Development of a Web-Based Gout Self-Management Program SUBJECTS AND DATA COLLECTION
|
|
|
- Gervase Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Development of a Web-Based Gout Self-Management Program HyunSoo Oh JiSuk Park WhaSook Seo OBJECTIVE: This study was conducted to develop a webbased gout self-management program that can be applicable to each gout stage and to evaluate the validity of the developed program. METHODS: A web-based gout self-management program was developed and evaluated in 5 stages: analysis (needs assessment on 60 gout patients and content analysis through a systematic review of literature and websites), design, development, implementation, and evaluation. RESULTS AND CONCLUSION: The gout-related information section was structured with overview, causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, progress, treatments, and complications. The self- management section consisted of diet/nutrition, weight control, alcohol management, exercise, and pain and stress management. The program included bulletin board and expert section to promote bidirectional interactions between program users and providers. Self-assessment tool of gout stages and self-management checklist were provided. Program contents and ease of site navigation ( were found to be appropriate and satisfactory to both patient and expert groups. Gout occurs when uric acid builds up in the blood and forms urate crystals in the joints due to either an increase in uric acid production or a decrease in urinary uric acid excretion (Schumacher & Chen, 2008). Although the exact cause is still unknown, significant risk factors of gout have been identified. These include age, gender, obesity, purine rich meat products and seafood, hyperlipidemia, and drugs such as thiazide diuretics and low-dose aspirin (Choi & Curhan, 2007; Eggebeen, 2007; Roddy, 2008). When gout remains untreated, it may progress to become chronic and result in joint disability and serious complications associated with kidney and heart, which can cause death. Although the pathophysiology and treatment of gout have long been known, the management of gout remains challenging (Wortmann, 2006), mainly because of poor compliance with gout medication. Only around 50% of gout patients adhere to medications (de Klerk et al., 2003; Riedel et al., 2004; Schumacher & Chen, 2008). For patients with chronic diseases including gout, the most important medical and nursing managements should aim to improve self-management ability on a daily basis. Web-based programs are an efficient tool for improving the self-management ability of patients with chronic disease and, in particular, for facilitating social interactions of peers with peers or supporters (Shigaki et al., 2008). Gout appears to be well-suited to a web-based approach because it occurs most often in men, and men tend to be more active in computer-related learning. In addition, a web-based gout program may improve poor treatment compliance in gout patients by providing accurate gout-related information and supporting useful communications between patients and professionals about their experiences. Despite this potential, very few webbased gout intervention studies have been published. A few websites for gout patients have been developed in Korea, but they tend to be operated for advertising purposes by private clinics and include only rudimentary information. The present study developed an informationrich and user-friendly web-based gout self-management program applicable to each stage of gout. Methods RESEARCH DESIGN The study adopted a methodological research design to develop a web-based gout self-management program using the instruction guidelines for web-based education system proposed by Na (2005). For needs analysis/assessment and validity testing, a nonexperimental survey research design was used. For contents analysis, a systematic literature review on related studies was performed. SUBJECTS AND DATA COLLECTION For needs assessment, 60 gout patients were recruited from outpatient settings at the University Hospital, Incheon, South Korea. Only subjects who were able to communicate and consent to participation were included in needs assessment. After the developed program HyunSoo Oh, PhD, RN, Professor, Department of Nursing, Inha University, Incheon, Republic of Korea. JiSuk Park, MSN, RN, Doctoral student, Department of Nursing, Inha University, Incheon; Nurse, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Republic of Korea. WhaSook Seo, PhD, RN, Professor, Department of Nursing, Inha University, Incheon, Republic of Korea. The authors have disclosed that they have no financial interests to any commercial company related to this educational activity. DOI: /NOR.0b013e31822c5c3f Orthopaedic Nursing September/October 2011 Volume 30 Number 5 333
2 was installed on a web server, preimplementing and validity testing of the developed program were conducted on 20 conveniently selected subjects who participated in needs assessment. The selection criteria for these 20 subjects were (1) ability to conduct a computer-based Internet search and (2) experience in acquiring goutrelated information from the Internet. Preimplementing and validity testing of the program were also conducted by an expert panel consisting of four physicians, one outpatient nurse, and 20 inpatient nurses including the head nurse in the rheumatoid arthritis clinic in the hospital where the data were collected. MEASUREMENTS To assess patients needs, face-to-face semistructured interviews were conducted. The interview contained both close- and open-end questions and allowed the patients to express their own views freely. The following topics and questions were prepared beforehand and used as a framework for semistructured interviews: (1) everyday lifestyle; (2) current state of gout; (3) knowledge on gout causes, treatments, prognosis, and selfmanagement; (4) self-management technique currently used; (5) gout-related information source; (6) usefulness of information obtained; (7) experience of Internet searching to gather gout-related information; (8) usefulness of gout-related information obtained from the Internet; (9) intention to participate web-based education; and (10) information needed to be included in the web-based gout self-management program. All responses were recorded as written by the first author. For validity testing of the developed web-based gout self-management program, a structured interview was conducted. Validity test questions consisted of two main sections: appropriateness or satisfaction with program contents and ease of site navigation and content access. Questions regarding the appropriateness or satisfaction with the program contents included (1) level of overall satisfaction on the program, (2) level of satisfaction on gout-related knowledge provided in the program, (3) level of satisfaction on gout self-management techniques provided in the program, (4) any additional content needed, and (5) ease of understanding of the program contents. Questions regarding the ease of site navigation and content access included (1) ease of access to the website, (2) ease of exploring the website, (3) success of the site in stimulating user interest, (4) intention to revisit the website, and (5) usefulness of the audiovisual materials. Except for a question concerning content that should be added, all validity test questions were answered using a 5- or 7-point Likert scale. PROCEDURES A web-based gout self-management program was developed in five stages: analysis, design, development, preimplementation, and evaluation. Analysis At this stage, needs assessment, content analysis, target user analysis, and technical support and environmental analysis were conducted (see Table 1). Needs assessment on 60 gout patients was performed to analyze patients TABLE 1. PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT PROCESS: ANALYSIS, DESIGN, AND DEVELOPMENT STAGES Stages Development Process Analysis stage Need analysis Explore knowledge, experience of gout, and problems related to self-management of gout. Content analysis Conduct systematic review of related studies and websites Client analysis Examine the usage of internet Technical, Identify hardware, instruments, web designer environmental analysis and program developers Design stage Information design Design contents of self-management program of gout. Interaction design Design interaction methods or tools. Motivation design Design motivation methods for clients. Preliminary examination Conduct preliminary examination about contents, motivation, and interaction. Development stage Content frame Develop contents. Multimedia Develop visual materials, images, and video simulations. Integration Develop web program and install the program. Demonstration Preimplemented web program toward physician, nurses, and gout patients. Validity test Test of validity about contents and system toward physician, nurses, and gout patients. 334 Orthopaedic Nursing September/October 2011 Volume 30 Number 5
3 everyday lifestyle, current state of gout, knowledge about gout, self-management technique, and Internet searching experience. Target user analysis on the same 60 gout patients was performed to analyze the degree of utility and feasibility of a computer system for target users. Content analysis was performed through a systematic review of related literature and existing websites. A total of 113 goutrelated studies were primarily selected through searches of PubMed, KoreaMed, and CINHAL using the key words gout, systematic review, epidemiology, treatment, or self-management. The 113 study abstracts were prereviewed. Twenty-seven were directly relevant and the full texts of the articles were reviewed (see Table 2). In addition, the contents of 13 gout-related websites were analyzed. Technical support and environmental analysis was conducted to define specific hardware and instruments needed. An expert panel consisting of four physicians, one outpatient nurse, and 20 inpatient nurses including the head nurse was also established. Design and Development Specific contents and presentation methods of the program were finalized through information, interaction, and motivation design approaches (see Table 1). In terms of information design, various presentation mediums (text, images, and multimedia) and image creating tools (Illustration, PowerPoint, and Photoshop) were considered. Frameworks for text and image in detail were determined on the basis of needs assessment. Interaction and motivation designing was performed through discussions with professional web designers and program developers. Implementation and Evaluation The developed program was installed on a web server ( and then preimplemented with 20 conveniently selected gout subjects and the expert panel. One week after the launch of the preimplementation, the appropriateness or satisfaction of the program contents, ease of site navigation, and content access were evaluated with the subjects in a face-to-face or telephone interview, or communication. DATA ANALYSIS Statistical analysis was performed using Predictive Analytics Software version Data from needs assessment and validity test were analyzed using descriptive analysis. Results NEEDS, CONTENT, TARGET USERS, AND TECHNICAL ANALYSIS Needs Analysis Needs assessment was conducted on 60 male gout patients (mean age years; see Figure 1). Of these subjects, 78.9% reported drinking alcohol: 45.2% TABLE 2. SUMMARY OF A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEWS ON STUDIES RELATED TO RISK FACTORS OF GOUT, AND GOUT TREATMENTS AND SELF-MANAGEMENT. Author(s) (Year of Publication) Meiner (2001); Kim et al. (2003); Luk and Simkin (2005); Saag and Choi (2006); Choi and Curhan (2007); Eggebeen (2007); Weaver (2008); Roddy (2008) Meiner (2001); Kim et al. (2003); Choy (2005); Hong and Lee (2005); Schlesinger, Moore, Sun, and Schumacher (2006), Wortmann (2006); Fang et al. (2006); Hoskison and Wortmann (2006); Chen and Schumacher (2006); Perez-Ruiz and Schlesinger (2008); Hoskison and Wortmann (2007); Eggebeen (2007); Pillinger and Keenan (2008); Schumacher and Chen (2008); Schlesinger, Dalbeth, and Perez-Ruiz (2009); Conway and Schwartz (2009) Meiner (2001); Hong and Lee (2005); Saag and Choi (2006); Perez-Ruiz and Schlesinger (2008); Eggebeen (2007); Mineo, Kamiya, and Tsukuda (2008); Schumacher and Chen (2008); Pillinger and Keenan (2008); Becker and Chohan (2008); Hak and Choi (2008); Terkeltaub, Zelman, Scavulli, Perez-Ruiz, and Liote (2009); Choi (2010) Risk factors of gout Nonmodifiable risk factors: age, gender Modifiable risk factors: serum uric acid concentration, hyperuricemic drugs, diseases, diet, alcohol drinking, obesity, etc. Treatments for gout Acute gout treatment (management of pain and inflammation): non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs, COX-1 inhibitors (indomethacin, naproxen, ibuprofen), COX-2 inhibitors (etoricoxib, colecoxib), Colchicine, steroids Treatment for intercritical gout: prevention of the recurrence of gout attack (drugs, diet, regular blood test) Medication to treatment hyperuricemia: uricosuric agents (probenecid, sulfopyrazone), allopurinol, or newer drugs (xanthine oxidase, Febuxostat, anticytokine treatment) Self-management Foods increase or decrease blood uric acid levels: red meat, bean, high-carbohydrate diet, carbonated drink, milk, coffee, black bean, dark color fruits, spinach, bean sprouts, nuts, etc.) Alcohol management: blood uric acid levels and alcohol beverages (beer, hard liquor, wine, etc.), strategies to avoid alcohol consumption Weight control: concurrence of metabolic diseases (hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease) in gout patients, low-fat diet, exercise Health supplements: vitamin C, omega-3, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, etc. Orthopaedic Nursing September/October 2011 Volume 30 Number 5 335
4 FIGURE 1. The results of need analysis/assessments related to lifestyle. Internet use: 1 (yes); 2 (no), Alcohol consumption: 1 (yes); 2 (no) Number of consuming alcohol: 1 (1 2 times/month); 2 (1 2 times/week); 3 (3 4 times/week); 4 (every day) Amount of consuming alcohol (Soju, Korean distilled spirits, 300 ml/bottle): 1 (0.5 1 bottle); 2 (1.5 2 bottles); 3 ( 2.5 bottles) Diet: 1 (vegetable based diet): 2 (vegetable-based diet with fish); (vegetable-based diet with meat); 4 (meat based diet) Obesity: 1 (yes); 2 (no) Smoking: 1 (yes); 2 (no) drank 3 4 times weekly and 28.6% drank daily, with the mean amount of alcohol consumed per sitting being bottles of Soju (a Korean distilled spirits available in 300 ml). In terms of diet, 9.5% of subjects indicated having a vegetable-based diet, 9.5% a vegetable-based diet with fish, and 59.5% a meat-based diet. Twenty-five percent of the subjects were of normal body weight, and 75% were overweight. Most of the subjects did not know about their current state of gout, and 38.3% treated their gout only using medications. Of the latter, 15% did not take medications continuously (see Figure 2). Gout-related knowledge level was high, moderate, and low in 11.7%, 45%, and 42.6% of the subjects, respectively. Gout-related information was obtained mostly from medical personnel, followed by Internet posts. Thirty-four percent of subjects found both sources of information useless and 64.6% valued it as useful information. Regarding Internet searching experience, 43.3% of the subjects used the Internet to search for gout-related information only after being first diagnosed with gout, with no searches conducted thereafter. In addition, 45.8% of the subjects strongly desired a web-based gout program, and 42.2% would consider using such a program in the future. Subjects indicated that a web-based program needed to include information concerning medications (65.4%), self-management techniques (57.0%), nonmedication treatments (48.5%), and diet (17.5%). Content Analysis A systematic review of 27 gout-related studies identified three types of causes/risk factors of gout: lifestyle-, disease-, and drug-related (see Table 2). Lifestyle-related risk factors were a purine-enriched diet, alcohol consumption, high-protein diet, and obesity. Diseaserelated risk factors were hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and renal failure. Drug-related risk factors were diuretics, low dose of aspirin, L-dopa and posttransplant medications. In terms of gout treatment, content analysis of related studies shows that medications are most commonly used gout treatments to provide gout symptom relief and prevent recurrence and progression to the chronic stage. To relieve acute gout attack, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicines, and steroids are frequently used. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the first-line gout medication because of the many side effects experienced with colchicines. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and/or COX-2. The recently developed COX-2 inhibitors, etricoxib and colecoxib, have become popular (Hoskison & Wortmann, 2007). On the contrary, to prevent recurrence and progression to chronic stage, probenecide (which improves the kidney s ability to eliminate uric acid) and allopurinol (which inhibits uric acid production) are commonly used (Meiner, 2001; Kim, Schumacher, Hunsche, Wertheimer, & Kong 2003; Schumacher & Chen, 2008). 336 Orthopaedic Nursing September/October 2011 Volume 30 Number 5
5 FIGURE 2. The results of need assessments and target user analysis. Since individuals answered at more than one categortze, some of combined percentages were more than 100%. Gout state: 1 (individual knows that gout was managed with medication for reducing serum uric acid); 2 (do not know). Gout knowledge: 1 (high level); 2 (moderate level); 3 (low level); 4 (not at all); 5 (do not have interest). Gout self-management: 1 (self-managed very well in every aspects); 2 (only medication and managing alcohol consumption); 3 (only medication and diet management); 4 (only taking medicationl); 5 (not even taking medication regularly); 6 (do not know how to self-manage gout). Family understanding about gout: 1(high level); 2 (moderate level); 3 (low level); 4 (not at all). Ways of obtaining knowledge about gout: 1 (physicians or nurses); 2 (leaflets); 3 (family, relatives, friends); 4 (mess media); 5 (other gout patients); 6 (internet site); 7 (not at all). Usefulness of obtaining information: 1 (highly helpful); 2 (moderately helpful); 3 (somewhat helpful); 4 (uselessness). Frequency of Internet search for gout: 1 (often); 2 (sometimes); 3 (only immediately after gout diagnosis); 4 (never). Usefulness of Internet information of gout: 1(highly helpful); 2 (moderately helpful); 3 (somewhat helpful); 4 (uselessness). Intention to participate to website education: 1 (having strong intention); 2 (considering participating); 3 (do not know); 4 (won t participate). Information that need to self-manage gout: 1 (medication); 2 (diet); 3 (disease progression); 4 (nonpharmacological modalities); 5 (self-management). Probenecide and allopurinol reduce and maintain the level of plasma uric acid level at 6 mg/dl or less and prevent uric acid crystal formation (Becker & Chohan, 2008; Perez-Ruiz & Schlesinger, 2008). Febuxostat, a newly developed selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, may be a potential alternative to allopurinol. Anticytokine therapy has also proven effective for managing acute gout attacks and preventing recurrence (Pillinger & Keenan, 2008; see Table 2). Thirteen websites were analyzed for their content. The websites were mayoclinic.com, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), adam.about.com (Health Topics A-Z), GOUT.com, MedicineNet.com, niams.nih. gov, webmd.com, wikipedia.org, medcity.com, angelpharm.co.kr, HealthKorea.net, healthcare.joins. com, and goutpal.com. Most of the websites for gout patients that have been designed in Korea were not included in this content analysis because they are operated for advertising purposes by private clinics and included rudimentary information. Commonly included information in the 13 gout websites were definition, symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnostic tests, treatment, and self-management. Some websites included information on gout stages, but none included information on specific treatments or management according to each gout stage. Target User, Technical Support, and Environmental Analysis All 60 gout subjects had a computer with an Internet connection at home and 58.3% were experienced in Internet use. Even those who did not have Internet experience were able to learn with the assistance of one of their children. Therefore, presentation of the information in a web-based format was not an obstacle. Based on the results of technical support and environmental Orthopaedic Nursing September/October 2011 Volume 30 Number 5 337
6 analysis, specific hardware and instruments needed were identified and supplied, and the aforementioned expert panel was established. DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT STAGE Information Design The program contents were structured on the basis of the results of needs assessment and content analysis through systematic reviews on related literature and websites (see Table 3). Gout-related information consisted of seven headings: overview, causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, progress, and treatments and complications. Each heading was further divided into subheadings. Overview of gout included definition, frequency, and historical evidence. Causes of gout included information about blood uric acid levels and gout. Risk factors of gout were presented in three different categories: lifestyle-, drug-, and disease-related risk factors. A self-diagnostic questionnaire for gout risk factor was provided. Symptoms of gout included characteristics of a gout attack and common sites. Diagnosis of gout included direct and indirect tests. Progress and treatment of gout were presented according to four gout stages: stage 1 (asymptomatic hyperuricemic stage), stage 2 (acute gout stage), stage 3 (intermittent stage), and stage 4 (chronic tophaceous stage). A self-diagnostic questionnaire for gout stage was also provided (see Table 3). In addition to gout-related information, self-management techniques were included in the last part of the program. Five main subjects were presented: diet and nutrition, weight control, alcohol management, exercise, and pain and stress management. In the diet and nutrition section, purine-rich foods and low-purine diet were introduced. In the weight control section, a combination of diet and regular exercise was suggested. In the alcohol management section, the effect of alcohol on gout and various tips to limit or avoid alcohol consumption were included. In the exercise section, specific exercise types with detailed explanation and illustrations for gout patients were included. In the pain and stress management section, the effects of tension and stress on health and pain were described and stress management techniques were presented (see Table 3). Recommended diet menus and recipes for gout patients were provided. A bulletin board was established to post patients gout-related experiences. In addition, an expert section was made to introduce recent information about gout management and treatment compliance. An online questionnaire was made available on the website to evaluate the effects of the program on treatment compliance, health-related quality of life, and self-care ability. Program contents had been modified several times on the basis of discussions of the expert panel. Web design was done by the authors and professional web designers and program developers. Interaction Design The bulletin board and expert section were to facilitate user program, user expert, and user user interactions. In particular, user expert interactions were supported through the bulletin board and , and user user interactions were supported through the bulletin board and information section. Motivation Design Each subject was monitored by the system operator in terms of the time and duration that a subject had logged into the program. On the basis of the data, each subject was telephoned by the first author and encouraged to visit the website more than three times a week. In addition, frequent site updates provided the most recent information about gout treatments or management techniques as a means of motivating frequent site visit. Website Development The overall framework of the presently developed website is shown in Figure 3. To make the website easy to understand, text contents were written in a simple and brief way, and image contents (figures, illustrations, and diagrams) were fully used to increase visual effects. Image contents were created using PowerPoint and Photoshop. IMPLEMENTATION AND EVALUATION STAGE The developed program was installed on a web server ( and preimplemented to 20 gout subjects and the panel of 25 gout experts. Appropriateness or satisfaction with the program contents and ease of site navigation and content access were evaluated. Regarding causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, and prognosis of gout, 90% of gout subjects and 80% 88% of the experts indicated that such information was useful to understand gout. Regarding self-management techniques, 90% of gout subjects and 84% of the gout experts indicated satisfaction. In addition, 90% of gout subjects and 88% of the experts responded that the website was useful in the understanding of patients gout-related experiences. In terms of site navigation and content access, 85% 90% of all the gout subjects indicated that the site was easy to access and navigate. However, only 70% of gout subjects and 44% of the experts opined that the website aroused their interest. All subjects indicated a willingness to use the website frequently. Further information on diet and gout progress/medications was suggested by 75% of gout subjects and 60% of experts, respectively. Discussion The results of the needs assessment showed that most of the surveyed subjects did not know about the general gout process and their current state of gout. This implied that the clinical progression and chronic complications of gout needed to be emphasized in the program. Accordingly, four stages of gout (asymptomatic hyperuricemic, acute gout, intermittent, and chronic tophaceous stage) and potential gout complications on kidney and cardiovascular system were presented in detail on the website. Approximately 80% of the study subjects reported drinking alcohol, with two thirds being considered as heavy drinkers (3 4 times a week). Sixty percent of 338 Orthopaedic Nursing September/October 2011 Volume 30 Number 5
7 TABLE 3. PROGRAM CONTENTS Subheadings Contents Overview What is gout? Definition; occurrence rate; historical evidence Causes of gout Uric acid levels in the blood; what is uric acid?; characteristics of uric acid; what causes uric acid build up? Risk factors of gout Lifestyle-related risk factors; drug-related risk factors; disease-related risk factors; other risk factors; gout risk factor questionnaire; your risk factors? Symptoms and diagnosis Symptoms of gout What are the symptoms?; what is gout attack?; characteristics of a gout attack; common sites of gout attack Diagnosis of gout Direct test; indirect test Progress and treatments Progress of gout Stages 1 4; your stage of gout? Treatment for gout Stage 1 (Asymptomatic hyperuricemic stage) Self-care (diet, alcohol restriction); routine blood test Stage 2 (Acute gout stage) Dealing with acute gout attack; gout attack treatment; prevention of the recurrence of gout attacks (hypouricemic drug: Allopurinol); newer drugs Stage 3 (Intermittent stage) Gout attack treatment; prevention of the progression to chronic stage (self-care: hypouricemic drug, diet, alcohol restriction, weight control) Stage 4 (Chronic tophaceous stage) What is tophi or chronic nodule?; treatment for chronic tophaceous gout; drugs; complications of gout Self-Care for Gout Diet and nutrition Low purine diet gout recipe; high and low purine foods; recommended diet menu Weight control Low-fat diet; exercise Alcohol management Alcohol and uric acid; high purine alcohol beverage; strategies to limit or avoid alcohol consumption Exercise Gout and exercise; how to exercise; what types of exercise are best for gout patients?; joint exercise Pain and stress management How do tension and stress affect on health?; coping to pain and stress; deep breath; muscle relaxation; guided imagery; some useful tips to reduce stress Expert section Most recent issues related to Barriers to gout management; recent trends in the gout and treatment gout treatment; new conceptualization of treatment compliance compliance; a new conceptualization of treatment compliance according to the variation theory of learning Bulletin board Provide a place to share gout-related experiences between program users; provide a place for Q&A between program users and experts; provide a place for experts to understand the patient s experience Questionnaire Evaluation of appropriateness and satisfaction about the program contents and ease of site navigation and content access Orthopaedic Nursing September/October 2011 Volume 30 Number 5 339
8 FIGURE 3. Framework of the web-based gout self-management program contents. subjects consumed a meat-based diet and 75% were overweight. These findings are consistent with previous findings (Choi & Curhan, 2007; Eggebeen, 2007; Roddy, 2008; Weaver, 2008), which reported alcohol drinking, a meat-enriched diet, and obesity as risk factors of gout. Therefore, self-management techniques related to alcohol drinking, diet, and weight control were specifically concentrated in the program. Because 38.3% of subjects indicated that they did not currently use any specific self-management practices, such as weight control, diet therapy, and alcohol restriction, but treated their gout only by medications. Of those patients treated only by medication, 15% did not take medications regularly, indicating an extremely poor compliance with treatment. This might result from a lack of knowledge on drug actions or consequences of uncontrolled uric acid due to an inconsistent use of medication. Strategies to improve patient understanding about gout drug actions and the relationship between gout and uncontrolled blood uric acid levels are needed to increase compliance with medication use and self-management practices. According to the variation theory of learning, interventions to improve treatment compliance should focus on the qualitative change of experiencing or understanding a disease rather than focusing on obedience, behavior, or transfer of knowledge (Friberg & Scherman, 2005). To change patient experience and understanding, an important suggested strategy has been to encourage and facilitate the sharing of patient experiences with other patients, and to compare their understanding with others. In addition, healthcare professionals also need to understand patients experiences and recognize their ways of understanding the same disease. An online-based program may be most suitable to achieve bidirectional communications between patients and patients professionals. In this regard, the present program supports user expert and user user interactions through a bulletin board and an expert section. Content analysis of the 13 websites indicated that text-centered websites were less likely to arouse interest in the user, indicating the importance of visual image presentation. Therefore, we included illustrations as much as possible to enhance visual effects. In addition, we found that most other websites for gout patients transferred information unidirectionally from program producer to users. We made a self-assessment questionnaire for gout stage and a self-management checklist to help program users evaluate their current gout stage and their self-management performance available. We also found that there were no family participation sections in other web-based gout programs. Most gout victims are middle-aged men. To facilitate use of the website by a patient s spouse, recommended diet menus and recipes were included (and illustrated) in the program. Results of evaluation of appropriateness or satisfaction with program contents and ease of site navigation and content access showed that both patient and expert groups were highly satisfied. Conclusions and Recommendations The present study was conducted to develop a web-based gout self-management program that can be applicable to each gout stage and to evaluate the validity of the developed program. Based on the results of needs assessment of gout patients and content analysis of related literature and preexisting websites, the gout-related information section of the program were structured with seven main topic areas: overview, causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, progress, and treatments and complications. The self-management section of the program consisted of five main topic areas: diet and nutrition, weight control, alcohol management, exercise, and pain and stress management. The program also includes a bulletin board and an expert section to promote bidirectional interactions between program users and providers. A self-assessment tool of gout stages and self-management checklist are provided. The program contents and ease of site navigation and content access were judged to be appropriate and satisfactory by patient users and gout experts. According to suggestions from the program users, real images related to gout symptoms and detailed information about everyday Korean foods that should be avoided or recommended would be a very useful addition to the website, in aiding the development of a gout self-management program. In addition, more systematic evaluation studies will be needed to determine the effect of a web-based gout self-management program on treatment adherence, self-management ability, and quality of life. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported by Fundamental Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (39525) and Inha University Research Grant. REFERENCES Becker, M. A., & Chohan, S. (2008). We can make gout management more successful now. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 20, Chen, X. L., & Schumacher, H. R. (2006). Gout: Can we create an evidence-based systematic approach to diagnosis and management? Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology, 20(4), Choi, H. K. (2010). A prescription for lifestyle change in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 22, Orthopaedic Nursing September/October 2011 Volume 30 Number 5
9 Choi, H. K., & Curhan, G. (2007). Coffee, tea, and caffeine consumption and serum uric acid level: The third national health and nutrition examination survey. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 57(5), Choy, G. (2005). An update on the treatment options for gout and calcium pyrophosphate deposition. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy, 6(14), Conway, N., & Schwartz, S. (2009). Diagnosis and management of acute gout. Medicine & Health/Rhode Island, 92(11), Eggebeen, A. (2007). Gout: An update. American Family Physician, 76(6), Fang, W., Zeng, X., Li, M., Chen, L. X., & Schumacher, H. R. (2006). The management of gout at an academic healthcare center in Beijing: A physician survey. The Journal of Rheumatology, 33, Friberg, F., & Scherman, M. H. (2005). Can a teaching and learning perspective deepen understanding of the concept of compliance? A theoretical discussion. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences, 19(3): Hak, A. E., & Choi, H. K. (2008). Lifestyle and gout. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 20, Hong, Y. H., & Lee, C. K. (2005). Management of gout. Korean Journal of Medicine, 69(4), Hoskison, T. K., & Wortmann, R. L. (2006). Advances in the management of gout and hyperuricaemia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology, 35(4), Hoskison, K. T., & Wortmann, R. L. (2007). Management of gout in older adults: Barriers to optimal control. Drugs & Aging, 24(1), Kim, K. Y., Schumacher, H. R., Hunsche, E., Wertheimer, A. I., & Kong, S. X. (2003). A literature review of the epidemiology and treatment of acute gout. Clinical Therapeutics, 25(6), de Klerk, E., van der Heijde, D., Landewe, R., van der Tempel, H., Urquhart, J., & van der Linden, S. (2003). Patient compliance in rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatic, and gout. The Journal of Rheumatology, 30(1), Luk, A. J., & Simkin, P. A. (2005). Epidemiology of hyperuricemia and gout. The American Journal of Managed Care, 11(15), S435 S442. Meiner, S. E. (2001). Gouty arthritis: Not just a big toe problem. Geriatric Nursing, 22(3), Mineo, I., Kamiya, H., & Tsukuda, A. (2008). Practical strategies for lifestyle modification in people with hyperuricemia and gout treatment through diet, physical activity, and reduced alcohol consumption. Nippon Rinsho, 66(4), Na, I. J. (2005). Web-based education. Seoul, South Korea: Kwahakkyoksa Publishing. Perez-Ruiz, F., & Schlesinger, N. (2008). Management of gout. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology, 37, Pillinger, M. H., & Keenan, R. T. (2008). Update on the management of hyperuricemia and gout. Bulletin of the NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases, 66(3), Riedel, A. A., Nelson, M., Joseph-Ridge, N., Wallace, K., MacDonald, P., & Becker, M. (2004). Compliance with allopurinol therapy among managed care enrollees with gout: a retrospective analysis of administrative claims. The Journal of Rheumatology, 31(8), Roddy, E. (2008). Hyperuricemia, gout, and lifestyle factors. The Journal of Rheumatology, 35(9), Saag, K. G., & Choi, H. K. (2006). Epidemiology, risk factors, and lifestyle modification for gout. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 8(Suppl 1), S2. doi: /ar1907. Schlesinger, N., Moore, D. F., Sun, J. D., & Schumacher, H. R. (2006). A survey of current evaluation and treatment of gout. The Journal of Rheumatology, 33(10), Schlesinger, N., Dalbeth, N., & Perez-Ruiz, F. (2009). Gout what are the treatment options? Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy, 10(8), Schumacher, H. R., & Chen, L. X. (2008). The practical management of gout. Cleveland Clinical Journal of Medicine, 75(Suppl 5), S22 S25. Shigaki, C. L., Smarr, K. L., Yang Gong, Donovan-Hanson, K., Siva, C., Johnson, R. A., Ge, B., & Musser, D. R. (2008). Social interactions in an online self-management program for rheumatoid arthritis. Chronic Illness, 4(4), Terkeltaub, R., Zelman, D., Scavulli, J., Perez-Ruiz, F., & Liote, F. (2009). Gout study group: Update on hyperuricemia and gout. Joint Bone Spine, 76, Wortmann, R. L. (2006). The management of gout: It should be crystal clear. The Journal of Rheumatology, 33(10), Weaver, A. L. (2008). Epidemiology of gout. Cleveland Clinical Journal of Medicine, 75(Suppl 5), S9 S12. For 36 additional continuing nursing education articles on orthopaedic topics, go to nursingcenter.com/ce. Orthopaedic Nursing September/October 2011 Volume 30 Number 5 341
Gout. Clinical features Most commonly affects middle-aged males. It is an acute and usually relapsing selflimiting
 Gout Gout is a syndrome caused by an inflammatory response to the formation of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals which develop secondary to hyperuricemia. Acute and chronic forms are recognized. Hyperuricemia
Gout Gout is a syndrome caused by an inflammatory response to the formation of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals which develop secondary to hyperuricemia. Acute and chronic forms are recognized. Hyperuricemia
What will happen in the future? How will gout be diagnosed? How is gout treated? prevent
 Rheumatology Day Unit Dr J Hamilton 0191 4458359 0191 4455240 (9-5 Mon-Fri) Dr C Heycock 0191 4452198 Answer phone on 24hours Dr C Kelly 0191 4452193 Dr V Saravanan 0191 4456055 Dr M Rynne 0191 4458359
Rheumatology Day Unit Dr J Hamilton 0191 4458359 0191 4455240 (9-5 Mon-Fri) Dr C Heycock 0191 4452198 Answer phone on 24hours Dr C Kelly 0191 4452193 Dr V Saravanan 0191 4456055 Dr M Rynne 0191 4458359
1. To review the diagnosis of gout and its differential. 2. To understand the four stages of gout
 Objectives 1. To review the diagnosis of gout and its differential GOUT 2. To understand the four stages of gout 3. To develop an approach for the acute treatment of gout Anthony Lim 9/13/12 Cycle 3 4.
Objectives 1. To review the diagnosis of gout and its differential GOUT 2. To understand the four stages of gout 3. To develop an approach for the acute treatment of gout Anthony Lim 9/13/12 Cycle 3 4.
CHAPTER:2 GOUT. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 CHAPTER:2 GOUT BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY DEFINITION Gout is defined as a peripheral arthritis, resulting from the deposition of MSU crystals
CHAPTER:2 GOUT BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY DEFINITION Gout is defined as a peripheral arthritis, resulting from the deposition of MSU crystals
Gout A rapid review. Jeremy Jones
 Gout A rapid review Jeremy Jones The Hyperuricemia Cascade Dietary purines Tissue nucleic acids Urate Endogenous purine synthesis Overproduction Hyperuricemia Underexcretion Silent tissue deposition Gout
Gout A rapid review Jeremy Jones The Hyperuricemia Cascade Dietary purines Tissue nucleic acids Urate Endogenous purine synthesis Overproduction Hyperuricemia Underexcretion Silent tissue deposition Gout
Managing Gout A Review of the Research for Adults
 Managing Gout A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* has said that you have gout. You are age 18 or
Managing Gout A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* has said that you have gout. You are age 18 or
Gout is a disease of relatively low prevalence. Clinical, Humanistic, and Economic Outcomes of Gout REPORTS
 Clinical, Humanistic, and Economic Outcomes of Gout Diana I. Brixner, RPh, PhD; and Mei-Jen Ho, PharmD Abstract Gout is a low prevalence disease not often considered by managed care organizations with
Clinical, Humanistic, and Economic Outcomes of Gout Diana I. Brixner, RPh, PhD; and Mei-Jen Ho, PharmD Abstract Gout is a low prevalence disease not often considered by managed care organizations with
COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF EFFICACY AND SAFETY PROFILE OF FEBUXOSTAT WITH ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH HYPERURICEMIA AND GOUT
 Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2013 P K Agarwal and Bijay Kumar, 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 2, No. 4, October 2013 2013 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF
Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2013 P K Agarwal and Bijay Kumar, 2013 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 2, No. 4, October 2013 2013 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF
Gout -revisited. Shrenik Shah
 Gout -revisited Shrenik Shah definition Monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition episodic and later persistent joint inflammation and tophi All MSU crystal deposition- broader definition EULAR- European
Gout -revisited Shrenik Shah definition Monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition episodic and later persistent joint inflammation and tophi All MSU crystal deposition- broader definition EULAR- European
Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides and gout. György Nagy
 Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides and gout György Nagy Dec 4, 2017 Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Chronic, progressive, autoimmune disorder of the joints with extra-articular
Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides and gout György Nagy Dec 4, 2017 Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Chronic, progressive, autoimmune disorder of the joints with extra-articular
GOUT. Dr Krishnan Baburaj West herts NHS Trust
 GOUT Dr Krishnan Baburaj West herts NHS Trust podagra Gout A disease of kings, the king of diseases History Louis XIV Emperor Augustus Henry VIII Introduction Gout an inflammatory arthritic condition that
GOUT Dr Krishnan Baburaj West herts NHS Trust podagra Gout A disease of kings, the king of diseases History Louis XIV Emperor Augustus Henry VIII Introduction Gout an inflammatory arthritic condition that
Gout 2.0. Scott Vogelgesang, M.D. Division of Immunology: Rheumatology & Allergy
 Gout 2.0 Scott Vogelgesang, M.D. Division of Immunology: Rheumatology & Allergy Case 48 year old man presents with swollen, painful left toe that started overnight. Didn t hurt when he went to bed. No
Gout 2.0 Scott Vogelgesang, M.D. Division of Immunology: Rheumatology & Allergy Case 48 year old man presents with swollen, painful left toe that started overnight. Didn t hurt when he went to bed. No
Gout: Update in therapeutics
 Summary Gout: Update in therapeutics 29/11/14 Caroline van Durme CHU de Liège Maastricht University Medical Centre+ Why treating gout? Guidelines: ACR 12 Drugs: Colchicine Allopurinol: what about the kidney?
Summary Gout: Update in therapeutics 29/11/14 Caroline van Durme CHU de Liège Maastricht University Medical Centre+ Why treating gout? Guidelines: ACR 12 Drugs: Colchicine Allopurinol: what about the kidney?
Case presentation. serum uric acid = 11.5 mg/dl 24-hour uric acid excretion = 300 mg
 GOUT 55 y/o male 12 hours pain in my big toe & ankle went to bed last night feeling fine felt as if had broken toe this morning similar problems in right ankle & left wrist Case presentation lab studies
GOUT 55 y/o male 12 hours pain in my big toe & ankle went to bed last night feeling fine felt as if had broken toe this morning similar problems in right ankle & left wrist Case presentation lab studies
A Patient s Guide to Gout. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Gout Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Gout Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Essence of the Revised Guideline for the Management of Hyperuricemia and Gout
 Research and Reviews Essence of the Revised Guideline for the Management of Hyperuricemia and Gout JMAJ 55(4): 324 329, 2012 Hisashi YAMANAKA,* 1 The Guideline Revising Committee of Japanese Society of
Research and Reviews Essence of the Revised Guideline for the Management of Hyperuricemia and Gout JMAJ 55(4): 324 329, 2012 Hisashi YAMANAKA,* 1 The Guideline Revising Committee of Japanese Society of
An update on the management of gout
 An update on the management of gout 8 The management of gout involves treatment of an acute attack, lifestyle modification and urate lowering treatment to achieve a target serum urate level. Recent evidence
An update on the management of gout 8 The management of gout involves treatment of an acute attack, lifestyle modification and urate lowering treatment to achieve a target serum urate level. Recent evidence
Rheumatology Cases for the Internist
 Rheumatology Cases for the Internist Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology Vice Chair, Department of Medicine University of Maryland School
Rheumatology Cases for the Internist Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology Vice Chair, Department of Medicine University of Maryland School
Urate Lowering Efficacy of Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol in Hyperuricemic Patients with Gout
 Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Meta-Analysis Urate Lowering Efficacy of Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol in Hyperuricemic Patients with Gout Erika Bianca S. Villazor-Isidro, M.D.*; John Carlo G.
Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Meta-Analysis Urate Lowering Efficacy of Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol in Hyperuricemic Patients with Gout Erika Bianca S. Villazor-Isidro, M.D.*; John Carlo G.
Plus: How to gain control of symptoms A gout-friendly eating style Lifestyle changes that can help prevent future attacks
 about Gout What You Need to Know about Gout & Uric Acid Plus: How to gain control of symptoms A gout-friendly eating style Lifestyle changes that can help prevent future attacks We re doing everything
about Gout What You Need to Know about Gout & Uric Acid Plus: How to gain control of symptoms A gout-friendly eating style Lifestyle changes that can help prevent future attacks We re doing everything
Uloric Step Therapy Program
 Uloric Step Therapy Program Policy Number: 5.01.584 Last Review: 7/2017 Origination: 7/2014 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for brand
Uloric Step Therapy Program Policy Number: 5.01.584 Last Review: 7/2017 Origination: 7/2014 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for brand
Nutrition Counseling among Patients with Gout
 International Journal of Public Health Science (IJPHS) Vol.6, No.4, December 2017, pp. 360~364 ISSN: 2252-8806, DOI: 10.11591/ijphs.v6i4.pp360-364 360 Nutrition Counseling among Patients with Gout Susyani
International Journal of Public Health Science (IJPHS) Vol.6, No.4, December 2017, pp. 360~364 ISSN: 2252-8806, DOI: 10.11591/ijphs.v6i4.pp360-364 360 Nutrition Counseling among Patients with Gout Susyani
Achieving Gout Goals in Your Practice An Interview with Paul P. Doghramji, MD, FAAFP
 Achieving Gout Goals in Your Practice An Interview with Paul P. Doghramji, MD, FAAFP Dr. Paul Doghramji is attending physician at the Pottstown Memorial Medical Center and medical director of Health Services
Achieving Gout Goals in Your Practice An Interview with Paul P. Doghramji, MD, FAAFP Dr. Paul Doghramji is attending physician at the Pottstown Memorial Medical Center and medical director of Health Services
Gout Hanan Abdel Rehim
 Review article 35 Gout Hanan Abdel Rehim Department of Internal Medicine, Kasr-Al Aini School of Medicine, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt Correspondence to Hanan Abdel Rehim, MD, 11 Ismaiel Wahby Street,
Review article 35 Gout Hanan Abdel Rehim Department of Internal Medicine, Kasr-Al Aini School of Medicine, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt Correspondence to Hanan Abdel Rehim, MD, 11 Ismaiel Wahby Street,
Purine-rich foods intake and recurrent gout attacks
 Clinical and epidemiological research 1 Clinical Epidemiology Research and Training Unit, Department of Medicine, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts, USA 2 Data Coordinating Center,
Clinical and epidemiological research 1 Clinical Epidemiology Research and Training Unit, Department of Medicine, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts, USA 2 Data Coordinating Center,
Oxford Kidney Unit. Dietary advice for managing gout Information for patients
 Oxford Kidney Unit Dietary advice for managing gout Information for patients page 2 This leaflet is for you if you are suffering from gout. It will give you information to help manage your symptoms. What
Oxford Kidney Unit Dietary advice for managing gout Information for patients page 2 This leaflet is for you if you are suffering from gout. It will give you information to help manage your symptoms. What
GOUT GO FOR SIX WITH. Everything You Need to Know About Gout & Uric Acid PLUS:
 GO FOR SIX WITH Everything You Need to Know About Gout & Uric Acid GOUT PLUS: How to gain control of symptoms A gout-friendly eating style Medication recommendations to discuss with your doctor Lifestyle
GO FOR SIX WITH Everything You Need to Know About Gout & Uric Acid GOUT PLUS: How to gain control of symptoms A gout-friendly eating style Medication recommendations to discuss with your doctor Lifestyle
Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: Gout
 Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: Gout 1. Focused summary of gout relevant to primary care Significance: Gout is a chronic, progressive, inflammatory disease requiring appropriate long-term management. Gout
Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: Gout 1. Focused summary of gout relevant to primary care Significance: Gout is a chronic, progressive, inflammatory disease requiring appropriate long-term management. Gout
The Urate-lowering Efficacy and Safety of Febuxostat in Korean Patients with Gout
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 2, No. 4, August 213 http://dx.doi.org/1.478/jrd.213.2.4.223 Original Article The Urate-lowering Efficacy and Safety of in Korean Patients with Gout Sung Hwan Park 1,
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 2, No. 4, August 213 http://dx.doi.org/1.478/jrd.213.2.4.223 Original Article The Urate-lowering Efficacy and Safety of in Korean Patients with Gout Sung Hwan Park 1,
Gout in the UK and Germany: prevalence, comorbidities and management in general practice
 1 IMS Health, Brussels, Belgium; 2 Department of Public Health, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium; 3 School of Pharmacy, Brussels University, Brussels, Belgium; 4 IMS Health, London, UK; 5 Ipsen, Paris,
1 IMS Health, Brussels, Belgium; 2 Department of Public Health, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium; 3 School of Pharmacy, Brussels University, Brussels, Belgium; 4 IMS Health, London, UK; 5 Ipsen, Paris,
Study of Febuxostat for the Management of Hyperuricemia in Gout
 Human Journals Review Article October 2015 Vol.:4, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Sachin S. Shinde et al. Study of Febuxostat for the Management of Hyperuricemia in Gout Keywords: Febuxostat, Hyperuricemia,
Human Journals Review Article October 2015 Vol.:4, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Sachin S. Shinde et al. Study of Febuxostat for the Management of Hyperuricemia in Gout Keywords: Febuxostat, Hyperuricemia,
Drugs Used to Treat Gout. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drugs Used to Treat Gout Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by recurrent episodes of acute arthritis
Drugs Used to Treat Gout Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by recurrent episodes of acute arthritis
Gout Treatment Guidelines
 Gout Treatment Guidelines Gout is a disorder that manifests as a spectrum of clinical and pathologic features built on a foundation of an excess body burden of uric acid, manifested in part by hyperuricemia,
Gout Treatment Guidelines Gout is a disorder that manifests as a spectrum of clinical and pathologic features built on a foundation of an excess body burden of uric acid, manifested in part by hyperuricemia,
Effectiveness of Web-Based Multimedia Mental Health Educational Program on Anxiety, Depression, Self Concept and School Adjustment in Adolescents
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.10 No.5, May 2010 59 Effectiveness of Web-Based Multimedia Mental Health Educational Program on Anxiety, Depression, Self Concept
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.10 No.5, May 2010 59 Effectiveness of Web-Based Multimedia Mental Health Educational Program on Anxiety, Depression, Self Concept
ARD Online First, published on November 2, 2007 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on November 2, 2007 as 10.1136/ard.2007.076232 Gout in the UK and Germany: prevalence, comorbidities and management in general practice 2000 2005 L Annemans, E Spaepen, M Gaskin,
ARD Online First, published on November 2, 2007 as 10.1136/ard.2007.076232 Gout in the UK and Germany: prevalence, comorbidities and management in general practice 2000 2005 L Annemans, E Spaepen, M Gaskin,
The 2010 Competency Standards addressed by this activity include (but may not be limited to): 4.2.2, 4.2.3, 6.1.2, 6.2.1, 7.1.2, 7.1.3,
 UPDATE ON GOUT Learning objectives: After completing this activity, pharmacists should be able to: 1. describe the mechanisms underlying hyperuricaemia 2. state the risk factors for development of gout
UPDATE ON GOUT Learning objectives: After completing this activity, pharmacists should be able to: 1. describe the mechanisms underlying hyperuricaemia 2. state the risk factors for development of gout
Journal of Advanced Scientific Research
 Bijoy Kumar Panda et al, J Adv Scient Res, 2012, 3(2): 03-11 3 Journal of Advanced Scientific Research Available online through http://www.sciensage.info/jasr ISSN 0976-9595 Review Article Febuxostat,
Bijoy Kumar Panda et al, J Adv Scient Res, 2012, 3(2): 03-11 3 Journal of Advanced Scientific Research Available online through http://www.sciensage.info/jasr ISSN 0976-9595 Review Article Febuxostat,
GOUT GO FOR SIX WITH. Everything You Need to Know about Gout & Uric Acid PLUS:
 GO FOR SIX WITH Everything You Need to Know about Gout & Uric Acid GOUT PLUS: How to gain control of symptoms A gout-friendly eating style Medication recommendations to discuss with your doctor Lifestyle
GO FOR SIX WITH Everything You Need to Know about Gout & Uric Acid GOUT PLUS: How to gain control of symptoms A gout-friendly eating style Medication recommendations to discuss with your doctor Lifestyle
Literature Scan: Analgesics for Gout. Month/Year of Review: April 2015 Date of Last Review: January 2014
 Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301 1079 Phone 503 947 5220 Fax 503 947 1119 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights
Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301 1079 Phone 503 947 5220 Fax 503 947 1119 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights
Acute hot swollen joint. Dr Edward Roddy Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology and Consultant Rheumatologist
 Acute hot swollen joint Dr Edward Roddy Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology and Consultant Rheumatologist Acute monoarthritis: differential diagnosis Septic arthritis Crystal arthritis (gout, pseudogout) Haemarthrosis
Acute hot swollen joint Dr Edward Roddy Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology and Consultant Rheumatologist Acute monoarthritis: differential diagnosis Septic arthritis Crystal arthritis (gout, pseudogout) Haemarthrosis
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the USMLE Step One Exam. Howard J. Sachs, MD
 Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Gout for the
About diet and arthritis
 About diet and arthritis Yes, the right diet can certainly help some people with arthritis and rheumatism. Recent research has also discovered several new links between arthritis and diet. This article
About diet and arthritis Yes, the right diet can certainly help some people with arthritis and rheumatism. Recent research has also discovered several new links between arthritis and diet. This article
Clinical Study Allopurinol, Benzbromarone, or a Combination in Treating Patients with Gout: Analysis of a Series of Outpatients
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Rheumatology Volume 2014, Article ID 263720, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/263720 Clinical Study Allopurinol, Benzbromarone, or a Combination
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Rheumatology Volume 2014, Article ID 263720, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/263720 Clinical Study Allopurinol, Benzbromarone, or a Combination
Metabolic Stone Work-Up For Stone Prevention. Dr. Hazem Elmansy, MD, MSC, FRCSC Assistant Professor, NOSM, Urology Department
 Metabolic Stone Work-Up For Stone Prevention Dr. Hazem Elmansy, MD, MSC, FRCSC Assistant Professor, NOSM, Urology Department Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Slide Faculty: Hazem Elmansy Relationships with
Metabolic Stone Work-Up For Stone Prevention Dr. Hazem Elmansy, MD, MSC, FRCSC Assistant Professor, NOSM, Urology Department Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Slide Faculty: Hazem Elmansy Relationships with
YOU ARE WHAT YOU EAT
 YOU ARE WHAT YOU EAT How diet plays a role in good health, mobility and aging 210050500_Cov_a 210050500_Cov_b 210050500_Cov_c 210050500_Cov_d 210050500_02a While the phrase 210050500_03a you are what you
YOU ARE WHAT YOU EAT How diet plays a role in good health, mobility and aging 210050500_Cov_a 210050500_Cov_b 210050500_Cov_c 210050500_Cov_d 210050500_02a While the phrase 210050500_03a you are what you
Women With Gout: Efficacy and Safety of Urate-Lowering With Febuxostat and Allopurinol
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 64, No. 2, February 2012, pp 256 261 DOI 10.1002/acr.20680 2012, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Women With Gout: Efficacy and Safety of Urate-Lowering
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 64, No. 2, February 2012, pp 256 261 DOI 10.1002/acr.20680 2012, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Women With Gout: Efficacy and Safety of Urate-Lowering
Gout- Treatment Updates. Harinder Singh, MD Rheumatology Mercy Internal Medicine Clinic Mason City, IA
 Gout- Treatment Updates Harinder Singh, MD Rheumatology Mercy Internal Medicine Clinic Mason City, IA Gout Outline of purine metabolism: (1) amidophosphoribosyltransferase (2) hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
Gout- Treatment Updates Harinder Singh, MD Rheumatology Mercy Internal Medicine Clinic Mason City, IA Gout Outline of purine metabolism: (1) amidophosphoribosyltransferase (2) hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF FEBUXOSTAT OR ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH GOUT AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (The CARES Trial)
 CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF FEBUXOSTAT OR ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH GOUT AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (The CARES Trial) William B. White, MD for the CARES Investigators Calhoun Cardiology Center University
CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF FEBUXOSTAT OR ALLOPURINOL IN PATIENTS WITH GOUT AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE (The CARES Trial) William B. White, MD for the CARES Investigators Calhoun Cardiology Center University
Gout: A Clinical Update. Why talk about Gout? Why talk about Gout? Populations at risk: Why is Gout Less Common in Women? US Gout Population: 2009
 Gout: A Clinical Update Peng Thim Fan, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Why talk about Gout? Large increase in gout in the last 20
Gout: A Clinical Update Peng Thim Fan, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Why talk about Gout? Large increase in gout in the last 20
Patients' knowledge and beliefs concerning gout and its treatment: a population based study
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Meyers Primary Care Institute Publications and Presentations Meyers Primary Care Institute 9-21-2012 Patients' knowledge and beliefs concerning
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Meyers Primary Care Institute Publications and Presentations Meyers Primary Care Institute 9-21-2012 Patients' knowledge and beliefs concerning
GOUT IN THE ELDERLY. Learning Objectives. Disclosure. Geriatric Grand Rounds. Geriatric Grand Rounds
 Visit web sites: Tuesday, June 2, 2009 12:00 noon Dr. Bill Black Auditorium Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital In keeping with Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital policy, speakers participating in this event
Visit web sites: Tuesday, June 2, 2009 12:00 noon Dr. Bill Black Auditorium Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital In keeping with Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital policy, speakers participating in this event
2.0. Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved. 24 The Nurse Practitioner Vol. 40, No. 8
 2.0 CONTACT HOURS 24 The Nurse Practitioner Vol. 40, No. 8 www.tnpj.com Treatment and gout prevention of o leva Abstract: Gout is a disorder of purine metabolism that primarily occurs in adult males. Elevated
2.0 CONTACT HOURS 24 The Nurse Practitioner Vol. 40, No. 8 www.tnpj.com Treatment and gout prevention of o leva Abstract: Gout is a disorder of purine metabolism that primarily occurs in adult males. Elevated
OBJECTIVES GOUT GOUTY INFLAMMATION 6/10/2016 GOUT INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE MONOSODIUM URATE CRYSTAL DEPOSITION DISEASE
 GOUT Lisa Talbert, MD Family Medicine Update June 15, 2016 OBJECTIVES To be familiar with the clinical presentation and pathophysiology of gouty arthritis Be able to incorporate current guidelines when
GOUT Lisa Talbert, MD Family Medicine Update June 15, 2016 OBJECTIVES To be familiar with the clinical presentation and pathophysiology of gouty arthritis Be able to incorporate current guidelines when
Diet for Kidney Stone Prevention
 Diet for Kidney Stone Prevention National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH How does diet affect the risk
Diet for Kidney Stone Prevention National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH How does diet affect the risk
Solomon Islands guidelines. for the management of major non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in primary health care
 Solomon Islands guidelines for the management of major non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in primary health care Contents Foreword Introduction 1. Cardiovascular risk assessment and diabetes screening 1
Solomon Islands guidelines for the management of major non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in primary health care Contents Foreword Introduction 1. Cardiovascular risk assessment and diabetes screening 1
Risk Management Plan Etoricoxib film-coated tablets
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
HARVARD PILGRIM HEALTH CARE RECOMMENDED MEDICATION REQUEST GUIDELINES
 Generic Brand HICL GCN Exception/Other PEGLOTICASE KRYSTEXXA 37154 GUIDELINES FOR USE 1. Does the patient have a diagnosis of symptomatic chronic gout (prior to initiating Krystexxa therapy) with clinical
Generic Brand HICL GCN Exception/Other PEGLOTICASE KRYSTEXXA 37154 GUIDELINES FOR USE 1. Does the patient have a diagnosis of symptomatic chronic gout (prior to initiating Krystexxa therapy) with clinical
Module. Module. Managing Other Chronic Conditions. Managing Other Chronic Conditions
 Managing Other Chronic Conditions 8 Managing Other Chronic Conditions Taking Control of Heart Failure Important Information Please write down important contact information in the space below. You may also
Managing Other Chronic Conditions 8 Managing Other Chronic Conditions Taking Control of Heart Failure Important Information Please write down important contact information in the space below. You may also
A Subjectivity Study on Eating Habits among Female College Students
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(), DOI: 0.8/ijst/0/v9i/089, December 0 ISSN (Print) : 09-8 ISSN (Online) : 09- A Subjectivity Study on Eating Habits among Female College Students JeeHee
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(), DOI: 0.8/ijst/0/v9i/089, December 0 ISSN (Print) : 09-8 ISSN (Online) : 09- A Subjectivity Study on Eating Habits among Female College Students JeeHee
Update on Gout for GPs
 Update on Gout for GPs Dr Patrick Kiely PhD FRCP Consultant Physician and Rheumatologist St George s, London 2/3 1/3 Gut bacteria have uricase Chronic erosive arthropathy Clinical spectrum Making the diagnosis
Update on Gout for GPs Dr Patrick Kiely PhD FRCP Consultant Physician and Rheumatologist St George s, London 2/3 1/3 Gut bacteria have uricase Chronic erosive arthropathy Clinical spectrum Making the diagnosis
Reimund Serafica, PhD, MSN, RN Assistant Professor of Nursing Gardner-Webb University
 Reimund Serafica, PhD, MSN, RN Assistant Professor of Nursing Gardner-Webb University Background One of the Healthy People 2020 goals is to increase the proportion of adults who are at healthy weight and
Reimund Serafica, PhD, MSN, RN Assistant Professor of Nursing Gardner-Webb University Background One of the Healthy People 2020 goals is to increase the proportion of adults who are at healthy weight and
MEDICAL POLICY PEGLOTICASE (KRYSTEXXA ) POLICY NUMBER MP POLICY TITLE. Original Issue Date (Created): January 1, 2011
 Original Issue Date (Created): January 1, 2011 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): September 24, 2013 Effective Date: November 1, 2013 I. POLICY PREAUTHORIZATION REQUIRED Note: Requests for pegloticase
Original Issue Date (Created): January 1, 2011 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): September 24, 2013 Effective Date: November 1, 2013 I. POLICY PREAUTHORIZATION REQUIRED Note: Requests for pegloticase
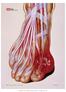
3/2/2014. Got Gout? Get a Plumber. Objectives. Disclosures
 Got Gout? Get a Plumber. Heidi Garcia, PA-C Department of Rheumatology Division of Internal Medicine Mayo Clinic Arizona 2013 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Recall some of the history of Gout. Describe the pathophysiology
Got Gout? Get a Plumber. Heidi Garcia, PA-C Department of Rheumatology Division of Internal Medicine Mayo Clinic Arizona 2013 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Recall some of the history of Gout. Describe the pathophysiology
Instructor s Manual for Unit 2 The Inside Story about Nutrition and Health
 Instructor s Manual for Unit 2 The Inside Story about Nutrition and Health Class Preparation Materials in the Instructor s Manual for Unit 2 Learning Objectives Brief Chapter Outline Answers to Global
Instructor s Manual for Unit 2 The Inside Story about Nutrition and Health Class Preparation Materials in the Instructor s Manual for Unit 2 Learning Objectives Brief Chapter Outline Answers to Global
Gout affects approximately 8.3 million people in the
 RESEARCH Benefit Restrictions and Gout Treatment Sharon M. Wang, PharmD, MS; Gustavus A. Aranda, Jr., PharmD, MS; Sara Gao, MS; and Bimal V. Patel, PharmD, MS ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Gout is a chronic rheumatic
RESEARCH Benefit Restrictions and Gout Treatment Sharon M. Wang, PharmD, MS; Gustavus A. Aranda, Jr., PharmD, MS; Sara Gao, MS; and Bimal V. Patel, PharmD, MS ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Gout is a chronic rheumatic
Practice research in the field of gout - clinical pharmacology of antihyperuricemic drugs Reinders, Mattheus Karsien
 University of Groningen Practice research in the field of gout - clinical pharmacology of antihyperuricemic drugs Reinders, Mattheus Karsien IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
University of Groningen Practice research in the field of gout - clinical pharmacology of antihyperuricemic drugs Reinders, Mattheus Karsien IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
D espite reasonable understanding of its pathogenesis
 1312 EXTENDED REPORT EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part II: Management. Report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee For International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics
1312 EXTENDED REPORT EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part II: Management. Report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee For International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics
Effectiveness of a pharmacist-based gout care management programme in a large integrated health plan: results from a pilot study
 Research Effectiveness of a pharmacist-based gout care management programme in a large integrated health plan: results from a pilot study Robert D Goldfien, 1 Michele S Ng, 2 Goldie Yip, 2 Alice Hwe, 2
Research Effectiveness of a pharmacist-based gout care management programme in a large integrated health plan: results from a pilot study Robert D Goldfien, 1 Michele S Ng, 2 Goldie Yip, 2 Alice Hwe, 2
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) PUBLIC SUMMARY ETORICOXIB ORION (ETORICOXIB) 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG & 120 MG FILM-COATED TABLET DATE: , VERSION 1.
 RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) PUBLIC SUMMARY ETORICOXIB ORION (ETORICOXIB) 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG & 120 MG FILM-COATED TABLET DATE: 07-10-2016, VERSION 1.2 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib Orion
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) PUBLIC SUMMARY ETORICOXIB ORION (ETORICOXIB) 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG & 120 MG FILM-COATED TABLET DATE: 07-10-2016, VERSION 1.2 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib Orion
Healthier Lifestyle Choices
 Healthier Lifestyle Choices The Liverpool Heart and Chest Hospital is a health promoting hospital and actively supports the Making Every Contact Count national initiative known as MECC. This leaflet is
Healthier Lifestyle Choices The Liverpool Heart and Chest Hospital is a health promoting hospital and actively supports the Making Every Contact Count national initiative known as MECC. This leaflet is
Long-term Treatment of Gout: New Opportunities for Improved Outcomes
 Long-term Treatment of Gout: New Opportunities for Improved Outcomes Paul P. Doghramji, MD, FAAFP CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Make a presumptive diagnosis of gout based on history
Long-term Treatment of Gout: New Opportunities for Improved Outcomes Paul P. Doghramji, MD, FAAFP CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Make a presumptive diagnosis of gout based on history
Implementing AHRQ Effective Health Care Reviews Helping Clinicians Make Better Treatment Choices
 Implementing AHRQ Effective Health Care Reviews Helping Clinicians Make Better Treatment Choices Gout: Diagnosis and Management Practice Pointers by MATTHEW R. NOSS, DO, MSEd, U.S. Army Health Clinic,
Implementing AHRQ Effective Health Care Reviews Helping Clinicians Make Better Treatment Choices Gout: Diagnosis and Management Practice Pointers by MATTHEW R. NOSS, DO, MSEd, U.S. Army Health Clinic,
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Seetha Monrad, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Seetha Monrad, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
New Hypertension Guideline Recommendations for Adults July 7, :45-9:30am
 Advances in Cardiovascular Disease 30 th Annual Convention and Reunion UERM-CMAA, Inc. Annual Convention and Scientific Meeting July 5-8, 2018 New Hypertension Guideline Recommendations for Adults July
Advances in Cardiovascular Disease 30 th Annual Convention and Reunion UERM-CMAA, Inc. Annual Convention and Scientific Meeting July 5-8, 2018 New Hypertension Guideline Recommendations for Adults July
Crystal induced arthropathies. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal
 Crystal induced arthropathies Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal 1 Crystal induced Arthropathies Gout Pseudogout Debilitating illnesses; Recurrent episodes of pain and joint inflammation; Formation and deposition of
Crystal induced arthropathies Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal 1 Crystal induced Arthropathies Gout Pseudogout Debilitating illnesses; Recurrent episodes of pain and joint inflammation; Formation and deposition of
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Biochemical effectiveness of allopurinol and allopurinol-probenecid in previously benzbromarone-treated gout patients Reinders, M.K.; van Roon, Eric; Houtman, Pieternella; Brouwers,
University of Groningen Biochemical effectiveness of allopurinol and allopurinol-probenecid in previously benzbromarone-treated gout patients Reinders, M.K.; van Roon, Eric; Houtman, Pieternella; Brouwers,
Gout FACTSHEET REAL LIFE STORY
 1 What is gout? Gout is a type of arthritis where swelling and severe pain develops rapidly in joints, especially at the base of the big toe. Gout affects approximately one in 30 adults, most commonly
1 What is gout? Gout is a type of arthritis where swelling and severe pain develops rapidly in joints, especially at the base of the big toe. Gout affects approximately one in 30 adults, most commonly
New Drug Evaluation: lesinurad tablet, oral
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Gout. Edward Roddy, 1 Christian D Mallen, 1 Michael Doherty 2 CLINICAL REVIEW
 Gout Edward Roddy, 1 Christian D Mallen, 1 Michael Doherty 2 1 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre, Primary Care Sciences, Keele University, Keele ST5 5BG, UK 2 Academic Rheumatology, University
Gout Edward Roddy, 1 Christian D Mallen, 1 Michael Doherty 2 1 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre, Primary Care Sciences, Keele University, Keele ST5 5BG, UK 2 Academic Rheumatology, University
Effectiveness of a pharmacist-based gout care management program in a large integrated health plan: Results from a pilot study For peer review only
 BMJ Open Effectiveness of a pharmacist-based gout care management program in a large integrated health plan: Results from a pilot study Journal: BMJ Open Manuscript ID: bmjopen--00 Article Type: Research
BMJ Open Effectiveness of a pharmacist-based gout care management program in a large integrated health plan: Results from a pilot study Journal: BMJ Open Manuscript ID: bmjopen--00 Article Type: Research
Effects of Breast Cancer and Breast Self-Examination Education using Breast Models on Nursing Students Knowledge, Health Beliefs, and Compliance
 Vol.128 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.28-32 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. Effects of Breast Cancer and Breast Self-Examination Education using Breast Models on Nursing Students Knowledge, Health
Vol.128 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.28-32 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. Effects of Breast Cancer and Breast Self-Examination Education using Breast Models on Nursing Students Knowledge, Health
Healthy Hearts, Healthy Lives Health and Wellness Journal
 Healthy Hearts, Healthy Lives Health and Wellness Journal Healthy Hearts, Healthy Lives You Are in Charge You can prevent and control heart disease by making some lifestyle changes. Keeping your journal
Healthy Hearts, Healthy Lives Health and Wellness Journal Healthy Hearts, Healthy Lives You Are in Charge You can prevent and control heart disease by making some lifestyle changes. Keeping your journal
Febuxostat: a safe and effective therapy for hyperuricemia and gout
 DRUG EVALUATIO Febuxostat: a safe and effective therapy for hyperuricemia and gout atasha Jordan & Geraldine M McCarthy Author for correspondence Mater Misericordiae University Hospital, Eccles St. Dublin
DRUG EVALUATIO Febuxostat: a safe and effective therapy for hyperuricemia and gout atasha Jordan & Geraldine M McCarthy Author for correspondence Mater Misericordiae University Hospital, Eccles St. Dublin
Clinical Study Urate Lowering Therapy with Febuxostat in Daily Practice A Multicentre, Open-Label, Prospective Observational Study
 International Rheumatology, Article ID 123105, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/123105 Clinical Study Urate Lowering Therapy with Febuxostat in Daily Practice A Multicentre, Open-Label, Prospective
International Rheumatology, Article ID 123105, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/123105 Clinical Study Urate Lowering Therapy with Febuxostat in Daily Practice A Multicentre, Open-Label, Prospective
ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF THE PATIENTS SUFFERING FROM GOUT IN KASHMIR TASHI DOLKAR & UZMA ALI
 International Journal of Agricultural Science and Research (IJASR) ISSN(P): 2250-0057; ISSN(E): 2321-0087 Vol. 7, Issue 1, Feb 2017, 385-396 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF THE PATIENTS
International Journal of Agricultural Science and Research (IJASR) ISSN(P): 2250-0057; ISSN(E): 2321-0087 Vol. 7, Issue 1, Feb 2017, 385-396 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF THE PATIENTS
Participation - Demographics. Age Ranges*
 Participation - Demographics January 1, 2017 - March 31, 2017 Age Ranges* 50% n = 139 42.4% Total 38% 25% 20.9% 20.1% 13% 12.9% 3.6% 0% 18-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60+ * Age ranges
Participation - Demographics January 1, 2017 - March 31, 2017 Age Ranges* 50% n = 139 42.4% Total 38% 25% 20.9% 20.1% 13% 12.9% 3.6% 0% 18-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60+ * Age ranges
uric acid Non electrolytes of the plasma
 73 uric acid Non electrolytes of the plasma 1 Purines and uric acid Fig 2 JFI Uric acid is the major product of catabolism of the purine nucleosides adenosine and guanosine, Uric acid is sparingly soluble
73 uric acid Non electrolytes of the plasma 1 Purines and uric acid Fig 2 JFI Uric acid is the major product of catabolism of the purine nucleosides adenosine and guanosine, Uric acid is sparingly soluble
Zurampic. (lesinurad) New Product Slideshow
 Zurampic (lesinurad) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Zurampic Generic name: Lesinurad Pharmacological class: URAT1 inhibitor Strength and Formulation: 200mg; tablets Manufacturer: Ironwood
Zurampic (lesinurad) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Zurampic Generic name: Lesinurad Pharmacological class: URAT1 inhibitor Strength and Formulation: 200mg; tablets Manufacturer: Ironwood
Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions
 Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions MANAGING ARTHRITIS PAIN For people with arthritis, pain management is more complex than just taking aspirin. Arthritis is a chronic disease
Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions MANAGING ARTHRITIS PAIN For people with arthritis, pain management is more complex than just taking aspirin. Arthritis is a chronic disease
Febuxostat: a new treatment for hyperuricaemia in gout
 Rheumatology 2009;48:ii15 ii19 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep088 Febuxostat: a new treatment for hyperuricaemia in gout N. Lawrence Edwards 1 Febuxostat is a new non-purine xanthine oxidase inhibitor that
Rheumatology 2009;48:ii15 ii19 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep088 Febuxostat: a new treatment for hyperuricaemia in gout N. Lawrence Edwards 1 Febuxostat is a new non-purine xanthine oxidase inhibitor that
GOUT FREE: Beat Gout With Diet And Lifestyle Changes And Live Life Gout Free! By Karl Minner READ ONLINE
 GOUT FREE: Beat Gout With Diet And Lifestyle Changes And Live Life Gout Free! By Karl Minner READ ONLINE Gout Diet Including Food, Drink & Lifestyle Gout can be eliminated through healthy diet and lifestyle
GOUT FREE: Beat Gout With Diet And Lifestyle Changes And Live Life Gout Free! By Karl Minner READ ONLINE Gout Diet Including Food, Drink & Lifestyle Gout can be eliminated through healthy diet and lifestyle
Recent Diuretic Use and the Risk of Recurrent Gout Attacks: The Online Case-Crossover Gout Study
 Recent Diuretic Use and the Risk of Recurrent Gout Attacks: The Online Case-Crossover Gout Study DAVID J. HUNTER, MICHAEL YORK, CHRISTINE E. CHAISSON, RYAN WOODS, JINGBO NIU, and YUQING ZHANG ABSTRACT.
Recent Diuretic Use and the Risk of Recurrent Gout Attacks: The Online Case-Crossover Gout Study DAVID J. HUNTER, MICHAEL YORK, CHRISTINE E. CHAISSON, RYAN WOODS, JINGBO NIU, and YUQING ZHANG ABSTRACT.
Research Shows Healthy Living is Longer Living
 December 2018 Research Shows Healthy Living is Longer Living Research shows that living a healthy lifestyle can add a Researchers from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health conducted a study of
December 2018 Research Shows Healthy Living is Longer Living Research shows that living a healthy lifestyle can add a Researchers from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health conducted a study of
MUSCULOSKELETAL PHARMACOLOGY. A story of the inflamed
 MUSCULOSKELETAL PHARMACOLOGY A story of the inflamed 1 INFLAMMATION Pathophysiology Inflammation Reaction to tissue injury Caused by release of chemical mediators Leads to a vascular response Fluid and
MUSCULOSKELETAL PHARMACOLOGY A story of the inflamed 1 INFLAMMATION Pathophysiology Inflammation Reaction to tissue injury Caused by release of chemical mediators Leads to a vascular response Fluid and
Gout is the most common inflammatory. Evolving Concepts in Gout Diagnosis and Treatment. Objectives
 C L I N I C A L I S S U E S Objectives Evolving Concepts in Gout Diagnosis and Treatment Here s the latest update on this most common inflammatory condition. 1) To examine the significant role of uric
C L I N I C A L I S S U E S Objectives Evolving Concepts in Gout Diagnosis and Treatment Here s the latest update on this most common inflammatory condition. 1) To examine the significant role of uric
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Febuxostat is a medicine used in adults with gout to reduce high levels of uric acid in the blood. Gout results from a build up
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Febuxostat is a medicine used in adults with gout to reduce high levels of uric acid in the blood. Gout results from a build up
EpiDoC data set. W0 EpiReumaPt (CESOP) W0 EpiReumaPt (CESOP)
 EpiDoC data set 1. Data collection Start date 19/09/2011 26/03/2013 01/09/2015 End date 20/12/2013 27/07/2015 Face-to-face Clinical Telephonic Data collection interview assessment interviews n 10,661 3,877
EpiDoC data set 1. Data collection Start date 19/09/2011 26/03/2013 01/09/2015 End date 20/12/2013 27/07/2015 Face-to-face Clinical Telephonic Data collection interview assessment interviews n 10,661 3,877
Copyright 2016 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
 14 The Nurse Practitioner Vol. 41, No. 14 www.tnpj.com 2.5 CONTACT HOURS 2.5 CONTACT HOURS Gout An update on for primary care providers Abstract: This article discusses the current beliefs regarding the
14 The Nurse Practitioner Vol. 41, No. 14 www.tnpj.com 2.5 CONTACT HOURS 2.5 CONTACT HOURS Gout An update on for primary care providers Abstract: This article discusses the current beliefs regarding the
