Sonographic and Mammographic Appearances of Breast Hemangioma
|
|
|
- Oswin Milo Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Women s Imaging Clinical Observations Mesurolle et al. Sonography and Mammography of reast Hemangioma Women s Imaging Clinical Observations WOMEN S IMGING enoît Mesurolle 1 Vitaly Sygal 1 Lucie Lalonde 2 ndré Lisbona 3 Michel-Pierre Dufresne 4 Jean H. Gagnon 1 Ellen Kao 1 Mesurolle, Sygal V, Lalonde L, et al. Keywords: breast tumor, hemangioma, mammography, sonography DOI: /JR Received September 14, 2007; accepted after revision January 29, Department of Radiology, Cedar reast Clinic, McGill University Health Center, Royal Victoria Hospital, 687 Pine ve. W, Montréal, PQ H3G 14, Canada. ddress correspondence to. Mesurolle (bmesurolle@yahoo.fr). 2 Département de Radiologie, Centre d Imagerie du Sein, Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal (CHUM), Montréal, PQ, Canada. 3 Department of Radiology, Sir Mortimer. Davis-Jewish General Hospital, Montréal, PQ, Canada. 4 Département de Radiologie, Hôpital Maisonneuve- Rosemont, Montréal, PQ, Canada. CME This article is available for CME credit. See for more information. WE This is a Web exclusive article. JR 2008; 191:W17 W X/08/1911 W17 merican Roentgen Ray Society Sonographic and Mammographic ppearances of reast Hemangioma OJECTIVE. The purpose of our study was to retrospectively evaluate the clinical, imaging, and pathologic findings of breast hemangiomas in 16 patients. CONCLUSION. mass displaying an oval or lobular shape with well-circumscribed or microlobulated margins on mammography and sonography, and in a superficial location, should alert the radiologist to the possible diagnosis of hemangioma. Imaging-guided biopsy appears sufficiently reliable to rule out any malignant or premalignant component and to avoid a surgical excision if doing so is clinically appropriate. H emangiomas have been described in many anatomic locations, but there are few recorded examples of hemangiomas arising primarily in the breast [1, 2]. The mammographic and sonographic appearances of breast hemangiomas have been described in a few case reports [3 7] but, to our knowledge, no case series including long-term follow-up imaging have been published. search of the surgical pathology records at four institutions of breast biopsies performed from 2000 to 2005 identified 16 patients with pathologically proven breast hemangiomas. Clinical, mammographic, and sono graphic features were reviewed, with particular emphasis on sonographic findings. Materials and Methods Study Population The combined data were obtained from four large institutions affiliated with two academic medical centers (McGill University and University of Montréal). total of 23 pathologically proven hemangiomas diagnosed by either sonographically guided, stereotactically guided, or surgical excision biopsy performed between January 2000 and December 2005 were identified. Seven patients for whom no imaging was available were excluded. Sixteen women (age range, years; mean age, 59.7 years) who met these criteria are the subject of this article. Two radiologists, specialists in breast imaging, retrospectively reviewed in consensus the mammographic and sonographic features of the hemangiomas. pproval by the institutional review board was not required for this retrospective analysis. Mammographic Findings Mammography was performed in two standard imaging planes, mediolateral oblique and craniocaudal, using dedicated film-screen mammo graphic equipment. Mammographic characteris tics were assessed according to the merican College of Radiology reast Imaging Reporting and Data System (I-RDS) [8]. Mammographic findings are shown in Figures 1 4. Sonographic Findings reast sonography was performed to evaluate specific abnormalities discovered either at clinical examination or on mammography. ll 16 patients under went a breast sonographic examination (Figs. 1 4), but a mass was sonographically de tected in only nine patients (Figs. 1 3). The sono graphic characteristics of the nine masses were assessed according to the merican College of Radiology I-RDS criteria [8]. Studies were reviewed on hard-copy films (five patients) or on PCS images (four patients). Core Needle iopsy Fifteen patients underwent an imaging-guided core needle biopsy. One patient underwent surgical excision without preoperative biopsy. iopsy of masses was performed with either sonographic or stereotactic guidance. If the mass was clearly identified sonographically, the biopsy was performed under sonographic guidance. If not, the biopsy was performed under stereotactic guid ance. Stereotactic biopsies were performed with dedicated prone stereotactic biopsy tables (n = 7). Sonographically guided biopsy was performed with patients in the supine position and with high-resolution sonographic equipment (15L8W broad band transducer, Sequoia, JR:191, July 2008 W17
2 Mesurolle et al. C Fig. 1 symptomatic 75-year-old woman., Right mediolateral oblique mammogram shows 0.8-cm mass in superior aspect of breast. Mass (arrow) displays lobular shape and circumscribed margins., Close-up view of mass, also in right mediolateral oblique orientation. C, reast sonogram shows 0.8-cm oval solid mass (arrows) with circumscribed margins, parallel orientation, abrupt interface, neutral sound transmission, and complex echotexture. Surgical excision revealed hemangioma, cavernous type. C Fig. 2 symptomatic 62-year-old woman. and, Left craniocaudal screening mammogram shows 1.2-cm lobular mass (arrow) with microlobulated margins in upper inner aspect of breast. Mass (arrow) shows interval increase in size compared with previous mammogram 8 years earlier (). C, reast sonogram using tissue harmonic imaging shows 1.1-cm subtle mass superficially situated against fatty background. Lesion is ovoid with microlobulated margins, hypoechoic echotexture, parallel orientation, and mild posterior acoustic shadowing (arrows). Sonographically guided core biopsy using 14-gauge needle yielded cavernous hemangioma. Follow-up imaging after 2 years (not shown) confirmed stability of lesion. W18 JR:191, July 2008
3 Sonography and Mammography of reast Hemangioma Fig year-old woman with palpable mass in lateral aspect of left breast. and, Left craniocaudal close-up image () and left mediolateral oblique image () show mass (arrow) displaying irregular shape and microlobulated margin and having no microcalcifications. C, reast sonogram shows 1.5-cm solid mass with irregular shape and indistinct margins (arrows), parallel orientation, neutral sound transmission, and hyperechoic echotexture. Sonographically guided biopsy using 14-gauge needle yielded capillary hemangioma. Surgical excision confirmed hemangioma, capillary type. Fig. 4 symptomatic 58-year-old woman with screening-detected mass. Mammogram of right breast showed 1-cm mass., Radiograph obtained during stereotactic biopsy with 14-gauge needle in place shows round mass with circumscribed margins and punctuate microcalcifications. reast sonogram did not identify any mass. Stereotactically guided biopsy using 14-gauge needle yielded cavernous hemangioma., Follow-up right craniocaudal close-up mammogram obtained 2 years later shows 0.7-cm mass (arrow). Siemens Medical Sys tems; high-frequency Matrix trans ducer PLT1204X, plio, Toshiba; model 700, GE Healthcare; and HDL, TL) (n = 8). Generally, 10- to 15-MHz transducers were used. Fourteengauge automated core biopsy needles were used for stereotactically and sonographically guided biopsies. Surgical Excision Of the 15 patients who underwent core needle biopsy, three underwent subsequent surgical excision. One patient underwent surgical excision without preoperative biopsy. Pathologic Findings The prospective pathology reports by the institutional pathologists at the time of core needle biopsy (12 patients with no subsequent surgery) and at the time of the surgical excision (four patients, including three with previous core needle biopsy) were considered to indicate the definitive pathologic results. Results Clinical Data Patients were referred to our institutions because of a palpable mass (n = 2), a screeningdetected mass (n = 8), or an increase in size of a previously screening-detected mass (n = 6). Mammographic Findings In the 16 patients studied, mammographic parenchymal density was I-RDS class 3 (heterogeneously dense) in three patients (18.75%), class 2 (scattered fibroglandular densities) in five (31.25%), and class 1 (fatty) in eight (50%). One mammogram was normal (class 2), the mass being palpable and situated in the axillary region. Fifteen mammograms showed a mass (mean size, 1.2 cm; range, cm) (Fig. 5). Mammographic findings are summarized in Table 1. The most common mammographic features were masses with a lobular shape (n = 8), circumscribed (n = 8) or microlobulated (n = 7) margins, and density equal to that of the breast parenchyma (n = 14) (Figs. 1 and 2). One patient had punctate microcalcifications in a mass (Fig. 4). Sonographic Findings Sonographic findings are summarized in Table 2. Nine masses were identified at sonographic examination (Figs. 1 3). The mean sono graphic size was 1.3 cm (range, cm) in the largest diameter (Fig. 6). The most common sonographic features of hemangiomas were oval shape (n = 8); circumscribed margins (n = 5); superficial with an abrupt interface (n = 9); and nonhyperechoic (i.e., hypoechoic, isoechoic, or complex) echotextures (n = 6). The two lesions displaying indistinct margins had a hyperechoic echotexture (Fig. 3). Pathologic Findings Final pathologic examination identified 14 cavernous-type hemangiomas and two capillary-type hemangiomas. mong the four patients who underwent excisional biopsy, no malignancy was diagnosed. Surgical excision confirmed the diagnosis of hemangioma C JR:191, July 2008 W19
4 Mesurolle et al. Lesion Size (cm) No. of Lesions TLE 1: Mammographic Characteristics of 15 Hemangiomas ccording to I-RDS Lexicon [8] Mass Characteristic No. % Shape Round Oval Lobular Irregular Margins Circumscribed Microlobulated Obscured 0 0 Indistinct 0 0 Spiculated 0 0 Density High Equal Low 0 0 Fat 0 0 Calcifications in three patients and established the diagnosis in one patient Fig. 5 Scatterplot shows size of 15 masses that were visible on mammography. TLE 2: Sonographic Characteristics of Nine Hemangiomas ccording to I-RDS Lexicon [8] Mass Characteristic No. % Shape Irregular 1 11 Round 0 0 Oval 8 89 Margins Circumscribed 5 56 Microlobulated 2 22 ngular 0 0 Spiculated 0 0 Indistinct 2 22 Orientation Parallel Not parallel 0 0 Lesion boundary brupt interface Echogenic halo 0 0 Echo pattern Hypoechoic 2 22 Isoechoic 1 11 Hyperechoic 3 33 Complex 3 33 Surveillance Four patients (25%) underwent surgical excisional biopsy (Figs. 1 and 3). Eight patients (50%) underwent mammographic surveillance and were followed up for a mean of 3.7 years (range, 2 6 years) (Figs. 2 and 4). mong these eight patients, six breast masses were mammographically stable and two showed a decrease in size. Four of the 16 patients (25%) had no mammographic surveillance. mong a subgroup of patients referred for increase in size of a previously screeningdetected mass (n = 6), two had no mammographic surveillance, three showed mammographically stable masses (3 6 years), and one showed a decrease in size of the mass on mammography. Discussion Vascular tumors of the breast are rare lesions. Three main entities have been reported: hemangiomas, angiolipomas, and angiosarcomas [9]. Hemangiomas are benign vascular tumors of two common types (capillary or cavernous) that are based on the size of the vessels involved. reast hemangiomas are found in 1.2% of mastectomy specimens and 11% of postmortem specimens of the female breast [9]. In our case series we focused our observations exclusively on the benign form of vascular tumors of the breast, the hemangiomas. Most of the breast hemangiomas in our series appeared on mammography as oval or lobular isodense masses with well-circumscribed margins, similar to the classic appearance of a hemangioma noted in previous case reports [3, 6]. These findings are not sufficiently specific and might explain the low incidence of diagnosed and recognized breast hemangiomas, a significant number probably being classified as I-RDS category 3 and not differentiated from fibroadenomas or cysts [10 12]. lthough these lesions were superficial in location (subdermal or in the subcutaneous tissues), this location made it difficult to visualize them on regular craniocaudal and mediolateral oblique views; tangential views are necessary to prove the superficial nature of the mass. Only one patient showed a mass displaying benign round calcifications that were presumably related to phleboliths. few cases of hemangiomas displaying suspicious mammographic or clinical features have been reported [5, 13]. One article reports a large palpable mass measuring 12 cm, occupying the lower quadrant of the left breast, showing reddish discoloration of the overlying skin and nipple areolar complex, and mimicking an inflammatory carcinoma [5]. second article reported a spiculated mass on mammography, leading the radiologists to classify the mass as I-RDS category 5 [13]. In our series, no such features were noted. Only one patient had calcifications in the mass. Fine, punctuate, or phlebolith-type calcifications have been reported in breast hemangiomas [3]. lthough calcifications are classic, their frequency has not been established. They can be of the venous type because of phleboliths, or they may be coarse [3]. s noted in several articles, the sonographic appearance of breast hemangioma is variable. The shape and margins are usually consistent with benign lesions and similar to the mammographic features. The lesions display an ovoid shape with well-circumscribed margins (Fig. 1). Microlobulations or indistinct margins are less often seen; the latter have W20 JR:191, July 2008
5 Sonography and Mammography of reast Hemangioma Lesion Size (cm) No. of Lesions been associated with hyperechoic lesions. The echotexture of hemangiomas is variable; one third display a hyperechoic echotexture and two thirds display an isoechoic (to the fat), hypoechoic, or complex echotexture. Interestingly, the echotexture is complex in a significant number of cases (Fig. 1). This relative echotextural heterogeneity may be related to the presence of multiple small vascular channels seen pathologically in hemangiomas (large blood-filled spaces or sinuses being seen in cavernous hemangiomas) [3, 7]. The isoechoic or slightly hypoechoic appearances likely explain the difficulty in identifying such lesions against a fatty background. For this reason, hemangiomas are less conspicuous sonographically than they are clinically or mammographically [7]. This characteristic might account for the invisibility of the lesions on sonography in seven of our patients, despite these lesions being readily visible on mammography as well-defined masses surrounded by fatty tissue. In such cases, the knowledge of the superficial location of the lesion alerts the radiologist to focus the examination on the subcutaneous region (adequate focus positioning), which allows better identification of the lesions. In addition, the use of specific settings on sonography, such as tissue harmonic imaging, increases the visibility of such lesions against a fatty background [14] (Fig. 2). Superficial location is another characteristic of these lesions. The subcutaneous location may theoretically help to select the correct diagnosis from the differential diagnosis, which includes hematoma, hemangioma, and sebaceous cyst [6]. To ascertain the subcutaneous location, the mass must be located anterior to the superficial pectoralis fascia [15], which is often difficult to visualize. In our study, the lesions appeared superficial and Fig. 6 Scatterplot shows size of nine masses that were visible on sonography. were presumed to be in the subcutaneous tissue even though the superficial pectoralis fascia was not visualized. Complete excision is usually recommended when a hemangioma is diagnosed at biopsy. The two main reasons for excision would be to exclude the possibility of an underlying angiosarcoma and to avoid progression to angiosarcoma. On one hand, imaging-guided biopsy appears sufficiently reliable to rule out any malignant or premalignant component; therefore, if no pathologic radiologic discordance is noted, the diagnosis of angiosarcoma can probably be excluded. On the other hand, progression of hemangioma to angiosarcoma has been reported but is controversial [16]. ecause microscopic hemangioma shows a relatively high incidence at autopsy (11%) [17] and because the incidence of angiosarcoma is extremely low, progression of hemangiomas to angiosarcoma is extremely rare if it exists at all. Hence, although needle biopsies may produce false-negative results, we consider that a superficial breast mass displaying the classic mammographic and sonographic appearances of a hemangioma and diagnosed as a hemangioma (cavernous or capillary type, without atypia) by imaging-guided core biopsy, can be followed up with periodic imaging surveillance without surgical excision. ecause of the established validity of mammographic surveillance, follow-up with mammography alone at 12-month intervals for the first 2 years should be sufficient to show stability. Our study has some limitations. The small size of the population and the retrospective nature of the study probably limit our results. Nevertheless, although 25% of patients had no follow-up imaging, we emphasize the benefit of imaging surveillance in the management of patients diagnosed with breast hemangioma by imaging-guided biopsy if no discord exists among mammographic, sonographic, and pathologic findings. In conclusion, a mass displaying an oval or lobular shape, with well-circumscribed or microlobulated margins on mammography and sonography, and showing a superficial location should alert the radiologist to a possible diagnosis of hemangioma. Imaging-guided biopsy appears to be sufficiently reliable to rule out any malignant or premalignant component and to avoid surgical excision in the absence of radiologic pathologic discordance. References 1. Jozefczyk M, Rosen PP. Vascular tumors of the breast. II. Perilobular hemangiomas and hemangiomas. m J Surg Pathol 1985; 9: Rosen PP. Vascular tumors of the breast. V. Nonparenchymal hemangiomas of mammary subcutaneous tissues. m J Surg Pathol 1985; 9: Webb L, Young JR. Case report: haemangioma of the breast appearances on mammography and ultrasound. Clin Radiol 1996; 51: Chung SY, Oh KK. Mammographic and sonographic findings of a breast subcutaneous hemangioma. J Ultrasound Med 2002; 21: Gopal SV, Nayak P, Dharanipragada K, Krishnamachari S. reast hemangioma simulating an inflammatory carcinoma. reast J 2005; 11: Siewert, Jacobs T, aum JK. Sonographic evaluation of subcutaneous hemangioma of the breast. JR 2002; 178: Glazebrook KN, Morton MJ, Reynolds C. Vascular tumors of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, and MRI appearances. JR 2005; 184: merican College of Radiology. reast imaging reporting and data system: breast imaging atlas, 4th ed. Reston, V: merican College of Radiology, Lesueur GC, rown RW, hathal PS. Incidence of perilobular hemangioma in the female breast. rch Pathol Lab Med 1983; 107: Graf O, Helbich TH, Hopf G, Graf C, Sickles E. Probably benign breast masses at US: is follow-up an acceptable alternative to biopsy? Radiology 2007; 244: Sickles E. Probably benign lesions: when should follow-up be recommended and what is the optimal follow-up protocol? Radiology 1999; 213: Graf O, Helbich TH, Fuchsjaeger MH, et al. Followup of palpable circumscribed noncalcified solid breast masses at mammography and US: can biopsy be averted? Radiology 2004; 233: Mariscal, Casas JD, alliu E, Castella E. reast JR:191, July 2008 W21
6 Mesurolle et al. hemangioma mimicking carcinoma. reast 2002; 11: Mesurolle, Helou T, El-Khoury M, Edwardes M, Sutton EJ, Kao E. Tissue harmonic imaging, frequency compound imaging, and conventional imaging: use and benefit in breast sonography. J Ultrasound Med 2007; 26: Fornage D, McGavran MH, Duvic M, et al. Imaging of the skin with 20-MHz US. Radiology 1993; 189: Rupec M, atzenschlager I. Pseudoangiosarcoma (Masson): a histological study [in German]. Z Hautkr 1981; 56: Hoda S, Cranor ML, Rosen PP. Hemangiomas of the breast with atypical histological features: further analysis of histological subtypes confirming their benign character. m J Surg Pathol 1992; 16: FOR YOUR INFORMTION This article is available for CME credit. See for more information. W22 JR:191, July 2008
Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients
 Clinical Radiology (2009) 64, 628e636 ORIGINAL PAPER Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients B. Mesurolle a, *, M. El-Khoury
Clinical Radiology (2009) 64, 628e636 ORIGINAL PAPER Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients B. Mesurolle a, *, M. El-Khoury
Sinusoidal hemangioma of the breast: diagnostic evaluation management and literature review
 Case Report Sinusoidal hemangioma of the breast: diagnostic evaluation management and literature review Nikolaos S. Salemis Breast Unit, 2nd Department of Surgery, Army General Hospital, Athens, Greece
Case Report Sinusoidal hemangioma of the breast: diagnostic evaluation management and literature review Nikolaos S. Salemis Breast Unit, 2nd Department of Surgery, Army General Hospital, Athens, Greece
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Amlendu Nagar
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Original Report. Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical, Mammographic, and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
Mammography and Subsequent Whole-Breast Sonography of Nonpalpable Breast Cancers: The Importance of Radiologic Breast Density
 Isabelle Leconte 1 Chantal Feger 1 Christine Galant 2 Martine Berlière 3 Bruno Vande Berg 1 William D Hoore 4 Baudouin Maldague 1 Received July 11, 2002; accepted after revision October 28, 2002. 1 Department
Isabelle Leconte 1 Chantal Feger 1 Christine Galant 2 Martine Berlière 3 Bruno Vande Berg 1 William D Hoore 4 Baudouin Maldague 1 Received July 11, 2002; accepted after revision October 28, 2002. 1 Department
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: Imaging Findings With Pathologic and Clinical Correlation
 Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Jones et al. Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay WOMEN S IMGING Katie N. Jones 1 Katrina N. Glazebrook 1 arol Reynolds 2 Jones KN, Glazebrook
Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Jones et al. Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay WOMEN S IMGING Katie N. Jones 1 Katrina N. Glazebrook 1 arol Reynolds 2 Jones KN, Glazebrook
Breast Imaging Lexicon
 9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
BI-RADS Update. Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital
 BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast as Cystic Lesions: Sonographic-Pathologic Correlation
 Women s Imaging Original Research Kim et al. Breast Tumors as Cystic Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Sun Mi Kim 1,2 Hak Hee Kim 1 Doo Kyung Kang 3 Hee Jung Shin 1 Nariya Cho 4
Women s Imaging Original Research Kim et al. Breast Tumors as Cystic Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Sun Mi Kim 1,2 Hak Hee Kim 1 Doo Kyung Kang 3 Hee Jung Shin 1 Nariya Cho 4
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast:
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Reassessment and Follow-Up Results of BI-RADS Category 3 Lesions Detected on Screening Breast Ultrasound
 Women s Imaging Original Research Chae et al. I-RDS Category 3 Lesions Found on Screening Ultrasound Women s Imaging Original Research Eun Young Chae 1 Joo Hee Cha Hee Jung Shin Woo Jung Choi Hak Hee Kim
Women s Imaging Original Research Chae et al. I-RDS Category 3 Lesions Found on Screening Ultrasound Women s Imaging Original Research Eun Young Chae 1 Joo Hee Cha Hee Jung Shin Woo Jung Choi Hak Hee Kim
Incidence and Management of Complex Fibroadenomas
 Incidence and Management of Complex Fibroadenomas Women s Imaging Original Research 214.fm 11/29/07 WOMEN S IMAGING Miri Sklair-Levy 1 Tamar Sella 1 Tanir Alweiss 2 Ilia Craciun 1 Eugene Libson 1 Bella
Incidence and Management of Complex Fibroadenomas Women s Imaging Original Research 214.fm 11/29/07 WOMEN S IMAGING Miri Sklair-Levy 1 Tamar Sella 1 Tanir Alweiss 2 Ilia Craciun 1 Eugene Libson 1 Bella
Short-Term Follow-Up of Palpable Breast Lesions With Benign Imaging Features: Evaluation of 375 Lesions in 320 Women
 Women s Imaging Original Research Follow-Up Imaging of Palpable Breast Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Jennifer A. Harvey 1 Brandi T. Nicholson 1 Alexander P. LoRusso 1,2 Michael
Women s Imaging Original Research Follow-Up Imaging of Palpable Breast Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Jennifer A. Harvey 1 Brandi T. Nicholson 1 Alexander P. LoRusso 1,2 Michael
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications
 Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma with Fibrotic Focus: Mammographic and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Ultrasonography. Methods. Brief Description. Indications. Device-related Prerequisites. Technical Requirements. Evaluation Criteria
 1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
Cairo/EG, Khartoum/SD, London/UK Biological effects, Diagnostic procedure, Ultrasound, Mammography, Breast /ecr2015/C-0107
 Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Vascular abnormalities of the breast: A multimodality imaging approach to diagnosis
 Vascular abnormalities of the breast: A multimodality imaging approach to diagnosis Poster No.: C-0186 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. P. SANCHEZ-CAMACHO, A. Almenar, C. C.
Vascular abnormalities of the breast: A multimodality imaging approach to diagnosis Poster No.: C-0186 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. P. SANCHEZ-CAMACHO, A. Almenar, C. C.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Artifacts and Pitfalls in Sonographic Imaging of the Breast
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 80.243.135.192 on 02/26/18 from IP address 80.243.135.192. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved rtifacts and Pitfalls in Sonographic Imaging of
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 80.243.135.192 on 02/26/18 from IP address 80.243.135.192. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved rtifacts and Pitfalls in Sonographic Imaging of
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features
 Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN
 Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass
 Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Interpectoral Venous Angioma Presenting as a Breast Mass
 Case Report Interpectoral Venous ngioma Presenting as a reast Mass Dae Jung Kim, MD, Eun Ju Son, MD, Soon Won Hong, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Ki Keun Oh, MD, Joon Jeong, MD C hest wall
Case Report Interpectoral Venous ngioma Presenting as a reast Mass Dae Jung Kim, MD, Eun Ju Son, MD, Soon Won Hong, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Ki Keun Oh, MD, Joon Jeong, MD C hest wall
Sonographic Appearance of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast According to Histologic Grade
 Women s Imaging Original Research Blaichman et al. Efficacy of Sonographic Features in BI-RADS Lexicon Women s Imaging Original Research Jason Blaichman 1 James C. Marcus Tahra Alsaadi Mona El-Khoury Sarkis
Women s Imaging Original Research Blaichman et al. Efficacy of Sonographic Features in BI-RADS Lexicon Women s Imaging Original Research Jason Blaichman 1 James C. Marcus Tahra Alsaadi Mona El-Khoury Sarkis
Imaging-Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Papillary Lesions of the Breast
 Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Triple Receptor Negative Breast Cancer: Imaging and Clinical Characteristics
 Women s Imaging Original Research Krizmanich-Conniff et al. Triple Receptor Negative Breast Cancer Women s Imaging Original Research Kristin M. Krizmanich-Conniff 1 Chintana Paramagul 2 Stephanie K. Patterson
Women s Imaging Original Research Krizmanich-Conniff et al. Triple Receptor Negative Breast Cancer Women s Imaging Original Research Kristin M. Krizmanich-Conniff 1 Chintana Paramagul 2 Stephanie K. Patterson
Breast Ultrasound: Improving Your Skills & Patient Care
 Breast Ultrasound: Improving Your Skills & Patient Care Objectives Discuss US techniques available for image optimization. Review & compare the US appearances of benign & malignant masses. Cherie M. Kuzmiak,
Breast Ultrasound: Improving Your Skills & Patient Care Objectives Discuss US techniques available for image optimization. Review & compare the US appearances of benign & malignant masses. Cherie M. Kuzmiak,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings.
 Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Breast imaging in general practice
 Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Cystic Masses of the Breast
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Eisenberg ystic Masses of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Neely Hines 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Hines N, Slanetz
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Eisenberg ystic Masses of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Neely Hines 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Hines N, Slanetz
High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography
 Article High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography Beverly E. Hashimoto, MD, Dawna J. Kramer, MD, Vincent J. Picozzi,
Article High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography Beverly E. Hashimoto, MD, Dawna J. Kramer, MD, Vincent J. Picozzi,
Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB)
 Original article Annals of Oncology 14: 450 454, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh088 Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB)
Original article Annals of Oncology 14: 450 454, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh088 Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB)
Architectural Distortion of
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gaur et al. rchitectural Distortion of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.203.116 on 01/05/18 from IP address
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gaur et al. rchitectural Distortion of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.203.116 on 01/05/18 from IP address
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Practical and illustrated summary of updated BI-RADS for ultrasonography
 Practical and illustrated summary of updated I-RS for ultrasonography Jiyon Lee epartment of Radiology, NYU School of Medicine, NYU ancer Institute, reast Imaging enter, New York, NY, US The merican ollege
Practical and illustrated summary of updated I-RS for ultrasonography Jiyon Lee epartment of Radiology, NYU School of Medicine, NYU ancer Institute, reast Imaging enter, New York, NY, US The merican ollege
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas
 Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
CURRENT METHODS IN IMAGE GUIDED BREAST BIOPSY
 CURRENT METHODS IN IMAGE GUIDED BREAST BIOPSY Stuart Silver April 24, 2004 OBJECTIVES Review development of current techniques Discuss stereotactic breast biopsy Discuss US guided breast biopsy 1 OBJECTIVES
CURRENT METHODS IN IMAGE GUIDED BREAST BIOPSY Stuart Silver April 24, 2004 OBJECTIVES Review development of current techniques Discuss stereotactic breast biopsy Discuss US guided breast biopsy 1 OBJECTIVES
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology
 Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Validation of the fifth edition BI-RADS ultrasound lexicon with comparison of fourth and fifth edition diagnostic performance using video clips
 Validation of the fifth edition BI-RADS ultrasound lexicon with comparison of fourth and fifth edition diagnostic performance using video clips Jung Hyun Yoon 1, Min Jung Kim 1, Hye Sun Lee 2, Sung Hun
Validation of the fifth edition BI-RADS ultrasound lexicon with comparison of fourth and fifth edition diagnostic performance using video clips Jung Hyun Yoon 1, Min Jung Kim 1, Hye Sun Lee 2, Sung Hun
The Radiology Aspects
 REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation
 Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, L. Koren,
Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, L. Koren,
Gynecomastia and Its Mimics: Not All Male Breast Lesions are Benign
 Gynecomastia and Its Mimics: Not All Male Breast Lesions are Benign Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. A. Choudhery, P. Gupta, S. Foshee, F. Garcia-Morales, G.
Gynecomastia and Its Mimics: Not All Male Breast Lesions are Benign Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. A. Choudhery, P. Gupta, S. Foshee, F. Garcia-Morales, G.
Immersion Ultrasonography of Excised Nonpalpable Breast Lesion Specimens after Ultrasound-Guided Needle Localization
 Immersion Ultrasonography of Excised Nonpalpable reast Lesion Specimens after Ultrasound-Guided Needle Localization Ki Yeol Lee, MD 1 o Kyoung Seo, MD 1 nn Yi, MD 1 o-kyung Je, MD 1 Kyu Ran Cho, MD 2 Ok
Immersion Ultrasonography of Excised Nonpalpable reast Lesion Specimens after Ultrasound-Guided Needle Localization Ki Yeol Lee, MD 1 o Kyoung Seo, MD 1 nn Yi, MD 1 o-kyung Je, MD 1 Kyu Ran Cho, MD 2 Ok
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation
 Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds
 215 Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds ratio 719 (100) 305(100) Shape Oval 445 (61.9) 019
215 Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds ratio 719 (100) 305(100) Shape Oval 445 (61.9) 019
Diagnosis of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Ultrasonography Findings and Different Biopsy Methods
 Yonsei Med J 49(5):757-764, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.5.757 Diagnosis of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Ultrasonography Findings and Different Biopsy Methods Yoon Jung Choi, 1
Yonsei Med J 49(5):757-764, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.5.757 Diagnosis of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Ultrasonography Findings and Different Biopsy Methods Yoon Jung Choi, 1
Segmental Breast Calcifications
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE. 170 Ultrasonography 33(3), July 2014 e-ultrasonography.org
 Positive predictive value of additional synchronous breast lesions in wholebreast ultrasonography at the diagnosis of breast cancer: clinical and imaging factors Ah Hyun Kim 1 *, Min Jung Kim 1, Eun-Kyung
Positive predictive value of additional synchronous breast lesions in wholebreast ultrasonography at the diagnosis of breast cancer: clinical and imaging factors Ah Hyun Kim 1 *, Min Jung Kim 1, Eun-Kyung
Ductal carcinoma in situ, underestimation, ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy
 Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1
 5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Manifested Solely as Microcalcifications on Sonography
 Sonography of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Head and Neck Imaging Clinical Observations Jin Young Kwak 1 Eun-Kyung Kim 1 Eun Ju Son 1 Min Jung Kim 1 Ki Keun Oh 1 Ji Young Kim 2 Kwang Il Kim 2 Kwak JY, Kim
Sonography of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Head and Neck Imaging Clinical Observations Jin Young Kwak 1 Eun-Kyung Kim 1 Eun Ju Son 1 Min Jung Kim 1 Ki Keun Oh 1 Ji Young Kim 2 Kwang Il Kim 2 Kwak JY, Kim
A Case Report of Breast Sparganosis in a Patient with Ipsilateral Breast Cancer: MRI and Ultrasonographic Findings 1
 Case Report of reast Sparganosis in a Patient with Ipsilateral reast Cancer: MRI and Ultrasonographic Findings 1 Yoo Jin Lee, M.D., Ki Seok Choo, M.D. 2, Young Tae ae, M.D. 3, Jee Yeon Kim, M.D. 4 Sparganosis
Case Report of reast Sparganosis in a Patient with Ipsilateral reast Cancer: MRI and Ultrasonographic Findings 1 Yoo Jin Lee, M.D., Ki Seok Choo, M.D. 2, Young Tae ae, M.D. 3, Jee Yeon Kim, M.D. 4 Sparganosis
Ultrasound Assessment of Invasive Breast Cancer:
 Ultrasound Assessment of Invasive Breast Cancer: Correlation with Histologic Grade 1 Joo Hee Cha, M.D., Woo Kyung Moon, M.D. 2, Nariya Cho, M.D. 2, Sun Mi Kim, M.D. 2, Seung Ja Kim, M.D. 2, Seong Ho Park,
Ultrasound Assessment of Invasive Breast Cancer: Correlation with Histologic Grade 1 Joo Hee Cha, M.D., Woo Kyung Moon, M.D. 2, Nariya Cho, M.D. 2, Sun Mi Kim, M.D. 2, Seung Ja Kim, M.D. 2, Seong Ho Park,
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy Breast Cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the United
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy Breast Cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the United
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1
 Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING
 OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
Pictorial Review of the Ultrasound Appearances of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
 Pictorial Review of the Ultrasound Appearances of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Poster No.: R-0079 Congress: 2016 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. G. D. U. M. Wijesinghe, D. Gunawardena, D. B. Taylor
Pictorial Review of the Ultrasound Appearances of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Poster No.: R-0079 Congress: 2016 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. G. D. U. M. Wijesinghe, D. Gunawardena, D. B. Taylor
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY
 Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Pseudoaneurysm of the Breast During Vacuum-Assisted Removal
 Case Report Pseudoaneurysm of the Breast During Vacuum-Assisted Removal Yu-Mee Sohn, MD, Min Jung Kim, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Sang Hoon Chung, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Hee Jung Moon, MD, Soo Jin Kim, MD
Case Report Pseudoaneurysm of the Breast During Vacuum-Assisted Removal Yu-Mee Sohn, MD, Min Jung Kim, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Sang Hoon Chung, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Hee Jung Moon, MD, Soo Jin Kim, MD
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS. Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions
 SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
Hyperechoic Lesions of the Breast: Not Always Benign
 Women s Imaging Original Research Linda et al. Hyperechoic Breast Lesions Are Not Always Benign Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Anna Linda 1 Chiara Zuiani 1 Michele Lorenzon 1 Alessandro
Women s Imaging Original Research Linda et al. Hyperechoic Breast Lesions Are Not Always Benign Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMAGING Anna Linda 1 Chiara Zuiani 1 Michele Lorenzon 1 Alessandro
Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical and Radiological Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical and Radiological Findings with Histopathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-2078 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. AlSharif
Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical and Radiological Findings with Histopathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-2078 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. AlSharif
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
New Palpable Breast Lump With Recent Negative Mammogram: Is Repeat Mammography Necessary?
 Women s Imaging Original Research Leung et al. Repeat Mammogram for Breast Lump Found After Negative Mammogram Women s Imaging Original Research Stephanie E. Leung 1 Ilanit Ben-Nachum Anat Kornecki Leung
Women s Imaging Original Research Leung et al. Repeat Mammogram for Breast Lump Found After Negative Mammogram Women s Imaging Original Research Stephanie E. Leung 1 Ilanit Ben-Nachum Anat Kornecki Leung
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast:
 J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
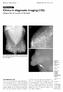 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities. Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine
 Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Solid Breast Nodules: Use of Sonography to Distinguish between Benign and Malignant Lesions
 A. Thomas Stavros, MD #{149} David Thickman, MD #{149} Cynthia L. Rapp, RT, RDMS Mark A. Dennis, MD #{149} Steve H. Parker, MD #{149} Gale A. Sisney, MD Solid Breast Nodules: Use of Sonography to Distinguish
A. Thomas Stavros, MD #{149} David Thickman, MD #{149} Cynthia L. Rapp, RT, RDMS Mark A. Dennis, MD #{149} Steve H. Parker, MD #{149} Gale A. Sisney, MD Solid Breast Nodules: Use of Sonography to Distinguish
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Imaging Differences in Metaplastic and Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the Breast
 Yang et al. Metaplastic Versus Invasive Ductal reast Carcinoma Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Wei Tse Yang 1 ryan Hennessy 2 Kristine roglio 3 Chadwick Mills 1,4 Nour Sneige 5 W. Grant
Yang et al. Metaplastic Versus Invasive Ductal reast Carcinoma Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Wei Tse Yang 1 ryan Hennessy 2 Kristine roglio 3 Chadwick Mills 1,4 Nour Sneige 5 W. Grant
Sonographically-Guided 14-Gauge Core Needle Biopsy for Papillary Lesions of the Breast
 Sonographically-Guided 14-Gauge Core Needle Biopsy for Papillary Lesions of the Breast Eun Sook Ko, MD Nariya Cho, MD Joo Hee Cha, MD Jeong Seon Park, MD Sun Mi Kim, MD Woo Kyung Moon, MD Index terms:
Sonographically-Guided 14-Gauge Core Needle Biopsy for Papillary Lesions of the Breast Eun Sook Ko, MD Nariya Cho, MD Joo Hee Cha, MD Jeong Seon Park, MD Sun Mi Kim, MD Woo Kyung Moon, MD Index terms:
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient. Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester
 Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Flat Epithelial Atypia of the Breast: Pathological-Radiological Correlation
 Women s Imaging Original Research Solorzano et al. Pathological-Radiological Correlation of Breast Flat Epithelial Atypia Women s Imaging Original Research Silma Solorzano 1 Benoît Mesurolle Attila Omeroglu
Women s Imaging Original Research Solorzano et al. Pathological-Radiological Correlation of Breast Flat Epithelial Atypia Women s Imaging Original Research Silma Solorzano 1 Benoît Mesurolle Attila Omeroglu
OF HEMATOMA INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE
 SCOPE TUTORIAL RADIOLOGY CT BRIAN BREASTS US MRCP Natrada Rawdhetubhai, M.D. Radiology Department, Lerdsin General Hospital CT OF HEMATOMA INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE Intra-axial Extra-axial Intraventricular
SCOPE TUTORIAL RADIOLOGY CT BRIAN BREASTS US MRCP Natrada Rawdhetubhai, M.D. Radiology Department, Lerdsin General Hospital CT OF HEMATOMA INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE Intra-axial Extra-axial Intraventricular
Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions?
 Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions? Poster No.: C-0332 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions? Poster No.: C-0332 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Primary Breast Liposarcoma
 Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
BIRADS 3 and 4 lesions viewed by ultrasound and not seen in digital mammograms and tomosynthesis.
 Original article Anales de Radiología México 2016 Jul;15(3):205-213. BIRADS 3 and 4 lesions viewed by ultrasound and not seen in digital mammograms and tomosynthesis. García-Quintanilla JF 1, González-Coronado
Original article Anales de Radiología México 2016 Jul;15(3):205-213. BIRADS 3 and 4 lesions viewed by ultrasound and not seen in digital mammograms and tomosynthesis. García-Quintanilla JF 1, González-Coronado
Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3906195, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3906195 Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3906195, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3906195 Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
 Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 62 (2011) 50e59 www.carjonline.org Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging / Imagerie cardiaque et imagerie thoracique Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 62 (2011) 50e59 www.carjonline.org Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging / Imagerie cardiaque et imagerie thoracique Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
