Subject Index. DAS, see Disability Assessment Schedule
|
|
|
- Amice Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acedia 79 Acetylcholine release 387 Adjustment -, premorbid 131, 155, , social 135 Adolescent - psychiatry schizophrenia 221 Aetiology -, heterogeneity 250 Affect 244, constricted flattening 35, 164, inappropriate 35 Age at onset , ,232 Akathisia 322 Ambivalence 269 AMDP, see Association for Methodology and Documentation in Psychiatry system Amotivational state Amphetamine 319, 320, , 331 -, drug abuse 93 Amygdala 296, 307 Anergia 332, 412 Anhedonia 79-95, 130, 165, 276, 317 -, antipsychotic medication , discriminative validity 92 -, physical 80 -, social 80 -, temporal stability 92 Apathy 80, 165, syndrome Apomorphine 110, 319, 380 Asociality 82 Assessment - of negative symptoms 28-70, , reliability 29-34, , validity 58 - of positive symptoms , reliability Association for Methodology and Documentation in Psychiatry System 54, Association, loss of 269 Ataxia, social 103 Attention 165, 234, 403 Autarky, impairment of 215 Autism 244, 269 Autoreceptor, see Dopamine Autoreceptor Avoliton Basal ganglia 292, 294 Basic disorder 139, 403 Biology Biochemical factors 292 BPRS, see Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale Brain - abnormalities - -, functional 46-48, 131, 134, 305, , , structural 45-46, 131, imaging studies morphology 121 Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale 54, 129, 322, 369, 412 Brockton-Harvard Project 280 Catatonia 292 Catecholamine 330 CATEGO 162 Cellae medias 303 Cerebral - blood flow 48, 305, 307, spinal fluid 318, 326, 332, 333 Child psychiatry ,454,455 Childhood psychoses , age of first manifestation , classification 219 -, course 220 -, development state 219 -, early-onset schizophrenia 247 -, late-onset psychoses 221 -, premorbid personality 221 -, sex differences 222 Cholecystokinin 321 Classification -, multiaxial scheme (lcd 9) of childhood psychoses 319
2 462 Clinical-anatomical correlations 296, 304 Clonidin 331 Clozapine Cocaine, drug abuse 93 Cognitive - disturbances 232, 276, treatment of negative symptoms 402 Cologne long-term study Concept - of inhibition - of positive and negative schizophrenia 128,, , history 8-29, in adolescent psychiatry in child psychiatry of positive and negative symptoms , external valida tors , history 8-29, , validity of schizophrenia Conceptual history of positive and negative signals 8-27 Coping behavior 141,400,416, Corpus callosum 294, 303 Correlations - of positive and negative symptoms Cortex -, frontal 131,294, , parietal , prefrontal 317, 320 Course models of adolescent schizophrenia of childhood schizophrenia of mixed schizophrenia , - of negative schizophrenia , - of positive schizophrenia , - of positive and negative symptoms ,221 -, shift of symptoms , 223 -,stability Cranial size 303 Criteria -, negative schizophrenia 225 -, positive schizophrenia 225 CSF, see Cerebral spinal fluid CT scan studies 45, Cytoarchitectural changes 296, 308 DAS, see Disability Assessment Schedule Defect -, neurointegrative 84 -, schizophrenic 135, 167, syndrome 136 Deficiencies -, post-psychotic 244 Deficit symptoms , 392, 403 -, as state condition 84 -, as trait condition 84 -, post-psychotic schizophrenia, criteria 448 Deliquency 103 Denervation, chronic 391 Depression 72, 143, , 246, 280 Diachrony 14 Diagnosis - of Schizophrenia 71 Diagnostic systems 270 -, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSMIIIjR) 162, 224, 270, 280 -, International Classification of diseases (lcd 9) 223 -, Present State Examination (PSE) 162, 270 -, Research Diagnostic criteria (RDC) 224, 270, 280 Disability - in social roles study 142, 162, Disability Assessment Schedule 163, Dopamine - activity ,328 - agonists, drug abuse 93 - autoreceptors 379, , hypersensitivity , subsensitivity 391 -, cortical hypothesis 377, metabolism overactivity 270, l-receptors Receptors 317, 331, system Drug - abuse , amphetamine , cocaine , dopamine agonists 93 -, antipsychotic induced symptoms response , antipsychotic 317 Dualism, ontological 97 Dyskinesia, acute 379
3 463 Educational level Emotional - blunting disturbances 232 Epilepsy, temporal lobe 297,308 Expressed emotions 102,402 Evolution of symptoms over time Evolutionism 9 Family - status 200, therapy 402 First rank symptoms 71-78, and phenomenological method 72 -, ideal types 74 -, identification in clinical practice , made thougths 75,77 -,operational definitions 72 -, rating scale 76 -, subject probability , typification statement 74 Fissure -, interhemispheric 300, 301, 303, 309 -, silvian 299, 302 Flat affect 82, , 269 Fluctuation of positive and negative symptoms 221 Follow-up studies ,243 - in child psychiatry 238 Frontal lobe area 131, , 306, 307, 309 GAS, see Global Assessment Scale Genetics , , adoption studies 265 -, and adolescent schizophrenia 232 -, and negative symptomatology 268 -, and positive symptomatology 268 -, family studies 252,265, , heritability 260, 266 -, homotypia 253 -, in psychiatry 268 -, in Schizophrenia , King's College Hospital Study , liability continuum 261 -, linkage analysis 266, 287 -, models 251 -, morbid risk of schizophrenia 256 -, phenotype, schizophrenia-related 274 -, phenotypic heterogeneity 266 -, polygenic inheritance 266 -, schizotypal marker , segregation studies 268 -, severity-liability model 135, 160, 254, ,261 -, spectrum 266 -, threshold models 254, 257, 261 -, twin data 252, 253, 258, 279 German structuralism 97 Gestalt psychology 99 Global Assessment scale , Globus pallidus 292 Group therapy 402 Growth hormone 319 Gyrus parahippocampal 305 Heterogeneity -, aetiological 250 -, clinical 250 Hippocampus 296, 307 History, conceptual 8-27 Homovanillic acid 318, 319, HVA, see Homovanillic acid Hypersensitivity -, autoreceptor hypersensitivity 390 -, post-synaptic receptor hypersensitivity 387 Hypofrontality 46, IMDS, see Inpatient Multidimensional Psychiatric Scale Inpatient Multidimensional Psychiatric Scale 54 Instrument for the retrospective assessment of the onset of schizophrenia Integrated psychological therapy Intelligence , language-independent 234 Intentionality -, amorphous counter Model IPT, see Integrated psychological therapy IRAOS, see Instrument for the retrospective assessment of the onset of schizophrenia Isolation, social 273 Laterality 297 Life-events 102 Limbic - pathway, subcortical system ,295 Locus coeruleus 325 Longitudinal research 154 Long-term course - of adolescent schizophrenia of childhood schizophrenia , follow-up studies , of schizophrenia
4 464 Magical Ideation Scale 286 Magical thinking 272 Magnet resonance imaging, see MRI Mannheim Disability Study Marker, schizotypal 278 Mental - automatism 19 - representatives 97 Mesocortical projections 390 Mesotemporal structures 307 Methylphenidate methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol, see MHPG MHPG 319,326,327,328, Micropsychosis 276 Mixed schizophrenia -, course , -, stability 172, Modularity models 17 Monomorphism of course Morbid risk of schizophrenia 256 Motivation -, conceptualization 79 -, lack of 317 -, operationalization 79 MRI studies 45, 110, ,319 Negative schizophrenia -, concept , , course , -, criteria 225, 447 -, onset , outcome , premorbid features Negative Symptom Rating Scale 270 Negative symptoms -, and brain morphology 121 -, and genetics 268 -, and outcome , and treatment outcome 121 -, assessment 28-70, , , -, multi-modal approach , -, reliability 29-34, 58 -, -, validity 58, 166 -,concept 1-7,28-51, , correlation with positive symptoms , course , , definition 52, , evaluation criteria 52-70, 163 -, history 8-29, 52, 134, in adolescence schizophrenia in childhood schizophrenia 221 -, instruments of evaluation 52 -, onset 151 -,operationalisation 161 -, pathophysiological theory 391 -, primary 129 -, rating scales 55 -, secondary 129, 392 -, specifitity , stability , , test theory, classic 57 -, treatment -, - effects 36-38, , -, cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy 402 -, -, nonpharmacological concepts , -, psychological programs , - response , -, social programs , - with atypical neuroleptics , - with autoreceptor agonist , - with clozapine , - with typical neuroleptics , validity , vulnerability model 400,419 Neurasthenia 322 Neurobiochemical studies Neurological signs 131 Neuropathological studies Neuropeptids 321 Neuropsychological impairment 271 Neurosis 72 -, social 81 Neurotoxins 318 Noradrenalin 318,327, 331 -, activity 317, Dopamin connection 331 NSRS, see Negative Symptom Rating Scale Occupation at onset Oneiroid state, psychotic 99 Onset - of illness - -, late of negative symptoms of positive symptoms 151, of psychosis 154 Ontological Dualism 97 Operational Criteria Checklist for Psychotic Illness 256 Organic brain diseases 297, 308 Outcome , and negative symptoms , Global Assessment Scale , prediction , social 155, PANSS, see Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale
5 465 Passivity 322 Parahippocampal - dysfunction gyrus 305 Pathology, temporo-limbic 308 Personality -, anhedonic 81 - disorder , as-if-personalities , paranoid , schizoid , schizotypal 81, 265, 271, inventories 103 -, premorbid 103, , 221, 231, 246, 248 PET studies 46, 131, 305 Pimozide , 332 PIRS, see Psychological Impairments Rating Schedule Pleasure deficiency 81, 275 Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale 70 Positive schizophrenia -, concept , , course -, criteria 225, 447 -, onset , , outcome , premorbid features Positive symptoms -, and genetics 268 -, assessment 28-51, , -, reliability ,concept 1-7, , correlation with negative symptoms , course , definition , history 8-29, 134,442 - in childhood schizophrenia 245 -, onset 151 -,operationalisation 161 -, provocation of 115 -, specifity , stability over the course , -, treatment -, - effects 36-38, , - response , validity Positron emission tomography, see PET studies Postmortem brain studies , morphometric , qualitative 295 Poverty of speech 269 Predictors - of course 156, of outcome 156, 236, of treatment outcome 118 Premorbid - adjustment 155, features personality 103, , 221, 231, 246, 248 Prodrome 141, 328 Prognosis - of adult schizophrenia of childhood schizophrenia of mixed schizophrenia of negative schizophrenia of positive schizophrenia , poor 319 Projections -, glutamatergic 390 -, mesocortical 390 Pseudoneurotic schizophrenia 275 Psychological Impairments Rating Schedule 145, 163, 213 Psychosis 327 -, development pattern in adolescence , age of first manifestation , course in childhood , age of first manifestation , classification , course 220 -, onset 154 Psychosocial factors 293 Rating Scale for Emotional Blunting 270 Receptors -, alphal , alpha , beta , D , D2-317, 331, 378 -, Dopamin autoreceptors 379 Rehabilitation Program 231 Residual syndrome, see defect RSEB, see Rating Scale for Emotional Blunting SADS, see Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia SANS, see Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms SAPS, see Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms 28,82, 127, 164, 166,270, 327,417
6 466 Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms 28 Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia 270 Schizophrenia -, ambulatory 276 -,concept 1-7, ,174,425,440 -, genetics 265 -, first episode 109, in childhood and adolescence , long-term course , outcome , pseudoneurotic 275 -, subtypes Schizophrenia-like psychoses, genetics 267 Schizotaxia 275 Schizo typal - marker personality disorder 265, Scheiderian first rank symptoms 270 Serotonin 320, 321 Sex - differences distribution and subtypes 199, Shift of symptoms , 223, 226, 238, Sign-field disturbances 100 Silvian fissure 299 Social - adjustment class consequences of the illness 213 Specifity - of negative symptoms of positive symptoms SPECT studies 46, 305 Speech disturbances 245 Stability of diagnosis Structural - brain abnormalities 45-46, 131,271 - distortion 101 Structured Interview for Schizotyp 286 Subcortical limbic pathway 270 Subtypes of schizophrenia 1-7, , 166, 230, 234, 238, and sex distribution , type 1/11 129, 136, 169, 251, 260 Sulci -, frontal 299, 301 -, global widening 326 -, parieto-occipital cortical 299 Symptom shift 223, 226 Symptomatology 226 -, effects of treatment 113 -, evolution over time , negative, and outcome 109, 125 Symptoms, drug-induced 328 Temporal horn 300, 302, 303, 305, 306 Temporal lobe 293, 303, 308 Thalamus 131 Third ventricle 299, 301, 303, 306 Treatment , amphetamine and symptom shift 226 -, antipsychotic drugs 84-92, , dopamine agonists , -, apomorphine 380, 382 -, -, bromocriptine 383 -, -, Roxindol (EM 49980) 387, , -, Talipexole (B-HT 920) effects - - on negative symptoms 36-38, on positive symptoms , ECT 378 -, methylphenidate , neuroleptics 110, , -, haloperidol 325 -, -, pimozide , outcome 111,121 -, psychostimulants , predictors response , acute , behavioral , - to clozapine , - to Methylphenidate , shift of symptoms 223 -, side effects -, -, akathesia 322 -, -, dyskinesia 379 -, -, parkinsonism 379 -, -, sedation, apomorphine-induced 384 Trema 99 Validity - of dichotomy models of negative symptoms of positive symptoms VBR, see Ventricles to brain ratio Ventricle, third 299, 301, 303, 306 Ventricles to brain ratio (VBR) 45, 298, 317, 328 Ventricular - enlargement system 304, 305 Viral infections 297 Withdrawal - Iretardation factor (BPRS) 322 -, social 83, 148, 272
Chapter 12. Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders. PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI
 Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenic twin. Normal twin
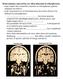 Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Disorders
 and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Age Distribution of Onset 2/24/2009. Schizophrenia. Hallmark trait is psychosis
 Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Dr. Fred Rose. Schizophrenia. Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview. Prevalence of Schizophrenia 10/20/10. Schizophrenia vs.
 Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health
 Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses
 Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Chapter 13
 Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders?
 Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Psychology, 3 Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology,
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 115 124) QUANTITATIVE CEREBRAL ANATOMY
PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 115 124) QUANTITATIVE CEREBRAL ANATOMY
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com
 Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Disease Modification in Schizophrenia: Overview of the Issues. ISCTM February 18 th 2014 Ravi Anand, MD Switzerland
 Disease Modification in Schizophrenia: Overview of the Issues ISCTM February 18 th 2014 Ravi Anand, MD Switzerland Need for a New Treatment Paradigm in Schizophrenia Sixty years after approval for the
Disease Modification in Schizophrenia: Overview of the Issues ISCTM February 18 th 2014 Ravi Anand, MD Switzerland Need for a New Treatment Paradigm in Schizophrenia Sixty years after approval for the
Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003
 Psychological Disorders: General Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 1. What are psychological disorders? 2. What was the main treatment for some psychological disorders prior to the 1950 s? 3. What
Psychological Disorders: General Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 1. What are psychological disorders? 2. What was the main treatment for some psychological disorders prior to the 1950 s? 3. What
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal
 ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Update on First Psychotic Episodes in Childhood and Adolescence. Cheryl Corcoran, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Columbia University
 Update on First Psychotic Episodes in Childhood and Adolescence Cheryl Corcoran, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Columbia University Childhood-Onset Psychosis 8% of psychiatrically referred youth
Update on First Psychotic Episodes in Childhood and Adolescence Cheryl Corcoran, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Columbia University Childhood-Onset Psychosis 8% of psychiatrically referred youth
Chapter Sixteen. Psychological Disorders
 Chapter Sixteen Psychological Disorders Prevalence of Psychological Disorders? Approximately 25% of the Adult Population here in the U.S. of A. Higher percentages in areas / countries with high poverty
Chapter Sixteen Psychological Disorders Prevalence of Psychological Disorders? Approximately 25% of the Adult Population here in the U.S. of A. Higher percentages in areas / countries with high poverty
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
8/22/2016. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia - continued
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Neuroimaging for Diagnosis of Psychiatric Disorders
 Psychiatric Disorder Neuroimaging for Diagnosis of Psychiatric Disorders JMAJ 45(12): 538 544, 2002 Yoshio HIRAYASU Associate Professor, Department of Neuropsychiatry Kyorin University School of Medicine
Psychiatric Disorder Neuroimaging for Diagnosis of Psychiatric Disorders JMAJ 45(12): 538 544, 2002 Yoshio HIRAYASU Associate Professor, Department of Neuropsychiatry Kyorin University School of Medicine
CHAPTER 3. Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment
 CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abuse substance. See Substance abuse Acquired disorders presenting as psychosis in children and young adults, 581 608. See also specific
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abuse substance. See Substance abuse Acquired disorders presenting as psychosis in children and young adults, 581 608. See also specific
Schizophrenia. Nikita Verma 2017 Page 1
 Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
ADHD SIV FASCI, MD FAAP DEVELOPMENTAL-BEHAVIORAL PEDIATRICS DELL CHILDREN S MEDICAL CENTER 9TH ANNUAL PEDIATRIC CONFERENCE - MARCH 24, 2016
 ADHD SIV FASCI, MD FAAP DEVELOPMENTAL-BEHAVIORAL PEDIATRICS DELL CHILDREN S MEDICAL CENTER 9TH ANNUAL PEDIATRIC CONFERENCE - MARCH 24, 2016 Objectives Epidemiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Co-morbidities
ADHD SIV FASCI, MD FAAP DEVELOPMENTAL-BEHAVIORAL PEDIATRICS DELL CHILDREN S MEDICAL CENTER 9TH ANNUAL PEDIATRIC CONFERENCE - MARCH 24, 2016 Objectives Epidemiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Co-morbidities
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives
 Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
4. General overview Definition
 4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
Biomarkers Workshop In Clinical Trials Imaging for Schizophrenia Trials
 Biomarkers Workshop In Clinical Trials Imaging for Schizophrenia Trials Research focused on the following areas Brain pathology in schizophrenia and its modification Effect of drug treatment on brain structure
Biomarkers Workshop In Clinical Trials Imaging for Schizophrenia Trials Research focused on the following areas Brain pathology in schizophrenia and its modification Effect of drug treatment on brain structure
Psychosis. Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah
 Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
The psychological disorders
 The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Schizophrenia. Introduction. Overview and Facts
 Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Ethical Research Comittee
 How should we take care of Schizophrenia today? Dr Laurence LACOSTE Saint Louis Hospital, Paris, France Ethical Research Comittee 1 Introduction: Schizophrenia and Psychiatry In psychiatric hospitals,
How should we take care of Schizophrenia today? Dr Laurence LACOSTE Saint Louis Hospital, Paris, France Ethical Research Comittee 1 Introduction: Schizophrenia and Psychiatry In psychiatric hospitals,
Neurocognition and Neuroimaging Correlates of Persistent Negative Symptoms. Cindy Hovington Dr. Martin Lepage
 Neurocognition and Neuroimaging Correlates of Persistent Negative Symptoms Cindy Hovington Dr. Martin Lepage NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS Anhedonia Loss of Pleasure Asociality Decreased Social Drive Avolition Lack
Neurocognition and Neuroimaging Correlates of Persistent Negative Symptoms Cindy Hovington Dr. Martin Lepage NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS Anhedonia Loss of Pleasure Asociality Decreased Social Drive Avolition Lack
25 Things To Know. disorders
 Biological Psych 25 Things To Know Schizo phrenia disorders Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Schizophrenia Demographic Data Slightly
Biological Psych 25 Things To Know Schizo phrenia disorders Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Schizophrenia Demographic Data Slightly
Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders
 1 6 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders 16 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders The Toll of Psychiatric Disorders Is Huge Schizophrenia is the major neurobiological
1 6 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders 16 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders The Toll of Psychiatric Disorders Is Huge Schizophrenia is the major neurobiological
Schizophrenia. Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior.
 Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia & the Antipsychotics
 splitting of mind (cognition/emotion) from reality 1% of population globally shamans or mentally ill Several subtypes: paranoid / catatonic / disorganized / undifferentiated / residual positive ( exaggerated)
splitting of mind (cognition/emotion) from reality 1% of population globally shamans or mentally ill Several subtypes: paranoid / catatonic / disorganized / undifferentiated / residual positive ( exaggerated)
9/3/2014. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Is The Routine CT Head Scan Justified for Psychiatric Patients? A Prospective Study
 RESEARCH PAPERS Is The Routine CT Head Scan Justified for Psychiatric Patients? A Prospective Study Jambur Ananth, M.D., Reda Gamal, M.D., Milton Miller, M.D., Marcy Wohl, R.N., Steven Vandewater, Ph.D.
RESEARCH PAPERS Is The Routine CT Head Scan Justified for Psychiatric Patients? A Prospective Study Jambur Ananth, M.D., Reda Gamal, M.D., Milton Miller, M.D., Marcy Wohl, R.N., Steven Vandewater, Ph.D.
A review of MRI studies of progressive brain changes in schizophrenia
 J Med Dent Sci 2001; 48: 61 67 Review A review of MRI studies of progressive brain changes in schizophrenia Yoshiro Okubo 1,2, Tomoyuki Saijo 2,3 and Kenji Oda 4 1) Department of Biofunctional Informatics,
J Med Dent Sci 2001; 48: 61 67 Review A review of MRI studies of progressive brain changes in schizophrenia Yoshiro Okubo 1,2, Tomoyuki Saijo 2,3 and Kenji Oda 4 1) Department of Biofunctional Informatics,
10. Psychological Disorders & Health
 10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
schizophrenia :The latest news By Dr. Gamal Suliman Elgorashi MB BS,DPM, MRCpsych Consultant psychiatrist Kent & Medway NHS Trust UK
 schizophrenia :The latest news By Dr. Gamal Suliman Elgorashi MB BS,DPM, MRCpsych Consultant psychiatrist Kent & Medway NHS Trust UK The argument Schizophrenia has for too long been known as a single
schizophrenia :The latest news By Dr. Gamal Suliman Elgorashi MB BS,DPM, MRCpsych Consultant psychiatrist Kent & Medway NHS Trust UK The argument Schizophrenia has for too long been known as a single
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
The Neuropsychology of
 The Neuropsychology of Stroke Tammy Kordes, Ph.D. Northshore Neurosciences Outline What is the Role of Neuropsychology Purpose of Neuropsychological Assessments Common Neuropsychological Disorders Assessment
The Neuropsychology of Stroke Tammy Kordes, Ph.D. Northshore Neurosciences Outline What is the Role of Neuropsychology Purpose of Neuropsychological Assessments Common Neuropsychological Disorders Assessment
Final Exam PSYC2022. Fall (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication with cannabis.
 Final Exam PSYC2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Give 2 reasons why it is important for psychological disorders to be accurately diagnosed. (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication
Final Exam PSYC2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Give 2 reasons why it is important for psychological disorders to be accurately diagnosed. (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abuse alcohol, aggression and, 52 53 substance, aggression and, 52 54 ACE. See Aid to Capacity Evaluation (ACE). AEDs. See Antiepileptic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abuse alcohol, aggression and, 52 53 substance, aggression and, 52 54 ACE. See Aid to Capacity Evaluation (ACE). AEDs. See Antiepileptic
MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS
 MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS DIAGNOSIS OF MENTAL DISORDERS DSM-IV-TR Published by APA ( 2000 ) Multiaxial system 5 categories called axes Facilitate holistic assessment for care Is a great resource
MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS DIAGNOSIS OF MENTAL DISORDERS DSM-IV-TR Published by APA ( 2000 ) Multiaxial system 5 categories called axes Facilitate holistic assessment for care Is a great resource
Schizophrenia. Brooke Jones Charity Payne Alyssa Stewart
 Schizophrenia Brooke Jones Charity Payne Alyssa Stewart Brogan s Story Definition Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder in which people interpret reality abnormally. Schizophrenia may result in some
Schizophrenia Brooke Jones Charity Payne Alyssa Stewart Brogan s Story Definition Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder in which people interpret reality abnormally. Schizophrenia may result in some
Subtyping Schizophrenia According to Outcome or Severity: A Search for Homogeneous Subgroups
 Subtyping Schizophrenia According to Outcome or Severity: A Search for Homogeneous Subgroups Abstract by MarC'Andre Roy, Chanted Merette, and Michel There is a growing consensus that current definitions
Subtyping Schizophrenia According to Outcome or Severity: A Search for Homogeneous Subgroups Abstract by MarC'Andre Roy, Chanted Merette, and Michel There is a growing consensus that current definitions
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
 Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
OF THE ILLNESS. Manote Lotrakul. Aug 2015
 SCHIZOPHRENIA: ALL PHASES OF THE ILLNESS Manote Lotrakul Aug 2015 Outline Diagnostic criteria Clinical features Treatments DSM-5 : Schizophrenia A. Two (or more) of the following, each present for a significant
SCHIZOPHRENIA: ALL PHASES OF THE ILLNESS Manote Lotrakul Aug 2015 Outline Diagnostic criteria Clinical features Treatments DSM-5 : Schizophrenia A. Two (or more) of the following, each present for a significant
Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις
 Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 19 Ψυχασθένειες (Mental Illness) Introduction Neurology Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and
Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 19 Ψυχασθένειες (Mental Illness) Introduction Neurology Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and
behaviorism psychoanalytic theory humanism cognitive perspective evolutionary psychology biological perspective None
 PSYC 2301 STUDENT SUPPLEMENTAL HANDBOOK WEITEN PSYCHOLOGY: THEMES & VARIATIONS, BRIEFER VERSION 8 TH EDITION I. INTRODUCTION (These terms appear in either bold-face italics or non-bold italics in the text.
PSYC 2301 STUDENT SUPPLEMENTAL HANDBOOK WEITEN PSYCHOLOGY: THEMES & VARIATIONS, BRIEFER VERSION 8 TH EDITION I. INTRODUCTION (These terms appear in either bold-face italics or non-bold italics in the text.
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Biological Psych Schizophrenia
 Biological Psych Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Slightly more common in men Earlier onset, more severe Originally: dementia
Biological Psych Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Slightly more common in men Earlier onset, more severe Originally: dementia
Methods of Visualizing the Living Human Brain
 Methods of Visualizing the Living Human Brain! Contrast X-rays! Computerized Tomography (CT)! Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)! Positron Emission Tomography (PET)! Functional MRI! Magnetoencephalography
Methods of Visualizing the Living Human Brain! Contrast X-rays! Computerized Tomography (CT)! Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)! Positron Emission Tomography (PET)! Functional MRI! Magnetoencephalography
Schizophrenia: Uncovering a molecular origin so humanity may better deal with insanity
 Schizophrenia: Uncovering a molecular origin so humanity may better deal with insanity : What is Schizophrenia? Literally split mind A mental disorder comprising most major psychotic disorders; characterized
Schizophrenia: Uncovering a molecular origin so humanity may better deal with insanity : What is Schizophrenia? Literally split mind A mental disorder comprising most major psychotic disorders; characterized
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception
 Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Introduction, use of imaging and current guidelines. John O Brien Professor of Old Age Psychiatry University of Cambridge
 Introduction, use of imaging and current guidelines John O Brien Professor of Old Age Psychiatry University of Cambridge Why do we undertake brain imaging in AD and other dementias? Exclude other causes
Introduction, use of imaging and current guidelines John O Brien Professor of Old Age Psychiatry University of Cambridge Why do we undertake brain imaging in AD and other dementias? Exclude other causes
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
Three Minute Review. Test Yourself. and Dissociative Identity Disorder
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder A Neuro-Anatomical Approach to diagnosis and treatment
 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder A Neuro-Anatomical Approach to diagnosis and treatment Damon Lipinski, Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist Center for Pediatric Neuropsychology What is Attention? Different
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder A Neuro-Anatomical Approach to diagnosis and treatment Damon Lipinski, Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist Center for Pediatric Neuropsychology What is Attention? Different
Schizophrenia. Positive Symptoms. Course of Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders
 Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
The human brain. of cognition need to make sense gives the structure of the brain (duh). ! What is the basic physiology of this organ?
 The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
OLD AGE PSYCHIATRY. Dementia definition TYPES OF DEMENTIA. Other causes. Psychiatric disorders of the elderly. Dementia.
 Psychiatric disorders of the elderly OLD AGE PSYCHIATRY Dementia Depression Delusional disorder/late onset schizophrenia Delirium Dementia definition LOCALISATION OF CEREBRAL FUNCTION Impairment of multiple
Psychiatric disorders of the elderly OLD AGE PSYCHIATRY Dementia Depression Delusional disorder/late onset schizophrenia Delirium Dementia definition LOCALISATION OF CEREBRAL FUNCTION Impairment of multiple
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
Brain-Behavior Network. Central Nervous System. Cerebral Cortex Gyrus and Sulcus. Nervous System
 Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
SCHIZOPHRENIA and PSYCHOSES
 SCHIZOPHRENIA and PSYCHOSES Schizophrenia is a diagnosis which includes psychoses symptoms Greek - Skhizen (to split) Phren (mind) Splitting of the mind or it s function NOT a split personality. Psychoses
SCHIZOPHRENIA and PSYCHOSES Schizophrenia is a diagnosis which includes psychoses symptoms Greek - Skhizen (to split) Phren (mind) Splitting of the mind or it s function NOT a split personality. Psychoses
The Neurobiology of Attention
 The Neurobiology of Attention by Nadia Fike, MD/PhD Pediatric Neurology Center for Neurosciences Disclosures Nadia Fike, MD/PhD No relevant financial or nonfinancial relationships to disclose. Objectives
The Neurobiology of Attention by Nadia Fike, MD/PhD Pediatric Neurology Center for Neurosciences Disclosures Nadia Fike, MD/PhD No relevant financial or nonfinancial relationships to disclose. Objectives
HDSA Annual Convention June 2013 Behavior Issues: Irritability and Depression Peg Nopoulos, M.D.
 HDSA Annual Convention June 2013 Behavior Issues: Irritability and Depression Peg Nopoulos, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry, Neurology, and Pediatrics University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa The information provided
HDSA Annual Convention June 2013 Behavior Issues: Irritability and Depression Peg Nopoulos, M.D. Professor of Psychiatry, Neurology, and Pediatrics University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa The information provided
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
 Autism Spectrum Disorder 1) Approximately 1 out of every children in the United States will have an ASD. a) 44 b) 88 c) 122 d) 244 2) Asperger s syndrome presents more frequently in boys than it does in
Autism Spectrum Disorder 1) Approximately 1 out of every children in the United States will have an ASD. a) 44 b) 88 c) 122 d) 244 2) Asperger s syndrome presents more frequently in boys than it does in
The Brain Studying & Structures. Unit 3
 The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Roseanna Parkhurst-Gatewood MSN FNP-BC, PMHNP-BC DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder 3 A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (major depressive
Roseanna Parkhurst-Gatewood MSN FNP-BC, PMHNP-BC DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder 3 A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (major depressive
Early Stages of Psychosis. Learning Objectives
 Early Stages of Psychosis Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Learning Objectives Summarize the five domains of psychosis Describe how psychotic
Early Stages of Psychosis Stephan Heckers, MD MSc Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Vanderbilt University Learning Objectives Summarize the five domains of psychosis Describe how psychotic
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Role of Clozapine in Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia
 Disease Management and Treatment Strategies Elkis H, Meltzer HY (eds): Therapy-Resistant Schizophrenia. Adv Biol Psychiatry. Basel, Karger, 2010, vol 26, pp 114 128 Role of Clozapine in Treatment-Resistant
Disease Management and Treatment Strategies Elkis H, Meltzer HY (eds): Therapy-Resistant Schizophrenia. Adv Biol Psychiatry. Basel, Karger, 2010, vol 26, pp 114 128 Role of Clozapine in Treatment-Resistant
Dementia. Assessing Brain Damage. Mental Status Examination
 Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
