Intracerebral Gangliogliomas in Patients with Partial Complex Seizures: CT and MR Imaging Findings
|
|
|
- Brianne Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 749 Intracerebral Gangliogliomas in Patients with Partial Complex Seizures: CT and MR Imaging Findings D. Tampieri 1 R. Moumdjian D. Melanson R. Ethier The clinical and radiologic findings in 19 patients with partial complex seizures and surgically proved intracerebral gangliogliomas were reviewed to characterize the radiologic features of these lesions. The CT and MR findings were not specific. On CT the gangliogliomas can be hypodense with no enhancement and they often have calcifications. On MR these tumors have a wide variety of signals. In five of our cases the tumor had a high-intensity signal with a cystlike component on proton density- and T2- weighted images. In five cases the lesion had an inhomogeneously intense signal on proton density-weighted images and high signal intensity on T2-weighted images. The tumor had high-intensity signal on both proton density- and T2-weighted images in four patients. Finally, in two cases the MR findings were normal. We recommend MR as the examination of choice for patients with partial complex seizures because it allows an artifact-free evaluation of the temporal region. However, CT should also be performed in order to recognize calcifications that may be missed on the MR examination. AJNR 12: , July/August 1991; AJR 157: October 1991 Gangliogliomas are rare, slow-growing, relatively benign neoplasms consisting of a mixture of adult ganglion cells and glial tumor cells. They are often responsible for a prolonged clinical course, characterized primarily by seizures. To better define the imaging characteristics of these tumors, we reviewed the clinical and radiologic findings in 19 patients presenting with partial complex seizures who were subsequently found to have surgically proved gangliogliomas. Materials and Methods Received October ; revision requested November ; revision received February 1, 1991 ; accepted February 4, ' All authors: Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Montreal Neurological Hospital and Institute, 4801 University St., Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3A 284. Address reprint requests to D. Tampieri /91/ American Society of Neuroradiology From January 1987 to August 1990, 19 patients, 11 men and eight women, 7 to 44 years old (mean age, 21 years), were referred to our institute for intractable partial complex seizures (PCoS). PCoS are one of the features found in temporal lobe epilepsy. They often, but not always, start with motor arrest typically followed by oroalimentary automatism lasting less than 1 min, which in turn is followed by post-ictal confusion and amnesia [1). These patients received a complete clinical and radiologic work-up and underwent surgery for removal of intracerebral space-occupying lesions histologically proved to be gangliogliomas. EEG fi ndings, skull radiographs, and CT scans were available for all patients. CT examinations were performed with an EMI scanner and a GE 9800 Quick scanner. In eight cases the CT scans were obtained without contrast enhancement; in six cases the examinations were performed after injection of contrast medium. Five patients had both plain and enhanced CT examinations. Eighteen patients were studied by MR imaging; in one patient (case 4) the examination was stopped because the boy had a seizure. In five cases, the MR examinations were performed with a Philips Gyroscan 0.5-T unit, and T1 -weighted, 500{30/2 (TRJTE/ excitations), proton density-weighted, and T2-weighted (1500{30,60/2) images were obtained. In 13 cases, a 1.5-T unit was used, and T1-weighted (500/30/2), proton densityweighted, and T2-weighted (21 00/30,60/2) images were obtained. Proton density- and T2- weighted images were obtained in axial and coronal views in all cases. T1-weighted images
2 750 TAMPIERI ET AL. AJNR:12, July/August 1991 TABLE 1: Clinical and Electroencephalographic Findings Case Age Type of Sex No. (years) Seizures Age at Onset (years) Free Interval Frequency of EEG (years) Attacks Focus Tumor Location 1 7 M PCoS + left fms 11 months 6 4/day R temp Rtemp 2 11 F PCoS + 1 gen fweek R posterior R posterotemp temp/ occ 3 12 M PCoS 2 10 L temp L temp 4 12 M PCoS 3 months 11 6fyear L temp L temp 5 14 M PCoS + da 11 3 L temp L temp 6 15 F PCoS + gen 5 10 Frequent L temp L temp 7 16 F PCoS /month R + L L temp temp 8" 17 M PCoS 14 3 L temp L frontoopercular 9 17 F PCoS fweek R temp R temp M PCoS /month R temp R temp 11 " 21 M PCoS fmonth L temp L temp M PCoS + gen 9 16 (PCoS)/8 12fmonth L temp L temp (gen) F PCoS R temp R temp M PCoS + gen fyr (gen) R temp R temp F PCoS + abs /month (abs) R abn R temp M PCoS + gen fyear R abn R frontoopercular F PCoS fday L abn L temp F PCoS + gen /day R temp R temp M PCoS + gen fmonth R temp Rtemp Note.-PCoS = partial complex seizures, fms = focal motor seizures, gen = generalized seizures, da = drop attacks, abs =absence episodes, R = right, L = left, temp = temporal lobe, occ = occipital lobe, abn = abnormality. Previous partial resection in another center. Previous partial corticectomy and partial amygdalo-hippocampectomy. were available only in seven cases. None of the MR studies were contrast enhanced, since this study was carried out before the clinical use of gadopentetate dimeglumine in Canada. Results Clinical and EEG Findings (Table 1) The familial and medical histories were unremarkable in 16 patients in our series. One patient (case 5) was born 3 weeks post-term without any evidence of perinatal sequela. Another patient (case 18) was suffering from Rosenthal syndrome caused by deficiency of factor XI. A 33-year-old woman (case 17) developed PCoS after an episode reported as encephalitis atage13. All the patients were referred for intractable PCoS. In seven cases, these episodes were associated at an older age with tonic-clonic seizures and secondary generalization. Case 1 presented with PCoS and left focal motor seizures. In one patient (case 5) the PCoS were associated with drop attacks, and in another (case 15) with absences, characterized by short episodes of loss of contact without automatism. The age of onset of seizure disorders ranged from 3 months to 31 years. The frequency of the attacks, when specified, ranged from four attacks per day to two per year at the time of admission. All the patients had a prolonged clinical course with an important free interval between the onset of the seizures and the radiologic diagnosis. This time interval ranged from 3 to 26 years (mean, 11 V2 years). The EEGs showed epileptiform abnormality in all the cases in our series. In seven patients the EEG reports described an abnormal discharge with a right temporal focus, and in seven cases the focus was found in the left temporal region. In case 7 the abnormal discharge was from both temporal lobes, and in case 2 the abnormality was from the right posterior temporooccipital area. In only three patients (cases 15, 16, and 17) did the EEG demonstrate an abnormal discharge lateralized to one cerebral hemisphere with no evidence of focal anomalies. Radiologic Findings (Table 2) Skull Radiographs. In no case did the plain films reveal any evidence of raised intracranial pressure or mass effect with displacement of the calcified pineal gland. In four patients flocular calcifications were visualized in the middle cranial fossa on the same side of the lesion. In cases 8 and 11, the plain films documented the previous craniotomy. CT Scans. The CT findings were available in all cases. In 15 patients it was positive: four lesions (cases 1, 4, 15, 16) were hypodense (Figs. 1 and 2); two lesions (cases 7 and 8) were ring-enhancing (Fig. 3), and in six patients (cases 2, 3, 6, 9, 10, 13) the examination demonstrated only calcifications (Fig. 4). Two CT studies (cases 14 and 18) showed asymmetry of the temporal horn (Fig. 5), the larger being on the tumoral side, and in case 12 the CT study demonstrated only a prominent left hippocampus. In three cases (5, 17, 19) the examination was negative, and, finally, in case 11 there was only evidence of the previous surgery. MR Images. Seventeen MR examinations were completed and available and the tumor was identified in 15 patients
3 AJNR :12. July/August 1991 INTRACEREBRAL GANGLIOGLIOMAS 751 TABLE 2: Radiologic Findings Case No. Age (years) Sex Skull CT Plain Enhanced T1 MR Proton Density T2 Location 1 7 M Neg Hypodense j is + cystlike j is + cystlike R temp 2 11 F Neg Calcifications No enh R posterotemp 3 12 M Calcifications Calcifications No enh lnh is + cyst- lnh is + cyst- L temp like like 4 12 M Neg Hypodense L temp 5 14 M Neg Neg l is lnh is j is L temp 6 15 F Neg Calcifications No enh jis j is L temp 7 16 F Neg Ring enh lso is j is + cystlike j is + cystlike L temp 8' 17 M Prev. crani- Ring enh + j is + cystlike j is + cystlike L frontoopercular otomy calcification 9 17 F Calcification Calcification No enh ISO is j is +small jis +small R temp void sig void sig M Calcifications Calcifications lnh is j is R temp 11 " 21 M Prev. crani- Prev. surgery L temp Prev. surgery otomy M Neg Prominent lso is j is j is L temp hippocampus F Calcifications Calcifications lnh is+ void j is + void R temp sig sig M Neg Asymmetric Asymmetric tem- Neg Neg Rtemp temporal poral horn R > L horn R > L F Neg Hypodense Hypo is + cystlike jis + cystlike j is + cystlike Rtemp M Hypodense No enh lnh is j is R frontoopercular F Neg Neg Neg Neg L temp F Neg Asymmetric l is lnh is j is R temp temporal horn R > L M Neg Neg j is j is R temp Note.-neg = negative examination, - = examination not done, no enh = no enhancement after injection, inh is = inhomogeneously intense signal, iso is = isointense signal, hypo is = hypointense signal, jis = high-intensity signal, Vs = low-intensity signal, void sig = void signal, R = right, L = left, temp = temporal lobe. ' Previous partial resection in another center. " Previous partial corticectomy and partial amygdalo-hippocampectomy. (88%). One MR examination (case 17) was negative; one (case 14) showed the right temporal horn to be larger than the left (Fig. 5); and one (case 11) demonstrated prior surgery but no evidence of residual tumor. The gangliogliomas demonstrated a wide variety of signals. In five patients (cases 1, 3, 7, 8, 15) the lesion had a signal similar to CSF on proton density-weighted images and higher than CSF on T2-weighted images (Figs. 1-3). In five cases the tumor had an inhomogenously intense signal on proton density-weighted images that became hyperintense on the T2-weighted images (cases 5, 10, 13, 16, 18). Finally, the lesion had a high-intensity signal on both proton density- and T2-weighted images in four patients (cases 6, 9, 12, 19). MR detected calcifications in only two patients (cases 9 and 13) (Fig. 4). T1-weighted images were available in only seven patients: they showed the lesions to be isointense in three cases, hypointense in two cases, and isointense with CSF in one case (Fig. 2). Discussion The first description of gangliogliomas was given by Courville in 1930 [2]. The term ganglioglioma clearly defines the structure of these uncommon tumors as a mixture of nerve cells and glial elements. They constitute just 0.4% of all CNS tumors [3, 4]. This percentage has been reported to be as high as 4.3% [5] and 7.6% [6] in studies that factor out the adult population, reflecting the fact that this tumor is more common among children. The tumors do not have any sex predilection, but some authors report a predominance in males [2, 7]. Gangliogliomas can occur in any number of locations in the CNS, and can involve both brain and spinal cord; however, the most common locations in the adult population seem to be the temporal lobe and the floor of the third ventricle [3, 8]. In the present series we included only lesions causing PCoS, and for this reason a preference for the temporal lobe, particularly the hippocampal gyrus, was found. In childhood, gangliogliomas seem to occur more frequently in the medulla and spinal cord [9] and the differential diagnosis with the more benign gangliocytoma has to be considered. This latter tumor, rarely supratentorial [1 0, 11] and purely neuronal without a glial component, is an extremely rare entity, accounting for 0.1 % of intracranial tumors [12] with a slight male predilection [13], and it cannot be radiologically differentiated from ganglioglioma. The clinical course suggests that gangliogliomas are slowgrowing neoplasms, and a malignant transformation is very uncommon. When it happens it is usually the glial element that is responsible for the change [14]. Metastasis in the CNS
4 752 TAMPIERI ET AL. AJNR:12, July/August 1991 Fig. 1.-Case 1. A and B, Unenhanced CT scans show two small, poorly defined areas of hypodensity (arrowheads). C, Axial proton density-weighted (2100/30/1) MR image better defines the lesion, which appears as two low-intensity cystlike areas surrounded by a high-intensity signal in right temporomesial region (arrowheads). D, Coronal T2-weighted (2100/80/1) MR image of tumor shows increased signal intensity. Cystlike component is surrounded by high-intensity signal, which involves the cortex and adjacent white matter (arrowhead). c D appears to be exceptional [14]. Some authors have also raised the possibility that gangliogliomas are hamartomatous lesions since they have been found in temporal lobes of patients with a long history of seizures [15] and because collections of heterotopic gray matter similar to ganglioglioma can cause seizures [16]. Nowadays, the literature seems to agree that gangliogliomas are true neoplasms and their removal has to be attempted [5, 17]. The EEG findings usually suggest the focal abnormality that must be confirmed by the imaging findings. Radiologically, gangliogliomas do not have a specific appearance. Calcifications can be visualized on a skull radiograph in 1 0% of patients [18]. Although the skull radiograph is a superfluous examination, it was performed in all our patients and we observed four cases (21 %) with flocular calcifications in the middle cranial fossa. CT findings also are nonspecific. Gangliogliomas are usually hypodense [19] with calcifications [20]. In our series CT scans were positive in 12 patients (63%); six of them (32%) dem- onstrated only abnormal calcifications, and the other six showed a wide variety of findings. In no case in our series did CT demonstrate edema or mass effect. In a small series [21] of four patients studied with MR imaging, two lesions had a cystic appearance while the other two displayed an increased signal on T1-weighted images and a decreased signal on T2-weighted images. The authors did not try to explain these findings. In a larger series of 14 patients reported by Castillo et al. [22] there were four cystic lesions (low signal on T1-weighted images and high signal on T2-weighted images) and 1 0 solid masses that demonstrated high-intensity signal on T2-weighted images. The authors did not mention whether the cystic nature of the lesions observed on MR was confirmed later at surgery. In our series, gangliogliomas presented different signals because of their heterogeneous components of glial and neuronal cells associated with calcifications. In five (29%) of the 17 patients who were studied with MR imaging, the gangliogliomas had a cystlike component (Figs. 1 and 2) and
5 AJNR :12, July/August 1991 INTRACEREBRAL GANGLIOGLIOMAS 753 A B C Fig. 2.-Case 15. A, Enhanced CT scan shows well-defined hypodense nonenhancing lesion (arrowhead). 8 and C, T1-weighted (500/30/1) (8) and T2-weighted (2100/80/1) (C) MR images show cystlike tumor (arrowhead) in right inferotemporal gyrus surrounded by some edema. A B c Fig. 3.-Case 7. A, Enhanced CT scan shows ring-enhancing lesion (arrowhead) in left posterior parahippocampal region. 8 and C, Axial (8) and coronal (C) T2-weighted (2100/80/1) MR images enable complete evaluation of the tumor, which involves the left hippocampus and parahippocampus gyri. The ganglioglioma has a high-intensity signal and a central cystlike nodule (arrowheads), which corresponds to the ringenhancing lesion seen on the enhanced CT scan. in five patients (29%) the lesions displayed inhomogeneous signal on proton density-weighted images and high-intensity signal on T2-weighted images. Finally, in four cases (24%) the tumors had high signals on both proton density- and T2- weighted images. In only two patients (12%) was MR able to detect calcifications (Fig. 4). We prefer to use the term cystlike appearance to describe the MR characteristic of a welldefined area with signal intensity similar to CSF on proton density-weighted images and higher than CSF on T2- weighted images. This is because the content of the lesions is not fluid but solid ; therefore, it cannot be drained but has to be removed, as was the case in the patients in our series. MR failed to show the tumor in two (12%) of the 17 cases. Owing to their frequent attacks of seizures and their EEG results, these patients eventually underwent temporal lobectomy; the histologic reports revealed the presence of the
6 754 T AMPIERI ET AL. AJNR :12, July/August 1991 Fig. 4.-Case 9. A, Contrast-enhanced CT scan shows floccular calcification (arrowhead) in right middle cranial fossa. 8, Coronal T2-weighted (2100/80/1) MR image confirms presence of calcification (arrow head) in right fusiform gyrus and shows a hyperintense signal that involves the amygdala, hippocampus and parahippocampus gyri, and adjacent white matter. c D Fig. 5.-Case 14. A-D, Unenhanced CT scans (A and 8) and T1- weighted (500/ 30/1) MR image (C) show slight asymmetry of temporal horn, with right (arrowhead) larger than left. T2-weighted (2100/80/1) MR shows no evidence of the ganglioglioma discovered later at surgery in the right temporal lobe. lesion. The CT and MR findings in these patients demonstrated an asymmetry of the temporal horns in one patient (case 14) and were completely normal in the other (case 17). In conclusion, gangliogliomas are uncommon lesions, but their presence has to be considered in patients with a long history of uncontrollable seizures. Since most of these tumors are located in the middle cranial fossa, MR is the examination of choice because it allows images free from bone artifact. Nevertheless, false-negative diagnoses are possible and we think that CT should also be performed in order to detect calcification, which can be missed on MR.
7 AJNR :12, July/August 1991 INTRACEREBRAL GANGLIOGLIOMAS 755 REFERENCES 1. Commission on Classification and Terminology of the International League Against Epilepsy. Proposal for revised classification of epilepsies and epileptic syndromes. Epilepsia 1989;30: Courville CB. Ganglioglioma: tumor of the central nervous system; review of the literature and report of two cases. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 1930;24: Zulch KJ. Brain tumors: their biology and pathology, 2nd ed. New York: Springer, Cox JO, Zimmerman HM, Haughton VM. Microcystic ganglioglioma treated by partial removal and radiation therapy. Cancer 1982;50: Sutton LN, Packer RJ, Rorke LB, et al. Cerebral gangliogliomas during childhood. Neurosurgery 1983;13: Johannsson JH, Rekate HL, Roessmann U. Gangliomas: pathological and clinical correlation. J Neurosurg 1981 ;54: Rommel T, Hamer J. Development of ganglioglioma in computed tomography. Neuroradiology 1983;24 : Zulch KJ. Progress in neurological surgery. Chicago: Yearbook, Albright L, Byrd RP. Ganglioglioma of the entire spinal cord. Child's Brain 1980;6 : Dom R, Brucher JM. Hamartoblastoma (gangliocytome diffus) unilateral de I' ecorce cerebrale associe a une degenerescence soudanophile de Ia substance blanche du cote oppose. Rev Neural (Pari s) 1969;120: Kawamoto K, Yamanouchi Y, Suwa J, Kurimoto T, Matsumura H. Ultrastructural study of a cerebral gangliocytoma. Surg Neurol 1985;24 : Roski RA, Roessmann U, Spetzler RF, Kaufman B. Nulsen FE. Clinical and pathological study of dysplastic gangliocytoma: a case report. J Neurosurg 1981 ;55: Altman NR. MR and CT characteristics of gangliocytoma: a rare cause of epilepsy in children. AJNR 1988;9: Russel OS, Rubinstein LJ. Pathology of tumors of the nervous system. London: Arnold, 1989: Cavanagh JB. On certain small tumors encountered in the temporal lobe. Brain 1958;81 : Layton DO. Heterotopic cerebral gray matter as an epileptogenic focus. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol1962;2 1 : Garrido E, Becker LF, Hoffman HJ, et al. Gangliogliomas in children: a clinicopathological study. Child's Brain 1978;4 : Katz MC, Kier EL, Schechter MM. The radiology of gangliogliomas and ganglioneuromas of the central nervous system. Neuroradiology 1972;4: Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT. Computed tomography of intracerebral gangliogliomas. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1979;3 : Dorne HL, O'Gorman AM, Melanson D. Computed tomography of intracranial gangliogliomas. AJNR 1986;7: Denierre B, Stinchnoth FA, Hori A, Spoerri 0. Intracerebral gangliogliomas. J Neurosurg 1986;65 : Castillo M, Davis PC, Takei Y, Hoffman JC. Intracranial ganglioglioma: MR. CT, and clinical findings in 18 patients. AJNR 1990;11 :
MR and CT Characteristics of Gangliocytoma: A Rare Cause of Epilepsy in Children
 917 MR and CT Characteristics of Gangliocytoma: A Rare Cause of Epilepsy in Children Nolan R. Altman 1 Three children were examined who had surgery to remove gangliocytomas in order to control seizures
917 MR and CT Characteristics of Gangliocytoma: A Rare Cause of Epilepsy in Children Nolan R. Altman 1 Three children were examined who had surgery to remove gangliocytomas in order to control seizures
Computed Tomography of Intracranial Gangliogliomas
 281 Computed Tomography of Intracranial Gangliogliomas Howard L. Dorne 1 Augustin M. O'Gorman 2 Denis Melanson 3 Thirteen patients with pathologically proven gangliogliomas were studied radiographically,
281 Computed Tomography of Intracranial Gangliogliomas Howard L. Dorne 1 Augustin M. O'Gorman 2 Denis Melanson 3 Thirteen patients with pathologically proven gangliogliomas were studied radiographically,
Intracranial Ganglioglioma: MR, CT,
 109 Intracranial Ganglioglioma: MR, CT, and Clinical Findings in 18 Patients Mauricio Castillo 1 Patricia C. Davis 1 Yoshii Takei 2 James C. Hoffman, Jr. 1 Eighteen cases of pathologically proved intracranial
109 Intracranial Ganglioglioma: MR, CT, and Clinical Findings in 18 Patients Mauricio Castillo 1 Patricia C. Davis 1 Yoshii Takei 2 James C. Hoffman, Jr. 1 Eighteen cases of pathologically proved intracranial
Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases
 Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases Ho Sung Kim, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Ae Kyung Jeong, MD 1 Ji Hoon Shin, MD 1 Choong Gon Choi, MD 1 Shin Kwang Khang, MD 2 We
Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases Ho Sung Kim, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Ae Kyung Jeong, MD 1 Ji Hoon Shin, MD 1 Choong Gon Choi, MD 1 Shin Kwang Khang, MD 2 We
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Value of MRI in the Evaluation of Patients with Seizures: An Illustrative Case
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurology Volume 7 Number 1 Value of MRI in the Evaluation of Patients with Seizures: An Illustrative Case Y Patel, H Pinkert, M Kaufman Citation Y Patel, H Pinkert, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurology Volume 7 Number 1 Value of MRI in the Evaluation of Patients with Seizures: An Illustrative Case Y Patel, H Pinkert, M Kaufman Citation Y Patel, H Pinkert, M
Hamartomas and epilepsy: clinical and imaging characteristics
 Seizure 2003; 12: 307 311 doi:10.1016/s1059 1311(02)00272-8 Hamartomas and epilepsy: clinical and imaging characteristics B. DIEHL, R. PRAYSON, I. NAJM & P. RUGGIERI Departments of Neurology, Pathology
Seizure 2003; 12: 307 311 doi:10.1016/s1059 1311(02)00272-8 Hamartomas and epilepsy: clinical and imaging characteristics B. DIEHL, R. PRAYSON, I. NAJM & P. RUGGIERI Departments of Neurology, Pathology
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD
 Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
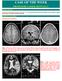 CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CLINICAL PICTURE: A 6 years old male patient presented clinically with intractable complex partial seizure. The child is mentally
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CLINICAL PICTURE: A 6 years old male patient presented clinically with intractable complex partial seizure. The child is mentally
The Asymmetric Mamillary Body: Association with Medial Temporal Lobe Disease Demonstrated with MR
 The Mamillary Body: Association with Medial Temporal Lobe Disease Demonstrated with MR Alexander C. Mamourian, Lawrence Rodichok, and Javad Towfighi PURPOSE: To determine whether mamillary body atrophy
The Mamillary Body: Association with Medial Temporal Lobe Disease Demonstrated with MR Alexander C. Mamourian, Lawrence Rodichok, and Javad Towfighi PURPOSE: To determine whether mamillary body atrophy
Pediatric and Adolescent Oligodendrogliomas
 Pediatric and Adolescent Oligodendrogliomas Harold Tice, 1 Patrick D. Barnes, 1 Liliana Goumnerova, 2 R. Michael Scott, 2 and Nancy J. Tarbell 3 PURPOSE: To review the clinical and imaging findings in
Pediatric and Adolescent Oligodendrogliomas Harold Tice, 1 Patrick D. Barnes, 1 Liliana Goumnerova, 2 R. Michael Scott, 2 and Nancy J. Tarbell 3 PURPOSE: To review the clinical and imaging findings in
Infratentorial and Intraparenchymal Subependymoma in the Cerebellum: Case Report
 Case Report Neuroimaging and Head and Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.151 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):151-155 Infratentorial and Intraparenchymal Subependymoma
Case Report Neuroimaging and Head and Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.151 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):151-155 Infratentorial and Intraparenchymal Subependymoma
Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumors: MR Appearance
 Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumors: MR Appearance Kelly K. Koeller, 1 2 and William P. Dillon 1 3 PURPOSE: Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (DNT) is a newly described, pathologically benign
Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumors: MR Appearance Kelly K. Koeller, 1 2 and William P. Dillon 1 3 PURPOSE: Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (DNT) is a newly described, pathologically benign
Gangliogliomas: clinical, radiological, and
 J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:1497-1502 Department of Neurosurgery J Zentner M G Campos J Schramm Departnent of Neuropathology H K Wolf Department of Neuroradiology B Ostertun
J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:1497-1502 Department of Neurosurgery J Zentner M G Campos J Schramm Departnent of Neuropathology H K Wolf Department of Neuroradiology B Ostertun
The Behavior of Pantopaque on MR: In Vivo and In Vitro
 997 The Behavior of Pantopaque on MR: In Vivo and In Vitro Analyses Ira F. Braun 1 John A. Maiko Patricia C. Davis James C. Hoffman, Jr. Louis H. Jacobs MR imaging is considered by many to be the procedure
997 The Behavior of Pantopaque on MR: In Vivo and In Vitro Analyses Ira F. Braun 1 John A. Maiko Patricia C. Davis James C. Hoffman, Jr. Louis H. Jacobs MR imaging is considered by many to be the procedure
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Early seizure propagation from the occipital lobe to medial temporal structures and its surgical implication
 Original article Epileptic Disord 2008; 10 (4): 260-5 Early seizure propagation from the occipital lobe to medial temporal structures and its surgical implication Naotaka Usui, Tadahiro Mihara, Koichi
Original article Epileptic Disord 2008; 10 (4): 260-5 Early seizure propagation from the occipital lobe to medial temporal structures and its surgical implication Naotaka Usui, Tadahiro Mihara, Koichi
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Epilepsy & Behavior Case Reports
 Epilepsy & Behavior Case Reports 1 (2013) 45 49 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Epilepsy & Behavior Case Reports journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ebcr Case Report Partial disconnection
Epilepsy & Behavior Case Reports 1 (2013) 45 49 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Epilepsy & Behavior Case Reports journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ebcr Case Report Partial disconnection
Surgery of posterior fossa arachnoid cyst causing hydrocephalus unmasking the cause of epilepsy
 CASE REPORTS ALBANIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL Surgery of posterior fossa arachnoid cyst causing hydrocephalus unmasking the cause of epilepsy Florian Dashi 1, Arben Rroji 1, Eugen Enesi 1, Suzana Gjeci 1, Ridvan
CASE REPORTS ALBANIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL Surgery of posterior fossa arachnoid cyst causing hydrocephalus unmasking the cause of epilepsy Florian Dashi 1, Arben Rroji 1, Eugen Enesi 1, Suzana Gjeci 1, Ridvan
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Intracranial Studies Of Human Epilepsy In A Surgical Setting
 Intracranial Studies Of Human Epilepsy In A Surgical Setting Department of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Presentation Goals Epilepsy and seizures Basics of the electroencephalogram
Intracranial Studies Of Human Epilepsy In A Surgical Setting Department of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Presentation Goals Epilepsy and seizures Basics of the electroencephalogram
Case reports functional imaging in epilepsy
 Seizure 2001; 10: 157 161 doi:10.1053/seiz.2001.0552, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Case reports functional imaging in epilepsy MARK P. RICHARDSON Medical Research Council Fellow, Institute
Seizure 2001; 10: 157 161 doi:10.1053/seiz.2001.0552, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Case reports functional imaging in epilepsy MARK P. RICHARDSON Medical Research Council Fellow, Institute
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution
 Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A
 Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
In 1988 Dumas-Duport et al. first used
 Copyright 2009, Barrow Neurological Institute Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor: A Review Mark Garrett, MD Jennifer Eschbacher, MD Peter Nakaji, MD Most DNETs are benign, low-grade lesions. However,
Copyright 2009, Barrow Neurological Institute Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor: A Review Mark Garrett, MD Jennifer Eschbacher, MD Peter Nakaji, MD Most DNETs are benign, low-grade lesions. However,
Morphometric MRI Analysis of the Parahippocampal Region in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
 Morphometric MRI Analysis of the Parahippocampal Region in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy NEDA BERNASCONI, a ANDREA BERNASCONI, ZOGRAFOS CARAMANOS, FREDERICK ANDERMANN, FRANÇOIS DUBEAU, AND DOUGLAS L. ARNOLD Department
Morphometric MRI Analysis of the Parahippocampal Region in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy NEDA BERNASCONI, a ANDREA BERNASCONI, ZOGRAFOS CARAMANOS, FREDERICK ANDERMANN, FRANÇOIS DUBEAU, AND DOUGLAS L. ARNOLD Department
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
Epilepsy and Brain Tumor. Apasri Lusawat M.D. Pediatric Neurology Prasat Neurological Institute
 Epilepsy and Brain Tumor Apasri Lusawat M.D. Pediatric Neurology Prasat Neurological Institute Outline Overview Pathogenesis : Tumor-> epilepsy Etiology of Epilepsy, age EPILEPSY AND BRAIN TUMORS CNS neoplasms
Epilepsy and Brain Tumor Apasri Lusawat M.D. Pediatric Neurology Prasat Neurological Institute Outline Overview Pathogenesis : Tumor-> epilepsy Etiology of Epilepsy, age EPILEPSY AND BRAIN TUMORS CNS neoplasms
The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1570 1574, September 2003 The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease Andrew Slater, Niall R. Moore, and Susan M. Huson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1570 1574, September 2003 The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease Andrew Slater, Niall R. Moore, and Susan M. Huson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
EEG WORKSHOP Nonepileptiform Abnormalities
 EEG WORKSHOP Nonepileptiform Abnormalities Kamornwan Katanyuwong MD Chiangmai University Hospital EST: 20th July 2010 EEG reading Age Background Epileptiform Non epileptiform Activation procedure normal
EEG WORKSHOP Nonepileptiform Abnormalities Kamornwan Katanyuwong MD Chiangmai University Hospital EST: 20th July 2010 EEG reading Age Background Epileptiform Non epileptiform Activation procedure normal
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Imaging for Epilepsy Diagnosis December 2, 2011
 Imaging for Epilepsy Diagnosis December 2, 2011 Samuel Wiebe, MD University of Calgary Canada American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure University of Calgary Hopewell Professorship of Clinical
Imaging for Epilepsy Diagnosis December 2, 2011 Samuel Wiebe, MD University of Calgary Canada American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure University of Calgary Hopewell Professorship of Clinical
Intracranial video-eeg and surgery for focal atonic seizures
 Clinical commentary with video sequences Epileptic Disord 2013; 15 (1): 62-6 Intracranial video-eeg and surgery for focal atonic seizures Martín Donadío, Gabriela Ugarnes, Mónica Segalovich, Naomi rakaki,
Clinical commentary with video sequences Epileptic Disord 2013; 15 (1): 62-6 Intracranial video-eeg and surgery for focal atonic seizures Martín Donadío, Gabriela Ugarnes, Mónica Segalovich, Naomi rakaki,
Adult-Onset Neurologic Dysfunction Associated with Cortical Malformations
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1037 1043, June/July 1999 Adult-Onset Neurologic Dysfunction Associated with Cortical Malformations Woo Ho Cho, David Seidenwurm, and A. James Barkovich BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1037 1043, June/July 1999 Adult-Onset Neurologic Dysfunction Associated with Cortical Malformations Woo Ho Cho, David Seidenwurm, and A. James Barkovich BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic Cleft
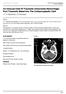 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case
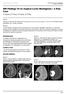 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
Prognostic factors in pediatric brain-stem gliomas
 J Neurosurg 65:751-755, 1986 Prognostic factors in pediatric brain-stem gliomas A. LLAND ALBRIGHT, M.D., A. NRMAN GUTHKLCH, M.CH., F.R.C.S., RGR J. PACKR, M.D., RBRT A. PRIC, M.D., AND LUCY B. RURK, M.D.
J Neurosurg 65:751-755, 1986 Prognostic factors in pediatric brain-stem gliomas A. LLAND ALBRIGHT, M.D., A. NRMAN GUTHKLCH, M.CH., F.R.C.S., RGR J. PACKR, M.D., RBRT A. PRIC, M.D., AND LUCY B. RURK, M.D.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Quek AM, Britton JW, McKeon A, et al. Autoimmune epilepsy: clinical characteristics and response to immunotherapy. Arch Neurol. Published online March 26, 2012. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.2985.
Supplementary Online Content Quek AM, Britton JW, McKeon A, et al. Autoimmune epilepsy: clinical characteristics and response to immunotherapy. Arch Neurol. Published online March 26, 2012. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.2985.
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods
 Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Gangliogliomas: A Report of Five Cases
 Case Report Gangliogliomas: A Report of Five Cases Nair V, Suri VS, Tatke M, Saran RK, Malhotra V, Singh D* Departments of Pathology and *Neurosurgery, G. B. Pant Hospital, New Delhi, India. Correspondence
Case Report Gangliogliomas: A Report of Five Cases Nair V, Suri VS, Tatke M, Saran RK, Malhotra V, Singh D* Departments of Pathology and *Neurosurgery, G. B. Pant Hospital, New Delhi, India. Correspondence
Sonography of Brain Tumors in Infants
 253 Sonography of Brain Tumors in Infants Bokyung K. Han 1 Diane S. Babcock Alan E. Oestreich Cranial sonograms of six children with brain tumors (one newborn, four infants, and one 4-year-old child) are
253 Sonography of Brain Tumors in Infants Bokyung K. Han 1 Diane S. Babcock Alan E. Oestreich Cranial sonograms of six children with brain tumors (one newborn, four infants, and one 4-year-old child) are
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
and MR Imaging Findings in Rasmussen Encephalitis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1291 1299, August 2001 18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography and MR Imaging Findings in Rasmussen Encephalitis David J. Fiorella, James M. Provenzale, R. Edward
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1291 1299, August 2001 18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography and MR Imaging Findings in Rasmussen Encephalitis David J. Fiorella, James M. Provenzale, R. Edward
MR Imaging of Intracranial Fluid Levels
 695 MR Imaging of Intracranial Fluid Levels James J. Abrahams 1 Mika Lidov Carlos Artiles Six patients with seven intracranial fluid levels were evaluated with both CT and MR at 1.5 T. A surgical diagnosis
695 MR Imaging of Intracranial Fluid Levels James J. Abrahams 1 Mika Lidov Carlos Artiles Six patients with seven intracranial fluid levels were evaluated with both CT and MR at 1.5 T. A surgical diagnosis
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE
 THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Cerebral MRI as an important diagnostic tool in temporal lobe epilepsy
 Cerebral MRI as an important diagnostic tool in temporal lobe epilepsy Poster No.: C-2190 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Puiu, D. Negru; Iasi/RO Keywords: Neuroradiology brain,
Cerebral MRI as an important diagnostic tool in temporal lobe epilepsy Poster No.: C-2190 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Puiu, D. Negru; Iasi/RO Keywords: Neuroradiology brain,
Successful Treatment of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Bilateral Hippocampal Atrophy and False Temporal Scalp Ictal Onset: A case report
 Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol. 61, No. 2, 37~41, June, 2012 HIJM 61 7 37 Successful Treatment of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Bilateral Hippocampal Atrophy and False Temporal Scalp Ictal Onset: A case
Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol. 61, No. 2, 37~41, June, 2012 HIJM 61 7 37 Successful Treatment of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Bilateral Hippocampal Atrophy and False Temporal Scalp Ictal Onset: A case
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Original Article Evaluation of Diagnostic Value of CT Scan and MRI in Brain Tumors and Comparison with Biopsy
 Original Article Evaluation of Diagnostic Value of CT Scan and MRI in Brain Tumors and Comparison with Biopsy Taghipour Zahir SH MD 1, Rezaei sadrabadi M MD 2, Dehghani F MD 3 1- Department of Clinical
Original Article Evaluation of Diagnostic Value of CT Scan and MRI in Brain Tumors and Comparison with Biopsy Taghipour Zahir SH MD 1, Rezaei sadrabadi M MD 2, Dehghani F MD 3 1- Department of Clinical
Case Report. Case Report
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review
 Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
MR of Intraparotid Masses
 MR of Intraparotid Masses Bruce N. Schlakman and David M. Yousem PURPOSE: To determine which MR techniques are best for identifying intraparotid masses and to assess the utility of MR for predicting specific
MR of Intraparotid Masses Bruce N. Schlakman and David M. Yousem PURPOSE: To determine which MR techniques are best for identifying intraparotid masses and to assess the utility of MR for predicting specific
Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma
 Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma Christine E. Fuller Keywords Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma; Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features 2.1 OVERVIEW Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) is an uncommon
Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma Christine E. Fuller Keywords Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma; Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features 2.1 OVERVIEW Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) is an uncommon
MR Imaging of CSF-Iike Choroidal Fissure and Parenchymal Cysts of the Brain
 1069 MR Imaging of CSF-Iike Choroidal Fissure and Parenchymal Cysts of the Brain John L. 2 The purposes of this study were to delineate the MR characteristics of CSF-like Ernest Carnponovo3 parenchymal
1069 MR Imaging of CSF-Iike Choroidal Fissure and Parenchymal Cysts of the Brain John L. 2 The purposes of this study were to delineate the MR characteristics of CSF-like Ernest Carnponovo3 parenchymal
The "Keyhole": A Sign of
 473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
Visual Rating Scale Reference Material. Lorna Harper Dementia Research Centre University College London
 Visual Rating Scale Reference Material Lorna Harper Dementia Research Centre University College London Background The reference materials included in this document were compiled and used in relation to
Visual Rating Scale Reference Material Lorna Harper Dementia Research Centre University College London Background The reference materials included in this document were compiled and used in relation to
Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions
 Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions Poster No.: C-3394 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro - Your latest results Authors: J. R. Docampo, M. Cabrini, C. Morales,
Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions Poster No.: C-3394 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro - Your latest results Authors: J. R. Docampo, M. Cabrini, C. Morales,
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Imaging Findings of CNS Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumors
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:476 480, March 2004 Case Report Imaging Findings of CNS Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumors Atilla Arslanoglu, Nafi Aygun, Deapak Tekhtani, Leslie Aronson, Ken Cohen, Peter C. Burger,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:476 480, March 2004 Case Report Imaging Findings of CNS Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumors Atilla Arslanoglu, Nafi Aygun, Deapak Tekhtani, Leslie Aronson, Ken Cohen, Peter C. Burger,
Henry Molaison. Biography. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Henry Molaison From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Henry Gustav Molaison (February 26, 1926 December 2, 2008), known widely as H.M., was an American memory disorder patient who had a bilateral medial
Henry Molaison From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Henry Gustav Molaison (February 26, 1926 December 2, 2008), known widely as H.M., was an American memory disorder patient who had a bilateral medial
Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6434623, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6434623 Case Report Intracranial Capillary Hemangioma in the Posterior Fossa of an Adult Male Jordan Nepute,
3.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system
 3.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system 1 3.02 Essential Questions What are the functions of the nervous system? What are some disorders of the nervous system? How are nervous
3.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the nervous system 1 3.02 Essential Questions What are the functions of the nervous system? What are some disorders of the nervous system? How are nervous
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
General Identification. Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27
 General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Electro-clinical manifestations of the epilepsy associated to the different anatomical variants of hypothalamic hamartomas
 Electro-clinical manifestations of the epilepsy associated to the different anatomical variants of hypothalamic hamartomas Alberto JR Leal Hospital Fernando Fonseca, Dep. Neurology Lisbon. Abstract Objective
Electro-clinical manifestations of the epilepsy associated to the different anatomical variants of hypothalamic hamartomas Alberto JR Leal Hospital Fernando Fonseca, Dep. Neurology Lisbon. Abstract Objective
Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma
 Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Seizure Semiology and Neuroimaging Findings in Patients with Midline Spikes
 Epilepsia, 42(12):1563 1568, 2001 Blackwell Science, Inc. International League Against Epilepsy Seizure Semiology and Neuroimaging Findings in Patients with Midline Spikes *Ekrem Kutluay, *Erasmo A. Passaro,
Epilepsia, 42(12):1563 1568, 2001 Blackwell Science, Inc. International League Against Epilepsy Seizure Semiology and Neuroimaging Findings in Patients with Midline Spikes *Ekrem Kutluay, *Erasmo A. Passaro,
Variable Appearances of Subacute Intracranial Hematomas on High-Field Spin-Echo MR
 1019 Variable Appearances of Subacute Intracranial Hematomas on High-Field Spin-Echo MR John M. Gomori' 2 Robert I. Grossman' David B. Hackney' Herbert I. Goldberg' Robert A. Zimmerman' Larissa T. Bilaniuk'
1019 Variable Appearances of Subacute Intracranial Hematomas on High-Field Spin-Echo MR John M. Gomori' 2 Robert I. Grossman' David B. Hackney' Herbert I. Goldberg' Robert A. Zimmerman' Larissa T. Bilaniuk'
IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT
 IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT Ramneet Wadi 1, Anil Kumar Shukla 2, Seetha Pramila V. V 3, Sabyasachi Basu 4, Sonam Sanjay 5 1Postgraduate Student, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT Ramneet Wadi 1, Anil Kumar Shukla 2, Seetha Pramila V. V 3, Sabyasachi Basu 4, Sonam Sanjay 5 1Postgraduate Student, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging
 Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Hemimegalencephaly without seizures: report of a case and review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Hemimegalencephaly without seizures: report of a case and review of literature Agrawal Atul, Dutta Gautam, Singh Daljit, Sachdeva
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Hemimegalencephaly without seizures: report of a case and review of literature Agrawal Atul, Dutta Gautam, Singh Daljit, Sachdeva
Advanced MR Imaging of Cortical Dysplasia with or without Neoplasm: A Report of Two Cases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1686 1691, November/December 2002 Case Report Advanced MR Imaging of Cortical Dysplasia with or without Neoplasm: A Report of Two Cases Jay J. Pillai, Richard B. Hessler, Jerry
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1686 1691, November/December 2002 Case Report Advanced MR Imaging of Cortical Dysplasia with or without Neoplasm: A Report of Two Cases Jay J. Pillai, Richard B. Hessler, Jerry
Imaging of Pediatric Epilepsy MRI. Epilepsy: Nonacute Situation
 Imaging of Pediatric Epilepsy Epilepsy: Nonacute Situation MR is the study of choice Tailor MR study to suspected epileptogenic zone Temporal lobe Extratemporal A. James Barkovich, MD University of California
Imaging of Pediatric Epilepsy Epilepsy: Nonacute Situation MR is the study of choice Tailor MR study to suspected epileptogenic zone Temporal lobe Extratemporal A. James Barkovich, MD University of California
Small and Big Operations: New Tools of the Trade for Brain Tumors. Disclosure. Incidence of Childhood Cancer
 Small and Big Operations: New Tools of the Trade for Brain Tumors Nalin Gupta MD PhD Chief, Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Departments of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of California San Francisco
Small and Big Operations: New Tools of the Trade for Brain Tumors Nalin Gupta MD PhD Chief, Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Departments of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of California San Francisco
High Resolution Ictal SPECT: Enhanced Epileptic Source Targeting?
 High Resolution Ictal SPECT: Enhanced Epileptic Source Targeting? Marvin A Rossi MD, PhD RUSH Epilepsy Center Research Lab http://www.synapticom.net Chicago, IL USA Medically-Refractory Epilepsy 500,000-800,000
High Resolution Ictal SPECT: Enhanced Epileptic Source Targeting? Marvin A Rossi MD, PhD RUSH Epilepsy Center Research Lab http://www.synapticom.net Chicago, IL USA Medically-Refractory Epilepsy 500,000-800,000
EEG IN FOCAL ENCEPHALOPATHIES: CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE, NEOPLASMS, AND INFECTIONS
 246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors
 Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Case Report Complex Form Variant of Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Cerebellum
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2012, Article ID 718651, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/718651 Case Report Complex Form Variant of Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Cerebellum Jesús Vaquero, 1,
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2012, Article ID 718651, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/718651 Case Report Complex Form Variant of Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor of the Cerebellum Jesús Vaquero, 1,
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
The Changing Surgical Landscape in Kids
 The Changing Surgical Landscape in Kids December 7, 2013 Howard L. Weiner, MD NYU Langone Medical Center American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure none American Epilepsy Society 2013 Annual Meeting
The Changing Surgical Landscape in Kids December 7, 2013 Howard L. Weiner, MD NYU Langone Medical Center American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure none American Epilepsy Society 2013 Annual Meeting
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Men think epilepsy divine, merely because they do not understand it. But if they called everything divine which they do not understand, why, there would be no end to divine things.
Chapter 1 Introduction Men think epilepsy divine, merely because they do not understand it. But if they called everything divine which they do not understand, why, there would be no end to divine things.
Peter Canoll MD. PhD.
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions
 Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions Poster No: C-3394 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J R Docampo, M Cabrini, C Morales, C Bruno; Buenos Aires/ AR
Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracraneal lesions Poster No: C-3394 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J R Docampo, M Cabrini, C Morales, C Bruno; Buenos Aires/ AR
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.113 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.113 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation
