A POSSIBLE CASE OF OEDEMATOUS FIBROMA WITH INFLAMMATORY CHANGES
|
|
|
- Oscar Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thorax (1951), 6, 154. A POSSIBLE CASE OF OEDEMATOUS FIBROMA WITH INFLAMMATORY CHANGES BY VIGGO ESKELUND From the Institute of Pathological Anatomy, University of Copenhagen With the advances made in lung surgery during the last decades, interest in benign tumours of the lung has greatly increased. In the past these tumours were usually seen at necropsy, but to-day, with improved diagnosis and extensive routine examinations for tuberculosis, they can be detected early enough to be treated by surgery. Surgical treatment is generally advisable, because it is nct possible to exclude malignant change with certainty-for example, in hamartoma. The following case illustrates how an unusual benign tumour can cause difficulties in diagnosis. CASE REPORT The patient was a woman aged 52. At 29 years she had had pleurisy on the right side, and was admitted to hospital and later to a tuberculosis sanatorium. Since then she has been admitted to hospitals more than 20 times for disease of the right lung, which she believes originated in the pleurisy. In 1942 she was in a tuberculosis hospital in Copenhagen, where it was thought that her main symptom, dyspnoea, was caused by cystic lungs and a spontaneous pneumothorax. Screening of the lungs showed irregular translucent areas in the upper and middle lobes of the right lung with displacement of the mediastinum to the left (Fig. A). Puncture of the right pleural cavity showed a positive pressure, varying up to 14 cm. of water, which fell rapidly, relieving the dyspnoea, but rose again after five to ten minutes. At one time the patient had an excessive, foul-smelling sputum, particularly on movement. Tubercle bacilli were never found; she had never had a haemoptysis. Her main complaints were dyspnoea, both with exercise and at rest in a horizontal position, and an almost constant pain in the right side of the thorax. The pain felt "like a wound"; it was not aggravated by respiration or coughing. She also complained of oppressive pain in the precordial region, sometimes accompanied by palpitations. In December, 1947, she had a serious attack of dyspnoea with angina-like pain. She was admitted to Naestved Hospital, and the symptoms promptly disappeared after puncture of the pleural cavity and release of air from the pleural cavity. A cystic right lung with pneumothorax was diagnosed. The sedimentation rate was 88 on admission and fell to 17. The Mantoux reaction was weakly positive. The electrocardiogram was normal. She had been operated on for an ovarian tumour when she was young. She had never been pregnant; she reached the menopause at the age of 50. At 51 she had "kidney trouble," with fever and frequent micturition. The symptoms disappeared after treatment with sulphonamides. In September, 1948, she was admitted to the Department of Thoracic Surgery. Rigshospitalet. She was rather thin and tired. The temperature was normal. Auscultation revealed diminished respiration over the whole of the right side; there
2 OEDEMATOUS FIBROMA WITH INFLAMMATORY CHANGES FiG. A were no rales. Radiography (Figs. A and B) of the chest showed a slight distension of the right side with depression of the right diaphragm. The entire right lung showed an increase in the usual markings which was most marked towards the base, and in the lateral view appeared to consist of cystic translucencies of various sizes. No patches of infiltration or mottling were seen and there was no evidence of pneumothorax. The heart, which was probably rotated, the trachea, and the mediastinum were displaced to the left. The left lung was normal. A cystic right lung, due possibly to valve formations in the walls of the cysts, was diagnosed. Other findings were: blood pressure 140/90; sedimentation rate 44 (Westergren); serum protein level 8; haemoglobin 90% ; Wassermann reaction negative; urine normal; Mantoux reaction weakly positive. Operation was performed on October 7, 1948, under general anaesthesia. This was intratracheal nitrous oxide-oxygen-ether, using a respirator. Access to the lung was obtained through a postero-lateral incision with resection of the fifth rib and division of the sixth and seventh ribs posteriorly. The lung was very adherent to the inside of the chest wall; pneumothoracic spaces and lung cysts were entered when the pleura was opened. The greater part of the lung had to be separated from the chest wall extrapleurally. and the pleura was opened when the hilum was reached. When the lung had been completely freed it was seen that the upper lobe occupied nearly the whole of the thoracic cavity. This lobe consisted of soft, spongy tissue containing a few large and many small cysts. The middle and lower lobes were atelectatic and pressed down on to the diaphragm. The interlobular space was easily entered; the hilus was dissected free and forceps were put on the arteries, veins, and 155
3 156 VIGGO ESKELUND FIG. B bronchus to the upper lobe. Double ligatures were put on the vessels and the bronchus was closed with silk sutures. It was then possible to inflate the middle and lower lobes. Although these together were not bigger than a grapefruit, and had correspondingly small vessels and bronchi, it was decided to preserve them. The phrenic nerve was resected; a pezzar catheter was inserted inferiorly and posteriorly and 200,000 units of penicillin were run into the thoracic cavity. The wound was closed with linen thread. During the operation transfusions amounting to 2,300 ml. in all were given. The drain was removed after 48 hours. During the first ten days the temperature was rather high, swinging up to 40 C. afterwards it remained constant at about 380 C. On the third day after operation the patient suddenly became severely shocked. The blood pressure was too low to be measured and there were long pauses in respiration. She recovered after a blood transfusion, and some tenacious plugs of sputum were removed by bronchoscopic aspiration. During the following period repeated pleural punctures, which released air and haemorrhagic fluid, were necessary. Penicillin was given, but was discontinued as the tongue became red and irritated. Injections of streptomycin were then given The patient's condition deteriorated: a wide-bore drainage tube was inserted into the
4 FIG. 3 FIG. 1 FIG. 1.-Area from the border zone of the process showing irregular, isletlike thickening of the septa. FIG. 2.-The growing patches, rendering the tissue more compact; compressed spaces are still visible. FIGS. 3 and 4.-Compact tissue from the upper part of the resected lung. FIG. 5.-Section from the border zone showing thickened septa which continue into an islet-like swelling. ;s>;; V FIG. 6.-Loose tissue with capillaries and inflammatory changes, parti- 0-*F ~ i3 cularly in the periphery. FIG. 4 oamfig Fibrous streak in the upper part of the lung. FIG. 2 FIG. 8.-Concretions in compressed bronchioles. FIG. 9.-Loose oedematous tissue with coarse collagenous fibrils.
5 FiG. 7 FIG. 5 FIG. 6 Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 June Downloaded from FIG. 9 FIG. 8 on 15 September 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
6 OEDEMATOUS FIBROMA WITH INFLAMMATORY CHANGES 159 pleural cavity, and large quantities of foul-smelling, blood-stained fluid were drained off. Since then the general health of the patient has improved, but there is still some discharge from the drainage site. PATHOLOGY The resected lobe measured 25 x 20 x 5 cm. The surface was very uneven. Section showed numerous cavities, varying from a few mm. to 6 cm. in diameter; some contained a mucous fluid. The intervening tissue was whitish, soft, and nodular, the single lumps measuring up to 7 cm. in diameter. Inferiorly in the lobe the lumps were small and widely spaced, whereas superiorly they were confluent and generally firmer. No normal lung tissue was found. Microscopic examination (Figs. 1-9) of the tissue showed that it was made up of cells with oval nuclei and somewhat jagged protoplasm. The nuclei showed little variation and were small. In most places these cells were scattered in an oedematous matrix with coarse, wavy, and branched, or streak, arrangement of the collagenous fibrils. There were a number of spaces in the tissue, but in some places it was compact and lobules of varying size could be distinguished; these lobules were bounded indefinitely by streaks of varying thickness, rather rich in cells. In other places the lobules were bounded by narrow spaces with and without low cylindrical or cuboid epithelial cells. Cysts had formed where these spaces were widest. There were numerous large and small groups of lymphocytes, surrounded by infiltrations of plasma cells. There were no signs of acute inflammation and no reaction foci. Most of the groups of lymphocytes were near the cysts and spaces. In these spaces, which we considered to be rudimentary bronchioles and alveoli, some phagocytic cells and occasional foreign body giant cells containing vacuoles were seen. Concentric concretions were also found in some areas. The firmer parts in the upper region of the resected lung were richer in collagenous fibrils, which sometimes formed dense streaks. Irregular streaks of smooth muscular tissue were also present. There were many blood vessels, and the loose tissue contained a number of capillary vessels. Round the larger vessels there were compact streaks of collagenous connective tissue, radiating into the surrounding tissue. There were haemorrhages and clumps of haemosiderophages. There was no necrosis. There was a smooth transition from the loose oedematous tissue, which in places was markedly, and diffusely, infiltrated with plasma cells and lymphocytes, to the denser fibrous tissue. The border zone showed partly compressed alveolar septa of normal thickness, partly broad, thickened septa with loose oedematous stroma, and partly irregular thickening of the septa, forming islet-like patches of varying size. The inflammatory changes in these patches and thickened septa were usually localized to the superficial layers. In the surrounding compressed lung tissue there were a number of small concretions similar to those described above. There was no evidence of tuberculosis. Mucous stains showed no mucin. DISCUSSION The radiographs and clinical findings excluded tuberculosis and syphilis, and the likely diagnosis seemed to us to be a " cystic lung." Among cystic formations of the lung we considered it possible to exclude dermoid cysts, hydatid cysts, and ectopic gastric cysts. There remained congenital cystic lung; in this condition the cysts are usually of bronchial origin; they may be single or multiple, localized or diffuse,
7 160 VIGGO ESKELUND unilateral or bilateral. They are found in persons of all ages. They are often complicated by inflammation and valvular pneumothorax formation, with compression and displacement of the mediastinum. Rupture of the cyst, or cysts, and pneumothorax formation with possible infection and pyopneumothorax are not uncommon. In the case described here there had been several episodes of valvular pneumothorax formation and febrile pulmonary inflammation. Clinically and pre-operatively, the only possible diagnosis was congenital cystic lung with complications. But the findings at operation and on histological examination showed this to be a rather unusual case. The most characteristic thing about this lesion was the invasive growth in the lung of oedematous fibroma-like tissue, which had converted the lung into areas of dense tissue of varying size. The irregular invasive growth in the border zone, with compression of the bronchi and alveoli, explained the frequent valve formation. The tissue showed rather marked chronic inflammatory changes, particularly localized to the remains of the alveolar cavities. The inflammatory changes were non-specific. The cavities in the lobe were either devoid of epithelium or lined with a low cylindrical or cuboid epithelium. In view of these inflammatory changes we considered the possibility of a progressive, interstitial inflammation, with a similar histological picture to that found in nasal polypi, caused by inflammation. Such an inflammatory process has, so far as can be ascertained, not been described previously. The macroscopic appearance of the tissue seemed to us to be most like a tumour. Further, the inflammatory changes were often only slight in the border zone itself. On the other hand, we have not found a previous report of a fibroma of the lung with this appearance. Fibromata of the lung are rather rare, and those described are generally made up of typical compact fibrous tumours. In 1924 Sutherland, from the Mayo Clinic, reported a case of myxoma of the lung. The patient was a woman aged 41 years, who, eight years before admission to hospital, had been told that she had a lesion in the right apex. During the three years before admission she had had pain in the right arm and under the right scapula, and an enlargement on the right side of her neck had developed during the same period. She had lost 181 lb. in weight during the previous 18 months. Examination revealed dullness to percussion, decreased respiration, and increased fremitus at the right apex. Radiography showed a circumscribed area of increased density in the upper right thorax. At operation a solid fibrous tumour was found. It was not adherent to the thoracic wall or the mediastinum, but was adherent to the lung in the centre of the thorax and was continuous with the swelling in the neck and over the clavicle. Microscopic examination showed it to be a myxoma, which was not removed; the patient was referred for radiotherapy. This is the only case of myxoma of the lung that has been described, and neither the clinical course nor the radiographic appearances resemble the lesion described in this report. SUMKARY A case of chronic lung disorder, possibly a fibroma with inflammatory changes, which presented clinically and radiologically as a cystic lung, is reported. So far as can be ascertained, no similar case has previously been described. REFERENCE Sutherland, C. G. (1924). Radiology, 3, 161.
8 OEDEMATOUS FIBROMA WITH INFLAMMATORY CHANGES 161 BIBLIOGRAPHY Ball, H A (1 93!) Amer. J. Cancer, 15, Johns, E. P., and Sharpe, W. C. (1935). Ibid, 23, 45. Lyssunkin, 1 1 (1934). Fia' kfurt Z. Path., 46, i07. Scheidegger, S (:932). Z. Krebsforsch., 35, 172 Thibaudeau, A. A., and Kress, L. C. (193'). Amer. J. Cancer, 23, 267 Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 June Downloaded from on 15 September 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY
 Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS
 Thorax (1951), 6, 375. PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN BY COLIN A. ROSS From Shotley Bridge Hospital and Poole Sanatorium (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JULY 9, 1951) The literature concerning
Thorax (1951), 6, 375. PULMONARY RESECTION FOR TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN BY COLIN A. ROSS From Shotley Bridge Hospital and Poole Sanatorium (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JULY 9, 1951) The literature concerning
Mediastinal cyst containing mural pancreatic tissue
 Thorax, 1977, 32, 512-516 Mediastinal cyst containing mural pancreatic tissue M. J. T. CARR', A. K. DEIRANIYA', AND P. A. JUDD2 From the Cardiothoracic Unit', and Department of Pathology2, Queen Elizabeth
Thorax, 1977, 32, 512-516 Mediastinal cyst containing mural pancreatic tissue M. J. T. CARR', A. K. DEIRANIYA', AND P. A. JUDD2 From the Cardiothoracic Unit', and Department of Pathology2, Queen Elizabeth
The External Anatomy of the Lungs. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
THORACIC CHORDOMA. G. G. CROWE AND P. B. LL. MULDOON From City General Hospital, Stoke-on-Trent
 Thorax (1951), 6, 403. THORACIC CHORDOMA BY G. G. CROWE AND P. B. LL. MULDOON From City General Hospital, Stoke-on-Trent (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST 22, 1951) Remnants of the notochord sometimes become
Thorax (1951), 6, 403. THORACIC CHORDOMA BY G. G. CROWE AND P. B. LL. MULDOON From City General Hospital, Stoke-on-Trent (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION AUGUST 22, 1951) Remnants of the notochord sometimes become
THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION
 Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Multiple hamartomata of the lung
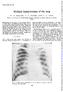 ".; < ;... *: *. > 6a. ;m_r,:i.: e,:...._'. L w X._w. -... ::.'.'. SQ.B SJ _. *.: : w.... :SW.,. _, :; 81 ej, irsr j2 _.:}:.:,::R o _i :.. Fs be 3.X _1 E!.,f3.-. 1t o. j_ 1\ r?!lfo9x., TRyi 1. 2l, >.,.,,co.qlz
".; < ;... *: *. > 6a. ;m_r,:i.: e,:...._'. L w X._w. -... ::.'.'. SQ.B SJ _. *.: : w.... :SW.,. _, :; 81 ej, irsr j2 _.:}:.:,::R o _i :.. Fs be 3.X _1 E!.,f3.-. 1t o. j_ 1\ r?!lfo9x., TRyi 1. 2l, >.,.,,co.qlz
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
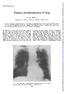 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives --()--
 IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Bronchioles. Alveoli. Type I alveolar cells are very thin simple squamous epithelial cells and form most of the lining of an alveolus.
 276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
An Image Repository for Chest CT
 An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection
 Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
Thorax (1970), 25, 41. Destructive pulmonary disease due to mixed anaerobic infection 0. SERIKI, A. ADEYOKUNNU, T. 0. DE LA CRUZ Departments of Paediatrics and Surgery, University College Hospital, Ibadan,
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th & 12 th Eds.)
 PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity.
 Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
Dana Alrafaiah. - Moayyad Al-Shafei. -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 - 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
- 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
ANATOMY OF THE PLEURA. Dr Oluwadiya KS
 ANATOMY OF THE PLEURA Dr Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Introduction The thoracic cavity is divided mainly into: Right pleural cavity Mediastinum Left Pleural cavity Pleural cavity The pleural
ANATOMY OF THE PLEURA Dr Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Introduction The thoracic cavity is divided mainly into: Right pleural cavity Mediastinum Left Pleural cavity Pleural cavity The pleural
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Two malignant pleural mesotheliomas with unusual histological features
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 375-379 Two malignant pleural mesotheliomas with unusual histological features B GOLDSTEIN From the National Research Institute for Occupational Diseases of the South African Medical
Thorax, 1979, 34, 375-379 Two malignant pleural mesotheliomas with unusual histological features B GOLDSTEIN From the National Research Institute for Occupational Diseases of the South African Medical
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Respiratory system. Applied Anatomy &Physiology
 Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine. Breast. Dr. Ahmed Salman. Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology
 Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Breast Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The breasts are specialized accessory glands of the skin that secretes milk. They are situated
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Breast Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The breasts are specialized accessory glands of the skin that secretes milk. They are situated
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
Lung & Pleura. The Topics :
 Lung & Pleura The Topics : The Trachea. The Bronchi. The Brochopulmonary Segments. The Lungs. The Hilum. The Pleura. The Surface Anatomy Of The Lung & Pleura. The Root & Hilum. - first of all, the lung
Lung & Pleura The Topics : The Trachea. The Bronchi. The Brochopulmonary Segments. The Lungs. The Hilum. The Pleura. The Surface Anatomy Of The Lung & Pleura. The Root & Hilum. - first of all, the lung
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC
 Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
HONEYCOMB LUNGS WITH PERICHOLANGITIS
 HONEYCOMB LUNGS WITH PERICHOLANGITIS BY S. SIVANESAN From the Department ofpathology, University of Malaya, Singapore (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL 3, 1959) Cystic lungs are diverse both morphologically
HONEYCOMB LUNGS WITH PERICHOLANGITIS BY S. SIVANESAN From the Department ofpathology, University of Malaya, Singapore (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL 3, 1959) Cystic lungs are diverse both morphologically
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
The Lymphoid System Pearson Education, Inc.
 23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
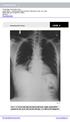 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN
 THE IMPORTANCE OF BRONCHOSCOPY IN THE RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN BODY IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY N. ASHERSON, M.A., M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S. Surgeon to the Central London Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital
THE IMPORTANCE OF BRONCHOSCOPY IN THE RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN BODY IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY N. ASHERSON, M.A., M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S. Surgeon to the Central London Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer
 Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy
 Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracoscopy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem. Or you may
Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracoscopy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem. Or you may
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Lung Cancer Resection
 Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
RESECTION OF TUBERCULOUS STRICTURES OF THE MAIN BRONCHI IN THREE CASES
 Thorax (1955), 10, 229. RESECTION OF TUBERCULOUS STRICTURES OF THE MAIN BRONCHI IN THREE CASES BY J. W. JACKSON, P. H. JONES, AND T. HOLMES SELLORS From the London Chest and Harefield Hospitals (RECEIVED
Thorax (1955), 10, 229. RESECTION OF TUBERCULOUS STRICTURES OF THE MAIN BRONCHI IN THREE CASES BY J. W. JACKSON, P. H. JONES, AND T. HOLMES SELLORS From the London Chest and Harefield Hospitals (RECEIVED
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma
 July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Collaborative Stage. Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG
 Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
RUPTURED AORTIC VALVE WITH MYCOTIC
 RUPTURED AORTC VALVE WTH MYCOTC ANEURYSM DUE TO ACUTE BACTERAL ENDOCARDTS BY C. W. CURTS BAN AND S. WRAY From the Cardiographic and Pathological Departments, Harrogate General Hospital Received March 28,
RUPTURED AORTC VALVE WTH MYCOTC ANEURYSM DUE TO ACUTE BACTERAL ENDOCARDTS BY C. W. CURTS BAN AND S. WRAY From the Cardiographic and Pathological Departments, Harrogate General Hospital Received March 28,
PRIMARY neoplasms of the pericardium are rare. Yater 1 in a comprehensive
 HAMARTOMA OF PERICARDIUM LYMPHATIC TYPE Case Report EDWIN R. FISHER, M.D., Department of Pathology CHARLES S. BALLINGER, M.D. and DONALD B. EFFLER, M.D. Department of Thoracic Surgery PRIMARY neoplasms
HAMARTOMA OF PERICARDIUM LYMPHATIC TYPE Case Report EDWIN R. FISHER, M.D., Department of Pathology CHARLES S. BALLINGER, M.D. and DONALD B. EFFLER, M.D. Department of Thoracic Surgery PRIMARY neoplasms
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Anatomy Lecture 8. In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy:
 Anatomy Lecture 8 In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy: 1-Apex:it lies 1 inch above the medial third of clavicle. 2-Anterior border: it starts from apex to the midpoint
Anatomy Lecture 8 In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy: 1-Apex:it lies 1 inch above the medial third of clavicle. 2-Anterior border: it starts from apex to the midpoint
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Pneumothorax. Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms
 Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE
 Thorax (1954), 9, 2 1. TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE BY PETER BEACONSFIELD, H. S. COULTHARD, AND F. G. KERGIN From the Toronto Hospital for the
Thorax (1954), 9, 2 1. TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE BY PETER BEACONSFIELD, H. S. COULTHARD, AND F. G. KERGIN From the Toronto Hospital for the
Lec #2 histology. Bronchioles:
 Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
Evaluation of the chest
 Evaluation of the chest part 1 Nagy Endre SZEGEDI TUDOMÁNYEGYETEM ÁOK, RADIOLÓGIAI KLINIKA, SZEGED Indication In case of complaints or symptoms: In suspicion of lesions, diseases or injuries of the chest
Evaluation of the chest part 1 Nagy Endre SZEGEDI TUDOMÁNYEGYETEM ÁOK, RADIOLÓGIAI KLINIKA, SZEGED Indication In case of complaints or symptoms: In suspicion of lesions, diseases or injuries of the chest
Lung manifestations in leptospirosis
 Lung manifestations in leptospirosis S. C. POH and C. S. SOH Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Thorax (1970), 25, 751. Two cases of leptospirosis presenting with cough and haemoptysis are described, together
Lung manifestations in leptospirosis S. C. POH and C. S. SOH Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Thorax (1970), 25, 751. Two cases of leptospirosis presenting with cough and haemoptysis are described, together
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 2: ATELECTASIS AND EMPHYSEMA
 DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 2: ATELECTASIS AND EMPHYSEMA INTRODUCTION In this lecture we will discuss atelectasis which is a complication of several medical and surgical
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 2: ATELECTASIS AND EMPHYSEMA INTRODUCTION In this lecture we will discuss atelectasis which is a complication of several medical and surgical
8/14/2017. Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features
 What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS
 Thorax (1956), 11, 241. THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF RADIATION FIBROSIS OF THE LUNGS* BY WILLIAM M. ROSS From Newcastle Regional Hospital Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 23,
Thorax (1956), 11, 241. THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF RADIATION FIBROSIS OF THE LUNGS* BY WILLIAM M. ROSS From Newcastle Regional Hospital Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 23,
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Retroperitoneal Teratoma Heather Borders, MD
 Retroperitoneal Teratoma Heather Borders, MD 03/04/2012 History Newborn with congenitally diagnosed mass. No other clinical symptoms. Diagnosis Retroperitoneal Teratoma; Immature teratoma, grade 1, with
Retroperitoneal Teratoma Heather Borders, MD 03/04/2012 History Newborn with congenitally diagnosed mass. No other clinical symptoms. Diagnosis Retroperitoneal Teratoma; Immature teratoma, grade 1, with
Respiratory System. Clinical notes. Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz)
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz) Respiratory System The test of the respiratory system follows the general rules for written tests (see Continuous
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz) Respiratory System The test of the respiratory system follows the general rules for written tests (see Continuous
A 50-year-old male with fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss and night sweats
 Petru Emil Muntean muntean.petruemil@yahoo.com Pulmonology, Spitalul Clinic Judetean Mures, Targu Mures, Romania. A 50-year-old male with fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss and night sweats
Petru Emil Muntean muntean.petruemil@yahoo.com Pulmonology, Spitalul Clinic Judetean Mures, Targu Mures, Romania. A 50-year-old male with fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss and night sweats
PULMONARY AND LOBAR ATELECTASIS
 Thorax (1951), 6, 137. OBSERVATONS ON THE HAEMODYNAMCS OF PULMONARY AND LOBAR ATELECTASS BY J. C. GLROY, V. H. WLSON, AND PAUL MARCHAND From the Department of Medicine and the i horacic Surgical Unit,
Thorax (1951), 6, 137. OBSERVATONS ON THE HAEMODYNAMCS OF PULMONARY AND LOBAR ATELECTASS BY J. C. GLROY, V. H. WLSON, AND PAUL MARCHAND From the Department of Medicine and the i horacic Surgical Unit,
Chest and cardiovascular
 Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
PERFORATION OF THE TRACHEA AND BRONCHUS BY THE BRONCHOSCOPE
 Thlorax (1950), 5, 369. PERFORATION OF THE TRACHEA AND BRONCHUS BY THE BRONCHOSCOPE BY Fronm the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge Hospital, Newcastle-upon-Tyne (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION
Thlorax (1950), 5, 369. PERFORATION OF THE TRACHEA AND BRONCHUS BY THE BRONCHOSCOPE BY Fronm the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge Hospital, Newcastle-upon-Tyne (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION
FIBROMA OF THE VISCERAL PLEURA*
 Thorax (1953), 8, 180. FIBROMA OF THE VISCERAL PLEURA* BY SIR CLEMENT PRICE THOMAS AND C. E. DREW From the Brompton and Westminster Hospitals, London Intrathoracic fibromas are rare tumours, but as might
Thorax (1953), 8, 180. FIBROMA OF THE VISCERAL PLEURA* BY SIR CLEMENT PRICE THOMAS AND C. E. DREW From the Brompton and Westminster Hospitals, London Intrathoracic fibromas are rare tumours, but as might
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
X-Rays. Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM
 X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
Report of two cases. and disorders of fat metabolism. as nose drops, sprays, or laxatives, these lesions
 Thorax (1973), 28, 214. Paraffinoma of lung: Report of two cases JOHN BORRIE and JAMES F. lipoid pneumonia GWYNNE Departments of Thoracic Surgery and Pathology, University of Otago Medical School and Southern
Thorax (1973), 28, 214. Paraffinoma of lung: Report of two cases JOHN BORRIE and JAMES F. lipoid pneumonia GWYNNE Departments of Thoracic Surgery and Pathology, University of Otago Medical School and Southern
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
