CLINICAL, LABORATORY AND THERAPEUTIC PROFILE OF LICHEN PLANUS
|
|
|
- Ashlee Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 1 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS ORIGINAL PAPERS CLINICAL, LABORATORY AND THERAPEUTIC PROFILE OF LICHEN PLANUS Daciana Elena Brănișteanu 1, A. Pintilie 1, Andreea Dimitriu 1*, Anca Cerbu 1, Delia Ciobanu 2, A. Oanţă 3, A. L. Tatu 4 Grigore T. Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iasi Faculty of Medicine 1. Department of Medical Specialties (III) 2. Department of Morpho-functional Sciences (I) University of Medicine Transilvania, Braşov 3. Department of Dermatology Dunarea de Jos University, Galati Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy 4. Department of Dermatology *Corresponding author. dr.andreeadimitriu@gmail.com CLINICAL, LABORATORY AND THERAPEUTIC PROFILE OF LICHEN PLANUS (Abstract): Aim: Retrospective study of the clinical manifestations and clinical forms of lichen planus, investigation methods and therapeutic means using data from patients admitted to the Dermatology Clinic of the "Sf. Spiridon" County Clinical Emergency Hospital Iasi, in the interval January 1 st -December 30 th, 2015; the obtained results were compared with the data in the literature. Material and methods: Forty-five patients were included in the study. The data were interpreted by using various statistical notions: arithmetic mean, percentage distribution, standard deviation, coefficient of variation, "t-student" test. Histopathological examination was performed in most cases to enhance diagnosis certainty. Results and discussion: The analysis of the study group (29 women and 16 men) produced many results in agreement with literature data. In 2015 the prevalence of lichen planus in the patients admitted to the Clinic of Dermatology, regardless of clinical form was 4.01% with a female preponderance (female/male ratio 2: 1). The mean age of the study patients was years and 79.98% of total cases were in the fourth and six decades of life. The main infectious risk factor for the development and progression of lichen planus is hepatitis C virus (13.3%). The most co m- mon form of lichen planus (88.8%) was the cutaneous form. Conclusions: Lichen planus is a chronic autoimmune disease with undulating course and different clinical subtypes that can affect multiple body regions. Keywords: LICHEN PLANUS, PAPULE, AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES, LICHENOID REACTIONS. Lichen planus is a mucocutaneous inflammatory dermatosis of uncertain etiology, with chronic or subacute course, often self-limited (1). The classic description of lichen planus eruption is given by the 5 Ps: purple, planar, polygonal, pruritic, papules (2). The estimated prevalence of lichen planus in the general population is in the range of 0.2% to 4%. It occurs more fre- 25
2 Daciana Elena Brănișteanu et al. quently in the fifth or sixth decades of life, predominantly in women. Lichen planus in children is uncommon, but cases with familial aggregation have been reported (3). The cause of lichen planus is still unknown. The etiologic hypotheses include genetic, infectious, psychological and autoimmune factors (1). Lichenoid eruptions (LDE-probably a type IV hypersensitivity reaction) are reactive mucocutaneous lesions that are nearly identical clinically and histologically with those in idiopathic lichen planus. Drugs more frequently associated with LDE are the synthetic antimalarials, gold salts, D- penicillamine, methyldopa, B-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, spironolactone, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, thiazide, phenothiazine derivatives, allopurinol, tetracycline, sulphonylurea (1). Notable is the association of lichen planus with such autoimmune diseases as systemic lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis, dermatomyositis, ulcerative colitis, chronic active hepatitis, pemphigus vulgaris, dermatitis herpetiformis, bullous pemphigoid, alopecia areata, vitiligo, Sjogren's disease, systemic sclerosis. It supports the immunological hypothesis in the pathogenesis of lichen planus (1). MATERIAL AND METHODS This open and retrospective study was conducted on a sample of 45 patients admitted with a diagnosis of lichen planus to the Dermatology Clinic of the "Sf. Spiridon" Clinical Emergency Hospital Iasi between January 1 st and December 30 th, Data on clinical manifestations, clinical forms, investigation methods and therapeutic approaches were collected. The obtained data allowed us to classify the patients by gender, age, area of residence, etiology, affected areas, clinical form of lichen planus, association with certain diseases, type of administered treatment and its efficacy, and to compare the obtained results with the literature data. The clinical and histopathological examinations proved to be essential in making the diagnosis. In patients who experienced multiple hospitalizations we focused on the criteria for evaluating treatment efficacy and occurrence of side effects. For data interpretation, we used various statistic notions: arithmetic mean, percentage distribution, standard deviation (to highlight dispersion of data around the calculated value), coefficient of variation (which is an index of dispersion used to compare statistical series), student s t test (indicating the presence or absence of a significant difference between the two means and between two statistical series that could be correlated with the intervention of objective factors). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In 2015 the prevalence of lichen planus in the patients admitted to the Clinic of Dermatology, regardless of clinical form was 4.01%. Per the literature data, the estimated prevalence of lichen planus in the general population is in the range of 0.2% to 4% (3), with geographic area variations. Among the study patients the urban/rural ratio was 1:1.5. This difference could be related to prolonged occupational sun exposure (farming), multiple studies suggesting a relationship between exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light and disease severity, while improvement in lesions is obtained using UV protection (4). There was a female preponderance in our study (female/male ratio 2: 1) (fig. 1), result in accordance with the literature data (5). 26
3 Clinical, laboratory and therapeutic profile of lichen planus Female 64,50% Male, 35,50% Fig. 1. Sex distribution of the lichen planus patients The mean age of the study patients was years (range 9 to 87 years). The data are consistent with the literature data, per which lichen planus may occur at any age, with a peak incidence in the third to the sixth decades of life (5). In this study, 79.98% of total cases were in the fourth and six decades of life (fig. 2). A case of childhood lichen planus was recorded in a 9-year-old girl, accounting for 2.22% of all cases, but without familial aggregation of lichen planus (6). Fig. 2. Percentage distribution by age-group of lichen planus patients As for the clinical manifestations of lichen planus, the study protocol aimed to analyze the following: disease history, general and local physical examination, association with other diseases. The onset was insidious in most cases, with a progressive development of symptoms and lesions. Of the medications administered prior to the occurrence of the disease the most common were the drugs for cardiovascular diseases (66.66%) and non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (15.6%), drug classes known as having an important role in the onset or further progression of lichen planus. Another factor responsible for the development and progression of lichen planus is the infectious one, hepatitis C virus being the most studied agent. Laboratory investigations revealed that 6 (13.3%) of the study patients had chronic hepatitis C, a high percentage considering that the seroprevalence of hepatitis C virus in the general population is about 5% (7). These patients presented mucocutaneous involvement. Other viral infections incriminated are those with herpes family of viruses: herpes simplex, Epstein- Barr, cytomegalovirus and herpesvirus 6. Helicobacter pylori infection (8) was detected in 3 patients. 27
4 Daciana Elena Brănișteanu et al. Local physical examination is useful for the classification of lichen planus cases based on clinical form, lesion morphology and anatomical region. Of the 45 patients, 40 (88.8%) had cutaneous LP, 5 presented only mucosal involvement (11.1%), and 15 patients both cutaneous and mucosal involvement, accounting for 33.3% of all cases (per the literature data, 30-70% have lichen planus with mucosal involvement (5)). In the 40 cases of lichen planus with cutaneous involvement, the most common morphological subtype was represented by the classic form (18 cases, 45%) (fig. 3). follicular subtype, 5 patients (fig. 5), 4 of them women presenting alopecia plaques on the scalp and one male patient with lesions on the chest. Fig. 4. Multiple papular, itchy, violaceous lesions, arranged in a reticulate fashion (hypertrophic lichen planus) Fig. 3. Flat, polygonal, erythematousviolet, small, shiny, isolated, itchy papules on the flexor surface of the hand (classic lichen planus) The second most common subtype was the atrophic form. Long-term use of potent and super potent topical corticosteroids may lead to the development of this form of lichen planus. In the present study, only 2 of the 7 patients with atrophic lichen planus were known to have lichen planus and were on treatment, the remaining 5 being at their first hospital admission. Other common subtypes were the hypertrophic subtype, 5 patients (fig. 4), and Fig. 5. Flat, follicular, polygonal, erythematous-violet, bright, isolated papules on the scalp (follicular lichen planus) Of the 45 patients included in this study 20 (44.4%) presented mucosal involvement. Oral lesions were the most common, and most patients were females (tab. I). Of the 13 patients with oral involvement 7 presented the reticular form, which is the most common form. Five patients had the erosive form, the symptoms consisting of pain, burning sensation, sometimes dysphagia. One of these 7 patients, 28
5 Clinical, laboratory and therapeutic profile of lichen planus an 87-year-old male, presented atrophicerosive lichen planus lesions (fig. 6). TABLE I Distribution of mucosal lesions by anatomical areas Affected mucosal region Number of patients Total % Males Females Oral cavity Genital mucosa Total * 100 *the total corresponds to 23 patients as some of them presented both oral and genital involvement Fig.6. Exulceration, slightly depressed, irregular contour, painful, covered by a pseudo membrane Seven patients (24.13%) presented vulvovaginal involvement, of which 5 (17.24%) with the erosive form, sometimes in association with atrophic lesions. Three (10.34%) of these presented complications, the most common being represented by the agglutination and resorption of the labia minora, accompanied in 2 cases (6.89%) by the narrowing the vaginal ostium. Included in this group was a case (3.44%) of vulvovaginal-gingival syndrome, the patient associating erosive vulvovaginal and oral lichen planus at the level of jugal mucosa. Genital involvement was found in 3 males (18.75%), 2 with the erosive form and one with the classic papular form. In this study, the diseases most frequently associated with lichen planus were hypertension, diabetes mellitus and chronic venous insufficiency. A number of autoimmune diseases have been found to be associated with lichen planus: alopecia areata (2 cases, 4.44%), autoimmune thyroiditis/graves' disease (6 cases, 13.3%), systemic lupus erythematosus (3 cases, 6.66%), vitiligo (3 cases, 6.66%), vasculitis (1 case, 2.22%), plaque morphea (1 case, 2.22%), scleroderma (1 case, 2.22%), pemphigus vulgaris (2 cases, 4.44%), psoriasis (2 cases, 4.44%), making a total of 21 patients, representing 46.6% of the study group. Also, the association with hypersensitivity reactions is mentioned in numerous studies (9): arthritis (3 cases, 6.66%), allergies to various compounds (8 cases, 17.7%), asthma (1 case, 2.22%), gastritis (2 cases, 4.44%), atopic dermatitis (1 case, 2.22%), making a total of 15 patients (33.33%). The results are consistent with the data in the literature and support the autoimmune theory (1). The triad of oral lichen planus, diabetes mellitus and hypertension, association known as Grünspan s syndrome was found in two patients (4.44% share). The results of laboratory investigations are nonspecific, excluding direct and indirect immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry and histopathology. Histopathological examination was performed in most cases to enhance diagnostic certainty, in agreement with the data in the literature (10). The most common changes are the orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, acanthosis, tapered rete ridges, band-like lymphoplasmocytic inflammatory infiltrate at the dermoepidermal junction the presence of Civatte bodies (apoptotic keratinocytes). These are exemplified in the following iconography, 29
6 Daciana Elena Brănișteanu et al. with images of biopsies collected from our patients (fig. 7, 8, 9, 10). Fig. 7. Hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, acanthosis Classic lichen planis. HE 4x Fig. 8. Spongiosis with exocytosis, Civatte bodies Lichenoid eruption. HE 10x Fig. 9. Submucosal bullae Oral lichen planus. HE 4x Fig. 10. Discrete perifollicular inflammatory infiltrate Follicular lichen planus. HE 4x Regarding the treatment of lichen planus, the following ones were mainly administered: topical (88.88%), systemic (17.7%) and intralesional corticosteroid therapy (2.2%), therapy with immunosuppressive agents (2.2%), PUVA therapy (2.2%), antihistamines (93.3%), vitamin C (88.8%) and calcium gluconate (82.2%) (as adjuvants to the main therapy). The main treatment option was topical corticosteroids and in 6 cases (13.3%) was also associated systemic therapy. Systemic corticosteroid therapy was used in 8 cases (17.7%) of lichen planus with severe multiple of both the skin and mucous membranes. Thus, 4 of these cases (8.8%) had rash extended and oral lesions insufficiently responsive to topical treatment, and 3 cases (6.6%) with rash, erosive oral and genital, only one case of lichen planus eruptive generalized unresponsive to topical therapy. Individualized treatment regimens were tailored for each patient, their efficacy, occurrence of possible side-effects and the interaction with the medication used to treat the associated diseases associated being closely monitored. The course and prognosis are generally favorable, most patients (73.3%) showing 30
7 Clinical, laboratory and therapeutic profile of lichen planus complete or partial remission of the lesions on treatment. In the patients (26.6%) with persistent lesions the treatment was reconsidered. Clinical forms with negative evolution or absence of remission were the mucosal lichen planus cases, both the oral and genital mucosa. 6 patients (13.3%) had various complications. Thus, three of them (6.6%) suffered diffuse or localized cicatricial alopecia, one man (2.2%) with erosive lichen planus genital complicates with phimosis, and two females (4.4%) develop agglutination of labia minora. Given the risk of complications, sometimes debilitating in lichen planopilaris and mucosal lichen planus, and of malignant transformation of the erosive mucosal forms, patients were informed about these risks and periodic clinical, biological and therapy reassessment visits were recommended. CONCLUSIONS The profile of the patients enrolled in this study is consistent with the data in the literature. Thus, our findings emphasize frequently with the association between liver damage and lichen planus, especially HCV infection (6 patients, 13.3%) and cirrhosis (3 cases, 6.6%). In our study, dyslipidemia was found in 48.88% of cases with lichen planus, the most frequent association was made with the cutaneous form (35.5%) followed by the oral (22.2%) and genital form (8.88%). In 2016, Lai YC et al (12) published similar results regarding the association between lichen planus and dyslipidemia. Although, palm-plantar lichen is very rare (1-2% according the literature), in our study it was present in 10% of cases, being characterized by multiple, bilateral lesions associated with severe pruritus. Forward studies will explain this statistics results. Lichen planus may have a psychosocial impact affecting the quality of life of patients, our study revealing that 8.8% of cases were diagnosed with depression. Giving attention to pathogenesis, clinical picture and an early diagnosis are essential for selecting the most appropriate treatment. Our data referring to the therapeutic options have been aligned with European standards of treatment. Given the undulating nature of the disease, periodic monitoring of disease course and therapeutic efficacy are required. REFERENCES 1. Hertl M. Autoimmune Diseases of the Skin. 3 rd Edition. Springer, Wagner G, Rose C, Sachse M. Clinical variants of lichen planus. JDDG 2013; 11: Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Lichen Planus. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: Mohan S, Ghanta S, Verma S, Agarwal N, Gupta N, Singh U. Meteorological influences on the incidence of lichen planus in a north Indian population. J Oral Sci 2013; 55: Bolognia J, Jorizzo J, Schaffer J. Dermatology. USA: Elsevier Saunders, 3 rd Edition, Walton K, Bowers E, Drolet B, Holland K. Childhood Lichen Planus: demographics of a U.S. population. Pediatr Dermatol 2010; 27: Petti S, Rabiei M, De Luca M, Scully C. The magnitude of the association between hepatitis C virus infection and oral lichen planus: meta-analysis and case control study. Odontol 2011; 99: Girardi C, Luz C, Cherubini K, de Figueiredo MAZ, Nunes MLT, Salum FG. Salivary cortisol and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) levels, psychological factors in patients with oral lichen planus. Arch Oral Biol 2011; 56(9):
8 Daciana Elena Brănișteanu et al. 9. Friedman P, Cohen E, Marcucci C, Peralta R, Cabo H. Dermoscopic findings in different clinical variants of lichen planus. Is dermoscopy useful? Dermatol Pract Concept 2015; 5(4): Moscarella E, Gonzalez S, Agozzino M. Pilot study on reflectance confocal microscopy imaging of Lichen Planus: a real-time, non-invasive aid for clinical diagnosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2012; 26(10): Coondoo A, Phiske M, Verma S, Lahir K. Side-effects of topical steroids: A long overdue revisit. Indian Dermatol Online J 2014; 5: Lai YC, Yew YW, Schwartz RA. Lichen planus and dyslipidemia: a systematic review and metaanalysis of observational studies. Int J Dermatol 2016; 55(5): NOUTĂȚI NEWS CDH17 IS A MORE SENSITIVE MARKER FOR GASTRIC ADENOCARCINOMA THAN CK20 AND CDX2 Metastatic cancers can be difficult to diagnose in a clinical setting with most being carcin o- mas. In the past, a panel consisting of cytokeratin (CK) 7, CK20, and CDX2 antibodies has been used to assess gastrointestinal (GI) tumors of unknown primary. Expression of CK7 is observed in a wide variety of carcinomas, thus, it is an important marker in diagnosis. CK20 expression is specific to certain types of cancer and is typically used in combination with CK7 to distinguish different types of tumors. CDX2 is a homeobox gene that encodes an intestine-specific transcription factor and is expressed in the nuclei of epithelial cells throughout the GI tract. Immunohistochemical expression of CDX2 protein in primary and metasta t- ic colorectal carcinomas has been previously documented. CK7 along with CK20 or CDX2 markers constitute an important panel for the diagnosis of GI tumors versus tumors of unknown origin. However, in difficult cases, expression patterns may vary and the presence or absence of these markers may not lead to a definitive diagnosis. Cadherin 17 (CDH17), also called liver-intestine cadherin, is a cell-adhesion protein that is transcriptionally regulated by CDX2, and is involved in tumor invasion and metastasis. CDH17 is a novel diagnostic mar k- er for GI tract carcinoma with greater sensitivity than CDX2 in colon cancers. Recently, a mouse monoclonal CDH17 (clone IH3) antibody has been developed to aid pathologists in interpreting GI adenocarcinomas, especially in cases of unknown primary origin. There have been conflicting results with CDH17 antibodies, even when using the same designated clone as presented in this study. This study will present an immunohistochemical evaluation in a side by-side comparison with antibodies CDH17, CK20, and CDX2 in various neoplastic tissues, with emphasis on GI adenocarcinomas. CDH17 may also be helpful in cases that are negative for CK7, CDX2, and CK20. The study results confirm that CDH17 expression analysis may be of significant value in the diagnosis of GI tumors and those of unknown origin (Altree-Tacha D, Tyrrell J, Haas T. CDH17 Is a More Sensitive Marker for Gastric Adenocarcinoma Than CK20 and CDX2. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017; 141: ). Doina Butcovan 32
Epidemiological study of Lichen Planus
 Year: 2014; Volume: 1; Issue: 1 Article ID: MD14 20; Pages: 1-9 BioMed Research The Open Access Publisher BMR Medicine Research Article Epidemiological study of Lichen Planus Shankar Gouda Ireddy 1 and
Year: 2014; Volume: 1; Issue: 1 Article ID: MD14 20; Pages: 1-9 BioMed Research The Open Access Publisher BMR Medicine Research Article Epidemiological study of Lichen Planus Shankar Gouda Ireddy 1 and
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations
 Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
ETHIOPATOGENIC HYPOTHESES IN LICHEN PLANUS
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2016 vol. 120, no. 4 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS UPDATES ETHIOPATOGENIC HYPOTHESES IN LICHEN PLANUS Daciana Elena Brănişteanu 1, A. Pintilie 1, Laura Elena Andreş
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2016 vol. 120, no. 4 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS UPDATES ETHIOPATOGENIC HYPOTHESES IN LICHEN PLANUS Daciana Elena Brănişteanu 1, A. Pintilie 1, Laura Elena Andreş
Clinico - Histopathological features of Lichen Planus-an Appraisal
 Original Article Clinico - Histopathological features of Lichen Planus-an Appraisal Raghavendra B N 1, Jaffer Basha S K 1 Associate Professor, Department of Dermatology, M V J Medical College and Research
Original Article Clinico - Histopathological features of Lichen Planus-an Appraisal Raghavendra B N 1, Jaffer Basha S K 1 Associate Professor, Department of Dermatology, M V J Medical College and Research
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I. Immunopathology Part I
 INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
Dermoscopic patterns in active and regressive lichen planus and lichen planus variants: a morphological study
 DERMTOLOGY PRCTICL & CONCEPTUL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic patterns in active and regressive lichen planus and lichen planus variants: a morphological study Şule Güngör 1, Ilteriş O. Topal 1, Emek K. Göncü
DERMTOLOGY PRCTICL & CONCEPTUL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic patterns in active and regressive lichen planus and lichen planus variants: a morphological study Şule Güngör 1, Ilteriş O. Topal 1, Emek K. Göncü
DESCRIPTIONS FOR MED 3 ROTATIONS Dermatology A3S
 Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
Lichen planus along with Blaschko lines "Blaschkoian lichen planus"
 Original Article Lichen planus along with Blaschko lines "Blaschkoian lichen planus" Hossein Kavoussi, Mazaher Ramazani, Elias Salimi Dermatology Department, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences,
Original Article Lichen planus along with Blaschko lines "Blaschkoian lichen planus" Hossein Kavoussi, Mazaher Ramazani, Elias Salimi Dermatology Department, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences,
Disorders of the vulva
 Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Vulval lesions Disorders of the vulva Terminology standardised by the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease(ISSVD) Classification 1.Nonneoplastic epithelial disorders of vulva Lichen
Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern
 Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor
Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor
Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions. Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX
 1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology. Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders. Acne. Acne Vulgaris. Pomade Acne. Steroid Acne
 Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
A CLINICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF LICHEN PLANUS
 A CLINICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF LICHEN PLANUS Ch. Madhu Babu 1, P. Padmaja 2, M. Roopa Shree 3 1Professor, Department of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology, Osmania Medical College and General
A CLINICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF LICHEN PLANUS Ch. Madhu Babu 1, P. Padmaja 2, M. Roopa Shree 3 1Professor, Department of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology, Osmania Medical College and General
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus. Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university
 Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
ISPUB.COM. A Case of Actinic Lichen Planus. K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
Immunoflourescent assessment of Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) type 1 in oral lichen planus
 Immunoflourescent assessment of Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) type 1 in oral lichen planus Muthanna K. Ali, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background: Oral lichen planus is one of the most common dermatological
Immunoflourescent assessment of Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) type 1 in oral lichen planus Muthanna K. Ali, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background: Oral lichen planus is one of the most common dermatological
Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus
 Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica. 2010; 89: 966 970 SHORT REPORT Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus ANNE LISE ORDING HELGESEN 1,2,3, PETTER GJERSVIK 3,4, PETER JEBSEN 5, ROLF KIRSCHNER
Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica. 2010; 89: 966 970 SHORT REPORT Vaginal involvement in genital erosive lichen planus ANNE LISE ORDING HELGESEN 1,2,3, PETTER GJERSVIK 3,4, PETER JEBSEN 5, ROLF KIRSCHNER
Atypical Case of Pityriasis Rosea in a Child Following Streptococcal Erythema Nodosum
 CASE REPORT DERMATOLOGY // INFECTOLOGY Atypical Case of Pityriasis Rosea in a Child Following Streptococcal Erythema Nodosum Anca Chiriac 1,2,3, Piotr Brzezinski 4, Cristian Podoleanu 5, Simona Stolnicu
CASE REPORT DERMATOLOGY // INFECTOLOGY Atypical Case of Pityriasis Rosea in a Child Following Streptococcal Erythema Nodosum Anca Chiriac 1,2,3, Piotr Brzezinski 4, Cristian Podoleanu 5, Simona Stolnicu
Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus
 Original Research Paper Dermatology Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus Dr. Rikeeta S. Deshmukh Dr. Raju G. Chaudhary ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Introduction: Unique,
Original Research Paper Dermatology Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus Dr. Rikeeta S. Deshmukh Dr. Raju G. Chaudhary ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Introduction: Unique,
Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
Dermoscopic findings in different clinical variants of lichen planus. Is dermoscopy useful?
 DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic findings in different clinical variants of lichen planus. Is dermoscopy useful? Paula Friedman 1, Emilia Cohen Sabban 2, Carolina Marcucci
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Dermoscopic findings in different clinical variants of lichen planus. Is dermoscopy useful? Paula Friedman 1, Emilia Cohen Sabban 2, Carolina Marcucci
ETIOPATHOGENIC AND CLINICAL CORRELATIONS BETWEEN LICHEN PLANUS AND ASSOCIATED DISEASES
 ORIGINAL PAPERS ETIOPATHOGENIC AND CLINICAL CORRELATIONS BETWEEN LICHEN PLANUS AND ASSOCIATED DISEASES NICOLETA-BIANCA GEORGESCU*, LAURA GHEUCÃ-SOLOVÃSTRU*,**, ANDREEA BÃRBUÞÃ*, ANDREEA DANIELA NECHITA*,
ORIGINAL PAPERS ETIOPATHOGENIC AND CLINICAL CORRELATIONS BETWEEN LICHEN PLANUS AND ASSOCIATED DISEASES NICOLETA-BIANCA GEORGESCU*, LAURA GHEUCÃ-SOLOVÃSTRU*,**, ANDREEA BÃRBUÞÃ*, ANDREEA DANIELA NECHITA*,
A. Erythema multiforme and related diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Grover s disease: A case report.
 320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
2018 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Denis Lynch, DDS, PhD
 2018 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Denis Lynch, DDS, PhD Course 9148: Diagnosis and Treatment of Recurrent Oral Ulcers Friday, April 6 9 am - 12 pm Diagnosis and Treatment of Recurrent Oral Ulcers
2018 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Denis Lynch, DDS, PhD Course 9148: Diagnosis and Treatment of Recurrent Oral Ulcers Friday, April 6 9 am - 12 pm Diagnosis and Treatment of Recurrent Oral Ulcers
A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus
 #2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
#2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
Pathology of the skin. Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE
 Pathology of the skin Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE The skin Biggest organ Kb. 1.8 nm Kb. 10 kg Most frequent site for tumor development (BCC) Pathology of the skin
Pathology of the skin Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE The skin Biggest organ Kb. 1.8 nm Kb. 10 kg Most frequent site for tumor development (BCC) Pathology of the skin
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
atorvastatin 10mg, amlodipine 5mg and dilitazem 60mg. He had unexplained iron deficiency anaemia (hemoglobin-8.4gm/dl, ferritin- 4.73ng/ml, total iron
 Pemphigus herpetiformis : A rare clinical variant of pemphigus Shrestha P 1, Tajhya RB 2, Pokharel A 3 1,2 Consultant Dermatologist, Department of Dermatology, Vayodha Hospital Pvt. Ltd, Balkhu, Kathmandu,
Pemphigus herpetiformis : A rare clinical variant of pemphigus Shrestha P 1, Tajhya RB 2, Pokharel A 3 1,2 Consultant Dermatologist, Department of Dermatology, Vayodha Hospital Pvt. Ltd, Balkhu, Kathmandu,
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
ISSN X (Print)
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(9A):3211-3215 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(9A):3211-3215 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
b) SKILLS The student should be able to
 1. GOAL The aim of teaching the undergraduate student in Dermatology, S.T.D. and Leprology is to impart such knowledge and skills that may enable him to diagnose and treat common ailments and to refer
1. GOAL The aim of teaching the undergraduate student in Dermatology, S.T.D. and Leprology is to impart such knowledge and skills that may enable him to diagnose and treat common ailments and to refer
Clinical and histopathological spectrum of lichen planus
 Original Article Clinical and histopathological spectrum of lichen planus Rohit Rampal, Sunil K. Gupta, Neena Sood*, Anupama Rampal**, Shweta Karkara, Jaspreet Kaur Department of Dermatology, Dayanand
Original Article Clinical and histopathological spectrum of lichen planus Rohit Rampal, Sunil K. Gupta, Neena Sood*, Anupama Rampal**, Shweta Karkara, Jaspreet Kaur Department of Dermatology, Dayanand
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Update in deposition diseases
 Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
THERE IS A GROUP OF PAtients. Defining Urticarial Dermatitis. A Subset of Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Pattern
 STUDY Defining Urticarial Dermatitis A Subset of Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Pattern Steven Kossard, FACD; Ian Hamann, FACD; Barbara Wilkinson, BSc Background: Urticarial dermatitis may represent
STUDY Defining Urticarial Dermatitis A Subset of Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Pattern Steven Kossard, FACD; Ian Hamann, FACD; Barbara Wilkinson, BSc Background: Urticarial dermatitis may represent
Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2
 Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
C.V. Updated on November, 2015
 C.V. Updated on November, 2015 Name: Khitam Salem Odeh Al-Refu Date of Birth: 01/08/1972 Place of Birth: Amman/ Jordan. Nationality: Jordanian Marital Status: Married with three children. Home Address:
C.V. Updated on November, 2015 Name: Khitam Salem Odeh Al-Refu Date of Birth: 01/08/1972 Place of Birth: Amman/ Jordan. Nationality: Jordanian Marital Status: Married with three children. Home Address:
Eczema. By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University
 Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
Pemphigus in younger age group in Bangladeshi population
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE in younger age group in Bangladeshi population Abdul Wahab 1, MD, Lubna Khondker 1, MD, Jamal Uddin 1, MD, Ishrat Bhuiyan 2, MD Shirajul Islam Khan 3, MD, Zafrul Islam 1, MD, Rahmat Ali
ORIGINAL ARTICLE in younger age group in Bangladeshi population Abdul Wahab 1, MD, Lubna Khondker 1, MD, Jamal Uddin 1, MD, Ishrat Bhuiyan 2, MD Shirajul Islam Khan 3, MD, Zafrul Islam 1, MD, Rahmat Ali
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 1: 14, June 2010
 Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
S003 CPC Self-Assessment
 S003 CPC Self-Assessment Alina G. Bridges, D.O. Associate Professor Program Director, Dermatopathology Fellowship Department of Dermatology, Division of Dermatopathology and Cutaneous Immunopathology Mayo
S003 CPC Self-Assessment Alina G. Bridges, D.O. Associate Professor Program Director, Dermatopathology Fellowship Department of Dermatology, Division of Dermatopathology and Cutaneous Immunopathology Mayo
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Successful treatment of Oral Lichen Planus (OLP) with 0.1% topical Tacrolimus in a patient with impaired liver enzymes: A Case report
 American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com Vol-2: No-1: 7-11:2014 Case Report Successful treatment of Oral Lichen Planus (OLP) with 0.1% topical Tacrolimus in a patient with impaired
American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com Vol-2: No-1: 7-11:2014 Case Report Successful treatment of Oral Lichen Planus (OLP) with 0.1% topical Tacrolimus in a patient with impaired
INFECTION WITH CYTOMEGALOVIRUS
 Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula:Protecţia Mediului Vol. XIV, 009 INFECTION WITH CYTOMEGALOVIRUS 854 Negruţ Nicoleta University of Oradea, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Department of Public
Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula:Protecţia Mediului Vol. XIV, 009 INFECTION WITH CYTOMEGALOVIRUS 854 Negruţ Nicoleta University of Oradea, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Department of Public
Interesting Case Series. Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis
 Interesting Case Series Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis Sean Chen, BA, a Peter Mattei, MD, a Max Fischer, MD, MPH, a Joshua D. Gay, PA-C, b Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS, b and Leigh Ann
Interesting Case Series Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis Sean Chen, BA, a Peter Mattei, MD, a Max Fischer, MD, MPH, a Joshua D. Gay, PA-C, b Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS, b and Leigh Ann
Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery
 Dermoscopy in the evaluation and treatment of hair loss Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Antonella Tosti, MD
Dermoscopy in the evaluation and treatment of hair loss Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Antonella Tosti, MD
THE TRIAD OF LICHEN PLANUS, THYMOMA AND LIVER CIRRHOSIS-HEPATOMA. FIRST REPORTED CASE
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 7, No. 2, July 2000 (38-42) CASE REPORT THE TRIAD OF LICHEN PLANUS, THYMOMA AND LIVER CIRRHOSIS-HEPATOMA. FIRST REPORTED CASE J. A. Hassan, Saadiah S, Roslina
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 7, No. 2, July 2000 (38-42) CASE REPORT THE TRIAD OF LICHEN PLANUS, THYMOMA AND LIVER CIRRHOSIS-HEPATOMA. FIRST REPORTED CASE J. A. Hassan, Saadiah S, Roslina
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar
 Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Introduction. Results. Discussion. Histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings. Results. conclusions,
 1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (Ultraviolet A [PUVA] and B [UBV])
![Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (Ultraviolet A [PUVA] and B [UBV]) Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (Ultraviolet A [PUVA] and B [UBV])](/thumbs/89/99382632.jpg) Origination: 09/27/07 Revised: 08/2/17 Annual Review: 11/2/17 Purpose: To provide Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (PUVA and UBV) guidelines for the Medical Department staff to reference when
Origination: 09/27/07 Revised: 08/2/17 Annual Review: 11/2/17 Purpose: To provide Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (PUVA and UBV) guidelines for the Medical Department staff to reference when
Acute generalized lichen planus with diffuse palmoplantar involvement in a 4-year old child: A case report and review
 CASE REPORT Acute generalized lichen planus with diffuse palmoplantar involvement in a 4-year old child: A case report and review Arun Joshi, MD, Manish Rijhwani, MD, Mohammed Alajmi, MD Department of
CASE REPORT Acute generalized lichen planus with diffuse palmoplantar involvement in a 4-year old child: A case report and review Arun Joshi, MD, Manish Rijhwani, MD, Mohammed Alajmi, MD Department of
Pyrex Journals
 Pyrex Journals 235-212 Pyrex Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol 2 (2) pp 31-36 May, 215 http:///pjmms Copyright 215 Pyrex Journals Full Length Research Paper Lichen Planus Not Associated With
Pyrex Journals 235-212 Pyrex Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol 2 (2) pp 31-36 May, 215 http:///pjmms Copyright 215 Pyrex Journals Full Length Research Paper Lichen Planus Not Associated With
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Papular dermatitis: response to cyclosporin
 Journal of Dermatological Treatment (2000) 11, 253 257 2000 Journal of Dermatological Treatment. All rights reserved. ISSN 0954 6634 253 Papular dermatitis: response to cyclosporin E Alvarez, A Hendi,
Journal of Dermatological Treatment (2000) 11, 253 257 2000 Journal of Dermatological Treatment. All rights reserved. ISSN 0954 6634 253 Papular dermatitis: response to cyclosporin E Alvarez, A Hendi,
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham
 Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
A48-year-old Hispanic woman
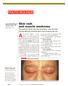 Jamie Goodall, MS4, and Richard P. Usatine, MD University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Skin rash and muscle weakness The patient s facial rash was spreading and she was having difficulty
Jamie Goodall, MS4, and Richard P. Usatine, MD University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Skin rash and muscle weakness The patient s facial rash was spreading and she was having difficulty
Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of
 Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases
 Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases Erin Wei MD Brigham and Women s Hospital, Department of Dermatology Instructor, Harvard Medical School Director, Bullous Disease Clinic No disclosures Conflict of
Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases Erin Wei MD Brigham and Women s Hospital, Department of Dermatology Instructor, Harvard Medical School Director, Bullous Disease Clinic No disclosures Conflict of
Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care
 Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care G. Scott Drew, DO, FAAD, FAOCD Smith Clinic Department of Dermatology Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation April 27, 2018 Acute Cutaneous Lupus
Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care G. Scott Drew, DO, FAAD, FAOCD Smith Clinic Department of Dermatology Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation April 27, 2018 Acute Cutaneous Lupus
Comparison of the narrow band UVB versus systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of lichen planus: A randomized clinical trial
 Received: 10.7.2011 Accepted: 5.12.2011 Original Article Comparison of the narrow band UVB versus systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of lichen planus: A randomized clinical trial Fariba Iraji, 1
Received: 10.7.2011 Accepted: 5.12.2011 Original Article Comparison of the narrow band UVB versus systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of lichen planus: A randomized clinical trial Fariba Iraji, 1
Diploma examination. Dermatopathology: First paper. Tuesday 21 March Candidates must answer FOUR questions ONLY. Time allowed: Three hours
 Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 21 March 2017 1. Discuss the role of fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) and emerging molecular techniques in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanocytic lesions,
Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 21 March 2017 1. Discuss the role of fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) and emerging molecular techniques in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanocytic lesions,
Histopathological spectrum of non-infectious erythematous, papulo-squamous lesions
 Histopathological spectrum of non-infectious erythematous, papulo-squamous lesions B. Rajasekhar Reddy 1*, Nalini Krishna.M 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Mediciti Institute of Medical
Histopathological spectrum of non-infectious erythematous, papulo-squamous lesions B. Rajasekhar Reddy 1*, Nalini Krishna.M 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Mediciti Institute of Medical
Epidemiology of Oral Lichen Planus in a Cohort of South Indian Population: A Retrospective Study
 JOURNAL OF CANCER PREVENTION Vol. 21, No. 1, March 2016 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-3-30 http://dx.doi.org/10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55 pissn
JOURNAL OF CANCER PREVENTION Vol. 21, No. 1, March 2016 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-3-30 http://dx.doi.org/10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55 pissn
Oral Medicine. Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN
 Oral Medicine Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN ORAL MEDICINE Oral medicine is the specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the oral health care of medically compromised patients and with the diagnosis and nonsurgical
Oral Medicine Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN ORAL MEDICINE Oral medicine is the specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the oral health care of medically compromised patients and with the diagnosis and nonsurgical
Contents. 3 Diagnostic Tests and Studies Introduction Examination... 27
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Oral Lichen Planus A Case Report with Current Trends Review of Literature
 ISSN 2455-4499; Vol.05, Issue 01 (2016) Institute of Research Advances Pg. no. 6-17 http://research-advances.org/index.php/irajas Oral Lichen Planus A Case Report with Current Trends Review of Literature
ISSN 2455-4499; Vol.05, Issue 01 (2016) Institute of Research Advances Pg. no. 6-17 http://research-advances.org/index.php/irajas Oral Lichen Planus A Case Report with Current Trends Review of Literature
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY
 WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
DERMATOLOGY & VENEREOLOGY
 DECEMBER 2O1O DERMATOLOGY & VENEREOLOGY PAPER - I Time : 3 hours Max. Marks : 100 DVD/D/10/06/l '.i Attempt all questions in order. Each question carries 10 marks 1. Discuss the differential diagnosis
DECEMBER 2O1O DERMATOLOGY & VENEREOLOGY PAPER - I Time : 3 hours Max. Marks : 100 DVD/D/10/06/l '.i Attempt all questions in order. Each question carries 10 marks 1. Discuss the differential diagnosis
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY ORAL CAVITY. Oral Cavity Subsites 4/10/2013 LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANES PALATE TONGUE ORAL LYMPHOID TISSUES
 LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
Benign Oral cavity lesions. Mohammed ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery
 Benign Oral cavity lesions Mohammed ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery Anatomy Histology Physiology Pathology Clinical cases Introduction The oral cavity
Benign Oral cavity lesions Mohammed ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery Anatomy Histology Physiology Pathology Clinical cases Introduction The oral cavity
What's New in Oncodermatopathology: Immunotherapy Reactions
 What's New in Oncodermatopathology: Immunotherapy Reactions Emily Y. Chu, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania March
What's New in Oncodermatopathology: Immunotherapy Reactions Emily Y. Chu, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania March
Immune tolerance, autoimmune diseases
 Immune tolerance, autoimmune diseases Immune tolerance Central: negative selection during thymic education deletion of autoreactive B-lymphocytes in bone marrow Positive selection in the thymus Negative
Immune tolerance, autoimmune diseases Immune tolerance Central: negative selection during thymic education deletion of autoreactive B-lymphocytes in bone marrow Positive selection in the thymus Negative
Cutaneous metastases. Thaddeus Mully. University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology
 Cutaneous metastases Thaddeus Mully University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Thaddeus Mully Course C005 Essential
Cutaneous metastases Thaddeus Mully University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Thaddeus Mully Course C005 Essential
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease:
 Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
4. Pityriasis lichenoides
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details usually more than 5 cm in diameter and accompanied by poikiloderma. Some but not all patients may develop mycosis fungoides (Fig. 22.35).
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details usually more than 5 cm in diameter and accompanied by poikiloderma. Some but not all patients may develop mycosis fungoides (Fig. 22.35).
A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients
 Volume 1, Issue 3 Research Article A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients Darukarnphut P, Rattanakaemakorn P *, Rajatanavin N Division
Volume 1, Issue 3 Research Article A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients Darukarnphut P, Rattanakaemakorn P *, Rajatanavin N Division
Narrow-band UVB PHOTOTHERAPY for Skin Diseases
 Narrow-band UVB PHOTOTHERAPY for Skin Diseases By Dr. Manal Bosseila Cairo University, Egypt HISTORICAL ASPECT In 1978: Irradiation cabin with broad band UVB tubes was introduced for psoriasis & uremic
Narrow-band UVB PHOTOTHERAPY for Skin Diseases By Dr. Manal Bosseila Cairo University, Egypt HISTORICAL ASPECT In 1978: Irradiation cabin with broad band UVB tubes was introduced for psoriasis & uremic
THE TIP OF THE ICEBERG SAMER BOLIS, DO PGY-3 LEHIGH VALLEY HEALTH NETWORK, ALLENTOWN PA
 THE TIP OF THE ICEBERG SAMER BOLIS, DO PGY-3 LEHIGH VALLEY HEALTH NETWORK, ALLENTOWN PA Case The patient is a 48 year-old female, who recently returned from a trip to Puerto Rico. She presents to the ED
THE TIP OF THE ICEBERG SAMER BOLIS, DO PGY-3 LEHIGH VALLEY HEALTH NETWORK, ALLENTOWN PA Case The patient is a 48 year-old female, who recently returned from a trip to Puerto Rico. She presents to the ED
Oncology and surgery Yolanda Gilaberte. Hospital Universitario Miguel Servet, Zaragoza
 Oncology and surgery Yolanda Gilaberte. Hospital Universitario Miguel Servet, Zaragoza Dermatologic adverse events of oncologic drugs Grading of Dermatologic Adverse Events (ver 5.0) 5 grades: mild, moderate,
Oncology and surgery Yolanda Gilaberte. Hospital Universitario Miguel Servet, Zaragoza Dermatologic adverse events of oncologic drugs Grading of Dermatologic Adverse Events (ver 5.0) 5 grades: mild, moderate,
Definitive and Differential Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis Through Direct Immunofluorescence Studies
 Volume 83 Number 10 Definitive and Differential Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis Through Direct Immunofluorescence Studies Lakshmanan Suresh* and Mirdza E. Neiders* Background: Desquamative gingivitis
Volume 83 Number 10 Definitive and Differential Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis Through Direct Immunofluorescence Studies Lakshmanan Suresh* and Mirdza E. Neiders* Background: Desquamative gingivitis
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Case 18. M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is:
 Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed with Dermatological Diseases
 JCDP ORIGINAL RESEARCH Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2191 with Dermatological Diseases Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed with Dermatological Diseases 1 Sanjay
JCDP ORIGINAL RESEARCH Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2191 with Dermatological Diseases Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed with Dermatological Diseases 1 Sanjay
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS
 A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
Lichen planopilaris and its variants. Antonella Tosti. Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery
 Lichen planopilaris and its variants Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Antonella Tosti, MD S023 Lichen planopilaris
Lichen planopilaris and its variants Antonella Tosti Fredric Brandt Endowed Professor of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Antonella Tosti, MD S023 Lichen planopilaris
Some skin conditions
 Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Sign In: pemphigus.org/form
 Pemphigus and Pemphigoid The Unique Role of the Dental Professional Dr. Carol Anne Murdoch Kinch Sign In: pemphigus.org/form The International Pemphigus & Pemphigoid Foundation (IPPF) kindly asks all attendees
Pemphigus and Pemphigoid The Unique Role of the Dental Professional Dr. Carol Anne Murdoch Kinch Sign In: pemphigus.org/form The International Pemphigus & Pemphigoid Foundation (IPPF) kindly asks all attendees
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
الاكزيماتيد= Eczematid
 1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
Summary. Accepted for publication 18 May Key words genital lichen planus, oral lichen planus, vulval lichen planus
 CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07480.x Prevalence of vulval lichen planus in a cohort of women with oral lichen planus: an interdisciplinary study P. Belfiore, O. Di
CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07480.x Prevalence of vulval lichen planus in a cohort of women with oral lichen planus: an interdisciplinary study P. Belfiore, O. Di
