Yasuhiko Matsumori, Jialing Liu, Philip R. Weinstein, Takamasa Kayama ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Millicent Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Yamagata Med J ) Yasuhiko Matsumori, Jialing Liu, Philip R. Weinstein, Takamasa Kayama Department of Neurosurgery, Yamagata University School of Medicine, Yamagata, Japan Department of Neurological Surgery, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, California, USA Accepted April 18, 2003 ABSTRACT Neuronal self-renewal following injuries to the adult brain has been clarified by many recent studies. Ischemic brain injuries have now been demonstrated as a trigger for neurogenesis via endogenous neural stem cells or progenitor cells located in the dentate subgranular zone, the subventricular lining of the lateral ventricle, and the posterior periventricle adjacent to the hippocampus. New neurons migrate to the granule cell layer or to the damaged CA1 region and striatum, where they express morphological markers characteristic of the local neurons. If the new neurons are fully integrated and become functional, a novel therapeutic strategy might be developed for stroke in humans. Key words stem cell, neurogenesis, stroke INTRODUCTION Ischemic brain injury remains as one of the most common causes for death and disability throughout the world. Unlike many other tissues, the mature brain has limited regenerative capacity, due to its unusual degree of cellular specialization which restrains the residural healthy tissue from assuming its function. However, recent studies have demon- strated that new neurons are derived from neural stem cells or progenitor cells which persist in the adult mammalian brains including those of rodents and primates 1)-7). Thus, stimulation of endogenous neural stem cells and progenitor cells in the adult brain might lead to a novel therapeutic strategy for stroke 8). Neurogenesis in the adult brain The adult brain possesses persistent neural stem cells with self-renewal capacity and Address for Correspondence Takamasa Kayama, Department of Neurosurgery, Yamagata University School of Medicine, Iida-Nishi, Yamagata , Japan
2 Matsumori, Liu, Weinstein, Kayama multiple potentiality. Isolated cells from the adult mammalian brain form colonies of undifferentiated cells in vitro that can be dissociated to form many more secondary colonies, demonstrating renewal. These cells are also multipotent since they can be induced to differentiate into neuron, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes 7), 9)-11). Stem cells can give rise to other stem cells as well as progenitor cells. Progenitor cells give rise to neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. Both stem cells and progenitor cells occurs in discrete regions, including the rostral subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricles 12) and the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the dentate gyrus (DG) 13). Neurons that arise in the SVZ travel via the rostral migratory stream to the olfactory bulb 14) and also enter association neocortex 4), while new neurons leaving the SGZ migrate into the adjacent DG granule cell layer. Neurogenesis in these regions increases in conditions such as exogenous neurotrophic factor supplement 15),16), enriched environment 17), anti-depressant treatment 18), seizure 19), and ischemia 20),21). It decreases under stress 3) and supplementation of excitatory amino acids 22) or adrenal steroids 23). Ischemia induces neurogenesis Ischemic brain injuries trigger molecular and cellular repair mechanisms including neurogenesis that might contribute to recovery in the adult brain. Liu, et al. showed that neurogenesis increased in SGZ of gerbils after transient global ischemia induced by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion 20). Immunohistochemistry was performed to detect the incorporation of the thymidine analog 5-bromo- 2'-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate (BrdU) into newly synthesized DNA, and that 60% of newborn cells expressed neuronal markers neuronal nuclear antigen (NeuN), calbindin- D28K, and micro tuble-associated protein 2 (MAP-2). The newborn cells migrate into the granule cell layer (GCL) and become mature neurons. Neurogenesis is also increased by focal ischemia (Fig.1). Arvidsson, et al. showed middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) leads to a marked increase of neurogenesis in the ipsilateral SGZ 24). These effects in the SGZ are not dependent on ischemic hippocampal damage since it rarely occurs after focal ischemia. The stroke-induced neurogenesis is most likely mediated through glutamatergic mechanisms acting on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Clinicaly, the striatum and cerebral cortex are main sites injured by stroke. Recent studies also show neurogenesis in the SVZ. Parent JM, et al. showed that striatal neurogenesis occurs following MCAO in adult rats 25). Cell proliferation is increased in the SVZ, and newly generated neuroblasts migrate into the periinfarct striatum. The new neurons express morphological markers of striatal mediumsized spiny neurons. Thus, stroke induces new neurons to differentiate into the phenotype of the majority of the neurons lost to ischemia. Gu, et al. used photothrombotic lesion to identify a small proportion of proliferated, BrdU-positive cells co-labeled with NeuN in the cortical penumbral zone 26). The same group subsequently reported the presence of double labeled cells in the cerebral cortex, particularly in the periinfarct area after MCAO 28). However, other studies did not detect any BrdU-positive cells co-labeled with neuronal marker in the injured cortex following MCAO 29). Thus, the cortical neurogenesis is still controversial.
3 Neurogenesis and Ischemic Fig.1. Ischemia increases cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of adult rats. Animals were subjected to 90 min, of right distal middle cerebral artery occlusion. BrdU was administered 1 day before the animal was killed, and brains were processed BrdU immunohistochemistry. A, Control: sham surgery. B, 90 min, ischemia. Neural transplantation for stroke Transplantation of human neural cells is a new approach for improving functional deficits caused by brain injury or disease. Several investigators have evaluated the effects of transplanted fetal neural tissue, immortalized cell lines, or embryonic stem cells into rodent stroke models 30). The standardization of these models is invaluable to the reliable testing of various experimental protective and regenerative therapies. Among them, cell transplantation of fetal hippocampal neurons has shown that they can survive and integrate in the ischemic brain 31). A number of different mechanisms relate with cell survival and integration. These include provision of neurotrophic support, provision of neurotransmitters, reestablishment of local interneuronal connections, cell differentiation and integration, and improvement of regional oxygen tension. Methodological issues are still to be resolved since subsequent studies questioned the capacity of rat fetal neocortical tissues, implanted in an infarcted area, in integrating to the surrounding host tissue 32). However, it has been shown that the chronic ischemia region can support graft tissue. CONCLUSION Recovery from stroke is thought to involve reactivation of molecular and cellular processes quiescent since development. These processes may include not only mechanisms in promoting cell survival or function but also the regeneration of lethally injured cell population. Ischemic brain injuries still rank high among the common causes of death and disability in humans. The treatments to restore brain function after stroke are largely confined to rehabilitation therapies. Obviously, the self-renewal mechanisms are currently insufficient and functional recovery is incomplete. However, the recent findings that neuron can arise in adult mammalian brain from resident, or even circulating precursors
4 Matsumori, Liu, Weinstein, Kayama raise the possibility that amplification of selfrenewal mechanisms might in the future come to be of thrapeutic value for patients affected by ischemic brain injuries. REFERENCES 1. McKay R: Stem cells in the central nervous system. Science 1997; 276: Martinez-Serrano A, Bjorklund A: Immortalized neural progenitor cells for CNS gene transfer and repair. Trends Neurosci 1997; 20: Gould E, Tanapat P, McEwen BS, Flugge G, Fuchs E: Proliferation of granule cell precursors in the dentate gyrus of adult monkeys is diminished by stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: Gould E, Reeves AJ, Graziano MS, Gross CG: Neurogenesis in the neocortex of adult primates. Science 1999; 286: Scheffler B, Horn M, Blumcke I, Laywell ED, Coomes D, Kukekov VG, et al.: Marrowmindedness: a perspective on neuropoiesis. Trends Neurosci 1999; 22: van der Kooy D, Weiss S: Why stem cells? Science 2000; 287: Gage FH: Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 2000; 287: Horner PJ, Gage FH: Regenerating the damaged central nervous system. Nature 2000; 407: Reynolds BA, Weiss S: Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science 1992; 255: Weiss S, van der Kooy D: CNS stem cells: where's the biology (a.k.a. beef)? J Neurobiol 1998; 36: McKay RD: Brain stem cells change their identity. Nat Med 1999; 5: Luskin MB: Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron 1993; 11: Kaplan MS, Hinds JW: Neurogenesis in the adult rat: electron microscopic analysis of light radioautographs. Science 1977; 197: Lois C, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A: Chain migration of neuronal precursors. Science 1996; 271: Craig CG, Tropepe V, Morshead CM, Reynolds BA, Weiss S, van der Kooy D: In vivo growth factor expansion of endogenous subependymal neural precursor cell populations in the adult mouse brain. J Neurosci 1996; 16: Aberg MA, Aberg ND, Hedbacker H, Oscarsson J, Eriksson PS: Peripheral infusion of IGF-I selectively induces neurogenesis in the adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 2000; 20: Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH: More hippocampal neurons in adult mice living in an enriched environment. Nature 1997; 386: Malberg JE, Eisch AJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS: Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 2000; 20: Parent JM, Yu TW, Leibowitz RT, Geschwind DH, Sloviter RS, Lowenstein DH: Dentate granule cell neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 1997; 17: Liu J, Solway K, Messing RO, Sharp FR: Increased neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus after transient global ischemia in gerbils. J Neurosci 1998; 18: Jin K, Minami M, Lan JQ, Mao XO, Batteur S, Simon RP, et al.: Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98:
5 Neurogenesis and Ischemic 22. Cameron HA, McEwen BS, Gould E: Regulation of adult neurogenesis by excitatory input and NMDA receptor activation in the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 1995; 15: Cameron HA, Tanapat P, Gould E: Adrenal steroids and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation regulate neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult rats through a common pathway. Neuroscience 1998; 82: Arvidsson A, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O: N- methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated increase of neurogenesis in adult rat dentate gyrus following stroke. Eur J Neurosci 2001; 14: Parent JM, Vexler ZS, Gong C, Derugin N, Ferriero DM: Rat forebrain neurogenesis and striatal neuron replacement after focal stroke. Ann Neurol 2002; 52: Gu W, Brannstrom T, Wester P: Cortical neurogenesis in adult rats after reversible photothrombotic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2000; 20: Jiang W, Gu W, Brannstrom T, Rosqvist R, Wester P: Cortical neurogenesis in adult rats after transient middle cerebral artery occlu- sion. Stroke 2001; 32: Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Chopp M: Proliferation and differentiation of progenitor cells in the cortex and the subventricular zone in the adult rat after focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 2001; 105: Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O: Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med 2002; 8: Borlongan CV, Tajima Y, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Sanberg PR: Cerebral ischemia and CNS transplantation: differential effects of grafted fetal rat striatal cells and human neurons derived from a clonal cell line. Neuroreport 1998; 9: Aoki H, Onodera H, Yae T, Jian Z, Kogure K: Neural grafting to ischemic CA1 lesions in the rat hippocampus: an autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 1993; 56: Grabowski M, Johansson BB, Brundin P: Neocortical grafts placed in the infarcted brain of adult rats: few or no efferent fibers grow from transplant to host. Exp Neurol 1995; 134:
Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing. Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2
 ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
Neurogenesis in Adult Central Nervous System: Death of a Dogma
 Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece, Nov. 2007 Neurogenesis in Adult Central Nervous System: Death of a Dogma Anton B. Tonchev Division of Cell Biology, Varna University of Medicine, Bulgaria
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece, Nov. 2007 Neurogenesis in Adult Central Nervous System: Death of a Dogma Anton B. Tonchev Division of Cell Biology, Varna University of Medicine, Bulgaria
Neurogenesis and brain injury: managing a renewable resource for repair
 SPOTLIGHT Neurogenesis and brain injury: managing a renewable resource for repair Anna F. Hallbergson, Carmen Gnatenco, and Daniel A. Peterson Neural Repair and Neurogenesis Laboratory, Department of Neuroscience,
SPOTLIGHT Neurogenesis and brain injury: managing a renewable resource for repair Anna F. Hallbergson, Carmen Gnatenco, and Daniel A. Peterson Neural Repair and Neurogenesis Laboratory, Department of Neuroscience,
Brain ischemia, neurogenesis, and neurotrophic receptor expression in primates
 Archives Italiennes de Biologie, 149: 225-231, 2011. Brain ischemia, neurogenesis, and neurotrophic receptor expression in primates A.B. Tonchev Laboratory of Cell Biology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical
Archives Italiennes de Biologie, 149: 225-231, 2011. Brain ischemia, neurogenesis, and neurotrophic receptor expression in primates A.B. Tonchev Laboratory of Cell Biology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical
The adult mammalian brain retains neuronal stem cells,
 Enriched Environment Attenuates Cell Genesis in Subventricular Zone After Focal Ischemia in Mice and Decreases Migration of Newborn Cells to the Striatum Josefine Nygren, PhD; Tadeusz Wieloch, PhD; Jelena
Enriched Environment Attenuates Cell Genesis in Subventricular Zone After Focal Ischemia in Mice and Decreases Migration of Newborn Cells to the Striatum Josefine Nygren, PhD; Tadeusz Wieloch, PhD; Jelena
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, Jeremy Miller Scientist I
 Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Mini-Review Adult Neurogenesis and Neural Stem Cells of the Central Nervous System in Mammals
 Journal of Neuroscience Research 69:745 749 (2002) Mini-Review Adult Neurogenesis and Neural Stem Cells of the Central Nervous System in Mammals Philippe Taupin * and Fred H. Gage * Laboratory of Genetics,
Journal of Neuroscience Research 69:745 749 (2002) Mini-Review Adult Neurogenesis and Neural Stem Cells of the Central Nervous System in Mammals Philippe Taupin * and Fred H. Gage * Laboratory of Genetics,
Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex?
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
SUPPLEMENTARY REFERENCES FOR TABLE 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY REFERENCES FOR TABLE 1 Genetic Background Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH. 1997. Genetic influence on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:10409--14
SUPPLEMENTARY REFERENCES FOR TABLE 1 Genetic Background Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH. 1997. Genetic influence on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:10409--14
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus
 Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke.
 Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Arvidsson, Andreas; Collin, Tove; Kirik, Deniz; Kokaia, Zaal; Lindvall, Olle Published in: Nature Medicine DOI: 10.1038/nm747
Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Arvidsson, Andreas; Collin, Tove; Kirik, Deniz; Kokaia, Zaal; Lindvall, Olle Published in: Nature Medicine DOI: 10.1038/nm747
Neurogenesis has been studied extensively in the last decade
 Neurogenesis in Rats After Focal Cerebral Ischemia is Enhanced by Indomethacin Benjamin D. Hoehn, PhD; Theo D. Palmer, PhD; Gary K. Steinberg, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Newborn cells may participate
Neurogenesis in Rats After Focal Cerebral Ischemia is Enhanced by Indomethacin Benjamin D. Hoehn, PhD; Theo D. Palmer, PhD; Gary K. Steinberg, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Newborn cells may participate
In most parts of normal adult mammalian brains, neurons
 Cortical Neurogenesis in Adult Rats After Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Wei Jiang, BSc; WeiGang Gu, MD, PhD; Thomas Brännström, MD, PhD; Roland Rosqvist, FD; Per Wester, MD, PhD Background
Cortical Neurogenesis in Adult Rats After Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Wei Jiang, BSc; WeiGang Gu, MD, PhD; Thomas Brännström, MD, PhD; Roland Rosqvist, FD; Per Wester, MD, PhD Background
Increased Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus After Transient Global Ischemia in Gerbils
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 1, 1998, 18(19):7768 7778 Increased Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus After Transient Global Ischemia in Gerbils Jialing Liu, 1 Karen Solway, 1 Robert O. Messing, 2
The Journal of Neuroscience, October 1, 1998, 18(19):7768 7778 Increased Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus After Transient Global Ischemia in Gerbils Jialing Liu, 1 Karen Solway, 1 Robert O. Messing, 2
Experimental stroke leads to increased generation of new
 Enriched Environment Increases Neural Stem/Progenitor Cell Proliferation and Neurogenesis in the Subventricular Zone of Stroke-Lesioned Adult Rats Mila Komitova, MD; Bengt Mattsson, BSc; Barbro B. Johansson,
Enriched Environment Increases Neural Stem/Progenitor Cell Proliferation and Neurogenesis in the Subventricular Zone of Stroke-Lesioned Adult Rats Mila Komitova, MD; Bengt Mattsson, BSc; Barbro B. Johansson,
Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury Stimulates Subventricular Zone Proliferation and Neurogenesis in the Neonatal Rat
 0031-3998/05/5803-0600 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 58, No. 3, 2005 Copyright 2005 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury Stimulates Subventricular Zone
0031-3998/05/5803-0600 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 58, No. 3, 2005 Copyright 2005 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury Stimulates Subventricular Zone
Rat Forebrain Neurogenesis and Striatal Neuron Replacement after Focal Stroke
 Rat Forebrain Neurogenesis and Striatal Neuron Replacement after Focal Stroke Jack M. Parent, MD, 1 Zinaida S. Vexler, PhD, 2,3 Chao Gong, MD, PhD, 1 Nikita Derugin, MA, 4 and Donna M. Ferriero, MD 2,3
Rat Forebrain Neurogenesis and Striatal Neuron Replacement after Focal Stroke Jack M. Parent, MD, 1 Zinaida S. Vexler, PhD, 2,3 Chao Gong, MD, PhD, 1 Nikita Derugin, MA, 4 and Donna M. Ferriero, MD 2,3
Environment-dependent fate of implanted neural stem cells in the brain
 Environment-dependent fate of implanted neural stem cells in the brain PhD theses Anita Zádori MD Semmelweis University János Szentágothai Doctoral School of Neurosciences Supervisor: Dr. Emília Madarász
Environment-dependent fate of implanted neural stem cells in the brain PhD theses Anita Zádori MD Semmelweis University János Szentágothai Doctoral School of Neurosciences Supervisor: Dr. Emília Madarász
Activity-dependent Extrinsic Regulation of Adult Olfactory Bulb and Hippocampal Neurogenesis
 INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON OLFACTION AND TASTE Activity-dependent Extrinsic Regulation of Adult Olfactory Bulb and Hippocampal Neurogenesis Dengke K. Ma, a,b Woon Ryoung Kim, b,c Guo-li Ming, a,b,c and
INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON OLFACTION AND TASTE Activity-dependent Extrinsic Regulation of Adult Olfactory Bulb and Hippocampal Neurogenesis Dengke K. Ma, a,b Woon Ryoung Kim, b,c Guo-li Ming, a,b,c and
Brain Plasticity. Brain Plasticity. Recovery from Deprivation 1/2/11. Dogma. Modern neuroscience. Deprivation can lower IQ. Deprivation reversed
 Brain Plasticity Brain Plasticity Dogma Adult brain is stable, unchanging Lose neurons Do not grow/repair neurons Modern neuroscience Brain changes throughout life plasticity Extra capacity Face life s
Brain Plasticity Brain Plasticity Dogma Adult brain is stable, unchanging Lose neurons Do not grow/repair neurons Modern neuroscience Brain changes throughout life plasticity Extra capacity Face life s
Lecture 42: Final Review. Martin Wessendorf, Ph.D.
 Lecture 42: Final Review Martin Wessendorf, Ph.D. Lecture 33 cortex Heilbronner 5 lobes of the cortex Lateral view (left side) Mid-saggital view (right side) Cellular organization of cortex White matter
Lecture 42: Final Review Martin Wessendorf, Ph.D. Lecture 33 cortex Heilbronner 5 lobes of the cortex Lateral view (left side) Mid-saggital view (right side) Cellular organization of cortex White matter
Doublecortin-immunoreactive Neuroblasts in Each Layer of the Main Olfactory Bulb After Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Gerbils
 Lab. Anim. Res. 2010: 26(1), 121-125 -FUUFS Doublecortin-immunoreactive Neuroblasts in Each Layer of the Main Olfactory Bulb After Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Gerbils Jung Hoon Choi 1,2, Ki-Yeon Yoo
Lab. Anim. Res. 2010: 26(1), 121-125 -FUUFS Doublecortin-immunoreactive Neuroblasts in Each Layer of the Main Olfactory Bulb After Transient Cerebral Ischemia in Gerbils Jung Hoon Choi 1,2, Ki-Yeon Yoo
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012
 Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
Increased Generation of Neuronal Progenitors after Ischemic Injury in the Aged Adult Human Forebrain
 13114 The Journal of Neuroscience, December 13, 2006 26(50):13114 13119 Brief Communications Increased Generation of Neuronal Progenitors after Ischemic Injury in the Aged Adult Human Forebrain Jadranka
13114 The Journal of Neuroscience, December 13, 2006 26(50):13114 13119 Brief Communications Increased Generation of Neuronal Progenitors after Ischemic Injury in the Aged Adult Human Forebrain Jadranka
Effects of Progesterone Derivatives, Dihydroprogesterone and Tetrahydroprogesterone, on the Subependymal Layer of the Adult Rat
 Effects of Progesterone Derivatives, Dihydroprogesterone and Tetrahydroprogesterone, on the Subependymal Layer of the Adult Rat Claudio Giachino, 1 Mariarita Galbiati, 2 Aldo Fasolo, 1 Paolo Peretto, 1
Effects of Progesterone Derivatives, Dihydroprogesterone and Tetrahydroprogesterone, on the Subependymal Layer of the Adult Rat Claudio Giachino, 1 Mariarita Galbiati, 2 Aldo Fasolo, 1 Paolo Peretto, 1
Stroke is a major contributor to neonatal morbidity
 Erythropoietin Increases Neurogenesis and Oligodendrogliosis of Subventricular Zone Precursor Cells After Neonatal Stroke Fernando F. Gonzalez, MD; Amara Larpthaveesarp, BS; Patrick McQuillen, MD; Nikita
Erythropoietin Increases Neurogenesis and Oligodendrogliosis of Subventricular Zone Precursor Cells After Neonatal Stroke Fernando F. Gonzalez, MD; Amara Larpthaveesarp, BS; Patrick McQuillen, MD; Nikita
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
Microscopic study of cell division in the cerebral cortex of adult brains after experimental focal cerebral ischemia
 Microscopic study of cell division in the cerebral cortex of adult brains after experimental focal cerebral ischemia Weigang Gu 1,2 and Per Wester 1 1 Umeå Stroke Center, Department of Public Health and
Microscopic study of cell division in the cerebral cortex of adult brains after experimental focal cerebral ischemia Weigang Gu 1,2 and Per Wester 1 1 Umeå Stroke Center, Department of Public Health and
Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Antidepressant Treatment Ronald S. Duman, Ph.D., Shin Nakagawa, M.D., and Jessica Malberg, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Antidepressant Treatment Ronald S. Duman, Ph.D., Shin Nakagawa, M.D., and Jessica Malberg, Ph.D. Demonstration of neurogenesis in adult brain represents a major advance
Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Antidepressant Treatment Ronald S. Duman, Ph.D., Shin Nakagawa, M.D., and Jessica Malberg, Ph.D. Demonstration of neurogenesis in adult brain represents a major advance
PERSPECTIVES. How widespread is adult neurogenesis in mammals?
 OPINION How widespread is adult neurogenesis in mammals? Elizabeth Gould Abstract It is now widely accepted that neurogenesis occurs in two regions of the adult mammalian brain the hippocampus and the
OPINION How widespread is adult neurogenesis in mammals? Elizabeth Gould Abstract It is now widely accepted that neurogenesis occurs in two regions of the adult mammalian brain the hippocampus and the
Adult Neurogenesis in the Mammalian Central Nervous System
 Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005. 28:223 50 doi: 10.1146/ annurev.neuro.28.051804.101459 Copyright c 2005 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on March 17, 2005
Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005. 28:223 50 doi: 10.1146/ annurev.neuro.28.051804.101459 Copyright c 2005 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on March 17, 2005
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature25975 Supplementary Table 1 CONTROL Case No. Age Gender Experimental Use Clinical History 1 14GW F IHC, mapping spontaneous abortion 2 17GW M IHC amniotic infection
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature25975 Supplementary Table 1 CONTROL Case No. Age Gender Experimental Use Clinical History 1 14GW F IHC, mapping spontaneous abortion 2 17GW M IHC amniotic infection
The Role of EphA4 in Glial Scar Formation Following Injury
 University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Spring 5-10-2009 The Role of EphA4 in Glial Scar Formation Following Injury Krysti Todd University of Connecticut
University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Spring 5-10-2009 The Role of EphA4 in Glial Scar Formation Following Injury Krysti Todd University of Connecticut
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Cerebrolysin Enhances Neurogenesis in the Ischemic Brain and Improves Functional Outcome After Stroke
 88:3275 3281 (2010) Cerebrolysin Enhances Neurogenesis in the Ischemic Brain and Improves Functional Outcome After Stroke Chunling Zhang, 1 Michael Chopp, 1,2 Yisheng Cui, 1 Lei Wang, 1 Ruilan Zhang, 1
88:3275 3281 (2010) Cerebrolysin Enhances Neurogenesis in the Ischemic Brain and Improves Functional Outcome After Stroke Chunling Zhang, 1 Michael Chopp, 1,2 Yisheng Cui, 1 Lei Wang, 1 Ruilan Zhang, 1
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
Seafood Contaminants causing Foodborne Diseases
 Seafood Contaminants causing Foodborne Diseases Bacteria and Viruses Vibrio species Viruses: Norwalk-like (NLV) and Hepatitis A (HAV) Industrial Compounds Mercury Polyclorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Natural
Seafood Contaminants causing Foodborne Diseases Bacteria and Viruses Vibrio species Viruses: Norwalk-like (NLV) and Hepatitis A (HAV) Industrial Compounds Mercury Polyclorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Natural
The wufless-ness of glutamate!
 The wufless-ness of glutamate! EXCITOTOXINS are substances, usually acidic amino acids, that react with specialized receptors in the brain in such a way as to lead to destruction of certain types of neurons.
The wufless-ness of glutamate! EXCITOTOXINS are substances, usually acidic amino acids, that react with specialized receptors in the brain in such a way as to lead to destruction of certain types of neurons.
A Progressive and Cell Non-Autonomous Increase in Striatal Neural Stem Cells in the Huntington s Disease R6/2 Mouse
 10452 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 11, 2006 26(41):10452 10460 Neurobiology of Disease A Progressive and Cell Non-Autonomous Increase in Striatal Neural Stem Cells in the Huntington s Disease R6/2
10452 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 11, 2006 26(41):10452 10460 Neurobiology of Disease A Progressive and Cell Non-Autonomous Increase in Striatal Neural Stem Cells in the Huntington s Disease R6/2
Epidermal Growth Factor and Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Have Different Effects on Neural Progenitors in the Adult Rat Brain
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 1, 1997, 17(15):5820 5829 Epidermal Growth Factor and Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Have Different Effects on Neural Progenitors in the Adult Rat Brain H. Georg Kuhn, 1
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 1, 1997, 17(15):5820 5829 Epidermal Growth Factor and Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Have Different Effects on Neural Progenitors in the Adult Rat Brain H. Georg Kuhn, 1
Compensatory Neurogenesis in the Injured Adult Brain
 4 Compensatory Neurogenesis in the Injured Adult Brain Bronwen Connor Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, Centre for Brain Research Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, The University
4 Compensatory Neurogenesis in the Injured Adult Brain Bronwen Connor Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, Centre for Brain Research Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, The University
Controversy Question. Student 6. Pass, with high enthusiasm from all graders.
 The notion that new neurons are added to the adult brain has been the subject of controversy ever since the mid-1980s, when Fernando Nottebohm s lab reported that adult neurogenesis occurs in the canary
The notion that new neurons are added to the adult brain has been the subject of controversy ever since the mid-1980s, when Fernando Nottebohm s lab reported that adult neurogenesis occurs in the canary
Cell-based therapies for disorders of the CNS
 Review Monthly Focus: Central & Peripheral Nervous Systems Cell-based therapies for disorders of the CNS 1. Introduction 2. Cell-based therapeutic approaches 3. Expert opinion Stanley E Lazic & Roger A
Review Monthly Focus: Central & Peripheral Nervous Systems Cell-based therapies for disorders of the CNS 1. Introduction 2. Cell-based therapeutic approaches 3. Expert opinion Stanley E Lazic & Roger A
Neurogenesis in humans
 European Journal of Neuroscience European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 33, pp. 1170 1174, 2011 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07616.x Neurogenesis in humans Maurice A. Curtis, Monica Kam and Richard L.
European Journal of Neuroscience European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 33, pp. 1170 1174, 2011 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07616.x Neurogenesis in humans Maurice A. Curtis, Monica Kam and Richard L.
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Inhibition of convulsive status epilepticus-induced abnormal neurogenesis by sodium valproate. Peng Wu 1, Yue Hu 1, Xiujuan Li 1, Min
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Inhibition of convulsive status epilepticus-induced abnormal neurogenesis by sodium valproate. Peng Wu 1, Yue Hu 1, Xiujuan Li 1, Min
NeuroReport 2009, 20: a Department of Neurology, Children s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University
 Regeneration and transplantation 295 In-vitro effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on neural progenitor/stem cells from rat hippocampus Tingsong Li a,b, Li Jiang a, Xiaoping Zhang b and Hengsheng
Regeneration and transplantation 295 In-vitro effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on neural progenitor/stem cells from rat hippocampus Tingsong Li a,b, Li Jiang a, Xiaoping Zhang b and Hengsheng
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month
 Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
THE EFFECTS OF bfgf TREATMENT IN THE AGED BRAIN FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2010 THE EFFECTS OF bfgf TREATMENT IN THE AGED BRAIN FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Michael Zeigler Virginia
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2010 THE EFFECTS OF bfgf TREATMENT IN THE AGED BRAIN FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Michael Zeigler Virginia
Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Bromodeoxyuridine
 Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
ErbB4 migrazione I parte. 3- ErbB4- NRG1
 ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
Application of neural stem cells in curing traumatic brain injury(tbi)
 20 4 2008 8 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 20, No.4 Aug., 2008 1004-0374(2008)04-0646-05 1 200092 2 201203 3 200040 (neural stem cells, NSCs) NSCs NSCs NSCs NSCs NSCs Q813 R745.1 A Application
20 4 2008 8 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 20, No.4 Aug., 2008 1004-0374(2008)04-0646-05 1 200092 2 201203 3 200040 (neural stem cells, NSCs) NSCs NSCs NSCs NSCs NSCs Q813 R745.1 A Application
Prolonged Seizures Increase Proliferating Neuroblasts in the Adult Rat Subventricular Zone Olfactory Bulb Pathway
 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2002, 22(8):3174 3188 Prolonged Seizures Increase Proliferating Neuroblasts in the Adult Rat Subventricular Zone Olfactory Bulb Pathway Jack M. Parent, 1 Vivian V.
The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2002, 22(8):3174 3188 Prolonged Seizures Increase Proliferating Neuroblasts in the Adult Rat Subventricular Zone Olfactory Bulb Pathway Jack M. Parent, 1 Vivian V.
Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Brain
 Glial Nature of Adult Neural Stem Cells 29 Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Brain Implications of Their Glial Characteristics 2 Daniel A. Lim and Arturo Alvarez-Buylla INTRODUCTION It is now widely accepted
Glial Nature of Adult Neural Stem Cells 29 Neural Stem Cells in the Adult Brain Implications of Their Glial Characteristics 2 Daniel A. Lim and Arturo Alvarez-Buylla INTRODUCTION It is now widely accepted
NMDA and AMPA/Kainate Glutamate Receptors Modulate Dentate Neurogenesis and CA3 Synapsin-I in Normal and Ischemic Hippocampus
 Journal at Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 20:1669-1680
Journal at Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 20:1669-1680
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development
 Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
Neurogenesis and its Association to Epileptogenesis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
 Neurogenesis and its Association to Epileptogenesis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Vanessa Marques Donegá Cover page: Figure adapted from Siebzehnrubl FA. and Blumcke I., 2008 Supervisor: Dr. P.N.E. de Graan
Neurogenesis and its Association to Epileptogenesis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Vanessa Marques Donegá Cover page: Figure adapted from Siebzehnrubl FA. and Blumcke I., 2008 Supervisor: Dr. P.N.E. de Graan
Typical and Atypical Neural Stem Cell Niches
 Typical and Atypical Neural Stem Cell Niches Stefano Pluchino 1, *, Luca Bonfanti 2, ** 1 DIBIT and Institute of Experimental Neurology (InSpe)-San Raffaele Scientific Institute, via Olgettina 58, I-20132,
Typical and Atypical Neural Stem Cell Niches Stefano Pluchino 1, *, Luca Bonfanti 2, ** 1 DIBIT and Institute of Experimental Neurology (InSpe)-San Raffaele Scientific Institute, via Olgettina 58, I-20132,
Original Article Neuroprotective and regenerative effects of melatonin on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(5):8014-8022 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0019565 Original Article Neuroprotective and regenerative effects of melatonin on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(5):8014-8022 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0019565 Original Article Neuroprotective and regenerative effects of melatonin on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats
Nitric Oxide Is a Physiological Inhibitor of Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Subventricular Zone and Olfactory Bulb
 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 7, 2004 24(1):85 95 85 Development/Plasticity/Repair Nitric Oxide Is a Physiological Inhibitor of Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Subventricular Zone and Olfactory
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 7, 2004 24(1):85 95 85 Development/Plasticity/Repair Nitric Oxide Is a Physiological Inhibitor of Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Subventricular Zone and Olfactory
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Concise Review: Prospects of Stem Cell Therapy for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy ASHOK K. SHETTY, a,b BHARATHI HATTIANGADY a,b a Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery), Duke University
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Concise Review: Prospects of Stem Cell Therapy for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy ASHOK K. SHETTY, a,b BHARATHI HATTIANGADY a,b a Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery), Duke University
Functional significance of adult neurogenesis Gerd Kempermann 1, Laurenz Wiskott 2 and Fred H Gage,3
 Functional significance of adult neurogenesis Gerd Kempermann 1, Laurenz Wiskott 2 and Fred H Gage,3 Function is the key criterion for determining whether adult neurogenesis be it endogenous, induced,
Functional significance of adult neurogenesis Gerd Kempermann 1, Laurenz Wiskott 2 and Fred H Gage,3 Function is the key criterion for determining whether adult neurogenesis be it endogenous, induced,
Adult Neurogenesis and Hippocampal Memory Function: New Cells, More Plasticity, New Memories?
 Neurosurg Clin N Am 18 (2007) 105 113 Adult Neurogenesis and Hippocampal Memory Function: New Cells, More Plasticity, New Memories? Yasuji Kitabatake, MD, PhD, Kurt A. Sailor, BS, Guo-li Ming, MD, PhD,
Neurosurg Clin N Am 18 (2007) 105 113 Adult Neurogenesis and Hippocampal Memory Function: New Cells, More Plasticity, New Memories? Yasuji Kitabatake, MD, PhD, Kurt A. Sailor, BS, Guo-li Ming, MD, PhD,
ErbB4 migrazione II parte
 ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
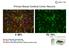 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis. 's-hertogenbosch: Boxpress.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis Mamber, C.E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis Mamber, C.E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
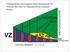 During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Progenitors are Contained within Unique Domains and Tangentially Fixed. EMBRYO ADULT Migratory Behavior
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Progenitors are Contained within Unique Domains and Tangentially Fixed. EMBRYO ADULT Migratory Behavior
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurosurg Clin N Am 18 (2007) 191 198 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AC133 antigen, in brain tumor cancer cells, 32 35 Activity-based restoration therapy, for spinal
Neurosurg Clin N Am 18 (2007) 191 198 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AC133 antigen, in brain tumor cancer cells, 32 35 Activity-based restoration therapy, for spinal
Cellular Therapies December 9, 2013
 Cellular Therapies December 9, 2013 Scott C. Baraban, Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Neurona Therapeutics Co-founder BioCrea - Consultant
Cellular Therapies December 9, 2013 Scott C. Baraban, Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Neurona Therapeutics Co-founder BioCrea - Consultant
Brain Development III
 Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Neurogenic Potential of Clitoria ternatea Aqueous Root Extract A Basis for Enhancing Learning and Memory
 Neurogenic Potential of Clitoria ternatea Aqueous Root Extract A Basis for Enhancing Learning and Memory Kiranmai S.Rai* Abstract The neurogenic potential of many herbal extracts used in Indian medicine
Neurogenic Potential of Clitoria ternatea Aqueous Root Extract A Basis for Enhancing Learning and Memory Kiranmai S.Rai* Abstract The neurogenic potential of many herbal extracts used in Indian medicine
Human Adult Olfactory Bulb Neurogenesis? Novelty Is the Best Policy
 Human Adult Olfactory Bulb Neurogenesis? Novelty Is the Best Policy The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation
Human Adult Olfactory Bulb Neurogenesis? Novelty Is the Best Policy The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation
NEUROGENESIS IN DISEASES OF AGING
 NEUROGENESIS IN DISEASES OF AGING Injury of several types can stimulate neurogenesis, or the birth of new neurons, in the adult brain. A major outstanding issue regarding the potential clinical importance
NEUROGENESIS IN DISEASES OF AGING Injury of several types can stimulate neurogenesis, or the birth of new neurons, in the adult brain. A major outstanding issue regarding the potential clinical importance
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Running Rescues Defective Adult Neurogenesis by Shortening the Length of the Cell Cycle of Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells STEFANO FARIOLI VECCHIOLI, a ANDREA MATTERA, a LAURA
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Running Rescues Defective Adult Neurogenesis by Shortening the Length of the Cell Cycle of Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells STEFANO FARIOLI VECCHIOLI, a ANDREA MATTERA, a LAURA
Inhibitory effect of group II mglur agonist 2R, 4R-APDC on cell proliferation in dentate gyrus in rats with epileptic seizure
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 2922-2927 Inhibitory effect of group II mglur agonist 2R, 4R-APDC on cell proliferation in dentate gyrus in rats with epileptic seizure
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 2922-2927 Inhibitory effect of group II mglur agonist 2R, 4R-APDC on cell proliferation in dentate gyrus in rats with epileptic seizure
The regulation of adult rodent hippocampal neurogenesis by deep brain stimulation
 J Neurosurg 108:132 138, 2008 The regulation of adult rodent hippocampal neurogenesis by deep brain stimulation Laboratory investigation HIROKI TODA, M.D., PH.D., 1,2 CLEMENT HAMANI, M.D., PH.D., 1 ADRIAN
J Neurosurg 108:132 138, 2008 The regulation of adult rodent hippocampal neurogenesis by deep brain stimulation Laboratory investigation HIROKI TODA, M.D., PH.D., 1,2 CLEMENT HAMANI, M.D., PH.D., 1 ADRIAN
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Cortical contusion injury disrupts olfactory bulb neurogenesis in adult mice
 Radomski et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:142 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cortical contusion injury disrupts olfactory bulb neurogenesis in adult mice Kryslaine L Radomski, Qiong Zhou, Kevin J Yi and
Radomski et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:142 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cortical contusion injury disrupts olfactory bulb neurogenesis in adult mice Kryslaine L Radomski, Qiong Zhou, Kevin J Yi and
Adult neurogenesis, neuroinflammation and therapeutic potential of adult neural stem cells
 Int. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 5 127 Review International Journal of Medical Sciences ISSN 1449-1907 www.medsci.org 2008 5(3):127-132 Ivyspring International Publisher. All rights reserved Adult neurogenesis,
Int. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 5 127 Review International Journal of Medical Sciences ISSN 1449-1907 www.medsci.org 2008 5(3):127-132 Ivyspring International Publisher. All rights reserved Adult neurogenesis,
Less neurogenesis and inflammation in the immature than in the juvenile brain after cerebral hypoxia-ischemia
 Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (26), 1 1 & 26 ISCBFM All rights reserved 271-678X/6 $3. www.jcbfm.com Less neurogenesis and inflammation in the immature than in the juvenile brain after cerebral
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (26), 1 1 & 26 ISCBFM All rights reserved 271-678X/6 $3. www.jcbfm.com Less neurogenesis and inflammation in the immature than in the juvenile brain after cerebral
Recipes for Making Human Interneurons from Stem Cells Require Multiple Factors, Careful Timing, and Long Maturation Periods
 Current Literature In Basic Science Recipes for Making Human Interneurons from Stem Cells Require Multiple Factors, Careful Timing, and Long Maturation Periods Directed Differentiation and Functional Maturation
Current Literature In Basic Science Recipes for Making Human Interneurons from Stem Cells Require Multiple Factors, Careful Timing, and Long Maturation Periods Directed Differentiation and Functional Maturation
Harnessing endogenous stem cells to treat neurodegenerative disorders of the basal ganglia
 Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 10 (2004) 259 264 www.elsevier.com/locate/parkreldis Harnessing endogenous stem cells to treat neurodegenerative disorders of the basal ganglia Paul Mohapel*, Patrik
Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 10 (2004) 259 264 www.elsevier.com/locate/parkreldis Harnessing endogenous stem cells to treat neurodegenerative disorders of the basal ganglia Paul Mohapel*, Patrik
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Extending Injury- and Disease-Tolerant Phenotypes by Repetitive Conditioning
 Extending Injury- and Disease-Tolerant Phenotypes by Repetitive Conditioning Promoting Long-Lasting Protection in the CNS Jeff Gidday PhD Neurosurgery Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences Cell Biology & Physiology
Extending Injury- and Disease-Tolerant Phenotypes by Repetitive Conditioning Promoting Long-Lasting Protection in the CNS Jeff Gidday PhD Neurosurgery Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences Cell Biology & Physiology
STRESS INHIBITS THE PROLIFERATION OF GRANULE CELL PRECURSORS IN THE DEVELOPING DENTATE GYRUS
 Pergamon Int[ J[ Devl Neuroscience\ Vol[ 05\ No[ 2:3\ pp[ 124Ð128\ 0887 Þ 0887 ISDN[ Published by Elsevier Science Ltd All rights reserved[ Printed in Great Britain 9625Ð4637:87,08[99 9[99 PII ] S9625Ð4637"87#99918ÐX
Pergamon Int[ J[ Devl Neuroscience\ Vol[ 05\ No[ 2:3\ pp[ 124Ð128\ 0887 Þ 0887 ISDN[ Published by Elsevier Science Ltd All rights reserved[ Printed in Great Britain 9625Ð4637:87,08[99 9[99 PII ] S9625Ð4637"87#99918ÐX
Function of neural stem cells in ischemic brain repair processes
 Review Article Function of neural stem cells in ischemic brain repair processes Ruilan Zhang 1, Zhenggang Zhang 2 and Michael Chopp 1,2 Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 2016, Vol. 36(12) 2034
Review Article Function of neural stem cells in ischemic brain repair processes Ruilan Zhang 1, Zhenggang Zhang 2 and Michael Chopp 1,2 Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 2016, Vol. 36(12) 2034
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour
 Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Long-Term, Selective Gene Expression in Developing and Adult Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons Using Focal In Utero Electroporation
 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 9, 2007 27(19):5007 5011 5007 Toolbox Editor s Note: Toolboxes are intended to briefly highlight a new method or a resource of general use in neuroscience or to critically
The Journal of Neuroscience, May 9, 2007 27(19):5007 5011 5007 Toolbox Editor s Note: Toolboxes are intended to briefly highlight a new method or a resource of general use in neuroscience or to critically
Aberrant Neurogenesis After Stroke A Retroviral Cell Labeling Study
 Aberrant Neurogenesis After Stroke A Retroviral Cell Labeling Study Fanny Niv, MD; Silke Keiner, PhD; Krishna-K, PhD; Otto W. Witte, MD; Dieter Chichung Lie, MD; Christoph Redecker, MD Background and Purpose
Aberrant Neurogenesis After Stroke A Retroviral Cell Labeling Study Fanny Niv, MD; Silke Keiner, PhD; Krishna-K, PhD; Otto W. Witte, MD; Dieter Chichung Lie, MD; Christoph Redecker, MD Background and Purpose
Administration of CD34 + cells after stroke enhances neurogenesis via angiogenesis in a mouse model
 Research article Related Commentary, page 312 Administration of CD34 + cells after stroke enhances neurogenesis via angiogenesis in a mouse model Akihiko Taguchi, 1 Toshihiro Soma, 2 Hidekazu Tanaka, 3
Research article Related Commentary, page 312 Administration of CD34 + cells after stroke enhances neurogenesis via angiogenesis in a mouse model Akihiko Taguchi, 1 Toshihiro Soma, 2 Hidekazu Tanaka, 3
In the dentate gyrus (DG) of the adult brain, new functional
 Intraventricular Infusion of TrkB-Fc Fusion Protein Promotes Ischemia-Induced Neurogenesis in Adult Rat Dentate Gyrus Elin Gustafsson, PhD; Olle Lindvall, MD, PhD; Zaal Kokaia, PhD Background and Purpose
Intraventricular Infusion of TrkB-Fc Fusion Protein Promotes Ischemia-Induced Neurogenesis in Adult Rat Dentate Gyrus Elin Gustafsson, PhD; Olle Lindvall, MD, PhD; Zaal Kokaia, PhD Background and Purpose
COPYRIGHT 2003 SCIENTIFIC AMERICAN, INC. BRAIN,
 BRAIN, REPAIR YOURSELF HOW DO YOU FIX A BROKEN BRAIN? THE ANSWERS MAY LITERALLY LIE WITHIN OUR HEADS. THE SAME APPROACHES MIGHT ALSO BOOST THE POWER OF AN ALREADY HEALTHY BRAIN BY FRED H. GAGE MELISSA
BRAIN, REPAIR YOURSELF HOW DO YOU FIX A BROKEN BRAIN? THE ANSWERS MAY LITERALLY LIE WITHIN OUR HEADS. THE SAME APPROACHES MIGHT ALSO BOOST THE POWER OF AN ALREADY HEALTHY BRAIN BY FRED H. GAGE MELISSA
Mechanism of Stem Cells in the Central Nervous System
 JOURNAL OF CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY 196:409 418 (2003) REVIEW ARTICLES Mechanism of Stem Cells in the Central Nervous System CLAS B. JOHANSSON* Department of Cell- and Molecular Biology, Medical Nobel Institute,
JOURNAL OF CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY 196:409 418 (2003) REVIEW ARTICLES Mechanism of Stem Cells in the Central Nervous System CLAS B. JOHANSSON* Department of Cell- and Molecular Biology, Medical Nobel Institute,
Neurogenesis and neuronal regeneration in status epilepticus. Peter Rotheneichner, Julia Marschallinger, Sebastien Couillard-Despres, Ludwig
 Neurogenesis and neuronal regeneration in status epilepticus Peter Rotheneichner, Julia Marschallinger, Sebastien Couillard-Despres, Ludwig Aigner Institute of Molecular Regenerative Medicine, Spinal Cord
Neurogenesis and neuronal regeneration in status epilepticus Peter Rotheneichner, Julia Marschallinger, Sebastien Couillard-Despres, Ludwig Aigner Institute of Molecular Regenerative Medicine, Spinal Cord
Changes in the Proliferation of the Subventricular Zone Neural Stem Cell Pool throughout Aging in the Murine Brain
 University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Winter 12-1-2010 Changes in the Proliferation of the Subventricular Zone Neural Stem Cell Pool throughout Aging
University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Winter 12-1-2010 Changes in the Proliferation of the Subventricular Zone Neural Stem Cell Pool throughout Aging
Journal of Asian Scientific Research EFFECTS OF FLOURIDE ON CA3 REGION OF HIPPOCAMPUS IN ADULT ALBINO RATS. Nazim Nasir. Mohammad Rehan Asad
 Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 EFFECTS OF FLOURIDE ON CA3 REGION OF HIPPOCAMPUS IN ADULT ALBINO RATS Nazim Nasir Department of Applied
Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 EFFECTS OF FLOURIDE ON CA3 REGION OF HIPPOCAMPUS IN ADULT ALBINO RATS Nazim Nasir Department of Applied
Soft-diet feeding inhibits adult ne Title hippocampus of mice. Yamamoto, T; Hirayama, A; Hosoe, N; Author(s) Hirano, S
 Soft-diet feeding inhibits adult ne Title hippocampus of mice Yamamoto, T; Hirayama, A; Hosoe, N; Author(s) Hirano, S Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1081 Right
Soft-diet feeding inhibits adult ne Title hippocampus of mice Yamamoto, T; Hirayama, A; Hosoe, N; Author(s) Hirano, S Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/1081 Right
Neuronal stem cells in adults
 Experimental Gerontology 41 (2006) 111 116 Mini Review Neuronal stem cells in adults www.elsevier.com/locate/expgero Hans-Christian Bauer *, Herbert Tempfer, Gustav Bernroider, Hannelore Bauer Department
Experimental Gerontology 41 (2006) 111 116 Mini Review Neuronal stem cells in adults www.elsevier.com/locate/expgero Hans-Christian Bauer *, Herbert Tempfer, Gustav Bernroider, Hannelore Bauer Department
