Asthma/COPD. Asthma synopsis. chronic inflammation of bronchial airways bronchi lining bronchi muscles mucus
|
|
|
- Kristian McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Asthma & COPD
2 Asthma synopsis chronic inflammation of bronchial airways bronchi lining bronchi muscles mucus 2
3 Asthma synopsis chest tightness tachypnea wheezing acute broncho-constriction cough shortness of breath resolution? 3
4 Asthma synopsis generally not progressive remitting-relapsing M vs. M goals of therapy: - relieving symptoms - preventing recurrence - preventing bronchial remodeling - decreasing morbidity and related costs 4
5 oral vs. inhaled inhalation Tx: main advantage - main disadvantage - 5
6 oral vs. inhaled 6
7 corticosteroids β 2 -adrenergic agonists theophylline cromolyn/nedocromil ipratropium leukotriene modifiers omalizumab 7
8 corticosteroids β 2 -adrenergic agonists theophylline cromolyn/nedocromil ipratropium leukotriene modifiers omalizumab 8
9 Corticosteroids inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) - 1 st -line for: 9 persistent asthma + rescue SABAs required> 2/wk ICS improve asthma control more effectively in both children and adults than any other single, long-term control medication do. [NHLBI guidelines 2007] ICS are currently the most effective antiinflammatory medications for the treatment of persistent asthma [GINA report 2010]
10 ICS budesonide (Budicort ) fluticasone (Flixotide ) beclomethasone (Qvar ) 10
11 ICS - Mechanism: anti-inflammatory effect airway smooth muscle dilation 11
12 ICS - PK: proper inhalation reduces systemic exposure fate of non-inhaled drug? hepatic metabolism? 12
13 ICS - PK: poor inhaling technique PREVENTION: good inhaling technique 13 use of spacer
14 Spacer use Shake the inhaler well before use (3-4 shakes) 2. Remove the cap from your inhaler, and from your spacer, if it has one 3. Put the inhaler into the spacer 4. Breathe out, away from the spacer 5. Bring the spacer to your mouth, put the mouthpiece between your teeth and close your lips around it 6. Press the top of your inhaler once 7. Breathe in very slowly until you have taken a full breath. If you hear a whistle sound, you are breathing in too fast.slowly breath in. 8. Hold your breath for about ten seconds, then breath out.
15 ICS - benefits chronic use: the most effective Tx for long-term control of asthma in children and adults reduces airway hyper-responsiveness to various bronchial stimulators oral-corticosteroids sparing 15
16 Systemic corticosteroids IV/PO: may be required in acute, severe exacerbations ( status asthmaticus ) upon improvement - tapering off over 1-2wk refractory cases may need PO support for certain periods long-term PO use rarely required (persistent-severe uncontrolled asthma) 16
17 Corticosteroids - general short-term ADEs increase appetite insomnia nervousness anxiety adrenal suppression growth retardation (children) Cushing s syndrome 17
18 Corticosteroids - general long-term ADEs osteoporosis peptic ulcers diabetes weight gain adrenal suppression growth retardation (children) hypokalemia HTN skin thinning immuno-suppression triglycerides, cholesterol infection masking Cushing s syndrome more.. 18
19 ICS - general ADEs overall, ADEs risk significantly reduced with ICS local infections in mouth and pharynx importance of cough long-term high-dose ICS: - cataract (monitor) - osteoporosis (monitor, consider Ca ++ +vit. D) 19 - easy bruising
20 Corticosteroids - DDIs by CYP-450 inducers (phenytoin, phenobarbital, rifampin) / anticoagulant effect antacids ( oral absorption) estrogen ( clearance) live-attenuated vaccines (immuno-suppression) hypokalemic drugs, digoxin generally insignificant with ICS 20
21 corticosteroids β 2 -adrenergic agonists theophylline cromolyn/nedocromil ipratropium leukotriene modifiers omalizumab 21
22 β 2 -adrenergic agonists bronchodilation? anti-inflammatory? 22
23 β 2 -adrenergic agonists short acting (SABAs): salbutamol=albuterol (Ventolin ) terbutaline (Bricalin, Terbulin ) drugs of choice for mild asthma 23
24 β 2 -adrenergic agonists short acting (SABAs): rapid peak effect (0.5-2hr) moderate duration (3-6hr) suitable for.... proper inhalation technique minimizes ADEs ADEs: tachycardia, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, tremor 24
25 β 2 -adrenergic agonists long acting (LABAs): salmeterol (Serevent ) formoterol (Foradil, Oxis ) 25
26 β 2 -adrenergic agonists long acting: delayed peak effect (3-4hr) long duration (12hr) acute vs. chronic use? ADEs generally similar to those of short-acting 26
27 β 2 -adrenergic agonists Long-term safety concerns Controversy has surrounded the use of beta-agonists in asthma patients ever since their introduction over 50 years ago. Numerous studies over many years have shown regular use of beta-agonists are associated with worsening of disease control. Observational studies have consistently shown that the risk of life threatening and fatal asthma attacks increase with the use of these medications. 27
28 β 2 -adrenergic agonists Long-term safety concerns SMART, Chest 2006;129:
29 β 2 -adrenergic agonists Long-term safety concerns - SMART 28 weeks >6,100 centers >26,000 patients (of 60,000 intended) early termination 29
30 β 2 -adrenergic agonists Long-term safety concerns - SMART 30
31 β 2 -adrenergic agonists Long-term safety concerns - conflicting meta-analyses, management: use LABAs in accordance with guidelines: - not 1 st -line! - not as monotherapy! - not for mild asthma! - consider patient characteristics! (adherence, follow-up) 31
32 β 2 -adrenergic agonists LABAs: June 2 nd 2010 Use of a LABA alone without use of a long-term asthma control medication, such as an inhaled corticosteroid, is contraindicated (absolutely advised against) in the treatment of asthma. LABAs should not be used in patients whose asthma is adequately controlled on low or medium dose inhaled corticosteroids. 32
33 33 β 2 -adrenergic agonists LABAs: June 2 nd 2010 LABAs should only be used as additional therapy for patients with asthma who are currently taking but are not adequately controlled on a long-term asthma control medication, such as an ICS. Once asthma control is achieved and maintained, patients should be assessed at regular intervals and step down therapy should begin (e.g., discontinue LABA), if possible without loss of asthma control, and the patient should continue to be treated with a long-term asthma control medication, such as an ICS.
34 Inhaled LABA-CS combinations - salmeterol/fluticasone (Seretide ) - formoterol/budesonide (Symbicort ) for patients requiring both classes adherence promotion 34
35 corticosteroids β 2 -adrenergic agonists theophylline cromolyn/nedocromil ipratropium leukotriene modifiers omalizumab 35
36 Theophylline (Theotrim, Theotard ) methylxanthine derivative structurally-related to caffeine originally isolated from tea (1888) administered orally (sustained release) 36
37 Theophylline - mechanism A number of proposed mechanisms 1. bronchodilator (higher dose, >10mg/kg/d): - phosphodiesterase inhibitor ( camp ) - adenosine receptor antagonist? (adenosine histamine and leukotriene release) 37
38 Theophylline - mechanism A number of proposed mechanisms 2. anti-inflammatory (lower dose): active inflammatory gene transcription site corticosteroids recruitment histone deacetylase inhibition acetylated core histones 38 increased activity low-dose theophylline inflammatory gene transcription inflammatory process
39 Theophylline - PK near-complete absorption significant hepatic metabolism mainly hepatic elimination (varies due to multiple effects) T 1/2 : adults - 8hr, smokers - 5hr, elderly - 12hr 39
40 Theophylline - ADEs narrow therapeutic index: target of mcg/ml ADEs generally concentration-dependent: serum concentration mcg/l mcg/l >35 mcg/l adverse reactions GI nausea, vomiting, pain, CNS insomnia, headache, agitation, tremor, nervousness CV tahcycardia, occasional PVBs VT, frequent PVBs, seizures 40 TDM: 2hr post-oral dose
41 Theophylline - DDIs theophylline effect cimetidine, corticosteroids, macrolides (erythromycin), quinolones (ciprofloxacin), CCBs, BBs, loop diuretics, more theophylline effect antacids (absorption), phenytoin, phenobarbital, rifampin, cigarette smoke, ritonavir, ketoconazole, more.. 41
42 Theophylline - place in therapy decreasing use (ADEs, DDIs, better options); 3 rd -line combination with ICS (steroid-sparing) refractory cases possible comeback as low-dose practice (anti-inflammatory)? 42
43 corticosteroids β 2 -adrenergic agonists theophylline cromolyn/nedocromil ipratropium leukotriene modifiers omalizumab 43
44 Cromolyn/nedocromil mast-cell stabilizers 44
45 Cromolyn/nedocromil mast-cell stabilizers block mast-cell calcium channels mast cell degranulation histamine (+ leukotriene) release inflammatory response 45
46 Cromolyn/nedocromil mast-cell stabilizers for acute asthma attacks: 46
47 Cromolyn/nedocromil only effective as prophylaxis (ineffective for acute episodes) given as inhalation minimal systemic effects (local: irritation, bitter taste, dry mouth) useful in prevention of allergen-induced asthma safe in children, pregnancy 47
48 corticosteroids β 2 -adrenergic agonists theophylline cromolyn/nedocromil ipratropium leukotriene modifiers omalizumab 48
49 Ipratropium (Atrovent ) anticholinergic agent (atropine derivative) blocks vagally-mediated contraction of smooth muscle peak effect: 1.5-2hr duration of effect: 4-6hr negligible ADEs (does not penetrate BBB) for preventive Tx rarely used for asthma 49
50 β 2 -adrenergic agonists corticosteroids theophylline cromolyn/nedocromil ipratropium leukotriene modifiers omalizumab 50
51 Leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) cysteinyl leukotrienes 51
52 Leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) montelukast (Singulair ) selective, reversible antagonist of cysteinyl-1 receptor for long-term control once-daily (evening) oral administration (chewable) extensive hepatic metabolism fecal excretion 52
53 Leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) montelukast (Singulair ) selective, reversible antagonist of cysteinyl-1 receptor once-daily (evening) oral administration (chewable) extensive hepatic metabolism fecal excretion ADEs: headache (18%), impaired LFTs, dyspepsia, cough DDIs: 40% by phenobarbital (rifampin?) 53
54 LTRAs montelukast (Singulair ) for long-term control LABA/ICS sparing additional indication: prophylaxis of exercise-induced bronchospasm 54
55 corticosteroids β 2 -adrenergic agonists theophylline cromolyn/nedocromil ipratropium leukotriene modifiers omalizumab 55
56 Omalizumab (Xolair ) recombinant DNA-derived selective IgE monoclonal antibody USA 2003 data: 60% of asthma allergen-induced 56
57 Omalizumab (Xolair ) recombinant DNA-derived selective IgE monoclonal antibody SC administration every 2 or 4 weeks peak serum concentrations after 7-8 days tissue elimination (intracellular) T 1/2-26 days anaphylactic reactions in 0.2% cancer? 57
58 Omalizumab (Xolair ) indicated for children over 12 and adults with: poorly controlled moderate-severe persistent asthma year-round allergies (proven allergic reaction) inadequate control despite routine ICS use in these patients: free circulating IgE reduced by 96% decreased incidence of asthma exacerbations 58
59 Asthma classification episode frequency spirometry (FEV 1 ) acute Tx long-term Tx mild-intermittent 2/week >80% SABA none mild-persistent >2/week >80% SABA low-dose ICS moderatepersistent daily 60-80% SABA Low/medium dose ICS + LABA severe-persistent continuous <60% SABA high-dose ICS + LABA 59
60 60
61 Pharmacological markers for uncontrolled asthma acute SABA required >2/wk oral CS bursts required >2/yr 61
62 Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Summary Report
63 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease chronic, irreversible airflow obstruction two entities: - - slowly-progressive airway damage symptoms appear after years of exposure 63
64 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease chronic, irreversible airflow obstruction 4 th leading cause of death (USA) deadlier than asthma morbidity and mortality rising estimated USA annual cost >$30,000,000,000 64
65 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease chronic, irreversible airflow obstruction causes: 65
66 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease chronic, irreversible airflow obstruction symptoms/diagnosis: chronic cough (productive/non-productive) excessive mucus production shortness of breath (mild exertion) frequent throat-clearing chest tightness respiratory function tests (spirometry) 66
67 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Non-pharmacological Tx avoid triggers smoking dust/chemicals air-pollution [get better genes] 67
68 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Pharmacotherapy non-curable, non-reversible: control symptoms 1 st -line: inhaled bronchodilators - SABAs/LABAs (LABAs advantageous for nocturnal episodes) - anticholinergic (tiotropium = Spiriva ) - combination 68 once-daily anticholinergic bronchodilator
69 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Pharmacotherapy non-curable, non-reversible: control symptoms 2 nd -line: ICS - moderate-severe COPD uncontrolled with 1st-line - modest effect in most COPD patients - differing efficacy in asthma vs. COPD related to different inflammatory mediators 69
70 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Pharmacotherapy non-curable, non-reversible: control symptoms 2 nd /3 rd -line: theophylline - past 1 st -line - presently lost favor (ADEs) - option for those unable to optimally operate inhalers 70
71 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Pharmacotherapy Severity mild moderate severe FEV 1 >80% 30-80% <30% Long-term Tx SABA, as needed SABA/LABA/anticholinergic ± ICS as in moderate, - antibiotics for acute exacerbations - O 2 71
72 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Pharmacotherapy 72
73 COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD vs. asthma typical onset exacerbation Tx sequence Tx effect asthma childhood - young adulthood allergen, exercise, cold air ICS LABA symptom-free periods COPD adulthood (>40s) respiratory infections LABA ( ICS) nearly daily symptoms 73
74 Pharmacotherapy asthma/copd DRUGS FOR EXAM inhaled corticosteroids fluticasone beta-2 adrenergic agonists - short-acting: salbutamol - long-acting: salmeterol theophylline cromolyn ipratropium/tiotropium montelukast omalizumab 74
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD
 Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Respiratory Health. Asthma and COPD
 Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
II: Moderate Worsening airflow limitations Dyspnea on exertion, cough, and sputum production; patient usually seeks medical
 Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES. School Nurses November 2015
 ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
31 - Respiratory System
 31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
Foundations of Pharmacology
 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
Bronchial asthma. MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL
 Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Key features and changes to these four components of asthma care include:
 Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Adults Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions regarding
Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Adults Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions regarding
Bronchial Asthma and COPD
 Bronchial Asthma and COPD Red : important Black : in male / female slides Pink : in female s slides only Blue : in male s slides only Females doctor notes Grey: Males doctor notes OBJECTIVES: Different
Bronchial Asthma and COPD Red : important Black : in male / female slides Pink : in female s slides only Blue : in male s slides only Females doctor notes Grey: Males doctor notes OBJECTIVES: Different
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Asthma medications: Know your options - MayoClinic.com. Asthma medications: Know your options
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients. Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources
 Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE INCIDENCE UP TO 380,000 PEOPLE IN IRELAND HSE FIGURES 110,000 DIAGNOSED AND 200,000 UNDIAGNOSED. AFFECTS MORE MEN THAN WOMEN BUT RATES ARE RISING 1500 DEATHS PER YEAR
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE INCIDENCE UP TO 380,000 PEOPLE IN IRELAND HSE FIGURES 110,000 DIAGNOSED AND 200,000 UNDIAGNOSED. AFFECTS MORE MEN THAN WOMEN BUT RATES ARE RISING 1500 DEATHS PER YEAR
Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide
 Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide Second Edition November 2012 Queensland Health a Better Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide is a joint project
Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide Second Edition November 2012 Queensland Health a Better Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide is a joint project
LONG-ACTING BETA AGONISTS
 LONG-ACTING BETA AGONISTS AND ICS/LABA COMBINATIONS DISCLOSURE Dr. Francisco has no financial interest in any commercial entity discussed in this presentation Dr. Francisco will not discuss experimental
LONG-ACTING BETA AGONISTS AND ICS/LABA COMBINATIONS DISCLOSURE Dr. Francisco has no financial interest in any commercial entity discussed in this presentation Dr. Francisco will not discuss experimental
Tips on managing asthma in children
 Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Learning Objective. Asthma. Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Asthma 2/22/2017
 Marianne Curran, PA C 3/1/17 Learning Objective Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Definition many variations Chronic Disorder with Reversible (Intermittent
Marianne Curran, PA C 3/1/17 Learning Objective Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Definition many variations Chronic Disorder with Reversible (Intermittent
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Drugs that Affect the Respiratory System BROOKE BENTLEY, PHD, APRN
 Drugs that Affect the Respiratory System BROOKE BENTLEY, PHD, APRN Goals of Therapy Asthma Prevent symptoms COPD Reduce COPD symptoms Decrease use of SABAs Maintain normal pulm function & prevent loss
Drugs that Affect the Respiratory System BROOKE BENTLEY, PHD, APRN Goals of Therapy Asthma Prevent symptoms COPD Reduce COPD symptoms Decrease use of SABAs Maintain normal pulm function & prevent loss
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma
 Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines
 RSPT 2317 Clinical Indications Theophylline management of asthma and COPD treatment of apnea of prematurity (AOP) diuretic (obsolete use) classified as a bronchodilator, but is weaker than β agonists effects
RSPT 2317 Clinical Indications Theophylline management of asthma and COPD treatment of apnea of prematurity (AOP) diuretic (obsolete use) classified as a bronchodilator, but is weaker than β agonists effects
From the Text. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines
 From the Text RSPT 2217 Gardenhire Chapter 8 Key Terms and Definitions page 151 Xanthine Derivatives Used as Bronchodilators Table 8-1; page 152 Adverse Reactions Seen with Theophylline Box 8-1; page 157
From the Text RSPT 2217 Gardenhire Chapter 8 Key Terms and Definitions page 151 Xanthine Derivatives Used as Bronchodilators Table 8-1; page 152 Adverse Reactions Seen with Theophylline Box 8-1; page 157
Asthma By Mayo Clinic staff
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
COPD. Helen Suen & Lexi Smith
 COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Asthma. Definition. Symptoms
 Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
COPD: A Renewed Focus. Disclosures
 COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma :
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
Atrovent Administration
 Atrovent Administration ICEMA Training 2007 Sherri Shimshy RN OBJECTIVES Describe the pharmacology of Atrovent Identify the indications for use of Atrovent in the Adult Population Identify the indications
Atrovent Administration ICEMA Training 2007 Sherri Shimshy RN OBJECTIVES Describe the pharmacology of Atrovent Identify the indications for use of Atrovent in the Adult Population Identify the indications
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Asthma. Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital. Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence,
 Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Allergy and inflammation
 and inflammation 1 Allergic population hyper-producers of IgE consistently increasing western societies: ~20% of general population 2 Allergic population 3 Allergic triggers 4 Allergic triggers abnormal
and inflammation 1 Allergic population hyper-producers of IgE consistently increasing western societies: ~20% of general population 2 Allergic population 3 Allergic triggers 4 Allergic triggers abnormal
Asthma Management in Pregnancy HEATHER HOWE, MD UNIVERSITY OF UTAH PULMONARY DIVISION
 Asthma Management in Pregnancy HEATHER HOWE, MD UNIVERSITY OF UTAH PULMONARY DIVISION Asthma Management in Pregnancy Effects of asthma on pregnancy outcomes Effects of pregnancy on asthma control Management
Asthma Management in Pregnancy HEATHER HOWE, MD UNIVERSITY OF UTAH PULMONARY DIVISION Asthma Management in Pregnancy Effects of asthma on pregnancy outcomes Effects of pregnancy on asthma control Management
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
FIGURE 17. USUAL DOSAGES FOR LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS*
 FIGURE 17. USUAL DOSAGES FOR LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS* 0 4 Years Age and Adults Potential Adverse Effects Inhaled Corticosteroids (See Figure 18, Estimated Comparative Daily Dosages for ICSs. ) Oral
FIGURE 17. USUAL DOSAGES FOR LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS* 0 4 Years Age and Adults Potential Adverse Effects Inhaled Corticosteroids (See Figure 18, Estimated Comparative Daily Dosages for ICSs. ) Oral
Position within the Organisation
 ASTHMA TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma Version 4.0 Ratification date September
ASTHMA TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma Version 4.0 Ratification date September
Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma
 Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma Non-pharmacological options for ALL patients, consider at ALL stages Make sure diagnosis
Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma Non-pharmacological options for ALL patients, consider at ALL stages Make sure diagnosis
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
COPD: Current Medical Therapy
 COPD: Current Medical Therapy Angela Golden, DNP, FNP-C, FAANP Owner, NP from Home, LLC Outcomes As a result of this activity, learners will be able to: 1. List the appropriate classes of medications for
COPD: Current Medical Therapy Angela Golden, DNP, FNP-C, FAANP Owner, NP from Home, LLC Outcomes As a result of this activity, learners will be able to: 1. List the appropriate classes of medications for
7.2 Part VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary
 7.2 Part VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary 7.2.1 Part VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by persistent airflow limitation that is usually
7.2 Part VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary 7.2.1 Part VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by persistent airflow limitation that is usually
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment. John R. Holcomb, M.D.
 Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists
 Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications
 The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II
 Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm. Michael A Lucia, MD, FCCP Asst Clinical Professor, UNR School of Medicine Sierra Pulmonary & Sleep Institute
 Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm Michael A Lucia, MD, FCCP Asst Clinical Professor, UNR School of Medicine Sierra Pulmonary & Sleep Institute EIB Episodic bronchoconstriction with exercise May be an exacerbation
Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm Michael A Lucia, MD, FCCP Asst Clinical Professor, UNR School of Medicine Sierra Pulmonary & Sleep Institute EIB Episodic bronchoconstriction with exercise May be an exacerbation
Alberta Childhood Asthma Pathway for Primary Care
 Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Asthma in Pediatric Patients. DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP. Disclosures. None
 Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Working Together to Better Manage Childhood Asthma
 Working Together to Better Manage Childhood Asthma Bennie McWilliams, M.D. Howard Rosenblatt, M.D. Meena Ganesh, M.D. Chris Valmores, B.S.C.S.M., R.R.P.T. Carol Reagan, R.Ph. Johnny Smith Johnny is a 5
Working Together to Better Manage Childhood Asthma Bennie McWilliams, M.D. Howard Rosenblatt, M.D. Meena Ganesh, M.D. Chris Valmores, B.S.C.S.M., R.R.P.T. Carol Reagan, R.Ph. Johnny Smith Johnny is a 5
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease CareOregon Pharmacy Abridged sample of presentation content Home Equipment Pathophysiology Exacerbations Guidelines Lifestyle Modification Medication Management Sample
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease CareOregon Pharmacy Abridged sample of presentation content Home Equipment Pathophysiology Exacerbations Guidelines Lifestyle Modification Medication Management Sample
10/18/2012. Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C
 Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
COPD and Asthma Update. April 29 th, 2017 Rachel M Taliercio, DO Staff, Respiratory Institute
 COPD and Asthma Update April 29 th, 2017 Rachel M Taliercio, DO Staff, Respiratory Institute What we ll be talking about COPD: diagnosis, management of stable COPD, COPD exacerbations Asthma: diagnosis,
COPD and Asthma Update April 29 th, 2017 Rachel M Taliercio, DO Staff, Respiratory Institute What we ll be talking about COPD: diagnosis, management of stable COPD, COPD exacerbations Asthma: diagnosis,
Omalizumab (Xolair ) ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September Indication
 ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
A New Look At Asthma
 nhsmanagers.net Briefing 23 May 2016 Medicine for Managers Dr Paul Lambden BSc MB BS BDS FDSRCSEng MRCS LRCP DRCOG MHSM FRSH A New Look At Asthma Probably everyone knows that asthma is an increasingly
nhsmanagers.net Briefing 23 May 2016 Medicine for Managers Dr Paul Lambden BSc MB BS BDS FDSRCSEng MRCS LRCP DRCOG MHSM FRSH A New Look At Asthma Probably everyone knows that asthma is an increasingly
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control
 Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Assessing Severity. Management of Stable COPD. General Approach. Short Acting Bronchodilators. Staging System (GOLD)
 William P. Saliski Jr. DO Montgomery Pulmonary Consultants Management of Stable COPD Pharmacotherapy Oxygen Smoking Cessation Vaccinations Rehabilitation Surgery Future Discussions Assessing Severity Staging
William P. Saliski Jr. DO Montgomery Pulmonary Consultants Management of Stable COPD Pharmacotherapy Oxygen Smoking Cessation Vaccinations Rehabilitation Surgery Future Discussions Assessing Severity Staging
Chapter 55. Changes in the Airway With COPD. Manifestations of Severe COPD. Drugs Used to Treat Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders
 Chapter 55 Drugs Used to Treat Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders Changes in the Airway With COPD Manifestations of Severe COPD Air is trapped in the lower respiratory tract The alveoli degenerate and fuse
Chapter 55 Drugs Used to Treat Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders Changes in the Airway With COPD Manifestations of Severe COPD Air is trapped in the lower respiratory tract The alveoli degenerate and fuse
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline. MedStar Health
 Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions
Provider Respiratory Inservice
 Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva (budesonide / formoterol)
 EMA/639304/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva, which
EMA/639304/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva, which
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Salmeterol (Serevent)
 Prior to administration: Assess for presence/history of chronic asthma, exercise induced asthma, acute asthma attacks, and acute upper airway obstruction. Assess respiratory rate and lung sounds, pulse
Prior to administration: Assess for presence/history of chronic asthma, exercise induced asthma, acute asthma attacks, and acute upper airway obstruction. Assess respiratory rate and lung sounds, pulse
Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma. April 21, Spring Managed Care Forum
 Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma April 21, 2016 2016 Spring Managed Care Forum David M. Mannino, M.D. Professor Department of Preventive Medicine and Environmental Health University
Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma April 21, 2016 2016 Spring Managed Care Forum David M. Mannino, M.D. Professor Department of Preventive Medicine and Environmental Health University
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
Difficult Asthma Assessment: A systematic approach
 Difficult Asthma Assessment: A systematic approach Dr Naghmeh Radhakrishna Respiratory, Sleep & Allergy Physician Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology Service The Alfred Hospital Melbourne, Australia
Difficult Asthma Assessment: A systematic approach Dr Naghmeh Radhakrishna Respiratory, Sleep & Allergy Physician Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology Service The Alfred Hospital Melbourne, Australia
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Asthma - Chronic. Presentations of asthma Cough Wheeze Breathlessness Chest tightness
 Asthma - Chronic Definition of asthma Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways 3 components: o Reversible and variable airflow obstruction o Airway hyper-responsiveness to stimuli o Inflammation of
Asthma - Chronic Definition of asthma Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways 3 components: o Reversible and variable airflow obstruction o Airway hyper-responsiveness to stimuli o Inflammation of
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol)
 EMA/675937/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax, which details the measures
EMA/675937/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax, which details the measures
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes
 Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
2/12/2015. ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang. Asthma General Information. Asthma General Information
 ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management?
 Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management? Ting Fan LEUNG, MBChB, MD, FRCPCH, FAAAAI Professor and Chairman Department of Paediatrics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Asthma and Allergy by
Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management? Ting Fan LEUNG, MBChB, MD, FRCPCH, FAAAAI Professor and Chairman Department of Paediatrics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Asthma and Allergy by
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange
 Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016?
 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016? GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention GINA: A Brief History Established in 1993 Collaboration between NHLBI and WHO Multiple
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016? GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention GINA: A Brief History Established in 1993 Collaboration between NHLBI and WHO Multiple
Adult Asthma Clinical Practice Guideline Summary
 Adult Asthma Clinical Practice Guideline Summary The following evidence-based guideline was developed to assist Primary Care physicians and other clinicians in the management of asthma in adults. It was
Adult Asthma Clinical Practice Guideline Summary The following evidence-based guideline was developed to assist Primary Care physicians and other clinicians in the management of asthma in adults. It was
Presented by the California Academy of Family Physicians 2013/California Academy of Family Physicians
 Family Medicine and Patient-Centered Asthma Care Presented by the California Academy of Family Physicians Faculty: Hobart Lee, MD Disclosures: Jeffrey Luther, MD, Program Director, Memorial Family Medicine
Family Medicine and Patient-Centered Asthma Care Presented by the California Academy of Family Physicians Faculty: Hobart Lee, MD Disclosures: Jeffrey Luther, MD, Program Director, Memorial Family Medicine
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
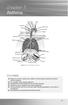 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
