NO chemiluminescence in exhaled air: interference of compounds from endogenous or exogenous sources
|
|
|
- Homer Randall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eur Respir J 2; 16: 499±53 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2 European Respiratory Journal ISSN NO chemiluminescence in exhaled air: interference of compounds from endogenous or exogenous sources N. Binding, W. MuÈ ller, P.A. Czeschinski, U. Witting NO chemiluminescence in exhaled air: interference of compounds from endogenous or exogenous sources. N. Binding. W. MuÈller, P.A. Czeschinski, U. Witting. #ERS Journals Ltd 2. ABSTRACT: Nitric oxide determination in exhaled air using chemiluminescence analysers is increasingly used, but may be affected by various other components of the air sample. The influence of several compounds originating from endogenous or exogenous sources on NO readings has been studied. Defined amounts of water vapour, carbon dioxide, acetone, heptane, acetonitrile, oxygen, nitrous oxide and enflurane were added to air samples with NO concentrations ±25 parts per billion. Marked and significant decreases in NO readings, which strongly depend on the concentration of the respective interfering compound, were found for water vapour (.155% per 1% relative humidity), carbon dioxide (1.97% per 1% CO 2 volume/volume (v/v)) and nitrous oxide (.68% per 1% v/v N 2 O). While acetone in concentrations up to 8.5% v/v had no measurable effect on NO readings, heptane and acetonitrile led to marked decreases. Oxygen in concentrations of up to 95% (v/v) had no effect on NO determination. NO readings were markedly decreased by >1% per 1% (v/v) of the anaesthetic enflurane. However, due to large variations in NO values, these decreases were not statistically significant. Furthermore, enflurane reacted with the molybdenum converter of the NO x analyser in use, resulting in major damage to the instrument. Eliminating, or at least considering, interferences by compounds present in exhaled air is an urgent prerequisite for reliable and precise nitric oxide determination. Eur Respir J 2; 16: 499±53. Institute of Occupational Medicine, University of MuÈnster, MuÈnster, Germany. Correspondence: N. Binding, Institut fuèr Arbeitsmedizin der WestfaÈlischen Wilhelms-UniversitaÈt MuÈnster, Robert-Koch- Str. 51, D MuÈnster, Germany. Fax: Keywords: chemiluminescence enflurane interferences nitric oxide nitrous oxide water vapour Received: December Accepted after revision May 2 2 Nitric oxide (NO) produced via NO synthases is detectable in exhaled air of healthy subjects [1]. As NO plays an important role in physiology (e.g. neurotransmission, vascular regulation, airway function regulation [2]) and the pathophysiology of different diseases (e.g. inflammatory airway diseases [3±5], chronic heart disease [6], respiratory tract infections [7], septic shock [8], systemic sclerosis [9]) the determination of exhaled NO might be of considerable diagnostic and therapeutic importance. Monitoring NO in exhaled air might thus provide a noninvasive method for the clinical control of diseases and especially of the success of therapeutic interventions. The hypothesis that NO exhalation is elevated in asthma, sepsis, and airway as well as pulmonary inflammations [8, 1, 11] or decreased in chronic heart diseases [6], has been confirmed by numerous working groups. The measurement of exhaled NO is performed using chemiluminescence detectors providing the required measurement range [12] of.1±1, parts per billion (ppb). NO is oxidized to high energy, excited state NO 2 *by reaction with ozone (O 3 ). When passing to the ground state, a fraction of the excess energy of NO 2 * is dissipated by emission of photons (chemiluminescence); this is used for quantitative detection. Major fractions of energy are dissipated by interactions with other components of the analysed sample in the reaction chamber. The extent of this energy transfer (quenching) by collisions with other molecules is determined mainly by the chamber pressure and the sample composition [13, 14]. Thus, variations in sample composition may influence the chemiluminescence signal. Exhaled air represents a complex mixture of substances with more than 3 detected volatile compounds of exogenous or endogenous origin [15, 16], which might have considerable effects on the result of NO measurement. These are primarily carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water, but also different substances originating from metabolic processes, e.g. heptane, acetonitrile, and acetone. Elevated exhalation of some of these compounds occurs in certain diseases, e.g. acetone in heart diseases [17] and diabetes mellitus [18], pentane in arthritis and acute myocardial infarction [19] or ethanol in arthritis, lung cancer, and schizophrenia [2]. Furthermore, substances from exogenous sources, especially when applied in high doses during medical treatment (e.g. volatile anaesthetics or oxygen during oxygen therapy), might influence NO quantification. In this study, interferences of CO 2, water, heptane, acetonitrile, acetone, N 2 O and enflurane with the chemiluminescence process are investigated to improve reliability and reproducibility of NO measurements in exhaled air. Methods NO was analysed with a TE 42S NO x analyser (Thermo Environmental Instruments, Franklin, Massachusetts, USA)
2 5 N. BINDING ET AL. gaseous compunds air bypass valve valve liquid compunds flow controllers mixing tube sample outlet analyser Fig. 1. ± Schematic drawing of the open tube mixing device. waste equipped with two separate channels for NO and NO 2 measurements. The detection range for NO was.1±24 ppb, the sampling rate was 1 L.min -1. A special feature of this analyser is that NO-free gas ("zero gas") is produced from aliquots of the sampled mixtures by cyclic passage through an internal prereaction chamber. NO is completely oxidized to NO 2 before passing the main reaction chamber. Thus, a sample-specific zero correction for background noise is performed by comparison of the signals of internal zero gas and sample. For the determination of NO 2,the sample is alternatingly passed through a molybdenum converter where a complete reduction of NO 2 to NO is performed prior to the oxidation step in the ozone reaction chamber. From the resulting total value for NO 2 and NO, the concentration of NO 2 is calculated by subtracting the NO value assessed without the reduction step. Samples with defined NO concentrations were prepared by diluting a certified reference gas (1 ppm NO in N 2 ; Westfalen AG, MuÈnster, Germany) either with N 2 of high purity (99.995%; Westfalen AG) for instrument calibration or with certified NO-free air (Westfalen AG) for all other measurements. Addition of further components was performed by dividing the air stream and bubbling air via a bypass through a flask with the respective liquid component (water, heptane, acetone, acetonitrile, enflurane) or by adding gaseous components (CO 2,O 2, nitrous oxide) via high precision valves and flow controllers. Thorough mixing of the components was accomplished by passing the air stream through a tube with an irregular inner surface generating a turbulent stream. Concentrations of added gaseous components were adjusted by flow control, and those of liquid components by variation of the bypass air flow. Figure 1 shows a schematic drawing of the open tube mixing device providing a continuous sample flow. High precision valves, tubings and fittings, and flow controllers were of polytetrafluoroethylene, stainless steel or glass. The CO 2 concentration (after dilution with air) and the humidity of the samples were monitored with a Testo 4 multifunctional sensor (Testo, Lenzkirch, Germany). The resulting concentrations of heptane, acetone, acetonitrile, N 2 O, and enflurane were determined by gas chromatography with an HP 589 chromatograph with FID (or ECD for N 2 O and enflurane), HP ChemStation software, 3 m HP-Plot molecular sieve 5 A column for N 2 O (ID:.53 mm, film thickness 25 mm) or 5 m HP-5 capillary column for all other substances (ID:.32 mm, film thickness:.52 mm) (Hewlett Packard, Palo Alto, USA). N 2 was used as carrier gas in all separations. Samples were taken near the end of the open tube mixing device (fig. 1). To prevent aspiration of external air, the sample flow was kept constantly above the analyser's sampling rate of 1 L.min -1 (total sample flow: 2 L.min -1 ). The influence of CO 2 on NO determination was tested with CO 2 concentrations of 1±1%. The influence of water was measured in a range of ±92% relative humidity; concentration ranges for the other components were: heptane: ±3.5%, acetonitrile: ±1.7%, acetone: ±8.5%, oxygen: 2±95%, enflurane: ±2%, N 2 O: ±6%. NO concentrations were ±25 ppb. Measurements were performed in triplicate for each sample. Results A significant decrease in NO readings was found when CO 2 was added as interfering compound with concentrations of 1±1% v/v. The slope of the calibration line for air containing 5% (v/v) CO 2 ( ; p<.1; 95% confidence interval (CI).849±.881) was significantly different from the line for CO 2 -free samples (line of identity) (fig. 2). The mean decrease was % per 1% (v/v) CO 2 (p<.1) (fig. 3). Humidification (92% relative humidity) led to a comparable decrease in readings. The slope of the calibration line was (p<.1; 95% CI.785±.846). With increasing humidity, a mean decrease of.155.4% (p<.1) for each 1% relative humidity step was found. The influence of some components of exhaled air originating from endogenous sources was studied for heptane, acetonitrile and acetone. While acetone in concentrations up to 8.5% (v/v) had no measurable effect, heptane (.75± 3.5% (v/v)) and acetonitrile (.8±1.7% (v/v)) led to marked decreases in NO readings. However, in contrast to the findings with CO 2 and humidity, the percentage of deviation decreased with increasing NO concentrations (fig. 4), thus pointing to different mechanisms of interference. Measured NO concerntration ppb Input NO concerntration ppb Fig. 2. ± Calibration lines for nitric oxide (NO) in pure air (*) and for NO in air containing 5% (v/v) CO 2 (s). ppb: parts per billion.
3 INTERFERENCES IN NO DETERMINATION 51 Measured NO concentration ppb Carbon dioxide % During medical treatment of patients some compounds from exogenous sources, e.g. O 2 from O 2 therapy or volatile anaesthetics during and after anaesthesia, might interfere with NO measurement. Therefore the influence of high concentrations of O 2,N 2 O, and enflurane on NO determination was studied. O 2 in concentrations up to 95% (v/v) had no measurable effect on NO readings. N 2 Owas added up to a concentration of 6% (v/v), which is commonly used in anaesthesia. A significant decrease in NO readings was found (mean decrease per 1% (v/v) N 2 O:.68.33%, p<.1). With a maximum N 2 O concentration of 6% (v/v), the slope of the calibration line was (p<.1, CI.62±.626). The influence of enflurane, a volatile halogenated anaesthetic, was investigated in common anaesthetic concentrations up to 2% (v/v). Again a marked decrease of NO readings was found. Statistical analysis of the data revealed that due to the large variation of NO values measured and the poor linearity of the calibration line, this decrease was not significant (mean decrease per 1% (v/v) enflurane: %, p<.87). The main reason for the poor reproducibility of NO determination was found in an unexpected reaction of enflurane with the analyser's molybdenum converter. Deposits of the reaction products (identified as Fig. 3. ± Decrease in nitric oxide (NO) readings with increasing CO 2 concentration at different starting concentrations of NO. molybdenum oxichloride by mass spectrometric analysis) in nearly all internal tubings led to instrument failure. The reaction of molybdenum with enflurane and other halogenated compounds and its influence on the performance of the NO analyser has been further investigated, but the results would exceed the scope of this article and are to be published elsewhere. Discussion The results presented in this paper confirm that compounds present in exhaled air interfere with chemiluminescence detection of NO. CO 2 and water vapour as major constituents of exhaled air both led to significant reductions in NO readings. This is in agreement with findings reported by VAN DER MARK et al. [21], though there are some discrepancies in the percentage decrease: 1.4% [21] versus 1.97% (present study) decrease per 1% (v/v) CO 2 and 12.% decrease at a water vapour pressure of 2.81 kpa [21] versus 14.3% (present study) at a vapour pressure of 2.15 kpa (~92% relative humidity at 28C). These discrepancies may be attributed to the different analysers used. Since low pressure in the reaction chamber reduces quenching effects [8], the higher values recorded in this study may be due to the chamber pressure of 4 kpa, which is considerably higher than that of 5.2 kpa in the analyser used by VAN DER MARK et al. [21]. However, both studies led to the same conclusions, which are discussed in detail by VAN DER MARK et al. [21] and are therefore only summarized in this paper. The influence of CO 2 in physiological concentrations of ~4% on NO determination is limited and may be considered for the respective analyser. Differences between mixed expired and end-tidal CO 2 concentrations up to 2% would lead to negligible variations in NO readings for concentrations exhaled by normal healthy humans, but might be of importance when exogenous NO in higher concentrations is administered to patients for therapeutic reasons. The influence of water vapour is more pronounced with a decrease of 14.3% at a sample temperature of 28C and a relative humidity of 92% (~2.15 kpa water vapour pressure). With water-saturated exhaled air at a) 25 b) 12 Deviation of NO readings % Input NO concentration ppb Input NO concentration ppb Fig. 4. ± Deviation (%) of nitric oxide readings as a function of NO concentration for a) a heptane concentration of 3.75% (v/v); and b) an acetonitrile concentration of 1.55% (v/v).
4 52 N. BINDING ET AL. temperatures 3±378C, water vapour pressure would be 4.24±6.28 kpa, resulting in a decrease of 27±39% in NO readings. The water vapour content of an exhaled air sample is thus determined by the sample temperature at the analyser's sample inlet, which depends inter alia on the means of sampling and the length of the sample transfer tubings. To avoid variations in NO readings by CO 2 and especially by water vapour, which might be of the same magnitude as the differences in NO exhalation described for healthy and asthmatic subjects, the use of both CO 2 and water absorbers is recommended [21]. But it has to be considered that, depending on the absorber material, NO adsorption might occur. This is the reason why the use of adsorbers is not recommended in the latest recommendations published by the American Thoracic Society (ATS) [22]. Instead, errors due to humidity should be addressed by each instrument manufacturer or, alternatively, avoided by use of Nafion tubes in the sample line, which equilibrates samples and calibration gas to ambient humidity. Instrument tolerances for quenching by CO 2 and water vapour should be <1% NO for each 1% level of interfering compound. Acetone, heptane and acetonitrile in exhaled air originate either from metabolic processes [16] or from bioaccumulation of inhaled pollutants [15]. Concentrations found in samples of exhaled air from healthy humans were 1±1, ng.l -1 [16]. Elevated concentrations of acetone may be found in certain diseases (diabetes mellitus [18], chronic heart disease [17]), while heptane and acetonitrile exhalation may be increased for example after occupational exposure. Acetone up to 8.5% (v/v), which is well above the concentrations found in patients with diabetes mellitus (~.4% (v/v) [23]), did not influence NO measurements. Heptane and acetonitrile led to marked decreases in NO readings which, in contrast to the findings with CO 2 and H 2 O, depend both on the concentrations of the interfering compounds and on NO concentration. These results point to a different mechanism of interference. Nevertheless, for heptane and acetonitrile concentrations found in exhaled air of healthy human subjects, the interference is within the range of variation of NO determination and thus might be ignored. Only when higher concentrations of these compounds have to be assumed, for example after occupational exposure, possible interferences have to be considered. Substances administered in higher concentrations for therapeutic reasons might be another source of interference in NO determination in exhaled air. This might apply for example to O 2 in O 2 therapy or to volatile anaesthetics, which are major components of exhaled air during surgical operations and recovery from anaesthesia. Increasing the O 2 content of samples up to 95% (v/v) had no measurable effect on NO determination. Differences observed were within the variation of NO readings. These results differ from those reported for the measurement of NO from combustion systems, where O 2 in high concentrations led to a small but significant quenching of the NO signal [13]. Again the use of different analysers might be the reason for these discrepancies. Monitoring NO in the exhaled air of patients during anaesthesia or during the recovery phase might be of considerable diagnostic importance, for example as an early predictor of sepsis [8]. N 2 O led to marked and significant decreases in NO readings. At anaesthetic concentrations of 6% N 2 O, a decrease of 36% was found. Correct NO concentrations might be calculated for the respective chemiluminescence analyser if N 2 O concentrations are known. Thus simultaneous N 2 O monitoring during anaesthesia and during the recovery phase is a prerequisite for precise NO determination. The halogenated anaesthetic enflurane led to marked decreases in NO readings. However, due to large variations in NO values, this influence was not significant. The main reason for this poor reproducibility was a reaction of enflurane with molybdenum from the converter of the NO 2 channel, which resulted in major damage to the analyser. Therefore, NOx analysers with molybdenum converters should not be used with air samples containing halogenated anaesthetics unless the NO 2 channel is closed. With growing knowledge of the pathophysiological role of NO, applications for NO determination in exhaled air as a diagnostic tool will increase. As the chemiluminescence process used for NO quantification is subject to interferences by quenching compounds, a knowledge of these interferences is an urgent need with respect to quality control. The influence of most organic compounds normally present only in low concentrations in exhaled air of healthy subjects is negligible. Interferences from higher concentrated substances (e.g. water vapour, CO 2, anaesthetic gases, organic compounds after occupational exposure) have always to be considered. Suitable steps to minimize errors in NO measurements for example according to the recommendations of the ATS [22] should then be taken. References 1. Gustafsson LE, Leone AM, Persson MG, Wiklund NP, Moncada S. Endogenous nitric oxide is present in the exhaled air of rabbits, guinea pigs and humans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1991; 181: 852± Barnes PJ. Nitric oxide and airway disease. Ann Med 1995; 27: 389± Lundberg JON, Weitzberg E, Lundberg JM, Alving K. Nitric oxide in exhaled air. Eur Respir J 1996; 9: 2671± Alving K, Weitzberg E, Lundberg JM. Increased amount of nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatics. Eur Respir J 1993; 6: 1268± Barnes PJ. NO or no NO in asthma? Thorax 1996; 51: 218± Sumino H, Sato K, Sakamaki T, et al. Decreased basal production of nitric oxide in patients with heart disease. Chest 1998; 113: 317± Kharitonov SA, Yates D, Barnes PJ. Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of normal human subjects with upper respiratory tract infection. Eur Respir J 1995; 8: 295± Hussain SNA, Abdul-Hussain MN, El-Dwairi Q. Exhaled nitric oxide as a marker for serum nitric oxide concentration in acute endotoxemia. J Crit Care 1996; 11: 167± Fajac I, Kahan A, MenkeÁs CJ, Dessanges JF, Dall'Ava- Santucci J, Dinh-Xuan AT. Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1998; 16: 547± Kharitonov SA, Yates D, Robbins RA, Logan-Sinclair R, Shinebourne E, Barnes PJ. Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Lancet 1994; 343: 133± 135.
5 INTERFERENCES IN NO DETERMINATION Dinh-Xuan AT. RoÃle du monoxyde d'azote en physiologic respiratoire et dans la physiopathologie des maladies pulmonaires. Rev Mal Resp 1996; 13: 381± Kharitonov S, Alving K, Barnes PJ. Exhaled and nasal nitric oxide measurements: recommendations. Eur Respir J 1997; 1: 1683± Tidona RJ, Nizami AA, Cernansky NP. Reducing interference effects in the chemiluminescent measurement of nitric oxides from combustion systems. JAPCA 1988; 38: 86± Zabielski MF, Seery DJ, Dodge LG. Influence of mass transport and quenching on nitric oxide chemiluminescent analysis. Environ Sci Technol 1984; 18: 88± Krotoszyoski BK, O'Neill HJ. Involuntary bioaccumulation of environmental pollutants in nonsmoking heterogeneous human population. J Environ Sci Health 1982; A17: 855± Krotoszynski B, Gabriel G, O'Neill H, Claudio MPA. Characterization of human expired air: a promising investigative and diagnostic technique. J Chromatogr Sci 1977; 15: 239± Skrupsky VA. Gas chromatographic analysis of ethanol and acetone in the air exhaled by the patients. Klin Lab Diagnost 1995; 4: 35± Rooth G, OÈ stenson S. Acetone in alveolar air, and in the control of diabetes. Lancet 1966; 19: 112± Weitz ZW, Birnbaum AJ, Sobotka PA, Zarling EJ, Skosey JL. High breath pentane concentrations during acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 1991; 337: 933± Phillips M, Greenberg J. Ion-trap detection of volatile organic compounds in alveolar breath. Clin Chem 1992; 38: 6± van der Mark ThW, Kort E, Meijer RJ, Postma DS, KoeÈter GH. Water vapour and carbon dioxide decrease nitric oxide readings. Eur Respir J 1997; 1: 212± American Thoracic Society. Recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide in adults and children Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 16: 214± Owen OK, Trapp VE, Skutches CL, et al. Acetone metabolism during diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes 1982; 31: 242±248.
Exhalation flow and pressure-controlled reservoir collection of exhaled nitric oxide for remote and delayed analysis
 Thorax 998;5:775 779 775 Department of Thoracic Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine at the National Heart and Lung Institute, Dovehouse Street, London SW 6LY, UK P Paredi S Loukides S A Kharitonov
Thorax 998;5:775 779 775 Department of Thoracic Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine at the National Heart and Lung Institute, Dovehouse Street, London SW 6LY, UK P Paredi S Loukides S A Kharitonov
ASTHMA TREATMENT EFFICACY ASSESSMENT BY FeNO MEASUREMENT
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 5 (54) No. 2-2012 ASTHMA TREATMENT EFFICACY ASSESSMENT BY FeNO MEASUREMENT Dana ALEXANDRESCU 1 Abstract: The author of
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 5 (54) No. 2-2012 ASTHMA TREATMENT EFFICACY ASSESSMENT BY FeNO MEASUREMENT Dana ALEXANDRESCU 1 Abstract: The author of
Part 1: Imaging Spectroscopy: From air quality investigations to healthcare applications
 Part 1: Imaging Spectroscopy: From air quality investigations to healthcare applications Part 2: Chemical Ionisation Reaction Mass Spectrometry (CIR-MS) for Breath Analysis Research 12 th March 2009 Roland
Part 1: Imaging Spectroscopy: From air quality investigations to healthcare applications Part 2: Chemical Ionisation Reaction Mass Spectrometry (CIR-MS) for Breath Analysis Research 12 th March 2009 Roland
Inhaled fluticasone decreases bronchial but not alveolar nitric oxide output in asthma
 Eur Respir J 21; 18: 635 639 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 21 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Inhaled fluticasone decreases bronchial but not alveolar nitric oxide
Eur Respir J 21; 18: 635 639 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 21 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Inhaled fluticasone decreases bronchial but not alveolar nitric oxide
Exhaled Nitric Oxide after 2 -agonist Inhalation and Spirometry in Asthma
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide after 2 -agonist Inhalation and Spirometry in Asthma PHILIP E. SILKOFF, SUGURU WAKITA, JOSE CHATKIN, KHALIL ANSARIN, CARLOS GUTIERREZ, MARLOVA CARAMORI, PATRICIA MCCLEAN, ARTHUR S.
Exhaled Nitric Oxide after 2 -agonist Inhalation and Spirometry in Asthma PHILIP E. SILKOFF, SUGURU WAKITA, JOSE CHATKIN, KHALIL ANSARIN, CARLOS GUTIERREZ, MARLOVA CARAMORI, PATRICIA MCCLEAN, ARTHUR S.
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 8
 CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 8 DETERMINATION OF WATER IN THE MAINSTREAM SMOKE OF CIGARETTES BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS (August 1991) 1. FIELD OF APPLICATION The method is applicable to the particulate
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 8 DETERMINATION OF WATER IN THE MAINSTREAM SMOKE OF CIGARETTES BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS (August 1991) 1. FIELD OF APPLICATION The method is applicable to the particulate
Expired nitric oxide levels in adult asthmatics
 Allergology International (1996) 45: 85-89 Original Article Expired nitric oxide levels in adult asthmatics Chiharu Okada, Akihiko Tamaoki, Yasushi Tanimoto, Ryo Soda and Kiyoshi Takahashi National Sanatorium
Allergology International (1996) 45: 85-89 Original Article Expired nitric oxide levels in adult asthmatics Chiharu Okada, Akihiko Tamaoki, Yasushi Tanimoto, Ryo Soda and Kiyoshi Takahashi National Sanatorium
A diagnosis of asthma is made on the basis of compatible
 383 ASTHMA Exhaled nitric oxide in the diagnosis of asthma: comparison with bronchial provocation tests N Berkman, A Avital, R Breuer, E Bardach, C Springer, S Godfrey... See end of article for authors
383 ASTHMA Exhaled nitric oxide in the diagnosis of asthma: comparison with bronchial provocation tests N Berkman, A Avital, R Breuer, E Bardach, C Springer, S Godfrey... See end of article for authors
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 8454 Third edition 2007-06-01 Cigarettes Determination of carbon monoxide in the vapour phase of cigarette smoke NDIR method Cigarettes Dosage du monoxyde de carbone dans la
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 8454 Third edition 2007-06-01 Cigarettes Determination of carbon monoxide in the vapour phase of cigarette smoke NDIR method Cigarettes Dosage du monoxyde de carbone dans la
10801 Sixth St, Rancho Cucamonga, CA Tel (909) Fax (909) Visit our web site at:
 for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma and Other Pulmonary Disorders IEHP Policy: Based on a review of the currently available literature, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of FE NO
for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma and Other Pulmonary Disorders IEHP Policy: Based on a review of the currently available literature, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of FE NO
Influence of atopy on exhaled nitric oxide in patients with stable asthma and rhinitis
 Eur Respir J 1999; 14: 897±901 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 1999 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Influence of atopy on exhaled nitric oxide in patients with
Eur Respir J 1999; 14: 897±901 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 1999 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Influence of atopy on exhaled nitric oxide in patients with
What are the Human Health Effects of Air Pollution?
 What are the Human Health Effects of Air Pollution? Dr. Judy Guernsey Department of Community Health and Epidemiology Dalhousie University Nova Scotia Department of Environment and Labour Outdoor Air Quality
What are the Human Health Effects of Air Pollution? Dr. Judy Guernsey Department of Community Health and Epidemiology Dalhousie University Nova Scotia Department of Environment and Labour Outdoor Air Quality
On the influence of inhaled volatile organic compounds (VOCs) on exhaled VOCs concentrations
 Karl Unterkofler and Susanne Teschl On the influence of inhaled volatile organic compounds (VOCs) on exhaled VOCs concentrations 07 - Translationale Gesundheitsforschung Brücken bauen von Grundlagenwissenschaft
Karl Unterkofler and Susanne Teschl On the influence of inhaled volatile organic compounds (VOCs) on exhaled VOCs concentrations 07 - Translationale Gesundheitsforschung Brücken bauen von Grundlagenwissenschaft
Laboratory Evaluation Aeroqual S-500 OZU Ozone Sensor
 Laboratory Evaluation Aeroqual S-5 OZU Ozone Sensor Background Three Aeroqual Series S-5 (model OZU, -.15ppm) portable ozone monitors that were previously field-tested at the SCAQMD Rubidoux fixed ambient
Laboratory Evaluation Aeroqual S-5 OZU Ozone Sensor Background Three Aeroqual Series S-5 (model OZU, -.15ppm) portable ozone monitors that were previously field-tested at the SCAQMD Rubidoux fixed ambient
This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY
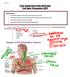 Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
Measuring Lipid Composition LC-MS/MS
 Project: Measuring Lipid Composition LC-MS/MS Verification of expected lipid composition in nanomedical controlled release systems by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry AUTHORED BY: DATE: Sven
Project: Measuring Lipid Composition LC-MS/MS Verification of expected lipid composition in nanomedical controlled release systems by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry AUTHORED BY: DATE: Sven
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
10.1 The Pulmonary-Circulatory System
 pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
IDENTIFICATION AND CONTROLOFRESIDUALSOLVENTS Identification and control of residual solvents EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.
 EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.0 2.4.24. Identification and control of residual solvents paper and wash each filter with 3 quantities, each of 15 ml, of methylenechlorider.placethecombinedfiltrateand washings
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.0 2.4.24. Identification and control of residual solvents paper and wash each filter with 3 quantities, each of 15 ml, of methylenechlorider.placethecombinedfiltrateand washings
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.5-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standard
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.5-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standard
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements
 Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Assessment of a rapid liquid based cytology method for measuring sputum cell counts
 Assessment of a rapid liquid based cytology method for measuring sputum cell counts Martin MJ, Lee H, Meakin G, Green A, Simms RL, Reynolds C, Winters S*, Shaw DE, Soomro I*, Harrison TW The Asthma Centre
Assessment of a rapid liquid based cytology method for measuring sputum cell counts Martin MJ, Lee H, Meakin G, Green A, Simms RL, Reynolds C, Winters S*, Shaw DE, Soomro I*, Harrison TW The Asthma Centre
An optical dosimeter for the selective detection of gaseous phosgene with ultra-low detection limit
 Supporting information for An optical dosimeter for the selective detection of gaseous phosgene with ultra-low detection limit Alejandro P. Vargas, Francisco Gámez*, Javier Roales, Tània Lopes-Costa and
Supporting information for An optical dosimeter for the selective detection of gaseous phosgene with ultra-low detection limit Alejandro P. Vargas, Francisco Gámez*, Javier Roales, Tània Lopes-Costa and
CORESTA Recommended Method No. 84
 Cooperation Centre for Scientific Research Relative to Tobacco E-Vapour Sub-Group CORESTA Recommended Method No. 84 DETERMINATION OF GLYCERIN, PROPYLENE GLYCOL, WATER, AND NICOTINE IN THE AEROSOL OF E-CIGARETTES
Cooperation Centre for Scientific Research Relative to Tobacco E-Vapour Sub-Group CORESTA Recommended Method No. 84 DETERMINATION OF GLYCERIN, PROPYLENE GLYCOL, WATER, AND NICOTINE IN THE AEROSOL OF E-CIGARETTES
A Primer on Acute Inhalation Toxicity Testing
 A Primer on Acute Inhalation Toxicity Testing Where do Alternative Methods Fit? Jon A. Hotchkiss, PhD Toxicology and Environmental Research and Consulting The Dow Chemical Company 1 Outline Why do we test?
A Primer on Acute Inhalation Toxicity Testing Where do Alternative Methods Fit? Jon A. Hotchkiss, PhD Toxicology and Environmental Research and Consulting The Dow Chemical Company 1 Outline Why do we test?
SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF VALSARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE IN TABLETS BY RP-HPLC METHOD
 170 Original Article SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF VALSARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE IN TABLETS BY RP-HPLC METHOD *Lakshmana Rao A, 1 Bhaskara Raju V *V.V. Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Gudlavalleru,
170 Original Article SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF VALSARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE IN TABLETS BY RP-HPLC METHOD *Lakshmana Rao A, 1 Bhaskara Raju V *V.V. Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Gudlavalleru,
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
 VALVE FLOW CAPACITIES METERING SIZING Flow capacity tables 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 (pages 38 to 41) are based on calibrations at standard conditions, meaning 14.7 psia (1 atm) pressure and 70 F F (21.1 F C).
VALVE FLOW CAPACITIES METERING SIZING Flow capacity tables 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 (pages 38 to 41) are based on calibrations at standard conditions, meaning 14.7 psia (1 atm) pressure and 70 F F (21.1 F C).
Development and Validation of a Simultaneous HPLC Method for Quantification of Amlodipine Besylate and Metoprolol Tartrate in Tablets
 Journal of PharmaSciTech 0; ():- Research Article Development and Validation of a Simultaneous HPLC Method for Quantification of Amlodipine Besylate and Metoprolol Tartrate in Tablets * Sayyed Hussain,
Journal of PharmaSciTech 0; ():- Research Article Development and Validation of a Simultaneous HPLC Method for Quantification of Amlodipine Besylate and Metoprolol Tartrate in Tablets * Sayyed Hussain,
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
 VALVE FLOW CAPACITIES TABLE 1 - MFV TM STYLE VALVE FLOW CAPACITIES 10 psig (0.7 kg/cm2) INLET PRESSURE, ATMOSPHERIC EXHAUST ORIFICE AIR HELIUM WATER NUMBER sml/min scfh sml/min scfh ml/min gph 1 200 0.42
VALVE FLOW CAPACITIES TABLE 1 - MFV TM STYLE VALVE FLOW CAPACITIES 10 psig (0.7 kg/cm2) INLET PRESSURE, ATMOSPHERIC EXHAUST ORIFICE AIR HELIUM WATER NUMBER sml/min scfh sml/min scfh ml/min gph 1 200 0.42
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
ACETONE DETECTION USING THIN TUNGSTEN OXIDE (WO 3 ) FILM BASED GAS SENSOR
 ACETONE DETECTION USING THIN TUNGSTEN OXIDE (WO 3 ) FILM BASED GAS SENSOR Smiti Sachdeva 1,2, Rahul Prajesh 2, Jitendra Bhargava 2, Ashok Kumar Sharma 2, Ajay Agarwal 2, Ravinder Agarwal 1 1 Thapar University,
ACETONE DETECTION USING THIN TUNGSTEN OXIDE (WO 3 ) FILM BASED GAS SENSOR Smiti Sachdeva 1,2, Rahul Prajesh 2, Jitendra Bhargava 2, Ashok Kumar Sharma 2, Ajay Agarwal 2, Ravinder Agarwal 1 1 Thapar University,
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
#8 - Respiratory System
 Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Respiratory System Mechanics
 M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
Key words: asthma; dyspnea; exercise-induced bronchoconstriction; nitric oxide
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide as a Predictor of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction* Samy M. ElHalawani, DO; Nam T. Ly, MD; Richard T. Mahon, MD; and Dennis E. Amundson, DO Introduction: Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction
Exhaled Nitric Oxide as a Predictor of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction* Samy M. ElHalawani, DO; Nam T. Ly, MD; Richard T. Mahon, MD; and Dennis E. Amundson, DO Introduction: Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction
3-Acetyldeoxynivalenol. 15-Acetyldeoxynivalenol
 3-Acetyldeoxynivalenol 15-Acetyldeoxynivalenol [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards] 1 Simultaneous analysis of trichothecene mycotoxin by gas chromatography [Feed Analysis Standards, Chapter
3-Acetyldeoxynivalenol 15-Acetyldeoxynivalenol [Methods listed in the Feed Analysis Standards] 1 Simultaneous analysis of trichothecene mycotoxin by gas chromatography [Feed Analysis Standards, Chapter
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: exhaled_nitric_oxide_measurement 2/2009 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Asthma is
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: exhaled_nitric_oxide_measurement 2/2009 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Asthma is
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Materials and Methods Measurement of NO formation by ozone-based chemiluminescence. Supplementary References
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Materials and Methods Measurement of NO formation by ozone-based chemiluminescence Nitric oxide (NO) production was measured by ozonebased chemiluminescence using a Sievers
Supplementary Data Supplementary Materials and Methods Measurement of NO formation by ozone-based chemiluminescence Nitric oxide (NO) production was measured by ozonebased chemiluminescence using a Sievers
WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator. Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients.
 EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
June 2011 Bill Streett-Training Section Chief
 Capnography 102 June 2011 Bill Streett-Training Section Chief Terminology Capnography: the measurement and numerical display of end-tidal CO2 concentration, at the patient s airway, during a respiratory
Capnography 102 June 2011 Bill Streett-Training Section Chief Terminology Capnography: the measurement and numerical display of end-tidal CO2 concentration, at the patient s airway, during a respiratory
Exhaled nitric oxide measurements with dynamic flow restriction in children aged 4 8 yrs
 Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 919 924 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.01282002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Exhaled nitric oxide measurements
Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 919 924 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.01282002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Exhaled nitric oxide measurements
Characterization of exhaled nitric oxide: introducing a new reproducible method for nasal nitric oxide measurements
 Eur Respir J ; 16: 236±241 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Characterization of exhaled nitric oxide: introducing a new reproducible
Eur Respir J ; 16: 236±241 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Characterization of exhaled nitric oxide: introducing a new reproducible
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator. Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients.
 EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
Forensic Analysis of Blood Alcohol Concentration
 Application Note Forensics Forensic Analysis of Blood Alcohol Concentration Using the Agilent 886 GC with Agilent J&W DB BAC1 UI and Agilent J&W DB-BAC2 UI columns and the Agilent 7697A headspace sampler
Application Note Forensics Forensic Analysis of Blood Alcohol Concentration Using the Agilent 886 GC with Agilent J&W DB BAC1 UI and Agilent J&W DB-BAC2 UI columns and the Agilent 7697A headspace sampler
Supporting information
 1 2 3 Supporting information SO 2 Uptake on Oleic Acid: A New Formation Pathway of Organosulfur Compounds in the Atmosphere 4 5 Jing Shang, Monica Passananti, Yoan Dupart, Raluca Ciuraru, Liselotte Tinel,
1 2 3 Supporting information SO 2 Uptake on Oleic Acid: A New Formation Pathway of Organosulfur Compounds in the Atmosphere 4 5 Jing Shang, Monica Passananti, Yoan Dupart, Raluca Ciuraru, Liselotte Tinel,
DETERMINATION OF FATTY ACIDS IN EDIBLE OILS BY CAPILARY GC
 DETERMINATION OF FATTY ACIDS IN EDIBLE OILS BY CAPILARY GC Vesna Kostik 1 University Goce Delcev Stip Faculty of Medicine Department of Pharmacy 1 WHY FATTY ACID (FA) ANALYSIS IN EDIBLE OILS The content
DETERMINATION OF FATTY ACIDS IN EDIBLE OILS BY CAPILARY GC Vesna Kostik 1 University Goce Delcev Stip Faculty of Medicine Department of Pharmacy 1 WHY FATTY ACID (FA) ANALYSIS IN EDIBLE OILS The content
Exercise and Air Pollution
 Exercise and Air Pollution Two Major Groups of Air Pollutants Primary From a single source of pollution CO, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, particulants Secondary Result from an interaction
Exercise and Air Pollution Two Major Groups of Air Pollutants Primary From a single source of pollution CO, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, particulants Secondary Result from an interaction
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Nitrogen
 1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
Determination of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) reference values in healthy Thai population
 Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Determination of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) reference values in healthy Thai population Yiwa Suksawat, Punchama Pacharn, Orathai
Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Determination of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) reference values in healthy Thai population Yiwa Suksawat, Punchama Pacharn, Orathai
DETERMINATION OF CANNABINOIDS, THC AND THC-COOH, IN ORAL FLUID USING AN AGILENT 6490 TRIPLE QUADRUPOLE LC/MS
 FORENSICS AND TOXICOLOGY ANALYSIS DETERMINATION OF CANNABINOIDS, THC AND THC-COOH, IN ORAL FLUID USING AN AGILENT 6490 TRIPLE QUADRUPOLE LC/MS Solutions for Your Analytical Business Markets and Applications
FORENSICS AND TOXICOLOGY ANALYSIS DETERMINATION OF CANNABINOIDS, THC AND THC-COOH, IN ORAL FLUID USING AN AGILENT 6490 TRIPLE QUADRUPOLE LC/MS Solutions for Your Analytical Business Markets and Applications
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
SCIEX Vitamin D 200M Assay for the Topaz System
 The First FDA-Cleared LC-MS/MS Assay for Vitamin D SCIEX Vitamin D 200M Assay for the Topaz System The first FDA-cleared LC-MS/MS assay for Vitamin D Vitamin D is an important building block for human
The First FDA-Cleared LC-MS/MS Assay for Vitamin D SCIEX Vitamin D 200M Assay for the Topaz System The first FDA-cleared LC-MS/MS assay for Vitamin D Vitamin D is an important building block for human
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.85-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.85-2016
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.85-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.85-2016
B Y L E S L I E K U M P F, R R T, C P F T, A E - C
 FeNO B Y L E S L I E K U M P F, R R T, C P F T, A E - C LESLIE KUMPF RRT, CPFT, AE-C Graduated from Henry Ford with a degree in Respiratory Therapy in 2006 Currently working on my BSRT Help start the RRT
FeNO B Y L E S L I E K U M P F, R R T, C P F T, A E - C LESLIE KUMPF RRT, CPFT, AE-C Graduated from Henry Ford with a degree in Respiratory Therapy in 2006 Currently working on my BSRT Help start the RRT
DETERMINATION OF COMPOSITION OF TRIACYLGLYCEROLS AND COMPOSITION AND CONTENT OF DI-ACYLGLYCEROLS BY CAPILLARY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY, IN VEGETABLE OILS
 INTERNATIONAL OLIVE COUNCIL COI/T.20/Doc. No 32 November 2013 ENGLISH Original: ENGLISH Príncipe de Vergara, 154 28002 Madrid España Telef.: +34 915 903 638 Fax: +34 915 631 263 - e-mail: iooc@internationaloliveoil.org
INTERNATIONAL OLIVE COUNCIL COI/T.20/Doc. No 32 November 2013 ENGLISH Original: ENGLISH Príncipe de Vergara, 154 28002 Madrid España Telef.: +34 915 903 638 Fax: +34 915 631 263 - e-mail: iooc@internationaloliveoil.org
Evaluation of Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Schoolchildren at Different Exhalation Flow Rates
 0031-3998/02/5203-0393 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 52, No. 3, 2002 Copyright 2002 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Evaluation of Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Schoolchildren at
0031-3998/02/5203-0393 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 52, No. 3, 2002 Copyright 2002 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Evaluation of Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Schoolchildren at
Super Clean TM. Gas Filters BIG TRAP INLINE FILTERS. Ideal for Central Purifying Solutions Largest Big Trap Available High Pressure Stainless Steel
 Super Cln TM Gas Filters BIG TRAP INLINE FILTERS EP-B 04774871.0 U.S. Patent Pending 10/567,949 2015 WWW.SGT-NL.COM Idl for Central Purifying Solutions Largest Big Trap Available High Pressure Stainless
Super Cln TM Gas Filters BIG TRAP INLINE FILTERS EP-B 04774871.0 U.S. Patent Pending 10/567,949 2015 WWW.SGT-NL.COM Idl for Central Purifying Solutions Largest Big Trap Available High Pressure Stainless
Comparison of patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry
 GE Healthcare Comparison of patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry Test results are based on the Master s thesis, Comparison between patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry by Saana Jenu, 2011
GE Healthcare Comparison of patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry Test results are based on the Master s thesis, Comparison between patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry by Saana Jenu, 2011
Describe regional differences in pulmonary blood flow in an upright person. Describe the major functions of the bronchial circulation
 OBJECTIVES Describe regional differences in pulmonary blood flow in an upright person Define zones I, II, and III in the lung, with respect to pulmonary vascular pressure and alveolar pressure Describe
OBJECTIVES Describe regional differences in pulmonary blood flow in an upright person Define zones I, II, and III in the lung, with respect to pulmonary vascular pressure and alveolar pressure Describe
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD NÄ 9
 CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD NÄ 9 DETERMINATION OF NICOTINE IN CIGARETTE FILTERS BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS (April 2009) 0. INTRODUCTION In 2001 the CORESTA Routine Analytical Chemistry Sub-Group was
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD NÄ 9 DETERMINATION OF NICOTINE IN CIGARETTE FILTERS BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS (April 2009) 0. INTRODUCTION In 2001 the CORESTA Routine Analytical Chemistry Sub-Group was
Savillex Technical Note
 Savillex Technical Note C400d PFA Concentric Nebulizer for ICP-MS Summary The Savillex C-Flow 400d (C400d) PFA concentric nebulizer combines the reliability of a low flow glass concentric nebulizer with
Savillex Technical Note C400d PFA Concentric Nebulizer for ICP-MS Summary The Savillex C-Flow 400d (C400d) PFA concentric nebulizer combines the reliability of a low flow glass concentric nebulizer with
Penthrox TM. The leader in emergency pain relief. Medical Developments International Limited
 Penthrox TM The leader in emergency pain relief Medical Developments International Limited There is more to basic pre-hospital and emergency first aid than basic life support The standard pre-hospital
Penthrox TM The leader in emergency pain relief Medical Developments International Limited There is more to basic pre-hospital and emergency first aid than basic life support The standard pre-hospital
Effects of inhaled versus systemic corticosteroids on exhaled nitric oxide in severe acute asthma
 Respiratory Medicine (2009) 103, 614e620 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed Effects of inhaled versus systemic corticosteroids on exhaled nitric oxide in
Respiratory Medicine (2009) 103, 614e620 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed Effects of inhaled versus systemic corticosteroids on exhaled nitric oxide in
Pelagia Research Library
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2015, 6(1):6-10 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Validated RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of metformin hydrochloride
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2015, 6(1):6-10 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Validated RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of metformin hydrochloride
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
PROTOCOL End Tidal CO2 Measurements for The POM Mask, Product #1003- PED Pediatric During Dual Bronchoscope Probe Use.
 PROTOCOL 18-0018 #1003- PED Pediatric During Dual Bronchoscope Probe Use March 11, 2018 Dave Piper, PE Piper Medical Products 1053 Village Ln Chico, CA 95926 Tel 530-588-6119 Dave@PiperMedical.com www.pipermedical.com
PROTOCOL 18-0018 #1003- PED Pediatric During Dual Bronchoscope Probe Use March 11, 2018 Dave Piper, PE Piper Medical Products 1053 Village Ln Chico, CA 95926 Tel 530-588-6119 Dave@PiperMedical.com www.pipermedical.com
LUNG FUNCTION MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT
 LUNG FUNCTION MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT THE WHISTLER IS THE FIRST HANDHELD, WIRELESS DEVICE IN THE WORLD FOR PERFORMING PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BOTH BABIES AND PRESCHOOL CHILDREN 2 3 THE WHISTLER MAKES
LUNG FUNCTION MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT THE WHISTLER IS THE FIRST HANDHELD, WIRELESS DEVICE IN THE WORLD FOR PERFORMING PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BOTH BABIES AND PRESCHOOL CHILDREN 2 3 THE WHISTLER MAKES
ISSN: ; CODEN ECJHAO E-Journal of Chemistry 2011, 8(3),
 ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2011, 8(3), 1275-1279 Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol, Phenylephrine Hydrochloride, Oxolamine Citrate and Chlorpheniramine
ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2011, 8(3), 1275-1279 Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol, Phenylephrine Hydrochloride, Oxolamine Citrate and Chlorpheniramine
Available online at Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (3):157-161 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (3):157-161 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
BIO-CHEMICALS FROM CONVERSION OF BIO-ETHANOL USING VARIOUS SINGLE OXIDES
 BIO-CHEMICALS FROM CONVERSION OF BIO-ETHANOL USING VARIOUS SINGLE OXIDES Nattapron Siribanluehan a, Sirirat Jitkarnka a a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
BIO-CHEMICALS FROM CONVERSION OF BIO-ETHANOL USING VARIOUS SINGLE OXIDES Nattapron Siribanluehan a, Sirirat Jitkarnka a a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
Respiratory Nitric Oxide Levels in Experimental Human Influenza*
 Respiratory Nitric Oxide Levels in Experimental Human Influenza* Andrew W. Murphy, MD; Thomas A.E. Platts-Mills, MD, PhD; Monica Lobo, MD; and Frederick Hayden, MD Background: Exhaled oral nitric oxide
Respiratory Nitric Oxide Levels in Experimental Human Influenza* Andrew W. Murphy, MD; Thomas A.E. Platts-Mills, MD, PhD; Monica Lobo, MD; and Frederick Hayden, MD Background: Exhaled oral nitric oxide
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(2):770-775 Validation of Rapid Liquid Chromatographic
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(2):770-775 Validation of Rapid Liquid Chromatographic
Assessment of accuracy and applicability of a new electronic peak flow meter and asthma monitor
 Eur Respir J 18; 12: 45 42 DOI: 18/1.8.5 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 18 European Respiratory Journal ISSN - 1 Assessment of accuracy and applicability of a new electronic
Eur Respir J 18; 12: 45 42 DOI: 18/1.8.5 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 18 European Respiratory Journal ISSN - 1 Assessment of accuracy and applicability of a new electronic
Correlation of Lethal Doses of Industrial Chemicals between Oral or Intraperitoneal Administration and Inhalation Exposure#
 Industrial Health 1998, 36, 273-281 Correlation of Lethal Doses of Industrial Chemicals between Oral or Intraperitoneal Administration and Inhalation Exposure# Takeshi HONMA* and Megumi SUDA Division of
Industrial Health 1998, 36, 273-281 Correlation of Lethal Doses of Industrial Chemicals between Oral or Intraperitoneal Administration and Inhalation Exposure# Takeshi HONMA* and Megumi SUDA Division of
Development and validation of stability indicating RP-LC method for estimation of calcium dobesilate in pharmaceutical formulations
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2016, 8 (11):236-242 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2016, 8 (11):236-242 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
HUMAN LIVER SLICE EXPERIMENT 1 Effects of Propylene Glycol on Ethylene Glycol Metabolism
 HUMAN LIVER SLICE EXPERIMENT 1 Effects of Propylene Glycol on Ethylene Glycol Metabolism Determination of Ethylene Glycol, Propylene Glycol, Oxalic Acid and Glycolic Acid BioReliance Study Number Testing
HUMAN LIVER SLICE EXPERIMENT 1 Effects of Propylene Glycol on Ethylene Glycol Metabolism Determination of Ethylene Glycol, Propylene Glycol, Oxalic Acid and Glycolic Acid BioReliance Study Number Testing
8/13/11. RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3. Humidification Equipment. Aerosol Therapy
 1 RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3 Wilkins: Chapter 35, p. 775-799 Cairo: Chapter 4, p. 88-143 2 Humidification Equipment A humidifier is a device that adds molecular liquid (e.g. water vapor)
1 RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3 Wilkins: Chapter 35, p. 775-799 Cairo: Chapter 4, p. 88-143 2 Humidification Equipment A humidifier is a device that adds molecular liquid (e.g. water vapor)
MAGNITUDE OF SAMPLING AND ANALYTICAL VARIATIONS IN BLOOD AND BREATH ALCOHOL MEASUREMENTS
 MAGNITUDE OF SAMPLING AND ANALYTICAL VARIATIONS IN BLOOD AND BREATH ALCOHOL MEASUREMENTS A. W. Jones, K. Jensson and P.M. Williams Department of alcohol Toxicology,j National Laboratory of Forensic Chemistry
MAGNITUDE OF SAMPLING AND ANALYTICAL VARIATIONS IN BLOOD AND BREATH ALCOHOL MEASUREMENTS A. W. Jones, K. Jensson and P.M. Williams Department of alcohol Toxicology,j National Laboratory of Forensic Chemistry
Fizzy Extraction of Volatile and Semivolatile Compounds into the Gas Phase
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Fizzy Extraction of Volatile and Semivolatile Compounds into the Gas Phase Cheng-Hao Chang, Pawel L. Urban* Department of Applied Chemistry, National Chiao Tung University 1001 University
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Fizzy Extraction of Volatile and Semivolatile Compounds into the Gas Phase Cheng-Hao Chang, Pawel L. Urban* Department of Applied Chemistry, National Chiao Tung University 1001 University
Agilent 1220 Infinity LC System Performance Specifications
 IET International Equipment Trading, Ltd. www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment Agilent 1220 Infinity LC System Performance
IET International Equipment Trading, Ltd. www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment Agilent 1220 Infinity LC System Performance
Nitric Resource Manual
 Nitric Resource Manual OBJECTIVES Describe the biologic basis for inhaled nitric oxide therapy Describe the indications for inhaled nitric oxide therapy Describe the potential hazards, side effects and
Nitric Resource Manual OBJECTIVES Describe the biologic basis for inhaled nitric oxide therapy Describe the indications for inhaled nitric oxide therapy Describe the potential hazards, side effects and
Independent Column Temperature Control Using an LTM Oven Module for Improved Multidimensional Separation of Chiral Compounds
 Independent Column Temperature Control Using an LTM Oven Module for Improved Multidimensional Separation of Chiral Compounds Application Note Food and Flavors Author Frank David Research Institute for
Independent Column Temperature Control Using an LTM Oven Module for Improved Multidimensional Separation of Chiral Compounds Application Note Food and Flavors Author Frank David Research Institute for
Breathomics: potential applications in respiratory and occupational medicine
 Breathomics: potential applications in respiratory and occupational medicine Paolo Montuschi, MD Department of Pharmacology Catholic University of the Sacred Heart University Hospital A. Gemelli Rome Non-invasive
Breathomics: potential applications in respiratory and occupational medicine Paolo Montuschi, MD Department of Pharmacology Catholic University of the Sacred Heart University Hospital A. Gemelli Rome Non-invasive
sphere A diameter / cm 1 3 (i) The student calculated the surface area: volume ratio of sphere B as 2:1.
 1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
A. Incorrect! The alveolus is where gas exchange takes place. B. Correct! Surfactant is the lipid-rich material that permits lung inflation.
 Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
CHAPTER 3. Correction factors for oxygen and flow-rate effects on neonatal Fleisch and Lilly pneumotachometers
 CHAPTER 3 Correction factors for oxygen and flow-rate effects on neonatal Fleisch and Lilly pneumotachometers Yvonne Snepvangers Peter de Winter Huibert Burger Hens Brouwers Jan Bogaard Kors van der Ent
CHAPTER 3 Correction factors for oxygen and flow-rate effects on neonatal Fleisch and Lilly pneumotachometers Yvonne Snepvangers Peter de Winter Huibert Burger Hens Brouwers Jan Bogaard Kors van der Ent
Mass-Based Purification of Natural Product Impurities Using an Agilent 1260 Infinity II Preparative LC/MSD System
 Application Note Food Testing and Agriculture Mass-Based Purification of Natural Product Impurities Using an Agilent 126 Infinity II Preparative LC/MSD System Authors Florian Rieck and Jörg Hippler Agilent
Application Note Food Testing and Agriculture Mass-Based Purification of Natural Product Impurities Using an Agilent 126 Infinity II Preparative LC/MSD System Authors Florian Rieck and Jörg Hippler Agilent
The effect of active and passive smoking on inhaled drugs in respiratory patients
 CHAPTER 12 The effect of active and passive smoking on inhaled drugs in respiratory patients G. Invernizzi*, A. Ruprecht*, P. Paredi #, R. Mazza*, C. De Marco*, R. Boffi* *Tobacco Control Unit, National
CHAPTER 12 The effect of active and passive smoking on inhaled drugs in respiratory patients G. Invernizzi*, A. Ruprecht*, P. Paredi #, R. Mazza*, C. De Marco*, R. Boffi* *Tobacco Control Unit, National
Development, Estimation and Validation of Lisinopril in Bulk and its Pharmaceutical Formulation by HPLC Method
 ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2012, 9(1), 340-344 Development, Estimation and Validation of Lisinopril in Bulk and its Pharmaceutical Formulation by PLC Method V.
ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2012, 9(1), 340-344 Development, Estimation and Validation of Lisinopril in Bulk and its Pharmaceutical Formulation by PLC Method V.
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Anaesthetic and respiratory equipment Nebulizing systems and components
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 27427 First edition 2009-05-01 Anaesthetic and respiratory equipment Nebulizing systems and components Matériel d'anesthésie et de réanimation respiratoire Systèmes de nébulisation
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 27427 First edition 2009-05-01 Anaesthetic and respiratory equipment Nebulizing systems and components Matériel d'anesthésie et de réanimation respiratoire Systèmes de nébulisation
NUTRITIONAL COMPONENTS OF SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE EXTRACTED WHEAT GERM OIL
 NUTRITIONAL COMPONENTS OF SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE EXTRACTED WHEAT GERM OIL Nurhan Turgut Dunford 1* and Jose L. Martinez 2 1 Oklahoma State University, Department of Plant and Soil Sciences and Food
NUTRITIONAL COMPONENTS OF SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE EXTRACTED WHEAT GERM OIL Nurhan Turgut Dunford 1* and Jose L. Martinez 2 1 Oklahoma State University, Department of Plant and Soil Sciences and Food
Recent Advances in the Analysis of Ethanol in Saliva: Evaluation of the QED Device
 Recent Advances in the Analysis of Ethanol in Saliva: Evaluation of the QED Device A.W. Jones and k A. Jünsson Departments of Alcohol Toxicology and Internal Medicine, University Hospital, 581 85 Linköping,
Recent Advances in the Analysis of Ethanol in Saliva: Evaluation of the QED Device A.W. Jones and k A. Jünsson Departments of Alcohol Toxicology and Internal Medicine, University Hospital, 581 85 Linköping,
Capnography. Capnography. Oxygenation. Pulmonary Physiology 4/15/2018. non invasive monitor for ventilation. Edward C. Adlesic, DMD.
 Capnography Edward C. Adlesic, DMD University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine 2018 North Carolina Program Capnography non invasive monitor for ventilation measures end tidal CO2 early detection
Capnography Edward C. Adlesic, DMD University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine 2018 North Carolina Program Capnography non invasive monitor for ventilation measures end tidal CO2 early detection
