Original Report. Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical, Mammographic, and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
|
|
|
- Marilynn Copeland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital, ornova, Izmir, Turkey. ddress correspondence to I. Günhan-ilgen. 2 Department of Pathology, Ege Üniversity Hospital, Izmir, Turkey. JR 2002;178: X/02/ merican Roentgen Ray Society Original Report Metaplastic Carcinoma of the reast: Clinical, Mammographic, and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation OJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to investigate the mammographic and sonographic findings of metaplastic carcinoma of the breast and to correlate the radiologic features with clinical and histopathologic findings. CONCLUSION. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast often manifests as a rapidly growing, palpable mass that has high density on mammography and may be microlobulated on sonography. Complex echogenicity with solid and cystic components may be seen sonographically and is related to necrosis and cystic degeneration found histopathologically. lthough it is a rare breast malignancy and these features are not unique, metaplastic carcinoma should be included in the differential diagnosis for breast masses with these imaging features. M ost benign and malignant tumors of the breast arise from glandular epithelium. However, in some cases, glandular epithelium differentiates into nonglandular mesenchymal tissue, a process called metaplasia [1]. Metaplastic changes, including squamous cell, spindle cell, and heterologous mesenchymal growth, occurs in fewer than 5% of breast carcinomas [2 6]. Carcinosarcomas, a subgroup of metaplastic carcinomas, are the rarest primary malignancies of the breast (found in < 0.1% of cases) [7]. The differential diagnosis is important for the purposes of treatment and prognosis [1, 4]. lthough the pathologic and clinical aspects of these rare tumors have been described in various reports, to our knowledge, only a few reports, mostly case studies, have been published on the mammographic features [1, 8 13] and sonographic findings [10, 13]. The purpose of this study was to investigate the mammographic and sonographic findings of metaplastic carcinoma of the breast and to correlate the radiologic features with clinical and histopathologic findings. Materials and Methods retrospective review of the mammograms of 1845 histopathologically proven breast cancer cases diagnosed in our mammography unit during the last 15 years revealed eight cases of histopathologically proven metaplastic carcinoma. The history, physical examination, and radiologic (mammographic and sonographic) findings were analyzed in all patients. Patients ranged in age from 44 to 63 years old (mean, 53.8 years). Mammography with two routine positions (craniocaudal and mediolateral oblique) was performed in all the patients using a Senographe Senix 600T (General Electric CGR, Issy Les Moulineaux, France) or a Mammomat 3000 (Siemens, Solna, Sweden) system. ll mammograms were retrospectively reviewed by two radiologists who were specialists in breast imaging. The evaluation was performed as consensus interpretations. Mammograms were evaluated with radiologists unaware of the information from the physical examination or sonography records but aware of the histopathologic diagnosis. Each mammographic lesion was characterized according to size, mass characteristics (shape, margins, density, size, and location), presence and type of microcalcifications, associated architectural distortion, and skin changes. Pa- JR:178, June
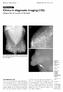
2 Günhan-ilgen et al. renchymal patterns were categorized as fatty, scattered fibroglandular tissue, heterogeneously dense, and extremely dense using the merican College of Radiology s reast Imaging Reporting and Data System (I-RDS) [14]. Sonography was performed in all the patients using a 7.5-mHz transducer (SL 70; Toshiba, Tokyo, Japan) or a broadband 5- to 11-MHz transducer (HDL 1000; dvanced Technology Laboratories, othell, W). The sonographic prints and records of each patient were reviewed after the mammograms, in the same evaluation session. Sonograms were assessed for lesion shape, margin, and echogenicity. In the retrospective study, information about preoperative needle biopsies was available in one patient. ll lesions were surgically excised. Microscopic slides of samples of all patients were reviewed by two pathologists who were breast pathology specialists. Each case was reviewed by the two pathologists as a consensus evaluation. The specific metaplastic components were identified. Mammographic and sonographic findings were then correlated with histopathology. Pathologic size, predominant pathologic findings, and lymph node status were obtained from the surgical pathology reports. Results ll eight patients were women, aged years old (mean age, 53.8 years). Only one patient had a risk factor for breast cancer (her sister died of breast cancer at 46 years). In all eight patients referred to our mammography unit for the first time, the presenting complaint was palpable breast mass, and in two of the patients, a rapid growth was noted by the patients. Only one patient had associated bloody nipple discharge, and one patient had a palpable axillary mass. None of the patients had screening mammograms. t physical examination, the size of the masses ranged between 1.5 and 5 cm (mean, 2.6 cm). In two patients, the mass was mobile. In one patient, a dilated superficial vein was noted on the skin near the medial contour of the mass. On the mammograms, in relation to the parenchymal pattern, four breasts were fatty, and four were heterogenously dense. ll eight patients had masses without associated microcalcifications or architectural distortion. In three patients, the margins of the mass were partially obscured by the surrounding breast parenchyma (Fig. 1). The margins of the masses were well circumscribed in two patients and microlobulated (Figs. 2, 3, and 3) in three patients. None of the masses showed prominent spiculations. ll masses were highly dense, and the shape was round in six patients and oval in two. The size varied between 1.5 and 4.5 cm (mean, 2.6 cm). Unfortunately, prior mammograms were not available in any of the patients, so the rapid growth that was noted by the patient could not be confirmed radiologically. The location of the masses were upper outer quadrant in five patients, upper central quadrant in one, lower central quadrant in one, and lower inner quadrant in one. In one patient, the neighboring skin showed focal thickening. On sonographic examination, two masses had discrete well-circumscribed oval contours, whereas six masses showed microlobulation (Figs. 2 and 3C). In one patient, the mass showed heterogenous echogenicity. The mass had both solid and cystic areas (Fig. 1). Fig year-old woman with a rapidly growing 5-cm palpable left breast mass and bloody nipple discharge., Craniocaudal mammogram shows 4.5-cm high-density mass in left inner hemisphere. Posterior margin (small arrow ) of mass is ill-defined, whereas anterior margin (large arrow ) is obscured by fibroglandular tissue and cannot be defined., Transverse sonogram shows mass with irregular margins and heterogenous echogenicity. Mass has both solid (small arrow ) and cystic (large arrow ) components. In another patient, the mass was round, homogeneous, and solid with smooth margins. lthough the mammographic and sonographic features were consistent with a benign mass, such as fibroadenoma, because of the patient s age (44 years) and family history (her sister died of breast cancer at 46 years), histopathologic examination, which disclosed carcinosarcoma, was strongly recommended. reast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy with axillary node dissection) was performed in one patient who showed axillary lymph node involvement. Two years after surgery, she developed local recurrence, contralateral breast masses, supraclavicular lymphadenopathy, and pulmonary nodules consistent with metastasis, although metastatic disease was not proven histopathologically. The other seven patients were treated with modified radical mastectomy, with the axilla showing no metastatic involvement. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of the lesion that was available in one patient was diagnosed as malignant epithelial tumor. t histopathologic examination, the metaplastic components of the lesions were squamous cell type in three patients (Figs. 2C and 2D), matrix-producing type in two, carcinosarcomatoid in two (Figs. 3D and 3E), and a mixture of spindle cell and matrix-producing type in one. In the complex mass, which showed heterogenous echogenicity with solid and cystic components on sonography, necrosis and cystic degeneration were found at histopathology. ll eight patients underwent axillary lymph node dissection, and involvement was positive in only one JR:178, June 2002
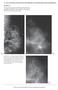
3 Mammography and Sonography of Metaplastic Carcinoma C D Fig year-old woman with 2-cm, firm, mobile, and palpable left breast mass., Mediolateral oblique mammogram shows microlobulated, 2-cm round mass (arrows)., Transverse sonogram shows round, solid mass with homogeneous echogenicity and microlobulated margins (arrow). C, Photomicrograph shows mammarian ductulus on left side. On right side, metaplastic breast carcinoma and squamous cell groups can be seen. (H and E, 200) D, Photomicrograph shows squamous differentiation areas in metaplastic breast carcinoma. (H and E, 400) Discussion Metaplastic breast carcinomas are regarded as ductal carcinomas that undergo metaplasia into a nonglandular growth pattern [1, 6, 8]. The mixed cell origin is corroborated by histopathologic staining for mesenchymal cells (vimentin), epithelial cells (cytokeratin), and myoepithelial cells (S-100 protein, actin, and high-molecular-weight cytokeratin) [1]. Wargotz and Norris [3, 5, 15] and Wargotz et al. [4] suggested four variants of metaplastic carcinoma, including matrix-producing carcinoma, spindle cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and carcinosarcoma. Oberman [6] suggested that all such tumors be categorized JR:178, June 2002 as metaplastic carcinoma of the breast, deemphasizing whether the metaplastic component is of mesenchymal or epithelial origin. lthough these rare tumors show pathologic features of both carcinoma and sarcoma, because metaplastic carcinoma with a sarcomatous component is a different entity from primary breast sarcoma, we believe differentiation is significant to characterize them as distinct entities for purposes of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Metaplastic carcinomas are usually seen in women who are more than 50 years old [2, 3, 5, 6, 9]. The ages of our patients were between 44 and 63 years old; only two patients were less than 50 years old. The presenting symptom is usually a palpable mass, and axillary lymph node metastasis is infrequent [2 5]. ll our patients had palpable masses, and only one (12.5%) had axillary lymph node involvement. The number of our patients is too few to accurately determine the frequency of lymph node involvement in a larger patient population. The mammographic appearance of metaplastic breast carcinoma has been described in case reports or in small series [1, 8 13]. To our knowledge, only four reports have been published that correlate mammographic and pathologic features of this rare tumor [1, 8, 10, 12]. renner et al. [1], in their study of three 1423
4 Günhan-ilgen et al. C Fig year-old woman with 2-cm palpable left breast mass., Craniocaudal mammogram shows microlobulated, round mass (arrows)., Microlobulation of margins is better shown on spot mammogram. C, Transverse sonogram shows microlobulated hypoechoic solid mass. D, Photomicrograph shows admixture of cohesive carcinoma cells and malignant stromal spindle cells. (H and E, 200) E, Photomicrograph shows spindle cells in metaplastic carcinoma. (H and E, 400) D patients, described the mass as well circumscribed, irregular, or spiculated, whereas Patterson et al. [8], in their series on nine patients, reported a predominantly circumscribed, noncalcified mass with a spiculated portion. Samuels et al. [13] described the margins of five masses, which were oval, as indistinct and partially well circumscribed; in three of them, the tumor margin was also partly spiculated. Park et al. [10], in their study of 16 patients, described the characteristic appearance as an ill-defined or obscured round mass with associated architectural distortion. s for the presence of microcalcifications, Evans et al. [12], in their case report of osseous metaplasia, described a predominantly circumscribed mass with a densely calcified center and an osteoid matrix. renner et al. reported a 2-cm smooth mass with macrocalcifications, and Park et al. reported one patient with clustered microcalcifications without an associated mass. In our series, the margins of the tumors were either obscured (37.5%), microlobulated (37.5%), or well circumscribed (25%). ll the masses had high density without spiculations 1424 or associated microcalcifications on mammography. In contrast to the study of Park et al. [10], associated architectural distortion was not noted in our patients. When we compare and combine the mammographic findings of the masses in all the previously reported series and in this study, we could probably conclude that no specific or distinctive descriptor for mass margin is characteristic of metaplastic carcinoma. However, a high-density mass without associated microcalcifications might be useful in suggesting the diagnosis. lthough seen rarely and possibly not a characteristic finding, metaplastic carcinoma could be included in the differential diagnosis of predominantly circumscribed, noncalcified masses seen on mammography. Metaplastic carcinomas are likely to have circumscribed margins, especially when the tumor is composed solely of spindle cells [8]. In one of our patients, the mass was so well circumscribed that it mimicked a fibroadenoma. However, histopathologic examination disclosed carcinosarcoma. One important feature that may be helpful in distinguishing metaplastic carcino- E mas from predominantly circumscribed noncalcified masses is the concurrence of a circumscribed portion with a spiculated portion, which is seen in carcinomas with a mixture of growth patterns of metaplastic and invasive carcinoma not otherwise specified [8]. On sonographic examination, one of the masses showed complex internal echogenicity with solid and cystic components, which was consistent with necrosis and cystic degeneration at pathologic examination. The sonographic features of metaplastic carcinoma have been previously reported [10, 13]. Samuels et al. [13], in their study of five patients, of whom four had sonographic examinations, showed both cystic and solid components in two of the masses. The histopathologic diagnosis of these tumors was predominantly squamous cell carcinoma. Park et al. [10], in their study of 16 patients, of whom 11 had sonograms, observed complex internal echogenicity with solid and cystic components in six lesions. Four of these six lesions also had hemorrhagic or cystic necrosis at pathologic examination. We believe that metaplastic carcinoma, although a rare tu- JR:178, June 2002
5 Mammography and Sonography of Metaplastic Carcinoma mor, should be considered in the differential diagnosis of breast masses with solid and cystic components. In most metaplastic carcinomas, foci of transition between invasive ductal carcinoma and the metaplastic element are detected, sometimes only after extensive sampling. In tumors in which the metaplastic spindle component constitutes almost the entire tumor, the distinction from a sarcoma may be difficult. In some of these cases, ductal carcinoma in situ adjacent to the tumor often suggests that the spindle cells were of epithelial origin [8]. The diagnosis of metaplastic breast carcinoma may be made with aspiration cytology or core biopsy, but excisional biopsy is preferred because diagnostic errors resulting from inadequate samples are avoided, especially in cases of associated necrosis or hemorrhage [8, 12, 16]. Patterson et al. [8] have stated that the distinction between metaplastic breast cancer and sarcoma is clinically important because the surgical treatment, chemotherapy regimens, and metastatic pathways are different. Typically, axillary lymph node involvement is rare in breast sarcoma even when the disease is diffusely disseminated, whereas lymph node metastases are reported in 25 30% of cases with metaplastic carcinomas [1, 8]. ll eight patients in our series underwent axillary lymph node dissection, and metastasis was detected in only one patient (12.5%); at histopathologic examination, the metaplastic component of the tumor was carcinosarcomatoid type. However, the number of our cases is too few to accurately determine the frequency of lymph node involvement in a larger patient population. lthough no series has been sufficiently large to determine overall prognosis, survival most likely depends on tumor size, histologic type, grade, lymph node status, and perhaps most directly on the type and grade of the mesenchymal component. The overall 5- year survival rate is approximately 40% [1]. Chemotherapy is usually directed toward the sarcomatous component of the disease on the basis of the patterns of metastases [1]. In conclusion, metaplastic carcinoma of the breast manifests as a rapidly growing, palpable mass that has high density on mammography and may be microlobulated on sonography. Complex echogenicity with solid and cystic components may be seen sonographically and is related to necrosis and cystic degeneration found histopathologically. lthough metaplastic carcinoma is a rare breast malignancy, and these features are not unique, metaplastic carcinoma should be included in the differential diagnosis. References 1. renner RJ, Turner RR, Schiller V, rndt RD, Giuliano. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: report of three cases. Cancer 1998;82: Pitts WC, Rojas V, Gaffey MJ, et al. Carcinomas with metaplasia and sarcomas of the breast. m J Clin Pathol 1991;95: Wargotz ES, Norris HJ. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. I. Matrix-producing carcinoma. Human Pathol 1989;20: Wargotz ES, Deos PH, Norris HJ. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. II. Spindle cell carcinoma. Human Pathol 1989;20: Wargotz ES, Norris HJ. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. IV. Squamous cell carcinoma of ductal origin. Cancer 1990;65: Oberman H. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. m J Surg Pathol 1987;11: Feder JM, de Paredes ES, Hogge JP, Wilken JJ. Unusual breast lesions: radiologic pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics 1999;19[suppl]:S11 S26 8. Patterson SK, Tworek J, Roubidoux M, Helvie M, Oberman H. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: mammographic appearance with pathologic correlation. JR 1997;169: Taylor D, damson R, Minchin DE, Reading L. Carcinoma of the breast with sarcomatous metaplasia. ustralas Radiol 1994;38: Park JM, Han K, Moon WK, Choe YH, hn SH, Gong G. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: mammographic and sonographic findings. J Clin Ultrasound 2000;28: Tashjian J, Kuni CC, ohn LE. Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the breast: mammographic findings. Can ssoc Radiol J 1989;40: Evans H, Shaughnessy E, Nikiforov YE. Infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast with osseous metaplasia: imaging findings with pathologic correlation. JR 1999;172: Samuels TH, Miller N, Manchul L, DeFreitas G, Panzarella T. Squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. Can ssoc Radiol J 1996;47: merican College of Radiology. reast imaging reporting and data system (I-RDS), 3rd ed. Reston, V: merican College of Radiology, Wargotz ES, Norris HJ. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. III. Carcinosarcoma. Cancer 1989;64: Kline TS, Kline IK. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: diagnosis by aspiration biopsy cytology report of two cases and literature review. Diagn Cytopathol 1990;6:63 67 JR:178, June
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Imaging Differences in Metaplastic and Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the Breast
 Yang et al. Metaplastic Versus Invasive Ductal reast Carcinoma Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Wei Tse Yang 1 ryan Hennessy 2 Kristine roglio 3 Chadwick Mills 1,4 Nour Sneige 5 W. Grant
Yang et al. Metaplastic Versus Invasive Ductal reast Carcinoma Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Wei Tse Yang 1 ryan Hennessy 2 Kristine roglio 3 Chadwick Mills 1,4 Nour Sneige 5 W. Grant
Cairo/EG, Khartoum/SD, London/UK Biological effects, Diagnostic procedure, Ultrasound, Mammography, Breast /ecr2015/C-0107
 Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features
 Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma with Fibrotic Focus: Mammographic and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients
 Clinical Radiology (2009) 64, 628e636 ORIGINAL PAPER Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients B. Mesurolle a, *, M. El-Khoury
Clinical Radiology (2009) 64, 628e636 ORIGINAL PAPER Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients B. Mesurolle a, *, M. El-Khoury
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammography and Subsequent Whole-Breast Sonography of Nonpalpable Breast Cancers: The Importance of Radiologic Breast Density
 Isabelle Leconte 1 Chantal Feger 1 Christine Galant 2 Martine Berlière 3 Bruno Vande Berg 1 William D Hoore 4 Baudouin Maldague 1 Received July 11, 2002; accepted after revision October 28, 2002. 1 Department
Isabelle Leconte 1 Chantal Feger 1 Christine Galant 2 Martine Berlière 3 Bruno Vande Berg 1 William D Hoore 4 Baudouin Maldague 1 Received July 11, 2002; accepted after revision October 28, 2002. 1 Department
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging. Medical University of South Carolina Charleston
 Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast:
 J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
57th Annual HSCP Spring Symposium 4/16/2016
 An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
BI-RADS Update. Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital
 BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: Imaging Findings With Pathologic and Clinical Correlation
 Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Jones et al. Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay WOMEN S IMGING Katie N. Jones 1 Katrina N. Glazebrook 1 arol Reynolds 2 Jones KN, Glazebrook
Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Jones et al. Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay WOMEN S IMGING Katie N. Jones 1 Katrina N. Glazebrook 1 arol Reynolds 2 Jones KN, Glazebrook
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Breast Imaging Lexicon
 9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast:
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Amlendu Nagar
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast as Cystic Lesions: Sonographic-Pathologic Correlation
 Women s Imaging Original Research Kim et al. Breast Tumors as Cystic Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Sun Mi Kim 1,2 Hak Hee Kim 1 Doo Kyung Kang 3 Hee Jung Shin 1 Nariya Cho 4
Women s Imaging Original Research Kim et al. Breast Tumors as Cystic Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Sun Mi Kim 1,2 Hak Hee Kim 1 Doo Kyung Kang 3 Hee Jung Shin 1 Nariya Cho 4
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Ductal carcinoma in situ, underestimation, ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy
 Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING
 OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report
 Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Imaging-Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Papillary Lesions of the Breast
 Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation
 Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, L. Koren,
Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, L. Koren,
Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography
 Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
ARTICLE IN PRESS. doi: /j.ijrobp METAPLASTIC CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST: A RETROSPECTIVE REVIEW
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.024 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. xx, No. x, pp. xxx, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.024 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. xx, No. x, pp. xxx, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front matter
Ultrasonography. Methods. Brief Description. Indications. Device-related Prerequisites. Technical Requirements. Evaluation Criteria
 1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
Breast Cancer. Saima Saeed MD
 Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Manifested Solely as Microcalcifications on Sonography
 Sonography of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Head and Neck Imaging Clinical Observations Jin Young Kwak 1 Eun-Kyung Kim 1 Eun Ju Son 1 Min Jung Kim 1 Ki Keun Oh 1 Ji Young Kim 2 Kwang Il Kim 2 Kwak JY, Kim
Sonography of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Head and Neck Imaging Clinical Observations Jin Young Kwak 1 Eun-Kyung Kim 1 Eun Ju Son 1 Min Jung Kim 1 Ki Keun Oh 1 Ji Young Kim 2 Kwang Il Kim 2 Kwak JY, Kim
Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions?
 Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions? Poster No.: C-0332 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions? Poster No.: C-0332 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1
 5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging
 Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas
 Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings.
 Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications
 Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation
 Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Sonographic and Mammographic Appearances of Breast Hemangioma
 Women s Imaging Clinical Observations Mesurolle et al. Sonography and Mammography of reast Hemangioma Women s Imaging Clinical Observations WOMEN S IMGING enoît Mesurolle 1 Vitaly Sygal 1 Lucie Lalonde
Women s Imaging Clinical Observations Mesurolle et al. Sonography and Mammography of reast Hemangioma Women s Imaging Clinical Observations WOMEN S IMGING enoît Mesurolle 1 Vitaly Sygal 1 Lucie Lalonde
Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds
 215 Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds ratio 719 (100) 305(100) Shape Oval 445 (61.9) 019
215 Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds ratio 719 (100) 305(100) Shape Oval 445 (61.9) 019
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology
 Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings
 Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Breast imaging in general practice
 Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Using T2-Weighted Sequences to More Accurately Characterize Breast Masses Seen on MRI
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis: A Case Detected by Breast Cancer Screening Examination
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
Pleomorphic adenoma of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari
 of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari Introduction, also known as mixed tumour, is a benign tumour which typically presents as a painless,
of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari Introduction, also known as mixed tumour, is a benign tumour which typically presents as a painless,
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
BI-RADS and Breast MRI. Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018
 BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical and Radiological Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical and Radiological Findings with Histopathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-2078 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. AlSharif
Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical and Radiological Findings with Histopathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-2078 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. AlSharif
Primary Breast Liposarcoma
 Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Screen Detected Breast Carcinoma, with Coarse Calcification
 Screen Detected Breast Carcinoma, with Coarse Calcification Poster No.: R-0168 Congress: RANZCR ASM 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Ebrahim, D. Abeywardhana, D. Dissanayake, C. Metcalf, E. Wylie;
Screen Detected Breast Carcinoma, with Coarse Calcification Poster No.: R-0168 Congress: RANZCR ASM 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Ebrahim, D. Abeywardhana, D. Dissanayake, C. Metcalf, E. Wylie;
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses. Case #1
 University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy
 66 One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy Example 2.13 A 36-year-old woman who recentlyfelt a small hard lump in the upper-outer quadrant of her
66 One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy Example 2.13 A 36-year-old woman who recentlyfelt a small hard lump in the upper-outer quadrant of her
Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the breast: a rare entity, representation of two cases
 International Surgery Journal Siripurapu Y et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Aug;4(8):2848-2853 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173434
International Surgery Journal Siripurapu Y et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Aug;4(8):2848-2853 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173434
Solitary Pancreatic Metastasis From Breast Matrix-Producing Carcinoma: A First Case Report
 Int Surg 2017;102:294 298 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-17-00064.1 Solitary Pancreatic Metastasis From Breast Matrix-Producing Carcinoma: A First Case Report Yoshiyuki Kiyasu 1,2, Ken Hayashi 1, Go Miyahara 1,
Int Surg 2017;102:294 298 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-17-00064.1 Solitary Pancreatic Metastasis From Breast Matrix-Producing Carcinoma: A First Case Report Yoshiyuki Kiyasu 1,2, Ken Hayashi 1, Go Miyahara 1,
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice
 Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice Francesca Caumo, Erminia Manfrin, Franco Bonetti,
Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the mammographic findings retrospectively detected in inflammatory breast cancer: usefulness in clinical practice Francesca Caumo, Erminia Manfrin, Franco Bonetti,
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS
 BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection
 Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS
 A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS Hideaki Shirai M.D., M. Sakurai M.D., K. Yoshida M.D., N. Usuda M.D., H. Masuoka M.D., I. Shimokawara M.D, K. Asaishi M.D. Sapporo Kotoni Breast Clinic,
A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS Hideaki Shirai M.D., M. Sakurai M.D., K. Yoshida M.D., N. Usuda M.D., H. Masuoka M.D., I. Shimokawara M.D, K. Asaishi M.D. Sapporo Kotoni Breast Clinic,
Architectural Distortion of
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gaur et al. rchitectural Distortion of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.203.116 on 01/05/18 from IP address
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gaur et al. rchitectural Distortion of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.203.116 on 01/05/18 from IP address
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN
 Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Pathologic outcomes of coarse heterogeneous calcifications detected on mammography
 Pathologic outcomes of coarse heterogeneous calcifications detected on mammography Poster No.: C-1957 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H. J. Lim, K. R. Cho, K. W. Hwang, B. K. Seo, O.
Pathologic outcomes of coarse heterogeneous calcifications detected on mammography Poster No.: C-1957 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H. J. Lim, K. R. Cho, K. W. Hwang, B. K. Seo, O.
BreastScreen Victoria Annual Statistical Report
 BreastScreen Victoria Annual Statistical Report 005 Produced by: BreastScreen Victoria Coordination Unit Level, Pelham Street, Carlton South Victoria 05 PH 0 9660 6888 FX 0 966 88 EM info@breastscreen.org.au
BreastScreen Victoria Annual Statistical Report 005 Produced by: BreastScreen Victoria Coordination Unit Level, Pelham Street, Carlton South Victoria 05 PH 0 9660 6888 FX 0 966 88 EM info@breastscreen.org.au
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
A GP S APPROACH TO BREAST LUMPS AND SYMPTOMS DR KK CHEUNG GPGC WORKSHOP
 A GP S APPROACH TO BREAST LUMPS AND SYMPTOMS DR KK CHEUNG GPGC WORKSHOP 18.08.18 HAVE A SYSTEM HISTORY EXAMINATION INVESTIGATION FOLLOW UP BREAST SYMPTOMS HISTORY DON T FORGET SKIN CHANGES AND NIPPLE CHANGES
A GP S APPROACH TO BREAST LUMPS AND SYMPTOMS DR KK CHEUNG GPGC WORKSHOP 18.08.18 HAVE A SYSTEM HISTORY EXAMINATION INVESTIGATION FOLLOW UP BREAST SYMPTOMS HISTORY DON T FORGET SKIN CHANGES AND NIPPLE CHANGES
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: MRI, Ultrasound, and Mammographic Appearances
 Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Eiada et al. Imaging Papillary Lesions of the reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.194 on 01/27/18 from IP address 37.44.198.194.
Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Eiada et al. Imaging Papillary Lesions of the reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.194 on 01/27/18 from IP address 37.44.198.194.
Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
 Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 62 (2011) 50e59 www.carjonline.org Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging / Imagerie cardiaque et imagerie thoracique Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 62 (2011) 50e59 www.carjonline.org Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging / Imagerie cardiaque et imagerie thoracique Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8568-8572 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010093 Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8568-8572 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010093 Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up; Description of a Case-Series
 18 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 18-23 Open Access Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up; Description of a Case-Series W.A. Donk *, R.J. Oostenbroek, R.K.
18 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 18-23 Open Access Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up; Description of a Case-Series W.A. Donk *, R.J. Oostenbroek, R.K.
Journal of Breast Cancer
 CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2016 December; 19(4): 459-464 Increased Malignant Microcalcifications after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in dvanced reast Cancer Gi Won Shin, Young Mi Park,
CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2016 December; 19(4): 459-464 Increased Malignant Microcalcifications after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in dvanced reast Cancer Gi Won Shin, Young Mi Park,
