Spotlight on the diagnosis of extrinsic allergic alveolitis (hypersensitivity pneumonitis)
|
|
|
- Blaze Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Baur et al. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology (2015) 10:15 DOI /s METHODOLOGY Spotlight on the diagnosis of extrinsic allergic alveolitis (hypersensitivity pneumonitis) Xaver Baur 1,3*, Axel Fischer 1,3 and Lygia T Budnik 2,3 Open Access Abstract Repeated inhalative exposures to antigenic material from a variety of sources, mainly from moulds, thermophilic Actinomycetes, and avians, respectively, can induce immune responses with the clinical picture of extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) or hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Delays of years or even decades till the diagnosis is made are not uncommon; frequent misdiagnoses include allergic asthma, COPD, recurrent flue and other infections. We provide here the state of the art references, a detailed case description and recommend a current diagnostics schema. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) or hypersensitivity pneumonitis is an immunologically mediated disease caused by sensitization to repeated inhalation of antigenic organic material derived from a variety of sources, such as mouldy hay, mouldy wood bark, bacterially contaminated metal working fluid or humidifier water (Figures 1, 2, 3 and 4), avian bloom proteins, but also chemicals such as isocyanates may cause this disorder [1-8], (Table 1). EAA is predominantly an occupational disease with most common antigens from thermophilic Actinomycetes species, various moulds and avian proteins. The prevalence of extrinsic allergic alveolitis varies depending on the climate, geographic conditions, occupational and industry factors, and is mostly is in the range of [9-11] percent with farmer's lung or bird fancier s lung as the prevailing one in most regions. Sensitized subjects may develop an acute, subacute (intermittent), and chronic progressive course depending on degree of sensitisation, intensity and duration of exposure. EAA is associated with diffuse inflammation of lung parenchyma and airways in sensitized subjects including non-caseating interstitial granulomas and peribronchial mononuclear cell infiltration with giant cells. Although most affected subjects typically have high serum concentrations of circulating immunoglobulin G antibodies specific for the causative antigen(s), the diagnosis may be * Correspondence: Xaver.Baur@charite.de 1 Institute for Occupational Medicine, Charité University Medicine Berlin, Berlin, Germany 3 European Society for Environmental and Occupational Medicine, EOM, Berlin, Germany Full list of author information is available at the end of the article difficult as the symptoms are often non-specific, have typically a latency period of several hours, or may appear constitutional with malaise and weight loss; frequently they are gradually progressive over years, finally with persisting respiratory distress independent of the inducing exposure (Figures 1, 2, 3 and 4). Delays of years or even decades till the diagnosis is made are not uncommon, misdiagnoses include allergic asthma, COPD, recurrent flue and other infections. We recommend the following diagnostics schema for the disease pattern. Diagnostics (Table 2) [4,12] 1. Case history: 4-8 hours following heavy exposure to an inciting agent patients develop fever, chills, malaise, cough, dyspnea, headache (acute course). Some cases don t develop acute symptoms, rather, they have an insidious onset of these symptoms. Especially at lower exposures, patients gradually develop productive chronic cough, dyspnea on exertion, fatigue, anorexia, weight loss (subacute or intermittent course) (Table 2). These findings may be also present in patients who experience repeated acute attacks. 2. Physical examination: During the acute attack there are fever, tachypnea, and diffuse fine bibasilar end-inspiratory crackles upon auscultation. Further frequent findings include muscle wasting, weight loss, in the chronic pronounced form also clubbing, tachypnea, respiratory distress. 3. Lung function testing: A restrictive ventilatory pattern (i.e. reduced total lung capacity, vital 2015 Baur et al.; licensee BioMed Central. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Baur et al. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology (2015) 10:15 Page 2 of 6 Figure 1 Agents causing extrinsic allergic alveolitis, specific inhalative challenge testing, and bronchoalveolar lavage cells. A. Mouldy hay causing farmer s lung disease in the subject shown in Figure 1D and Figure 4 B. Bronchoalveolar lavage with extensive neutrophilia present six hours post challenge in an subject with pigeon breeder s lung. C. Water and sediment of a humidifier water of a printing plant (of the subject shown in Figure 3). Microscopic examinations demonstrated a variety of bacteria and moulds in this specimen. D. Occupational type specific inhalative challenge test with mouldy hay (Figure 1A). capacity, and lung compliance) and impaired gas exchange parameters (reduced diffusing capacity, hypoxemia during exercise or even at rest) are typical features of the advanced chronic course. Also a mixed obstructive and restrictive ventilation pattern can develop. 4. IgG antibodies and other laboratory findings: High serum concentrations of IgG antibodies specific for causative antigens are found in c. 70% of affected patients (Figure 2). More problematic from the diagnostic view is that more than 50% of the prevailing exposed healthy subjects may show such Figure 2 Acute extrinsic allergic alveolitis after indicative challenge by mouldy hay. The figure shows a summary of the clinical diagnostic findings of the patient described as case 1. Clinical evidence: Several hours post challenge, fever, malaise, cough, associated with a restrictive ventilation pattern, and impaired gas exchange. The data shows lung function and other clinical findings in a time scale after the challenge [h]: f: Vital capacity VC [L], e: P a,o2 arterial oxygen pressure [mmhg], d. Diffusion capacity/transfer coefficient for carbon monoxide (T L,CO )factor[ml/min*kpa], c: Specific airway resistance (sraw) measured by whole body plethysmography [kpa*s]; Further parameter shown are: b: Temperature profile gradation [ C], a. Blood leukocytes counts *1000/mm 3 ].
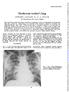
3 Baur et al. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology (2015) 10:15 Page 3 of 6 Figure 3 Chest x-ray of a 33 year old worker of a printing plant, suffering from subacute humidifier lung disease. For details see text. There are patchy infiltrates predominantly in the lower and middle lung fields. antibodies, depending on the causative antigen(s) and sensitivity and specificity of the laboratory test used. So far, for most causative antigens validated laboratory tests are not available on the market. In addition to an immunocomplex-mediated process, cell-mediated immunity obviously plays an important pathophysiological role. However, no routine diagnostic test for displaying this cellular response is available yet. Other abnormal laboratory findings during acute and subacute courses include leukocytosis, neutrophilia, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and increased levels of quantitative immunoglobulins and C-reactive protein. 5. Radiological findings: The typical pictures are centrilobular micronodular (HRCT), patchy or reticular opacities which are mostly prominent in lower lung zones (Figure 3). Ground-glass opacities in the lower and middle lung zones and an interstitial pneumonitis-like pattern may be present during acute attacks. The end stage of the chronic course is characterized by fibrosis and even honeycombing predominant in the lower parts of the lungs. Emphysema may also occur [13]. 6. Serial lung function testing during antigen exposure periods and days off (exhibiting changes as outlined under SIC and restitution of symptoms and impaired lung function during days off). 7. Specific inhalative challenge test (SIC): This is a laborious and time consuming diagnostic test by the use of the suspected causative agent. It should only Figure 4 Presence of specific IgG antibodies in blood sera of 23 subjects suffering from isocyanate alveolitis. Note that all but five subjects show significant levels of such antibodies. The diisocyanates toluylene disocyanate (TDI), methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) bound to human serum albumin (HSA) were used for immune absorbent assay (CAP immunoanalysis) as described. For methodological details see Baur [4], Budnik et al. [18]. Specific IgG antibodies in blood sera from a patient suffering from humidifier lung due to exposure to contaminated humidifier water (Figure 1C). Shown is ELISA assay with anti IgG antibodies recognising dose specific reaction to various concentrations of workplace related humidifier water antigens. The negative and positive controls show lab intern positive and negative samples from patients with strong signal (positive reaction) and pool serum from healthy subjects without contact with humidifier aerosols (negative control, unspecific binding). be performed by well-experienced physicians. If done correctly it is a very sensitive and specific diagnostic method. See Table 2 and example in Figures. 1D, methodological methods have been published elsewhere [14,15], with the supplementary material from the European task force on SIC published online asthma additional Handbook of procedures for specific inhalation challenge testing content/suppl/2014/03/07/ dc1/ Final_Handbook.pdf 8. Bronchoalveolar lavage: Bronchoalveolar lavage shows leukocytosis (neutrophilia) in the alveoli and small airways in the acute course followed by an
4 Baur et al. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology (2015) 10:15 Page 4 of 6 Table 1 Sources and major antigens of extrinsic allergic alveolitis (hypersensitivity pneumonitis) Disease Causative exposure Antigens Farmer's lung Mouldy hay Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula (Micropolyspora faeni), Thermoactinomyces vulgaris, Aspergilli Bagassosis Mouldy sugar cane fiber Thermoactinomyces sacchari Humidifier/air-conditioner lung Contaminated forced-air systems, S. rectivirgula, T. vulgaris, various fungi heated water reservoirs Bird breeder's lung Pigeons, parakeets, fowl Avian proteins (of bloom or faeces) Metal working hypersensitivity pneumonitis Microbially contaminated metal working fluid Various moulds and bacteria Cheese worker's lung Cheese mould Penicillium casei Malt worker s lung Mouldy malt Aspergillus clavatus Paprika splitter s lung Paprika dust Mucor stolonifer Mollusk shell hypersensitivity Shell dust Proteins in dust from sea snail shells or mother-of-pearl shells Chemical worker s lung, isocyanate alveolitis Manufacture of plastics, polyurethane foam, rubber Trimellitic anhydride, diisocyanates influx of mononuclear cells (Figure 1D). In the subacute and chronic courses lymphocytosis with increased CD8 + cells and a CD4+/CD8+ ratio of < 1 are observed 6 hours post challenge. 9. Lung histology: Invasive diagnostics, i.e. lung biopsy, is usually not needed. In the acute course leukocytic inflammation is dominating. Lymphocyte-dominant interstitial inflammatory cell infiltration, well-formed interstitial epitheliod cell nonnecrotizing granulomas with giant cells are characteristic for the subacute and chronic courses. Cellular bronchiolitis and foci of bronchiolitis obliterans and intra-alveolar fibrosis may also occur. The chronic course includes an interstitial Table 2 Diagnostic parameters of extrinsic allergic alveolitis Symptoms: Exposure (work)-related cough, chest tightness, dyspnea, fever, with latency period of several hrs Progressive flu-like symptoms during the exposure periods (e.g. working week) with solution at days off Dyspnea on exertion Weight loss in the absence of any other reason Clinical/physical examination: Fine bibasilar end-inspiratory crackles in advanced chronic forms clubbing and respiratory distress Serology: Presence of high serum concentrations of antigen-specific IgG antibodies Lung function testing: FVC < 80% predicted (below lower limit of normal) or FVC < 70% pred. and/or T L,CO < 80% pred. or T L,CO < 60% pred. or hypoxemia during exercise Radiology: Abnormal chest x-ray (nodular, patchy and/or diffuse ground glass pattern) Abnormal HRCT (ground glass, nodular and/ or patchy opacities, mosaic or UIP pattern Serial lung function testing and clinical investigations during antigen exposure periods and days off (for minimal diagnostic changes see SIC below): Specific inhalation challenge (minimal changes after 5-12 hrs): FVC and TLC -15% T L,CO -15% or P a,o2 7 mmhg New fine bibasilar end-inspiratory crackles Systemic symptoms (temperature + 1 C and leukocytosis /L)
5 Baur et al. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology (2015) 10:15 Page 5 of 6 (organizing) pneumonia like pattern with sub pleural patchy fibrosis, fibroblastic foci with centrilobular fibrosis, finally alveolar destruction (honeycombing) [16,17]. 10. Integrated diagnostic approach: Above steps 1 through 5 present basic routine diagnostics. If all of them exhibit concordant positive findings diagnosis of extrinic allergic alveolitis is sufficiently likely. If one or more of the respective 6 parameters is/are negative or equivocal at least one additional diagnostic procedure is needed, i.e. serial lung function testing during antigen exposure periods and days off (combined with follow-up of clinical symptoms) or specific inhalation challenge test, bronchoalveolar lavage or lung biopsy (Table 3). Case examples Case 1 (farmers lung) Case history: The 53 year old farmer has suffered for 5 years from cough, progressive shortness of breath during exertion, chills and fever in late evenings and nights during winter months. He always feed his 40 cows hay which was frequently mouldy. Physical examination: Inspiratory crackles on basal lung fields. Lung function testing: A restrictive ventilatory pattern (i.e. reduced total lung capacity, vital capacity, and lung compliance) and impaired gas exchange parameters. IgG antibodies: High serum concentrations of IgG antibodies for aspergillus species and. Specific inhalative challenge test (Figures. 1D) of this patient suffering from farmers lungbyaprobeof his mouldy hay (Figure 1A); for the outcome see Figure 4. Radiological findings: Patchy opacities on both lower and middle lung fields. Bronchoalveolar lavage: Bronchoalveolar lavage showed leukocytosis (neutrophilia) in the alveoli and small airways in the acute phase followed by an influx of mononuclear cells. Case 2 (humidifier lung) Figure 1C shows humidifier water of a printing plant where several heavily microbially contaminated humidifiers were installed and our 33 year old patient was employed. For chest x-ray findings see Figure 3. Case history: He had complained of flu-like symptoms and chronic productive cough for more than 6 years without seasonal variation and increasing shortness of breath on exertion. IgG antibodies: Serum IgG antibody analysis (Figure 2B) showed extremely high concentrations for the extract of the probe shown in Figure 1C, and lower concentrations for a variety of moulds and bacteria. Specific inhalative challenge test: This was done by means of this humidifier water probe produced after a latency of 4 hours increasing cough, dyspnea, fever, a significant falls of vital capacity and arterial oxygen partial pressure, lasting for 3 hours. Prevention and Treatment The best outcome is offered by early recognition and consistent prevention of further exposures. To avoid the causative agent(s) is also the only effective measure to prevent relapses, the typically progressive disorder and permanently impaired lung function. Corticosteroids may be needed in cases with severe acute courses (starting with mg prednisone/kg). Less sever acute courses abate without treatment. Table 3 Summary of diagnostic criteria Routine, basic diagnostics: Case history: Exposure to relevant antigen(s) Exposure-related respiratory and systemic symptoms Specific IgG antibodies to relevant antigens (i.e. antigen-hsa-conjugates) Bibasilar end-inspiratory crackles (lower lung) Lung nodular, patchy and/or ground glass pattern in chest x-ray or HRCT Restrictive ventilation pattern (FVC, TLC) and reduced gas exchange parameters (T L,CO ;P a,o2 ) Facultative diagnostic parameter. If not all of the before-mentioned parameters are fulfilled at least one additional positive parameter is needed Serial lung function testing during antigen exposure periods and days off (exhibiting changes as outlined under SIC as well as restitution of symptoms and impaired lung function during days off) or specific inhalative challenge test (exhibiting changes as outlined in Table 2) BAL showing lymphocytosis with ratio of CD4/CD8 < 1 or typical histopathological findings Note: we do not recommend the evaluation point system, but rather a careful valuation of the clinical findings and laboratory data in each individual case (see above).
6 Baur et al. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology (2015) 10:15 Page 6 of 6 Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests whether with a product company or a lobby group. Authors contributions XB, LTB, AF performed the literature review, XB examined the patients and provided the clinical data on cases; LTB supervised the laboratory analyses; XB, LTB drafted the manuscript; XB, AF, LTB edited and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. 17. Takemura T, Akashi T, Ohtani Y, Inase N, Yoshizawa Y. Pathology of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008;14: Budnik LT, Preisser AM, Permentier H, Baur X. Is specific IgE antibody analysis feasible for the diagnosis of methylenediphenyl diisocyanate-induced occupational asthma? Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2013;86: Disclosure XB testified in occupational diseases litigation on behalf of here described plaintiff cases and provide independent expert opinion for social courts or statutory insurances. Author details 1 Institute for Occupational Medicine, Charité University Medicine Berlin, Berlin, Germany. 2 Division Occupational Toxicology and Immunology, Institute for Occupational and Maritime Medicine (ZfAM), University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf. University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany. 3 European Society for Environmental and Occupational Medicine, EOM, Berlin, Germany. Received: 25 November 2014 Accepted: 2 April 2015 References 1. Blatman KH, Grammer LC. Chapter 19: Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012;33 Suppl 1:S Lacasse Y, Girard M, Cormier Y. Recent advances in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2012;142: Selman M, Pardo A, King Jr TE. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: insights in diagnosis and pathobiology. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186: Baur X. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (extrinsic allergic alveolitis) induced by isocyanates. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;95: Robertson W, Robertson AS, Burge CB, Moore VC, Jaakkola MS, Dawkins PA, et al. Clinical investigation of an outbreak of alveolitis and asthma in a car engine manufacturing plant. Thorax. 2007;62: Weiss W, Baur X. Antigens of powdered pearl-oyster shell causing hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 1987;91: Baur X, Behr J, Dewair M, Ehret W, Fruhmann G, Vogelmeier C, et al. Humidifier lung and humidifier fever. Lung. 1988;166: Fox J, Anderson H, Moen T, Gruetzmacher G, Hanrahan L, Fink J. Metal working fluid-associated hypersensitivity pneumonitis: an outbreak investigation and case-control study. Am J Ind Med. 1999;35: Lacasse Y, Cormier Y. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006;1: Rose C, King Jr TE. Controversies in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;145: Dalphin JC, Debieuvre D, Pernet D, Maheu MF, Polio JC, Toson B, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for chronic bronchitis and farmer's lung in French dairy farmers. Br J Ind Med. 1993;50: Lacasse Y, Selman M, Costabel U, Dalphin JC, Ando M, Morell F, et al. Clinical diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168: Hanak V, Golbin JM, Hartman TE, Ryu JH. High-resolution CT findings of parenchymal fibrosis correlate with prognosis in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2008;134: Munoz X, Sanchez-Ortiz M, Torres F, Villar A, Morell F, Cruz MJ. Diagnostic yield of specific inhalation challenge in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Eur Respir J. 2014;44: Vandenplas O, Suojalehto H, Aasen TB, Baur X, Burge PS, De Blay F, et al. Specific inhalation challenge in the diagnosis of occupational asthma: consensus statement. Eur Respir J. 2014;43: Lima MS, Coletta EN, Ferreira RG, Jasinowodolinski D, Arakaki JS, Rodrigues SC, et al. Subacute and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: histopathological patterns and survival. Respir Med. 2009;103: Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS
 HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Epidemiology and Classification
 Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Epidemiology and Classification Ulrich Costabel, MD University of Duisburg-Essen, Ruhrlandklinik Department of Pneumology/Allergy Objectives Definitions, Etiology Epidemiology
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Epidemiology and Classification Ulrich Costabel, MD University of Duisburg-Essen, Ruhrlandklinik Department of Pneumology/Allergy Objectives Definitions, Etiology Epidemiology
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P
 Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
LUNG DISEASES DUE TO ORGANIC&INORGANIC DUSTS. Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P
 LUNG DISEASES DUE TO ORGANIC&INORGANIC DUSTS Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P efinition of hypersensitivity pneumonitis(extrinsic allergic alveolitis): Inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls
LUNG DISEASES DUE TO ORGANIC&INORGANIC DUSTS Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P efinition of hypersensitivity pneumonitis(extrinsic allergic alveolitis): Inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls
4/17/2010 C ini n ca c l a Ev E a v l a ua u t a ion o n of o ILD U dat a e t e i n I LDs
 Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School, University of Crete Prague, June 2014
 Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Causes, clinical course, diagnosis and differential diagnosis, treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Causes, clinical course, diagnosis and differential diagnosis, treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf
 Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Spectrum of High-Resolution CT and Pathologic Findings
 CT of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay C. Isabela S. Silva 1 ndrew Churg 2 Nestor L. Müller 1 Silva CIS, Churg, Müller NL Keywords: high-resolution CT, hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
CT of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay C. Isabela S. Silva 1 ndrew Churg 2 Nestor L. Müller 1 Silva CIS, Churg, Müller NL Keywords: high-resolution CT, hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
Case Presentations in ILD. Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco
 Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
DIAGNOSTIC NOTE TEMPLATE
 DIAGNOSTIC NOTE TEMPLATE SOAP NOTE TEMPLATE WHEN CONSIDERING A DIAGNOSIS OF IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS (IPF) CHIEF COMPLAINT HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS Consider IPF as possible diagnosis if any of the
DIAGNOSTIC NOTE TEMPLATE SOAP NOTE TEMPLATE WHEN CONSIDERING A DIAGNOSIS OF IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS (IPF) CHIEF COMPLAINT HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS Consider IPF as possible diagnosis if any of the
Can serial PEF measurements separate occupational asthma from allergic alveolitis?
 Occupational Medicine 2015;65:251 255 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqv013 Can serial PEF measurements separate occupational asthma from allergic alveolitis? P. S. Burge 1, V. C. Moore 1, C. B. S. G. Burge 1, A.
Occupational Medicine 2015;65:251 255 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqv013 Can serial PEF measurements separate occupational asthma from allergic alveolitis? P. S. Burge 1, V. C. Moore 1, C. B. S. G. Burge 1, A.
International consensus statement on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
Outline Definition of Terms: Lexicon. Traction Bronchiectasis
 HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
Imaging findings in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - a pictorical review.
 Imaging findings in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - a pictorical review. Poster No.: C-1655 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Araujo, A. F. S. Simões, M. S. C. Rodrigues, J. Pereira;
Imaging findings in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - a pictorical review. Poster No.: C-1655 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Araujo, A. F. S. Simões, M. S. C. Rodrigues, J. Pereira;
NONE OVERVIEW FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF (UIP) FOR PATHOLOGISTS. IPF = Idiopathic UIP Radiologic UIP Path UIP
 UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference. Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2
 June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
Replacement of air with fluid, inflammatory. cells or cellular debris. Parenchymal, Interstitial (Restrictive) and Vascular Diseases.
 Parenchymal, Interstitial (Restrictive) and Vascular Diseases Alain C. Borczuk, M.D. Dept of Pathology Replacement of air with fluid, inflammatory cells Pulmonary Edema Pneumonia Hemorrhage Diffuse alveolar
Parenchymal, Interstitial (Restrictive) and Vascular Diseases Alain C. Borczuk, M.D. Dept of Pathology Replacement of air with fluid, inflammatory cells Pulmonary Edema Pneumonia Hemorrhage Diffuse alveolar
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in Japan: A nationwide epidemiologic survey
 Environmental and occupational disorders Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in Japan: A nationwide epidemiologic survey Yasuyuki Yoshizawa, MD, a Yoshio Ohtani, MD, a Hiroshi Hayakawa, MD, b Atsuhiko
Environmental and occupational disorders Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in Japan: A nationwide epidemiologic survey Yasuyuki Yoshizawa, MD, a Yoshio Ohtani, MD, a Hiroshi Hayakawa, MD, b Atsuhiko
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Common Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas
 Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Common Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas Rishi Raj MD Director, Interstitial Lung Diseases Program Clinical Professor of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Stanford University
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Common Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas Rishi Raj MD Director, Interstitial Lung Diseases Program Clinical Professor of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Stanford University
5/9/2015. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Interstitial Lung Disease. SS Visser, Lung Unit, UP.
 Interstitial Lung Disease SS Visser, Lung Unit, UP. ILD - Definition Heterogenous group of diseases with involvement of alveolar walls and peri- alveolar tissue -nonmalignant, non-infective. ± 180 diseases
Interstitial Lung Disease SS Visser, Lung Unit, UP. ILD - Definition Heterogenous group of diseases with involvement of alveolar walls and peri- alveolar tissue -nonmalignant, non-infective. ± 180 diseases
Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging
 July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
Asthma. Advisor. Occupational. The Asthma. enter. Education and Research Fund. A. Introduction. B. causes of oa
 The Asthma C enter Education and Research Fund Advisor Occupational Asthma A. Introduction Occupational Asthma (OA) is a form of asthma associated with work or a hobby involving inhalation of a chemical,
The Asthma C enter Education and Research Fund Advisor Occupational Asthma A. Introduction Occupational Asthma (OA) is a form of asthma associated with work or a hobby involving inhalation of a chemical,
Restrictive lung diseases
 Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
H ypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) comprises a group of
 665 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Chronic bird fancier s lung: histopathological and clinical correlation. An application of the 2002 ATS/ERS consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias
665 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Chronic bird fancier s lung: histopathological and clinical correlation. An application of the 2002 ATS/ERS consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias
Parenchymal, Interstitial i (Restrictive) i and Vascular Diseases
 Pulmonary Diseases: Structure-Function Correlation II Parenchymal, Interstitial i (Restrictive) i and Vascular Diseases Alain C. Borczuk, M.D. Dept of Pathology Pulmonary Diseases: Structure-Function Correlation
Pulmonary Diseases: Structure-Function Correlation II Parenchymal, Interstitial i (Restrictive) i and Vascular Diseases Alain C. Borczuk, M.D. Dept of Pathology Pulmonary Diseases: Structure-Function Correlation
A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases. Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco
 A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping. Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington
 Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP
 Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is a diffuse,
 HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS: ESSENTIAL RADIOLOGIC AND PATHOLOGIC FINDINGS Teri J. Franks, MD a, *, Jeffrey R. Galvin, MD b,c KEYWORDS Hypersensitivity pneumonitis Hypersensitivity pneumonia Extrinsic
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS: ESSENTIAL RADIOLOGIC AND PATHOLOGIC FINDINGS Teri J. Franks, MD a, *, Jeffrey R. Galvin, MD b,c KEYWORDS Hypersensitivity pneumonitis Hypersensitivity pneumonia Extrinsic
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Hypersensitivity pneumonia, also known as extrinsic. Hypersensitivity Pneumonia. Role of Surgical Lung Biopsy
 Lung biopsy often plays a key role in identifying patients with hypersensitivity pneumonia, especially in the absence of a typical history. A 69-year-old woman with a 2-year history of unexplained dyspnea
Lung biopsy often plays a key role in identifying patients with hypersensitivity pneumonia, especially in the absence of a typical history. A 69-year-old woman with a 2-year history of unexplained dyspnea
Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II
 Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
Déjà vu all over again
 Disclosures Déjà vu all over again None Jonathan Singer MD MS University of California, San Francisco HPI 49 y/o woman presents for lung transplant evaluation for Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Exposures:
Disclosures Déjà vu all over again None Jonathan Singer MD MS University of California, San Francisco HPI 49 y/o woman presents for lung transplant evaluation for Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Exposures:
pulmonary and critical care pearls
 pulmonary and critical care pearls A 12-Year-Old Girl With Dyspnea and a Normal Chest Radiographic Finding* Kristin B. Highland, MD; and Patrick A. Flume, MD, FCCP (CHEST 2001; 120:1372 1376) A 12-year-old
pulmonary and critical care pearls A 12-Year-Old Girl With Dyspnea and a Normal Chest Radiographic Finding* Kristin B. Highland, MD; and Patrick A. Flume, MD, FCCP (CHEST 2001; 120:1372 1376) A 12-year-old
THE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics. F. Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA OCCUPATIONAL ASTHMA
 THE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics 2003 F. Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA OCCUPATIONAL ASTHMA 1 OCCUPATIONAL ASTHMA Occupational Asthma: the most prevalent
THE UNIVERSITY OF WESTERN ONTARIO Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics 2003 F. Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA OCCUPATIONAL ASTHMA 1 OCCUPATIONAL ASTHMA Occupational Asthma: the most prevalent
Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Evidence-Based Guidelines
 Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Evidence-Based Guidelines Rebecca Keith, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine National Jewish Health, Denver, CO Objectives
Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Evidence-Based Guidelines Rebecca Keith, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine National Jewish Health, Denver, CO Objectives
A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases
 Outline A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
Outline A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
Asbestosis: diagnosis and attribution criteria. Eduardo Algranti Serviço de Medicina FUNDACENTRO
 Asbestosis: diagnosis and attribution criteria Eduardo Algranti Serviço de Medicina FUNDACENTRO Asbestosis A declining disease in developed countries Most cases of asbestosis are due to occupational exposure
Asbestosis: diagnosis and attribution criteria Eduardo Algranti Serviço de Medicina FUNDACENTRO Asbestosis A declining disease in developed countries Most cases of asbestosis are due to occupational exposure
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is an immunologically. Inhalation Provocation Tests in Chronic Bird Fancier s Lung*
 Inhalation Provocation Tests in Chronic Bird Fancier s Lung* Yoshio Ohtani, MD; Kaoru Kojima, MD; Yuki Sumi, MD; Megumi Sawada, MD; Naohiko Inase, MD; Shuji Miyake, MD; Yasuyuki Yoshizawa, MD, PhD, FCCP
Inhalation Provocation Tests in Chronic Bird Fancier s Lung* Yoshio Ohtani, MD; Kaoru Kojima, MD; Yuki Sumi, MD; Megumi Sawada, MD; Naohiko Inase, MD; Shuji Miyake, MD; Yasuyuki Yoshizawa, MD, PhD, FCCP
Pulmonary Pearls. Medical Pearls. Case 1: Case 1 (cont.): Case 1: What is the Most Likely Diagnosis? Case 1 (cont.):
 Pulmonary Pearls Christopher H. Fanta, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Medical Pearls Definition: Medical fact that is
Pulmonary Pearls Christopher H. Fanta, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Medical Pearls Definition: Medical fact that is
American Osteopathic College of Occupational and Preventive Medicine 2011 Annual Meeting, Orlando, Florida, November 1, 2011
 Occupational Lung Disease Practical Applications of The Respiratory Standard Lance Walker D.O. MPH Objectives 1. Review of Occupational Lung Diseases 2. OSHA Respiratory Standard Refresher 3. Discuss spirometry
Occupational Lung Disease Practical Applications of The Respiratory Standard Lance Walker D.O. MPH Objectives 1. Review of Occupational Lung Diseases 2. OSHA Respiratory Standard Refresher 3. Discuss spirometry
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (Esbriet /pirfenidone, Ofev /nintedanib)
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (Esbriet /pirfenidone, Ofev /nintedanib)
Bronkhorst colloquium Interstitiële longziekten. Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog
 Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
Diagnostic challenges in IPF
 Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences Diagnostic challenges in IPF Dr Ian Glaspole Central and Eastern Clinical School, Alfred Hospital and Monash University March 2015 Disclosures Consultancy fees from
Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences Diagnostic challenges in IPF Dr Ian Glaspole Central and Eastern Clinical School, Alfred Hospital and Monash University March 2015 Disclosures Consultancy fees from
Schlueter et al., 1969). The object of this study. was to investigate by measurements of lung. mechanics the nature of airflow obstruction in
 Mechanical properties of the lung in extrinsic allergic alveolitis1 C. P. W. WARREN, K. S. TSE, AND R. M. CHERNIACK Thorax, 1978, 33, 315-321 From the Departments of Medicine and Immunology, University
Mechanical properties of the lung in extrinsic allergic alveolitis1 C. P. W. WARREN, K. S. TSE, AND R. M. CHERNIACK Thorax, 1978, 33, 315-321 From the Departments of Medicine and Immunology, University
CASE REPORT. Introduction. Case Report
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1142-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Analysis of Surgical Lung Biopsy and Explanted Lung Specimens Sheds Light on the Pathological Progression of Chronic Bird-related
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1142-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Analysis of Surgical Lung Biopsy and Explanted Lung Specimens Sheds Light on the Pathological Progression of Chronic Bird-related
Lung Allograft Dysfunction
 Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Chest imaging II. Interstitial lung diseases
 Chest imaging II. Interstitial lung diseases Dávid L. Tárnoki MD, PhD Ádám D. TárnokiMD, PhD Department of Radiology Semmelweis University Topics 1. Interstitial lung diseases 2. Occupational lung diseases
Chest imaging II. Interstitial lung diseases Dávid L. Tárnoki MD, PhD Ádám D. TárnokiMD, PhD Department of Radiology Semmelweis University Topics 1. Interstitial lung diseases 2. Occupational lung diseases
Bird Fancier s Disease in a 50 Year Old Woman
 doi:10.17659/01.2017.0050 Journal of Case Reports 2017;7(2):180-183 Bird Fancier s Disease in a 50 Year Old Woman Patrick Asdell, Nicole Fox Saint James School of Medicine, Anguilla. Corresponding Author:
doi:10.17659/01.2017.0050 Journal of Case Reports 2017;7(2):180-183 Bird Fancier s Disease in a 50 Year Old Woman Patrick Asdell, Nicole Fox Saint James School of Medicine, Anguilla. Corresponding Author:
Cladosporium Species-Related Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis in Household Environments
 CASE REPORT Cladosporium Species-Related Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis in Household Environments Shigeki Chiba 1, Shinji Okada 1, Yasuko Suzuki 2, Zenta Watanuki 1, Yoichiro Mitsuishi 1, Ryotaro Igusa 1,
CASE REPORT Cladosporium Species-Related Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis in Household Environments Shigeki Chiba 1, Shinji Okada 1, Yasuko Suzuki 2, Zenta Watanuki 1, Yoichiro Mitsuishi 1, Ryotaro Igusa 1,
CTD-related Lung Disease
 13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Ahuva Grubstein a, Daniele Bendayan b, Ithak Schactman c, Maya Cohen a, David Shitrit b, Mordechai R. Kramer b,
 Respiratory Medicine (2005) 99, 948 954 Concomitant upper-lobe bullous emphysema, lower-lobe interstitial fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension in heavy smokers: report of eight cases and review of the literature
Respiratory Medicine (2005) 99, 948 954 Concomitant upper-lobe bullous emphysema, lower-lobe interstitial fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension in heavy smokers: report of eight cases and review of the literature
Allergic. Alveolitis. Asthma bronchiale richtig erkennen, richtig behandeln
 Allergic Asthma bronchiale richtig erkennen, Alveolitis richtig behandeln Dr. med. Florian Fuchs Division of Respiratory Medicine Department of Medicine 1 (Chairman: Prof. Dr. med. M.F. Neurath) florian.fuchs@uk-erlangen.de
Allergic Asthma bronchiale richtig erkennen, Alveolitis richtig behandeln Dr. med. Florian Fuchs Division of Respiratory Medicine Department of Medicine 1 (Chairman: Prof. Dr. med. M.F. Neurath) florian.fuchs@uk-erlangen.de
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99. Presented by: Jesicca Andrews
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
Respiratory Pathology. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County
 Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County 4400 persons underwent examination 950 persons were given referrals to more detailed investigation 600 persons were examined so far The results of more detailed
Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County 4400 persons underwent examination 950 persons were given referrals to more detailed investigation 600 persons were examined so far The results of more detailed
Isocyanate asthma: respiratory symptoms due to 1,5-naphthylene di-isocyanate
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 762-766 Isocyanate asthma: respiratory symptoms due to 1,5-naphthylene di-isocyanate M G HARRIES, P SHERWOOD BURGE, M SAMSON, A J NEWMAN TAYLOR, AND J PEPYS From the Brompton Hospital,
Thorax, 1979, 34, 762-766 Isocyanate asthma: respiratory symptoms due to 1,5-naphthylene di-isocyanate M G HARRIES, P SHERWOOD BURGE, M SAMSON, A J NEWMAN TAYLOR, AND J PEPYS From the Brompton Hospital,
Prepared by Sarah Bozeman, MD, University of Mississippi Healthcare, and John Seyerle, Ohio State University
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 53 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 53: Occupational Asthma Prepared by Sarah
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 53 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 53: Occupational Asthma Prepared by Sarah
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING. Purposes of Pulmonary Tests. General Categories of Lung Diseases. Types of PF Tests
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING Wyka Chapter 13 Various AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines Purposes of Pulmonary Tests Is lung disease present? If so, is it reversible? If so, what type of lung disease is present?
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING Wyka Chapter 13 Various AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines Purposes of Pulmonary Tests Is lung disease present? If so, is it reversible? If so, what type of lung disease is present?
Idiopathic Pulmonary of Care
 Chapter 6.1 Living Medical etextbook A Digital Tool at the Point of Care From Projects In Knowledge Pulmonology Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis @Point of Care IPF Case Study: Typical Presentation, Role of
Chapter 6.1 Living Medical etextbook A Digital Tool at the Point of Care From Projects In Knowledge Pulmonology Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis @Point of Care IPF Case Study: Typical Presentation, Role of
Paramedic Rounds. Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange
 Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
A case of a patient with IPF treated with nintedanib. Prof. Kreuter and Prof. Heussel
 A case of a patient with IPF treated with nintedanib Prof. Kreuter and Prof. Heussel Case Overview This case describes the history of a patient with IPF who, at the time of diagnosis, had symptoms typical
A case of a patient with IPF treated with nintedanib Prof. Kreuter and Prof. Heussel Case Overview This case describes the history of a patient with IPF who, at the time of diagnosis, had symptoms typical
Pathologic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease
 Pathologic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease Dry and itchy? It could be eczema or fungal infection. We don t need to worry, the drugs aren t that dangerous. Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept. of Pathology
Pathologic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease Dry and itchy? It could be eczema or fungal infection. We don t need to worry, the drugs aren t that dangerous. Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept. of Pathology
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW
 SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION!
 UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION! STÉPHANE JOUNEAU 11 JULY 2014 Respiratory Medicine Department, Pontchaillou Hospital, Rennes, France CASE OVERVIEW This case highlights how a usual
UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION! STÉPHANE JOUNEAU 11 JULY 2014 Respiratory Medicine Department, Pontchaillou Hospital, Rennes, France CASE OVERVIEW This case highlights how a usual
Lines and crackles. Making sense of ILD
 Lines and crackles Making sense of ILD Case JM 65 year old male Gradual shortness of breath, going on over a year Some dry cough Ex-smoker, quit 10 years ago Crackles in the bases CXR presented Sent to
Lines and crackles Making sense of ILD Case JM 65 year old male Gradual shortness of breath, going on over a year Some dry cough Ex-smoker, quit 10 years ago Crackles in the bases CXR presented Sent to
Mushroom worker's lung
 Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
Extrinsic allergic alveolitis caused by misting fountains $
 Respiratory Medicine (2005) 99, 943 947 Extrinsic allergic alveolitis caused by misting fountains $ Dirk Koschel a,, Wolfram Stark b, Fritz Karmann c, Jochen Sennekamp d, Dietrich Müller-Wening a a Zusamklinik
Respiratory Medicine (2005) 99, 943 947 Extrinsic allergic alveolitis caused by misting fountains $ Dirk Koschel a,, Wolfram Stark b, Fritz Karmann c, Jochen Sennekamp d, Dietrich Müller-Wening a a Zusamklinik
Professor Rob Miller
 BHIVA AUTUMN CONFERENCE 2013 Including CHIVA Parallel Sessions Professor Rob Miller University College London Medical School COMPETING INTEREST OF FINANCIAL VALUE > 1,000: Speaker Name Prof Rob Miller
BHIVA AUTUMN CONFERENCE 2013 Including CHIVA Parallel Sessions Professor Rob Miller University College London Medical School COMPETING INTEREST OF FINANCIAL VALUE > 1,000: Speaker Name Prof Rob Miller
Pulmonary Function Testing The Basics of Interpretation
 Pulmonary Function Testing The Basics of Interpretation Jennifer Hale, M.D. Valley Baptist Family Practice Residency Objectives Identify the components of PFTs Describe the indications Develop a stepwise
Pulmonary Function Testing The Basics of Interpretation Jennifer Hale, M.D. Valley Baptist Family Practice Residency Objectives Identify the components of PFTs Describe the indications Develop a stepwise
Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy JMAJ 46(11): 469 474, 2003 Yukihiko SUGIYAMA Professor, Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy JMAJ 46(11): 469 474, 2003 Yukihiko SUGIYAMA Professor, Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of
V CHRONIC DIFFUSE INFILTRATIVE LUNG DISEASE
 V CHRONIC DIFFUSE INFILTRATIVE LUNG DISEASE Gerald W. Staton, Jr., m.d. Roland H. Ingram, Jr., m.d. Chronic diffuse infiltrative lung disease encompasses a wide variety of disorders that primarily affect
V CHRONIC DIFFUSE INFILTRATIVE LUNG DISEASE Gerald W. Staton, Jr., m.d. Roland H. Ingram, Jr., m.d. Chronic diffuse infiltrative lung disease encompasses a wide variety of disorders that primarily affect
Diagnosis of Respiratory Bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease
 Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2006; 65: 2, 96-101 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Respiratory Bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease C. Robalo Cordeiro 1, S. Freitas 1, B. Rodrigues 1, A. Catarino 1,
Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2006; 65: 2, 96-101 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Respiratory Bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease C. Robalo Cordeiro 1, S. Freitas 1, B. Rodrigues 1, A. Catarino 1,
The Relationship between the Incidence of Summer-type Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Environmental Factors in Southern Tochigi Prefecture
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Relationship between the Incidence of Summer-type Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Environmental Factors in Southern Tochigi Prefecture Yuki Iijima, Yukihiko Sugiyama, Eri Suzuki,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Relationship between the Incidence of Summer-type Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Environmental Factors in Southern Tochigi Prefecture Yuki Iijima, Yukihiko Sugiyama, Eri Suzuki,
ANTIBODIES OF INTEREST IN MYCOLOGY
 ANTIBODIES OF INTEREST IN MYCOLOGY Belgian Society of Human and Animal Mycology, november 19, 2015 Stephanie Everaerts MD, PhD student Pneumology Antibodies of interest in mycology Introduction Specific
ANTIBODIES OF INTEREST IN MYCOLOGY Belgian Society of Human and Animal Mycology, november 19, 2015 Stephanie Everaerts MD, PhD student Pneumology Antibodies of interest in mycology Introduction Specific
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
People with asthma who smoke. The combination of asthma, a chronic airway disease, and smoking increases the risk of COPD even more.
 COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Changes in HRCT findings in patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease after smoking cessation
 Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 453 461 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00015506 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Changes in HRCT findings in patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease after
Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 453 461 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00015506 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Changes in HRCT findings in patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease after
Diagnostic yield of specific inhalation challenge in hypersensitivity pneumonitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES Diagnostic yield of specific inhalation challenge in hypersensitivity pneumonitis Xavier Muñoz 1,2,3,Mónica Sánchez-Ortiz 1,2, Ferran Torres 4, Ana Villar 1,2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES Diagnostic yield of specific inhalation challenge in hypersensitivity pneumonitis Xavier Muñoz 1,2,3,Mónica Sánchez-Ortiz 1,2, Ferran Torres 4, Ana Villar 1,2,
IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte
 IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal lung diseases Exposure-related: - occupational - environmental - medication Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Idiopathic
IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal lung diseases Exposure-related: - occupational - environmental - medication Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Idiopathic
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases
 Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Causes: Acute alveolo-capillary sysfunction Interstitial disease Pleural disorders Chest wall disorders Neuromuscular disease Resistance Pathophysiology Reduced compliance
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Causes: Acute alveolo-capillary sysfunction Interstitial disease Pleural disorders Chest wall disorders Neuromuscular disease Resistance Pathophysiology Reduced compliance
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
