During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
|
|
|
- Austen Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
2 Progenitors are Contained within Unique Domains and Tangentially Fixed. EMBRYO ADULT
3 Migratory Behavior Varies According to Region
4 LGE
5 MGE
6 Radial Migration
7 Radial Glia Guided Migration Takes Young Neurons directly from the VZ to the Cortical Plate Guided by the Processes of Radial Glia; Maintains Topological Maps from thevz to the Cortical Plate Birth Migration Differentiation
8 Sequential Addition of Neurons During Development Desai and McConnell Development 127, (2000)
9
10 Radial Glial Fibers as Guides for Neuronal Migration Rakic, 1972
11 Protomap Hypothesis Rakic, 1988
12 Radial Glia Guided Migration Continues in the Adult Brain of some Vertebrate Species
13 13
14 Marin and Rubenstein Ann Rev Neurosci (2003)
15 Initiation, Adhesion, Locomotion, Termination Marin and Rubenstein Ann Rev Neurosci (2003)
16 Gap Junctions (Elias and Kriegstein, TINS, 2008)
17 Asymmetrical Cx expression in bifurcated migrating neurons Cx43 Vimentin - radial glia Tuj1 - neurons Cx26 Vimentin - radial glia Tuj1 - neurons
18 Gap junction adhesions in radial migration 1) Gap junctions are necessary for neuronal migration. 2) Gap junction adhesions, but not channels, are necessary and sufficient to rescue the shrna induced migration defect. 3) Gap junctions can provide adhesion in cortical cells and interact with the actin cytoskeleton. 4) Gap junction adhesions act dynamically in migrating neurons to stabilize the leading processes and aid in the translocation of the nucleus. Elias and Kriegstein, Nature, 2008
19 Tangential Migration MGE migration SVZ-OB migration
20 MGE migration
21 Expression of LacZ by the Dlx5/6-Enhancer in the Embryonic Telencephalon: Shows Migration of Cells From the Subpallium (Subcortex) to the Pallium (Cortex) Text From John
22 Dlx1/2 Mutants Have A Block In Tangen9al Migra9on From The Basal Ganglia To The Cortex Anderson et al., 1997
23 MGE
24 Ultrasound Guided Transplantation Wichterle et al. Development 2001
25 A Remarkable Journey: MGE progenitors invading cortex in vivo Wichterle et al. Development 2001
26 MGE cells: source of GABAergic Cortical Interneurons Wichterle et al. Development 2001
27 Routes on Interneuron Migration from MGE into Cortex
28 Stereotyped dynamic behavior of tangentially migrating interneurons Martini, F. J. et al. Development 2009;136:41-50
29 Gad65-GFP E12.5, E13.5 Leading process branching is common to many neurons in the developing brain. (A-D) Serial sections through the brain (A,B) and spinal cord (D) of Gad65-Gfp embryos at E12.5 (D) and E13.5 (A,B). In Gad65-Gfp embryos, Gfp expression is restricted to GABAergic neurons, some of which have typical morphologies of migrating cells. The schematic drawinsg in C depict the approximate localization of sections (A,B,D). (E-H) High-magnification images of cells migrating in the developing cortex (E), thalamus (F), midbrain reticular formation (G) and ventral spinal cord (H). All these cells display similar morphologies characterized by the presence of a branched leading process (arrowheads). H, hippocampus; Dh, dorsal horn of the spinal cord; dth, dorsal thalamus; dra, dorsal raphe nucleus; FP, floor plate; GP, globus pallidus; Hyp, hippothalamus; NCx, neocortex; NLL, nucleus of the lateral lemniscus; RF, reticular formation; RP, roof plate; Rt, reticular nucleus; SC, superior colliculus; Str, striatum; LC, locus coeruleus; Vh, ventral horn of the spinal cord. Scale bars: 300 µm in A,B,D; 10 µm in E-H
30 Gfp electroporated; MGE cells migration involves bifurcated leading processes. Why? Movie 1. Migratory dynamics of a tangentially migrating interneuron. Migration of an E13.5 Gfp-electroporated interneuron migrating from the subpallium to the cortex in a slice culture. Images were acquired every 15 minutes. The total duration of the movie is 7:25 hours. The movie shows successive translocations of the nucleus along one of the branches of the leading process from one bifurcation point to the next one.
31 dsred electroporated; Cells following relatively straight paths make branches with relatively small angles. Movie 3. Branch dynamics in migrating neurons following relatively constant trajectories. Interneurons were imaged while migrating through the subpallium after 12 hours of electroporating the MGE of a E13.5 slice with
32 Gad65-GFP; Changing directions involves making new branches and necleokinesis into the angled branch. Movie 4. Branch dynamics in migrating neurons rapidly changing direction. An E16.5 Gad65-Gfp interneuron migrating through the cortical plate in a slice culture. Images were
33 Branch dynamics during tangential migration Martini, F. J. et al. Development 2009;136:41-50 Fig. 2. Branch dynamics during tangential migration. (A) A telencephalic slice from an E16.5 Gad65-Gfp embryo. GABAergic cells are observed in green in the different regions in which migration was studied: subpallium (lateral ganglionic eminence, LGE), cortical subventricular zone (SVZ) and cortical plate (CP). Owing to the massive accumulation of migrating neurons in the subpallium, analysis of neurons migrating through the LGE was performed in slice cultures in which the MGE was electroporated with Gfp or dsred (as in Fig. 1). (B-D) Representative images of the morphology of cells migrating through the LGE (B), SVZ (C) or CP (D). (B'-D')
34 Branch dynamics during Neuregulin 1 (Nrg1) induced chemotaxis Martini, F. J. et al. Development 2009;136:41-50 Fig. 3. Branch dynamics during Nrg1-induced chemotaxis. (A-A'') Images of a dsred-electroporated slice perfused with a micropipette containing recombinant EGF domain from Nrg1 (13 nm) and Alexa 488 (green channel). To induce drastic changes in direction, cortical interneurons (red channel) migrating through the LGE were confronted with the micropipette at an angle that is perpendicular to their normal trajectory. (B-B') Schematic representation of the trajectory change followed by the cell shown in C. White arrow indicates the micropipette. (C) Representative time-lapse sequences of a migrating cell that developed drastic trajectory changes in response to the chemoattractant. The cell generates a new leading process toward the pipette immediately before changing its trajectory (t=1:35). The angle generated before the most significant change in direction is the largest made by the neuron during this sequence (C). The cell chose the branch oriented towards the chemoattractant to continue migration. The gradient is also visualized in red owing to laser cross-contamination. (C'-C'') Drawings illustrate the morphology of the cell shown in C. Diagrams in C'' depict the movement of this cell. New branches are shown in green; chosen branch is tipped with a red arrowhead. The numbers indicate the angle formed by the branches.
35 Tangential Migration of Local Circuit Neurons: GABA & ACh Marin and Rubenstein, Nature Neuroscience Reviews, 2001
36 Selective Guidance of different sub-populations of MGE cells Marin et al. Science 2001
37
38 GABA+ Potassium-Chloride Cotransporter (KCC2) = You Have Arrived Bortone and Polleux, 2009 Neuron
39 Telencephalic Interneurons Multiple interneuron subtypes in cortex, OB and striatum. Most contains GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). GABA interneurons can be further subdivided: - Ca++ binding proteins(calbindin, calretinin and parvalbumin) - neuropeptides (eg, neuropeptide Y). Not all interneurons are GABAergic: - dopamine - acetylcholine Not all GABA neurons are interneurons.
40 Tangential Migration SVZ-OB migration
41 Routes on Interneuron Migration from MGE into Cortex
42 Lois and Alvarez-Buylla PNAS Lois and Alvarez-Buylla, Science 1994
43 Chain Migration Lois, García-Verdugo and Alvarez-Buylla, Science 1996
44 The Adult Brain Contains an Extensive Network of Pathways for Chain Migration Wichterle et al. Neuron 1998
45 The Adult Brain Contains an Extensive Network of Pathways for Chain Migration cc NC SVZa M RMS Doetsch and Alvarez-Buylla PNAS. 1996
46 B SVZ Astrocyte C Amplifying Precursor A OB Interneurons B1 B2 A C E Doetsch et al, J. Neurosci Doetsch et al, Cell 1999
47 How do Cells Orient Over Such Large Territory?
48 Chemorepulsion guides SVZ neuroblasts? Wu, W., Wong, K., Chen, J., Jiang, Z., Dupuis, S., Wu, J.Y. and Rao, Y. Directional guidance of neuronal migration in the olfactory system by the protein Slit. Nature 400: , Hu, H. Chemorepulsion of neuronal migration by Slit2 in the developing mammalian forebrain. Neuron 23: , 1999.
49 Telling Direction of Migration Retrovirus encoding alkaline phosphatase (AP) Chain of neuroblasts (PSA-NCAM+) (Wichterle et al., 1997)
50 Map of Cell migration directions in the SVZ cell migration choroid plexus olfactory bulb RMS wall adhesion
51 Mapping the direction of CSF flow
52 Q: Is the CSF flow required for directional cell migration? Cell migration parallels the CSF flow cell migration cilia beating /CSF flow olfactory bulb choroid plexus site of wall adhesion RMS third ventricle
53 The Tg737orpk mice have small olfactory bulbs Volume of granule cell layer (mm3) Tg737 +/ Tg737orpk /orpk
54 The Tg737orpk mutant has defective ependymal cilia Tg737 +/+ Tg737 orpk/orpk NoelMurcia
55 The Tg737 orpk mutation disrupts normal network formation of migrating neuroblasts in SVZ Tg737 +/+ Tg737 orpk/orpk
56 slit1+/+;slit2+/+ slit1-/-;slit2-/- Slit proteins are required for repulsion of neurblasts by choroid plexus in collagen gel culture CP +/+ SVZ +/+ CP -/- SVZ +/+
57 cell migration olfactory bulb ectopic choroid plexus? choroid plexus Rostral migratory stream third ventricle
58 Ectopic CP GFP+ SVZ cells Ectopic choroid plexus inhibits migration of grafted SVZ cells into the olfactory bulb Control Choroid plexus-grafted Number of GFP+ cells in OB 5 days after transplantation (n=4) (n=5)
59 Slit proteins are partially involved in the repulsive activity of choroid plexus in vivo normal wild-type CP mutant CP
60 Slit2 protein secreted into CSF can reach SVZ and forms a concentration gradient
61 Sawamoto et al, Science 2006
62 Why Such a long Migration?
63 NSCs are: heterogeneous and restricted in potential organized in different domains NSC potential is: maintained during postnatal development determined by a cellautonomous mechanism
64
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
 During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Two mayor forms of neuronal migration: Radial and Tangential Leber & Sanes, 95 How do young neurons actually
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Two mayor forms of neuronal migration: Radial and Tangential Leber & Sanes, 95 How do young neurons actually
ErbB4 migrazione II parte
 ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
ErbB4 migrazione I parte. 3- ErbB4- NRG1
 ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012
 Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
A new subtype of progenitor cell in the mouse embryonic neocortex. Xiaoqun Wang, Jin-Wu Tsai, Bridget LaMonica & Arnold R.
 A new subtype of progenitor cell in the mouse embryonic neocortex Xiaoqun Wang, Jin-Wu Tsai, Bridget LaMonica & Arnold R. Kriegstein Supplementary Figures 1-6: Supplementary Movies 1-9: Supplementary
A new subtype of progenitor cell in the mouse embryonic neocortex Xiaoqun Wang, Jin-Wu Tsai, Bridget LaMonica & Arnold R. Kriegstein Supplementary Figures 1-6: Supplementary Movies 1-9: Supplementary
Neocortex. Cortical Structures in the Brain. Neocortex Facts. Laminar Organization. Bark-like (cortical) structures: Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12
 Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet?
 Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet? H. Troy Ghashghaei*, Cary Lai and E. S. Anton* Abstract The generation and targeting of appropriate numbers and types of neurons to where they are
Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet? H. Troy Ghashghaei*, Cary Lai and E. S. Anton* Abstract The generation and targeting of appropriate numbers and types of neurons to where they are
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development
 Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
The Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Sp8 Regulates the Generation and Diversity of Olfactory Bulb Interneurons
 Neuron 49, 503 516, February 16, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.01.018 The Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Sp8 Regulates the Generation and Diversity of Olfactory Bulb Interneurons
Neuron 49, 503 516, February 16, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.01.018 The Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Sp8 Regulates the Generation and Diversity of Olfactory Bulb Interneurons
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
The neuron. Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex
 The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, Jeremy Miller Scientist I
 Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 modulates neuroblast migration and placement in the adult forebrain
 Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 modulates neuroblast migration and placement in the adult forebrain E S Anton 1,8, H T Ghashghaei 1,8, Janet L Weber 2, Corey McCann 1, Tobias M Fischer 2, Isla D Cheung
Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 modulates neuroblast migration and placement in the adult forebrain E S Anton 1,8, H T Ghashghaei 1,8, Janet L Weber 2, Corey McCann 1, Tobias M Fischer 2, Isla D Cheung
Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex?
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Recipes for Making Human Interneurons from Stem Cells Require Multiple Factors, Careful Timing, and Long Maturation Periods
 Current Literature In Basic Science Recipes for Making Human Interneurons from Stem Cells Require Multiple Factors, Careful Timing, and Long Maturation Periods Directed Differentiation and Functional Maturation
Current Literature In Basic Science Recipes for Making Human Interneurons from Stem Cells Require Multiple Factors, Careful Timing, and Long Maturation Periods Directed Differentiation and Functional Maturation
Integration of GABAergic Interneurons into Cortical Cell Assemblies: Lessons from Embryos and Adults
 Integration of GABAergic Interneurons into Cortical Cell Assemblies: Lessons from Embryos and Adults Giorgia Bartolini, 1,2 Gabriele Ciceri, 1,2 and Oscar Marín 1, * 1 Instituto de Neurociencias, Consejo
Integration of GABAergic Interneurons into Cortical Cell Assemblies: Lessons from Embryos and Adults Giorgia Bartolini, 1,2 Gabriele Ciceri, 1,2 and Oscar Marín 1, * 1 Instituto de Neurociencias, Consejo
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
a 0,8 Figure S1 8 h 12 h y = 0,036x + 0,2115 y = 0,0366x + 0,206 Labeling index Labeling index ctrl shrna Time (h) Time (h) ctrl shrna S G2 M G1
 (GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
(GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
The neuron. Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex
 The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN
 UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
Telencephalic cells take a tangent: non-radial migration in the mammalian forebrain
 review Telencephalic cells take a tangent: non-radial migration in the mammalian forebrain Joshua G. Corbin, Susana Nery and Gord Fishell Developmental Genetics Program and the Department of Cell Biology,
review Telencephalic cells take a tangent: non-radial migration in the mammalian forebrain Joshua G. Corbin, Susana Nery and Gord Fishell Developmental Genetics Program and the Department of Cell Biology,
Young neurons born in the developing or adult brain have to
 Permissive corridor and diffusible gradients direct medial ganglionic eminence cell migration to the neocortex Hynek Wichterle*, Manuel Alvarez-Dolado, Lynda Erskine, and Arturo Alvarez-Buylla *The Rockefeller
Permissive corridor and diffusible gradients direct medial ganglionic eminence cell migration to the neocortex Hynek Wichterle*, Manuel Alvarez-Dolado, Lynda Erskine, and Arturo Alvarez-Buylla *The Rockefeller
Seafood Contaminants causing Foodborne Diseases
 Seafood Contaminants causing Foodborne Diseases Bacteria and Viruses Vibrio species Viruses: Norwalk-like (NLV) and Hepatitis A (HAV) Industrial Compounds Mercury Polyclorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Natural
Seafood Contaminants causing Foodborne Diseases Bacteria and Viruses Vibrio species Viruses: Norwalk-like (NLV) and Hepatitis A (HAV) Industrial Compounds Mercury Polyclorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Natural
Radial glia in the ventral telencephalon
 REVIEW ARTICLE Radial glia in the ventral telencephalon Miguel Turrero Garcıa and Corey C. Harwell Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Correspondence C. C. Harwell, Department
REVIEW ARTICLE Radial glia in the ventral telencephalon Miguel Turrero Garcıa and Corey C. Harwell Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Correspondence C. C. Harwell, Department
Development of the Nervous System. Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Introduction. Materials and Methods
 4240 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 2003 23(10):4240 4250 Multiple Cell Populations in the Early Postnatal Subventricular Zone Take Distinct Migratory Pathways: A Dynamic Study of Glial and Neuronal
4240 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 2003 23(10):4240 4250 Multiple Cell Populations in the Early Postnatal Subventricular Zone Take Distinct Migratory Pathways: A Dynamic Study of Glial and Neuronal
Distinct Origins of Neocortical Projection Neurons and Interneurons In Vivo
 Distinct Origins of Neocortical Projection Neurons and Interneurons In Vivo Stewart A. Anderson 2, Christine E. Kaznowski 1, Carrie Horn, John L.R. Rubenstein and Susan K. McConnell 1 Department of Psychiatry,
Distinct Origins of Neocortical Projection Neurons and Interneurons In Vivo Stewart A. Anderson 2, Christine E. Kaznowski 1, Carrie Horn, John L.R. Rubenstein and Susan K. McConnell 1 Department of Psychiatry,
Carl P. Wonders* and Stewart A. Anderson
 The origin and specification of cortical interneurons Carl P. Wonders* and Stewart A. Anderson Abstract GABA-containing interneurons are crucial to both the development and function of the cerebral cortex.
The origin and specification of cortical interneurons Carl P. Wonders* and Stewart A. Anderson Abstract GABA-containing interneurons are crucial to both the development and function of the cerebral cortex.
Embryology of the Nervous System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Development and specification of GABAergic cortical interneurons
 Kelsom and Lu Cell & Bioscience 2013, 3:19 Cell & Bioscience REVIEW Development and specification of GABAergic cortical interneurons Corey Kelsom and Wange Lu * Open Access Abstract GABAergic interneurons
Kelsom and Lu Cell & Bioscience 2013, 3:19 Cell & Bioscience REVIEW Development and specification of GABAergic cortical interneurons Corey Kelsom and Wange Lu * Open Access Abstract GABAergic interneurons
Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development and Cytoarchitecture
 Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development and Cytoarchitecture 2 The prenatal developmental of the mammalian cerebral cortex, including that of humans, is characterized by two sequential and interrelated
Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development and Cytoarchitecture 2 The prenatal developmental of the mammalian cerebral cortex, including that of humans, is characterized by two sequential and interrelated
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Huntington s Disease & MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE
 Huntington s Disease & Early Nervous System Development MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD The cups fell to the floor with a crash. Was this the alarm signal? Or was it forgetting
Huntington s Disease & Early Nervous System Development MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD The cups fell to the floor with a crash. Was this the alarm signal? Or was it forgetting
Preferential Origin and Layer Destination of GAD65-GFP Cortical Interneurons
 Preferential Origin and Layer Destination of GAD65-GFP Cortical Interneurons Guillermina López-Bendito 1, Katherine Sturgess 1, Ferenc Erdélyi 2, Gábor Szabó 2, Zoltán Molnár 1 and Ole Paulsen 3 1 Department
Preferential Origin and Layer Destination of GAD65-GFP Cortical Interneurons Guillermina López-Bendito 1, Katherine Sturgess 1, Ferenc Erdélyi 2, Gábor Szabó 2, Zoltán Molnár 1 and Ole Paulsen 3 1 Department
Radial Glial Dependent and Independent Dynamics of Interneuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex
 Radial Glial Dependent and Independent Dynamics of Interneuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Yukako Yokota 1, H. T. Ghashghaei 1, Christine Han 1, Hannah Watson 1, Kenneth J. Campbell 2,
Radial Glial Dependent and Independent Dynamics of Interneuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Yukako Yokota 1, H. T. Ghashghaei 1, Christine Han 1, Hannah Watson 1, Kenneth J. Campbell 2,
Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis. 's-hertogenbosch: Boxpress.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis Mamber, C.E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) GFAP as an understudy in adult neurogenesis Mamber, C.E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Martina-Mamber, C. E. (2014). GFAP as an understudy
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Science. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Science. 2010 February 26; 327(5969): 1145 1148. doi:10.1126/science.1183962. Cortical Plasticity Induced by Inhibitory Neuron Transplantation
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Science. 2010 February 26; 327(5969): 1145 1148. doi:10.1126/science.1183962. Cortical Plasticity Induced by Inhibitory Neuron Transplantation
Rat Dlx5 is expressed in the subventricular zone and promotes neuronal differentiation
 ISSN 0100-879X Volume 43 (02) 124-225 February 2010 BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES AND CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Braz J Med Biol Res, February 2010, Volume 43(2) 176-185 Rat Dlx5 is expressed in the subventricular zone
ISSN 0100-879X Volume 43 (02) 124-225 February 2010 BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES AND CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Braz J Med Biol Res, February 2010, Volume 43(2) 176-185 Rat Dlx5 is expressed in the subventricular zone
Supplementary Figure S1: Pial and periventricular vascular networks and the dual GABA neuron streams of the early embryonic mouse telencephalon
 Supplementary Figure S1: Pial and periventricular vascular networks and the dual GABA neuron streams of the early embryonic mouse telencephalon a) The profile of GABA neurons arriving at the pallial-subpallial
Supplementary Figure S1: Pial and periventricular vascular networks and the dual GABA neuron streams of the early embryonic mouse telencephalon a) The profile of GABA neurons arriving at the pallial-subpallial
Neocortex Zbtb20 / NFIA / Sox9
 Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Divergent functions of the proneural genes Mash1 and Ngn2 in the specification of neuronal subtype identity
 Divergent functions of the proneural genes Mash1 and Ngn2 in the specification of neuronal subtype identity Carlos M. Parras, 1,4 Carol Schuurmans, 1,3,4 Raffaella Scardigli, 1 Jaesang Kim, 2 David J.
Divergent functions of the proneural genes Mash1 and Ngn2 in the specification of neuronal subtype identity Carlos M. Parras, 1,4 Carol Schuurmans, 1,3,4 Raffaella Scardigli, 1 Jaesang Kim, 2 David J.
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Multipolar Migration: The Third Mode of Radial Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex
 9996 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 5, 2003 23(31):9996 10001 Brief Communication Multipolar Migration: The Third Mode of Radial Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Hidenori Tabata
9996 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 5, 2003 23(31):9996 10001 Brief Communication Multipolar Migration: The Third Mode of Radial Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Hidenori Tabata
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Tangential migration of neurons in the developing cerebral cortex
 Development 121, 2165-2176 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 2165 Tangential migration of neurons in the developing cerebral cortex Nancy A. O Rourke*, Daniel P. Sullivan,
Development 121, 2165-2176 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 2165 Tangential migration of neurons in the developing cerebral cortex Nancy A. O Rourke*, Daniel P. Sullivan,
When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded.
 When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded. Stein, V et al., (2003) J Neurosci, 23:5503-6606. Also found in Rat Barrel Cortex Ehrlich & Malinow (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:916-927 Over-expression
When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded. Stein, V et al., (2003) J Neurosci, 23:5503-6606. Also found in Rat Barrel Cortex Ehrlich & Malinow (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:916-927 Over-expression
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Brain Development III
 Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Regional Distribution of Cortical Interneurons and Development of Inhibitory Tone Are Regulated by Cxcl12/ Cxcr4 Signaling
 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 30, 2008 28(5):1085 1098 1085 Development/Plasticity/Repair Regional Distribution of Cortical Interneurons and Development of Inhibitory Tone Are Regulated by Cxcl12/
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 30, 2008 28(5):1085 1098 1085 Development/Plasticity/Repair Regional Distribution of Cortical Interneurons and Development of Inhibitory Tone Are Regulated by Cxcl12/
Evidence of Common Progenitors and Patterns of Dispersion in Rat Striatum and Cerebral Cortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 2002, 22(10):4002 4014 Evidence of Common Progenitors and Patterns of Dispersion in Rat Striatum and Cerebral Cortex Christopher B. Reid 1,2 and Christopher A. Walsh
The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 2002, 22(10):4002 4014 Evidence of Common Progenitors and Patterns of Dispersion in Rat Striatum and Cerebral Cortex Christopher B. Reid 1,2 and Christopher A. Walsh
CNS Developmental. Anke van Eekelen, PhD. Telethon Institute for Child Health Research
 CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
The Development of Hippocampal Interneurons in Rodents
 HIPPOCAMPUS 16:1032 1060 (2006) COMMENTARY The Development of Hippocampal Interneurons in Rodents Lydia Danglot,* Antoine Triller, and Serge Marty ABSTRACT: Interneurons are GABAergic neurons responsible
HIPPOCAMPUS 16:1032 1060 (2006) COMMENTARY The Development of Hippocampal Interneurons in Rodents Lydia Danglot,* Antoine Triller, and Serge Marty ABSTRACT: Interneurons are GABAergic neurons responsible
EGFRs mediate chemotactic migration in the developing telencephalon
 Development 128, 4203-4216 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV9789 4203 EGFRs mediate chemotactic migration in the developing telencephalon Damira Caric, Heather
Development 128, 4203-4216 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV9789 4203 EGFRs mediate chemotactic migration in the developing telencephalon Damira Caric, Heather
Visual system invades the endbrain: pathways to striatum and cortex (continued) Why this happened in evolution
 Visual system invades the endbrain: pathways to striatum and cortex (continued) Why this happened in evolution What were the adaptive advantages? Visual information reaching the striatum directly: Advantages
Visual system invades the endbrain: pathways to striatum and cortex (continued) Why this happened in evolution What were the adaptive advantages? Visual information reaching the striatum directly: Advantages
New Neurons Clear the Path of Astrocytic Processes for Their Rapid Migration in the Adult Brain
 Please cite this article in press as: Kaneko et al., New s Clear the Path of Astrocytic Processes for Their Rapid Migration in the Adult Brain, (2010), doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.06.018 Ar ticle New s Clear
Please cite this article in press as: Kaneko et al., New s Clear the Path of Astrocytic Processes for Their Rapid Migration in the Adult Brain, (2010), doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.06.018 Ar ticle New s Clear
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
CHAPTER I GENERAL INTRODUCTION. As I was contemplating how to start the GENERAL INTRODUCTION section of
 CHAPTER I GENERAL INTRODUCTION As I was contemplating how to start the GENERAL INTRODUCTION section of my thesis, the following idea came into my mind: since essentially all the scientific parts of the
CHAPTER I GENERAL INTRODUCTION As I was contemplating how to start the GENERAL INTRODUCTION section of my thesis, the following idea came into my mind: since essentially all the scientific parts of the
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CNTF/LIF/gp130 receptor complex signaling maintains a VZ precursor differentiation gradient in the developing ventral forebrain
 Research article 565 CNTF/LIF/gp130 receptor complex signaling maintains a VZ precursor differentiation gradient in the developing ventral forebrain Christopher Gregg and Samuel Weiss* Genes and Research
Research article 565 CNTF/LIF/gp130 receptor complex signaling maintains a VZ precursor differentiation gradient in the developing ventral forebrain Christopher Gregg and Samuel Weiss* Genes and Research
Multidirectional and multizonal tangential migration of GABAergic interneurons in the developing cerebral cortex
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 2167 Development 133, 2167-2176 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02382 Multidirectional and multizonal tangential migration of GABAergic interneurons in the developing cerebral cortex Daisuke H.
RESEARCH ARTICLE 2167 Development 133, 2167-2176 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02382 Multidirectional and multizonal tangential migration of GABAergic interneurons in the developing cerebral cortex Daisuke H.
Visualization of embryonic neural stem cells using Hes promoters in transgenic mice
 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymcne Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 31 (2006) 109 122 Visualization of embryonic neural stem cells using Hes promoters in transgenic mice Toshiyuki Ohtsuka, a,b, * Itaru Imayoshi, b Hiromi
www.elsevier.com/locate/ymcne Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 31 (2006) 109 122 Visualization of embryonic neural stem cells using Hes promoters in transgenic mice Toshiyuki Ohtsuka, a,b, * Itaru Imayoshi, b Hiromi
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Origin and Molecular Specification of Striatal Interneurons
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 15, 2000, 20(16):6063 6076 Origin and Molecular Specification of Striatal Interneurons Oscar Marín, Stewart A. Anderson, and John L. R. Rubenstein Department of Psychiatry,
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 15, 2000, 20(16):6063 6076 Origin and Molecular Specification of Striatal Interneurons Oscar Marín, Stewart A. Anderson, and John L. R. Rubenstein Department of Psychiatry,
Cellular components of CNS
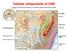 Cellular components of CNS Cellular components of CNS Neurons Glial cells: Astrocytes (including radial glia), oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells Epithelial cells of choroid plexus Endothelial
Cellular components of CNS Cellular components of CNS Neurons Glial cells: Astrocytes (including radial glia), oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells Epithelial cells of choroid plexus Endothelial
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
ANIMAL MODELS OF EPILEPSY Index
 INDEX A Action potentials BK channel effect on... 89 90 See also Synaptic transmission Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector gene therapy... 234 inhibitory GABA receptors and... 238 240 neuroactive peptides
INDEX A Action potentials BK channel effect on... 89 90 See also Synaptic transmission Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector gene therapy... 234 inhibitory GABA receptors and... 238 240 neuroactive peptides
Nervous system part 1. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A
 MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A FALL 2011 Name: Points: / 100 PID: I. SHORT ANSWERS (6 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Describe two contributions made by Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934) in terms
MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A FALL 2011 Name: Points: / 100 PID: I. SHORT ANSWERS (6 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Describe two contributions made by Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934) in terms
Dlx1&2-Dependent Expression of Zfhx1b (Sip1, Zeb2) Regulates the Fate Switch between Cortical and Striatal Interneurons
 Article Dlx1&2-Dependent Expression of Zfhx1b (Sip1, Zeb2) Regulates the Fate Switch between Cortical and Striatal Interneurons Gabriel L. McKinsey, 1,2 Susan Lindtner, 1 Brett Trzcinski, 3 Axel Visel,
Article Dlx1&2-Dependent Expression of Zfhx1b (Sip1, Zeb2) Regulates the Fate Switch between Cortical and Striatal Interneurons Gabriel L. McKinsey, 1,2 Susan Lindtner, 1 Brett Trzcinski, 3 Axel Visel,
Embryological origin of thalamus
 diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Searching for the Mind
 Searching for the Mind with Jon Lieff, M.D. The Very Intelligent Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cell September 20, 2015 Small lining cells along the border of the brain s ventricles are the gateway and supervisor
Searching for the Mind with Jon Lieff, M.D. The Very Intelligent Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cell September 20, 2015 Small lining cells along the border of the brain s ventricles are the gateway and supervisor
Contact: Course outline: Contact for other times.
 Contact: kdelaney@uvic.ca Course outline: http://web.uvic.ca/~kdelaney/b367 Scheduled office hours: 1:00-3:00, M&Th Cunn. 259A Contact kdelaney@uvic.ca for other times. Quiz (0.5 hrs) midterm (1.4 hrs)
Contact: kdelaney@uvic.ca Course outline: http://web.uvic.ca/~kdelaney/b367 Scheduled office hours: 1:00-3:00, M&Th Cunn. 259A Contact kdelaney@uvic.ca for other times. Quiz (0.5 hrs) midterm (1.4 hrs)
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus
 Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon
 Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Lori Sussel 1, *, Oscar Marin 1, Shioko Kimura 2 and John L. R. Rubenstein 1, SUMMARY
 Development 126, 3359-3370 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV8607 3359 Loss of Nkx2.1 homeobox gene function results in a ventral to dorsal molecular respecification
Development 126, 3359-3370 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV8607 3359 Loss of Nkx2.1 homeobox gene function results in a ventral to dorsal molecular respecification
Glia-independent chains of neuroblasts through the subcortical parenchyma of the adult rabbit brain
 Glia-independent chains of neuroblasts through the subcortical parenchyma of the adult rabbit brain F. Luzzati*, P. Peretto*, P. Aimar, G. Ponti, A. Fasolo*, and L. Bonfanti *Department of Animal and Human
Glia-independent chains of neuroblasts through the subcortical parenchyma of the adult rabbit brain F. Luzzati*, P. Peretto*, P. Aimar, G. Ponti, A. Fasolo*, and L. Bonfanti *Department of Animal and Human
Jonas Rose bird brains
 Jonas Rose bird brains Bird brains BIRDS? Who are they What tricks can they do What do their brains look like What don t we know yet What are the implications Bird evolution Birds are dinosaurs Henry Huxley
Jonas Rose bird brains Bird brains BIRDS? Who are they What tricks can they do What do their brains look like What don t we know yet What are the implications Bird evolution Birds are dinosaurs Henry Huxley
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal
 Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
