Imaging Differences in Metaplastic and Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the Breast
|
|
|
- Prosper Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Yang et al. Metaplastic Versus Invasive Ductal reast Carcinoma Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Wei Tse Yang 1 ryan Hennessy 2 Kristine roglio 3 Chadwick Mills 1,4 Nour Sneige 5 W. Grant Davis 5,6 Vicente Valero 7 Kelly K. Hunt 8 Michael Z. Gilcrease 5 Yang WT, Hennessy, roglio K, et al. Keywords: breast neoplasm, invasive ductal carcinoma, mammography, metaplastic breast carcinoma, sonography DOI: /JR Received February 16, 2007; accepted after revision June 30, Department of Diagnostic Imaging, The University of Texas M. D. nderson Cancer Center, PO ox , Unit 1350, Houston, TX ddress correspondence to W. T. Yang (wyang@di.mdacc.tmc.edu). 2 Department of Gynecology Medical Oncology, The University of Texas M. D. nderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX. 3 Quantitative Sciences Division, The University of Texas M. D. nderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX. 4 Present address: Department of Radiology, aylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX. 5 Department of Pathology, The University of Texas M. D. nderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX. 6 Present address: Physicians Reference Laboratory, Overland Park, KS. 7 Department of reast Medical Oncology, The University of Texas M. D. nderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX. 8 Department of Surgical Oncology, The University of Texas M. D. nderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX. CME This article is available for CME credit. See for more information. JR 2007; 189: X/07/ merican Roentgen Ray Society Imaging Differences in Metaplastic and Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the reast OJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to compare the imaging features of metaplastic breast carcinoma with those of invasive ductal carcinoma. MTERILS ND METHODS. Women diagnosed on preoperative mammography or sonography with metaplastic breast carcinoma and T-stage matched invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast from a single pathology database were included in the study. Clinical and pathologic information on all metaplastic cancers was documented. Mammography and sonography variables were recorded using the I-RDS lexicon. Groups were compared using Fisher s exact test, the chi-square test, or Wilcoxon s rank sum test, as appropriate. RESULTS. Forty-three patients diagnosed with metaplastic carcinoma were matched to 43 patients with ductal carcinoma by tumor T stage. Patients with metaplastic carcinoma were younger (median, 46 vs 53 years, p = 0.048) than those with ductal carcinoma. Mammographically, metaplastic carcinomas were less frequently irregular in shape (16% vs 74%, p < ) and less frequently showed microlobulated or spiculated margins (19% vs 56%, p = ) and calcifications (25% vs 51%, p = 0.02) when compared with ductal carcinomas. Sonographically, metaplastic carcinomas were less frequently irregular in shape (27% vs 69%, p = 0.001) and less frequently showed angular margins (9% vs 49%) and posterior acoustic shadowing (9% vs 49%, p < ). CONCLUSION. Characteristic malignant imaging features, including irregular shape, spiculated margins, segmentally distributed pleomorphic calcifications, and posterior acoustic shadowing, are uncommon in metaplastic carcinomas. These carcinomas tend to show more benign imaging features, such as round or oval shape with circumscribed margins, when compared with ductal carcinomas. nvasive breast carcinoma usually I has an epithelial morphology with ductal differentiation. Metaplastic carcinoma, on the other hand, is a heterogeneous group of neoplasms with mixed epithelial and mesenchymal differentiation. This mixed cell differentiation is seen both morphologically and immunophenotypically, as evidenced by immunohistochemical expression of markers of mesenchymal cells (vimentin), epithelial cells (pancytokeratin), and myoepithelial cells (S-100, smooth-muscle actin, and p63). Metaplastic breast carcinoma is uncommon, accounting for fewer than 5% of breast carcinomas [1 5]. Wargotz and Norris [1 3] and Wargotz et al. [4] suggested five principal variants, including matrix-producing carcinoma, spindle-cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, and metaplastic carcinoma with osteoclastic giant cells [6]. Recently, lowgrade fibromatosis-like tumors have been described as a biologically distinct subtype [7, 8]. The differential diagnosis between invasive ductal carcinoma and metaplastic carcinoma is important for treatment planning and prognosis. recent study described significantly worse overall survival for the metaplastic subtype compared with a control group [9]. We undertook a study to compare imaging features of invasive ductal carcinomas and metaplastic carcinomas to determine whether significant differences are shown on conventional imaging methods, including mammography and sonography. Materials and Methods Clinical Data and Pathology Forty-three patients from the surgical pathology database of a single institution who had a diagnosis of metaplastic breast carcinoma from January 1995 to June 2005 and who had undergone preoperative imaging with mammography or sonography were included in this study. second study group comprised 43 patients with invasive ductal carcinoma 1288 JR:189, December 2007
2 Metaplastic Versus Invasive Ductal reast Carcinoma TLE 1: Clinical Data and Pathology Features of 43 Metaplastic and 43 Ductal Cancers Metaplastic Ductal Feature No. % No. % xillary nodes at surgery Positive Negative Unknown Estrogen receptor status Positive Negative Unknown Progesterone receptor status Positive Negative Unknown HER2/neu overexpression Positive Negative Unknown Histologic subtype Predominantly sarcomatoid Mixed sarcomatoid and epithelial Squamous Low-grade fibromatosis Miscellaneous a Note Data are numbers of tumors. Percentages may not total 100 due to rounding. a One invasive ductal carcinoma with squamous differentiation and one matrix-producing carcinoma with squamous differentiation. from the same surgical pathology database diagnosed during the same time period who were matched to the patients with metaplastic carcinoma by tumor T stage (size) and who also had breast imaging available for review. Tumors in seven patients were classified as stage T1 (< 2 cm), in 34 patients as stage T2 (> 2 cm and < 5 cm), and in two patients as stage T3 (> 5 cm) in each group. total of 21,037 patients were diagnosed with invasive ductal carcinoma during this period. Information about histopathologic features was obtained from pathology reports or, for selected cases requiring clarification of the pathology findings, through review of H and E stained slides by one of two dedicated breast pathologists and one breast pathology fellow. The clinical charts were reviewed by a senior medical oncology fellow to collect information on tumor stage, estrogen and progesterone receptor status, HER2/neu status, and clinical follow-up. The clinical and pathologic tumor stages were determined using the sixth edition of the cancer staging manual of the merican Joint Committee on Cancer [10]. Imaging Mammography Mammography was performed using a Lorad M3 (Hologic) or a DMR series mammography unit (GE Healthcare). Standard twoview diagnostic mammography was performed, with additional views as deemed necessary. Two mammographers with 3 and 10 years experience in breast imaging reviewed all available mammograms and sonograms. These reviews were done independently and without knowledge of the clinical and pathologic findings. greement as to the presence or absence of findings was by consensus. reast parenchymal density was classified according to the merican College of Radiology I- RDS classifications [11]. Mammograms were reviewed for focal masses, calcifications, asymmetric density, architectural distortion, and associated features such as skin thickening and retraction, nipple retraction, and axillary lymphadenopathy. Sonography Real-time gray-scale sonography and color Doppler sonography were performed using an Elegra unit (Siemens Medical Solutions) by an attending radiologist who was one of a group of 10 radiologists (including two of the authors) assigned to breast sonography. Sonograms were assessed for masses (solid or cystic) and their shapes, margins, echo patterns, posterior acoustic features, calcifications, vascularity determined by color Doppler imaging, and effects on surrounding tissue, according to the I-RDS sonography lexicon [12, 13] as determined by the two mammographers. Disease was also assessed as unifocal, multifocal, or multicentric in all patients who underwent sonography. Sonographic assessment of the regional lymph node basins, including the axillary, infraclavicular, internal mammary, and supraclavicular regions, was documented according to previously published criteria [14, 15]. Whole-breast and nodal basin sonography are routinely performed at our institution because most patients present for staging of a known malignancy. Statistical Methods Mammography variables, including size, shape, margin, and density of masses as well as morphology and distribution of calcifications, were recorded according to I-RDS criteria. Sonography variables recorded included mass size, shape, margin, posterior acoustic phenomena, vascularity, and axillary lymph node status according to I-RDS criteria. Imaging features were tabulated and compared between groups using Fisher s exact test, the chisquare test, or Wilcoxon s rank sum test, as appropriate. Values for p are not presented when there were fewer than five patients in a category; p values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Results Patients with metaplastic breast carcinoma were slightly younger than patients with ductal carcinoma (p = 0.048). The median age for the patients with metaplastic carcinoma was 46 years (range, years) compared with 53 years (range, years) for those with ductal carcinoma. The median size of metaplastic carcinomas was 3 cm (range, 1 10 cm) compared with 2.4 cm (range, 1 5 cm) for ductal carcinomas. Thirty-seven (86%) of 43 patients with metaplastic carcinoma presented with a palpable mass, compared with 34 (79%) of 43 with ductal carcinoma. Table 1 describes the clinical and tumor characteristics of the 43 patients with metaplastic breast carcinomas. Most metaplastic breast carcinomas were hormone receptor negative (estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor) (39/40, 97.5% and 33/38, 86.8%, respectively) and HER2/neu-negative (22/23, 95.7%; unknown in 20/43, 46.5%) compared with estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor negativity rates of 25% (10/40) and 47.5% (19/40), re- JR:189, December
3 Yang et al. TLE 2: Mammographic Features Ductal (n = 43) Metaplastic (n = 43) Feature No. % No. % p Mass Yes No Increased density rchitectural distortion Mammography not performed Shape Round Oval Lobular Irregular < Margin Circumscribed Indistinct Microlobulated or spiculated Density High Isodense Calcifications Yes No Morphology Coarse or amorphous Pleomorphic, heterogeneous, or linear Distribution Grouped Segmental Diffuse Note Dash ( ) indicates p values not presented when there are fewer than five patients in a category. spectively, for ductal carcinoma, and HER2/neu negativity of 73.7% (28/38; unknown in 11.6% [5/43]). xillary lymph node disease was noted in 23.7% (9/38) of patients with metaplastic carcinoma compared with 47.5% (19/40) of patients with ductal carcinoma, and axillary nodal status was unknown in 11.6% (5/43) of patients with metaplastic carcinoma compared with 7.0% (3/43) of patients with ductal carcinoma. The median follow-up was 47 months (range, months). Four (9%) of 43 patients were lost to follow-up, 27 (62.7%) are currently alive with no evidence of disease, and 12 (27.9%) died. The cause of death was breast carcinoma in 11 patients and concurrent lymphoma in one. total of 17 recurrences were seen in 17 patients. Four of the recurrences were local, 12 were distant, and one was combined local and distant. The most common site of metastatic disease was the lung (n = 10), followed by liver and bone. The median time to recurrence was 12.5 months. Table 2 shows the mammography characteristics of metaplastic carcinomas. Mammography was not performed in three patients with metaplastic carcinoma. Mammographically, metaplastic carcinomas were more frequently round, oval, or lobular (Figs. 1 5) (84% vs 26%, p < ) and more frequently showed circumscribed margins (Figs. 1 and 3) (15% vs 1%, p = 0.001) than ductal carcinomas. Calcifications were more frequently noted in ductal (51% vs 25%, p = 0.02) than in metaplastic carcinomas (Fig. 1) and were more frequently linear, pleomorphic, or heterogeneous in morphology (40% vs 77%, p = 0.06) in ductal than in metaplastic carcinomas. Consistent with the size distribution of tumors, overlying skin thickening (13%) was relatively infrequent in this study because only three tumors were larger than 5 cm. Table 3 shows the sonographic characteristics of ductal and metaplastic carcinomas. Sonography was performed in 39 and 33 patients with invasive ductal and metaplastic carcinoma, respectively. typical malignant irregular shape was noted in 69% of ductal versus 27% of metaplastic carcinomas (p = 0.001). ngular margins were present in 49% of ductal versus 9% of metaplastic carcinomas. Circumscribed and indistinct margins were more frequent in metaplastic than in ductal carcinomas (55% vs 18%) (Fig. 4). Posterior acoustic shadowing was noted in 49% of ductal versus 9% of metaplastic carcinomas, and posterior acoustic enhancement (Figs. 2, 3, and 5) was noted in 18% of ductal versus 67% of metaplastic carcinomas (p < ). Discussion Metaplastic carcinomas displayed more benign mammographic features in our series and typically showed a round or oval mass with circumscribed margins compared with invasive ductal carcinomas, which typically showed an irregular shape and spiculated margins. significantly lower frequency of malignant-type pleomorphic, linear microcalcifications was observed in metaplastic than in ductal carcinomas. These findings concur with previous publications involving fewer patients [16 20]. Sonographically, metaplastic carcinomas showed more benign features characterized by an oval, round, or lobular solid hypoechoic mass with circumscribed or indistinct margins in our series when compared with ductal carcinomas. Metaplastic carcinomas frequently showed posterior acoustic enhancement, whereas posterior acoustic shadowing was more frequently associated with invasive ductal carcinomas. These combined mammographic and sonographic features may lead to misinterpretation of metaplastic carcinoma as a probably benign or a I-RDS category 3 lesion [11, 12], which could potentially result in delayed diagnosis of carcinoma even if appropriately categorized and evaluated. The differential diagnosis of an oval, round, or lobular solid mass with circumscribed margins includes the triad of circumscribed carcinomas: medullary, mucinous, and papillary carcinomas [21 25]. Recent publications have de JR:189, December 2007
4 Metaplastic Versus Invasive Ductal reast Carcinoma Fig. 1 Right mediolateral oblique mammogram shows lobular mass with internal coarse calcifications (arrows) in 66-year-old woman who presented with palpable mass. Final pathology showed invasive metaplastic carcinoma with malignant chondroosseous neoplasm. Fig year-old woman with palpable mass., Craniocaudad right mammogram shows high-density round mass with partially indistinct margins (long arrows) and partially circumscribed margins (short arrows)., Transverse sonogram shows oval mixed solid and cystic mass (long arrow) with partially indistinct margins showing posterior acoustic enhancement (short arrows). Final pathology revealed spindle cell carcinoma most consistent with sarcomatoid metaplastic carcinoma. Fig year-old woman with palpable mass., Left mediolateral oblique mammogram shows oval high-density mass with circumscribed margins (arrow)., Transverse sonogram of same breast shows solid oval mass with microlobulated margins (long arrow) and posterior acoustic enhancement (short arrows). Final pathology showed high-grade invasive sarcomatoid carcinoma. Fig year-old woman with palpable mass in left breast., Left mediolateral oblique mammogram shows highdensity lobular mass (long arrows) with associated left axillary adenopathy (short arrows)., Color Doppler transverse sonogram shows lobular circumscribed solid hypoechoic and hypervascular mass (arrows). Final pathology revealed high-grade invasive squamous cell carcinoma. JR:189, December
5 Yang et al. Fig year-old woman with palpable mass in left breast., Left craniocaudad mammogram shows high-density round mass with partially spiculated margins (arrows). Overlying marker denotes palpable mass., Transverse sonogram shows irregular mixed solid and cystic mass (long arrow) with mild posterior acoustic enhancement (short arrows). Final pathology revealed sarcomatoid carcinoma with osseous metaplasia. TLE 3: Sonographic Features Ductal (n = 39) Metaplastic (n =33) Feature No. % No. % p Shape Oval or round Lobular Irregular Margin Circumscribed Indistinct Microlobulated ngular Cystic and solid Solid Solid and cystic Posterior acoustic phenomena Enhancement None Shadowing < Calcifications No Yes Vascularity No Yes Not available xillary lymph nodes Negative Positive Note Dash ( ) indicates p values not presented when there are fewer than five patients in a category. scribed significantly more circumscribed malignant noncalcified mammographic masses representing high-grade invasive carcinomas in patients who have gene mutations than in the control group [26, 27]. Metaplastic breast carcinomas presented at a younger age than ductal carcinomas. However, this comparison of age between the two groups (metaplastic and ductal carcinoma) is limited by selection bias because the 43 matched invasive ductal carcinomas represent a small fraction ( 0.2%) of the total number of ductal carcinomas ( 21,037) diagnosed during this period. Some studies have found tumor size to be the most important determinant of patient outcome, and tumors greater than 5 cm have the poorest prognosis [2, 28]. The presenting symptom is usually a palpable mass, as was the case in our series, in which 86% of patients presented with a palpable breast mass. Metaplastic breast carcinoma displays a biologic behavior different from that of typical invasive ductal carcinoma. Metaplastic tumors tend to be large at presentation, to be hormone receptor and HER2/neu-negative, and to have a low incidence of regional lymph node involvement [5, 29]. The number of patients with documented axillary nodal metastasis at the time of axillary nodal dissection was 23.7% in our series. This figure is within the reported range for metaplastic breast carcinoma [30, 31] but is still lower than the expected yield for invasive ductal carcinoma [32] and the percentage of axillary nodal involvement of 48.8% in the control group of ductal carcinomas in this study. Metaplastic carcinomas have a greater tendency for early hematogenous dissemination. These tumors have uncertain prognostic significance. It has been suggested that metaplastic carcinomas have a worse prognosis than typical ductal carcinomas [9, 33], and that duration of symptoms, TNM stage, tumor size, and axillary nodal status are significant prognostic factors of survival [34]. We postulate that the poorer outlook associated with metaplastic carcinomas is the result of a difference in biology that reflects more the sarcomatoid than the epithelial spectrum of tumor behavior; the sarcomatoid spectrum is associated with higher hematogenous and lower lymphatic spread and higher hormone and HER2/neu receptor negativity. It is therefore incumbent on the breast imager to be aware of more-benign-appearing mammographic and sonographic lesions that can represent aggressive malignancies with poorer prognosis and overall survival [9, 33, 34]. wareness of this overlap in the imaging findings between metaplastic carcinomas, in JR:189, December 2007
6 Metaplastic Versus Invasive Ductal reast Carcinoma vasive carcinomas in patients who have oncologic genes, and probably benign lesions should prompt timely biopsy and ancillary testing of the histologic specimens. References 1. Wargotz ES, Norris HJ. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. I. Matrix-producing carcinoma. Hum Pathol 1989; 20: Wargotz ES, Norris HJ. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. IV. Squamous cell carcinoma of ductal origin. Cancer 1990; 65: Wargotz ES, Norris HJ. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. III. Carcinosarcoma. Cancer 1989; 64: Wargotz ES, Deos PH, Norris HJ. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. II. Spindle cell carcinoma. Hum Pathol 1989; 20: Oberman H. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: a clinicopathologic study of 29 patients. m J Surg Pathol 1987; 11: Wargotz ES, Norris HJ. Metaplastic carcinomas of the breast. V. Metaplastic carcinoma with osteoclastic giant cells. Hum Pathol 1990; 21: Gobbi H, Simpson JF, orowsky, Jensen R, Page DL. Metaplastic breast tumors with a dominant fibromatosis-like phenotype have a high risk of local recurrence. Cancer 1999; 85: Sneige N, Yaziji H, Mandavilli SR, et al. Low-grade (fibromatosis-like) spindle cell carcinoma of the breast. m J Surg Pathol 2001; 25: Luini, guilar M, Gatti G, et al. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast, an unusual disease with worse prognosis: the experience of the European Institute of Oncology and review of the literature. reast Cancer Res Treat 2007; 101: Epub 2006 Sep Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, et al. JCC cancer staging manual, 6th ed. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag, 2002: merican College of Radiology. CR I-RDS: mammography, 4th ed. In: CR reast Imaging Reporting and Data System: breast imaging atlas. FOR YOUR INFORMTION This article is available for CME credit. See for more information. Reston, V: merican College of Radiology, merican College of Radiology. CR I-RDS: ultrasound. In: CR reast Imaging Reporting and Data System: breast imaging atlas. Reston, V: merican College of Radiology, Mendelson E, erg W, Merritt CR. Toward a standardized breast ultrasound lexicon, I-RDS: ultrasound. Semin Roentgenol 2001; 36: Yang WT, huja, Tang, Suen M, King W, Metreweli C. High-resolution sonographic detection of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer. J Ultrasound Med 1996; 16: Vlastos G, Fornage D, Mirza NQ, et al. The correlation of axillary ultrasonography with histologic breast cancer downstaging after induction chemotherapy. m J Surg 2000; 179: Patterson SK, Tworek J, Roubidoux M, Helvie M, Oberman H. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: mammographic appearances with pathologic correlation. JR 1997; 169: Samuels TH, Miller N, Manchul L, DeFreitas G, Panzarella T. Squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. Can ssoc Radiol J 1996; 47: renner RJ, Turner RR, Schiller V, rndt RD, Giuliano. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: report of three cases. Cancer 1998; 82: Park JM, Han K, Moon WK, et al. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: mammographic and sonographic findings. J Clin Ultrasound 2000; 28: Günhan-ilgen I, Memis, Ustün EE, Zekioglu O, Ozdemir N. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: clinical, mammographic, and sonographic findings with histopathologic correlation. JR 2002; 178: Cardenosa G, Doudna C, Eklund GW. Mucinous (colloid) breast cancer: clinical and mammographic findings in 10 patients. JR 1994; 162: Conant EF, Dillon RL, Palazzo J, Ehrlich CM, Feig S. Imaging findings in mucin-containing carcinomas of the breast: correlation with pathologic features. JR 1994; 163: Chopra S, Evans J, Pinder SE, et al. Pure mucinous breast cancer: mammographic and ultrasound findings. Clin Radiol 1996; 51: Meyer JE, min E, Lindfors KK, Lipman JC, Stomper PC, Genest D. Medullary carcinoma of the breast: mammographic and US appearance. Radiology 1989; 170: Schneider J. Invasive papillary breast carcinoma: mammographic and sonographic appearance. Radiology 1989; 171: Kaas R, Kroger R, Hendriks JHCL, et al. The significance of circumscribed malignant mammographic masses in the surveillance of RC1/2 gene mutation carriers. Eur Radiol 2004; 14: Rhiem K, Flucke U, Schmutzler RK. RC1-associated breast carcinomas frequently present with benign sonographic features. (letter) JR 2006; 186:E11 E Gibson GR, Qian D, Ku JK, Lai LL. Metaplastic breast cancer: clinical features and outcomes. m Surg 2005; 71: Tse GM, Tan PH, Putti TC, Lui PC, Chaiwun, Law K. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast: a clinicopathological review. J Clin Pathol 2006; 59: Epub 2006 Feb eatty JD, twood M, Tickman R, Reiner M. Metaplastic breast cancer: clinical significance. m J Surg 2006; 191: Gutman H, Pollock RE, Janjan N, Johnston D. iologic distinctions and therapeutic implications of sarcomatoid metaplasia of epithelial carcinoma of the breast. J m Coll Surg 1995; 180: Gloeckler Ries L, Reichman ME, Lewis DR, Hankey F, Edwards K. Cancer survival and incidence from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program. Oncologist 2003; 8: Rayson D, djei, Suman VJ, Wold LE, Ingle JN. Metaplastic breast cancer: prognosis and response to systemic therapy. nn Oncol 1999; 10: Chao TC, Wang CS, Chen SC, Chen MF. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. J Surg Oncol 1999; 71: JR:189, December
Original Report. Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical, Mammographic, and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma with Fibrotic Focus: Mammographic and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Solitary Pancreatic Metastasis From Breast Matrix-Producing Carcinoma: A First Case Report
 Int Surg 2017;102:294 298 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-17-00064.1 Solitary Pancreatic Metastasis From Breast Matrix-Producing Carcinoma: A First Case Report Yoshiyuki Kiyasu 1,2, Ken Hayashi 1, Go Miyahara 1,
Int Surg 2017;102:294 298 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-17-00064.1 Solitary Pancreatic Metastasis From Breast Matrix-Producing Carcinoma: A First Case Report Yoshiyuki Kiyasu 1,2, Ken Hayashi 1, Go Miyahara 1,
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Triple Receptor Negative Breast Cancer: Imaging and Clinical Characteristics
 Women s Imaging Original Research Krizmanich-Conniff et al. Triple Receptor Negative Breast Cancer Women s Imaging Original Research Kristin M. Krizmanich-Conniff 1 Chintana Paramagul 2 Stephanie K. Patterson
Women s Imaging Original Research Krizmanich-Conniff et al. Triple Receptor Negative Breast Cancer Women s Imaging Original Research Kristin M. Krizmanich-Conniff 1 Chintana Paramagul 2 Stephanie K. Patterson
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti. Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS
 Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
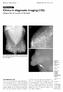 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features
 Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine
 Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
ARTICLE IN PRESS. doi: /j.ijrobp METAPLASTIC CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST: A RETROSPECTIVE REVIEW
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.024 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. xx, No. x, pp. xxx, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.024 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. xx, No. x, pp. xxx, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/05/$ see front matter
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
57th Annual HSCP Spring Symposium 4/16/2016
 An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8568-8572 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010093 Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8568-8572 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010093 Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast:
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients
 Clinical Radiology (2009) 64, 628e636 ORIGINAL PAPER Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients B. Mesurolle a, *, M. El-Khoury
Clinical Radiology (2009) 64, 628e636 ORIGINAL PAPER Mammographically non-calcified ductal carcinoma in situ: sonographic features with pathological correlation in 35 patients B. Mesurolle a, *, M. El-Khoury
Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast as Cystic Lesions: Sonographic-Pathologic Correlation
 Women s Imaging Original Research Kim et al. Breast Tumors as Cystic Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Sun Mi Kim 1,2 Hak Hee Kim 1 Doo Kyung Kang 3 Hee Jung Shin 1 Nariya Cho 4
Women s Imaging Original Research Kim et al. Breast Tumors as Cystic Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Sun Mi Kim 1,2 Hak Hee Kim 1 Doo Kyung Kang 3 Hee Jung Shin 1 Nariya Cho 4
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience.
 MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography
 Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings.
 Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma
 Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection
 Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds
 215 Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds ratio 719 (100) 305(100) Shape Oval 445 (61.9) 019
215 Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds ratio 719 (100) 305(100) Shape Oval 445 (61.9) 019
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging. Medical University of South Carolina Charleston
 Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
Breast Cancer. Saima Saeed MD
 Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Imaging Lexicon
 9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING
 OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
Ultrasound Assessment of Invasive Breast Cancer:
 Ultrasound Assessment of Invasive Breast Cancer: Correlation with Histologic Grade 1 Joo Hee Cha, M.D., Woo Kyung Moon, M.D. 2, Nariya Cho, M.D. 2, Sun Mi Kim, M.D. 2, Seung Ja Kim, M.D. 2, Seong Ho Park,
Ultrasound Assessment of Invasive Breast Cancer: Correlation with Histologic Grade 1 Joo Hee Cha, M.D., Woo Kyung Moon, M.D. 2, Nariya Cho, M.D. 2, Sun Mi Kim, M.D. 2, Seung Ja Kim, M.D. 2, Seong Ho Park,
Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: Imaging Findings With Pathologic and Clinical Correlation
 Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Jones et al. Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay WOMEN S IMGING Katie N. Jones 1 Katrina N. Glazebrook 1 arol Reynolds 2 Jones KN, Glazebrook
Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Jones et al. Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay WOMEN S IMGING Katie N. Jones 1 Katrina N. Glazebrook 1 arol Reynolds 2 Jones KN, Glazebrook
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings
 Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology
 Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Sonographic and Mammographic Appearances of Breast Hemangioma
 Women s Imaging Clinical Observations Mesurolle et al. Sonography and Mammography of reast Hemangioma Women s Imaging Clinical Observations WOMEN S IMGING enoît Mesurolle 1 Vitaly Sygal 1 Lucie Lalonde
Women s Imaging Clinical Observations Mesurolle et al. Sonography and Mammography of reast Hemangioma Women s Imaging Clinical Observations WOMEN S IMGING enoît Mesurolle 1 Vitaly Sygal 1 Lucie Lalonde
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012. Lymph Nodes. John McGrath
 Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay
 CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
and verbal and/or written consent was obtained from each of the patient at each visit during which their database was
 Imaging Characteristics of Triple Receptor Negative versus Triple Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Dr. Abdullateef Aliasghar M.B.CH.B., C.A.B.M.S-RAD, Lecturer, National Cancer Research Center, Baghdad
Imaging Characteristics of Triple Receptor Negative versus Triple Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Dr. Abdullateef Aliasghar M.B.CH.B., C.A.B.M.S-RAD, Lecturer, National Cancer Research Center, Baghdad
Case Scenario 1. 2/15/2011 The patient received IMRT 45 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction for 25 fractions.
 Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the breast: a rare entity, representation of two cases
 International Surgery Journal Siripurapu Y et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Aug;4(8):2848-2853 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173434
International Surgery Journal Siripurapu Y et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Aug;4(8):2848-2853 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173434
Clinicopathological features of metaplastic breast carcinoma
 Original papers Clinicopathological features of metaplastic breast carcinoma Oğuz Ahmet Hasdemir, A F, Serhat Tokgöz, B D, F, Fulya Köybaşıoğlu, B, C, E, Harun Karabacak, C, D, Cüneyt Yücesoy 3, B, F 4,
Original papers Clinicopathological features of metaplastic breast carcinoma Oğuz Ahmet Hasdemir, A F, Serhat Tokgöz, B D, F, Fulya Köybaşıoğlu, B, C, E, Harun Karabacak, C, D, Cüneyt Yücesoy 3, B, F 4,
Mammography and Subsequent Whole-Breast Sonography of Nonpalpable Breast Cancers: The Importance of Radiologic Breast Density
 Isabelle Leconte 1 Chantal Feger 1 Christine Galant 2 Martine Berlière 3 Bruno Vande Berg 1 William D Hoore 4 Baudouin Maldague 1 Received July 11, 2002; accepted after revision October 28, 2002. 1 Department
Isabelle Leconte 1 Chantal Feger 1 Christine Galant 2 Martine Berlière 3 Bruno Vande Berg 1 William D Hoore 4 Baudouin Maldague 1 Received July 11, 2002; accepted after revision October 28, 2002. 1 Department
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Amlendu Nagar
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY
 Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications
 Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
Metaplastic Carcinoma of Breast A Rare Tumour with Uncommon Presentation
 Metaplastic Carcinoma of Breast A Rare Tumour with Uncommon Presentation Krishna S; Naveen L; Shenoy R; Kadage V March 2017 Volume 13 Issue 1 Doctors Academy Publications Metaplastic breast carcinoma (MBC)
Metaplastic Carcinoma of Breast A Rare Tumour with Uncommon Presentation Krishna S; Naveen L; Shenoy R; Kadage V March 2017 Volume 13 Issue 1 Doctors Academy Publications Metaplastic breast carcinoma (MBC)
Pictorial Review of the Ultrasound Appearances of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
 Pictorial Review of the Ultrasound Appearances of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Poster No.: R-0079 Congress: 2016 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. G. D. U. M. Wijesinghe, D. Gunawardena, D. B. Taylor
Pictorial Review of the Ultrasound Appearances of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Poster No.: R-0079 Congress: 2016 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. G. D. U. M. Wijesinghe, D. Gunawardena, D. B. Taylor
High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography
 Article High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography Beverly E. Hashimoto, MD, Dawna J. Kramer, MD, Vincent J. Picozzi,
Article High Detection Rate of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Calcifications on Mammographically Directed High-Resolution Sonography Beverly E. Hashimoto, MD, Dawna J. Kramer, MD, Vincent J. Picozzi,
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient. Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester
 Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses. Case #1
 University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
Cellular Dyscohesion in Fine-Needle Aspiration of Breast Carcinoma Prognostic Indicator for Axillary Lymph Node Metastases?
 natomic Pathology / PROGNOSTIC INDICTOR FOR XILLRY LYMPH NODE METSTSES Cellular Dyscohesion in Fine-Needle spiration of reast Carcinoma Prognostic Indicator for xillary Lymph Node Metastases? nne. Schiller,
natomic Pathology / PROGNOSTIC INDICTOR FOR XILLRY LYMPH NODE METSTSES Cellular Dyscohesion in Fine-Needle spiration of reast Carcinoma Prognostic Indicator for xillary Lymph Node Metastases? nne. Schiller,
Micropapillary Lung Cancer with Breast Metastasis Simulating Primary Breast Cancer due to Architectural Distortion on Images
 Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.2.249 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(2):249-253 Micropapillary Lung Cancer with Breast Metastasis Simulating Primary Breast Cancer
Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.2.249 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(2):249-253 Micropapillary Lung Cancer with Breast Metastasis Simulating Primary Breast Cancer
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer
 Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas
 Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical and Radiological Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical and Radiological Findings with Histopathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-2078 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. AlSharif
Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical and Radiological Findings with Histopathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-2078 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. AlSharif
Sonographic and Mammographic Features of Phyllodes Tumours of the Breast: Correlation with Histological Grade
 Sonographic and Mammographic Features of Phyllodes Tumours of the Breast: Correlation with Histological Grade Poster No.: C-0046 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit C. Y.
Sonographic and Mammographic Features of Phyllodes Tumours of the Breast: Correlation with Histological Grade Poster No.: C-0046 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit C. Y.
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities. Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine
 Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: MRI, Ultrasound, and Mammographic Appearances
 Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Eiada et al. Imaging Papillary Lesions of the reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.194 on 01/27/18 from IP address 37.44.198.194.
Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Eiada et al. Imaging Papillary Lesions of the reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.194 on 01/27/18 from IP address 37.44.198.194.
Atypical papillary lesions after core needle biopsy and subsequent breast carcinoma
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 5 No. 2 April 2011; 243-248 DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0502.031 Original article Atypical papillary lesions after core needle biopsy and subsequent breast carcinoma Tuenchit Khamapirad
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 5 No. 2 April 2011; 243-248 DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0502.031 Original article Atypical papillary lesions after core needle biopsy and subsequent breast carcinoma Tuenchit Khamapirad
ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form
 S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis: A Case Detected by Breast Cancer Screening Examination
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach. Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina
 Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1753-1758, 2015 Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature YIZI CONG *, GUANGDONG QIAO *, HAIDONG ZOU, JUN LIN, XINGMIAO WANG,
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1753-1758, 2015 Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature YIZI CONG *, GUANGDONG QIAO *, HAIDONG ZOU, JUN LIN, XINGMIAO WANG,
Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast:
 J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
Unusual Breast Cancers: What do we know?
 Unusual Breast Cancers: What do we know? Poster No.: C-1267 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. A. Puentes Bejarano, C. Oliva Fonte, C. Sibaja Castro, J. Pereda Rodríguez, J. Gonzalez
Unusual Breast Cancers: What do we know? Poster No.: C-1267 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. A. Puentes Bejarano, C. Oliva Fonte, C. Sibaja Castro, J. Pereda Rodríguez, J. Gonzalez
BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1
 Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Sonographic Findings of High-Grade and Non High-Grade Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast
 Article Sonographic Findings of High-Grade and Non High-Grade Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast Ji-Sung Park, MD, Young-Mi Park, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Suk-Jung Kim, MD, Sang-Suk Han, MD, Sun-Joo
Article Sonographic Findings of High-Grade and Non High-Grade Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast Ji-Sung Park, MD, Young-Mi Park, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Suk-Jung Kim, MD, Sang-Suk Han, MD, Sun-Joo
Non-Calcified Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: Ultrasound and Mammographic Findings Correlated with Histological Findings
 Yonsei Med J 49(1):103-110, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.1.103 Non-Calcified Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: Ultrasound and Mammographic Findings Correlated with Histological Findings Kyu Ran Cho, 1 Bo Kyoung
Yonsei Med J 49(1):103-110, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.1.103 Non-Calcified Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: Ultrasound and Mammographic Findings Correlated with Histological Findings Kyu Ran Cho, 1 Bo Kyoung
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation
 Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Imaging-Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Papillary Lesions of the Breast
 Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
Breast Cancer Screening with Mammography
 Progress in Public Health Breast Cancer Screening with Mammography JMAJ 44(7): 318 324, 2001 Tokiko ENDO Director, Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast cancer has been increasing
Progress in Public Health Breast Cancer Screening with Mammography JMAJ 44(7): 318 324, 2001 Tokiko ENDO Director, Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast cancer has been increasing
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass
 Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Aggressive Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast with Osteoclastic Giant Cells
 Aggressive Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast with Osteoclastic Giant Cells Kathleen Khong 1*, Yanhong Zhang 2, Mary Tomic 2, Karen Lindfors 1, Shadi Aminololama-Shakeri 1 1. Department of Radiology,
Aggressive Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast with Osteoclastic Giant Cells Kathleen Khong 1*, Yanhong Zhang 2, Mary Tomic 2, Karen Lindfors 1, Shadi Aminololama-Shakeri 1 1. Department of Radiology,
RSNA, /radiol Appendix E1. Methods
 RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
