by excising small vertical ellipses. Importantly, conchomastoidal sutures must allow the concha to be set both medially and posteriorly, or external auditory canal stenosis can result. The wound is irrigated and closed as after the Mustarde [10] technique. A mastoid dressing is placed, and subsequent postoperative management is the same as that of antihelical fold surgery (Fig. 3). Combined technique The postauricular pinna and postauricular sulcus are infiltrated with local anesthetic. The patient is then prepped and draped. The central portion of the desired antihelix is marked in three places using an 18-gauge needle dipped in methylene Fig. 3. Furnas technique. blue and used to tattoo the desired areas. The surgical procedure is begun by removing a postauricular ellipse of skin. The posterior aspect of the auricular cartilage is exposed along the superior/inferior aspect of the pinna cartilage through helical rim. Small discs of cartilage are then scored and removed from the posterior aspect of the cavum conchae cartilage in areas where the patient has the most cartilage convexity. Conchalmastoid setback sutures are then placed. Using a 4-0 clear nylon suture, the conchal bowl is set back to its posterior medial extent. The antihelical fold is then created. Using the tattooed methylene blue markings, a horizontal mattress suture is placed with 4-0 nylon at the mid aspect of the desired antihelical fold. The perichondrium of the contralateral side is usually included in the surgical bite to avoid cheese-wiring of the suture through the cartilage over time. This is initially placed approximately 7 mm anterior to the blue marking and then 7 mm posteriorly in a symmetrical fashion. The skin is then closed with running locking 5-0 fast gut sutures. An identical procedure is performed on the contralateral side with careful attention to symmetry. After this procedure, the patient is placed in a secure dressing (Fig. 4). Complications Complications of otoplasty are not infrequently the consequences of poor surgical planning, although some may be unavoidable. Anterior surface irregularities, obliteration of the postauricular sulcus, and telephone ear deformity can be avoided with a meticulous surgical technique. Hematoma Hematomas occur in up to 3.5% of cases. Bleeding complications are typically an early complication due to incomplete 92
4 Correction of prominent ears completely resolved. Infection Wound infection occurs in <5% of otoplasties. Sterile technique is critical for prevention, and most surgeons include prophylactic antibiotics. As with hematomas, prompt identification and treatment are essential to avoid permanent deformity. Infections may present as pain, erythema, swelling, and drainage. Any suspicion of infection should be treated aggressively with oral antibiotics. Management includes drainage and irrigation of the wound, followed by treatment with oral anti-pseudomonas antibiotics. Patients with severe infection may require IV antibiotics. Late complications Loss of correction or relapse of auricular deformity: This occurs more commonly after cartilage-sparing techniques. There are multiple technical causes of inadequate correction, including pulling of sutures over time, improper suture placement, failure to correct a deformity during surgery, failure to anchor sutures firmly on the mastoid periosteum, and failure to weaken noncompliant cartilage. Inadequate correction requires revision otoplasty. Telephone and reverse telephone ear deformities: Telephone ear deformity occurs due to overcorrection in the middle third of the ear and relative under-correction of the superior and inferior poles. Reverse telephone ear deformity occurs when the middle third of the auricle remains prominent relative to the superior and inferior poles. Both deformities are avoidable with correct placement of the conchal setback sutures [11]. Conclusion Fig. 4. A 23-year-old boy with protruding ears before (left) and after (right) otoplasty using the combined technique. hemostasis during surgery. A common hallmark is bleeding around the dressing or severe unilateral pain. Urgent evacuation of the hematoma is critical to prevent fibrosis and, ultimately, permanent deformity of the auricle, known as cauliflower ear. Careful hemostasis during hematoma evacuation should be obtained, and a drain and pressure dressing should be placed around the ear. The patient should be discharged on oral antibiotics and followed closely until the hematoma has Otoplasty using the Mustard, Furnas, or combined techniques can result in successful outcomes, and these procedures are very useful for prominent ear patients. However, care must be taken to prevent complications such as hematoma, infection, under-correction, and telephone ear deformity. Acknowlegments This study was supported by research funds from Chosun University Hospital
5 Jiyun Choi Conflicts of interest The author has nothing to disclose. References 1. Adamson PA, Strecker HD. Otoplasty techniques. Facial Plast Surg 1995;11: Tolleth H. Artistic anatomy, dimensions, and proportions of the external ear. Clin Plast Surg 1978;5: Adamson JE, Horton CE, Crawford HH. The growth pattern of the external ear. Plast Reconstr Surg 1965;36: Farkas LG, Posnick JC, Hreczko TM. Anthropometric growth study of the ear. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 1992;29: Rogers BO. Microtic, lop, cup and protruding ears: four directly inheritable deformities? Plast Reconstr Surg 1968;41: Janis JE, Rohrich RJ, Gutowski KA. Otoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 2005;115:60e-72e. 7. Ellis DA, Keohane JD. A simplified approach to otoplasty. J Otolaryngol 1992;21: Kotler HS, Robertson K, Tardy ME Jr. Pre- and postoperative management in otoplasty. Facial Plast Surg 1994;10: Mustarde JC. The correction of prominent ears using simple mattress sutures. Br J Plast Surg 1963;16: Furnas DW. Correction of prominent ears by conchamastoid sutures. Plast Reconstr Surg 1968;42: Owsley TG, Biggerstaff TG. Otoplasty complications. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 2009;21:
ISPUB.COM. Cutting Burr Otoplasty. D Wynne, N Balaji INTRODUCTION ANATOMY CUTTING BURR TECHNIQUE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 1 D Wynne, N Balaji Citation D Wynne, N Balaji.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 7 Number 1. Abstract Prominent
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 1 D Wynne, N Balaji Citation D Wynne, N Balaji.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 7 Number 1. Abstract Prominent
Analysis in Otoplasty
 63 Analysis in Otoplasty FACIAL PLASTIC SURGERY CLINICS OF NORTH AMERICA Daniel G. Becker, MD, FACS*, Stephen S. Lai, MD, PhD, Jeffrey B. Wise, MD, Jacob D. Steiger, MD Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 14 (2006)
63 Analysis in Otoplasty FACIAL PLASTIC SURGERY CLINICS OF NORTH AMERICA Daniel G. Becker, MD, FACS*, Stephen S. Lai, MD, PhD, Jeffrey B. Wise, MD, Jacob D. Steiger, MD Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 14 (2006)
An alternative approach for correction of constricted ears of moderate severity
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 389 393 An alternative approach for correction of constricted ears of moderate severity M.M. Al-Qattan* Division of Plastic Surgery, King Saud University,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 389 393 An alternative approach for correction of constricted ears of moderate severity M.M. Al-Qattan* Division of Plastic Surgery, King Saud University,
Surgery to correct a prominent ear can profoundly
 Operative Strategies The authors believe that conchal hypertrophy plays a more significant role in ear prominence than has been indicated in the literature. Instead of focusing on the antihelical fold,
Operative Strategies The authors believe that conchal hypertrophy plays a more significant role in ear prominence than has been indicated in the literature. Instead of focusing on the antihelical fold,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between projection of the ear, the inferior crus, and the antihelical body: analysis based on computed tomography
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between projection of the ear, the inferior crus, and the antihelical body: analysis based on computed tomography (brief title): Ear projection and inferior crus HIROSHI SHINOHARA
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between projection of the ear, the inferior crus, and the antihelical body: analysis based on computed tomography (brief title): Ear projection and inferior crus HIROSHI SHINOHARA
Complications of Otoplasty
 Complications of Otoplasty Ethan B. Handler, MD, Tara Song, MD, Charles Shih, MD* KEYWORDS Otoplasty Complications Protruding ears Prominent ears Treatment KEY POINTS Do not overtighten antihelix horizontal
Complications of Otoplasty Ethan B. Handler, MD, Tara Song, MD, Charles Shih, MD* KEYWORDS Otoplasty Complications Protruding ears Prominent ears Treatment KEY POINTS Do not overtighten antihelix horizontal
Chapter 49 n Otoplasty
 Chapter 49 n Otoplasty Charles H. Thorne This chapter reviews otoplasty for common auricular deformities such as prominent ears, macrotia, ears with inadequate helical rim, constricted ear, Stahl s ear,
Chapter 49 n Otoplasty Charles H. Thorne This chapter reviews otoplasty for common auricular deformities such as prominent ears, macrotia, ears with inadequate helical rim, constricted ear, Stahl s ear,
Otoplasty. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with Your Surgeon or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with Your Surgeon or a licensed healthcare provider.
The Importance of a Conchal Bowl Element in the Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Framework in Total Auricular Reconstruction
 The Importance of a Conchal owl Element in the Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Framework in Total uricular Reconstruction Young Soo Kim ona Microtia and esthetic Ear Surgery Clinic, Seoul, Korea Original
The Importance of a Conchal owl Element in the Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Framework in Total uricular Reconstruction Young Soo Kim ona Microtia and esthetic Ear Surgery Clinic, Seoul, Korea Original
DOI: /01.PRS C9
 CME Otoplasty Jeffrey E. Janis, M.D., Rod J. Rohrich, M.D., and Karol A. Gutowski, M.D. Dallas, Texas; and Madison, Wis. Learning Objectives: After studying this article, the participant should be able
CME Otoplasty Jeffrey E. Janis, M.D., Rod J. Rohrich, M.D., and Karol A. Gutowski, M.D. Dallas, Texas; and Madison, Wis. Learning Objectives: After studying this article, the participant should be able
The Protruding Ear: Cosmetic and Reconstruction
 152 The Protruding Ear: Cosmetic and Reconstruction Kausar Ali, BA 1 Jesse D. Meaike, MD 2 Renata S. Maricevich, MD 1 Asaf Olshinka, MD 1 1 Division of Plastic Surgery, Michael E. DeBakey Department of
152 The Protruding Ear: Cosmetic and Reconstruction Kausar Ali, BA 1 Jesse D. Meaike, MD 2 Renata S. Maricevich, MD 1 Asaf Olshinka, MD 1 1 Division of Plastic Surgery, Michael E. DeBakey Department of
Prominent ear deformities with an otosomal transition pattern are
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Percutaneous Adjustable Closed Otoplasty for Prominent Ear Deformity Orhan Ozturan, MD, Remzi Dogan, MD, Sabri Baki Eren, MD, Fadlullah Aksoy, MD, and Bayram Veyseller, MD Objective: The
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Percutaneous Adjustable Closed Otoplasty for Prominent Ear Deformity Orhan Ozturan, MD, Remzi Dogan, MD, Sabri Baki Eren, MD, Fadlullah Aksoy, MD, and Bayram Veyseller, MD Objective: The
Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects. O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery
 Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery Nasal defects and deformities Cleft palate and Velopharyngeal incompetence Pharyngeal and oesophageal defects Pinnal
Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery Nasal defects and deformities Cleft palate and Velopharyngeal incompetence Pharyngeal and oesophageal defects Pinnal
underwent otoplasty procedures between January 2004 and September 2010, by the same senior surgeon.
 Research Original Investigation Cartilage Splitting Without Stitches Technique and Outcomes Déborah Obadia, MD; Julien Quilichini, MD; Vincent Hunsinger, MD; Patrick Leyder, MD IMPORTANCE Otoplasty procedures
Research Original Investigation Cartilage Splitting Without Stitches Technique and Outcomes Déborah Obadia, MD; Julien Quilichini, MD; Vincent Hunsinger, MD; Patrick Leyder, MD IMPORTANCE Otoplasty procedures
FOR THE CORRECTION OF
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Revision Otoplasty How to Manage the Disastrous Result Alexander Berghaus, MD; Thomas Braun, MD; John Martin Hempel, MD Objective: To describe how severe ear deformities after otoplasty
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Revision Otoplasty How to Manage the Disastrous Result Alexander Berghaus, MD; Thomas Braun, MD; John Martin Hempel, MD Objective: To describe how severe ear deformities after otoplasty
Comparative study between anterior and posterior scoring in otoplasty for bat ear
 Original Article Comparative study between anterior and posterior scoring in otoplasty for bat ear Abdelazim, Mohamed Hussein, Ismaeil, wael fawzy Department of Otorhinolaryngology, AlAzhar Faculty of
Original Article Comparative study between anterior and posterior scoring in otoplasty for bat ear Abdelazim, Mohamed Hussein, Ismaeil, wael fawzy Department of Otorhinolaryngology, AlAzhar Faculty of
Otoplasty for prominent ears deformity
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2014; 18: 3156-3165 P. FIORAMONTI, F. SERRATORE, M. TARALLO, M. RUGGIERI, D. RIBUFFO Unit of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2014; 18: 3156-3165 P. FIORAMONTI, F. SERRATORE, M. TARALLO, M. RUGGIERI, D. RIBUFFO Unit of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery
OTOLARYNGOLOGY ONLINE. Preauricular sinus. Management. Dr. T. Balasubramanian 6/17/2010
 1 OTOLARYNGOLOGY ONLINE Preauricular sinus Management Dr. T. Balasubramanian 6/17/2010 This e book discusses the Etiopathogenesis of preauricular sinus. Even though it is commonly encountered surgical
1 OTOLARYNGOLOGY ONLINE Preauricular sinus Management Dr. T. Balasubramanian 6/17/2010 This e book discusses the Etiopathogenesis of preauricular sinus. Even though it is commonly encountered surgical
The Ear. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
RECONSTRUCTION OF MICROtia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A 2-Stage Ear Reconstruction for Microtia Haiyue Jiang, MD; Bo Pan, MD; Yanyong Zhao, MD; Lin Lin, MD; Lei Liu, MD; Hongxing Zhuang, MD Objective: To introduce our 2-stage reconstruction
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A 2-Stage Ear Reconstruction for Microtia Haiyue Jiang, MD; Bo Pan, MD; Yanyong Zhao, MD; Lin Lin, MD; Lei Liu, MD; Hongxing Zhuang, MD Objective: To introduce our 2-stage reconstruction
Associate Professor of Plastic Surgery, Karol. Institute; Plastic Department, Serafimerlasarettet, Stockholm, Sweden
 A NEW METHOD OF SHAPING DEFORMED EARS By A. RAGNELL, M.D. Associate Professor of Plastic Surgery, Karol. Institute; Plastic Department, Serafimerlasarettet, Stockholm, Sweden NUMEROUS methods of shaping
A NEW METHOD OF SHAPING DEFORMED EARS By A. RAGNELL, M.D. Associate Professor of Plastic Surgery, Karol. Institute; Plastic Department, Serafimerlasarettet, Stockholm, Sweden NUMEROUS methods of shaping
PARTIAL RECONSTRUCTION OF THE AURICLE
 Hirosaki Med.J. 66:99 104,2016 REVIEW PARTIAL RECONSTRUCTION OF THE AURICLE Satoshi Urushidate,Katsunori Yokoi,Yosuke Watanabe, Makoto Mikami and Yuko Higuma Abstract Auricular reconstruction is often
Hirosaki Med.J. 66:99 104,2016 REVIEW PARTIAL RECONSTRUCTION OF THE AURICLE Satoshi Urushidate,Katsunori Yokoi,Yosuke Watanabe, Makoto Mikami and Yuko Higuma Abstract Auricular reconstruction is often
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
A new classification system of nasal contractures
 Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts
 Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
Since the first attempt at auricular reconstruction PEDIATRIC/CRANIOFACIAL. Single-Stage Autologous Ear Reconstruction for Microtia.
 PEDIATRIC/CRANIOFACIAL Single-Stage Autologous Ear Reconstruction for Microtia Leila Kasrai, F.R.C.S.C., M.P.H. Alison K. Snyder-Warwick, M.D. David M. Fisher, F.R.C.S.C., F.A.C.S. Toronto, Ontario, Canada;
PEDIATRIC/CRANIOFACIAL Single-Stage Autologous Ear Reconstruction for Microtia Leila Kasrai, F.R.C.S.C., M.P.H. Alison K. Snyder-Warwick, M.D. David M. Fisher, F.R.C.S.C., F.A.C.S. Toronto, Ontario, Canada;
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Ear lobe reconstruction Techniques revisited ANANTHARAJAN NATARAJAN Department of Plastic Reconstructive Surgery,
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Ear lobe reconstruction Techniques revisited ANANTHARAJAN NATARAJAN Department of Plastic Reconstructive Surgery,
EAR RECONSTRUCTION. Reconstruction of the ear is one of MICROTIA
 Ear Reconstruction EAR RECONSTRUCTION Reconstruction of the ear is one of the most challenging problems facing a reconstructive surgeon as it demands precise technique combined with artistic creativity.
Ear Reconstruction EAR RECONSTRUCTION Reconstruction of the ear is one of the most challenging problems facing a reconstructive surgeon as it demands precise technique combined with artistic creativity.
Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair
 Original Article Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair Yoon Seok Lee 1, Dong Hyeok Shin 1, Hyun Gon Choi 1, Jee Nam Kim 1, Myung Chul
Original Article Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair Yoon Seok Lee 1, Dong Hyeok Shin 1, Hyun Gon Choi 1, Jee Nam Kim 1, Myung Chul
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
Morphological Study of External Ear in Mentally Retarded and Healthy Subjects.
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Morphological Study of External Ear in Mentally Retarded and Healthy Subjects. Dashrath Haribhau Pimple, Geetha KN *, Karuna N Katti, and GV
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Morphological Study of External Ear in Mentally Retarded and Healthy Subjects. Dashrath Haribhau Pimple, Geetha KN *, Karuna N Katti, and GV
Peripheral Extracranial Neurostimulation for the treatment of Primary Headache and Migraine:
 Chapter 19 Peripheral Extracranial Neurostimulation for the treatment of Primary Headache and Migraine: Introduction 1) The occipital nerve is involved in pain syndromes originating from nerve trauma,
Chapter 19 Peripheral Extracranial Neurostimulation for the treatment of Primary Headache and Migraine: Introduction 1) The occipital nerve is involved in pain syndromes originating from nerve trauma,
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of incisionless otoplasty Incisionless surgery to correct protruding ears Protruding
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of incisionless otoplasty Incisionless surgery to correct protruding ears Protruding
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
CONGENITAL EAR DEFORMIties
 ORIGINL RTICLE 6-Year Experience in Flat Helix Correction With a Simple Procedure Efstathios G. Lykoudis, MD, PhD; Konstantinos Seretis, MD, MSc; Georgia-lexandra Ch. Spyropoulou, MD, PhD Objective: To
ORIGINL RTICLE 6-Year Experience in Flat Helix Correction With a Simple Procedure Efstathios G. Lykoudis, MD, PhD; Konstantinos Seretis, MD, MSc; Georgia-lexandra Ch. Spyropoulou, MD, PhD Objective: To
Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery
 Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery Topic Joo Heon Lee 1, Tae Suk Oh 2, Sung Wan Park 3, Jae Hoon Kim 3, Tanvaa Tansatit 4 1 Area88 Plastic Surgery Clinic, Seoul; 2 Department
Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery Topic Joo Heon Lee 1, Tae Suk Oh 2, Sung Wan Park 3, Jae Hoon Kim 3, Tanvaa Tansatit 4 1 Area88 Plastic Surgery Clinic, Seoul; 2 Department
The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 593 598 The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects Mohammed G. Ellabban*, Maamoun I. Maamoun, Moustafa Elsharkawi
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 593 598 The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects Mohammed G. Ellabban*, Maamoun I. Maamoun, Moustafa Elsharkawi
Commissioning guide:
 2013 Commissioning guide: Sponsoring organisation: British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons Date of evidence search: May 2013 Date of publication: November 2012 Date of review:
2013 Commissioning guide: Sponsoring organisation: British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons Date of evidence search: May 2013 Date of publication: November 2012 Date of review:
Scientific Forum. Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the Alar Rim
 Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
Four Limb Shaped Auricular Chondrocutaneous Composite Graft for the Alar and the Columellar Defects
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.14730/aaps.2017.23.3.149 Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg 2017;23(3):149-154 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 aaps Aesthetic Plastic Surgery Four Limb Shaped Auricular Chondrocutaneous
ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.14730/aaps.2017.23.3.149 Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg 2017;23(3):149-154 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 aaps Aesthetic Plastic Surgery Four Limb Shaped Auricular Chondrocutaneous
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
What is an otoplasty?
 What is an otoplasty? Otoplasty in an operation performed to reduce one or both prominent ears. Children with prominent ears have excess cartilage in the bowl or concha that protruded the ear out away
What is an otoplasty? Otoplasty in an operation performed to reduce one or both prominent ears. Children with prominent ears have excess cartilage in the bowl or concha that protruded the ear out away
Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A. Link to publication Citation for published
Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery
 Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Perichondrial Cutaneous Grafts in Facial Reconstruction
 IJHNS Jamie G Bizzell, Jennings R Boyette ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10001-1285 1 Jamie G Bizzell, 2 Jennings R Boyette ABSTRACT Aim: The purpose of this study is to review the indications, techniques,
IJHNS Jamie G Bizzell, Jennings R Boyette ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10001-1285 1 Jamie G Bizzell, 2 Jennings R Boyette ABSTRACT Aim: The purpose of this study is to review the indications, techniques,
Expanded Transposition Flap Technique for Total and Subtotal Resurfacing of the Face and Neck
 Expanded Transposition Flap Technique for Total and Subtotal Resurfacing of the Face and Neck Robert J. Spence, MD, FACS Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD Correspondence: rspence@jhmi.edu
Expanded Transposition Flap Technique for Total and Subtotal Resurfacing of the Face and Neck Robert J. Spence, MD, FACS Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD Correspondence: rspence@jhmi.edu
Colorectal procedure guide
 Colorectal procedure guide Illustrations by Lisa Clark Biodesign ADVANCED TISSUE REPAIR cookmedical.com 2 INDEX Anal fistula repair Using the Biodesign plug with no button.... 4 Anal fistula repair Using
Colorectal procedure guide Illustrations by Lisa Clark Biodesign ADVANCED TISSUE REPAIR cookmedical.com 2 INDEX Anal fistula repair Using the Biodesign plug with no button.... 4 Anal fistula repair Using
8 External Ear Canal Surgery
 30 Chapter 8 8 External Ear Canal Surgery Henning Hildmann, Holger Sudhoff Surgery in the external auditory canal without surgery in the middle ear may be necessary: 1. After surgery 2. After trauma 3.
30 Chapter 8 8 External Ear Canal Surgery Henning Hildmann, Holger Sudhoff Surgery in the external auditory canal without surgery in the middle ear may be necessary: 1. After surgery 2. After trauma 3.
CLASSIC AURICULAR POINTS
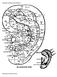 CLASSIC AURICULAR POINTS New Style Auricular Points (1) Anaesthesia forextraction of Teeth 1 At the postero-inferior of the 1st area. (2) Upper Jaw At the postero-inferior part of the 2nd area. (3) Lower
CLASSIC AURICULAR POINTS New Style Auricular Points (1) Anaesthesia forextraction of Teeth 1 At the postero-inferior of the 1st area. (2) Upper Jaw At the postero-inferior part of the 2nd area. (3) Lower
Onlay Rib Bone Graft in Elevation of Reconstructed Auricle: 17 Years of Experience
 Onlay Rib one Graft in Elevation of Reconstructed uricle: 17 Years of Experience Taehoon Kim, Jihyeon Han, Yoonho Lee Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Seoul National University College
Onlay Rib one Graft in Elevation of Reconstructed uricle: 17 Years of Experience Taehoon Kim, Jihyeon Han, Yoonho Lee Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Seoul National University College
(FIG.1) Landmarks of the external ear in dogs. (FIG.2) Anatomy of the ear.
 SURGICAL ANATOMY of Ear (FIG.1) Landmarks of the external ear in dogs. (FIG.2) Anatomy of the ear. An aural (auricular) hematoma is a collection of blood within the cartilage plate of the ear. Suture placement
SURGICAL ANATOMY of Ear (FIG.1) Landmarks of the external ear in dogs. (FIG.2) Anatomy of the ear. An aural (auricular) hematoma is a collection of blood within the cartilage plate of the ear. Suture placement
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
OF CONCHA-HELIX DEFECTS. BY JAMES K. MASSON, M.D. Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota
 British Journal qf Plastic Surgery (x97z), 7,5, 399-403 A SIMPLE ISLAND FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF CONCHA-HELIX DEFECTS BY JAMES K. MASSON, M.D. Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota AFTER
British Journal qf Plastic Surgery (x97z), 7,5, 399-403 A SIMPLE ISLAND FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF CONCHA-HELIX DEFECTS BY JAMES K. MASSON, M.D. Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota AFTER
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubric (ICO-OSCAR)
 International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubric (ICO-OSCAR) The International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubrics
International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubric (ICO-OSCAR) The International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubrics
Anatomy of the Ear Region. External ear Middle ear Internal ear
 Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
The history of face lift surgery encompasses a wide
 Richard Ellenbogen, MD; Anthony Youn, MD; Dan Yamini, MD; and Steven Svehlak, MD Dr. Ellenbogen, Dr. Yamini, and Dr. Svehlak are in private practice in Los Angeles, CA. Dr. Youn is in private practice
Richard Ellenbogen, MD; Anthony Youn, MD; Dan Yamini, MD; and Steven Svehlak, MD Dr. Ellenbogen, Dr. Yamini, and Dr. Svehlak are in private practice in Los Angeles, CA. Dr. Youn is in private practice
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 + Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
+ Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
A NEW METHOD FOR TOTAL RECONSTRUCTION OF THE NOSE : THE EARS AS DONOR AREAS
 A NEW METHOD FOR TOTAL RECONSTRUCTION OF THE NOSE : THE EARS AS DONOR AREAS By MIGUEL ORTICOCHEA, M.D. 1 Professor of Plastic Surgery, Medical School, Javeriana University, Bogotd, Colombia THE early history
A NEW METHOD FOR TOTAL RECONSTRUCTION OF THE NOSE : THE EARS AS DONOR AREAS By MIGUEL ORTICOCHEA, M.D. 1 Professor of Plastic Surgery, Medical School, Javeriana University, Bogotd, Colombia THE early history
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. and histological data. An additional confounding factor is infection, which oftendivertsthephysician sattention.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE First Branchial Cleft Anomalies A Study of 39 Cases and a Review of the Literature Jean-Michel Triglia, MD; Richard Nicollas, MD; Vincent Ducroz, MD; Peter J. Koltai, MD; Erea-Noël Garabedian,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE First Branchial Cleft Anomalies A Study of 39 Cases and a Review of the Literature Jean-Michel Triglia, MD; Richard Nicollas, MD; Vincent Ducroz, MD; Peter J. Koltai, MD; Erea-Noël Garabedian,
MICROTIA. The condition is a complex mix of cosmetic, functional, and often psychological difficulties. Microtia: Not only the ear.
 MICROTIA Underdevelopment /deformity of the auricle (pinna) varies from subtle deformities and small pre-auricular rudiments to gross developmental failure, distortion or malpositioned remnants. The external
MICROTIA Underdevelopment /deformity of the auricle (pinna) varies from subtle deformities and small pre-auricular rudiments to gross developmental failure, distortion or malpositioned remnants. The external
Auricular Reconstruction for Microtia: Part II. Surgical Techniques
 CME Auricular Reconstruction for Microtia: Part II. Surgical Techniques Robert L. Walton, M.D., and Elisabeth K. Beahm, M.D. Chicago, Ill., and Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After studying this article,
CME Auricular Reconstruction for Microtia: Part II. Surgical Techniques Robert L. Walton, M.D., and Elisabeth K. Beahm, M.D. Chicago, Ill., and Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After studying this article,
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander.
 Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current
 INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current Min-Hee Ryu, MD; David Kahng, MD; and Yongho Shin, MD, PhD Aesthetic Surgery Journal
INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current Min-Hee Ryu, MD; David Kahng, MD; and Yongho Shin, MD, PhD Aesthetic Surgery Journal
A PROSPECTIVE STUDY ON AURICULAR BURNS
 Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2013 Ramesha K T et al., 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 2, No. 4, October 2013 2013 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved A PROSPECTIVE STUDY ON AURICULAR BURNS
Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2013 Ramesha K T et al., 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 2, No. 4, October 2013 2013 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved A PROSPECTIVE STUDY ON AURICULAR BURNS
ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS OF HUMAN EXTERNAL EAR.
 ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS OF HUMAN EXTERNAL EAR. Sidra Shireen 1, Vrushali P. Karadkhelkar 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sidra Shireen, Vrushali P. Karadkhelkar. Anthropometric Measurements of Human External
ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS OF HUMAN EXTERNAL EAR. Sidra Shireen 1, Vrushali P. Karadkhelkar 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sidra Shireen, Vrushali P. Karadkhelkar. Anthropometric Measurements of Human External
INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR PROCEDURE GUIDE
 ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
INTRODUCTION. Typical secondary bilateral cleft lip nasal deformities present a short columella, a laterally-spreading dome of the alar cartilages
 The Correction of a Secondary ilateral Cleft Lip Nasal Deformity Using Refined Open Rhinoplasty with Reverse-U Incision, V-Y Plasty, and Selective Combination with Composite Grafting: Long-term Results
The Correction of a Secondary ilateral Cleft Lip Nasal Deformity Using Refined Open Rhinoplasty with Reverse-U Incision, V-Y Plasty, and Selective Combination with Composite Grafting: Long-term Results
Correcting the Lobule in Otoplasty Using The Fillet Technique
 Research Original Investigation Correcting the Lobule in Otoplasty Using The Fillet Technique Haneen Sadick, MD; Verena M. rtinger, MD; Frank Haubner, MD; Holger G. Gassner, MD IMPORTNCE Correction of
Research Original Investigation Correcting the Lobule in Otoplasty Using The Fillet Technique Haneen Sadick, MD; Verena M. rtinger, MD; Frank Haubner, MD; Holger G. Gassner, MD IMPORTNCE Correction of
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
A Novel Surgical Method Using Two Triangular Flaps for Accessory Tragus
 ORIGINL RTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.14730/.2016.22.2.63 rch esthetic Plast Surg 2016;22(2):63-67 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 Novel Surgical Method Using Two Triangular Flaps for ccessory Tragus Hyun
ORIGINL RTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.14730/.2016.22.2.63 rch esthetic Plast Surg 2016;22(2):63-67 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 Novel Surgical Method Using Two Triangular Flaps for ccessory Tragus Hyun
PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY
 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
Rotation-Advancement Principle. in Cleft Lip Closure. D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida
 Rotation-Advancement Principle in Cleft Lip Closure D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida Correction of prealveolar, alveolar, and postalveolar clefts poses a fivefold project: natural appearance,
Rotation-Advancement Principle in Cleft Lip Closure D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida Correction of prealveolar, alveolar, and postalveolar clefts poses a fivefold project: natural appearance,
An Economical Method of Auricular Splinting in Management of Auricular Pseudocyst
 220 Auricular splint in pseudocyst Original Article An Economical Method of Auricular Splinting in Management of Auricular Pseudocyst Karthik Rao*, Mohan Jagade, Vitthal Kale, Dev Kumar, Amol Hekare Grant
220 Auricular splint in pseudocyst Original Article An Economical Method of Auricular Splinting in Management of Auricular Pseudocyst Karthik Rao*, Mohan Jagade, Vitthal Kale, Dev Kumar, Amol Hekare Grant
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique. Description of Plate
 Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Frenuloplasty with A Splitthicknes Skin Graft
 Original Article Frenuloplasty with A Splitthicknes Skin Graft Ghodrat Mohammadi, Masoud Nnaderpour From Department of Otolaryngology, Tabriz University of Medical Science, Tabriz, Iran. Correspondence:
Original Article Frenuloplasty with A Splitthicknes Skin Graft Ghodrat Mohammadi, Masoud Nnaderpour From Department of Otolaryngology, Tabriz University of Medical Science, Tabriz, Iran. Correspondence:
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2
 RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL
 What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
The ear: some applied basic science
 Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
Rhinoplasty - Tip Augmentation by Extended Columellar Strip
 World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Rhinoplasty - Tip Augmentation by Extended Columellar Strip Authors: Vikas Sinha*, Viral A. Chhaya**, Dilavar A. Barot***, Keyur Mehta****,
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Rhinoplasty - Tip Augmentation by Extended Columellar Strip Authors: Vikas Sinha*, Viral A. Chhaya**, Dilavar A. Barot***, Keyur Mehta****,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION. Han-su Yoo, Sewoon Choi, Jeemyung Kim
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.14730/.2014.20.2.80 Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg 2014;20(2):80-84 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 Outcome Analysis Extended, Long, Curved Ostectomy with Outer Cortex
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.14730/.2014.20.2.80 Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg 2014;20(2):80-84 pissn: 2234-0831 eissn: 2288-9337 Outcome Analysis Extended, Long, Curved Ostectomy with Outer Cortex
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr.
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Fibular Bone Graft for Nasal Septal Reconstruction: A Case Report
 220 Nasal septal reconstruction Case Report Fibular Bone Graft for Nasal Septal Reconstruction: A Case Report Yakup Cil1* Diyarbakır Military Hospital, Department of Plastic Surgery 21000 Diyarbakır, Turkey
220 Nasal septal reconstruction Case Report Fibular Bone Graft for Nasal Septal Reconstruction: A Case Report Yakup Cil1* Diyarbakır Military Hospital, Department of Plastic Surgery 21000 Diyarbakır, Turkey
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
Product Information 04/10
 Product Information 04/10 Anthelix Scoring Instruments Benedict Type Unique instrument sets for use in minimally invasive approach Scoring Instruments for weakening of anthelical region in open and closed
Product Information 04/10 Anthelix Scoring Instruments Benedict Type Unique instrument sets for use in minimally invasive approach Scoring Instruments for weakening of anthelical region in open and closed
International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubric (ICO-OSCAR)
 International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubric (ICO-OSCAR) The International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubrics
International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubric (ICO-OSCAR) The International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubrics
Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) Ear reconstruction. E. Fred Aguilar III, MD, FACS a,b,c, *
 Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 87 91 Ear reconstruction E. Fred Aguilar III, MD, FACS a,b,c, * a Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and the Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery,
Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 87 91 Ear reconstruction E. Fred Aguilar III, MD, FACS a,b,c, * a Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and the Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery,
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
