NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION
|
|
|
- Job Allen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E:/Biomedica Vol.4 Jan. Jun. 008/Bio-R (A) NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION M. ATHAR JAVED, SAMAR ZIA, SARA ASHRAF AND SHAHID MEHMOOD Department of Neurology, King Edward medical University / Mayo Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan ABSTRACT This prospective observational study was conducted in the department of Neurology, King Edward Medical University / Mayo Hospital, Lahore over a period of six months from July to December 007. The objective was to study the clinical and laboratory features of Wilson Disease in local population and compare the results with national and International data. All consecutive patients who presented with Wilson s disease during this period were included in the study. Their clinical and laboratory features were recorded and compared with the available National and International data. We collected a total of 10 patients from 5 different families. Eight were confirmed cases examined and investigated by the authors. Two cases were probable and dead siblings of these families in whom clinical features strongly supported the diagnosis of Wilson s disease. Clinical and laboratory data of only confirmed cases was tabulated and compared. Of the eight patients six were males and two females with a male to female ratio of 3:1. Mean age at presentation was 1.6 years with a range of 6 to 19 years. ing features were as follows: dysarthria in 6 (75%); dystonia 5 (63%); extrapyramidal rigidity and bradykinesia 4 (50%); emotional lability 6(75%); cognitive decline (5%) and signs of chronic liver disease in 1 (13%). Hepatic functions were abnormal in 1 (13%) while 4 (50%) patients had coarse echo texture of liver on abdominal ultrasound. Serum copper levels were within normal range in 8 (100%) patients. Serum ceruloplasmin was low in 8 (100%) patients. Twenty four hour urinary copper excretion was elevated in 5 (63%), KF ring on slit lamp examination was positive in 8 (100%) patients. CT scan of brain was in 6 (75%) and showed hypodensity of basal ganglia mainly affecting the putamen and globus pallidus along with subcortical white matter disease in fronto-parietal region in 4 (50%) patients. MRI was in 5 (63%) patients and showed evidence of cortical atrophy with hyperintense signals in thalami, brain stem and basal ganglia in all five patients (100%). Six confirmed cases belonged to three families and no family history was available in two cases (5%). History of consanguineous marriage was positive in all (100%) cases. We conclude that Wilson s disease is not an uncommon problem in our population with patients presenting at an early age but with advanced stage of the disease. However, poor recognition is the possible cause of it s under and delayed diagnosis. Wilson s disease in children and young adults can present with neuropsychiatric features alone without any hepatic manifestations. Neuropsychiatric features along with KF ring and a low Serum Ceruloplasmin level are sufficient to establish a diagnosis of Wilson s disease. INTRODUCTION Wilson disease (W.D.), or hepatolenticular degeneration, is a neurodegenerative disease of copper metabolism. It is an autosomal recessive disorder. In 191, Samuel Kinnier Wilson first described it as a familial disorder associated with neurological symptoms and cirrhosis. 1 Wilson s disease is due to impairment in the ability of liver to incorporate copper into hepatic ceruloplasmin and to export copper from the liver into bile. This is due to the defective transport of copper by the copper-transporting P-type ATPase secondary to one of several mutations in the ATP7B gene. By genetic linkage studies, Bowcock and colleagues narrowed the assignment of the Wilson disease locus to 13q14- q1. As a result copper accumulates in the liver, brain, kidney, and cornea. According to the literature, patients with Wilson disease usually present with liver disease during the first decade of life or with neuropsychiatric illness during the the second or third decade. 3 In general, the younger the age of the patient at symptom onset, the greater is the degree of liver involvement. 4 The incidence rate is per million cases, with increased rates in areas of consanguinity. The frequency ranges worldwide from 1 case per 30,000 population in Japan to 1 case per 100,000 population in Australia. WD is biochemically characterized by low ceruloplasmin and serum copper levels, increased 4-
2 38 M. ATHAR JAVED, SAMAR ZIA, SARA ASHRAF hour urinary copper excretion, and abnormally high hepatic copper content. 5 Diagnosis of Wilson s disease is based on clinical symptoms and certain laboratory investigations (Leipzig s criteria). 6 We undertook this study to observe the clinical features especially neurological and neuropsychiatric along with laboratory features of the disease in local population and to compare them with other studies. METHODS This is a prospective observational study. It comprises of consecutive cases of Wilson disease diagnosed in Neurology Department Mayo Hospital, Lahore, during a period of six months from July 007 to December 007. Diagnosis was based on Leipzig s Criteria. 6 Scoring ranges from 0 to 4; a score of 4 = definitive WD; a score of 3 = likely WD; and a score of 0 1 = improbable WD. Patient and all siblings were screened and those fulfilling the criteria were included in the study. History and laboratory record (if any) of siblings who died were reviewed and mentioned in the results of the study as probable cases. Data collected from the case series was recorded on a proforma that included the following five sections: a) demographic details including name, age, and sex ;b) presenting clinical features; c) family history including history of consanguineous marriages; d) laboratory features including serum copper & ceruloplasmin levels, 4 hour urinary copper estimation, liver functions (LFTs), KF ring on slit lamp examination and abdominal ultrasound for liver and spleen; e) radiological features on CT Scan and / or MRI of brain. RESULTS We collected 8 confirmed and two probable cases from 5 different families. Of the eight patients six were male and two female with a male to female ratio of 3:1. Mean age was 1.6 years with a range of 6 to 19 years. ing features were as follows: dysarthria in 6 (75%); dystonia in 5 (63%); extrapyramidal rigidity and bradykinesia 4 (50%); emotional lability 6 (75%); cognitive decline (5%) and signs of chronic liver disease in 1 (13%). LFT s were abnormal in 1 (13%) while 4 (50%) had coarse echo texture of liver on abdominal ultrasound. Serum copper levels were within normal range in 8 (100%) patients, whereas serum ceruloplasmin was low in 8 (100%) patients. Twenty four hour urinary copper excretion was elevated in 5 (63%), KF ring on slit lamp examination was positive in 8 (100%) patients. CT scan of brain was in 6 (75%) and showed hypodensity of basal ganglia mainly affecting the putamen and globus pallidus along with subcortical white matter disease in fronto-parietal region in 4 (50%) patients. MRI was performed in 5 (63%) patients and showed evidence of cortical atrophy with hyperintense signals in thalami, brain stem and basal ganglia in all the five patients (100%). Six confirmed cases belonged to three families and no family history was available in two cases (5%). History of consanguineous marriage was positive in all (100%) cases. Clinical and laboratory features are shown in Table 1 and. DISCUSSION This study revealed that most (n = 75%) of the patients presented in second decade while only (5%) were below 10 years of age. We also observed a male preponderance in our study with male to female ratio of 3:1. This observation is in accordance with the data from the reports in which the age at presentation was 8 to 16 years with male preponderance. 7 Athough, it has been reported as late as 7 years of age, 8 the majority of patients become symptomatic before the age of In the Indian subcontinent, the disorder tends to manifest one decade earlier, which is possibly related to the traditional practice of cooking and eating food using copper utensils. 10 About 40-50% of patients present with liver disease, and 35-50%, with neurological or psychiatric symptoms. 7 In our study neuropsychiatric disturbances were most common initial manifestations and were seen in 6 (75%) patients. This may be due to the fact that study was conducted in neurology department where patients with neurological manifestations are brought. However, even on detailed analysis of other family members, we observed more neuropsychiatric manifestations than hepatic manifestations. We had only one patient who presented with symptoms of jaundice at the age of 6 year. Wilson s disease with hepatic involvement is usually present in first decade of life. One patient (case 4) had only psychiatric symptoms at presentation with excessively labile mood along with isolated dysarthria as the only neurological feature. He was evaluated on lines of Wilson s disease because of high clinical suspicion and a strongly positive family history. A previous study describes four distinct diagnostic categories based on patients major neurological findings: 1) Parkinsonian group distinguished by the paucity of expression and movement; ) Pseudosclerotic group had tremour resembling multiple sclerosis; 3) Dystonic group characterized by hypertonicity associated with abnormal limb movements; and 4) Choreic group characterised by choreoathetoid movements associated with dystonia. 11 There may be significant over-lap between these
3 NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON S DISEASE 39 Table 1: Clinical & Laboratory features in eight cases investigated for Wilson s disease. Clinical features Case1 Case Case3 Case4 Case5 Case6 Case7 Case 8 Age in yrs Sex Male Female Female Male Male Male Male Male Dysarthria Absent Absent Dystonia Absent Absent Absent Extrapyramidal rigidity Psychiatric symptoms Cognitive decline Hepatic involvement Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Family history +ve +ve +ve +ve +ve +ve +ve +ve 4 hour urinary copper mcg/dl Serum ceruloplasmin mg/dl Serum copper mcg/dl K-F ring CT scan: a) Hypodense basal ganglia b) Subcotical white matter disease MRI findings: Hyperintense signals in putamen and globus pallidus Normal Thalami Midbrain Pons Medulla Subcortical involvement Ventricular system Mildly dilated cisterns Mildly dilated None None Normal Normal Normal cerebellum Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal groups. Psychiatric manifestations can be divided into affective, behavioral, schizophrenia like and cognitive. Cases in our study had all of the above neurological manifestations except chorea (Table 1). Cognitive decline was seen in (5%) patients. Kayser-Fleischer rings were found in all patients (100%) in our study. Kayser-Fleischer rings have been reported to be present in 95% of patients with neurological symptoms, in 50-60% of patients without neurological symptoms and in
4 40 M. ATHAR JAVED, SAMAR ZIA, SARA ASHRAF Table : Analysis of families with confirmed and suspected cases of Wilson disease. Family no Family 1 Family Family 3 Family 4 Family 5 Total no of siblings Confirmed cases Probable cases (dead siblings with similar clinical features) History of consanguineous marriage Case 1 & 4 Case & 8 Case 3 & 7 1 Case Case 6 only 10% of asymptomatic siblings. 1 Patients presenting with neurological symptoms may also suffer from significant liver disease. In a substantial proportion, symptomatic liver disease pre-dates the occurrence of neurological signs. 13 We found that 50% of our patients had evidence of coarse texture of liver but only one patient (13%) had jaundice and raised liver enzymes consistent with chronic liver disease. Seven (87%) cases presented mainly with neurological and neuropsychiatric features but with biochemically normal liver function tests. Liver biopsy and histochemical examination was beyond the scope of this study. Hence we observed that it is not mandatory that all patients with neurological manifestations are likely to have clear cut hepatic impairments. According to previous reports, if a liver biopsy is performed in all patients presenting with neurological symptoms at diagnosis, the proportion of patients with cirrhosis is 38.7% and about one-half of patients have only minimal liver disease. 14 Leipzig Diagnostic Criteria used for the diagnosis of Wilson disease in this study was proposed in Leipzig Germany 001 at the 8 th international meeting which recommends the presence of KF rings, low serum ceruloplasmin and high 4 hour urinary copper excretion in patients with neurological symptoms for diagnosis of Wilson s disease. Standard criteria for asymptomatic patients is liver biopsy showing copper deposition of greater than 50g/g dry weight in hepatic tissue along with low serum ceruloplasmin. 5 In previous studies serum ceruloplasmin were shown to be a more sensitive indicator for the diagnosis as compared to 4 hour urinary copper levels. We found that 100% cases in our study had low serum ceruloplasmin level and 4 hour urinary copper excretion was elevated in 5 (63%) cases. This supports the previous finding that a low serum ceruloplasmin level is more sensitive marker than serum copper and 4 hour urinary copper excretion in diagnosing Wilson disease. CT scan and MRI were performed and revealed hypo dense areas in the basal ganglia on CT scan with sub cortical white matter changes mostly in the fronto-parietal regions of the brain. MRI findings were similar to the classical findings described in literature with hyper intense signals on T weighted images from the thalami, globus pallidus, putamen, and the brainstem. 15,16 Mild dilatation of the ventricular system was seen in two cases and no cerebellar involvement was observed. A positive family history was extremely significant in our study and was positive in 75% cases. Two patients had no family history (table ). Two siblings of case 3 had died undiagnosed. However, history given by the parents regarding their illness strongly suggested the diagnosis of Wilson s disease as the most probable cause of death. They were seen by local physicians and never referred to any tertiary care center. History of consanguineous marriage was present in all cases (100%). We conclude that Wilson s disease is not uncommon in our local population and most patients present with neurological or neuropsychiatric features at a relatively early age with a male preponderance and with advanced stage of the disease. Possibly poor recognition is the cause of it s under and delayed diagnosis. Wilson s disease can present in children with isolated neuropsychiatric features without any hepatic manifestation. KF rings along with neuropsychiatric features and a low ceruloplasmin level are sufficient to establish a diagnosis of Wilson s disease. Low Serum Ceruloplasmin (< 0 mg/dl) is more reliable in supporting the diagnosis of Wilson s disease than 4 hour urinary copper excretion and low serum copper levels. All young patients, below the age of 40 years, presenting with neurological or psychiatric features as initial manifestations should be thoroughly screened for Wilson s disease.
5 NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON S DISEASE 41 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors are thankful to their patients who allowed to study their disease, we are also thankful to Vice Chancellor of KEMU. REFERENCES 1. Wilson SAK (191) Progressive lenticular degeneration: a familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis of the liver. Brain 34: Bowcock AM, Farrer LA, Hebert JM, Agger M, Sternlieb I, Scheinberg IH, et al. Eight closely linked loci place the Wilson disease locus within 13q14- q1. Am J Hum Genet. Nov 1988; 43 (5): Das S K and Ray K.Wilson's disease: an update. Nature Clinical Practice Neurology 006: ; Sherlock S and Dooley J (Eds; 00) Wilson disease. In Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System, edn 11, Oxford: Blackwell Science Neurological presentation. 5. Sternlieb I. Perspectives on Wilson's disease. Hepatology 1990; 1: Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, et al. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Final report of the Proceedings of the Working Party at the 8th International Meeting on Wilson Disease and Menkes Disease, Leipzig/Germany, 001. Liver Int 003; 3: Celia H Chang. Wilson Disease [online e-medicine] updated May 18, Ala A et al. (005) Wilson disease in septuagenarian siblings: raising the bar for diagnosis. Hepatology 41: Le Witt P and Pfeiffe R (00) Neurologic aspects of Wilson's disease: clinical manifestations and treatment considerations. In Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders, edn 4, (Eds Jankovic JJ and Tolosa E) Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 10. Kalra V et al. (000) Wilson's disease: early onset and lessons from a pediatric cohort in India. Indian Pediatr 37: Walshe JM. Copper: its role in the pathogenesis of liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. Aug 1984; 4 (3): P. Ferenci.Diagnosis and Current Therapy of Wilson's Disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther004; 19 (): Scheinberg IH, Sternlieb I. Wilson's Disease. Vol. 3. Major Problems in Internal Medicine. Philadelphia: Saunders, Ferenci P, Steindl-Munda P, Vogel W, et al. Diagnostic value of quantitative hepatic copper determination in patients with Wilson disease. Lancet A. Hassan, F. Masood. Wilson s Disease:a review. J Pak Med Assoc 004; 54 (9): Page RA et al. Clinical correlation of brain MRI and MRS abnormalities in patients with Wilson disease. Neurology 006; 63: Kuruvilla A and Joseph S (000) 'Face of the giant Panda' sign in Wilson's disease: revisited. Neurol India 000; 48:
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
 Title Mutational analysis for Wilson's disease Author(s) Seto, WK; Mak, CM; But, D; Hung, I; Lam, CW; Tam, S; Yuen, MF; Lai, CL Citation The Lancet, 2009, v. 374 n. 9690, p. 662 Issued Date 2009 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/77405
Title Mutational analysis for Wilson's disease Author(s) Seto, WK; Mak, CM; But, D; Hung, I; Lam, CW; Tam, S; Yuen, MF; Lai, CL Citation The Lancet, 2009, v. 374 n. 9690, p. 662 Issued Date 2009 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/77405
Wilson Disease. Maggie Benson Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Physical Therapy
 Wilson Disease Maggie Benson Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Physical Therapy What is Wilson Disease? Wilson Disease (WD)= hepatolenticular degeneration Hereditary disorder Autosomal recessive
Wilson Disease Maggie Benson Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Physical Therapy What is Wilson Disease? Wilson Disease (WD)= hepatolenticular degeneration Hereditary disorder Autosomal recessive
YES NO UNKNOWN PENETRANCE ACTIONABILITY SIGNIFICANCE/BURDEN OF DISEASE NEXT STEPS. YES (Proceed to Stage II) YES ( 1 of above)
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: ATP7B DISORDER: Wilson Disease HGNC ID: 870 OMIM ID: 277900 ACTIONABILITY 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic review,
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: ATP7B DISORDER: Wilson Disease HGNC ID: 870 OMIM ID: 277900 ACTIONABILITY 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic review,
RESEARCH ARTICLE NEUROLOGICAL AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS OF WILSON DISEASE;
 RESEARCH ARTICLE NEUROLOGICAL AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS OF WILSON DISEASE; 1998-2005 A. Fallah MD Abstract Objective Wilson disease (WD) is an inherited copper metabolism dysfunction disease characterized
RESEARCH ARTICLE NEUROLOGICAL AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS OF WILSON DISEASE; 1998-2005 A. Fallah MD Abstract Objective Wilson disease (WD) is an inherited copper metabolism dysfunction disease characterized
Metabolic Liver Disease
 Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Unexplained Hepatic, Neurologic or Psychiatric Symptoms?
 A Diagnostic Tool For Physicians Unexplained Hepatic, Neurologic or Psychiatric Symptoms? Think WILSON DISEASE. ALGORITHMS FOR ASSESSMENT OF WILSON DISEASE Table 1. Clinical Features in Patients with Wilson
A Diagnostic Tool For Physicians Unexplained Hepatic, Neurologic or Psychiatric Symptoms? Think WILSON DISEASE. ALGORITHMS FOR ASSESSMENT OF WILSON DISEASE Table 1. Clinical Features in Patients with Wilson
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System
 Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy?
 Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Review Article Wilson's Disease: a review A. Hassan, F. Masood Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics*, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi.
 Review Article Wilson's Disease: a review A. Hassan, F. Masood Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics*, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. Introduction and Genetics Wilson's disease (WD; Hepatolenticular
Review Article Wilson's Disease: a review A. Hassan, F. Masood Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics*, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. Introduction and Genetics Wilson's disease (WD; Hepatolenticular
WILSON S DISEASE; NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN PATIENTS PRESENTING TO TERTIARY CARE FACILITY
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.957/TPMJ/15.11 ORIGINAL PROF-11 WILSON S DISEASE; NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN PATIENTS PRESENTING TO TERTIARY CARE FACILITY 1. Assistant Professor Isra University
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.957/TPMJ/15.11 ORIGINAL PROF-11 WILSON S DISEASE; NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN PATIENTS PRESENTING TO TERTIARY CARE FACILITY 1. Assistant Professor Isra University
Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski
 Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski Basic Genetics Wilson Disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of impaired copper metabolism. The Wilson Disease gene is composed
Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski Basic Genetics Wilson Disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of impaired copper metabolism. The Wilson Disease gene is composed
Magnetic resonance imaging findings in diagnosis and prognosis of Wilson disease
 Review Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in diagnosis and prognosis of Wilson disease Mehri Salari 1, Emad Fayyazi 1,2, Omid Mirmosayyeb 1,2 1 Isfahan Neurosciences Research Center, Alzahra Research
Review Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in diagnosis and prognosis of Wilson disease Mehri Salari 1, Emad Fayyazi 1,2, Omid Mirmosayyeb 1,2 1 Isfahan Neurosciences Research Center, Alzahra Research
Wilson disease an update for 2014 Enfermedad de Wilson. Actualización
 5 Congreso Argentino de Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición Pediátricas Wilson disease an update for 2014 Enfermedad de Wilson. Actualización Eve A. Roberts, M.D., M.A., FRCPC Division of Gastroenterology,
5 Congreso Argentino de Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición Pediátricas Wilson disease an update for 2014 Enfermedad de Wilson. Actualización Eve A. Roberts, M.D., M.A., FRCPC Division of Gastroenterology,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Molecular Diagnosis and Prophylactic Therapy for Presymptomatic Chinese Patients With Wilson Disease
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Molecular Diagnosis and Prophylactic Therapy for Presymptomatic Chinese Patients With Wilson Disease Zhi-Ying Wu, MD, PhD; Min-Ting Lin, MD; Shen-Xing Murong, MD; Ning Wang, MD, PhD
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Molecular Diagnosis and Prophylactic Therapy for Presymptomatic Chinese Patients With Wilson Disease Zhi-Ying Wu, MD, PhD; Min-Ting Lin, MD; Shen-Xing Murong, MD; Ning Wang, MD, PhD
*Department of pediatrics, Baghdad Medical College, University of Baghdad. **Children Welfare Teaching Hospital, Medical City, Baghdad.
 WILSON S THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE DISEASE IN CHILDREN MEDICAL JOURNAL Wilson s Disease in Children (Clinical Presentations & Diagnostic Difficulties) (Three years experience in Children Welfare Teaching
WILSON S THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE DISEASE IN CHILDREN MEDICAL JOURNAL Wilson s Disease in Children (Clinical Presentations & Diagnostic Difficulties) (Three years experience in Children Welfare Teaching
Original Article. Abstract
 Original Article Neurological Wilson Disease in children: a three years experience from Multan Nuzhat Noureen, Muhammad Tariq Rana Department of Paediatrics, Nishtar Hospital, Multan, Pakistan. Abstract
Original Article Neurological Wilson Disease in children: a three years experience from Multan Nuzhat Noureen, Muhammad Tariq Rana Department of Paediatrics, Nishtar Hospital, Multan, Pakistan. Abstract
Neuro Wilson s An Alien Presentation
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.1.RD3 Case Report ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Neuro Wilson s An Alien Presentation Sivakami R. Pradeepkumar 1, Ramesh Kumar Rudrappa 2, Sibhithran Rajakumar 3 1 Assistant
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.1.RD3 Case Report ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Neuro Wilson s An Alien Presentation Sivakami R. Pradeepkumar 1, Ramesh Kumar Rudrappa 2, Sibhithran Rajakumar 3 1 Assistant
International Journal of Biology January, 2010
 International Journal of Biology January, 2010 Spectrum of ATP7B Gene Mutations in Pakistani Wilson Disease Patients: A Novel Mutation Is Associated with Severe Hepatic and Neurological Complication Abdul
International Journal of Biology January, 2010 Spectrum of ATP7B Gene Mutations in Pakistani Wilson Disease Patients: A Novel Mutation Is Associated with Severe Hepatic and Neurological Complication Abdul
Metabolic Liver Diseases
 Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in Wilson s Disease and Its Comparison with Other Laboratory Tests and Paraclinical Findings
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Mar 20; Vol 22 (No 1), Pp: 26 Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in Wilson s Disease and Its Comparison with Other Laboratory Tests and Paraclinical Findings Fatemeh Mahjoub*
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Mar 20; Vol 22 (No 1), Pp: 26 Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in Wilson s Disease and Its Comparison with Other Laboratory Tests and Paraclinical Findings Fatemeh Mahjoub*
When the penny drops
 Department of Molecular Neuroscience, UCL Institute of Neurology, and National Hospital for Neurology & Neurosurgery, London, UK Correspondence to Dr Paola Giunti, Department of Molecular Neuroscience,
Department of Molecular Neuroscience, UCL Institute of Neurology, and National Hospital for Neurology & Neurosurgery, London, UK Correspondence to Dr Paola Giunti, Department of Molecular Neuroscience,
COPPER AND CAERULOPLASMIN: GUIDELINES FOR REQUESTING
 Version: 2.0 Ratified by: Clinical Biochemistry Senior Staff meeting Date ratified: 24 th March 2014 Name of originator/author: Director responsible for implementation: Elizabeth Hall/ Dr Joanne Carter
Version: 2.0 Ratified by: Clinical Biochemistry Senior Staff meeting Date ratified: 24 th March 2014 Name of originator/author: Director responsible for implementation: Elizabeth Hall/ Dr Joanne Carter
SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA)
 DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
Wilson Disease - Our Experience
 Wilson Disease Our Experience Hussein Shamaly M.D.. Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit Pediatric Department Clalit Health Services French Hospital, Nazareth Key Concepts Wilson disease is more often considered
Wilson Disease Our Experience Hussein Shamaly M.D.. Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit Pediatric Department Clalit Health Services French Hospital, Nazareth Key Concepts Wilson disease is more often considered
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
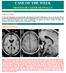 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: 27 years old male patient presented clinically with bilateral pyramidal manifestations, more on the left side, bilateral parkinsonian manifestations and bilateral cerebellar
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: 27 years old male patient presented clinically with bilateral pyramidal manifestations, more on the left side, bilateral parkinsonian manifestations and bilateral cerebellar
In 1912, a British neurologist, Samuel Wilson, described
 Neurologic Wilson disease: case series on a diagnostic and therapeutic emergency Romeo V. Porlas Jr, MD; Lennie Lynn C. de Castillo, MD; Carissa Paz C. Dioquino, MD Introduction Wilson disease is a rare
Neurologic Wilson disease: case series on a diagnostic and therapeutic emergency Romeo V. Porlas Jr, MD; Lennie Lynn C. de Castillo, MD; Carissa Paz C. Dioquino, MD Introduction Wilson disease is a rare
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN
 Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
MULTI SYSTEM ATROPHY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Dipu Bhuyan 1, Rohit Kr. Chandak 2, Pankaj Kr. Patel 3, Sushant Agarwal 4, Debjanee Phukan 5
 MULTI SYSTEM ATROPHY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Dipu Bhuyan 1, Rohit Kr. Chandak 2, Pankaj Kr. Patel 3, Sushant Agarwal 4, Debjanee Phukan 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Dipu Bhuyan, Rohit Kr. Chandak, Pankaj Kr.
MULTI SYSTEM ATROPHY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Dipu Bhuyan 1, Rohit Kr. Chandak 2, Pankaj Kr. Patel 3, Sushant Agarwal 4, Debjanee Phukan 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Dipu Bhuyan, Rohit Kr. Chandak, Pankaj Kr.
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Pathological Fracture of Femoral Neck Leading to a Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature
 J Bone Metab 2017;24:135-139 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2017.24.2.135 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Case Report Pathological Fracture of Femoral Neck Leading to a Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case
J Bone Metab 2017;24:135-139 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2017.24.2.135 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Case Report Pathological Fracture of Femoral Neck Leading to a Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case
Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases
 The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
Kinnier Wilson and Wilson s disease
 Symposium on Wilson s disease --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Symposium on Wilson s disease --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Familial dystonia with cerebral calcification
 Familial dystonia with cerebral calcification case report and genetic update M. Signaevski, A.K. Wszolek, A.J. Stoessel, R. Rademakers, and I.R. Mackenzie Vancouver General Hospital, BC, Canada Mayo Clinic
Familial dystonia with cerebral calcification case report and genetic update M. Signaevski, A.K. Wszolek, A.J. Stoessel, R. Rademakers, and I.R. Mackenzie Vancouver General Hospital, BC, Canada Mayo Clinic
Dystonia: Title. A real pain in the neck. in All the Wrong Places
 Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine
 International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 221927, 26 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2014.221927 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2014. Arnaoutoglou Marianthi, Kiryttopoulos
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 221927, 26 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2014.221927 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2014. Arnaoutoglou Marianthi, Kiryttopoulos
Two Cases of Chronic Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration with Parkinsonian Symptoms
 Two Cases of Chronic Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration with Parkinsonian Symptoms Won Chul Shin, Kang Ju Sung, Yong Woo Noh, Bon Dae Ku, M.D*., Dae-Il Chang, Kyung-Cheon Chung Department of Neurology,
Two Cases of Chronic Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration with Parkinsonian Symptoms Won Chul Shin, Kang Ju Sung, Yong Woo Noh, Bon Dae Ku, M.D*., Dae-Il Chang, Kyung-Cheon Chung Department of Neurology,
Wilson's Disease. A Guide. An explanation of what Wilson's disease is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
 A Guide An explanation of what Wilson's disease is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment What is Wilson's disease?... 4 Why does the body contain copper?... 4 What causes Wilson s disease?... 5 Are males
A Guide An explanation of what Wilson's disease is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment What is Wilson's disease?... 4 Why does the body contain copper?... 4 What causes Wilson s disease?... 5 Are males
Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161,
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson Disease: An Update
 AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson Disease: An Update Eve A. Roberts 1 and Michael L. Schilsky 2 This guideline has been approved by the American Association for the Study of Liver
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson Disease: An Update Eve A. Roberts 1 and Michael L. Schilsky 2 This guideline has been approved by the American Association for the Study of Liver
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Regression of Nodular Liver Lesions in Wilson's Disease
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Regression of Nodular Liver Lesions in Wilson's Disease D. Kozic, M. Svetel, I. Petrovic,
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Regression of Nodular Liver Lesions in Wilson's Disease D. Kozic, M. Svetel, I. Petrovic,
Wilson's disease: the problem of delayed
 692 University Department of Medicine and the Department of Neurology, Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, UK J M Walshe M Yealland Correspondence to: Dr Walshe, The Department of Neurology, The Middlesex
692 University Department of Medicine and the Department of Neurology, Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, UK J M Walshe M Yealland Correspondence to: Dr Walshe, The Department of Neurology, The Middlesex
Editorial: Is Heterozygosity for a Wilson s Disease Gene Defect an Important Underlying Cause of Infantile and Childhood Copper Toxicosis Syndromes?
 The Journal of Trace Elements in Experimental Medicine 13:249 254 (2000) Editorial: Is Heterozygosity for a Wilson s Disease Gene Defect an Important Underlying Cause of Infantile and Childhood Copper
The Journal of Trace Elements in Experimental Medicine 13:249 254 (2000) Editorial: Is Heterozygosity for a Wilson s Disease Gene Defect an Important Underlying Cause of Infantile and Childhood Copper
A Case Report of a Patient with Wilson s Disease and Coincidental Sarcoidosis
 IBIMA Publishing International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/ijcrm/ijcrm.html Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 221927, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2014. 221927 Case Report
IBIMA Publishing International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/ijcrm/ijcrm.html Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 221927, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2014. 221927 Case Report
Pediatric Wilson s disease: findings in different presentations. A cross-sectional study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2018.0210230718 Pediatric Wilson s disease: findings in different presentations. A cross-sectional study Şükrü Güngör I, Mukadder Ayşe Selimoğlu II, Fatma İlknur
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2018.0210230718 Pediatric Wilson s disease: findings in different presentations. A cross-sectional study Şükrü Güngör I, Mukadder Ayşe Selimoğlu II, Fatma İlknur
Wilson disease (WD; hepatolenticular degeneration) AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES A Practice Guideline on Wilson Disease. Preamble.
 Correction The following acknowledgement was inadvertently omitted from A Practice Guideline on Wilson Disease by Eve A. Roberts and Michael L. Schilsky (HEPATOLOGY 2003;37:1475-1492): This Guideline was
Correction The following acknowledgement was inadvertently omitted from A Practice Guideline on Wilson Disease by Eve A. Roberts and Michael L. Schilsky (HEPATOLOGY 2003;37:1475-1492): This Guideline was
variant led to a premature stop codon p.k316* which resulted in nonsense-mediated mrna decay. Although the exact function of the C19L1 is still
 157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
shortening in the bilateral globus pallidus. Another one had hyperintensity in the bilateral putamen, caudate nuclei, and substantia nigra on T 2
 Magn Reson Med Sci 2018; 17; 73 79 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0145 Published Online: May 18, 2017 MAJOR PAPER Magnetic Susceptibility Changes in the Basal Ganglia and Brain Stem of Patients with Wilson s
Magn Reson Med Sci 2018; 17; 73 79 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0145 Published Online: May 18, 2017 MAJOR PAPER Magnetic Susceptibility Changes in the Basal Ganglia and Brain Stem of Patients with Wilson s
Genotype phenotype correlation in Wilson s disease within families-a report on four south Indian families
 Online Submissions: wjg.wjgnet.com World J Gastroenterol 2008 August 7; 14(29): 4672-4676 wjg@wjgnet.com World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 1007-9327 doi:10.3748/wjg.14.4672 2008 The WJG Press. All
Online Submissions: wjg.wjgnet.com World J Gastroenterol 2008 August 7; 14(29): 4672-4676 wjg@wjgnet.com World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 1007-9327 doi:10.3748/wjg.14.4672 2008 The WJG Press. All
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM. Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
ADULT-ONSET (INFRATENTORIAL) LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY as PRESENTING MANIFESTATION of ERDHEIM-CHESTER DISEASE
 ADULT-ONSET (INFRATENTORIAL) LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY as PRESENTING MANIFESTATION of ERDHEIM-CHESTER SEASE GIULIO CAVALLI, M.D. INTERNAL MECINE AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY IRCCS SAN RAFFAELE HOSPITAL VITA-SALUTE
ADULT-ONSET (INFRATENTORIAL) LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY as PRESENTING MANIFESTATION of ERDHEIM-CHESTER SEASE GIULIO CAVALLI, M.D. INTERNAL MECINE AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY IRCCS SAN RAFFAELE HOSPITAL VITA-SALUTE
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
An approach to movement disorders. Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London
 An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL
 A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
Insomnia as a Rare Neuropsychiatric Presentation of Wilson Disease
 CASE REPORT Insomnia as a Rare Neuropsychiatric Presentation of Wilson Disease Pang N 1,2, Mat-Rosly M 2, Mohamed S 2 1 Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra
CASE REPORT Insomnia as a Rare Neuropsychiatric Presentation of Wilson Disease Pang N 1,2, Mat-Rosly M 2, Mohamed S 2 1 Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra
Wilson disease is an autosomal recessive disorder. Long-Term Exclusive Zinc Monotherapy in Symptomatic Wilson Disease: Experience in 17 Patients
 Long-Term Exclusive Zinc Monotherapy in Symptomatic Wilson Disease: Experience in 17 Patients Francisca H. H. Linn, 1-3 Roderick H. J. Houwen, 4 Jan van Hattum, 5 Stefan van der Kleij, 4 and Karel J. van
Long-Term Exclusive Zinc Monotherapy in Symptomatic Wilson Disease: Experience in 17 Patients Francisca H. H. Linn, 1-3 Roderick H. J. Houwen, 4 Jan van Hattum, 5 Stefan van der Kleij, 4 and Karel J. van
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Fracture in a Young Male Patient Leading to the Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case Report
 J Bone Metab 2015;22:33-37 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2015.22.1.33 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Case Report Fracture in a Young Male Patient Leading to the Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case
J Bone Metab 2015;22:33-37 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2015.22.1.33 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Case Report Fracture in a Young Male Patient Leading to the Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case
Chapter 11 summary definitief ineke brands.indd :57:59
 chapter 11 Summary chapter 11 Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus are associated with altered brain function, a complication referred to as diabetic encephalopathy. Previous studies have shown that
chapter 11 Summary chapter 11 Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus are associated with altered brain function, a complication referred to as diabetic encephalopathy. Previous studies have shown that
Cranial MR findings in Wilson's disease
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 02841851 (Print) 16000455 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Cranial MR findings in Wilson's disease I. Saatci, M. Topcu, F. F. Baltaoglu, G. Köse,
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 02841851 (Print) 16000455 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Cranial MR findings in Wilson's disease I. Saatci, M. Topcu, F. F. Baltaoglu, G. Köse,
MRI OF THE THALAMUS. Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI
 1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
Wilson Disease Watch. January-June vol 1
 Wilson Disease Watch January-June 2011. vol 1 -New articles : Summary and comments. - Minutes of EuroWilson Network meeting 2011 -Minutes of Patient Representatives Meeting 2011 - Presentation of Rare
Wilson Disease Watch January-June 2011. vol 1 -New articles : Summary and comments. - Minutes of EuroWilson Network meeting 2011 -Minutes of Patient Representatives Meeting 2011 - Presentation of Rare
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Diagnosis of Wilson Disease in Young Children: Molecular Genetic Testing and a Paradigm Shift from the Laboratory Diagnosis
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2012.15.4.197 Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition 2012 December 15(4):197-209 Invited Review PGHN Diagnosis of Wilson Disease
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2012.15.4.197 Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition 2012 December 15(4):197-209 Invited Review PGHN Diagnosis of Wilson Disease
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
Brief Communication Nuclear Medicine. In-Uk Song, MD 1, Sang-Won Ha, MD 2, Young-Soon Yang, MD 2, Yong-An Chung, MD 3 INTRODUCTION
 Brief Communication Nuclear Medicine http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.5.967 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(5):967-972 Differences in Regional Glucose Metabolism of the Brain
Brief Communication Nuclear Medicine http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.5.967 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(5):967-972 Differences in Regional Glucose Metabolism of the Brain
Dementia Update. October 1, 2013 Dylan Wint, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health Las Vegas, Nevada
 Dementia Update October 1, 2013 Dylan Wint, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health Las Vegas, Nevada Outline New concepts in Alzheimer disease Biomarkers and in vivo diagnosis Future trends
Dementia Update October 1, 2013 Dylan Wint, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health Las Vegas, Nevada Outline New concepts in Alzheimer disease Biomarkers and in vivo diagnosis Future trends
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
 Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Hepatopulmonary Syndrome as the First Manifestation of Wilson Disease
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2015;5(1):37-41 Hepatopulmonary Syndrome as the First Manifestation of Wilson Disease Durjoy Lahiri, Rakesh Agarwal, Debdeep Mondal, Manoj Kumar Roy, Nirmalendu Sarkar, Jotideb
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2015;5(1):37-41 Hepatopulmonary Syndrome as the First Manifestation of Wilson Disease Durjoy Lahiri, Rakesh Agarwal, Debdeep Mondal, Manoj Kumar Roy, Nirmalendu Sarkar, Jotideb
ABSTRACT. Iraqi Journal of. *DR. RababFarhanThijeel **DR.Halasameh ***DR.AhmedKhalil. Issue1 Vol.5
 *DR. RababFarhanThijeel **DR.Halasameh ***DR.AhmedKhalil ABSTRACT Background: Wilson'sdiseaseorhepatolenticulardegeneration isatreatable inheritedmetabolic diseaseinwhichcopperaccumulatesintissues,thesearemainlyliver
*DR. RababFarhanThijeel **DR.Halasameh ***DR.AhmedKhalil ABSTRACT Background: Wilson'sdiseaseorhepatolenticulardegeneration isatreatable inheritedmetabolic diseaseinwhichcopperaccumulatesintissues,thesearemainlyliver
ATP7B mutations in families in a predominantly southern Indian cohort of Wilson s disease patients
 Original Article ATP7B mutations in families in a predominantly southern Indian cohort of Wilson s disease patients S Santhosh, R V Shaji,* C E Eapen, V Jayanthi, S Malathi, # M Chandy,* M Stanley, S Selvi,
Original Article ATP7B mutations in families in a predominantly southern Indian cohort of Wilson s disease patients S Santhosh, R V Shaji,* C E Eapen, V Jayanthi, S Malathi, # M Chandy,* M Stanley, S Selvi,
Connections of basal ganglia
 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders
 Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
Financial Disclosure
 Benign Liver Masses Adil Abdalla, MBBS Creighton University-CHI Health August 25, 2018 Financial Disclosure Nothing to disclose Financial Disclosure 1 Objectives To assess patients with benign liver tumors
Benign Liver Masses Adil Abdalla, MBBS Creighton University-CHI Health August 25, 2018 Financial Disclosure Nothing to disclose Financial Disclosure 1 Objectives To assess patients with benign liver tumors
The Perils Of Excess : Wilson s Disease ----A Copper Connection
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. IX (May. 2016), PP 17-21 www.iosrjournals.org The Perils Of Excess : Wilson s Disease
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. IX (May. 2016), PP 17-21 www.iosrjournals.org The Perils Of Excess : Wilson s Disease
Huntington s Disease COGS 172
 Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
NEURO-IMAGING IN HUNTINGTON DISEASE (HD) A RARE PROGRESSIVE NEURO-DEGENERATIVE DISORDER
 NEURO-IMAGING IN HUNTINGTON DISEASE (HD) A RARE PROGRESSIVE NEURO-DEGENERATIVE DISORDER *Vipin Kumar Bakshi and DrMool Chand Baberwal Department of Radio-diagnosis, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College & Hospital,
NEURO-IMAGING IN HUNTINGTON DISEASE (HD) A RARE PROGRESSIVE NEURO-DEGENERATIVE DISORDER *Vipin Kumar Bakshi and DrMool Chand Baberwal Department of Radio-diagnosis, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College & Hospital,
Case Report Fulminant Wilson s Disease Managed with Plasmapheresis as a Bridge to Liver Transplant
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 672985, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/672985 Case Report Fulminant Wilson s Disease Managed with Plasmapheresis as a Bridge to Liver Transplant Talal Hilal
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 672985, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/672985 Case Report Fulminant Wilson s Disease Managed with Plasmapheresis as a Bridge to Liver Transplant Talal Hilal
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
Can Tango Help Improve Quality of Life for Patients with Parkinson s Disease?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Can Tango Help Improve Quality of Life
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Can Tango Help Improve Quality of Life
Clinical aspects of pterin disorders
 Clinical aspects of pterin disorders Thomas Opladen, MD University Children s Hospital Department of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Heidelberg Germany Introductory words Brain function depends on the capacity
Clinical aspects of pterin disorders Thomas Opladen, MD University Children s Hospital Department of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Heidelberg Germany Introductory words Brain function depends on the capacity
Evaluation of Wilson Disease With 18F-FDG PET/CT
 Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCE ISSN 2171-6625 DOI: 10.21767/2171-6625.1000223 Abstract Evaluation of Wilson Disease With 18F-FDG PET/CT Wilson disease
Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSCIENCE ISSN 2171-6625 DOI: 10.21767/2171-6625.1000223 Abstract Evaluation of Wilson Disease With 18F-FDG PET/CT Wilson disease
30- liver Transplantation for Inborn Errors of Metabolism*
 30- liver Transplantation for Inborn Errors of Metabolism* T. E. STARZL, C. W. PUTNAM and L. KOEP In this report, we propose to show how liver transplantation has been used to treat a number of inborn
30- liver Transplantation for Inborn Errors of Metabolism* T. E. STARZL, C. W. PUTNAM and L. KOEP In this report, we propose to show how liver transplantation has been used to treat a number of inborn
1.1. Parkinson disease
 1.TREMOR 1.1. Parkinson disease Parkinson Disease Progressive disorder: tremor, rigidity, and slowness of movements Neuronal loss of the substantia nigra Non motor features (dementia and dysautonomia),
1.TREMOR 1.1. Parkinson disease Parkinson Disease Progressive disorder: tremor, rigidity, and slowness of movements Neuronal loss of the substantia nigra Non motor features (dementia and dysautonomia),
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Wilson Disease Patient Lab Tracker
 Wilson Disease Patient Lab Tracker June, 2006 WDA Medical Advisory Committee Michael L. Schilsky M.D., Chair WILSON DISEASE PATIENT LAB TRACKER TREATMENT AND MONITORING OF WILSON DISEASE The following
Wilson Disease Patient Lab Tracker June, 2006 WDA Medical Advisory Committee Michael L. Schilsky M.D., Chair WILSON DISEASE PATIENT LAB TRACKER TREATMENT AND MONITORING OF WILSON DISEASE The following
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION
 Dystonia-Predominant Adult-Onset Huntington Disease Association Between Motor Phenotype and Age of Onset in Adults ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Elan D. Louis, MD, MS; Karen E. Anderson, MD; Carol Moskowitz, RN;
Dystonia-Predominant Adult-Onset Huntington Disease Association Between Motor Phenotype and Age of Onset in Adults ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Elan D. Louis, MD, MS; Karen E. Anderson, MD; Carol Moskowitz, RN;
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Congential scoliosis in Wilson s disease: case report and review of the literature
 Li et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:71 CASE REPORT Open Access Congential scoliosis in Wilson s disease: case report and review of the literature Zheng Li, Xin Yu, Jianxiong Shen * and Jinqian Liang Abstract
Li et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:71 CASE REPORT Open Access Congential scoliosis in Wilson s disease: case report and review of the literature Zheng Li, Xin Yu, Jianxiong Shen * and Jinqian Liang Abstract
Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic resonance imaging: a case report
 Nishibayashi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:194 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic
Nishibayashi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:194 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders
 Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
+ Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS)
 + Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) Le point de vue du neurologue n Gaëtan Garraux n CHU de Liège n www.movere.org + Background FXTAS was first described by Hagerman and coll. (2001) as they collected
+ Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) Le point de vue du neurologue n Gaëtan Garraux n CHU de Liège n www.movere.org + Background FXTAS was first described by Hagerman and coll. (2001) as they collected
Presentation of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 3 Mimicking Wilson Disease: Molecular Genetic Diagnosis and Response to Treatment
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2015.18.3.202 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2015 September 18(3):202-208 Case Report PGHN Presentation of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2015.18.3.202 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2015 September 18(3):202-208 Case Report PGHN Presentation of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic
