In 1912, a British neurologist, Samuel Wilson, described
|
|
|
- Byron Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neurologic Wilson disease: case series on a diagnostic and therapeutic emergency Romeo V. Porlas Jr, MD; Lennie Lynn C. de Castillo, MD; Carissa Paz C. Dioquino, MD Introduction Wilson disease is a rare genetic disease causing pathologic deposition of copper in the liver, brain, cornea, kidney, and cardiac muscles. Presented are two cases of neurologic Wilson disease with progressive movement disorder and Kayser-Fleischer rings with low serum copper, low ceruloplasmin, and increased 4-hour urine copper against a background of normal transaminases. Cranial imaging revealed symmetric basal ganglia hyperintensities in T/FLAIR. More often than not, these cases go unnoticed and misdiagnosed because of its rarity and varied presentation. Extensive workup is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. As for management, the earlier the intervention is initiated, the better prognosis would be for recovery. There are several treatment options and should be tailored to every patient with neurologic Wilson disease. Neurologic Wilson disease is considered as a copper toxicity; immediate diagnostic evaluation and early treatment initiation is a must. 8, AICH Servier Group Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 8;: Keywords: copper toxicity; Kayser-Fleischer rings; progressive hepatolenticular degeneration; Wilson disease Author affiliations: Department of Neurosciences, College of Medicine and Philippine General Hospital, University of the Philippines, Manila (Romeo Porlas, Lennie Lynn C. de Castillo, Carissa Paz C. Dioquino); National In 9, a British neurologist, Samuel Wilson, described a neurologic disorder with pathologic findings of degeneration of the lenticular nucleus in the brain and hepatocytes in the liver. It was then called progressive hepatolenticular degeneration, better known by its eponym, Wilson disease (WD).,,4 WD is attributed to a rare autosomal recessive genetic defect on ATP7B, a metal-transporting P-type adenosine triphosphate on chromosome 3q4.3. Deficiency or absence of the transporter protein results to decreased biliary excretion of copper and thereby excessive deposition of copper in the liver, central nervous system, cornea, kidney, and cardiac muscles. 3 WD has a prevalence rate of 5 to 3 cases per million, qualifying as a rare disease based on the criterion of European Commission on Public Health and Institute of Human Genetics. 4 The manifestations of WD are more likely to be hepatic in early childhood, and neurologic in adolescents and young adults. WD has varied presentations, classified into three movement disorder syndromes:. Dystonia (dystonic postures and choreoathethosis). Ataxia (ataxia with postural and intentional tremors) 3. Parkinsonian symptoms (hypokinesia, rigidity, and resting tremors) Poison Management and Control Center, Philippine General Hospital, University of the Philippines, Manila, Philippines (Carissa Paz C. Dioquino) Address for correspondence: Romeo V. Porlas, Jr, Sampaloc, Manila, National Capital Region, Philippines ( rom96@yahoo.com) Copyright 8 AICH Servier Group. All rights reserved 34
2 Emphasis should be given to reviewing vignettes, diagnostics, and treatment of patients in order to catch these rare conditions early and subsequently initiate treatment. We present two vignettes of WD. Clinical vignettes A -year-old female presented with -month history of slowing of movement and difficulty writing legibly, with occasional reports of postural tremors, right more than the left and blurring of vision. She developed slurring of speech and involuntary hand movements. Pertinent neurologic examination revealed a Mini- Mental Status Examination (MMSE) score of 9/3, with deficit in attention and choreiform movements in upper and lower extremities coupled with athetoid movements of the hands. Classic wing-beating tremors were observed in the right arm. On passive range of motion, there was mild rigidity, right more than the left, and bradykinesia noted on rapid fine movements of fingers. Generalized hyperreflexia and tendency to fall backward on walking were observed. Relevant neurologic findings were: MMSE of 7/8, with deficit in recall. Poor gutturals and tongue fasciculations were noted on cranial nerve examination. There was marked atrophy of the intrinsic muscles of the hand and posterior leg muscles with paradoxical hypertrophy of triceps and quadriceps. Dystonic inversion posturing of both feet was notable on walking. The patient also had generalized rigidity and kinetic tremors, more prominent on the right than the left. Diagnostic workup The two cases were worked up for WD and can be classified differently; the first case falls into the ataxic type with parkinsonian symptoms and the second case fits the dystonic with parkinsonian symptoms (Table I). 5,6 Both of the patients were subjected to slit-lamp examination revealing the presence of Kayser-Fleischer rings (Figure ). A complete hepatic workup was done, revealing normal liver function: transaminases and clotting factors but with gross structural abnormalities noted on sonography (Table II). Diagnostic workup for copper accumulation revealed low serum copper, A -year-old female presented initially with spontaneous abortion, and then had slurring of speech and stiffness of the jaw, with occasional reports of cramps of facial muscles. She then developed tremors and stiffening of right extremities, which progressed to involve the contralateral side with accompanying weakness over a span of 8 months. Over the succeeding 4 months, there was progression of stiffness causing posturing of legs and difficulty ambulating, and worsening kinetic tremors. There were also episodes of freezing of gait and uncontrolled grin. Figure. Kayser-Fleischer rings, copper deposition over Descemet s membrane. Kayser-Fleischer rings were said to be present in 5% of those with hepatic presentation and 99% of neurologic presentation. Vignette Age/sex Time to diagnosis / Female / Female months 8 months Presenting symptoms Worsening handwriting Slurring of speech Initial diagnosis Essential tremors Spasmodic dysphonia 34 Neurologic progression Classification UWDRS Micrographia tremors imbalance choreoathetoid movements Dysphonia tremors rigidity dystonia N (Ataxic with Parkinsonian) N (Dystonic) Table I. Clinical vignette summary; Wilson disease phenotypic classification; unified Wilson s Disease Rating Scale (UWDRS). I II 3 III 3 I II 8 III 54
3 Neurologic Wilson disease - Porlas et al Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience - Vol. No low ceruloplasmin, and increased urinary excretion of copper. 7, 8, 9, Genetic testing was not done on these patients. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain did not reveal the typical double panda sign but showed symmetrical T/FLAIR hyperintensities over the putamen, caudate and thalami nucleus (Figure and Figure 3)., Both findings were highly suggestive of mineral deposition. Furthermore, following the scoring by Leipzig et al, the two vignettes are definite cases of WD. 8,3,6 Because of the rarity of the disease, it is not cost-effective to initiate population-based screening. Screening however should be compulsory for patients presenting with unexplained neurological Vignette Slit lamp examination HoloAbdominal ultrasound Liver function tests Coagulation studies Serum copper Serum ceruloplasmin 4-hour urine copper Leipzig score (+) Kayser- Fleischer rings Normal sized liver with diffuse parenchymal disease hyperechoic solid nodule, segment IV of the liver AST 5 (nv 5-4) ALT (nv 4-54) PT 4./3./.96/. PTT 9.5/ µg/ml (nv µg/ ml) <. (nv.-58. mg/dl) 5 µg/ml (nv 5-6 µg/specimen) 8 (+) Kayser- Fleischer rings Cirrhotic liver changes with multiple hepatic nodules AST 7 (nv -35) ALT 5 (nv -35) PT 4./.7/83./. PTT 4/3.4.3 µg/ml (nv µg/ ml) 3. (nv.- 6. mg/dl) 43 µg/ml (nv 5-6 µg/specimen) 8 Serum ceruloplasmin: alpha-globulin copper binding protein, cleaved from apoceruloplasmin when copper is introduced by the ATP7B transporter protein 8th International Meeting on Wilson Disease Scoring System (Leipzig Score) Clinical symptoms and signs with initial diagnostics Kayser-Fleischer rings Present Additional workup and genetic testing Liver copper (in the absence of cholestasis) >5x of upper limit (>4 mol/g).8-4mol/g Normal (<.8 mol/g) Rhodanine-positive granules - Neurologic symptoms Severe Mild Serum ceruloplasmin <. g/l.. g/l Normal (>. g/l) Coombs-negative hemolytic anemia Present Total score 4 or more: Diagnosis established 3: Diagnosis possible, more tests needed : Diagnosis very unlikely Urinary copper (in the absence of acute hepatitis) Normal, but > 5x of upper limit after chelation > x of upper limit -x of upper limit Normal Mutation analysis On both chromosomes detected On chromosome detected No mutation detected Table II. Diagnostic examination summary; 8th International Meeting on Wilson disease scoring system
4 A B C D E A B C D E Figure. Representative images of T-weighted sequence of Case. A. Upper pontine and lower midbrain axial cut; there are hyperintensities over the dorsal region B. Upper midbrain axial cut; there are confluent hyperintensities over the midbrain tegmentum C. Sylvian fissure axial cut; there are prominent hyperintensities over the lateral thalami, caudate, and putaminal region D. Insular region axial cut; extensive bilateral hyperintensities over the thalami and basal ganglia are seen E. Corona radiata axial cut; bilateral centum semiovale were spared of any signal abnormality disease with or without associated liver disease. WD must be distinguished from mimickers such as essential tremor, young-onset Parkinson s disease, generalized dystonia, and other rare movement disorders like Huntington disease, Hallervorden-Spatz disease, Figure 3. Representative images of T-weighted sequences of Case. A. Upper pontine axial cut; there are hyperintensities over the dorsal pontine region B. Upper midbrain axial cut; there is normal looking red nucleus with hyperintensities over the area of substantia nigra C. Sylvian fissure axial cut; there are prominent hyperintensities over the putamen with areas of magnetic susceptibility artifacts, left more than the right D. Lateral ventricle region axial cut, continuous extensive hyperintensities over the putamen and caudate are seen E. Corona radiate axial cut, bilateral centum semiovale were spared of any signal abnormality idiopathic torsion dystonia, chorea-acanthocytosis and benign familial chorea. WD is therefore a diagnostic emergency, needing a complete and immediate work-up. Drug Mechanism of action Starting dose D-penicillamine Trientine Zinc salts Tetrathiomolybdate Chelator, acts by increasing urinary excretion of copper Chelator, acts by increasing urinary excretion of copper Induces intestinal cell metallothionein that prevents absorption of food cooper and salivary copper Acts by forming a tripartite complex with cooper and protein, preventing copper absorption 5 mg/ tab tab every 6 hours 75-5 mg in divided doses 5 mg/ tab tab thrice a day mg/ tab tab thrice a day Administration given hour before or hours meals given hour before or hours meals taken on an empty stomach given with food, higher doses are required if given without Table III. Summary of treatment options for neurologic Wilson disease. Side effects Effect on WD Monitoring Rash, immune complex nephropathy, thrombocytopenia, leucocytopenia, systemic lupus erythematosus Proteinuria, bone marrow suppression and autoimmune disease, gastric disturbance Gastric disturbances: bloating and nausea Bone marrow suppression 5% chance of neurologic worsening 5% chance of neurologic worsening during the initial course of medications Decoppering effect is slow, taking 4-8 months to be effective Good only for short-term use (8 weeks) 4-hour urine function tests 4-hour urine function tests, creatinine and urinalysis 4-hour urine function tests, creatinine and urinalysis Complete function tests 344
5 Neurologic Wilson disease - Porlas et al Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience - Vol. No Management As for the treatment, definitive treatment includes liver transplantation, especially for those with acute hepatitis or fulminant hepatic failure. For those with serious and debilitating neurologic sequelae, the best option is either to increase urinary excretion of cooper directly ie, D-penicillamine and trientine or block gastrointestinal absorption of copper ie, zinc acetate/salts and tetrathiomolybdate (Table III). 4,5,6,7 For both cases, low copper diet was a mainstay of treatment. Zinc supplementation was also initiated, with subsequent noting of remarkable improvements in speech, tremors, and stiffening of extremities. The first case underwent D-penicillamine treatment with slow uptitration of the drug to avoid hematologic consequences and to monitor for paradoxical neurological deterioration. As for the second case, the patient was maintained on zinc supplementation because of relatively severe baseline neurologic status and high risk for paraxodical neurologic worsening. Treatment should still be individualized since no two patients with WD are the same. 8,5,6 For patients with debilitating movement disorder refractory to chelation and medical treatment, botulinum toxin injection maybe offered. Screening of siblings of the patient and monitoring of their serum ceruloplasmin is also a big part of management. 8 Early intervention signifies better prognosis, thus can be considered as a therapeutic emergency as well. Synthesis Educating medical doctors about this neurologic condition and having a high index of suspicion can improve treatment of this debilitating condition. Familiarization of this rare genetic conditions may also pave way for future researches to ascertain the prevalence, to facilitate detection and to improve outcomes. o Disclosure/Acknowledgments: Dr Porlas, Dr de Castillo, and Dr Dioquino have nothing to disclose. REFERENCES. Walshe JM. History of Wilson disease: a personal account. In: Członkowska A, Schilsky ML, eds. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Volume 4 (3rd series), Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier; 7.. Lorincz MT. Neurologic Wilson s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. ;84: doi:./j x. 3. Wu F, Wang J, Pu C, Qiao L, Jiang C. Wilson s disease: a comprehensive review of the molecular mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 5;6(3): doi:.339/ijms Mak CM, Lam CW. Diagnosis of Wilson s disease: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 8;45(3):63-9. doi:.8/ Volpert HM, Pfeiffenberger J, Gröner JB, Stremmel W, Gotthardt DN, Schäfer M, Weiss KH, Weiler M. Comparative assessment of clinical rating scales in Wilson s disease. BMC Neurol. 7;7():4. doi:.86/ s Czlonkowska A, Tarnacka B, Möller JC, et al. Unified Wilson s Disease Rating Scale - a proposal for the neurological scoring of Wilson s disease patients. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 7;4():-. 7. Bandmann O, Weiss KH, Kaler SG. Wilson s disease and other neurological copper disorders. Lancet Neurol. 5;4():3-3. doi:.6/ S474-44(4) Rodriguez-Castro KI, Hevia-Urrutia FJ, Sturniolo GC. Wilson s disease: A review of what we have learned. World J Hepatol. 5;7(9): doi:.454/wjh.v7.i Ala A, Walker AP, Ashkan K, Dooley JS, Schilsky ML. Wilson s disease. Lancet. 7;369(9559): Medici V, Rossaro L and Sturniolo GC. Wilson Disease A practical approach to diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Dig Liver Dis. 7;39: Członkowska A, Litwin T, Chabik G. Wilson s disease neurologic features. In: Członkowska A, Schilsky ML, eds. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Volume 4 (3rd series), Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier; 7.. Cetlin RS, Rodrigues GR, Pena-Pereira MA, Oliveira DS, Souza CP, Tumas V. Teaching video neuroimages: excessive grinning in Wilson disease. Neurology. 9;73(4):e73. doi:./wnl.b3e38bacef. 3. Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, Mieli-Vergani G, Tanner S, Sternlieb I, Schilsky M, Cox D, Berr F. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver Int. 3;3(3): Brewer GJ. Wilson s Disease. In: Frucht SJ, ed. Movement Disorder Emergencies: Diagnosis and Treatment. Totowa, NJ: Human Press; Brewer, GJ. Zinc acetate for the treatment of Wilson s disease. Exp Opin Pharmacother. ;(9): Brewer GJ, Hill GM, Prasad AS, Cossack ST, and Rabbani P. Oral zinc therapy for Wilson s Disease. Ann Intern Med. 983;99(3): doi.org/.736/ Brewer GJ. Zinc and tetrathiomolybdate for the treatment of Wilson s disease and the potential efficacy of anticopper therapy in a wide variety of diseases. Metallomics. 9;(3):99-6. doi:.39/ b964g. 8. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wilson s Disease. J Hepatol. 56(3), org/.6/j.jhep
Wilson Disease. Maggie Benson Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Physical Therapy
 Wilson Disease Maggie Benson Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Physical Therapy What is Wilson Disease? Wilson Disease (WD)= hepatolenticular degeneration Hereditary disorder Autosomal recessive
Wilson Disease Maggie Benson Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Physical Therapy What is Wilson Disease? Wilson Disease (WD)= hepatolenticular degeneration Hereditary disorder Autosomal recessive
NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION
 E:/Biomedica Vol.4 Jan. Jun. 008/Bio-R (A) NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION M. ATHAR JAVED, SAMAR ZIA, SARA ASHRAF AND SHAHID MEHMOOD Department of Neurology,
E:/Biomedica Vol.4 Jan. Jun. 008/Bio-R (A) NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION M. ATHAR JAVED, SAMAR ZIA, SARA ASHRAF AND SHAHID MEHMOOD Department of Neurology,
Metabolic Liver Disease
 Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
YES NO UNKNOWN PENETRANCE ACTIONABILITY SIGNIFICANCE/BURDEN OF DISEASE NEXT STEPS. YES (Proceed to Stage II) YES ( 1 of above)
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: ATP7B DISORDER: Wilson Disease HGNC ID: 870 OMIM ID: 277900 ACTIONABILITY 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic review,
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: ATP7B DISORDER: Wilson Disease HGNC ID: 870 OMIM ID: 277900 ACTIONABILITY 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic review,
Anna Członkowska 1,2*, Tomasz Litwin 1, Karolina Dzieżyc 1, Michal Karliński 1, Johan Bring 3 and Carl Bjartmar 4
 Członkowska et al. BMC Neurology (2018) 18:34 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-018-1039-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Characteristics of a newly diagnosed Polish cohort of patients with neurological manifestations
Członkowska et al. BMC Neurology (2018) 18:34 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-018-1039-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Characteristics of a newly diagnosed Polish cohort of patients with neurological manifestations
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Molecular Diagnosis and Prophylactic Therapy for Presymptomatic Chinese Patients With Wilson Disease
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Molecular Diagnosis and Prophylactic Therapy for Presymptomatic Chinese Patients With Wilson Disease Zhi-Ying Wu, MD, PhD; Min-Ting Lin, MD; Shen-Xing Murong, MD; Ning Wang, MD, PhD
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Molecular Diagnosis and Prophylactic Therapy for Presymptomatic Chinese Patients With Wilson Disease Zhi-Ying Wu, MD, PhD; Min-Ting Lin, MD; Shen-Xing Murong, MD; Ning Wang, MD, PhD
Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski
 Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski Basic Genetics Wilson Disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of impaired copper metabolism. The Wilson Disease gene is composed
Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski Basic Genetics Wilson Disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of impaired copper metabolism. The Wilson Disease gene is composed
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System
 Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
Professor Tim Anderson
 Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
 Title Mutational analysis for Wilson's disease Author(s) Seto, WK; Mak, CM; But, D; Hung, I; Lam, CW; Tam, S; Yuen, MF; Lai, CL Citation The Lancet, 2009, v. 374 n. 9690, p. 662 Issued Date 2009 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/77405
Title Mutational analysis for Wilson's disease Author(s) Seto, WK; Mak, CM; But, D; Hung, I; Lam, CW; Tam, S; Yuen, MF; Lai, CL Citation The Lancet, 2009, v. 374 n. 9690, p. 662 Issued Date 2009 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/77405
Wilson Disease - Our Experience
 Wilson Disease Our Experience Hussein Shamaly M.D.. Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit Pediatric Department Clalit Health Services French Hospital, Nazareth Key Concepts Wilson disease is more often considered
Wilson Disease Our Experience Hussein Shamaly M.D.. Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit Pediatric Department Clalit Health Services French Hospital, Nazareth Key Concepts Wilson disease is more often considered
*Department of pediatrics, Baghdad Medical College, University of Baghdad. **Children Welfare Teaching Hospital, Medical City, Baghdad.
 WILSON S THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE DISEASE IN CHILDREN MEDICAL JOURNAL Wilson s Disease in Children (Clinical Presentations & Diagnostic Difficulties) (Three years experience in Children Welfare Teaching
WILSON S THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE DISEASE IN CHILDREN MEDICAL JOURNAL Wilson s Disease in Children (Clinical Presentations & Diagnostic Difficulties) (Three years experience in Children Welfare Teaching
When the penny drops
 Department of Molecular Neuroscience, UCL Institute of Neurology, and National Hospital for Neurology & Neurosurgery, London, UK Correspondence to Dr Paola Giunti, Department of Molecular Neuroscience,
Department of Molecular Neuroscience, UCL Institute of Neurology, and National Hospital for Neurology & Neurosurgery, London, UK Correspondence to Dr Paola Giunti, Department of Molecular Neuroscience,
RESEARCH ARTICLE NEUROLOGICAL AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS OF WILSON DISEASE;
 RESEARCH ARTICLE NEUROLOGICAL AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS OF WILSON DISEASE; 1998-2005 A. Fallah MD Abstract Objective Wilson disease (WD) is an inherited copper metabolism dysfunction disease characterized
RESEARCH ARTICLE NEUROLOGICAL AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS OF WILSON DISEASE; 1998-2005 A. Fallah MD Abstract Objective Wilson disease (WD) is an inherited copper metabolism dysfunction disease characterized
Professor Tim Anderson
 Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Dystonia: Title. A real pain in the neck. in All the Wrong Places
 Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Original Article. Abstract
 Original Article Neurological Wilson Disease in children: a three years experience from Multan Nuzhat Noureen, Muhammad Tariq Rana Department of Paediatrics, Nishtar Hospital, Multan, Pakistan. Abstract
Original Article Neurological Wilson Disease in children: a three years experience from Multan Nuzhat Noureen, Muhammad Tariq Rana Department of Paediatrics, Nishtar Hospital, Multan, Pakistan. Abstract
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
WILSON S DISEASE; NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN PATIENTS PRESENTING TO TERTIARY CARE FACILITY
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.957/TPMJ/15.11 ORIGINAL PROF-11 WILSON S DISEASE; NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN PATIENTS PRESENTING TO TERTIARY CARE FACILITY 1. Assistant Professor Isra University
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.957/TPMJ/15.11 ORIGINAL PROF-11 WILSON S DISEASE; NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN PATIENTS PRESENTING TO TERTIARY CARE FACILITY 1. Assistant Professor Isra University
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Trientine for Wilson disease (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Trientine for Wilson disease (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170094P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information Specialised Commissioning
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Trientine for Wilson disease (all ages) NHS England Reference: 170094P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information Specialised Commissioning
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy?
 Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
NHS England. Evidence review: Trientine dihydrochloride for Wilson s disease
 NHS England Evidence review: Trientine dihydrochloride for Wilson s disease 1 NHS England Evidence review: Trientine dihydrochloride for Wilson s disease First published: October 2016 Updated: Prepared
NHS England Evidence review: Trientine dihydrochloride for Wilson s disease 1 NHS England Evidence review: Trientine dihydrochloride for Wilson s disease First published: October 2016 Updated: Prepared
Moving fast or moving slow: an overview of Movement Disorders
 Moving fast or moving slow: an overview of Movement Disorders Mini Medical School October 25, 2018 Heather Rigby, MD, FRCPC 2014 MFMER slide-1 2014 MFMER slide-2 Basal Ganglia Dysfunction - Movement Disorders
Moving fast or moving slow: an overview of Movement Disorders Mini Medical School October 25, 2018 Heather Rigby, MD, FRCPC 2014 MFMER slide-1 2014 MFMER slide-2 Basal Ganglia Dysfunction - Movement Disorders
Comparative assessment of clinical rating scales in Wilson s disease
 Volpert et al. BMC Neurology (2017) 17:140 DOI 10.1186/s12883-017-0921-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparative assessment of clinical rating scales in Wilson s disease Hanna M. Volpert 1, Jan Pfeiffenberger
Volpert et al. BMC Neurology (2017) 17:140 DOI 10.1186/s12883-017-0921-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparative assessment of clinical rating scales in Wilson s disease Hanna M. Volpert 1, Jan Pfeiffenberger
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Wilson disease an update for 2014 Enfermedad de Wilson. Actualización
 5 Congreso Argentino de Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición Pediátricas Wilson disease an update for 2014 Enfermedad de Wilson. Actualización Eve A. Roberts, M.D., M.A., FRCPC Division of Gastroenterology,
5 Congreso Argentino de Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición Pediátricas Wilson disease an update for 2014 Enfermedad de Wilson. Actualización Eve A. Roberts, M.D., M.A., FRCPC Division of Gastroenterology,
Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Movement Disorder Department
 Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Movement Disorder Department Hyperkinetic movement disorders Increase in muscle movements causing involuntary motion Tremor Dystonia
Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Movement Disorder Department Hyperkinetic movement disorders Increase in muscle movements causing involuntary motion Tremor Dystonia
WELCOME. Parkinson s 101 for the Newly Diagnosed. Today s Topic: Parkinson s Basics presented by Cari Friedman, LCSW
 WELCOME Parkinson s 101 for the Newly Diagnosed Today s Topic: Parkinson s Basics presented by Cari Friedman, LCSW Parkinson s Disease 101 Presenter for Today Cari Friedman, LCSW Patient and Family Service
WELCOME Parkinson s 101 for the Newly Diagnosed Today s Topic: Parkinson s Basics presented by Cari Friedman, LCSW Parkinson s Disease 101 Presenter for Today Cari Friedman, LCSW Patient and Family Service
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
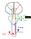 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161,
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
shortening in the bilateral globus pallidus. Another one had hyperintensity in the bilateral putamen, caudate nuclei, and substantia nigra on T 2
 Magn Reson Med Sci 2018; 17; 73 79 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0145 Published Online: May 18, 2017 MAJOR PAPER Magnetic Susceptibility Changes in the Basal Ganglia and Brain Stem of Patients with Wilson s
Magn Reson Med Sci 2018; 17; 73 79 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0145 Published Online: May 18, 2017 MAJOR PAPER Magnetic Susceptibility Changes in the Basal Ganglia and Brain Stem of Patients with Wilson s
PARKINSON S DISEASE 馬 萬 里. Chinese character for longevity (shou) Giovanni Maciocia
 PARKINSON S DISEASE Chinese character for longevity (shou) Giovanni Maciocia 馬 萬 里 PARKINSON'S DISEASE Parkinson's disease is a clinical syndrome characterized by impairment of movement, rigidity and tremor,
PARKINSON S DISEASE Chinese character for longevity (shou) Giovanni Maciocia 馬 萬 里 PARKINSON'S DISEASE Parkinson's disease is a clinical syndrome characterized by impairment of movement, rigidity and tremor,
An approach to movement disorders. Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London
 An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
Metabolic Liver Diseases
 Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Review Article Wilson's Disease: a review A. Hassan, F. Masood Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics*, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi.
 Review Article Wilson's Disease: a review A. Hassan, F. Masood Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics*, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. Introduction and Genetics Wilson's disease (WD; Hepatolenticular
Review Article Wilson's Disease: a review A. Hassan, F. Masood Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics*, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. Introduction and Genetics Wilson's disease (WD; Hepatolenticular
Wilson disease (WD; hepatolenticular degeneration) AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES A Practice Guideline on Wilson Disease. Preamble.
 Correction The following acknowledgement was inadvertently omitted from A Practice Guideline on Wilson Disease by Eve A. Roberts and Michael L. Schilsky (HEPATOLOGY 2003;37:1475-1492): This Guideline was
Correction The following acknowledgement was inadvertently omitted from A Practice Guideline on Wilson Disease by Eve A. Roberts and Michael L. Schilsky (HEPATOLOGY 2003;37:1475-1492): This Guideline was
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Magnetic resonance imaging findings in diagnosis and prognosis of Wilson disease
 Review Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in diagnosis and prognosis of Wilson disease Mehri Salari 1, Emad Fayyazi 1,2, Omid Mirmosayyeb 1,2 1 Isfahan Neurosciences Research Center, Alzahra Research
Review Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in diagnosis and prognosis of Wilson disease Mehri Salari 1, Emad Fayyazi 1,2, Omid Mirmosayyeb 1,2 1 Isfahan Neurosciences Research Center, Alzahra Research
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine
 International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 221927, 26 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2014.221927 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2014. Arnaoutoglou Marianthi, Kiryttopoulos
International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 221927, 26 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2014.221927 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2014. Arnaoutoglou Marianthi, Kiryttopoulos
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology
 Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Unexplained Hepatic, Neurologic or Psychiatric Symptoms?
 A Diagnostic Tool For Physicians Unexplained Hepatic, Neurologic or Psychiatric Symptoms? Think WILSON DISEASE. ALGORITHMS FOR ASSESSMENT OF WILSON DISEASE Table 1. Clinical Features in Patients with Wilson
A Diagnostic Tool For Physicians Unexplained Hepatic, Neurologic or Psychiatric Symptoms? Think WILSON DISEASE. ALGORITHMS FOR ASSESSMENT OF WILSON DISEASE Table 1. Clinical Features in Patients with Wilson
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Neuro Wilson s An Alien Presentation
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.1.RD3 Case Report ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Neuro Wilson s An Alien Presentation Sivakami R. Pradeepkumar 1, Ramesh Kumar Rudrappa 2, Sibhithran Rajakumar 3 1 Assistant
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.1.RD3 Case Report ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Neuro Wilson s An Alien Presentation Sivakami R. Pradeepkumar 1, Ramesh Kumar Rudrappa 2, Sibhithran Rajakumar 3 1 Assistant
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Wilson disease is an autosomal recessive disorder. Long-Term Exclusive Zinc Monotherapy in Symptomatic Wilson Disease: Experience in 17 Patients
 Long-Term Exclusive Zinc Monotherapy in Symptomatic Wilson Disease: Experience in 17 Patients Francisca H. H. Linn, 1-3 Roderick H. J. Houwen, 4 Jan van Hattum, 5 Stefan van der Kleij, 4 and Karel J. van
Long-Term Exclusive Zinc Monotherapy in Symptomatic Wilson Disease: Experience in 17 Patients Francisca H. H. Linn, 1-3 Roderick H. J. Houwen, 4 Jan van Hattum, 5 Stefan van der Kleij, 4 and Karel J. van
A Case Report of a Patient with Wilson s Disease and Coincidental Sarcoidosis
 IBIMA Publishing International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/ijcrm/ijcrm.html Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 221927, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2014. 221927 Case Report
IBIMA Publishing International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/ijcrm/ijcrm.html Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 221927, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2014. 221927 Case Report
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson Disease: An Update
 AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson Disease: An Update Eve A. Roberts 1 and Michael L. Schilsky 2 This guideline has been approved by the American Association for the Study of Liver
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson Disease: An Update Eve A. Roberts 1 and Michael L. Schilsky 2 This guideline has been approved by the American Association for the Study of Liver
Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in Wilson s Disease and Its Comparison with Other Laboratory Tests and Paraclinical Findings
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Mar 20; Vol 22 (No 1), Pp: 26 Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in Wilson s Disease and Its Comparison with Other Laboratory Tests and Paraclinical Findings Fatemeh Mahjoub*
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Mar 20; Vol 22 (No 1), Pp: 26 Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in Wilson s Disease and Its Comparison with Other Laboratory Tests and Paraclinical Findings Fatemeh Mahjoub*
2/18/ yo man with history of mild developmental delay and chorea of unclear etiology, with new complaints of speech difficulty
 18 yo man with history of mild developmental delay and chorea of unclear etiology, with new complaints of speech difficulty Audrey Foster-Barber UCSF Child Neurology February 18, 2011 Several years of
18 yo man with history of mild developmental delay and chorea of unclear etiology, with new complaints of speech difficulty Audrey Foster-Barber UCSF Child Neurology February 18, 2011 Several years of
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Differential Diagnosis of Hypokinetic Movement Disorders
 Differential Diagnosis of Hypokinetic Movement Disorders Dr Donald Grosset Consultant Neurologist - Honorary Professor Institute of Neurological Sciences - Glasgow University Hypokinetic Parkinson's Disease
Differential Diagnosis of Hypokinetic Movement Disorders Dr Donald Grosset Consultant Neurologist - Honorary Professor Institute of Neurological Sciences - Glasgow University Hypokinetic Parkinson's Disease
MULTI SYSTEM ATROPHY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Dipu Bhuyan 1, Rohit Kr. Chandak 2, Pankaj Kr. Patel 3, Sushant Agarwal 4, Debjanee Phukan 5
 MULTI SYSTEM ATROPHY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Dipu Bhuyan 1, Rohit Kr. Chandak 2, Pankaj Kr. Patel 3, Sushant Agarwal 4, Debjanee Phukan 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Dipu Bhuyan, Rohit Kr. Chandak, Pankaj Kr.
MULTI SYSTEM ATROPHY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Dipu Bhuyan 1, Rohit Kr. Chandak 2, Pankaj Kr. Patel 3, Sushant Agarwal 4, Debjanee Phukan 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Dipu Bhuyan, Rohit Kr. Chandak, Pankaj Kr.
An Approach to Patients with Movement Disorders
 An Approach to Patients with Movement Disorders Joaquim Ferreira, MD, PhD Laboratory of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics Faculty of Medicine University of Lisbon EDUCATIONAL TOOLS MDS video library
An Approach to Patients with Movement Disorders Joaquim Ferreira, MD, PhD Laboratory of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics Faculty of Medicine University of Lisbon EDUCATIONAL TOOLS MDS video library
Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson s disease
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
Wilson Disease Watch. January-June vol 1
 Wilson Disease Watch January-June 2011. vol 1 -New articles : Summary and comments. - Minutes of EuroWilson Network meeting 2011 -Minutes of Patient Representatives Meeting 2011 - Presentation of Rare
Wilson Disease Watch January-June 2011. vol 1 -New articles : Summary and comments. - Minutes of EuroWilson Network meeting 2011 -Minutes of Patient Representatives Meeting 2011 - Presentation of Rare
Headway Victoria Epilepsy and Parkinson s Centre
 Headway Victoria Epilepsy and Parkinson s Centre Parkinson s Overview and Medication Shannon Oatway Community Education/ Awareness Coordinator What is Parkinson s Disease? The basics It is a chronic and
Headway Victoria Epilepsy and Parkinson s Centre Parkinson s Overview and Medication Shannon Oatway Community Education/ Awareness Coordinator What is Parkinson s Disease? The basics It is a chronic and
Overview of Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation (NBIA) Disorders
 Overview of Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation (NBIA) Disorders What is NBIA? Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation is a group of inherited neurological disorders characterized by
Overview of Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation (NBIA) Disorders What is NBIA? Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation is a group of inherited neurological disorders characterized by
Wilson Disease Patient Lab Tracker
 Wilson Disease Patient Lab Tracker June, 2006 WDA Medical Advisory Committee Michael L. Schilsky M.D., Chair WILSON DISEASE PATIENT LAB TRACKER TREATMENT AND MONITORING OF WILSON DISEASE The following
Wilson Disease Patient Lab Tracker June, 2006 WDA Medical Advisory Committee Michael L. Schilsky M.D., Chair WILSON DISEASE PATIENT LAB TRACKER TREATMENT AND MONITORING OF WILSON DISEASE The following
Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation (STN-DBS)
 Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation (STN-DBS) A Neurosurgical Treatment for Parkinson s Disease Parkinson s Disease Parkinson s disease is a common neurodegenerative disorder that affects about
Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation (STN-DBS) A Neurosurgical Treatment for Parkinson s Disease Parkinson s Disease Parkinson s disease is a common neurodegenerative disorder that affects about
Case Report Fulminant Wilson s Disease Managed with Plasmapheresis as a Bridge to Liver Transplant
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 672985, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/672985 Case Report Fulminant Wilson s Disease Managed with Plasmapheresis as a Bridge to Liver Transplant Talal Hilal
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 672985, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/672985 Case Report Fulminant Wilson s Disease Managed with Plasmapheresis as a Bridge to Liver Transplant Talal Hilal
STEADY YOUR APPROACH TO TREMOR (OVERVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS)
 STEADY YOUR APPROACH TO TREMOR (OVERVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS) Karen M. Thomas D.O. Diplomate, ABPN Director of Movement Disorders Program Director of Comprehensive Parkinson s Disease Program Sentara
STEADY YOUR APPROACH TO TREMOR (OVERVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS) Karen M. Thomas D.O. Diplomate, ABPN Director of Movement Disorders Program Director of Comprehensive Parkinson s Disease Program Sentara
Regression of Nodular Liver Lesions in Wilson's Disease
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Regression of Nodular Liver Lesions in Wilson's Disease D. Kozic, M. Svetel, I. Petrovic,
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Regression of Nodular Liver Lesions in Wilson's Disease D. Kozic, M. Svetel, I. Petrovic,
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Wilson's Disease. A Guide. An explanation of what Wilson's disease is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
 A Guide An explanation of what Wilson's disease is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment What is Wilson's disease?... 4 Why does the body contain copper?... 4 What causes Wilson s disease?... 5 Are males
A Guide An explanation of what Wilson's disease is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment What is Wilson's disease?... 4 Why does the body contain copper?... 4 What causes Wilson s disease?... 5 Are males
Zinc monotherapy is effective in Wilson s disease patients with mild liver disease diagnosed in childhood: a retrospective study
 Ranucci et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2014, 9:41 RESEARCH Open Access Zinc monotherapy is effective in Wilson s disease patients with mild liver disease diagnosed in childhood: a retrospective
Ranucci et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2014, 9:41 RESEARCH Open Access Zinc monotherapy is effective in Wilson s disease patients with mild liver disease diagnosed in childhood: a retrospective
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders
 Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII
 463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
Data Collection Worksheets
 Data Collection Worksheets PhenX Measure: Antipsychotic Medication Extrapyramidal Side Effects (#661600) PhenX Protocol: Antipsychotic Medication Extrapyramidal Side Effects (#661601) Date of Interview/Examination/Bioassay
Data Collection Worksheets PhenX Measure: Antipsychotic Medication Extrapyramidal Side Effects (#661600) PhenX Protocol: Antipsychotic Medication Extrapyramidal Side Effects (#661601) Date of Interview/Examination/Bioassay
Pathological Fracture of Femoral Neck Leading to a Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature
 J Bone Metab 2017;24:135-139 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2017.24.2.135 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Case Report Pathological Fracture of Femoral Neck Leading to a Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case
J Bone Metab 2017;24:135-139 https://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2017.24.2.135 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Case Report Pathological Fracture of Femoral Neck Leading to a Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case
Anterior Segment Disease and the Systemic Link Mile Brujic, OD, FAAO
 Anterior Segment Disease and the Systemic Link Mile Brujic, OD, FAAO brujic@prodigy.net Summary As optometry s role in health care increases, so does our responsibility to appropriately diagnose and appropriately
Anterior Segment Disease and the Systemic Link Mile Brujic, OD, FAAO brujic@prodigy.net Summary As optometry s role in health care increases, so does our responsibility to appropriately diagnose and appropriately
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Multiple System Atrophy
 Multiple System Atrophy This document has been prepared to help you become more informed about Multiple System Atrophy. It is designed to answer questions about the condition and includes suggestions on
Multiple System Atrophy This document has been prepared to help you become more informed about Multiple System Atrophy. It is designed to answer questions about the condition and includes suggestions on
Source: *Dystonia facts medically edited by: Charles Patrick Davis, MD, PhD
 Source: http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=349 Dystonia facts* *Dystonia facts medically edited by: Charles Patrick Davis, MD, PhD Dystonia is a disorder of muscle control; it can
Source: http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=349 Dystonia facts* *Dystonia facts medically edited by: Charles Patrick Davis, MD, PhD Dystonia is a disorder of muscle control; it can
Tremor 101. Objectives 9/30/2015. Importance of tremors
 Tremor 101 Umer Akbar, MD Assistant Professor, Brown University Movement Disorders Program, Rhode Island Hospital & Butler Hospital Objectives Recognize and describe the qualities of common types of tremor
Tremor 101 Umer Akbar, MD Assistant Professor, Brown University Movement Disorders Program, Rhode Island Hospital & Butler Hospital Objectives Recognize and describe the qualities of common types of tremor
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders
 Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
Dystonias. How are the dystonias classified? One way of classifying the dystonias is according to the parts of the body they affect:
 Dystonias What are the dystonias? The dystonias are movement disorders in which sustained muscle contractions cause twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures. The movements, which are involuntary
Dystonias What are the dystonias? The dystonias are movement disorders in which sustained muscle contractions cause twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures. The movements, which are involuntary
CONTRIBUTORS The American Academy of Neurology Institute.
 Several of these multiple-choice questions were originally published in Continuum: Lifelong Learning in Neurology Movement Disorders, Volume 22, Issue 4, August 2016 based on the content in the issue developed
Several of these multiple-choice questions were originally published in Continuum: Lifelong Learning in Neurology Movement Disorders, Volume 22, Issue 4, August 2016 based on the content in the issue developed
ABSTRACT. Iraqi Journal of. *DR. RababFarhanThijeel **DR.Halasameh ***DR.AhmedKhalil. Issue1 Vol.5
 *DR. RababFarhanThijeel **DR.Halasameh ***DR.AhmedKhalil ABSTRACT Background: Wilson'sdiseaseorhepatolenticulardegeneration isatreatable inheritedmetabolic diseaseinwhichcopperaccumulatesintissues,thesearemainlyliver
*DR. RababFarhanThijeel **DR.Halasameh ***DR.AhmedKhalil ABSTRACT Background: Wilson'sdiseaseorhepatolenticulardegeneration isatreatable inheritedmetabolic diseaseinwhichcopperaccumulatesintissues,thesearemainlyliver
Pediatric Wilson s disease: findings in different presentations. A cross-sectional study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2018.0210230718 Pediatric Wilson s disease: findings in different presentations. A cross-sectional study Şükrü Güngör I, Mukadder Ayşe Selimoğlu II, Fatma İlknur
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2018.0210230718 Pediatric Wilson s disease: findings in different presentations. A cross-sectional study Şükrü Güngör I, Mukadder Ayşe Selimoğlu II, Fatma İlknur
Two Cases of Chronic Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration with Parkinsonian Symptoms
 Two Cases of Chronic Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration with Parkinsonian Symptoms Won Chul Shin, Kang Ju Sung, Yong Woo Noh, Bon Dae Ku, M.D*., Dae-Il Chang, Kyung-Cheon Chung Department of Neurology,
Two Cases of Chronic Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration with Parkinsonian Symptoms Won Chul Shin, Kang Ju Sung, Yong Woo Noh, Bon Dae Ku, M.D*., Dae-Il Chang, Kyung-Cheon Chung Department of Neurology,
A tale of two sisters with liver disease
 IM BOARD REVIEW EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider the various causes of acute liver failure MOHAMAD A. HANOUNEH, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Medicine Institute, Cleveland Clinic NIZAR
IM BOARD REVIEW EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider the various causes of acute liver failure MOHAMAD A. HANOUNEH, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Medicine Institute, Cleveland Clinic NIZAR
Issues for Patient Discussion
 onmotor complications radykinesia Screening Tools asked PD micrographia eurodegeneration Designed for Use by Family Practitioners remor on-off opamine agonists tiffness depression ostural instability wearing
onmotor complications radykinesia Screening Tools asked PD micrographia eurodegeneration Designed for Use by Family Practitioners remor on-off opamine agonists tiffness depression ostural instability wearing
Evaluation of Parkinson s Patients and Primary Care Providers
 Evaluation of Parkinson s Patients and Primary Care Providers 2018 Movement Disorders Half Day Symposium Elise Anderson MD Medical Co-Director, PBSI Movement Disorders 6/28/2018 1 Disclosures GE Speaker,
Evaluation of Parkinson s Patients and Primary Care Providers 2018 Movement Disorders Half Day Symposium Elise Anderson MD Medical Co-Director, PBSI Movement Disorders 6/28/2018 1 Disclosures GE Speaker,
Parkinson s Disease Foundation. PD ExpertBriefing: Managing the Motor Symptoms in PD
 Parkinson s Disease Foundation PD ExpertBriefing: Managing the Motor Symptoms in PD Led By: Sotirios A. Parashos, M.D. Minneapolis Clinic of Neurology and Struthers Parkinson's Center This session was
Parkinson s Disease Foundation PD ExpertBriefing: Managing the Motor Symptoms in PD Led By: Sotirios A. Parashos, M.D. Minneapolis Clinic of Neurology and Struthers Parkinson's Center This session was
Movement disorders in childhood: assessment and diagnosis. Lucinda Carr
 Movement disorders in childhood: assessment and diagnosis Lucinda Carr Movement disorders in childhood: Assessment Classification Causes Diagnosis Presentation of movement disorders in childhood: Concerns
Movement disorders in childhood: assessment and diagnosis Lucinda Carr Movement disorders in childhood: Assessment Classification Causes Diagnosis Presentation of movement disorders in childhood: Concerns
Identification number: TÁMOP /1/A
 Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: Parkinson s Disease
 Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: Parkinson s Disease 1. Focused summary of PD relevant to primary care Parkinson s Disease (PD) and Essential tremor (ET) are two of the most common movement disorders encountered
Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: Parkinson s Disease 1. Focused summary of PD relevant to primary care Parkinson s Disease (PD) and Essential tremor (ET) are two of the most common movement disorders encountered
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: 27 years old male patient presented clinically with bilateral pyramidal manifestations, more on the left side, bilateral parkinsonian manifestations and bilateral cerebellar
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: 27 years old male patient presented clinically with bilateral pyramidal manifestations, more on the left side, bilateral parkinsonian manifestations and bilateral cerebellar
International Journal of Biology January, 2010
 International Journal of Biology January, 2010 Spectrum of ATP7B Gene Mutations in Pakistani Wilson Disease Patients: A Novel Mutation Is Associated with Severe Hepatic and Neurological Complication Abdul
International Journal of Biology January, 2010 Spectrum of ATP7B Gene Mutations in Pakistani Wilson Disease Patients: A Novel Mutation Is Associated with Severe Hepatic and Neurological Complication Abdul
Clinical Application of Liver MR Imaging in Wilson s Disease
 Clinical Application of Liver MR Imaging in Wilson s Disease Jung-Eun Cheon, MD 1 In-One Kim, MD 1 Jeong Kee Seo, MD 2 Jae Sung Ko, MD 2 Jeong Min Lee, MD 1 Cheong-Il Shin, MD 1 Woo Sun Kim, MD 1 Kyung
Clinical Application of Liver MR Imaging in Wilson s Disease Jung-Eun Cheon, MD 1 In-One Kim, MD 1 Jeong Kee Seo, MD 2 Jae Sung Ko, MD 2 Jeong Min Lee, MD 1 Cheong-Il Shin, MD 1 Woo Sun Kim, MD 1 Kyung
Wilson's disease (WD), is an autosomal
 World Journal of Pediatrics Urinary copper/zinc ratio: a promising parameter for replacement of 24-hour urinary copper excretion for diagnosis of Wilson's disease in children Jian-She Wang, Yi Lu, Xiao-Hong
World Journal of Pediatrics Urinary copper/zinc ratio: a promising parameter for replacement of 24-hour urinary copper excretion for diagnosis of Wilson's disease in children Jian-She Wang, Yi Lu, Xiao-Hong
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Fracture in a Young Male Patient Leading to the Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case Report
 J Bone Metab 2015;22:33-37 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2015.22.1.33 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Case Report Fracture in a Young Male Patient Leading to the Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case
J Bone Metab 2015;22:33-37 http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2015.22.1.33 pissn 2287-6375 eissn 2287-7029 Case Report Fracture in a Young Male Patient Leading to the Diagnosis of Wilson s Disease: A Case
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN
 Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
