Angiomyofibroblastoma (AMFB) is a rare, benign,
|
|
|
- Colin Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: A diagnostic dilemma* By Katrina D. Romblon, MD and Rex Marco M. Poblete, MD, FPOGS, FPSUOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, De La Salle University Medical Center ABSTRACT Angiomyofibroblastoma (AMFB) is a rare, benign, well-circumscribed mesenchymal soft tissue neoplasm redominantly occurring in the vulvovaginal region among women of reproductive age (35-45 years old). Histologically, it is characterized by presence of alternating hypo and hypercellular areas containing spindle and round stromal cells admixed with blood vessels. At present, there are 137 cases reported since it was first described in Currently, there are no published cases of Angiomyofibroblastoma in the Philippines. This is a case report of a 31 year old, nulligravid patient who presented with unilateral labial enlargement which was noted to be painless and slow growing. The initial impression was that of a benign tumor of the labia. The mass was excised and histopathologic results were consistent with the microscopic findings of Angiomyofibroblastoma. Simple excision of the mass is the only treatment, as in this case, and is noted to have extremely low rate of recurrence. The clinical importance to distinguish this unusual neoplasm from Aggressive Angiomyxoma and other mesenchymal malignant neoplasm with metastatic potential should be emphasized for appropriate management. Keywords: Angiomyofibroblastoma, Mesenchymal Tumors, Vulva INTRODUCTION Angiomyofibroblastoma (AMFB) is a rare, benign, mesenchymal tumor that occurs mainly, but not exclusively, in the vulvar region of reproductive aged women. 1 More often, these tumors are encountered in the vulva. However, 10% to 15% occur in the vagina, occasionally in the perineum and the inguinal region while rare reports of fallopian tube lesions are also found. 2 Rare cases have also been reported to arise in the scrotum and the inguinal area in males. 3,4 This tumor is commonly seen in women of reproductive age as well as in perimenopausal women. The occurring average age of female is 45.8 years and is rather slow growing, from few weeks to 13 years, without pain. 5 There is female-to-male ratio found to be 10:1. In women, the vast majority of tumors are located in the vulva. 12 Angiomyofibroblastoma was first described in 1992 as a new entity that occurred exclusively in the vulvo vaginal area, predominantly of the vulva, of young to middle aged women. 6 Fletcher et al described 10 cases of previously unrecognized benign soft tissue tumor of the vulva that were misdiagnosed as Aggressive Angiomyxoma. 3 *Finalist, Philippine Obstetrical and Gynecological Society (Foundation), Inc. (POGS) Interesting Case Paper Contest, April 19, 2018, 7th Flr., Olive and Citron Function Rooms, Richmonde Hotel, Iloilo City Since then, 137 cases of Angiomyofibroblastoma have been reported in the English medical literature. 12 Currently, there are no published case reports of this rare neoplasm in the Philippines. This tumor is considered benign and of low recurrence rate after simple excision of the tumor. However, due to its rarity, misdiagnosis may happen. Correct identification of this tumor is important for appropriate management and rule out malignant neoplasms with widespread metastatic potential such as Aggressive Angiomyxoma. The knowledge of this tumor would help clinicians in avoiding significant delay in diagnosis, management and follow up. This report presents a case of a 30 year-old, nulligravid who presented with a slow growing and painless tumor of the labia majora. The patient underwent local excision of the tumor and histopathological findings revealed presence of spindle to round shaped cells with alternating hypo and hypercellular areas admixed with thin walled capillary type blood vessels. These microscopic findings were consistent to that of Angiomyofibroblastoma. CASE REPORT This is a case of E.C., a 31 year-old, nulligravid, single, Filipino, Roman Catholic patient from Dasmariñas, Cavite. She consulted at the outpatient department of a tertiary institution for the first time last March 2017 with a chief complaint of a right labial mass. 30 Volume 42, Number 3, May-June 2018
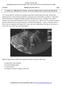
2 The patient was apparently well until three months prior to consult when she noted a non pruritic, non tender, erythematous, 2 x 2 cm lesion on the right lower labial area. No other symptoms were noted such as vaginal discharge, bleeding, discomfort noted. There were no dysuria, hypogastric pain noted. She did not take nor applied any medications. No consultation was done. During the interim, patient noted a gradual increase in size but still no symptoms mentioned above were noted. The lesion was approximately 3 x 3 cm in size but remained non pruritic, non tender and erythematous. Due to further increase in size of the lesion, the patient sought consultation at a tertiary hospital and the primary impression then was Bartholin s duct cyst. Past medical history revealed no history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma and other atopic diseases. No history of any cardiovascular, pulmonary, thyroid, hepatobiliary, gastroenterology or renal diseases noted. There were no other previous hospitalizations nor surgeries noted. Patient noted no heredofamilial diseases such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma and other atopic diseases. No history of any cardiovascular, pulmonary, thyroid, hepatobiliary, gastroenterology or renal diseases noted. No cancer or the same symptomatology noted from other members of the family. The patient is a college graduate and is a non smoker and non alcoholic beverage drinker. She has no preferred diet. She allegedly has no history of illicit drug use. The patient had her menarche by the age of 12 years old. Her cycle was noted to be regularly occurring with days interval and has a duration of approximately 5 days. She uses 6-8 regular pads, minimally soaked per day. She noted to have dysmenorrhea on the first day of her cycle and gradually decreases to null on the second to third day of menses. No other symptoms noted. Patient allegedly still has no sexual contact or any related sexual relationship at the time examination. Patient has no history of any form of contraceptive use. She noted no history of any vaginal pruritus, discharge or any infections or diseases pertaining to the female reproductive tract. She has not undergone papsmear or any medical examination pertaining to the female reproductive tract. Patient noted this was the first time growth of any masses has occurred in the vulvo perineal area. Upon examination of the genitalia, there was a 5 x 5 cm well circumscribed, non tender, erythematous mass on the inner mid to lower portion of the right labia majora. The mass was well circumscribed, soft to doughy, with no ulcerations noted. Other parts of the external genitalia and contralateral labia were grossly normal. All other systemic examinations were unremarkable. No internal examination done. Rectal examination revealed good sphincteric tone. Rectovaginal septum was smooth with no masses or lesions. The uterine corpus was small and no adnexal masses palpated or tenderness noted. No inguinal lymphadenopathy noted. The patient was subjected to have a transrectal/ translabial ultrasound on day 7 of cycle (Figures 1-3) and the primary consideration at that time was a benign vulvar mass, to consider Bartholin s Duct Cyst. The endometrium and cervix were noted to be unremarkable. The ovaries were noted to be polycystic. Transrectal/Translabial Ultrasound (03/30/2017) Uterine corpus: 4.8 x 2.4 x 2.4 cm anteverted Cervix: 2.9 x 2.4 x 2.4 cm Endometrium: 0.5 hyperechoic Adnexae: Right ovary: 3.2 x 3.7 x 2.2 cm vol= 13.2 ml (+) more than 12 small peripherally located follicles with dense stroma Left ovary: 3.3 x 3.0 x 2.1 cm vol= 11.0 ml (+) more than 12 small peripherally located follicles with dense stroma Others: Lateral and to the right of the lower third of the vagina is a 4.5 x 5.4 x 4.7 cm well circumscribed, heterogenous solid mass. There is no duct connection between the said mass and the urethral wall. No fluid on the posterior cul de sac. Impression: Normal sized anteverted uterus with intact endometrium, Normal cervix, Polycystic ovaries, Labial mass, right, consider Bartholin s duct cyst. Upon noting the transrectal ultrasound, the patient was advised to undergo elective excision of the labial mass. Approximately one week after consultation at the out patient department and upon patient s consent, she was scheduled and eventually underwent elective surgical excision of vulvar mass, right, under spinal anesthesia. Intraoperatively, there was an asymmetrical external genitalia with a soft to doughy mass located from the 6 o clock position to 11 o clock position extending anterolateral to the urethra located at the right labia measuring 5.0 x 5.0 x 3.5 cm, ovoid and was well circumscribed, with a soft to doughy consistency covered by skin on all sides (Figure 4). On cut section, the mass was soft to doughy, cream tan in color and showed whorled like pattern with no areas of hemorrhage and necrosis. Postoperatively, the diagnosis was Vulvar Mass, Right probably benign. Volume 42, Number 3, PJOG May-June
3 Translabial Ultrasound (03/30/2017) Transrectal Ultrasound (03/30/2017) A A B Figures 1A and 1B. Translabial Ultrasound revealed lateral and to the right of the lower third of the vagina is a 4.5 x 5.4 x 4.7 cm well circumscribed, heterogenous, solid mass. The sample was sent for histopathological examination. Multiple representative sections were taken and submitted for processing. Histological examination revealed a skin covered tissue showing hyper/hypocellular areas containing spindle and plump stromal cells admixed with blood vessels. The findings were compatible with the histologic features of Angiomyofibroblastoma, considering the presence of spindle cells admixed with thin walled blood vessels (Figure E). The resection proved to be curative with no recurrence until the last follow-up in September CASE DISCUSSION Angiomyofibroblastoma was initially said to be a vulva-specific neoplasm. However, there were several case reports showing it can also occur in the vagina, perineum and inguinal areas. It was hypothesized to be derived from mesenchymal cells in the subepithelial B C Figures 2A, 2B and 2C. Transrectal Ultrasound revealed normal sized anteverted uterus with intact endometrium and normal cervix. myxoid stromal zone that extends from the endocervix to the vulva. Angiomyofibroblastoma is positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors. This represents the hormone responsive nature of this lesion and may explain why it 32 Volume 42, Number 3, May-June 2018
4 Histopathologic pictures A B Figures 3A and 3B. Transrectal Ultrasound revealed polycystic ovaries. Gross picture of the right labial mass Figure 5. The following figures show the microscopic findings as round to spindle shaped cells (first and second photos) with hypo and hypercellular areas (third and forth photos) admixed with thin walled blood vessels (last photo). Histopathology report (April 5, 2017) PROCEDURE: Excision of Vulvar Mass (APRIL 1, 2017) Findings: Consistent with Angiofibromyoblastoma Figure 4 showed a gross photo of a well delineated, sessile right labial mass measuring 5.0 x 5.0 cm prior to surgical excision. The specimen labeled VULVAR MASS RIGHT LABIA consists of an irregularly shaped cream white to pinkish red, soft to doughy tissue with one side exhibiting whorled pattern surface measuring 5.0 x 5.0 x 3.5 cm. Cut sections show cream white homogenous solid surface. Volume 42, Number 3, PJOG May-June
5 is most common among reproductive aged women. This could also explain to some extent the predisposition of this tumor to arise in the lower genital tract since these hormone responsive receptors are normally found in the subepithelial stromal cells of the vulva and vagina. Angiomyofibroblastoma was first described was in a study done in 1992 as a new entity that occurred exclusively in the vulvo vaginal area, predominantly of the vulva, of young to middle aged women. 6 The authors described 10 cases of previously unrecognized benign soft tissue tumor of the vulva that were misdiagnosed as Aggressive Angiomyxoma. 3 Since then, only about 137 cases have been reported in the English medical literature. 12 Currently, there are no published case reports of this rare neoplasm in the Philippines. We are presented with a case of a 31 year-old, nulligravid patient with a three month history of a slow growing painless mass on the right vulva with no other symptoms noted such as dysuria, dyspareunia, vaginal bleeding and discharge. Grossly the mass was observed to be, firm, movable and non tender. Because of the said gross features, indolent behavior of the mass, and absence of systemic as well as local symptoms, such as weight loss, bleeding, dysuria, urinary retention, change in bowel movement, malignancy was ruled out. The initial diagnosis was that of a benign vulvar mass, to consider Bartholin s gland cyst. To rule out other possible benign lesions and possible extension of the mass to the internal genitalia, transrectal and translabial ultrasound was requested. The patient underwent elective surgical excision of the vulvar mass. Intraoperatively, it was described as well delineated, sessile and firm. Clinically, most of the tumors present as slow growing, painless masses, and are often misdiagnosed as Bartholin gland cyst, hydrocele of the canal of Nuck, inguinal hernia, leiomyoma, or mesenchymal tumors, such as lipoma and liposarcoma, and aggressive angiomyxoma. 8,9 However, rare symptoms include dyspareunia, localized burning sensation and/ or mild tenderness of growing mass. Grossly, it is often described as well delineated, sessile, smooth, and mobile. Its texture is usually described as ruberry or firm. There are only five cases of pedunculated vulvar Angiomyofibroblastoma reported on English literature. 11 Current journals noted that Angiomyofibroblastoma is indeed a diagnostic dilemma due to its gross features. Owing to its low incidence, Angiomyofibroblastoma and other vaginal soft tissue tumors can easily be confused clinically or sonographically with other, more common vaginal masses, such as Bartholin s cyst, rectocele, or urethral diverticulum. 12 No diagnostic modality has yielded high specificity and sensitivity in diagnosing Angiomyofibroblastoma. Sonographically, it was reported to be well demarcated with inhomogeneous echogenicity and multiple hypoechoic areas within an echogenic stroma. 12 In a study done in 2014, wherein the authors described two cases of Angiomyofibroblastoma out of 72 perineal tumors, they characterized it as solid cystic masses on the basis of ultrasonography. In contrast to these descriptions, the tumor found in this case was sonographically described as well circumscribed, heterogenous, solid mass. The purpose of doing other diagnostic imaging such as Computerized Tomography (CT) scan and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) on vulvovaginal masses is to describe its contiguity and determine surgical planes. It is important to determine if these masses are locally infiltrative and to rule out possible attachment to the other structures, specifically, the urethra. However, several studies concluded that indeed other imaging modalities may be used, but still yield vague results. In a study done in 2012, Angiomyofibroblastoma on Computerized Tomography imaging most likely show moderate-tostrong enhancement, which may reflect the prominent vascularity of these tumors. In a study done in 2015, it was noted that the obtained Magnetic Resonance images did not add much information to what was already known based on the ultrasound studies. In the said study, the authors concluded that Magnetic Resonance imaging is not mandatory in the evaluation of soft tissue lesions of the lower genital tract such as Angiomyofibroblastoma. The authors also noted that ultrasonography is cost effective, widely available and extremely valuable in characterizing and distinguishing these tumors preoperatively to be able to plan for appropriate management. This held true with our patient. Use of translabial ultrasound was able to determine that the described mass had no duct connection with the urethral wall. Several studies have shown, however, that postoperative pathological examination of the surgical specimen remains the only way to definitively establish a diagnosis of Angiomyofibroblastoma. 12 The treatment of choice is still local excision of the mass and is deemed curative. In the world medical literature, except for one case with sarcomatous transformation of Angiomyofibroblastoma in an 80 year old woman, there are currently no published reports of local recurrence or metastatic disease. 14,15 In this case, the patient underwent surgical excision of the vulvar mass. The patient was then discharged the day after the surgical procedure and was advised for weekly, then eventually to monthly, follow up at the out patient department of the same tertiary institution. No recurrence was noted during the six months of the follow up period. The specimen was sent for histologic examination. 34 Volume 42, Number 3, May-June 2018 Volume 42, Number 3 PJOG May - June
6 Microscopically, there were round to spindle shaped cells with alternating hypo and hypercellular areas admixed with several capillary type, thin walled blood vessels. These microscopic findings were were similar microscopically with Angiomyofibroblastoma as described by several published cases. Characteristically, it shows round to spindle-shaped cells with alternating hypo and hypercellular areas, particularly around thin walled blood vessels. It was also noted that Angiomyofibroblastoma may have edematous stroma without extravasation of red blood cells from the blood vessels. With regards to biologic behavior, all published reports suggest a benign clinical outcome in patients with Angiomyofibroblastoma. As previously stated, based on published reports, only one reported a case that underwent a sarcomatous transformation and no recurrence was noted. 8,15 Conventional morphologic analysis is paramount in the recognition of genital Angiomyofibroblastoma. Immunohistology may assist in excluding other differential diagnoses. Differential diagnosis of mesenchymal tumors in the vulvovaginal area includes a wide array of lesions that are overlapping in both their morphology and immunohistochemistry. Their low incidence attributes to the significant dilemma in making the correct diagnosis. Aside from this, Angiomyofibroblastoma should be distinguished from Aggressive Angiomyxoma and other myxoid malignant tumours with widespread metastatic potential. In a study done in Pakistan in 2012, it was noted that the differentiation of Angiomyofibroblastoma based on histological properties is conveyed on the two integral components: the stromal cells and the blood vessels. Grossly, it is well-circumscribed lesion and microscopically it is characterized by alternating hypercellular and hypocellular edematous legions with abundant blood vessels. There were noted plump round to spindle-shaped cells either in cluster or present in a linear array around numerous delicate capillary-sized vessels within a variable edematous to collagenous matrix. Nuclear atypia or mitotic figures are rare and the tumor cells tend to cluster around blood vessels. The histopathology of this case revealed the characteristic findings. Other differential diagnoses that may be considered are Leiomyoma and Aggressive Angiomyxoma. In this case, the absence of arrangement of cells in a whorls and fascicles ruled out Leiomyoma. Other tumors that predominantly occur in the perineum may be confused with Angiomyofibroblastoma such as Fibroepithelieal Polyp, Cellular Angiofibroma, Superficial Myofibroblastoma, and Aggressive Angiomyxoma. Fibroepithelial Stromal Polyp is usually exophytic, submucosal in location and are poorly circumscribed with frequent bizarre stromal cells. In contrast, Angiomyofibroblastoma are sessile, subcutaneous, well circumscribed and with bland cells. Cellular Angiofibroma are characterized by uniformly moderately cellular, uniformly moderately cellular, bland spindle cells with large thick walled vessels. Angiomyofibroblastoma has clusters of rounded, epithelioid cells, often around numerous small vessels with alternating hypercellular and hypocellular areas. On the other hand, Superficial Myofibroblastoma has stellate and spindled cells with inconspicuous vascularity. This may be distinguished from Angiomyofibroblastoma since the latter has perivascular epithelioid cells with prominent vascularity. The most crucial issue was to determine if this case was that of a malignant and Aggressive Angiomyxoma (AAM). Aggressive Angiomyxoma is most likely to be confused with Angiomyofibroblastoma because both disease entities share many features including age at presentation, location, clinical manifestations, and pathological entities. Clinically, Aggressive Angiomyxoma is also noted to occur in the vulvovaginal region predominantly among women of reproductive age. It may be an incidental finding due to its indolent course. However, grossly, Aggressive Angiomyxoma is usually poorly circumscribed due to its infiltrative nature and is nearly always >5-10 cm in size. Due to its infiltrative nature, patients may experience dull, aching pain on the mass, often with urinary symptoms such as dysuria and urinary retention. Patients may also present with dyspareunia and bleeding from the mass. Due to its propensity to grow more than 10 cm, pressure symptoms may also be experienced. 16 Histologically, it is a benign soft tissue tumor, with noted high risk of local recurrence as well as local infiltration that often results in entrapment of nerves and mucosal glands, thus making complete excision difficult. 2 Aggressive Angiomyxoma shows hypocellularity with sparse spindled or stellate cells and large thick walled vessels. In this case, Angiomyofibroblastoma was distinguished from Aggressive Angiomyxoma by the former s clinical presentation as a slow growing, painless and asymptomatic mass, its gross feature as well circumscribed, sessile, mobile and soft to doughy consistency, and microscopic finding of presence of alternating hypo and hypercellular areas, admixed with small thin walled blood vessels. The microscopic findings of lack thick walled hyalinized vessels and extravasation of Red Blood Cells, together with absence of necrosis and mitosis were also features in favor of an Angiomyofibroblastoma. Several studies have shown that immunohistochemistry reports are variable and thus it may not be reliable for separation. In a study done in Pakistan in 2011, the authors noted that that Aggressive Volume 42, Number 3, PJOG May-June
7 Angiomyxoma shares immunophenotypic similarities with Angiomyofibroblastoma. Hence, immunoreactivity does not appear to be helpful in distinguishing between these neoplasms. This was further supported by another study in 2016 wherein they noted that Desmin, Estrogen receptor and Progesterone receptor are no longer considered reliable markers for distinguishing Aggressive Angiomyxoma from Angiomyofibroblastoma. Since the immunohistological markers of Angiomyofibroblastoma are similar to those of Aggressive Angiomyxoma, differentiation between these two tumors is largely based on the appearance of the tumor morphologically. In summary, Angiomyofibroblastoma is a rare benign mesenchymal tumour. Critical evaluation should be performed to rule out Aggressive Angiomyxoma, which requires the resection with wide tumor-free margins to prevent recurrence. Rapid and accurate diagnosis should be performed if possible, to prevent delay in appropriate management and follow up. SUMMARY Angiomyofibroblastoma is a rare but benign entity and often cause a diagnostic dilemma. Although the exact cause is unknown, it is curable with simple excision. A thorough histopathological examination of vulvar masses helps in differentiating angiomyofibroblastoma from other mesenchymal tumors occurring at this site. It is important to identify this type of tumor so that unnecessary followup and intervention post excision may be prevented. REFERENCES 1. Canales BK, Weiland D, Hoffman N, Slaton J, Tran M. (2006) Angiomyofibroblastoma-like tumors (cellular angiofibroma). Int J Urol. 13: Ibnerasa S, Yasmeen F, Shami N. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the Vulva. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan. 2012; Vol. 22(2): Fletcher CD, Tsang WY, Fisher C, Lee KC, Chan JK. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva. A benign neoplasm distinct from aggressive angiomyxoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992; 16: Ockner DM, Sayadi H, Swanson PE, Ritter JH, Wick MR. Genital angiomyofibroblastoma: comparison with ag- gressive angiomyxoma and other myxoid neoplasms of skin and soft tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 1997; 107: Nielsen GP, Young RH. Mesenchymal tumors and tumor- like lesions of the female genital tract: a selective review with emphasis on recently described entities. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2001; 20: Jian W, Weiqi S, Xiaoyu T, Daren S, Xiongzeng Z, Renyuan Z. Clinicopathologic analysis of angiomyofibroblastoma of the female genital tract. Chinese Med J. 2000; 113: Takeshima Y, Shinkoh Y, Inai K. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the Vulva: A Mitotically Active Variant? Second Department of Pathology, Hiroshima University School of Medicine, Hiroshima and^department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, National Ohtake Hospital, Ohtake, Japan. 8. Tochika N, Takeshita A, Sonobe H, Matsumoto M, Ko- bayashi M, Araki K. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: report of a case. Surg Today. 2001; 31: Indraccolo U, DeSanctis E, Liberati F, Ippolio M, Indraccolo SR. Giant angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva. Scott Med J. 2008; 53: Gianella, L. et.al., Pedunculated Angiomyofibroblastoma of the Vulva: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Division of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Cesare Magati Hospital, Scandiano, Reggio Emilia, Italy. Received 1 June 2011; Accepted 21 July Wolf Et Al. Ultrasound Plays A Key Role In Imaging And Management Of Genital Angiomyofibroblastoma: A Case Report. Department Of Obstetrics And Gynecology, Leipzig University, Liebigstrasse 20a, Leipzig. Germanyjournal Of Medical Case Reports. 2015; 9: Wang X, Yang H, Zhang H, Shi T, Ren W. Transvaginal sonographic features of perineal masses in the female lower urogenital tract: a retrospective study of 71 patients. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014; 43: Nielsen GP, Young RH, Dickersin GR, Rosenberg AE. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva with sarcomatous transformation. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997; 21(9): Zehra Nes et.al. Angiomyofibroblastoma Of The Vulva: A Rare But Distinct Entity. From The Department Of Obstetrics & Gynecology And 2pathology, Marmara University Medical School, Istanbul, Turkey. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2000; 79: Barmon, D., et.al, Aggressive Angiomyxoma of the Vulva. Department of Gynecologic Oncology. Journal of Midlife Health Barat S, Tirgar-Tabari S, Shafaee S. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva. Arch Iran Med. 2008; 11: Volume 42, Number 3, May-June 2018
An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors
 An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel School of Medicine
An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel School of Medicine
Article begins on next page
 Leiomyoma of the Vulva Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50624/story/]
Leiomyoma of the Vulva Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50624/story/]
Ultrasound plays a key role in imaging and management of genital angiomyofibroblastoma: acasereport
 Wolf et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2015) 9:248 DOI 10.1186/s13256-015-0715-4 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Ultrasound plays a key role in imaging and management of genital
Wolf et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2015) 9:248 DOI 10.1186/s13256-015-0715-4 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Ultrasound plays a key role in imaging and management of genital
Giant fibroepithelial stromal polyp of the vulva: largest case reported
 Madueke-Laveaux et al. Annals of Surgical Innovation and Research 2013, 7:8 CASE REPORT Open Access Giant fibroepithelial stromal polyp of the vulva: largest case reported Obianuju Sandra Madueke-Laveaux
Madueke-Laveaux et al. Annals of Surgical Innovation and Research 2013, 7:8 CASE REPORT Open Access Giant fibroepithelial stromal polyp of the vulva: largest case reported Obianuju Sandra Madueke-Laveaux
Giant Acrochordon of Vulva
 Giant Madhusudan Dey, Reema Kumar, Raghu Sriram Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India Abstract Giant acrochordon or fibroepithelial stromal polyps usually occur
Giant Madhusudan Dey, Reema Kumar, Raghu Sriram Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India Abstract Giant acrochordon or fibroepithelial stromal polyps usually occur
Notice of Faculty Disclosure
 Mesenchymal Tumors of the Vulva: Old, New, Something(s) Different Napa Valley Conference Pathology Education Partners Inc May 15, 2018 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University,
Mesenchymal Tumors of the Vulva: Old, New, Something(s) Different Napa Valley Conference Pathology Education Partners Inc May 15, 2018 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University,
Giant pelvic angiomyofibroblastoma: case report and literature review
 Qiu et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2014, 9:106 CASE REPORT Open Access Giant pelvic angiomyofibroblastoma: case report and literature review Ping Qiu 1, Zhe Wang 2, Yao Li 1* and Guangbin Cui 3* Abstract
Qiu et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2014, 9:106 CASE REPORT Open Access Giant pelvic angiomyofibroblastoma: case report and literature review Ping Qiu 1, Zhe Wang 2, Yao Li 1* and Guangbin Cui 3* Abstract
Female Genital Tract Lab. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan
 Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1994, 39
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Leiomyoma of the Round Ligament Pre Matsuo, Shigetoshi; Soejima, Hideno Takashi Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1994, 39 Issue Date 1994-10-25 URL
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Leiomyoma of the Round Ligament Pre Matsuo, Shigetoshi; Soejima, Hideno Takashi Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1994, 39 Issue Date 1994-10-25 URL
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions.
 Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Ovarian fibroma feigning carcinoma in a young female: a rare case presentation
 Case Report: Ovarian fibroma feigning carcinoma in a young female: a rare case presentation Dr. Kandukuri Mahesh Kumar, Dr. Swarupa Ravuri, Dr. Sudhir Kumar Vujhini, Dr. V. Indira Name of the Institute/college:
Case Report: Ovarian fibroma feigning carcinoma in a young female: a rare case presentation Dr. Kandukuri Mahesh Kumar, Dr. Swarupa Ravuri, Dr. Sudhir Kumar Vujhini, Dr. V. Indira Name of the Institute/college:
A case of giant benign localized fibrous tumor of the pleura
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.30 / No. 4/2000 A case of giant benign localized fibrous tumor of the pleura ALİ KEMAL UZUNLAR 1, MEHMET YALDIZ 1, İBRAHİM H. ÖZERCAN 2, FAHRİ YILMAZ 1, AKIN E. BALCI 3 1
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.30 / No. 4/2000 A case of giant benign localized fibrous tumor of the pleura ALİ KEMAL UZUNLAR 1, MEHMET YALDIZ 1, İBRAHİM H. ÖZERCAN 2, FAHRİ YILMAZ 1, AKIN E. BALCI 3 1
A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen
 May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
A case of extremely rare ovarian tumor: Primary ovarian adenomyoma
 Kawasaki Medical Journal 233 A case of extremely rare ovarian tumor: Primary ovarian adenomyoma Shoji KAKU, Takuya MORIYA, Naoki KANOMATA, Tsuyoshi ISHIDA Yangsil CHANG, Norichika USHIODA, Yuichiro NAKAI
Kawasaki Medical Journal 233 A case of extremely rare ovarian tumor: Primary ovarian adenomyoma Shoji KAKU, Takuya MORIYA, Naoki KANOMATA, Tsuyoshi ISHIDA Yangsil CHANG, Norichika USHIODA, Yuichiro NAKAI
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors
 Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
Short communication: A rare case of vaginal dermoid cyst: A case report and review of literature
 Short communication: A rare case of vaginal dermoid cyst: A case report and review of literature Author(s): Mesfer S. Al-Shahrani and Mark Heywood Vol. 17, No. 2 (2006-05 - 2006-08) Biomedical Research
Short communication: A rare case of vaginal dermoid cyst: A case report and review of literature Author(s): Mesfer S. Al-Shahrani and Mark Heywood Vol. 17, No. 2 (2006-05 - 2006-08) Biomedical Research
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation
 246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
CASE REPORT PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE.
 PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
A giant skin Tag over labium majus: An unusual location of skin tag
 A giant skin Tag over labium majus: An unusual location of skin tag Garima Gupta 1, Ruchi Sinha 2, Sulekha Pandey 3, L. K. Pandey 3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Institute of Medical Sciences,
A giant skin Tag over labium majus: An unusual location of skin tag Garima Gupta 1, Ruchi Sinha 2, Sulekha Pandey 3, L. K. Pandey 3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Institute of Medical Sciences,
Division of Pathology
 Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Painless palpable scrotal mass
 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Urogenital Painless palpable scrotal mass Charis Anastasiadis, Georgia Kyriakopoulou, Charikleia Triantopoulou Radiology Department, Konstantopoulio General Hospital of Nea
Clinical Case - Test Yourself Urogenital Painless palpable scrotal mass Charis Anastasiadis, Georgia Kyriakopoulou, Charikleia Triantopoulou Radiology Department, Konstantopoulio General Hospital of Nea
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory.
 Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Endometrial Stromal Tumors
 Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER
 INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER 1 The Australia New Zealand Gynaecological Oncology Group is Australia s peak national research organisation. It raises awareness and funds for gynaecological
INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER 1 The Australia New Zealand Gynaecological Oncology Group is Australia s peak national research organisation. It raises awareness and funds for gynaecological
Disclosure. Case. Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix. I have nothing to disclose
 Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA UCSF Current Issues in Anatomic
Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA UCSF Current Issues in Anatomic
A RARER CASE OF A RARE DISEASE: AGGRESSIVE ANGIOMYXOMA (AAM) IN A SIXTEEN YEAR OLD.
 The West London Medical Journal 2013 Vol 5 No 1 pp 1-5 A RARER CASE OF A RARE DISEASE: AGGRESSIVE ANGIOMYXOMA (AAM) IN A SIXTEEN YEAR OLD. ABSTRACT Benjamin Faber *, Roisin Dunwoody, Naila Kamal A 16 year
The West London Medical Journal 2013 Vol 5 No 1 pp 1-5 A RARER CASE OF A RARE DISEASE: AGGRESSIVE ANGIOMYXOMA (AAM) IN A SIXTEEN YEAR OLD. ABSTRACT Benjamin Faber *, Roisin Dunwoody, Naila Kamal A 16 year
A case of pedunculated intraperitoneal leiomyoma
 Jichi Medical University Journal Chio Shuto Kuniyasu Soda Takayoshi Yoshida Fumio Konishi Abstract We report a very rare case of a pedunculated intraperitoneal leiomyoma in the parietal peritoneum of the
Jichi Medical University Journal Chio Shuto Kuniyasu Soda Takayoshi Yoshida Fumio Konishi Abstract We report a very rare case of a pedunculated intraperitoneal leiomyoma in the parietal peritoneum of the
57th Annual HSCP Spring Symposium 4/16/2016
 An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE
 Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Case Fibrothecoma of the ovary
 Case 10646 Fibrothecoma of the ovary Elisa Melo Abreu, Teresa Margarida Cunha Section: Genital (Female) Imaging Published: 2015, Jan. 2 Patient: 70 year(s), female Authors' Institution Department of Radiology,
Case 10646 Fibrothecoma of the ovary Elisa Melo Abreu, Teresa Margarida Cunha Section: Genital (Female) Imaging Published: 2015, Jan. 2 Patient: 70 year(s), female Authors' Institution Department of Radiology,
Endometrial polyp icd-10
 Endometrial polyp icd-10 Billable Medical Code for Polyp of Corpus Uteri Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 621.0. Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10. Free, official
Endometrial polyp icd-10 Billable Medical Code for Polyp of Corpus Uteri Diagnosis Code for Reimbursement Claim: ICD-9-CM 621.0. Code will be replaced by October 2015 and relabeled as ICD-10. Free, official
A Practical Approach to Adnexal Masses
 A Practical Approach to Adnexal Masses Darcy J. Wolfman, MD Section Chief of Genitourinary Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Clinical Associate Johns Hopkins Community Radiology Division
A Practical Approach to Adnexal Masses Darcy J. Wolfman, MD Section Chief of Genitourinary Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Clinical Associate Johns Hopkins Community Radiology Division
IN THE NAME OF GOD POV: CYSTIC OVARIAN LESION
 IN THE NAME OF GOD POV: CYSTIC OVARIAN LESION CASE 1 20 years old girl with AUB and pelvic pain from 2 weeks ago Impression :Simple unilocular 6 cm ovarian cyst Next step? Almost certainly benign so FU
IN THE NAME OF GOD POV: CYSTIC OVARIAN LESION CASE 1 20 years old girl with AUB and pelvic pain from 2 weeks ago Impression :Simple unilocular 6 cm ovarian cyst Next step? Almost certainly benign so FU
Case Report Ileocecal Intussusception due to a Lipoma in an Adult
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 684298, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/684298 Case Report Ileocecal Intussusception due to a Lipoma in an Adult Mehmet Bilgin, 1 Huseyin Toprak, 1 Issam Cheikh
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 684298, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/684298 Case Report Ileocecal Intussusception due to a Lipoma in an Adult Mehmet Bilgin, 1 Huseyin Toprak, 1 Issam Cheikh
ADENOMYOSIS CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN IMAGING CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN ADENOMYOSIS: PATHOLOGY ADENOMYOSIS
 CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN IMAGING CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN MOSTAFA ATRI, MD Dipl. Epid. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Non-menstrual pain of 6 months Prevalence 15%: 18-50 years of age 10-40% of gynecology
CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN IMAGING CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN MOSTAFA ATRI, MD Dipl. Epid. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Non-menstrual pain of 6 months Prevalence 15%: 18-50 years of age 10-40% of gynecology
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors
 The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology
 American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology
 Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of Primary Ovarian Leiomyosarcoma: a Case Report and Review of the Literature
 May, 2017 2017; Vol1; Issue4 http://iamresearcher.online Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of Primary Ovarian Leiomyosarcoma: a Case Report and Review of the Literature Lama M AlMudaimeegh Department of
May, 2017 2017; Vol1; Issue4 http://iamresearcher.online Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of Primary Ovarian Leiomyosarcoma: a Case Report and Review of the Literature Lama M AlMudaimeegh Department of
3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 01 Page January 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Uterine Myxoid Leiomyosarcoma with Paraneoplastic Syndrome- A Rare Combination Abstract Author Dr. Shubhadeep Bhattacharjee MBBS,MS (O&G),
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Uterine Myxoid Leiomyosarcoma with Paraneoplastic Syndrome- A Rare Combination Abstract Author Dr. Shubhadeep Bhattacharjee MBBS,MS (O&G),
Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report
 Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report Rosanna Nenna 1 Cosimo Damiano Inchingolo 1 Domenico Palmieri 2 Annalisa De Lucia 1 Giusy Elicio 1 Pina Miscioscia 1 ( 1 ) U.O.C. di Anatomia Patologica,
Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report Rosanna Nenna 1 Cosimo Damiano Inchingolo 1 Domenico Palmieri 2 Annalisa De Lucia 1 Giusy Elicio 1 Pina Miscioscia 1 ( 1 ) U.O.C. di Anatomia Patologica,
What is endometrial cancer?
 Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/20/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 34 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/20/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 34 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh
 Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma
 49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences
 Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Describe the typical imaging findings of GIST at initial
Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Describe the typical imaging findings of GIST at initial
MR Findings of Extrauterine Mu llerian Adenosarcoma Associated with Deep Pelvic Endometriosis 1
 MR Findings of Extrauterine Mullerian Adenosarcoma Associated with Deep Pelvic Endometriosis 1 Dae Kun Oh, M.D., Chan Kyo Kim, M.D., Byung Kwan Park, M.D., Ji Young Kim, M.D. 2 Extrauterine mu llerian
MR Findings of Extrauterine Mullerian Adenosarcoma Associated with Deep Pelvic Endometriosis 1 Dae Kun Oh, M.D., Chan Kyo Kim, M.D., Byung Kwan Park, M.D., Ji Young Kim, M.D. 2 Extrauterine mu llerian
Posterior Deep Endometriosis. What is the best approach? Posterior Deep Endometriosis. Should we perform a routine excision of the vagina??
 Posterior Deep Endometriosis What is the best approach? Dept Gyn Obst Polyclinique Hotel Dieu CHU Clermont Ferrand France Posterior Deep Endometriosis Organs involved - Peritoneum - Uterine cervix -Rectum
Posterior Deep Endometriosis What is the best approach? Dept Gyn Obst Polyclinique Hotel Dieu CHU Clermont Ferrand France Posterior Deep Endometriosis Organs involved - Peritoneum - Uterine cervix -Rectum
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Uterine Mesenchymal Tumors from a Gynaecological Point of View: A Mini-Review
 EC Gynaecology Special Issue - 2017 Uterine Mesenchymal Tumors from a Gynaecological Point of View: A Mini-Review Mini Review Dr. Huseyin Aydogmus, Dr. Servet Gencdal, Dr. Nihan Gencdal and Dr. Serpil
EC Gynaecology Special Issue - 2017 Uterine Mesenchymal Tumors from a Gynaecological Point of View: A Mini-Review Mini Review Dr. Huseyin Aydogmus, Dr. Servet Gencdal, Dr. Nihan Gencdal and Dr. Serpil
MULLERIAN PAPILLOMA ENTITY RECOGNITION FAILURE 04/04/2016 OUT OF SIGHT, OUT OF MIND: LESSER KNOWN LESIONS OF THE VULVOVAGINAL TRACT
 OUT OF SIGHT, OUT OF MIND: LESSER KNOWN LESIONS OF THE VULVOVAGINAL TRACT 23 rd ANNUAL SEMINAR IN PATHOLOGY 30 APRIL 2016 W. Dwayne Lawrence MD MSc (Path.) Chief of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Women
OUT OF SIGHT, OUT OF MIND: LESSER KNOWN LESIONS OF THE VULVOVAGINAL TRACT 23 rd ANNUAL SEMINAR IN PATHOLOGY 30 APRIL 2016 W. Dwayne Lawrence MD MSc (Path.) Chief of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Women
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain
 December 2016 59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain Contributed by: Divya Sharma, MD. Fellow, Gastrointestinal Pathology, Department of Pathology
December 2016 59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain Contributed by: Divya Sharma, MD. Fellow, Gastrointestinal Pathology, Department of Pathology
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis
 27 Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis Toru Hasegawa a Koichi Yoshida b Kazuhiro Matsui c a Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toyama,
27 Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis Toru Hasegawa a Koichi Yoshida b Kazuhiro Matsui c a Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toyama,
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT
 Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
Title: unusual case report of inflammatory. fibrous polyps in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Authors: Baifang Wang, Guoqing Xiang, Jia Zhu
 Title: An unusual case report of inflammatory fibrous polyps in the upper gastrointestinal tract Authors: Baifang Wang, Guoqing Xiang, Jia Zhu DOI: 10.17235/reed.2018.5734/2018 Link: PubMed (Epub ahead
Title: An unusual case report of inflammatory fibrous polyps in the upper gastrointestinal tract Authors: Baifang Wang, Guoqing Xiang, Jia Zhu DOI: 10.17235/reed.2018.5734/2018 Link: PubMed (Epub ahead
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 7 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 7 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies
 Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Radiological Appearance of Renal Leiomyoma: two cases report and review of the literature
 J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 139-143 Radiological Appearance of Renal Leiomyoma: two cases report and review of the literature Wei-Ni Liao 1 Chi-Kuan Chen 2 Fei-Shih Yang 1,3 Department of Radiology 1, Department
J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 139-143 Radiological Appearance of Renal Leiomyoma: two cases report and review of the literature Wei-Ni Liao 1 Chi-Kuan Chen 2 Fei-Shih Yang 1,3 Department of Radiology 1, Department
A Rare Case of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Extending to Endometrium and Right Fallopian Tube
 A Rare Case of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Extending to Endometrium and Right Fallopian Tube Kate Madhuri S 1, Gulhane Sushma R 2, Mane Sheetal V 3 1 Professor and Head, 2 Specialist cum
A Rare Case of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Extending to Endometrium and Right Fallopian Tube Kate Madhuri S 1, Gulhane Sushma R 2, Mane Sheetal V 3 1 Professor and Head, 2 Specialist cum
reproductive organs. Malignant neoplasms. 4. Inflammatory disorders of female reproductive organs 2 5. Infertility. Family planning.
 Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Images In Gastroenterology
 Images In Gastroenterology Thong-Ngam D, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2005 Vol. 6 No. 2 May - Aug. 2005 105 Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Pornpim Fuangtharnthip, M.D. Narumol Hargroove, M.D.
Images In Gastroenterology Thong-Ngam D, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2005 Vol. 6 No. 2 May - Aug. 2005 105 Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Pornpim Fuangtharnthip, M.D. Narumol Hargroove, M.D.
In the August 2016 issue of OBG Management,
 GYN coding changes to note for your maximized reimbursement Revised ICD-10 gynecologic diagnostic codes go into effect October 1. Here is a look at the added, expanded, and revised codes you will need
GYN coding changes to note for your maximized reimbursement Revised ICD-10 gynecologic diagnostic codes go into effect October 1. Here is a look at the added, expanded, and revised codes you will need
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid.
 Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
Newer soft tissue entities
 Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
Smooth Muscle and Similar Lesions. Disclosure Statement. Smooth Muscle Tumors. Elizabeth Montgomery
 Smooth Muscle and Similar Lesions Elizabeth Montgomery Disclosure Statement Dr. Montgomery reports no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests. Smooth Muscle Tumors Most are leiomyomas
Smooth Muscle and Similar Lesions Elizabeth Montgomery Disclosure Statement Dr. Montgomery reports no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests. Smooth Muscle Tumors Most are leiomyomas
BCCCP Approved ICD-9 Code List Fiscal Year 2010
 BCCCP Approved ICD-9 List Fiscal Year 2010 Diagnosis Description 174.0 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Nipple and areola 174.1 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Central portion 174.2 Malignant
BCCCP Approved ICD-9 List Fiscal Year 2010 Diagnosis Description 174.0 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Nipple and areola 174.1 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Central portion 174.2 Malignant
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
Ultrasound screening of soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity - a BSG guide for ultrasonographers and primary care
 Ultrasound screening of soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity - a BSG guide for ultrasonographers and primary care Introduction Soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity are common and most
Ultrasound screening of soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity - a BSG guide for ultrasonographers and primary care Introduction Soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity are common and most
General history. Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted: Married status : Married
 General history Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted:940510 Married status : Married General history Chief Complain : bilateral ovarian cyst incidentally being found out during pap smear. Present Illness
General history Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted:940510 Married status : Married General history Chief Complain : bilateral ovarian cyst incidentally being found out during pap smear. Present Illness
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
Case Report Cellular Angiofibroma of the Prostate: A Rare Tumor in an Unusual Location
 , Article ID 871530, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/871530 Case Report Cellular Angiofibroma of the Prostate: A Rare Tumor in an Unusual Location Inez Wyn, 1 Maria Debiec-Rychter, 2 Ben Van Cleynenbreugel,
, Article ID 871530, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/871530 Case Report Cellular Angiofibroma of the Prostate: A Rare Tumor in an Unusual Location Inez Wyn, 1 Maria Debiec-Rychter, 2 Ben Van Cleynenbreugel,
Case Report Leiomyosarcoma of the Vagina: An Exceedingly Rare Diagnosis
 Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 363895, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/363895 Case Report Leiomyosarcoma of the Vagina: An Exceedingly Rare Diagnosis Nathan A.
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 363895, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/363895 Case Report Leiomyosarcoma of the Vagina: An Exceedingly Rare Diagnosis Nathan A.
MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS OF THE BREAST MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS OF FEMALE GENITAL ORGANS
 MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS OF THE (INC. PAGET S DISEASE) 0 - Nipple and areola 1 - Central portion 2 - Upper-inner quadrant 3 - Lower-inner quadrant 4 - Upper-outer quadrant 5 - Lower-outer quadrant 6 - Axillary
MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS OF THE (INC. PAGET S DISEASE) 0 - Nipple and areola 1 - Central portion 2 - Upper-inner quadrant 3 - Lower-inner quadrant 4 - Upper-outer quadrant 5 - Lower-outer quadrant 6 - Axillary
An Anteriorly Positioned Midline Prostatic Cyst Resulting in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
 Case Report INJ 2010;14:125-129 An Anteriorly Positioned Midline Prostatic Cyst Resulting in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Joo-Yong Lee, Dong-Hyuk Kang, Hee-Young Park, Jung-Soo Park, Young-Woo Son, Hong-Sang
Case Report INJ 2010;14:125-129 An Anteriorly Positioned Midline Prostatic Cyst Resulting in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Joo-Yong Lee, Dong-Hyuk Kang, Hee-Young Park, Jung-Soo Park, Young-Woo Son, Hong-Sang
Cellular Pseudosarcomatous Fibroepithelial Stromal Polyp of the Vagina during Pregnancy: A Lesion That Is Overdiagnosed as a Malignant Tumor
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 494-498 CASE REPORT Cellular Pseudosarcomatous Fibroepithelial Stromal Polyp of the Vagina during Pregnancy: A Lesion That Is Overdiagnosed as a Malignant Tumor
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 494-498 CASE REPORT Cellular Pseudosarcomatous Fibroepithelial Stromal Polyp of the Vagina during Pregnancy: A Lesion That Is Overdiagnosed as a Malignant Tumor
Giant Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid gland- A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 14 Number 1 Giant Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid gland- A Case Report O M.E, U A.N, U Akpan, K J, I Bassey Citation O M.E, U A.N, U Akpan,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 14 Number 1 Giant Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid gland- A Case Report O M.E, U A.N, U Akpan, K J, I Bassey Citation O M.E, U A.N, U Akpan,
A Serous Borderline Tumor of the Fallopian Tube Detected Incidentally
 A Serous Borderline Tumor of the Fallopian Tube Detected Incidentally Imrana Tanvir, Ghania Ali, Haseeb Ahmed Khan and Ahmed Nasir Hanifi* Dept. of Histopathology, FMH College of Medicine & Dentistry,
A Serous Borderline Tumor of the Fallopian Tube Detected Incidentally Imrana Tanvir, Ghania Ali, Haseeb Ahmed Khan and Ahmed Nasir Hanifi* Dept. of Histopathology, FMH College of Medicine & Dentistry,
Case Report Ovarian Metastasis from Lung Cancer: A Rare Entity
 Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2013, Article ID 378438, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/378438 Case Report Ovarian Metastasis from Lung Cancer: A Rare Entity Huseyin Cengiz, Fükrü
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2013, Article ID 378438, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/378438 Case Report Ovarian Metastasis from Lung Cancer: A Rare Entity Huseyin Cengiz, Fükrü
doi: /j.anl
 doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2006.07.001 Synchronous unilateral parotid gland neoplasms of three different histological types Shuho Tanaka 1, Keiji Tabuchi 1, Keiko Oikawa 1, Rika Kohanawa 1, Hideki Okubo 1, Dai
doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2006.07.001 Synchronous unilateral parotid gland neoplasms of three different histological types Shuho Tanaka 1, Keiji Tabuchi 1, Keiko Oikawa 1, Rika Kohanawa 1, Hideki Okubo 1, Dai
An unusual case of a large fibroepithelial stromal polyp presenting as a nipple mass
 Shaaban et al. BMC Research tes 2013, 6:345 CASE REPORT Open Access An unusual case of a large fibroepithelial stromal polyp presenting as a nipple mass Abeer M Shaaban 1*, EPL Turton 2 and William Merchant
Shaaban et al. BMC Research tes 2013, 6:345 CASE REPORT Open Access An unusual case of a large fibroepithelial stromal polyp presenting as a nipple mass Abeer M Shaaban 1*, EPL Turton 2 and William Merchant
