aspergilloma? Analysis of 23 cases
|
|
|
- Antony Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 What happens to patients with pulmonary aspergilloma? Analysis of 23 cases Thorax 1983;38: PAUL RAFFERTY, BEVERLEY-ANN BIGGS, GRAHAM K CROMPTON, IAN WB GRANT From the Respiratory Unit, Northern General Hospital, Edinburgh ABSTRACT The problems associated with pulmonary aspergilloma were assessed retrospectively in 23 patients presenting from 1953 to Haemoptysis occurred in over half the patients and in two it was fatal. Invasive aspergillosis occurred in five patients, a higher proportion than in earlier reports, and two of these died. Amphotericin B in combination with either flucytosine or natamycin and, more recently, ketoconazole have proved useful in the treatment of this condition. Species of aspergillus fungi are found throughout the world in decaying vegetation and soil, and its spores are ubiquitous in rural and urban environments. The first report of pulmonary aspergillosis in man appeared in 1842' and several patterns of the disease have since been recognised,2 ranging from colonisation of damaged lung tissue by the fungus to invasive or necrotising pulmonary aspergillosis.3 The most distinctive lesion is the aspergilloma,4 which forms when the fungus grows on the wall of a lung cavity and mycelium and debris become detached to form a concretion of amorphous material containing tangled septate hyphae and altered blood elements. The natural history of pulmonary aspergilloma is poorly documented and there is no general agreement on the best form of management. This report analyses the treatment and outcome of all cases seen at the Northern General Hospital, Edinburgh, during the past 30 years. Patients Twenty-three patients with aspergilloma were studied in the period The criteria for a diagnosis of aspergilloma consisted of the classical radiological sign of an intracavitary mass with a surrounding crescent of air and either a positive result in the aspergillus precipitin test, a sputum culture positive for aspergillus, or (in most cases) both. The patients ranged in age from 40 to 81 years, Address for reprint requests: Dr Paul Rafferty, Respiratory Unit, Northern General Hospital, Edinburgh EH5 3BD. Accepted S April 1983 with a mean of 59 years. There were 11 men and 12 women and the follow-up period varied from four months to 30 years, with a mean of 4.5 years. Results PREDISPOSING CONDITIONS The commonest predisposing condition was pulmonary tuberculosis, which accounted for over twothirds of the cases; other conditions included ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, pulmonary sarcoidosis, postradiation fibrosis, lung abscess and bronchiectasis (table 1). Because of the nature and extent of the pulmonary lesions in these diseases, the lungs were often severely damaged by fibrosis and bronchiectasis before the development of the aspergilloma. SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS Patients most frequently presented with a productive cough, often accompanied by haemoptysis and weight loss (table 2). Half complained of dyspnoea but in most, if not all, this was related to underlying lung disease. In over half the cases finger clubbing was present. INVESTIGATIONS All patients had radiological evidence of an intracavitary mass separated from the surrounding wall by a crescent of air. This was often better demonstrated by tomography than by a plain posteroanterior film. Single lesions occurred with similar frequency in the two lungs. These were situated in the upper lobes in all but four patients; multiple lesions were present in six. 579
2 580 Table 1 Predisposing conditions in 23 cases ofpulmonary aspergilloma No (%) ofpatients Tuberculosis* 15 (65 Ankylosing spondylitis 2 Sarcoidosis 1 4 Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Ulcerative colitist 2 8 Postradiation fibrosist Lung abscess 1 Bronchiectasis 1 *One?atient with tuberculosis later developed sarcoidosis and a bronchial carcinoma, which was successfully treated with radiotherapy. tone patient with ulcerative colitis also developed ankylosing spondylitis. *The patient with postradiation fibrosis had received radiotherapy for a malignant thymoma associated with myasthenia gravis. Table 2 Clinical features in 23 cases ofpulmonary aspergilloma No (%0) ofpaients Productive cough 19 (83) Haemoptysis 12 (52) Dyspnoea 12 (52) Weight loss 9 (39) Fever 3 (13) Finger clubbing 14 (61) Sputum samples were obtained from 22 of the 23 patients and Aspergillus fumigatus was cultured from 20. In two cases A niger, A terreus, and A flavus were cultured in addition to A fumigatus. Serum from all 23 patients was tested for A fumigatus precipitins and a positive result was obtained in 20. Of the three patients with a negative result in the precipitin test, two were on long-term corticosteroid treatment and A fumigatus was cultured from the sputum; the third developed a mycetoma with a species of Penicillium and will be the subject of a later communication. Skinprick tests were carried out in 16 patients with a 5% solution of an aqueous extract of A fumigatus (Bencard); 13 showed positive reactions, with a wheal of more than 3 mm in diameter. A non-specific finding was a raised gammaglobulin level in over half the patients tested. COMPLICATIONS Haemoptysis occurred in 12 patients. Nine experienced recurrent haemoptysis that was slight (less than 150 ml in 24 hours) and subsided spontaneously. Three patients had major haemoptysis (more than 500 ml in 24 hours). One died at home; another, considered unfit for surgery, died within six hours of admission to hospital; and the third apparently responded to injections of vitamin K after he had been found to have a reduced prothrombin con- Rafferty, Biggs, Crompton, Grant centration. Only one of these patients had a previous history of haemoptysis. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis developed in five patients. This diagnosis was made when progressive pulmonary shadowing was noted in the absence of bacterial infection and mycelial elements were present in the sputum. In four of these patients an aspergilloma was known to be present before the development of this complication. In the other patient an aspergilioma was noted within the wider area of consolidation at the time of presentation. Three patients recovered after specific antifungal treatment and two died within 24 hours of admission. Postmortem examination confirmed the diagnosis in both patients, one of whom had evidence of systemic spread of the disease. A more common but less specific complication, which occurred in 17 patients, was recurrent cough productive of dark green purulent sputum. Although many patients had underlying lung disease to account for this, A fumigatus was the predominant organism found on culture of the sputum in over half of these cases. Three patients developed terminal respiratory failure as a result of underlying chronic lung disease and one as a consequence of myasthenia gravis (table 1). TREATMENT AND OUTCOME The treatment of the 23 patients varied widely and included antibacterial drugs, antifungal drugs, and surgery (table 3). Antifungal treatment included, either singly or in combination, natamycin by inhalation, clotrimazole, and ketoconazole by mouth and amphotericin, flucytosine (5FC), and econazole by intravenous infusion. None of these treament regimens reduced the size of the aspergilloma, but in some cases they relieved troublesome cough and haemoptysis. The mortality in treated and untreated patients was similar. Patients with purulent sputum were often given antibacterial chemotherapy initially, but if A fumigatus was found to be the predominant pathogen treatment with a specific antifungal agent was usually substituted. In one of two patients with haemoptysis who were treated with ampicillin for suspected bacterial infection the aspergilloma temporarily disappeared, and in the other it became smaller. In one patient treated with prednisolone there was symptomatic improvement and a reduction in size of the aspergilloma. Specific antifungal chemotherapy was given to eight patients without invasive aspergillosis on account of purulent sputum or haemoptysis associated with a heavy growth of A fumigatus in the sputum. The symptoms resolved in six of these patients, but in all eight the aspergilloma remained unchanged. Five patients with invasive aspergillosis
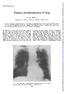
3 What happens to patients with pulmonary aspergilloma? an analysis of 23 cases Table 3 Treatment and outcome in 23 cases ofpulmonary aspergilloma Treatment No of Indication Response to Effect on Outcome patients treatment aspergilloma Antifungal Clotrimazole 3 Cough, sputum Improvement in 2 Unchanged 1 died (invasive aspergillosis) 1 died (unrelated cause) 1 lost to follow-up Natamycin inhalation 1 Cough, sputum Symptoms resolved Unchanged Died (unrelated cause) Natamycin, penicillin 1 Cough, sputum Symptoms resolved Unchanged Lost to follow-up Natamycin, prednisolone Cough, sputum Symptoms resolved Unchanged Died (unrelated cause) Natamycin, amphotericin Invasive aspergillosis Symptoms resolved Smaller Died (haemoptysis) Amphotericin, flucytosine Invasive aspergillosis Symptoms resolved Unchanged Alive Flucytosine 1 Cough, sputum Symptoms persisted Unchanged Died (unrelated cause) Ketoconazole 1 Invasive aspergillosis Symptoms resolved Unchanged Alive (-+prednisolone) Ketoconazole Haemoptysis Symptoms resolved Unchanged Alive Econazole 1 Invasive aspergillosis Deteriorated rapidly Unchanged Died (invasive aspergillosis) Surgical Local resection 1 Haemoptysis Chronic empyema Resected Alive Right upper lobectomy 1 Haemoptysis Bronchopleural fistula Resected Died (postoperative respiratory failure) Non-specific Prednisolone 1 Haemoptysis Symptoms resolved Smaller Alive Antibacterial drugs only 3 Cough, sputum Symptoms resolved Lysis in 1 1 died (haemoptysis) 2 died (unrelated causes) Vitamin K 1 Haemoptysis Symptoms resolved Unchanged Alive None 4 Asymptomatic Unchanged 1 alive 1 lost to follow-up 2 died (unrelated causes) were also treated with antifungal drugs. In all three survivors the chemotherapy included amphotericin or ketoconazole. Two patients were treated surgically, both for recurrent haemoptysis. The first developed a chronic empyema and the second died from respiratory failure in the postoperative period, having developed a bronchopleural fistula. In the whole group of 23 patients five deaths were directly attributable to the aspergilloma. Two of these were due to invasive aspergillosis and two to massive haemoptysis, and one followed surgery for recurrent haemoptysis. Three patients died from respiratory failure, two from bronchial carcinoma, one from intestinal malabsorption, and two at home from unknown causes. Seven are currently alive and the remaining three have been lost to follow-up. Discussion 581 The reasons why the natural history of intracavitary aspergilloma is poorly documented are that it is an uncommon disease and that the outcome is so often related to underlying non-specific pulmonary pathology. The most common predisposing condition in our patients was tuberculosis. This is in keeping with the findings of the British Tuberculosis Association, which in 1968 reported the development of an aspergilloma in 15% of persisting (sputum-negative) cavities larger than 2*5 cm, the highest incidence being found in cavities of 7-11 years' duration.5 Most patients have a chronic productive cough and occasionally develop the systemic features of fever, malaise, and weight loss. It is difficult to know whether these symptoms are due to the aspergilloma or to coexisting bacterial infection. Davies and Somner suggested that such symptoms may be due to a hypersensitivity reaction to aspergillus.6 This is supported by the similarity of the pattern of cytophilic antibodies found in these patients and in those with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis.7 Haemoptysis, a well-recognised complication of aspergilloma, occurred in over half of our patients. Of these, only two succumbed from massive bleeding. The frequency and severity of previous haemoptysis appeared to have little bearing on the final outcome. Other authors have reported lifethreatening haemoptysis in 20% of patients with aspergilloma and suggest that these patients should be treated surgically." In our experience, however, this is seldom feasible because most patients with aspergilloma have severely damaged lungs and poor pulmonary function. A more disturbing complication is that of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (fig). This occurred in five of
4 582 Rafferty, Biggs, Crompton, Grant our patients, two of whom died. This condition is usually found in debilitated or immunosuppressed &Z ~~~~~~~~~~atients. Four of our patients were in this category: two were receiving corticosteroid treatment and one had chronic empyema and the other ulcerative colitis. These findings are at variance with the experience of other workers,9 who suggest that the risk of aspergilloma progressing to invasive pulmonary dis-.sv _ r _ease is negligible. There is no general agreement on the management of pulmonary aspergilloma per se. The first surgical resection was reported in and for many years surgery was regarded as the treatment of choice for symptomatic disease, especially in the United States. More recently this view has been questioned.9 Analysis of the data from 140 pulmonary resections for aspergilloma revealed an overall mortality of 7%. Major postoperative complications such as bronchopleural fistulas, resistant air space problems, empyema, and haemorrhage occurred in 22% of cases. The two patients in our own series who were treated surgically fared badly. One died and the other was left with chronic empyema. Antifungal treatment in this series varied considerably from case to case and did not affect the size of the aspergilloma or mortality. Our experience, however, confirmed the potential value of amphotericin combined in some cases with flucytosine, and possibly of ketoconazole, in the treatment of secondary invasive aspergillosis. Ketoconazole is an oral anti- _, 3 -XA _! fungal agent in the imidazole group, which has been WI '- ^ shown to be effective in various superficial fungal infeotions and some systemic ones. Borelli et al have '_ reported that two patients with pulmonary aspergilloma failed to respond to treatment with ketoconazole;" but we used it successfully in one patient with invasive aspergillosis, and in another A patient symptomatic improvement coincided with the virtual elimination of A fumigatus from the sputum. This study exemplifies the unsystematic approach to the treatment of pulmonary aspergilloma during the past three decades, and the high mortality rate underlines the inadequacy of both medical and surgical treatment. There is very little evidence that either form of treatment influences the prognosis, except on the rare occasions when the risk of fatal haemoptysis can be eliminated by resection of the aspergilloma or when secondary invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, a more common complication than is generally recognised, can be controlled by intensive antifungal chemotherapy. (a) Pulmonary aspergilloma in the night upper lobe. (b) References Subsequent development of invasive aspergillosis in the same patient. 1 Bennet JH. On the parasitic vegetable structures found
5 What happens to patients with pulmonary aspergilloma? an analysis of 23 cases growing in living animals. Trans R Soc Edinb 1842;15: Turner-Warwick M. Aspergillus fumigatus and lung disease. Postgrad Med J 1979;55: Kennedy WPU,-Malone DN, Blyth W. Necrotising pulmonary aspergillosis. Thorax 1970;25: Campbell MJ, Clayton YM. Bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: a correlation of the clinical and laboratory findings in 272 patients investigated for bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1964;89: Research Committee of the British Tuberculosis Association. Aspergillus in persistent lung cavities after tuberculosis. Tubercle 1968;49:1. 6 Davies D, Somner AR. Pulmonary aspergillomas treated with corticosteroids. Thorax 1972;27: Assem ESK, Turner-Warwick M. Cytophilic antibodies in bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, aspergilloma and cytogenic pulmonary eosinophilia. Clin Exp Immunol 1976;26:67. Karas A, Hankins JR, Attar S, Miller JE, McLaughlin JS. Pulmonary aspergillosis: an analysis of 41 patients. Ann Thorac Surg 1976;22:1-7. Varkey B, Rose HD. Pulmonary aspergilloma: a rational approach to treatment. Am J Med 1976;61: Gerstl B, Weidman WH, Newman AV. Pulmonary aspergillosis: a report on 2 cases. Ann Intern Med 1948;26:661. IBorelli D, Fuentes J, Leiderman E, et al. Ketoconazole, an oral antifungal: laboratory and clinical assessment of imidazole drugs. Postgrad Med J 1979;55: Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 August Downloaded from on 16 October 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of. Pulmonary Mycetoma. Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu***
 Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of Pulmonary Mycetoma Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu*** Departments of *Respiratory Medicine, **Physiology, and ***Radiodiagnosis,
Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of Pulmonary Mycetoma Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu*** Departments of *Respiratory Medicine, **Physiology, and ***Radiodiagnosis,
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids
 Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
Pulmonary Aspergillosis: An Analysis of 41 Patients
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Vol22 No 1 July 1976 Pulmonary Aspergillosis: An Analysis of 41 Patients Avraam Karas, M.D., John R. Hankins, M.D., Safuh Attar, M.D., John E. Miller, M.D., and Joseph S.
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Vol22 No 1 July 1976 Pulmonary Aspergillosis: An Analysis of 41 Patients Avraam Karas, M.D., John R. Hankins, M.D., Safuh Attar, M.D., John E. Miller, M.D., and Joseph S.
Management of pulmonary aspergilloma in the
 Thorax 1984;39:862-867 Management of pulmonary aspergilloma in the presence of active tuberculosis ADEBAYO 0 ADEYEMO, EZEKIEL 0 ODELOWO, DOROTHY I MAKANJUOLA From the Departments ofsurgery and Radiology,
Thorax 1984;39:862-867 Management of pulmonary aspergilloma in the presence of active tuberculosis ADEBAYO 0 ADEYEMO, EZEKIEL 0 ODELOWO, DOROTHY I MAKANJUOLA From the Departments ofsurgery and Radiology,
Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Aspergilloma: A Series of 72 Cases
 Original Article Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Aspergilloma: A Series of 72 Cases Himanshu Pratap 1, R.K. Dewan 1, L. Singh 1, S. Gill 1 and S. Vaddadi 2 Departments of Thoracic Surgery 1 and Pulmonary
Original Article Surgical Treatment of Pulmonary Aspergilloma: A Series of 72 Cases Himanshu Pratap 1, R.K. Dewan 1, L. Singh 1, S. Gill 1 and S. Vaddadi 2 Departments of Thoracic Surgery 1 and Pulmonary
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis diagnosis and management in resource-limited setting
 Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis diagnosis and management in resource-limited setting Professor Retno Wahyuningsih Professor of Medical Mycology Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis diagnosis and management in resource-limited setting Professor Retno Wahyuningsih Professor of Medical Mycology Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas
Pulmonary aspergillus infection invading the pleura
 thorax 1981 ;36:745-751 Pulmonary aspergillus infection invading the pleura GUNNAR HILLERDAL From the Department ofpulmonary Medicine, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden ABSTRACT During a 10-year-period,
thorax 1981 ;36:745-751 Pulmonary aspergillus infection invading the pleura GUNNAR HILLERDAL From the Department ofpulmonary Medicine, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden ABSTRACT During a 10-year-period,
Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi
 Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
REVIEW ARTICLE. J. Biol. Chem. Research. Vol. 26, No. 2: (2009)
 J. Biol. Chem. Research. Vol. 26, No. 2: 28-34 (2009) (An International Journal of Life Sciences and Chemistry) All rights reserved ISSN 0970-4973 (Print) Published by Society for Advancement of Science
J. Biol. Chem. Research. Vol. 26, No. 2: 28-34 (2009) (An International Journal of Life Sciences and Chemistry) All rights reserved ISSN 0970-4973 (Print) Published by Society for Advancement of Science
Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected
 Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected Clinical symptoms which may indicate bronchiectasis for patients Take full respiratory history including presenting symptoms, past medical & family history Factors
Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected Clinical symptoms which may indicate bronchiectasis for patients Take full respiratory history including presenting symptoms, past medical & family history Factors
Aspergillus species. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis
 Pentalfa 3 maart 2016 The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis Pascal Van Bleyenbergh, Pneumologie UZ Leuven Aspergillus species First described in 1729 * >250 species * ubiquitous Inhalation of
Pentalfa 3 maart 2016 The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis Pascal Van Bleyenbergh, Pneumologie UZ Leuven Aspergillus species First described in 1729 * >250 species * ubiquitous Inhalation of
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: An Unusual Complication of Bronchial Asthma
 Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: An Unusual Complication of Bronchial Asthma Pages with reference to book, From 329 To 331 S. Fayyaz Hussain, Javaid A. Khan ( Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis: An Unusual Complication of Bronchial Asthma Pages with reference to book, From 329 To 331 S. Fayyaz Hussain, Javaid A. Khan ( Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan
Comparative Study between Parenchymapreservation Surgery and Lobectomy in Lung Aspergilloma - A Retrospective Analysis
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/239 Comparative Study between Parenchymapreservation Surgery and Lobectomy in Lung Aspergilloma - A Retrospective Analysis
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/239 Comparative Study between Parenchymapreservation Surgery and Lobectomy in Lung Aspergilloma - A Retrospective Analysis
fusions contributed to renal failure and coagulopathy. Pseudornonas sepsis developed, and the patient died on the twelfth postoperative day.
 Surgical Management of Symptomatic Pulmonary Aspergilloma James W. Battaglini, M.D., Gordon F. Murray, M.D., Blair A. Keagy, M.D., Peter J. K. Starek, M.D., and Benson R. Wilcox, M.D. ABSTRACT Pulmonary
Surgical Management of Symptomatic Pulmonary Aspergilloma James W. Battaglini, M.D., Gordon F. Murray, M.D., Blair A. Keagy, M.D., Peter J. K. Starek, M.D., and Benson R. Wilcox, M.D. ABSTRACT Pulmonary
Introduction. Study of fungi called mycology.
 Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
Underlying conditions in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis including simple aspergilloma
 Eur Respir J 2011; 37: 865 872 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00054810 CopyrightßERS 2011 Underlying conditions in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis including simple aspergilloma N.L. Smith and D.W. Denning ABSTRACT:
Eur Respir J 2011; 37: 865 872 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00054810 CopyrightßERS 2011 Underlying conditions in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis including simple aspergilloma N.L. Smith and D.W. Denning ABSTRACT:
Fever in aspergillus mycetoma
 Fever in aspergillus mycetoma C. HILVERING, E. A. M. STEVENS, N. G. M. ORIE University Hospital, Groningen, The Netherlands Thorax (1970), 25, 19. Two patients with aspergillus mycetoma presenting with
Fever in aspergillus mycetoma C. HILVERING, E. A. M. STEVENS, N. G. M. ORIE University Hospital, Groningen, The Netherlands Thorax (1970), 25, 19. Two patients with aspergillus mycetoma presenting with
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA
 ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
Aspergillosis in Dogs A Destructive Sinus & Nasal Disease
 Aspergillosis in Dogs A Destructive Sinus & Nasal Disease No one likes having a runny nose. Primary viral and secondary bacterial infections are common in pets and people. Most of the time these infections
Aspergillosis in Dogs A Destructive Sinus & Nasal Disease No one likes having a runny nose. Primary viral and secondary bacterial infections are common in pets and people. Most of the time these infections
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
Disease spectrum. IPA Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
 Aspergillus & ABPA Disease spectrum IPA Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis ABPA ABPA pathophysiology conidia of Aspergillus trapped in mucous and narrowed airways of asthmatics/cf germinate to form hyphae
Aspergillus & ABPA Disease spectrum IPA Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis ABPA ABPA pathophysiology conidia of Aspergillus trapped in mucous and narrowed airways of asthmatics/cf germinate to form hyphae
Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Radiographic findings from immunosuppressed patient to hyperreactive host.
 Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Radiographic findings from immunosuppressed patient to hyperreactive host. Poster No.: C-1442 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. P. Fernandez Ruiz, S. Isarria,
Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Radiographic findings from immunosuppressed patient to hyperreactive host. Poster No.: C-1442 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. P. Fernandez Ruiz, S. Isarria,
Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Radiographic findings from immunosuppressed patient to hyperreactive host.
 Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Radiographic findings from immunosuppressed patient to hyperreactive host. Poster No.: C-1442 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. P. Fernandez Ruiz, S. Isarria,
Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Radiographic findings from immunosuppressed patient to hyperreactive host. Poster No.: C-1442 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. P. Fernandez Ruiz, S. Isarria,
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST
 ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Dr J Garbino University Hospital Geneva ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST INTRODUCTION SWISS ASPERGILLOSIS SURVEY IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Introduction
ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Dr J Garbino University Hospital Geneva ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST INTRODUCTION SWISS ASPERGILLOSIS SURVEY IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Introduction
Common Fungi. Catherine Diamond MD MPH
 Common Fungi Catherine Diamond MD MPH Birth Month and Day & Last Four Digits of Your Cell Phone # BEFORE: http://tinyurl.com/kvfy3ts AFTER: http://tinyurl.com/lc4dzwr Clinically Common Fungi Yeast Mold
Common Fungi Catherine Diamond MD MPH Birth Month and Day & Last Four Digits of Your Cell Phone # BEFORE: http://tinyurl.com/kvfy3ts AFTER: http://tinyurl.com/lc4dzwr Clinically Common Fungi Yeast Mold
Chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis
 CASE REPORT Kulasegaran et al. 1 PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis Tivya Kulasegaran, Pranav Kumar ABSTRACT Aspergilloma is a fungus ball composed of hyphae, fibrin, mucus,
CASE REPORT Kulasegaran et al. 1 PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis Tivya Kulasegaran, Pranav Kumar ABSTRACT Aspergilloma is a fungus ball composed of hyphae, fibrin, mucus,
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit
 ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
Successful treatment of larynxtracheobronchial-pulmonary
 Case Report Successful treatment of larynxtracheobronchial-pulmonary aspergillosis in an immunocompetent host W.X. Qu, X.W. Feng and L. Zhao The First Respiratory Department of Shengjing Hospital, China
Case Report Successful treatment of larynxtracheobronchial-pulmonary aspergillosis in an immunocompetent host W.X. Qu, X.W. Feng and L. Zhao The First Respiratory Department of Shengjing Hospital, China
Pulmonary Aspergillosis
 May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
PULMONARY HYPERSENSITIVITY DISEASE DUE TO INHALED ORGANIC ANTIGENS
 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1966), 42, 698. PULMONARY HYPERSENSITIVITY DISEASE DUE TO INHALED ORGANIC ANTIGENS THE MECHANISMS of industrial pulmonary disease due to the inhalation of organic dusts are not well
POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1966), 42, 698. PULMONARY HYPERSENSITIVITY DISEASE DUE TO INHALED ORGANIC ANTIGENS THE MECHANISMS of industrial pulmonary disease due to the inhalation of organic dusts are not well
Chronic cavitatory aspergilloma in an old emaciated patient with review of three cases
 International Surgery Journal Kamble MA et al. Int Surg J. 2014 May;1(1):45-49 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: 10.5455/2349-2902.isj20140515 Chronic cavitatory
International Surgery Journal Kamble MA et al. Int Surg J. 2014 May;1(1):45-49 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: 10.5455/2349-2902.isj20140515 Chronic cavitatory
Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum
 Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Eosinophilic lung diseases
 Eosinophilic lung diseases Chai Gin Tsen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital The eyes do not see what the mind does not know Not very common A high index of suspicion
Eosinophilic lung diseases Chai Gin Tsen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital The eyes do not see what the mind does not know Not very common A high index of suspicion
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3. Chronic Cough Guidelines
 ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3 Chronic Cough Guidelines NHS Fife Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Cough in Adults In this section: 1. Introduction 2. Scope Guidelines for Management of Chronic
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3 Chronic Cough Guidelines NHS Fife Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Cough in Adults In this section: 1. Introduction 2. Scope Guidelines for Management of Chronic
Interesting cases in fungal asthma
 Interesting cases in fungal asthma Ritesh Agarwal MD, DM Professor of Pulmonary Medicine Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research Chandigarh, India Fungal asthma Broadly defined as the
Interesting cases in fungal asthma Ritesh Agarwal MD, DM Professor of Pulmonary Medicine Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research Chandigarh, India Fungal asthma Broadly defined as the
Case Studies in Fungal Infections and Antifungal Therapy
 Case Studies in Fungal Infections and Antifungal Therapy Wayne L. Gold MD, FRCPC Annual Meeting of the Canadian Society of Internal Medicine November 4, 2017 Disclosures No financial disclosures or industry
Case Studies in Fungal Infections and Antifungal Therapy Wayne L. Gold MD, FRCPC Annual Meeting of the Canadian Society of Internal Medicine November 4, 2017 Disclosures No financial disclosures or industry
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis?
 Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
Pneumonia. Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial
 Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
MSES consultants, inc.
 MSES consultants, inc. 609 West Main Street P.O. Drawer 190 Clarksburg, WV 26302-0190 304.624.9700 304.622.0981 304.842.3325 http://www.msesinc.com Office December 30, 2013 Project Number: 13-441 Mr. Joe
MSES consultants, inc. 609 West Main Street P.O. Drawer 190 Clarksburg, WV 26302-0190 304.624.9700 304.622.0981 304.842.3325 http://www.msesinc.com Office December 30, 2013 Project Number: 13-441 Mr. Joe
Diagnosis and Management of Fungal Allergy Monday, 9-139
 Diagnosis and Management of Fungal Allergy Monday, 9-139 13-2010 Alan P. Knutsen,, MD Director, Pediatric Allergy & Immunology Director, Jeffrey Modell Diagnostic Center for Primary Immunodeficiencies
Diagnosis and Management of Fungal Allergy Monday, 9-139 13-2010 Alan P. Knutsen,, MD Director, Pediatric Allergy & Immunology Director, Jeffrey Modell Diagnostic Center for Primary Immunodeficiencies
The role of fungi in respiratory allergies. David W. Denning University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester
 The role of fungi in respiratory allergies David W. Denning University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Allergic Aspergillus sinusitis Clinical features = nasal obstruction, recurrent
The role of fungi in respiratory allergies David W. Denning University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Allergic Aspergillus sinusitis Clinical features = nasal obstruction, recurrent
Combined Treatment for Pulmonary Aspergilloma
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Combined Treatment for Pulmonary Aspergilloma Erkan Y ld r m, MD; Rasih Yazkan, MD; Koray Dural, MD; Kadir Koç, MD; Serdar Han, MD; Ünal Sak nc, MD Department of Thoracic Surgery,
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Combined Treatment for Pulmonary Aspergilloma Erkan Y ld r m, MD; Rasih Yazkan, MD; Koray Dural, MD; Kadir Koç, MD; Serdar Han, MD; Ünal Sak nc, MD Department of Thoracic Surgery,
Inflammation class 2. Inflammation part 2. Rheumatic fever RF. Rheumatic fever - pathogenesis. Hypersensitivity reactions. Rheumatic fever RF
 Inflammation class 2 Inflammation part 2 Rheumatic endocarditis Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia Cytomegalic pneumonia Aspergillosis Actinomycosis Rheumatic fever RF An acute, immunologically mediated multisystem
Inflammation class 2 Inflammation part 2 Rheumatic endocarditis Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia Cytomegalic pneumonia Aspergillosis Actinomycosis Rheumatic fever RF An acute, immunologically mediated multisystem
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
WF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
 WF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
WF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
Fungal (Aspergillus and Candida) infections in Cystic fibrosis
 Fungal (Aspergillus and Candida) infections in Cystic fibrosis Malena Cohen-Cymberknoh, MD CF Center Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center Jerusalem, Israel Israeli Annual CF Conference, Herzlyia,
Fungal (Aspergillus and Candida) infections in Cystic fibrosis Malena Cohen-Cymberknoh, MD CF Center Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center Jerusalem, Israel Israeli Annual CF Conference, Herzlyia,
Case 1. Background. Presenting Symptoms. Schecter Case1 Differential Diagnosis of TB 1
 TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Pulmonary Aspergilloma in a Turkish Hospital Population
 CLINICAL STUDY Pulmonary Aspergilloma in a Turkish Hospital Population Hatice Türker, D 1 ; Zuhal Karakurt, D 1 ; Hakan Ak n, D 2 ; Ela Erdem, D 1 ; Emine Uysal, D 1 ; Nilüfer Kapakl, D 1 ; Ebru Sulu,
CLINICAL STUDY Pulmonary Aspergilloma in a Turkish Hospital Population Hatice Türker, D 1 ; Zuhal Karakurt, D 1 ; Hakan Ak n, D 2 ; Ela Erdem, D 1 ; Emine Uysal, D 1 ; Nilüfer Kapakl, D 1 ; Ebru Sulu,
Infection of the pleura by Aspergillus fumigatus
 Thorax (1970), 25, 245 PAWEL KRAKOWKA, EWA ROWI?ISKA, and HALINA HALWEG National Tuberculosis Research Institute, Warsaw, Poland Pleural aspergillosis occurs mostly in established cases of pleural empyema
Thorax (1970), 25, 245 PAWEL KRAKOWKA, EWA ROWI?ISKA, and HALINA HALWEG National Tuberculosis Research Institute, Warsaw, Poland Pleural aspergillosis occurs mostly in established cases of pleural empyema
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA) Retno Wahyuningsih
 Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA) Retno Wahyuningsih Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Kristen Indonesia,
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA) Retno Wahyuningsih Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Kristen Indonesia,
Bronchiectasis. What is bronchiectasis? What causes bronchiectasis?
 This factsheet explains what bronchiectasis is, what causes it, and how it is diagnosed and managed. More detailed information is available on the Bronchiectasis Patient Priorities website: www.europeanlunginfo.org/bronchiectasis
This factsheet explains what bronchiectasis is, what causes it, and how it is diagnosed and managed. More detailed information is available on the Bronchiectasis Patient Priorities website: www.europeanlunginfo.org/bronchiectasis
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1959, 16, 318. LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS BY R. ABBEY SMITH Fronm the Thoracic Surgical Unit, King Edward VII Memorial Chest Hospital, Warwick (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1959, 16, 318. LUNG CANCER IN COAL-MINERS BY R. ABBEY SMITH Fronm the Thoracic Surgical Unit, King Edward VII Memorial Chest Hospital, Warwick (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER
Fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient. Dr Kirsty Dodgson
 Fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient Dr Kirsty Dodgson Aims Discuss different types of fungi Overview of types of clinical infections Clinical Manifestations Fungus Includes Moulds Aspergillus
Fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient Dr Kirsty Dodgson Aims Discuss different types of fungi Overview of types of clinical infections Clinical Manifestations Fungus Includes Moulds Aspergillus
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor د.حامد الزعبي
 number Fungi#1 Done by نرجس الس ماك Corrected by مهدي الشعراوي Doctor د.حامد الزعبي Introduction to Mycology -Terms: -Medical Mycology: The study of mycosis and their etiological agents -Mycosis: Disease
number Fungi#1 Done by نرجس الس ماك Corrected by مهدي الشعراوي Doctor د.حامد الزعبي Introduction to Mycology -Terms: -Medical Mycology: The study of mycosis and their etiological agents -Mycosis: Disease
Histoplasma, Coccidioides, Aspergillus, Other Systemic Fungal Pathogens And Paragonimus westermani
 Histoplasma, Coccidioides, Aspergillus, Other Systemic Fungal Pathogens And Paragonimus westermani Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Dept. of Basic Medical Sciences Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
Histoplasma, Coccidioides, Aspergillus, Other Systemic Fungal Pathogens And Paragonimus westermani Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Dept. of Basic Medical Sciences Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
Condition First line Alternative Comments Candidemia Nonneutropenic adults
 Recommendations for the treatment of candidiasis. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Candidiasis: 2009 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Condition First line Alternative
Recommendations for the treatment of candidiasis. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Candidiasis: 2009 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Condition First line Alternative
Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease
 Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
Elements for a Public Summary. [Product Name] 40 mg/ml oral suspension. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
![Elements for a Public Summary. [Product Name] 40 mg/ml oral suspension. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Elements for a Public Summary. [Product Name] 40 mg/ml oral suspension. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology](/thumbs/81/82839413.jpg) VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary [Product Name] 40 mg/ml oral suspension VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Fungi (yeasts) are small organisms that feed by breaking down tissue. In humans, fungi
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary [Product Name] 40 mg/ml oral suspension VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Fungi (yeasts) are small organisms that feed by breaking down tissue. In humans, fungi
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach
 Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE
 Thorax (1954), 9, 2 1. TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE BY PETER BEACONSFIELD, H. S. COULTHARD, AND F. G. KERGIN From the Toronto Hospital for the
Thorax (1954), 9, 2 1. TREATMENT OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS BY THORA- COPLASTY IN PATIENTS OVER 50 YEARS OF AGE BY PETER BEACONSFIELD, H. S. COULTHARD, AND F. G. KERGIN From the Toronto Hospital for the
Managing chronic pulmonary aspergillosis infection
 Managing chronic pulmonary aspergillosis infection Jacques Cadranel Service de Pneumologie et Réanimation Conflict of interest statement : J Cadranel Principal investigator of the VERTIGO trial on behalf
Managing chronic pulmonary aspergillosis infection Jacques Cadranel Service de Pneumologie et Réanimation Conflict of interest statement : J Cadranel Principal investigator of the VERTIGO trial on behalf
Carcinoma of the Lung
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
Chapter 16. Lung Abscess. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lung Abscess 1 EDA PM C AFC RB A B Figure 16-1. Lung abscess. A, Cross-sectional view of lung abscess. B, Consolidation and (C) excessive bronchial secretions are common secondary anatomic alterations
Chapter 16 Lung Abscess 1 EDA PM C AFC RB A B Figure 16-1. Lung abscess. A, Cross-sectional view of lung abscess. B, Consolidation and (C) excessive bronchial secretions are common secondary anatomic alterations
Lethal pulmonary fungal disease think fungus early
 Lethal pulmonary fungal disease think fungus early David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Global Action Fund for Fungal Infections
Lethal pulmonary fungal disease think fungus early David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Global Action Fund for Fungal Infections
Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease
 Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract
 Before you start: You must read the slides! The Dr. did not bother to explain them all Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract - TB is a global problem that the WHO is trying to combat.
Before you start: You must read the slides! The Dr. did not bother to explain them all Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract - TB is a global problem that the WHO is trying to combat.
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Surgical treatment of bullous lung disease
 Surgical treatment of bullous lung disease PD POTGIETER, SR BENATAR, RP HEWITSON, AD FERGUSON Thorax 1981 ;36:885-890 From the Respiratory Clinic, Groote Schuur Hospita', and Departments of Medicine, Anaesthetics,
Surgical treatment of bullous lung disease PD POTGIETER, SR BENATAR, RP HEWITSON, AD FERGUSON Thorax 1981 ;36:885-890 From the Respiratory Clinic, Groote Schuur Hospita', and Departments of Medicine, Anaesthetics,
Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia
 Difference Between Pleural Effusion and Pneumonia www.differencebetween.com Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia Pleural effusion and pneumonia are two conditions that affect our respiratory
Difference Between Pleural Effusion and Pneumonia www.differencebetween.com Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia Pleural effusion and pneumonia are two conditions that affect our respiratory
Mycology. BioV 400. Subcutaneous Mycoses. Ecological associations. Geographic distribution World-wide
 BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
Allergic aspergillosis of the respiratory tract
 EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY UPDATE ALLERGIC RESPIRATORY ASPERGILLOSIS Allergic aspergillosis of the respiratory tract Ashok Shah 1 and Chandramani Panjabi 2 Affiliations: 1 Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Vallabhbhai
EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY UPDATE ALLERGIC RESPIRATORY ASPERGILLOSIS Allergic aspergillosis of the respiratory tract Ashok Shah 1 and Chandramani Panjabi 2 Affiliations: 1 Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Vallabhbhai
History of Aspergillus. History of Aspergillus. Biology of Aspergillus flavus Fungus Saphrophyte Haploid filamentous fungi Mycelium secrets enzymes
 Anthony Fossaceca Anthony Nuzzi Swati Vasireddy History of Aspergillus Pier Antonio Micheli Italian priest and Biologist Discovered the fungi in 1729 Structure Aspergillum (holy water sprinkler) Hence
Anthony Fossaceca Anthony Nuzzi Swati Vasireddy History of Aspergillus Pier Antonio Micheli Italian priest and Biologist Discovered the fungi in 1729 Structure Aspergillum (holy water sprinkler) Hence
Dr Conroy Wong. Professor Richard Beasley. Dr Sarah Mooney. Professor Innes Asher
 Professor Richard Beasley University of Otago Director Medical Research Institute of New Zealand Wellington Dr Sarah Mooney Physiotherapy Advanced Clinician Counties Manukau Health NZ Respiratory and Sleep
Professor Richard Beasley University of Otago Director Medical Research Institute of New Zealand Wellington Dr Sarah Mooney Physiotherapy Advanced Clinician Counties Manukau Health NZ Respiratory and Sleep
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Surgery versus non-surgical treatment for bronchiectasis (Review)
 Surgery versus non-surgical treatment for bronchiectasis (Review) Warburton CJ, Corless JA This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in
Surgery versus non-surgical treatment for bronchiectasis (Review) Warburton CJ, Corless JA This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Lung abscess in childhood
 Thorax (1968), 23, 216. PATRICIA H. MARK AND J. A. PETER TURNER' Froml the Depattmenit of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, and the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada Lung
Thorax (1968), 23, 216. PATRICIA H. MARK AND J. A. PETER TURNER' Froml the Depattmenit of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, and the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada Lung
Allergy Update. because you depend upon results. Abacus ALS
 Allergy Update Abacus ALS ALS ImmunoCAP sigg measurement ImmunoCAP Specific IgG Measures antigen-specific IgG antibodies in human serum and plasma. Part of the natural defence system of the body and develop
Allergy Update Abacus ALS ALS ImmunoCAP sigg measurement ImmunoCAP Specific IgG Measures antigen-specific IgG antibodies in human serum and plasma. Part of the natural defence system of the body and develop
Necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis
 Necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis W. P. U. KENNEDY, D. N. MALONE, and W. BLYTH Thorax (1970), 25, 691. Respiratory Diseases Unit, Northern General Hospital, Edinburgh, and Departments of Respiratory
Necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis W. P. U. KENNEDY, D. N. MALONE, and W. BLYTH Thorax (1970), 25, 691. Respiratory Diseases Unit, Northern General Hospital, Edinburgh, and Departments of Respiratory
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis
 Thorax (1975), 30, 316. Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis DEWI DAVIES, J. S. CROWTHER, and ANDREW MacFARLANE Ransom Hospital, Mansfield Davies, D, Crowther, J. S., and MacFarlane, A. (1975). Thorax,
Thorax (1975), 30, 316. Idiopathic progressive pulmonary fibrosis DEWI DAVIES, J. S. CROWTHER, and ANDREW MacFARLANE Ransom Hospital, Mansfield Davies, D, Crowther, J. S., and MacFarlane, A. (1975). Thorax,
Nontuberculous mycobacterial disease and Aspergillus-related lung disease in bronchiectasis
 Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 352 357 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00139005 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Nontuberculous mycobacterial disease and Aspergillus-related lung disease in bronchiectasis H. Kunst*, M.
Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 352 357 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00139005 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Nontuberculous mycobacterial disease and Aspergillus-related lung disease in bronchiectasis H. Kunst*, M.
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic
 Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
Surgery for MDR/XDR Tuberculosis
 Surgery for MDR/XDR Tuberculosis John D. Mitchell, M.D. Davis Endowed Chair in Thoracic Surgery Professor and Chief, General Thoracic Surgery Department of Surgery University of Colorado School of Medicine
Surgery for MDR/XDR Tuberculosis John D. Mitchell, M.D. Davis Endowed Chair in Thoracic Surgery Professor and Chief, General Thoracic Surgery Department of Surgery University of Colorado School of Medicine
NON-CF BRONCHIECTASIS IN ADULTS
 Séminaire de Pathologie Infectieuse Jeudi 25 juin 2008 Cliniques Universitaires UCL de Mont-Godinne, Yvoir NON-CF BRONCHIECTASIS IN ADULTS Dr Robert Wilson Royal Brompton Hospital, London, UK Aetiology
Séminaire de Pathologie Infectieuse Jeudi 25 juin 2008 Cliniques Universitaires UCL de Mont-Godinne, Yvoir NON-CF BRONCHIECTASIS IN ADULTS Dr Robert Wilson Royal Brompton Hospital, London, UK Aetiology
Update on Biologicals for ABPA and Asthma
 Update on Biologicals for ABPA and Asthma 5 th Advances Against Aspergillosis Istanbul 27 Jan 2012 Richard B. Moss MD Professor of Pediatrics Stanford University Palo Alto CA USA Disease of chronic airway
Update on Biologicals for ABPA and Asthma 5 th Advances Against Aspergillosis Istanbul 27 Jan 2012 Richard B. Moss MD Professor of Pediatrics Stanford University Palo Alto CA USA Disease of chronic airway
EMA Pediatric Web Synopsis Protocol A November 2011 Final PFIZER INC.
 PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
