Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
|
|
|
- Cecil Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
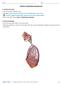
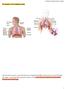
1 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration Carbon dioxide: a waste product generated in cellular respiration Four Processes of Respiration Breathing: the movement of air into and out of External respiration: the exchange of gases between inhaled air and Internal respiration: the exchange of gases between the blood and Cellular respiration: the process of using oxygen to produce within cells; this process also generates as a waste product The pathway of air Drawn into mouth or nose Pharynx ( ) Larynx ( ) Trachea ( ) Enters chest cavity Divides into two branches (left and right bronchus), one to each Bronchi branch inside lungs, forming smaller and smaller branches The smallest of these tubules branch to form ducts, called that lead to the (air sacs) Smooth muscles automatically control the opening and closing of bronchioles Lungs Located in cavity Contain millions of (air sacs) Surrounded by Where gas exchange occurs 9 What we breathe in Various airborne particles, such as dust, bacteria, pollen, and pollutants The trap Large particles become trapped in the mucus coating the epithelial linings of upper 1
2 respiratory tract (nasal passages, mouth cavity, pharynx, and trachea) Ciliated cells lining respiratory tract beat cilia, moving mucus upward toward mouth Mucus containing dust, bacteria, and other large particles may be swallowed or spit out Protects the lungs Smaller particles (fine particulates) may not become trapped in mucus, and make it all the way to the lungs Example: toxic metals such as mercury, and exhaust from diesel vehicles Can cause lung cancer When the mucus trap fails Doesn t always prevent all bacteria, viruses, and other particles from reaching lungs can decrease effectiveness of the ciliated cells lining the respiratory tract Sulfur dioxide gas in cigarette smoke May paralyze, or even kill, the ciliated cells Allows particles to enter lungs Smokers have more respiratory infections Interestingly, alcohol has same effect Getting Oxygen to the Cells Atmosphere is approximately % nitrogen and % oxygen gas Oxygen is generated by the of plants and other photosynthetic organisms When the air we breathe reaches the alveoli, gas exchange occurs Single-celled lining of the alveoli ( alveolar cells) Single-celled lining of the capillaries Mechanism: (movement of oxygen from an area of low high concentration to an area of low oxygen concentration) Oxygen then attaches to the molecules inside the red blood cells Is carried to the cells of the body via the arteries of the circulatory system Carbon dioxide: the opposite pathway Deoxygenated blood enters capillaries from the veins of the body Carbon dioxide diffuses from the capillaries into the Carbon dioxide is then expelled when we exhale Alveolar eat particles of dust, bacteria, and viruses that enter the alveoli Once they fill up, they embed themselves in the connective tissue of the lungs 2
3 Tobacco smoke contains so many particulates, causes MANY of these macrophages to fill up and embed in the lung tissue Gives a blackened appearance to lungs of smokers Similar effect may be seen in people who live in urban areas and breathe in large amounts of pollutants alveolar cells Secrete a lipid called Forms coating over thin layer of water over alveolar surface and prevents by reducing surface tension At air-water interface, water molecules stick to each other The surface tension of the water coating the alveolar epithelium could cause the thin walls of the alveoli to collapse Oily coating disrupts the pull of the water molecules toward each other Making Some Noise! Vocal cords are located in (voice box) Two Vibrate when air is released from lungs Sounds produced vary as tongue position and shape of oral cavity are changed Variation in length and thickness of vocal cords effects sound produced (different from person to person) Vocal cords in men usually longer and thicker, generating deeper voices Children have short, slender vocal cords higher pitched voices At puberty, a boy s voice changes: testosterone causes larynx to grow, and vocal cords to thicken Breathing Largely an involuntary action controlled by Inhalation: air is drawn into lungs Nerve impulses stimulate the to contract Sheet of muscle below the lungs Separates abdominal and chest cavities When diaphragm contracts, it flattens and lowers, causing Rib cage is also lifted upward and outward More space is available in chest cavity Exhalation: air is expelled from lungs Occurs after diaphragm and rib muscles Air is expelled 3
4 Breathing controlled by the breathing center of the brain Causes periodic impulses to be sent to diaphragm and rib muscles Contraction of these muscles results in When lungs fill, impulses stop being sent When muscles subsequently relax, you Diseases of Respiratory System Bronchitis: an infection of the Inflammation of lining of tubes Less air able to reach lungs Large amounts of mucus produced and coughed up Often associated with a cold bronchitis: when mucus-producing cough is present most days of the month for 3 months of the year for at least two years Can lead to scarring of bronchial tubes Excessive mucus is produced constantly Lungs can become scarred Infections more common #1 cause of chronic bronchitis: Other causes of bronchitis: bacterial and viral infections : walls of alveoli lose ability to stretch and recoil; sacs weaken and break Symptoms: shortness of breath and cough Usually caused by Effects of pollutants Asbestos Can cause lung cancer Can cause build up of scar tissue in lungs Asthma A type of, usually caused by dust, pollen, or pet dander Irritants stimulate increased production of mucus by bronchi and bronchioles Also cause bronchioles to Inflammation of respiratory tract occurs Breathing becomes more difficult 4
5 Lung Cancer Approximately 160,000 deaths from lung cancer each year #1 cause: (87% of cases due to smoking) Cigarette smoke contains >4,000 different chemicals, 69 of which are carcinogens After you stop smoking, normal cells gradually replace damaged cells, and risk of lung cancer drops Lung function increases 30% with 3 months After 10 years, risk of lung cancer approximately same as a non-smoker Second-hand smoke responsible for approximately 3,000 deaths each year A recent (2015) study has found that smoking causes even more diseases and deaths than previously thought 60,000 additional deaths Had already been linked to nearly half a million deaths due to 21 different diseases and 12 types of cancer Diseases newly linked to smoking include disease, diseases due to inadequate blood flow, increased risk for, and heart and lung ailments not previously linked to smoking Smoking weakens the immune system; causes diabetes and high blood pressure, which damages kidneys; artery disease from smoking can reduce blood supply to intestines, damaging the intestines Bonus Activity Ohio State University is just one of a growing number of institutions and businesses that is tobacco free. Discuss with your group the pro s and con s of such a policy, and list major arguments for/against going tobacco free. E-Cigarettes are gaining popularity as a healthier option to smoking. Are they safe? Read the article Vaping and Health. Then, pretend your group is a committee that has been tasked with making the decision as to whether or not to continue to make e- cigarettes part of the OSU no-tobacco policy. Write a consensus statement for your group. All for today 5
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
What is RESPIRATION?
 Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from?
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
Respiration. Chapter 35
 Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS
 FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals
 Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Chapter 16. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 2 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 2 pages 417-419 Hemoglobin has 4 separate protein chains. Each protein chain has a single iron atom (Fe 3+ ). Each iron atom can bind to a single
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 2 pages 417-419 Hemoglobin has 4 separate protein chains. Each protein chain has a single iron atom (Fe 3+ ). Each iron atom can bind to a single
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Chapter 17. Clearing the Air: Respiratory, Cardiovascular, and Excretory Systems. Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System
 17.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Chapter 17 Clearing the Air: Respiratory, Cardiovascular, and Excretory Systems Exhaled smoke + smoke directly from cigarette tip = (ETS) Affects and (non-smoker
17.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Chapter 17 Clearing the Air: Respiratory, Cardiovascular, and Excretory Systems Exhaled smoke + smoke directly from cigarette tip = (ETS) Affects and (non-smoker
Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
 Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Write It! Station Directions
 Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Bronchioles. Bronchi. Pharynx epiglottis. (bronchus) Nose mouth. Diaphragm. Alveoli [alveolus] Larynx Trachea. Respiratory Structure
![Bronchioles. Bronchi. Pharynx epiglottis. (bronchus) Nose mouth. Diaphragm. Alveoli [alveolus] Larynx Trachea. Respiratory Structure Bronchioles. Bronchi. Pharynx epiglottis. (bronchus) Nose mouth. Diaphragm. Alveoli [alveolus] Larynx Trachea. Respiratory Structure](/thumbs/83/88046543.jpg) Respiratory Structure Nose mouth Function Pharynx epiglottis Larynx Trachea Bronchi (bronchus) Bronchioles Alveoli [alveolus] Diaphragm Jan 13 1:28 PM 1 NOSE Pharynx LUNGS Larynx/Trachea Bronchi/Bronchioles
Respiratory Structure Nose mouth Function Pharynx epiglottis Larynx Trachea Bronchi (bronchus) Bronchioles Alveoli [alveolus] Diaphragm Jan 13 1:28 PM 1 NOSE Pharynx LUNGS Larynx/Trachea Bronchi/Bronchioles
Nasal Cavity. The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the. (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!)
 Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATION- Life function. Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Circulatory and Respiratory
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. The
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. The
10.1 The Pulmonary-Circulatory System
 pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Chapter 8. Bellringer. Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System
 Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Bellringer Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Objectives Trace the path of blood through the
Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Bellringer Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Objectives Trace the path of blood through the
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
? Pulmonary Respiratory System
 The Structure of The Respiratory System The respiratory system is composed of groups of organelles that filters and transports air into the lungs. The organs comprising of the respiratory system include
The Structure of The Respiratory System The respiratory system is composed of groups of organelles that filters and transports air into the lungs. The organs comprising of the respiratory system include
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
 11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to
 1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives --()--
 IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Summary The Circulatory System Blood and the Lymphatic System. Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Summary 37-1 The Circulatory System The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together with the respiratory
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Summary 37-1 The Circulatory System The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together with the respiratory
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
Respiratory system. Applied Anatomy &Physiology
 Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body
 In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body. 1. 2. (2) Describe what gaseous exchange is and clearly state where it takes
In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body. 1. 2. (2) Describe what gaseous exchange is and clearly state where it takes
