DEMONSTRATING IMPROVED RO SYSTEM PERFORMANCE WITH NEW LOW DIFFERENTIAL (LD) TECHNOLOGY. Abstract
|
|
|
- Agnes Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEMONSTRATING IMPROVED RO SYSTEM PERFORMANCE WITH NEW LOW DIFFERENTIAL (LD) TECHNOLOGY Rich Franks, Craig Bartels, PhD., Alex Anit, Hydranautics, Oceanside, CA. Abstract A new low differential (LD) pressure brine spacer technology has been developed for the spiral wound element which reduces fouling and improves RO system performance. The new technology uses a chemically enhanced, thicker feed/brine spacer with a unique geometry to reduce biogrowth and colloidal fouling. The use of the new brine spacer leads to less fouling, fewer cleanings, a reduction in differential pressures losses, and lower operating cost. The ability of the new spacer to improve performance and reduce fouling has been demonstrated in the laboratory and in several full scale RO systems. Laboratory testing compared the accumulation of foulants on the conventional spacer and the enhanced spacer in both static and dynamic tests. The conventional spacer accumulated heavier fouling while the improved spacer accumulated less particulate foulants and suppressed biogrowth. The improved spacer was also tested in full scale RO systems and compared to elements with conventional spacer technology. When fouling occurred and differential pressures increased, the systems with the conventional spacer displayed a greater increase in the differential pressure than the systems with the improved spacer technology. To further investigate the benefits of the improved spacer, the elements were removed from these RO systems and analyzed after several months of operation. Elements with the conventional spacer were found to have heavier fouling than elements manufactured with the improved spacer. Both the laboratory testing and the field studies clearly demonstrate the advantage of the improved spacer. The new technology can be used in RO systems to reduce operating cost by reducing fouling and the rate of differential pressure increase and by increasing the effectiveness of chemical cleanings and the time between chemical cleanings.
2 Introduction Fouling is a common aspect of operating an RO system. Successfully designed and operated RO systems with proper pretreatment typically require cleaning four to six times per year. However, as RO membranes are being used to treat more challenging feed waters, there is an increase in the frequency and severity of membrane fouling. Foulants from challenging feed waters come in different forms including colloidal/particulate fouling and biological fouling. A combination of these different foulants makes stable RO operation even more challenging. The potential for colloidal or particulate fouling is measured using the Silt Density Index (SDI) and turbidity. Though membrane manufacturers allow a maximum SDI of 5.0 and a maximum turbidity of 1.0 NTU, lower levels, such as SDI less than 3.0 and turbidity less than 0.1, are more conducive to stable RO operation. The potential for colloidal or particulate fouling is significantly reduced if microfilter or ultrafilter membranes are used as pretreatment ahead of the RO. Unfortunately, the initial capital cost sometimes deters the use of membrane pretreatment. The most difficult type of fouling to mitigate is biological fouling. This stems from the incompatibility of the polyamdie RO membrane with oxidants, such as chlorine, which are commonly used to control biofouling. Alternatives to chlorine for the control of biofouling in an RO system, such as DBNPA or chloramines, are sometimes used. However, their use may be limited by cost, environmental regulations, or ineffectiveness. The development of new Low Differential (LD) pressure brine spacer technology addresses fouling associated with treating challenging feedwaters. The LD technology uses a thicker, 34 mil brine spacer while still maintaining 400 sq ft of active surface area in the eight inch RO element. The thicker spacer reduces the tendency for colloidal material to accumulate in the spacer mesh. The use of a thicker spacer, along with the modified geometry, also reduces hydraulic pressure losses and thus saves energy. Additionally, the new spacer is chemically enhanced to reduce biofouling. Studies done in the laboratory and in the field have proven the spacer s effectiveness at reducing biogrowth on and around the spacer and thus mitigating the increase in system differential pressures associated with biofouling. This leads to a reduction in the number of required cleanings. The improved spacer technology is best utilized in treating any feeds with high colloidal and/or biological fouling potential Thicker Brine Spacer With Improved Geometry When manufacturing the spiral wound RO element, a trade off is made between the thickness of the feed/brine spacer and the amount of active membrane surface area that can be packaged into the element. The conventional spiral wound element, with a diameter of eight inches, is manufactured with 400 square feet of membrane when using a 26 or 28 mil spacer. Historically, if a thicker 31 mil or 34 mil spacer was selected, the membrane surface area would be reduced to 365 square feet. However, due to advances in materials and automated manufacturing, including using robotics for the precise placement of the glue lines, today s element can be constructed with a thicker 34 mil spacer while maintaining 400 square feet of active membrane area. The use of a thicker spacer offers several
3 advantages including lower differential pressures, lower fouling potential, improved membrane cleanings, and better flux distribution between the lead and tail elements of an RO system. By going from a 28 mil spacer to a 34 mil spacer, the thickness of the channel through which the feed flows is increased by 20%. A thicker channel means that less pressure is lost as water travels from the feed to the brine end of the element. In a low pressure RO or NF system with two or three stages and six elements per vessel, the water travels through twelve to eighteen elements before exiting on the brine end of the system. The viscous flow through these 18 element leads to a substantial loss in pressure. Using a thicker spacer, however, can reduce this hydraulic pressure loss. This reduction in differential pressure loss is a significant percentage of the net driving pressure and will result in a reduction in overall system feed pressure. Using a three stage nano filtration plant as an example, a system loaded with 28 mil spacer elements and operating at 85% recovery would require water to travel through 18 elements in series. Feed pressure would be 6.9 bar and differential pressure loss would be 2.0 bar. By increasing spacer thickness to 34 mil, the same system would experience half of the differential pressure loss and operate at a feed pressure of 6.1 bar a 12% reduction in feed pressure and associated energy cost. The thicker spacer also has the advantage of reducing particulate fouling. The thicker channel allows particulate matter to move more freely from the feed to brine end of the element without becoming trapped in the spacer mesh. For those particulates that do become trapped, the thicker channel allows the foulant to be more easily removed during chemical cleanings. A field study done using elements of varying thicknesses illustrates the advantages of the thicker brine spacer. The study was done on high fouling surface water with an average SDI of 4.5 and SDI spikes as high as 6.0. Three separate runs were completed during the study. Each of the three runs lasted more than 250 days and used different spiral elements with brine spacer thicknesses of 28 mil, 31mil, and 34 mil. Performance parameters were monitored and a periodic clean in place () was initiated as necessary. Figure 1 below shows more stable differential pressures and fewer s when using the thicker 34 mil spacer. In the case of the 34 mil spacer, there was almost no increase in differential pressure and no cleanings were required during the 250 day test period.
4 5 Delta-Pressure of 1st stage (bar) mil 31 mil 34 mil Operation Period (days) Figure 1. Performance of RO elements with different brine spacer thickness operating on high fouling feed water with SDI between 4 and 5. Chemically Enhanced Brine Spacer Technology Chemically Enhanced Spacer Technology Demonstrated in Laboratory In addition to an increase in thickness to reduce particulate fouling, the improved spacer is chemically enhanced with a biostatic agent to reduce biofouling. The effectiveness of the biospacer was first demonstrated in the laboratory in static tests. Samples of the conventional spacer and the chemically enhanced spacer were placed in Petri dishes containing bacteria cultured on a 100 ul nutrient. After a five day incubation period, the samples were visually inspected. The biospacer consistently showed minimal growth while the conventional spacer showed heavy growth. Figure 2, for example, shows the difference in growth on the conventional spacer compared to the biospacer after five days of incubation using the colon bacillus bacteria. Similar results were found with a variety of different bacteria tested, including Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. It is important to note that the inhibition of biogrowth occurs not only on the chemically enhanced spacer itself, but also on the area surrounding the spacer. This would suggest that biogrowth would be inhibited on the membrane surface as well. The reduction of biogrowth on the spacer and on the membrane surface surrounding the spacer is confirmed in field studies discussed in more detail below.
5 A B Figure 2. Bacterial growth after five days of incubation in colon bacillus on A) chemically enhanced spacer B) conventional spacer Dynamic studies were also conducted in the laboratory using cell testing with a conventional spacer in parallel with a chemically enhanced spacer (Figure 3). The two cells were exposed to a continuous 0.5 L/min (0.13 gpm) flow of wastewater for a period of one month. Visual inspection of the two brine spacers revealed less fouling on the chemically enhanced spacer than on the conventional spacer. A B Figure 3. Biofouling on A) conventional spacer and B) biospacer after one month of continuous exposure to 0.5 L/min stream of waste water. Chemically Enhanced Spacer Technology Demonstrated in RO Systems The new spacer technology was also tested in several full scale RO systems alongside conventional spacer technology. When biofouling occurred in these systems and differential pressures increased, the elements with the conventional spacer were found to have greater biofouling than elements manufactured with chemically enhanced feed spacer. One RO system in which the chemically enhanced feed spacer was tested alongside the conventional spacer was treating municipal effluent for use in cooling towers at a natural gas power plant in Southern California. The RO system consisted of two trains, Train A and Train B. Each train operated as a single stage with six parallel pressure vessels. Each pressure vessel housed six spiral wound elements in series. System average flux was 10 gfd. Because the trains were single stage
6 running at only 55% recovery, no acid or antiscalant was injected. Due to the absence of chloramines, the trains were routinely flushed with DBNPA twice each week. Pretreatment before the trains consisted of hollow fiber ultrafiltration producing filtrate with an SDI less than 3.0. On February 1, 2009, Train A was loaded with elements containing 32 mil conventional spacer. Train B was loaded with elements containing 32 mil chemically enhanced feed spacer. A single element with conventional spacer was loaded in the lead position of the bottom vessel to act as the control for Train B (Figure 4). Both trains started with similar performance including similar feed pressures of 130 psi and similar differential pressures of 14 psi to 16 psi. Element with conventional spacer Train A with conventional spacer Train B with chemically enhanced spacer + single element with conventional spacer Figure 4. Two single stage trains with four vessels and six elements per vessel. Each train is running at 55% recovery and flux of 10 gfd. Train A is loaded with elements with 32 mil conventional spacer. Train B is loaded with elements with 32 mil chemically enhanced feed spacer spacer and a single element with conventional spacer. After startup, both trains experienced an initial 15% loss in permeability within the first week due to organic fouling. This is typical of an RO system treating municipal wastewater. After the initial loss in permeability, both trains stabilized. The two trains operated stably for a period of two months. Neither train experienced a significant increase in differential pressure due to DBNPA soaking two times per week. Then, starting in the first week of May, 2009, the DBNPA soaking was mistakenly neglected for several weeks. The absence of DBNPA soaking set off a severe biofouling event which caued a rise in differential pressure (dp) in both trains and a loss of normalized flux. Figure 5 shows that the increase in dp was gradual in both trains at first, however, after three or four days, the differential pressure in Train A with conventional spacer began an exponential increase in differential pressure while Train B, with chemically enhanced feed spacer continued a more gradual increase in differential pressure. Fifteen days into the biofoulng event and the differential pressure of the conventional spacer system had increased by 90% from its stable dp value. The system with chemically enhanced feed spacer elements increased in dp by only 30% during the same period.
7 Relative Increase in Differential Pressure Biostatic Spacer vs Conventional Spacer 2.0 Increase in Differential Pressure Relative to Stable Differential Pressures May 3-May Train A - Elements with conventional spacer Train B - Elements with biostatic spacer 4-May 5-May 6-May 7-May 8-May 9-May 10-May 11-May 12-May 13-May 14-May 15-May Date 16-May 17-May 18-May 19-May 20-May 21-May 22-May 23-May 24-May 25-May Figure 5. Relative increase in differential pressure of two RO trains running side by side during a severe biofouling event. Train A (red) operated with conventional spacer elements while Train B (blue) operated with a chemically enhanced spacer elements. Fifteen days after the biofouling event began, the DBNPA flushes were reinstated, but had little effect on recovering performance. A high ph clean was performed on both trains, but had little effect. The biofouling had become too severe. At this point, the four lead elements (three with chemically enhanced spacer and one with conventional spacer) were removed from Train B and returned to the manufacturer for retest, autopsy, and analysis. After draining off excess water, the elements were weighed to determine the mass of any biogrowth that may have accumulated in the elements. The typical weight of an unfouled, wet element is 35 lbs. The weight of the element operating in Train B containing chemically enhanced feed spacer was 36.2 lbs, indicating 1.2 lbs of biomass. The element with the conventional spacer weighed 41.5 lbs, suggesting that 6.5 lbs of biomass had accumulated in the element. The returned lead elements were tested at a standard test condition of 225 psi and 15% recovery on a 1500 ppm NaCl feed solution. Flow, rejection and differential pressure losses were compared to their original performance. As expected, all elements increased in differential pressure, but the increase in dp of the element with the standard spacer was greater than the increase in dp of the element with the chemically enhanced feed spacer. The conventional spacer element had increased from 3.5 psid to 8.8 psid. The element with advanced spacer had increased from a 3.5 psid to 7.3 psid. A similar side by side study was conducted on a system treating high fouling surface water. Two lead elements (one with conventional spacer and one with chemically enhanced feed spacer) were returned after six months of operation. The elements were autopsied and visually inspected. An examination of the brine spacer and the membrane surface of the element with conventional spacer
8 revealed a slimy biofilm. More biofilm coated the lead portion of the element compared to the tail portion. Figure 6 A shows the lead portion of the autopsied element with conventional spacer as the spacer is being lifted away from the membrane surface. The biofilm is clearly seen in the membrane mesh. In contrast, the element with chemically enhanced feed spacer was found to have very little biofilm. Both the membrane surface and the spacer mesh were free of significant biogrowth. As seen in Figure 6 B, the mesh is clear and the membrane surface below the mesh can be easily viewed through the mesh. A B Figure 6. Autopsied membrane and from lead elements that had been operating side by side treating high biofouling surface water. One element A) with conventional spacer and one element B) with chemically enhanced spacer. Conclusion Fouling and cleaning are a common aspect of RO system operation. As more challenging waters are treated by RO and less capital is available for robust pretreatment, fouling becomes more severe and cleanings become more frequent. A new brine spacer has been developed to specifically reduce colloidal fouling and biological fouling. The thickness of the spacer has been increased from the standard 28 mil to a thicker 34 mil. The spacer has also been chemically enhanced with a biostatic agent. This combination of properties is important because fouling is often a complex event. It often has components that relate both to colloidal and to biologically active fouling mechanisms. This new advanced spacer has improvements in thickness, geometry and chemistry to help minimize the impact of complex fouling events. Both laboratory testing and field studies demonstrate the ability of the new brine spacer to reduce fouling, reduce differential pressure losses, and reduce the number of cleanings. Though the advanced spacer does not completely solve the fouling challenges associated with treating very difficult feedwaters, it can be used as one of several strategies in an effort to achieve more stable RO performance and reduce RO operating costs.
FOULING RESISTANT REVERSE OSMOSIS MEMBRANES. Ja-young Koo, Sung Pyo Hong, Hoon Hyung, Young Hun Kim, Sungro Yoon, Soon Sik Kim
 FOULING RESISTANT REVERSE OSMOSIS MEMBRANES Ja-young Koo, Sung Pyo Hong, Hoon Hyung, Young Hun Kim, Sungro Yoon, Soon Sik Kim Filter Business Division Saehan Industries, Inc, 1 Jungsandong, Kyungsan city,
FOULING RESISTANT REVERSE OSMOSIS MEMBRANES Ja-young Koo, Sung Pyo Hong, Hoon Hyung, Young Hun Kim, Sungro Yoon, Soon Sik Kim Filter Business Division Saehan Industries, Inc, 1 Jungsandong, Kyungsan city,
Cross Flow Sampler Fouling Index
 FINAL PROJECT REPORT Cross Flow Sampler Fouling Index Co-Principal Investigators: Dr. Samer Adham, MWH Americas, Inc. Dr. Anthony Fane, University of New South Wales NWRI Final Project Report Cross Flow
FINAL PROJECT REPORT Cross Flow Sampler Fouling Index Co-Principal Investigators: Dr. Samer Adham, MWH Americas, Inc. Dr. Anthony Fane, University of New South Wales NWRI Final Project Report Cross Flow
A Novel Approach for Concentrate
 2018 Multi-States Salinity Summit A Novel Approach for Concentrate Minimization: Phase II February 8, 2018 With Hard Waters, More Water Softeners, More Water Quality Impacts City of Phoenix City of Scottsdale
2018 Multi-States Salinity Summit A Novel Approach for Concentrate Minimization: Phase II February 8, 2018 With Hard Waters, More Water Softeners, More Water Quality Impacts City of Phoenix City of Scottsdale
Introduction of Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) Karen Chan 16 May 2017
 Introduction of Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) Karen Chan 16 May 2017 What you will learn TFF principles and applications in mammalian cell processes TFF vocabulary definitions and key process parameters
Introduction of Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) Karen Chan 16 May 2017 What you will learn TFF principles and applications in mammalian cell processes TFF vocabulary definitions and key process parameters
Final Report. Task 2.5. Development of Salinity Reduction Technologies for Individual Source Waters
 Final Report Task 2.5. Development of Salinity Reduction Technologies for Individual Source Waters Subtask 2.5.2. Development of Salinity Reduction Technologies for Municipal Wastewater Research & Development
Final Report Task 2.5. Development of Salinity Reduction Technologies for Individual Source Waters Subtask 2.5.2. Development of Salinity Reduction Technologies for Municipal Wastewater Research & Development
Technical Summary Radial Deionization TM Low Cost Waste Water Desalination Atlantis Technologies
 Technical Summary Radial Deionization TM Low Cost Waste Water Desalination Atlantis Technologies www.atlantis-water.com Summary Atlantis Technologies has developed a low cost produced water desalination
Technical Summary Radial Deionization TM Low Cost Waste Water Desalination Atlantis Technologies www.atlantis-water.com Summary Atlantis Technologies has developed a low cost produced water desalination
nutrient loss in high moisture forage Department of Animal Sciences IFAS
 Reducing dry matter and nutrient loss in high moisture forage K. Arriola, O. Queiroz, E. Muniz, J. Romero, M. Zarate, J. Hamie and A.T. Adesogan Department of Animal Sciences IFAS Introduction Silage heating
Reducing dry matter and nutrient loss in high moisture forage K. Arriola, O. Queiroz, E. Muniz, J. Romero, M. Zarate, J. Hamie and A.T. Adesogan Department of Animal Sciences IFAS Introduction Silage heating
Completion Fluids Displacement & Cementing Spacers
 Completion Fluids Displacement & Cementing Spacers AADE FLUIDS MANAGEMENT GROUP April 24 th, 2013 Ed Robinson Spacer Objectives COMPLETION FLUID CEMENTING Minimize Thick mud fluid to thin contamination
Completion Fluids Displacement & Cementing Spacers AADE FLUIDS MANAGEMENT GROUP April 24 th, 2013 Ed Robinson Spacer Objectives COMPLETION FLUID CEMENTING Minimize Thick mud fluid to thin contamination
PROGRESS OF OF NANOFILTRATION MEMBRANES. 1 st Korea-US Nano Forum Kew-Ho Lee
 PROGRESS OF OF NANOFILTRATION MEMBRANES 1 st Korea-US Nano Forum 2003. 10. 14 Kew-Ho Lee Membrane and Separation Research Center Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology TEL) 82-42-860-7240 FAX)
PROGRESS OF OF NANOFILTRATION MEMBRANES 1 st Korea-US Nano Forum 2003. 10. 14 Kew-Ho Lee Membrane and Separation Research Center Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology TEL) 82-42-860-7240 FAX)
Amalgam Containment and Recycling: Attaining Zero Mercury Discharge in Dental Office Wastewater
 Amalgam Containment and Recycling: Attaining Zero Mercury Discharge in Dental Office Wastewater Legislation: Regulations Effective December 31, 2013 Amalgam Separator; installation and operation; Requirements.
Amalgam Containment and Recycling: Attaining Zero Mercury Discharge in Dental Office Wastewater Legislation: Regulations Effective December 31, 2013 Amalgam Separator; installation and operation; Requirements.
Anti-(bio)fouling composite membranes by Polyacrylic acid/poly(vinyl alcohol) electrospun layer
 Anti-(bio)fouling composite membranes by Polyacrylic acid/poly(vinyl alcohol) electrospun layer Berta Díez Odriozola Chemical Engineering Department Universidad de Alcalá Madrid Spain Introduction NEW
Anti-(bio)fouling composite membranes by Polyacrylic acid/poly(vinyl alcohol) electrospun layer Berta Díez Odriozola Chemical Engineering Department Universidad de Alcalá Madrid Spain Introduction NEW
Solubilization of organic materials in wastewater treatment
 United States Patent 4,882,059 Wong, et al. November 21, 1989 Solubilization of organic materials in wastewater treatment Abstract A method for solubilizing particulate or colloidal materials in wastewater
United States Patent 4,882,059 Wong, et al. November 21, 1989 Solubilization of organic materials in wastewater treatment Abstract A method for solubilizing particulate or colloidal materials in wastewater
THE ART TO CLEAR SOLUTIONS
 THE ART TO CLEAR SOLUTIONS FOOD AND BEVERAGE BEVERAGES Proteins and more... ln recent years membrane filtration as a modern and innovative technology has undergone significant developments and meanwhile
THE ART TO CLEAR SOLUTIONS FOOD AND BEVERAGE BEVERAGES Proteins and more... ln recent years membrane filtration as a modern and innovative technology has undergone significant developments and meanwhile
Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography.
 Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography. Representative low-magnification scanning electron micrographs of a) Black silicon (bsi) and b) Diplacodes bipunctata dragonfly
Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography. Representative low-magnification scanning electron micrographs of a) Black silicon (bsi) and b) Diplacodes bipunctata dragonfly
Flocon 885. Biodegradable Antiscalant for Reverse Osmosis
 Flocon 885 Biodegradable Antiscalant for Reverse Osmosis Flocon 885 General information Flocon 885 isa unique, biodegradable& Phosphorusfree antiscalant for Reverse Osmosis systems Based on Polycarboxylic
Flocon 885 Biodegradable Antiscalant for Reverse Osmosis Flocon 885 General information Flocon 885 isa unique, biodegradable& Phosphorusfree antiscalant for Reverse Osmosis systems Based on Polycarboxylic
3. Valorization of olive oil waste streams by the development of thin film composite membranes for selective removal of polyphenols BGU, Dr. C.
 3. Valorization of olive oil waste streams by the development of thin film composite membranes for selective removal of polyphenols BGU, Dr. C. Linder Development Objectives Cost effective Extraction of
3. Valorization of olive oil waste streams by the development of thin film composite membranes for selective removal of polyphenols BGU, Dr. C. Linder Development Objectives Cost effective Extraction of
WATER TREATMENT COMPONENTS. Membranes reverse osmosis and Ultra Filtration
 WATER TREATMENT COMPONENTS Membranes reverse osmosis and Ultra Filtration CSM 2 ½ Membranes LOW PRESSURE LPM MEMBRANES REF. OLD REF. MODEL NSF/ANSI DM174-2004 MCRE2514-TL DC060 RE2514-TL - Compliant MCRE2514-TLF
WATER TREATMENT COMPONENTS Membranes reverse osmosis and Ultra Filtration CSM 2 ½ Membranes LOW PRESSURE LPM MEMBRANES REF. OLD REF. MODEL NSF/ANSI DM174-2004 MCRE2514-TL DC060 RE2514-TL - Compliant MCRE2514-TLF
Unit 4 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 4 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 4 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
MEMBRANE SURFACE MODIFICATION BY NANOSILVER FOR BIOFOULING RESTRICTION
 MEMBRANE SURFACE MODIFICATION BY NANOSILVER FOR BIOFOULING RESTRICTION DOLINA Jan 1, DLASK Ondřej 2, LEDERER Tomáš 1 and DVOŘÁK Lukáš 1 1 Centre for Nanomaterials, Advanced Technologies and Innovation,
MEMBRANE SURFACE MODIFICATION BY NANOSILVER FOR BIOFOULING RESTRICTION DOLINA Jan 1, DLASK Ondřej 2, LEDERER Tomáš 1 and DVOŘÁK Lukáš 1 1 Centre for Nanomaterials, Advanced Technologies and Innovation,
Super Concentrated Coconut Water
 Super Concentrated Coconut Water Using Aquaporin Inside forward osmosis CONCENTRATE UP TO 65 BRIX UNIQUE CUTTING-EDGE PROCESS IMPROVED LOGISTICS Improved coconut water distribution logistics SUPER CONCENTRATION
Super Concentrated Coconut Water Using Aquaporin Inside forward osmosis CONCENTRATE UP TO 65 BRIX UNIQUE CUTTING-EDGE PROCESS IMPROVED LOGISTICS Improved coconut water distribution logistics SUPER CONCENTRATION
Using Membrane Filtration Techniques to Fractionate Greek Yogurt Acid Whey into Value Added Ingredients
 Using Membrane Filtration Techniques to Fractionate Greek Yogurt Acid Whey into Value Added Ingredients B. Chen 1, K. E. Smith 2, J. A. Lucey 1,2, R. Kalscheuer 2, and M. Molitor 2 1 University of Wisconsin
Using Membrane Filtration Techniques to Fractionate Greek Yogurt Acid Whey into Value Added Ingredients B. Chen 1, K. E. Smith 2, J. A. Lucey 1,2, R. Kalscheuer 2, and M. Molitor 2 1 University of Wisconsin
FIT TECHNICAL DATA. Summary of Research Studies and Production Trials
 FIT TECHNICAL DATA Summary of Research Studies and Production Trials Fit Efficacy vs. Bacteria Pathogens Bacteria Pathogen Staphylococcus Aureus (ATCC 8) Listeria Monocytogenes (ATCC 9) Escherichia Coli
FIT TECHNICAL DATA Summary of Research Studies and Production Trials Fit Efficacy vs. Bacteria Pathogens Bacteria Pathogen Staphylococcus Aureus (ATCC 8) Listeria Monocytogenes (ATCC 9) Escherichia Coli
Measuring Osmotic Potential
 Measuring Osmotic Potential INTRODUCTION All cells require essential materials to ensure their survival. Chemical, physical, and biological processes are used to move these materials inside of cells. Similar
Measuring Osmotic Potential INTRODUCTION All cells require essential materials to ensure their survival. Chemical, physical, and biological processes are used to move these materials inside of cells. Similar
Novel ceramic membranes for water purification and food industry Boffa, Vittorio
 Aalborg Universitet Novel ceramic membranes for water purification and food industry Boffa, Vittorio Published in: PPM 2013 abstracts Publication date: 2013 Document Version Early version, also known as
Aalborg Universitet Novel ceramic membranes for water purification and food industry Boffa, Vittorio Published in: PPM 2013 abstracts Publication date: 2013 Document Version Early version, also known as
Important: Use the INSTRUCTIONS at the end to fill out each question on this form.
 ONE-TIME COMPLIANCE REPORT FOR DENTAL DISCHARGERS To comply with 40 Code of Federal Regulations 441.50 relating to Effluent Limitation Guidelines and Standards for the Dental Office category, this form
ONE-TIME COMPLIANCE REPORT FOR DENTAL DISCHARGERS To comply with 40 Code of Federal Regulations 441.50 relating to Effluent Limitation Guidelines and Standards for the Dental Office category, this form
Ultrafiltration of protein based solution: Study of membrane fouling
 6 th International Conference on Sustainable Solid Waste Management NAXOS 2018 Ultrafiltration of protein based solution: Study of membrane fouling Simona M.Miron, Patrick Dutournié, Arnaud Ponche Institut
6 th International Conference on Sustainable Solid Waste Management NAXOS 2018 Ultrafiltration of protein based solution: Study of membrane fouling Simona M.Miron, Patrick Dutournié, Arnaud Ponche Institut
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore.
 This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Design and development of novel feed spacers in spiral wound membrane modules with 3D printing Author(s)
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Design and development of novel feed spacers in spiral wound membrane modules with 3D printing Author(s)
Name # Class Regents Review Human Body Systems
 Name # Class Regents Review Human Body Systems 1. An accident resulted in a man's hand being cut off from his arm. Paramedics arriving first on the scene placed the cut-off hand in ice. The man and his
Name # Class Regents Review Human Body Systems 1. An accident resulted in a man's hand being cut off from his arm. Paramedics arriving first on the scene placed the cut-off hand in ice. The man and his
Innovative Cement Spacer System for Effective Zonal Isolation in Lost Circulation Zones. Hector Castellanos, M & D Industries of Louisiana, Inc.
 Hector Castellanos, M & D Industries of Louisiana, Inc. Abstract Cementing is a critical operation for the construction of onshore and offshore wells. In recent years, cementing spacer developments have
Hector Castellanos, M & D Industries of Louisiana, Inc. Abstract Cementing is a critical operation for the construction of onshore and offshore wells. In recent years, cementing spacer developments have
V E T I V E R S Y S T E M U S E D I N W A S T E W A T E R T R E A T M E N T
 V E T I V E R S Y S T E M U S E D I N W A S T E W A T E R T R E A T M E N T Abstract: The concern for environmental health is a topic of discussion and a global alert that is reflected in many movements
V E T I V E R S Y S T E M U S E D I N W A S T E W A T E R T R E A T M E N T Abstract: The concern for environmental health is a topic of discussion and a global alert that is reflected in many movements
Information Reviewed and Reaffirmed September No. 40. (' %)Zik5.5 4G A WATER-RESISTANT ANIMAL GLUE
 (' %)Zik5.5 4t4 4G A WATER-RESISTANT ANIMAL GLUE Information Reviewed and Reaffirmed September 1955 No. 40 FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY MADISON 5, WISCONSIN UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST
(' %)Zik5.5 4t4 4G A WATER-RESISTANT ANIMAL GLUE Information Reviewed and Reaffirmed September 1955 No. 40 FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY MADISON 5, WISCONSIN UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST
TRANSPORT OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND NOM
 TRANSPORT OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND NOM IN NF AND TIGHT UF MEMBRANES Gun-Young Park *, Jaeweon Cho * Department of environmental science and engineering GIST, 1 Oryong-dong, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-712, Korea
TRANSPORT OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND NOM IN NF AND TIGHT UF MEMBRANES Gun-Young Park *, Jaeweon Cho * Department of environmental science and engineering GIST, 1 Oryong-dong, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-712, Korea
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Modified cellulosic nanofiltration membrane with improved characteristics for desalination and concentration of reactive dyest
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol.3,May 1996,pp. 131-135 Modified cellulosic nanofiltration membrane with improved characteristics for desalination and concentration of reactive dyest G Venkidachalam
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol.3,May 1996,pp. 131-135 Modified cellulosic nanofiltration membrane with improved characteristics for desalination and concentration of reactive dyest G Venkidachalam
UMR Series Features and Benefits... 3 How to order... 3 Dimensionsder... 4
 Table of Contents UMR Series...2-4 Features and enefits... 3 How to order... 3 Dimensionsder... 4 Numatics 2009 Rev. 1/06 2 UMR Series The UMR Series Mini Regenerative Desiccant Dryer offers a total cleaning
Table of Contents UMR Series...2-4 Features and enefits... 3 How to order... 3 Dimensionsder... 4 Numatics 2009 Rev. 1/06 2 UMR Series The UMR Series Mini Regenerative Desiccant Dryer offers a total cleaning
In-Use Evaluation Report
 In-Use Evaluation Report 160127.3WIN Pall QPoint TM Shower Water Filter Assembly Reusable Docking Station - Shower Assembly (QDS) and Disposable Filter Capsule for up to 62 Day Use - Shower (QR212 and
In-Use Evaluation Report 160127.3WIN Pall QPoint TM Shower Water Filter Assembly Reusable Docking Station - Shower Assembly (QDS) and Disposable Filter Capsule for up to 62 Day Use - Shower (QR212 and
EFFECTS OF OSMOTIC PRESSURE ON MICROBIAL GROWTH
 Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 5 EFFECTS OF OSMOTIC PRESSURE ON MICROBIAL GROWTH Principle and Purpose Microorganisms are surrounded by a selectively-permeable, plasma membrane that helps
Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 5 EFFECTS OF OSMOTIC PRESSURE ON MICROBIAL GROWTH Principle and Purpose Microorganisms are surrounded by a selectively-permeable, plasma membrane that helps
Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family.
 PEP CONNECT PEP Talk Outline P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n P r o g r a m Your Treatment Options Part 1 Peritoneal Dialysis Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family. This
PEP CONNECT PEP Talk Outline P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n P r o g r a m Your Treatment Options Part 1 Peritoneal Dialysis Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family. This
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Peritoneal Dialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. There are 2 types of PD: continuous ambulatory
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function. Biology 12 Chapter 4
 Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
UV Pure Ultraviolet Calf Milk Purifier. Revolutionary technology to purify calf milk using ultraviolet (UV) light
 UV Pure Ultraviolet Calf Milk Purifier Revolutionary technology to purify calf milk using ultraviolet (UV) light 2 GEA UV PURE ULTRAVIOLET CALF MILK PURIFIER Care of Your Young Calves Early nutrition is
UV Pure Ultraviolet Calf Milk Purifier Revolutionary technology to purify calf milk using ultraviolet (UV) light 2 GEA UV PURE ULTRAVIOLET CALF MILK PURIFIER Care of Your Young Calves Early nutrition is
LAB 04 Diffusion and Osmosis
 LAB 04 Diffusion and Osmosis Objectives: Describe the physical mechanisms of diffusion and osmosis. Understand the relationship between surface area and rate of diffusion. Describe how molar concentration
LAB 04 Diffusion and Osmosis Objectives: Describe the physical mechanisms of diffusion and osmosis. Understand the relationship between surface area and rate of diffusion. Describe how molar concentration
MMS AG Membrane Systems Milk Fractionation
 MMS AG Milk Fractionation George Bou-Habib MMS - Company background Founded in June 1995 Based in Zürich, Switzerland. 30 Employees In-house process development, engineering and construction. Industrial
MMS AG Milk Fractionation George Bou-Habib MMS - Company background Founded in June 1995 Based in Zürich, Switzerland. 30 Employees In-house process development, engineering and construction. Industrial
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
Dental Amalgam Rule Update
 Dental Amalgam Rule Update NACWA National Pretreatment Workshop San Antonio, Texas May 17, 2017 Jay Pimpare EPA New England Pretreatment Coordinator 1 40 CFR 441 Dental Rule Schedule Proposal Federal Register
Dental Amalgam Rule Update NACWA National Pretreatment Workshop San Antonio, Texas May 17, 2017 Jay Pimpare EPA New England Pretreatment Coordinator 1 40 CFR 441 Dental Rule Schedule Proposal Federal Register
Flume Installation Instructions
 Flume Installation Instructions To ensure a successful installation, it is important to keep the following points in mind: 1) There should be no bend, dips, elbows, or flow junction immediately upstream
Flume Installation Instructions To ensure a successful installation, it is important to keep the following points in mind: 1) There should be no bend, dips, elbows, or flow junction immediately upstream
12. ZINC - The Major Minor
 12. ZINC - The Major Minor It is the opinion of many that after nitrogen, zinc is the most limiting nutrient toward achieving maximum crop yields. More and more zinc deficiencies are being reported - many
12. ZINC - The Major Minor It is the opinion of many that after nitrogen, zinc is the most limiting nutrient toward achieving maximum crop yields. More and more zinc deficiencies are being reported - many
The Volume POD as an Optimisation Tool of Multiple NDT Inspections of Complex Geometries
 2nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2010 - We.5.B.3 The Volume POD as an Optimisation Tool of Multiple NDT Inspections of Complex Geometries Mato PAVLOVIC, Christina MÜLLER, BAM, Germany Christian
2nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2010 - We.5.B.3 The Volume POD as an Optimisation Tool of Multiple NDT Inspections of Complex Geometries Mato PAVLOVIC, Christina MÜLLER, BAM, Germany Christian
Description The 4000 Series offers up to 8600 in-lb of torque and 25 gpm (continuous ratings). This is the corner stone of the Char-Lynn line.
 Highlights Features ety of mounting flanges and output shafts options Benefits motor into a system tough applications Applications Description The 0 Series offers up to 0 in-lb of torque and gpm (continuous
Highlights Features ety of mounting flanges and output shafts options Benefits motor into a system tough applications Applications Description The 0 Series offers up to 0 in-lb of torque and gpm (continuous
High Precision UTDR Measurements by Sonic Velocity Compensation with Reference Transducer
 Sensors 2014, 14, 11682-11690; doi:10.3390/s140711682 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 1424-8220 www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors High Precision UTDR Measurements by Sonic Velocity Compensation with Reference
Sensors 2014, 14, 11682-11690; doi:10.3390/s140711682 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 1424-8220 www.mdpi.com/journal/sensors High Precision UTDR Measurements by Sonic Velocity Compensation with Reference
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page:
 Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
Allen Keim II Fisheries Technician Cooperative Nursery Unit
 Allen Keim II Fisheries Technician Cooperative Nursery Unit Mission: To protect, conserve, and enhance the Commonwealth s aquatic resources and provide fishing and boating opportunities Overview Advantages
Allen Keim II Fisheries Technician Cooperative Nursery Unit Mission: To protect, conserve, and enhance the Commonwealth s aquatic resources and provide fishing and boating opportunities Overview Advantages
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes
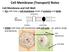 Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Control of irreversible fouling by application of dynamic membranes
 Desalination 192 (2006) 63 67 Control of irreversible fouling by application of dynamic membranes M.T. Pessoa de Amorim*, Ilia Rosa Afonso Ramos Department of Textile Engineering, University of Minho,
Desalination 192 (2006) 63 67 Control of irreversible fouling by application of dynamic membranes M.T. Pessoa de Amorim*, Ilia Rosa Afonso Ramos Department of Textile Engineering, University of Minho,
1 Development of Membrane Processes 1 K. Smith. 1.1 Historical background Basic principles of membrane separations 3
 1 Development of Membrane Processes 1 K. Smith 1.1 Historical background 1 1.2 Basic principles of membrane separations 3 1.2.1 Depth versus screen filters 3 1.2.2 Isotropic versus anisotropic membranes
1 Development of Membrane Processes 1 K. Smith 1.1 Historical background 1 1.2 Basic principles of membrane separations 3 1.2.1 Depth versus screen filters 3 1.2.2 Isotropic versus anisotropic membranes
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Introduction to Wolf Trax
 Introduction to Wolf Trax Wolf Trax INNOVATIVE NUTRIENTS Plant Nutrition Specialists Selling innovative nutrients since 2002 Sales in 90 regulatory jurisdictions worldwide Over 20 million acres of DDP
Introduction to Wolf Trax Wolf Trax INNOVATIVE NUTRIENTS Plant Nutrition Specialists Selling innovative nutrients since 2002 Sales in 90 regulatory jurisdictions worldwide Over 20 million acres of DDP
Hard Hat Services ph: hardhatinc.com 932 N. Wright St., Suite 160 Naperville, IL 60563
 Interstate Power and Light Company Burlington Generation Station CCR Surface Impoundment Annual Inspection Report 154.018.012.001 Report issued: December 21, 2016 Hard Hat Services ph: 877-630-7428 hardhatinc.com
Interstate Power and Light Company Burlington Generation Station CCR Surface Impoundment Annual Inspection Report 154.018.012.001 Report issued: December 21, 2016 Hard Hat Services ph: 877-630-7428 hardhatinc.com
Membranes 9/15/2016. Phospholipids. Phospholipid bilayer
 Membranes Phospholipids Type of complex lipid that forms biological membranes. Have a polar hydrophilic head and two nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Amphipathic. This causes the tails to cluster together in
Membranes Phospholipids Type of complex lipid that forms biological membranes. Have a polar hydrophilic head and two nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Amphipathic. This causes the tails to cluster together in
Introduction to Membrane
 Heinrich Strathmann Introduction to Membrane Science and Technology WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KG aa V Preface Symbols XIII XV 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Overview of Membrane Science and Technology
Heinrich Strathmann Introduction to Membrane Science and Technology WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KG aa V Preface Symbols XIII XV 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Overview of Membrane Science and Technology
Role of Microorganisms in Wastewater Treatment
 Role of Microorganisms in Wastewater Treatment The stabilization of organic matter is accomplished biologically using a variety of microorganisms Carbonaceous organic matter Gases + cell tissue Colloidal
Role of Microorganisms in Wastewater Treatment The stabilization of organic matter is accomplished biologically using a variety of microorganisms Carbonaceous organic matter Gases + cell tissue Colloidal
Warm Up 12/06/2018. In a Solution of Salt Water, which substance acts as the Solvent and which substance acts as the Solute?
 Warm Up 12/06/2018 In a Solution of Salt Water, which substance acts as the Solvent and which substance acts as the Solute? Cell Membrane and Cell Transport How Nutrients move in and Wastes Move Out of
Warm Up 12/06/2018 In a Solution of Salt Water, which substance acts as the Solvent and which substance acts as the Solute? Cell Membrane and Cell Transport How Nutrients move in and Wastes Move Out of
THE INFLUENCE OF CORN SILAGE FEEDING LEVEL ON BEEF STEER GROWTH PERFORMANCE AND CARCASS QUALITY
 THE INFLUENCE OF CORN SILAGE FEEDING LEVEL ON BEEF STEER GROWTH PERFORMANCE AND CARCASS QUALITY Summary P.L. McEwen Ridgetown College, University of Guelph Other growth rate and feed intake comparisons
THE INFLUENCE OF CORN SILAGE FEEDING LEVEL ON BEEF STEER GROWTH PERFORMANCE AND CARCASS QUALITY Summary P.L. McEwen Ridgetown College, University of Guelph Other growth rate and feed intake comparisons
There are ten different categories of commercial smokeless tobacco products:
 PhenX Measure: Physical Properties of Tobacco Products (#730500) PhenX Protocol: Physical Properties of Tobacco Products - Smokeless Tobacco (#730502) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): Sample
PhenX Measure: Physical Properties of Tobacco Products (#730500) PhenX Protocol: Physical Properties of Tobacco Products - Smokeless Tobacco (#730502) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): Sample
Outbreak of Bacillus cereus in a burn unit
 Outbreak of Bacillus cereus in a burn unit Annette Schuermans Katholieke Universiteit Leuven/ University Hospitals Leuven October 14 th 2010 UZ Leuven 1 3 1 2 2 1, 22, 22% TBSA due to a car accident 2,
Outbreak of Bacillus cereus in a burn unit Annette Schuermans Katholieke Universiteit Leuven/ University Hospitals Leuven October 14 th 2010 UZ Leuven 1 3 1 2 2 1, 22, 22% TBSA due to a car accident 2,
Polysorb TM. Braided, Synthetic Absorbable Suture STRENGTH AND SECURITY WHEN IT S NEEDED MOST
 Polysorb TM Braided, Synthetic Absorbable Suture STRENGTH AND SECURITY WHEN IT S NEEDED MOST We re all part of the same community. A community entrusted with enhancing and saving the lives of patients.
Polysorb TM Braided, Synthetic Absorbable Suture STRENGTH AND SECURITY WHEN IT S NEEDED MOST We re all part of the same community. A community entrusted with enhancing and saving the lives of patients.
New Reduced Toxicity cleaning system is granted EPA registration as a Sanitizer/Virucide (EPA Registration No. s and )
 New Reduced Toxicity cleaning system is granted EPA registration as a Sanitizer/Virucide (EPA Registration No. s 069268-1 and 069268-2) H 2 Orange 2 is a recently developed multi-purpose cleaning system
New Reduced Toxicity cleaning system is granted EPA registration as a Sanitizer/Virucide (EPA Registration No. s 069268-1 and 069268-2) H 2 Orange 2 is a recently developed multi-purpose cleaning system
Water Quality and Treatments
 Water Quality and Treatments Image credit: subbotina / 123RF.com While many challenges in greenhouse production are beyond our control, poor water quality should not be one of them. By John M. Dole Growing
Water Quality and Treatments Image credit: subbotina / 123RF.com While many challenges in greenhouse production are beyond our control, poor water quality should not be one of them. By John M. Dole Growing
No. GA Page 1 of 7 Effective Date: 03/04/ CFR (c), ANSI/ISEA Z TITLE: Chancellor Date: 03/04/16
 TEXAS STATE TECHNICAL COLLEGE STATEWIDE OPERATING STANDARD No. GA 1.6.9 Page 1 of 7 Effective Date: 03/04/16 DIVISION: SUBJECT: AUTHORITY: General Administration Eyewash and Shower Stations 29 CFR 1910.151(c),
TEXAS STATE TECHNICAL COLLEGE STATEWIDE OPERATING STANDARD No. GA 1.6.9 Page 1 of 7 Effective Date: 03/04/16 DIVISION: SUBJECT: AUTHORITY: General Administration Eyewash and Shower Stations 29 CFR 1910.151(c),
Osmosis and Diffusion: How biological membranes are important This page is a lab preparation guide for instructors.
 Osmosis and Diffusion: How biological membranes are important This page is a lab preparation guide for instructors. **All solutions and dialysis bags can easily be prepared prior to lab start to maximize
Osmosis and Diffusion: How biological membranes are important This page is a lab preparation guide for instructors. **All solutions and dialysis bags can easily be prepared prior to lab start to maximize
Strength Training Equipment
 Lesson Strength Training Equipment By Carone Fitness The health and fitness industry today is booming. Not only are various types of exercises constantly evolving and increasing in popularity, but the
Lesson Strength Training Equipment By Carone Fitness The health and fitness industry today is booming. Not only are various types of exercises constantly evolving and increasing in popularity, but the
I. Chemical Properties of Phospholipids. Figure 1: Phospholipid Molecule. Amphiphatic:
 I. Chemical Properties of Phospholipids Figure 1: Phospholipid Molecule Amphiphatic: a) The amphiphatic nature & cylindrical shape of phospholipids contributes to their ability to assume bilayers in an
I. Chemical Properties of Phospholipids Figure 1: Phospholipid Molecule Amphiphatic: a) The amphiphatic nature & cylindrical shape of phospholipids contributes to their ability to assume bilayers in an
Having a PEG tube inserted
 Having a PEG tube inserted This information leaflet is for patients who are having a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube inserted. It explains what is involved, what to expect and what significant
Having a PEG tube inserted This information leaflet is for patients who are having a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube inserted. It explains what is involved, what to expect and what significant
Liquid-Liquid Extraction Prof. Mukesh Doble Department Of Biotechnology Indian Institute Of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 19
 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Prof. Mukesh Doble Department Of Biotechnology Indian Institute Of Technology, Madras Lecture - 19 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Let us continue with the Liquid- Liquid Extraction.
Liquid-Liquid Extraction Prof. Mukesh Doble Department Of Biotechnology Indian Institute Of Technology, Madras Lecture - 19 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Let us continue with the Liquid- Liquid Extraction.
The problem of constipated barns Economics and throughput
 The problem of constipated barns Economics and throughput Focus on the Future conference March 27, 2007 Ben Woolley Vice President Sunterra Farms Ltd Constipation Noun 1. Irregular and frequent or difficult
The problem of constipated barns Economics and throughput Focus on the Future conference March 27, 2007 Ben Woolley Vice President Sunterra Farms Ltd Constipation Noun 1. Irregular and frequent or difficult
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Introduction...5 What the Wrong Kind of Water...5 Benefits of Alkaline Water...8
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...5 What the Wrong Kind of Water...5 Benefits of Alkaline Water...8 10 Reasons to Drink Alkaline Ionized Every Day...10 #1 Hydration...11 #2 Detoxification (Cleansing)...13
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...5 What the Wrong Kind of Water...5 Benefits of Alkaline Water...8 10 Reasons to Drink Alkaline Ionized Every Day...10 #1 Hydration...11 #2 Detoxification (Cleansing)...13
Lumbar Nerve Root Decompression for Foraminal Stenosis
 Lumbar Nerve Root Decompression for Foraminal Stenosis Issue 5: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed as
Lumbar Nerve Root Decompression for Foraminal Stenosis Issue 5: March 2016 Review date: February 2019 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed as
Cellular Transport. 1. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure below.
 Name: Date: 1. potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure below. Which diagram best represents the net movement of molecules?.. C. D. page 1 2. The following question(s) is/are
Name: Date: 1. potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure below. Which diagram best represents the net movement of molecules?.. C. D. page 1 2. The following question(s) is/are
ADVANCED VAPOUR DEGREASING WITHOUT OZONE DEPLETING SOLVENTS
 ABSTRACT ADVANCED VAPOUR DEGREASING WITHOUT OZONE DEPLETING SOLVENTS 1 of 5 An advanced vapour degreasing process has been developed which offers the ease of use, fast drying, and excellent cleaning performance
ABSTRACT ADVANCED VAPOUR DEGREASING WITHOUT OZONE DEPLETING SOLVENTS 1 of 5 An advanced vapour degreasing process has been developed which offers the ease of use, fast drying, and excellent cleaning performance
EFFECTS OF SUPPLEMENTAL PROTEIN REMOVAL ON TOTAL AND ACID-RESISTANT E. COLI, TOTAL COLIFORMS, AND PERFORMANCE IN FINISHING STEERS
 Cattlemen s Day 2003 EFFECTS OF SUPPLEMENTAL PROTEIN REMOVAL ON TOTAL AND ACID-RESISTANT E. COLI, TOTAL COLIFORMS, AND PERFORMANCE IN FINISHING STEERS M. A. Greenquist, J. S. Drouillard, R. K. Phebus,
Cattlemen s Day 2003 EFFECTS OF SUPPLEMENTAL PROTEIN REMOVAL ON TOTAL AND ACID-RESISTANT E. COLI, TOTAL COLIFORMS, AND PERFORMANCE IN FINISHING STEERS M. A. Greenquist, J. S. Drouillard, R. K. Phebus,
Ingredient Calculations
 Ingredient Calculations PROJECT COORDINATOR Theresa Stretch, MS, RDN, CP-FS EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR Aleshia Hall-Campbell, PhD, MPH Key Area: 2 Operations Code: 2100 Food Production 2019 Institute of Child
Ingredient Calculations PROJECT COORDINATOR Theresa Stretch, MS, RDN, CP-FS EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR Aleshia Hall-Campbell, PhD, MPH Key Area: 2 Operations Code: 2100 Food Production 2019 Institute of Child
BIO 2 GO! 3211b, 3212b Circulation and Excretion in Plants and Animals
 BIO 2 GO! 3211b, 3212b Circulation and Excretion in Plants and Animals The circulatory system, vascular system, and excretory system work together to feed and clean the body of multicellular organisms.
BIO 2 GO! 3211b, 3212b Circulation and Excretion in Plants and Animals The circulatory system, vascular system, and excretory system work together to feed and clean the body of multicellular organisms.
MONTANA FLUME. User s Manual. Montana (Short Parshall) Flume User s Manual
 MONTANA FLUME User s Manual i Montana (Short Parshall) Flume User s Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction to the Montana Flume... 1 Function... 1 Design... 1 Standards... 2 Accuracy... 3 Dimensions...
MONTANA FLUME User s Manual i Montana (Short Parshall) Flume User s Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction to the Montana Flume... 1 Function... 1 Design... 1 Standards... 2 Accuracy... 3 Dimensions...
Increase Strength, Flexibility, Range of Motion and Endurance. NeckXsystems Guidelines & Exercise. NeckX is Patent Pending
 Increase Strength, Flexibility, Range of Motion and Endurance NeckXsystems Guidelines & Exercise Instructions www.neckxsystems.com NeckX is Patent Pending Guidelines NeckX is an innovative neck exercise
Increase Strength, Flexibility, Range of Motion and Endurance NeckXsystems Guidelines & Exercise Instructions www.neckxsystems.com NeckX is Patent Pending Guidelines NeckX is an innovative neck exercise
PHYSIOEX 3.0 EXERCISE 33B: CARDIOVASCULAR DYNAMICS
 PHYSIOEX 3.0 EXERCISE 33B: CARDIOVASCULAR DYNAMICS Objectives 1. To define the following: blood flow; viscosity; peripheral resistance; systole; diastole; end diastolic volume; end systolic volume; stroke
PHYSIOEX 3.0 EXERCISE 33B: CARDIOVASCULAR DYNAMICS Objectives 1. To define the following: blood flow; viscosity; peripheral resistance; systole; diastole; end diastolic volume; end systolic volume; stroke
Water compartments inside and outside cells maintain a balanced distribution of total body water.
 Chapter 9 Water Balance Chapter 9 Lesson 9.1 Key Concepts Water compartments inside and outside cells maintain a balanced distribution of total body water. The concentration of various solute particles
Chapter 9 Water Balance Chapter 9 Lesson 9.1 Key Concepts Water compartments inside and outside cells maintain a balanced distribution of total body water. The concentration of various solute particles
Teacher Demo/Student Activity: Limit to Cell Size
 SNC2D/2P Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things/Tissues, Organs and Systems Teacher Demo/Student Activity: Limit to Cell Size Topics cell cycle the importance of cell division Timing preparation:
SNC2D/2P Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things/Tissues, Organs and Systems Teacher Demo/Student Activity: Limit to Cell Size Topics cell cycle the importance of cell division Timing preparation:
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane. Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5
 Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Storage of waters, underground, surface, sea and sewage, phenomenon is the more puzzling because the waters in their
 RELATION BETWEEN FOOD CONCENTRATION AND SURFACE FOR BACTERIAL GROWTH1 H. HEUKELEKIAN2 AND A. HELLER3 Agricultural Experiment Station, New Brunswick, New Jersey Received for publication April 19, 1940 Storage
RELATION BETWEEN FOOD CONCENTRATION AND SURFACE FOR BACTERIAL GROWTH1 H. HEUKELEKIAN2 AND A. HELLER3 Agricultural Experiment Station, New Brunswick, New Jersey Received for publication April 19, 1940 Storage
The Effects of Shampoo on Microbial Flora. Andrew Walker Grade 9 Central Catholic High School
 The Effects of Shampoo on Microbial Flora Andrew Walker Grade 9 Central Catholic High School Shampoo Hair care product used to clean hair of unwanted build up Combined soap, water, and herbs to make hair
The Effects of Shampoo on Microbial Flora Andrew Walker Grade 9 Central Catholic High School Shampoo Hair care product used to clean hair of unwanted build up Combined soap, water, and herbs to make hair
Sample Report Only - NOT INTENDED FOR USE
 Project Title: Evaluation of 3 Formulations of [Product] when applied to Stainless Steel Panels and Exposed to [Species]. Sample Report Only - NOT INTENDED FOR USE Project Code: [Code] Test Date(s): October
Project Title: Evaluation of 3 Formulations of [Product] when applied to Stainless Steel Panels and Exposed to [Species]. Sample Report Only - NOT INTENDED FOR USE Project Code: [Code] Test Date(s): October
Final Report. Department of Water Resources. Project: Role of Microfiltration (MF) Cake Layer Composition and Stability in Desalination Efficiency
 Final Report Department of Water Resources Project: Role of Microfiltration (MF) Cake Layer Composition and Stability in Desalination Efficiency Submitted by: Jana Safarik and Donald W. Phipps, Jr. Research
Final Report Department of Water Resources Project: Role of Microfiltration (MF) Cake Layer Composition and Stability in Desalination Efficiency Submitted by: Jana Safarik and Donald W. Phipps, Jr. Research
REPACKAGING. APPROVED CONTAINERS
 REPACKAGING. APPROVED CONTAINERS Working for the World of Tomorrow BOTTLES AGITATE THE PRODUCT BEFORE REPACKAGING The Bottles must fulfill the following requirements: Material: The mouth: The lid: Polyethylene
REPACKAGING. APPROVED CONTAINERS Working for the World of Tomorrow BOTTLES AGITATE THE PRODUCT BEFORE REPACKAGING The Bottles must fulfill the following requirements: Material: The mouth: The lid: Polyethylene
HARRISBURG UNIVERSITY PROJECT LEADERSHIP FORUM- CASE STUDY. Supporting the Marcellus Shale Boom
 HARRISBURG UNIVERSITY PROJECT LEADERSHIP FORUM- CASE STUDY Supporting the Marcellus Shale Boom Marc Reeves, P.G. May 6, 2011 Outline Intro to SAIC Basics on the Marcellus Shale Natural gas demand Nationwide
HARRISBURG UNIVERSITY PROJECT LEADERSHIP FORUM- CASE STUDY Supporting the Marcellus Shale Boom Marc Reeves, P.G. May 6, 2011 Outline Intro to SAIC Basics on the Marcellus Shale Natural gas demand Nationwide
Description The 4000 Series offers up to 8600 in-lb of torque and 25 gpm (continuous ratings). This is the corner stone of the Char-Lynn line.
 Highlights Features displacements, a variety of mounting flanges and output shafts Reliable, proven design High efficiency Environmental protection options Benefits Flexiblilty in designing this motor
Highlights Features displacements, a variety of mounting flanges and output shafts Reliable, proven design High efficiency Environmental protection options Benefits Flexiblilty in designing this motor
A Review of Membranes Classifications, Configurations, Surface Modifications, Characteristics and Its Applications in Water Purification
 Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 2017; 2(2): 57-82 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cbe doi: 10.11648/j.cbe.20170202.11 A Review of Membranes Classifications, Configurations, Surface Modifications,
Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 2017; 2(2): 57-82 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cbe doi: 10.11648/j.cbe.20170202.11 A Review of Membranes Classifications, Configurations, Surface Modifications,
EFFECTS OF CHROMIUM ON REPRODUCTION IN POLYCHAETES
 Philip S. Oshida EFFECTS OF CHROMIUM ON REPRODUCTION IN POLYCHAETES Chromium is discharged into the marine waters off southern California in industrial and municipal wastewater effluents. During the past
Philip S. Oshida EFFECTS OF CHROMIUM ON REPRODUCTION IN POLYCHAETES Chromium is discharged into the marine waters off southern California in industrial and municipal wastewater effluents. During the past
Preventing Legionella Transmission An Environmental Health View
 Preventing Legionella Transmission An Environmental Health View April 25, 2013 Erin Reinsborough Environmental Health Specialist Mission Statement Together with the Halton community, the Health Department
Preventing Legionella Transmission An Environmental Health View April 25, 2013 Erin Reinsborough Environmental Health Specialist Mission Statement Together with the Halton community, the Health Department
Page Number: 1 of
 Page Number: 1 of 7 SECTION 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name: AEROSOL PACKAGED CLEAR CAS Number N/A Hazard Rating: Health: 2 Fire: 4 Reactivity: 1 PPI: Company Identification: DAMPNEY CO
Page Number: 1 of 7 SECTION 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Product Name: AEROSOL PACKAGED CLEAR CAS Number N/A Hazard Rating: Health: 2 Fire: 4 Reactivity: 1 PPI: Company Identification: DAMPNEY CO
