A gene expression signature of FOXM1 predicts the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
|
|
|
- Kathleen Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OPEN (2018) 50, e418; doi: /emm Official journal of the Korean Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology ORIGINAL ARTICLE A gene expression signature of FOXM1 predicts the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma Bic-Na Song 1,2 and In-Sun Chu 1,2 FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1) is a key regulator of tumorigenesis. Previous studies demonstrated that FOXM1 overexpression was strongly correlated with poor prognosis in various cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this study, we examined an association between the gene expression signature of FOXM1 and HCC patient outcome. The co-expressed gene set of FOXM1, which is significantly associated with the prognosis of HCC patients, was identified by analyzing the gene expression profiles of 100 patients with HCC, and this gene set was validated in two independent HCC patient cohorts (n = 573). In multivariate analysis, the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 was the most significant prognostic factor for overall survival in patients with HCC (hazard ratio = 1.706, 95% confidence intervals = , P = 0.005). We also analyzed different types of cancer, including pancreatic adenocarcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, breast carcinoma and bladder urothelial carcinoma, to verify the association between the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 and patient prognosis, and we found a consistent prognostic significance, regardless of tumor type. Finally, we identified a putative signaling pathway in which mir-34a acts as an upstream regulator of the FOXM1-MYC signaling network; this pathway may be ultimately responsible for the poor prognosis of HCC patients. The prognostic subgroups defined by the gene expression signature of FOXM1 could help predict high-risk patients and may guide selection of the best treatment strategy. (2018) 50, e418; doi: /emm ; published online 5 January 2018 INTRODUCTION Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a major public health problem; it is the primary malignancy of the liver, one of the most common tumors worldwide, and one of the fastest growing causes of cancer-related death. In 2012, 782,500 new cases of liver cancer were diagnosed, and 745,500 deaths occurred worldwide. 1 Because of the clinical heterogeneity of this malignant disease, precisely predicting the prognosis of HCC patients remains challenging. With the advent of new technologies over the past decade, many genome-wide expression profiling studies have revealed the existence of biologically distinct subtypes of HCC, with prognostic implications. 2 4 Furthermore, genome-wide gene expression profiling studies have discovered several genomic predictors for the recurrence or survival of HCC. 5,6 However, it is currently unknown whether this signature is applicable to the development of new treatments. Recently, a number of putative prognostic markers for HCC, including FOXM1, have been proposed in various investigations. Although several studies have shown that FOXM1 overexpression was associated with poor outcomes in many types of cancer, 7 10 its clinical relevance as a prognostic and predictive biomarker is not yet fully understood. Furthermore, no studies have examined the prognostic impact of the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 and whether it can provide additional insights on the potential signaling pathway that is responsible for the poor prognosis of HCC patients. Here we examined an association between the gene expression signature of FOXM1 and HCC patient outcome using gene expression data sets. We also analyzed four different cancer types to verify the association between the gene expression signature of FOXM1 and patient outcome. To further validate the utility of the signature, we tested whether the gene expression signature of FOXM1 could identify the distinct subgroups of patients with different types of cancer in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) pan-cancer gene expression data set. Through gene-to-gene network and upstream regulator analyses, we also identified a putative signaling pathway composed of FOXM1, MYC and mir-34a that potentially mediates HCC patient outcome. 1 Korean Bioinformation Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Daejeon, Korea and 2 Department of Bioinformatics, KRIBB School of Bioscience, Korea University of Science and Technology (UST), Daejeon, Korea Correspondence: Dr I-S Chu, Korean Bioinformation Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Daejeon 34141, Korea. chu@kribb.re.kr Received 17 March 2017; accepted 11 May 2017
2 2 Prognostic markers of hepatocellular carcinoma MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients and gene expression data Gene expression data sets from the Korean and Fudan HCC cohorts, as reported in previous studies, were acquired from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. 6,11 ThemRNA-seqandmiRNA-seqdata sets of HCC patients from the TCGA project were obtained from Cancer Browser ( The Korean cohort (GSE16757, n = 100) was used as the exploration data set. The Fudan (GSE14520, n = 242) and TCGA (n = 331) cohorts were used for validation. Supplementary Table 1 shows the pathologic and clinical characteristics of the patients in all three HCC cohorts. The four gene expression data sets, which consist of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD, GSE21501, n = 132), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD, GSE31210, n = 246), breast invasive carcinoma (BRCA, GSE20486, n = 97), and bladder urothelial carcinoma (BLCA, GSE13507, n = 165) samples, were obtained from the NCBI GEO database. Of the 97 patients with BRCA, we only used the 81 patients who had estrogen-receptor-positive tumors. The TCGA pan-cancer gene expression data set (n = 9,755) was obtained from Cancer Browser. This data set is composed of 32 different cancer types. Among these, we focused on five cancer types: HCC (the TCGA cohort mentioned above, n = 331), PAAD (n = 161), LUAD (n = 468), BRCA (n = 1,055), and BLCA (n = 327). Of the 1,055 patients with BRCA, only 779 patients who had estrogenreceptor-positive tumors were selected. Therefore, a total of 2,066 patient samples were examined in this study (the Pan-cancer cohort, n = 2,066). Clinical data were obtained from the Supplementary Information of the corresponding literature or was requested from the authors. The patients with available survival time data were subjected to statistical analysis. Statistical analysis The non-tumor and replicated samples were removed based on the sample annotations attached to each data set. Gene expression profile data, regardless of platform, was separately log2 transformed and quantile normalized. For the exploration data set, genes were filtered out if they did not have at least a two-fold change relative to the median in more than 5% of the samples. For gene expression profiling from the RNA-seq data set, genes with a value of zero were set to the missing value after log2 transformation, and genes were filtered out if they had missing data in 430% of the samples. To identify the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1, we analyzed the gene expression profile data by employing the same procedure described in a previous study. 12 Briefly, we selected genes that had a significant correlation with the FOXM1 gene (Po0.001 by Pearson correlation coefficient; ro 0.4 or r40.4). Then, hierarchical clustering analysis was performed using a gene expression data matrix that consisted of FOXM1 and its correlated genes. We estimated patient prognosis using Kaplan Meier plots and the log-rank test. The prognostic association between the signature and risk factors was assessed using multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models. All statistical analyses were performed in the R language environment. Using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) tool ( com), gene set enrichment and upstream regulator analyses were performed as described in a previous study. 13 RESULTS Baseline characteristics The baseline characteristics of all eight data sets analyzed in this study are summarized in Table 1. In each data set, overall survival was defined as the number of months from the initial pathological diagnosis of the tumor until the patient was deceased or lost to follow-up. In the Fudan and TCGA cohorts, recurrence-free survival was defined as the time from surgery to the first confirmed recurrence. Prognostic utility of FOXM1 and its associated genes on HCC patients in the exploration data set We first tried to identify a gene set that was highly correlated with FOXM1 expression, then used that gene set to predict the prognosis of HCC patients. We identified 1,185 genes that were highly correlated with FOXM1 expression in the exploration data set. Based on hierarchical clustering analysis of the expression patterns of these genes, patients with HCC were divided into two subgroups: FOXM1-high (FH) and FOXM1- low (FL) (Figure 1a). The survival rate of the FH subgroup was significantly worse than that of the FL subgroup (P = 0.01 by log-rank test; Figure 1b). Validation of the gene expression signature of FOXM1 on HCC patient survival using the independent cohorts To validate our findings, we used gene expression profile data from an independent cohort of HCC patients. The gene expression profile data of the Fudan cohort (Affymetrix Table 1 Characteristics of data sets and patients included in this study Data set Data source Platform description GEO platform ID No. of patients Korean cohort GSE16757 Illumina Human-6 v2.0 GPL Fudan cohort GSE14520 Affymetrix Human Genome U133A Array GPL571/GPL TCGA cohort a Illumina RNA-seq NA 331 PAAD GSE21501 Agilent Whole Human Genome Microarray GPL LUAD GSE31210 Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array GPL BRCA GSE20486 Illumina HumanHT-12 V3.0 GPL BLCA GSE13507 Illumina Human-6 v2.0 GPL Pan-cancer cohort a Illumina RNA-seq NA 2,066 Abbreviations: BLCA, bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma; GEO, National Center for Biotechnology Information s Gene Expression Omnibus ( LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; PAAD, pancreatic adenocarcinoma. a UCSC Cancer Genome Browser (
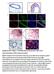
3 3 Figure 1 Gene expression patterns of the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 and the overall survival of HCC patients in the exploration data set (n = 100). (a) Gene expression patterns of FOXM1 and its associated genes. A total of 1,185 genes with expression patterns that highly correlated with FOXM1 were selected for cluster analysis. The patients were divided into two subgroups: FOXM1-high (FH) and FOXM1-low (FL). (b) Kaplan Meier plot of the overall survival of HCC patients, stratified by the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1. The survival rate of the FH subgroup was significantly worse than that of the FL subgroup (P = 0.01 by log-rank test). microarray platform) does not contain all of the gene symbols in the exploration data set (Illumina microarray platform). For this reason, we selected the 826 genes that overlapped with the 1,185 genes derived from the exploration data set. Applying the same procedure employed in the previous result, the patients in the Fudan cohort were divided into two subgroups (FH and FL). The FH subgroup in the Fudan cohort also had significantly worse survival than the FL subgroup (P = by log-rank test, Figure 2a). Furthermore, we also estimated the recurrence-free survival of each subgroup to assess whether the co-expressed genes could identify patients at high risk for recurrence. The recurrence rate was significantly higher in the FH subgroup than the FL subgroup (P = 0.03 by log-rank test; Figure 2b). The survival analysis was further validated with the TCGA RNA-seq data set (P = for the survival rate and P = 0.01 for the recurrence rate by log-rank test; Figure 2c and d). Taken together, these results demonstrate that the gene expression signature of FOXM1 is a robust prognostic indicator of HCC patient outcome. We next combined the clinical data from the Korean and Fudan cohorts (total n = 321) and assessed the prognostic association between the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 and other known clinical and pathologic factors for HCC using univariate Cox regression analyses. In addition to tumor size, Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) stage, and Barcelona Clinical Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage, all of which are already well-known risk factors, the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 was a significant indicator for overall survival (Supplementary Table 2). We also applied multivariate Cox regression analyses to verify the independent utility of the gene set. Importantly, the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 was the most important independent prognostic factor for overall survival (HR = 1.706, 95% CI = , P = 0.005; Supplementary Table 2). Prognostic utility of the gene expression signature of FOXM1 in different types of cancer Because the dysregulated expression and function of FOXM1 are not confined to certain types of cancer, 14 we next asked whether the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 was associated with the prognosis of patients with different types of cancer. From the NCBI GEO database, we selected the gene expression data sets of four cancers and identified 2,689, 4,211, 760 and 1,349 co-expressed genes of FOXM1 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), breast invasive carcinoma (BRCA) and bladder urothelial carcinoma (BLCA), respectively. We did not include other cancer types in this study because we could not identify a sufficient co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 in their data sets (due to a limited sample size or an inadequate follow-up time). Consistent with our previous result, survival analysis revealed that the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 was a significant predictor of overall survival in patients with different types of cancer (each Po0.05 by log-rank test, Figure 3). This finding strongly demonstrates that the gene expression signature of FOXM1 has prognostic significance, regardless of tumor type.
4 4 Figure 2 The validation of the gene expression signature of FOXM1 in independent cohorts. (a) Overall survival and (b) recurrence-free survival in HCC patients, stratified by the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1, were estimated in the Fudan cohort (n = 242). (c) Overall survival and (d) recurrence-free survival were also estimated in the TCGA cohort (n = 331). FH, FOXM1-high; FL, FOXM1-low. Two distinct subgroups of patients with different types of cancer in the Pan-cancer cohort Having identified two subgroups that show considerable differences in clinical outcomes in the five cancer types, we next examined whether we could identify two subgroups of patients with different cancer types in a large, pooled data set. Therefore, we used a gene expression data set that was generated by merging multiple TCGA RNA-seq data sets, including HCC, PAAD, LUAD, BRCA and BLCA. The co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 was identified by selecting the genes that highly correlated with FOXM1 expression in the Pan-cancer cohort. We applied hierarchical cluster analysis to the gene expression data matrix, which consisted of FOXM1 and its correlated genes, and the results showed that the cancer patients were divided into two distinct subgroups (FH and FL) based on the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1, not on the histological cancer type (Supplementary Figure 1). The results based on the gene expression profile data suggest that FOXM1 may be a master regulator of expression changes in genes associated with patient survival across cancer types. Biological insight into the gene expression signature of FOXM1 that is associated with the prognosis of HCC patients Gene set enrichment analysis was performed to identity the biological characteristics of the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 using the IPA tool. When applying the 1,185 genes obtained from the exploration data set to the IPA tool, genes involved in organismal injury and abnormalities, gastrointestinal disease and hepatic system disease were significantly enriched. Furthermore, genes involved in DNA replication, recombination and repair, such as BRCA1, EXO1, POLQ, POLD1, POLE, FANCD2, PRKDC and PARP1, were also significantly enriched. These results indicate that the
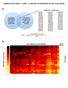
5 5 Figure 3 Kaplan Meier plots showing differences in overall survival for patients diagnosed with different types of cancer based on the gene expression signature of FOXM1. Data from(a) PAAD,(b) LUAD,(c) BRCA and(d) BLCA are shown. FH, FOXM1-high, FL, FOXM1-low. biological processes associated with the DNA repair system might be closely linked to the poor prognosis of HCC patients (Supplementary Figure 2). We next conducted upstream regulator analysis of the 1,185 genes to uncover potential upstream regulators of the molecular signature based on a co-expressed gene set of FOXM1. An examination of the enriched genes revealed the involvement of several important activated regulators; the strongest overrepresentation of these regulators was the predominant activation of MYC (Figure 4). The downstream effectors of MYC, such as E2F1, SUZ12, EZH2 and PARP1, were previously reported to be associated with tumor aggressiveness and metastasis, indicating that MYC is a key factor associated with the gene signature of FOXM1. Although the expression of MYC downstream genes is higher in the FH subgroup than in the FL subgroup, the expression of MYC is not altered in either the FH or FL subgroups, suggesting that MYC activation might not be driven by changes in gene expression levels, but by other mechanisms, such as amplifications or translocations. 18 FOXM1 was also a predominant regulator, and it was interconnected with another gene network hub that included MYC (Figure 4). All of the satellite genes in the gene network participate in the cell cycle, cellular growth and proliferation, and the DNA repair system, which corresponds to the well-known activities of FOXM1 and MYC. 18,19 These results indicate that activation of the FOXM1-MYC signaling network may be a key event associated with a poor prognosis in HCC. To identify an upstream regulator of the FOXM1-MYC signaling network, we used the path-exploring function of the IPA tool and observed the functional connectivity between MYC and mir-34a; MYC is a downstream effector of mir-34a (Figure 4). mir-34a is reported as a direct transcriptional target of p53, and it is frequently downregulated in various types of cancer, including HCC. 21 In the TCGA cohort, the expression level of mir-34a was significantly lower in the FH subgroup than in the FL subgroup (Po0.001 by two-sample t-test; Supplementary Figure 3). In addition, the close examination of gene networks revealed that CDK1 was a common downstream effector controlled by FOXM1, MYC and mir-34a (Figure 4). CDK1 has previously been reported to play an important role in cell cycle regulation. 23
6 6 Figure 4 The putative signaling pathway composed of FOXM1, MYC and mir-34a. Upregulated genes in the FOXM1-high (FH) subgroup are indicated in red. The intensity of color is indicative of the degree of overexpression. Orange- or blue-colored elements indicate predicted activation or inhibition, respectively. Each line and arrow represents the functional and physical interactions between the genes and the direction of regulation reported in the literature. The networks were generated using the Ingenuity Pathways Analysis tool ( Thus, CDK1 activation might account for the poorer prognosis of the FH subgroup than the FL subgroup. Among the other satellite genes in the gene network,ccnb1 and CCNE1, which have been shown to play critical roles in cancer progression, 12,13 were identified as common downstream effectors of FOXM1 and MYC. Taken together, these results suggest that the complicated molecular interactions of multiple gene networks are associated with the poor prognosis of HCC patients. DISCUSSION FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1) is one of the most commonly overexpressed genes in various cancer types, based on genome-wide gene expression profile analysis. In addition, it has been shown that the overexpression of FOXM1 is associated with aggressive tumor features and with the eventual prognosis of cancer patients, including those with HCC. 7 Importantly, the prognosis of patients may be affected not only by the overexpression of FOXM1 but also by other genes associated with its expression. Here we identified two distinct subgroups of cancer patients based on the gene expression signature of FOXM1. Survival analysis revealed a significant survival difference between the cancer patient subgroups. Finally, we identified a putative signaling pathway that might be responsible for the poor prognosis of HCC patients. FOXM1, a major oncogenic transcription factor, plays an essential role in the regulation of a wide spectrum of biological processes, suggesting that it has a fundamental role in tumor development and progression. 24 Although an association between the overexpression of FOXM1 and patient prognosis has been observed in several studies, 25 the prognostic relevance of a co-expressed gene set of FOXM1 has not been demonstrated. Through an estimation of prognosis using a co-expressed gene set of FOXM1, we discovered that an expression signature of FOXM1 and its associated genes has prognostic significance in various cancer types. By applying hierarchical cluster analysis to the gene expression profile data from a pool of five different cancer types from the TCGA RNA-seq data set, we showed the presence of two subgroups based on a co-expressed gene set of FOXM1, regardless of tumor type. These data suggested that the gene expression signature of FOXM1 could be used as a potential prognostic and predictive indicator in various cancers. Gene network analysis of the gene expression signature of FOXM1 identified a putative signaling pathway composed of FOXM1, MYC and mir-34a; this pathway is associated with the poor prognosis of HCC. Among several upstream candidates, FOXM1 and MYC were revealed as the two predominant regulators of the overexpressed genes in the FH subgroup, which is consistent with previous studies that show their regulatory role in HCC patients with poor prognosis. 7,26 mir-34a, an upstream regulator of MYC, was reported as a tumor suppressor gene by targeting many oncogenes related to
7 7 proliferation, apoptosis and invasion. A recent study suggested that mir-34a directly targets FOXM1 and MYC via binding the 3 untranslated regions in liver cancer cells, 27 which indicates that expression changes in mir-34a might be a critical factor for the diagnosis of HCC patients. By applying the co-expressed gene set of FOXM1, we were able to divide individuals with cancer into two subgroups that showed a significant difference in their clinical outcomes. These findings support the notion that FOXM1 is a key regulator of genes associated with patient survival in various types of cancer. Furthermore, the good or poor prognostic subgroups defined by the gene expression signature of FOXM1 could be exploited for use as a diagnostic tool to predict high-risk patients and to improve treatment responses. CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This research was supported by a grant from KRIBB Research Initiative Program. PUBLISHER S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. 1 Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: Hoshida Y, Villanueva A, Kobayashi M, Peix J, Chiang DY, Camargo A et al. Gene expression in fixed tissues and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. NEnglJMed2008; 359: Boyault S, Rickman DS, de Reynies A, Balabaud C, Rebouissou S, Jeannot E et al. Transcriptome classification of HCC is related to gene alterations and to new therapeutic targets. Hepatology 2007; 45: Lee JS, Heo J, Libbrecht L, Chu IS, Kaposi-Novak P, Calvisi DF et al. A novel prognostic subtype of human hepatocellular carcinoma derived from hepatic progenitor cells. Nat Med 2006; 12: Lee JS, Chu IS, Heo J, Calvisi DF, Sun Z, Roskams T et al. Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Hepatology 2004; 40: Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, Lee JS et al. A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res 2010; 70: Sun HC, Li M, Lu JL, Yan DW, Zhou CZ, Fan JW et al. Overexpression of Forkhead box M1 protein associates with aggressive tumor features and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 2011; 25: Bektas N, Haaf AT, Veeck J, Wild PJ, Lüscher-Firzlaff J, Hartmann A et al. Tight correlation between expression of the Forkhead transcription factor FOXM1 and HER2 in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2008; 8: Okada K, Fujiwara Y, Takahashi T, Nakamura Y, Takiguchi S, Nakajima K et al. Overexpression of forkhead box M1 transcription factor (FOXM1) is a potential prognostic marker and enhances chemoresistance for docetaxel in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2013; 20: Xu N, Jia D, Chen W, Wang H, Liu F, Ge H et al. FoxM1 is associated with poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients through promoting tumor metastasis. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e Kim SM, Leem SH, Chu IS, Park YY, Kim SC, Kim SB et al. Sixty-five gene-based risk score classifier predicts overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012; 55: Song BN, Kim SK, Chu IS. Bioinformatic identification of prognostic signature defined by copy number alteration and expression of CCNE1 in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Exp Mol Med 2017; 49: e Kim SK, Roh YG, Park K, Kang TH, Kim WJ, Lee JS et al. Expression signature defined by FOXM1-CCNB1 activation predicts disease recurrence in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: Kalin TV, Ustiyan V, Kalinichenko VV. Multiple faces of FoxM1 transcription factor: lessons from transgenic mouse models. Cell Cycle 2011; 10: Lee JS, Leem SH, Lee SY, Kim SC, Park ES, Kim SB et al. Expression signature of E2F1 and its associated genes predict superficial to invasive progression of bladder tumors. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: Lee SR, Roh YG, Kim SK, Lee JS, Seol SY, Lee HH et al. Activation of EZH2 and SUZ12 regulated by E2F1 predicts the disease progression and aggressive characteristics of bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: Choi EB, Yang AY, Kim SC, Lee J, Choi JK, Choi C et al. PARP1 enhances lung adenocarcinoma metastasis by novel mechanisms independent of DNA repair. Oncogene 2016; 35: Meyer N, Penn LZ. Reflecting on 25 years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: Lam EWF, Brosens JJ, Gomes AR, Koo CY. Forkhead box proteins: tuning forks for transcriptional harmony. Nat Rev Cancer 2013; 13: Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M, Nakagama H. Tumor-suppressive mir-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: Li N, Fu H, Tie Y, Hu Z, Kong W, Wu Y et al. mir-34a inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulation of c-met expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 2008; 275: Gallardo E, Navarro A, Vinolas N, Marrades RM, Diaz T, Gel B et al. mir-34a as a prognostic marker of relapse in surgically resected non-smallcell lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 2009; 30: Liu P, Kao TP, Huang H. CDK1 promotes cell proliferation and survival via phosphorylation and inhibition of FOXO1 transcription factor. Oncogene 2008; 27: Myatt SS, Lam EW. The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: Gentles AJ, Newman AM, Liu CL, Bratman SV, Feng W, Kim D et al. The prognostic landscape of genes and infiltrating immune cells across human cancers. Nat Med 2015; 21: Jang KY, Noh SJ, Lehwald N, Tao GZ, Bellovin DI, Park HS et al. SIRT1 and c-myc promote liver tumor cell survival and predict poor survival of human hepatocellular carcinomas. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e Xu X, Chen W, Miao R, Zhou Y, Wang Z, Zhang L et al. mir-34a induces cellular senescence via modulation of telomerase activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting FoxM1/c-Myc pathway. Oncotarget 2015; 6: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit r The Author(s) 2018 Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on website (
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Microarray Analysis and Liver Diseases
 Microarray Analysis and Liver Diseases Snorri S. Thorgeirsson M.D., Ph.D. Laboratory of Experimental Carcinogenesis Center for Cancer Research, NCI, NIH Application of Microarrays to Cancer Research Identifying
Microarray Analysis and Liver Diseases Snorri S. Thorgeirsson M.D., Ph.D. Laboratory of Experimental Carcinogenesis Center for Cancer Research, NCI, NIH Application of Microarrays to Cancer Research Identifying
A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8281-8287 A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer Z. LI 1, Z.-M. LIU 2, B.-H.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8281-8287 A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer Z. LI 1, Z.-M. LIU 2, B.-H.
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Expression of lncrna TCONS_ in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed.
 Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Cancer Cell Research 19 (2018)
 Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 LncRNA RP11-597D13.9 expression and clinical significance in serous Ovarian Cancer based on TCGA database Xiaoyan Gu 1, Pengfei Xu 2, Sujuan
Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 LncRNA RP11-597D13.9 expression and clinical significance in serous Ovarian Cancer based on TCGA database Xiaoyan Gu 1, Pengfei Xu 2, Sujuan
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles
 On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples
 Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for osteosarcoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer
 Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Analysis of the outcome of young age tongue squamous cell carcinoma
 Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs. (a) CNA analysis of expression microarray data obtained from 15 tumors in the SV40Tag
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs. (a) CNA analysis of expression microarray data obtained from 15 tumors in the SV40Tag
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
Long non-coding RNA Loc is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis
 Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical Informatics (CoSBBI) Outline. Molecular Biology of Cancer AND. Goals/Expectations. David Boone 7/1/2015
 Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association with Pathological Features
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays
 Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Long non-coding RNA ROR is a novel prognosis factor associated with non-small-cell lung cancer progression
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4087-4091 Long non-coding RNA ROR is a novel prognosis factor associated with non-small-cell lung cancer progression C.-H. QU 1, Q.-Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4087-4091 Long non-coding RNA ROR is a novel prognosis factor associated with non-small-cell lung cancer progression C.-H. QU 1, Q.-Y.
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer
 mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer. Cheol Min Kang 2018/04/05
 Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Comparison of Triple Negative Breast Cancer between Asian and Western Data Sets
 2010 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine Workshops Comparison of Triple Negative Breast Cancer between Asian and Western Data Sets Lee H. Chen Bioinformatics and Biostatistics
2010 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine Workshops Comparison of Triple Negative Breast Cancer between Asian and Western Data Sets Lee H. Chen Bioinformatics and Biostatistics
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy
 Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Models of cell signalling uncover molecular mechanisms of high-risk neuroblastoma and predict outcome
 Models of cell signalling uncover molecular mechanisms of high-risk neuroblastoma and predict outcome Marta R. Hidalgo 1, Alicia Amadoz 2, Cankut Çubuk 1, José Carbonell-Caballero 2 and Joaquín Dopazo
Models of cell signalling uncover molecular mechanisms of high-risk neuroblastoma and predict outcome Marta R. Hidalgo 1, Alicia Amadoz 2, Cankut Çubuk 1, José Carbonell-Caballero 2 and Joaquín Dopazo
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer. Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M. Hoffman, William L. Gerald Table of Contents
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M. Hoffman, William L. Gerald Table of Contents
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
How to apply HCC prediction models to practice?
 How to apply HCC prediction models to practice? Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine Woo Jin Chung HCC prediction models 독특하게간세포암환자들의생존은암의진행상태뿐아니라기저간기능의중증정도에영향을받는특성이있다.
How to apply HCC prediction models to practice? Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine Woo Jin Chung HCC prediction models 독특하게간세포암환자들의생존은암의진행상태뿐아니라기저간기능의중증정도에영향을받는특성이있다.
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
The transcription levels and prognostic values of seven proteasome alpha subunits in human cancers
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 3), pp: 4501-4519 The transcription levels and prognostic values of seven proteasome alpha subunits in human cancers Yunhai Li 1,2, Jing Huang 1, Jiazheng Sun 1, Shili Xiang 1, Dejuan
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 3), pp: 4501-4519 The transcription levels and prognostic values of seven proteasome alpha subunits in human cancers Yunhai Li 1,2, Jing Huang 1, Jiazheng Sun 1, Shili Xiang 1, Dejuan
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Increased long noncoding RNA LINP1 expression and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8749-8754 Increased long noncoding RNA LINP1 expression and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer X.-M. LIU 1, B. YANG 2,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8749-8754 Increased long noncoding RNA LINP1 expression and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer X.-M. LIU 1, B. YANG 2,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Exosomal Del 1 as a potent diagnostic marker for breast cancer : A prospective cohort study
 GBCC 2017: ABS-0017 Exosomal Del 1 as a potent diagnostic marker for breast cancer : A prospective cohort study Soo Jung Lee 1, Jeeyeon Lee 2, Jin Hyang Jung 2, Ho Yong Park 2, Chan Hyeong Lee 3, Pyong
GBCC 2017: ABS-0017 Exosomal Del 1 as a potent diagnostic marker for breast cancer : A prospective cohort study Soo Jung Lee 1, Jeeyeon Lee 2, Jin Hyang Jung 2, Ho Yong Park 2, Chan Hyeong Lee 3, Pyong
About OMICS Group Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
IPA Advanced Training Course
 IPA Advanced Training Course October 2013 Academia sinica Gene (Kuan Wen Chen) IPA Certified Analyst Agenda I. Data Upload and How to Run a Core Analysis II. Functional Interpretation in IPA Hands-on Exercises
IPA Advanced Training Course October 2013 Academia sinica Gene (Kuan Wen Chen) IPA Certified Analyst Agenda I. Data Upload and How to Run a Core Analysis II. Functional Interpretation in IPA Hands-on Exercises
HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA LEO TUNKLE *
 CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
Predicting clinical outcomes in neuroblastoma with genomic data integration
 Predicting clinical outcomes in neuroblastoma with genomic data integration Ilyes Baali, 1 Alp Emre Acar 1, Tunde Aderinwale 2, Saber HafezQorani 3, Hilal Kazan 4 1 Department of Electric-Electronics Engineering,
Predicting clinical outcomes in neuroblastoma with genomic data integration Ilyes Baali, 1 Alp Emre Acar 1, Tunde Aderinwale 2, Saber HafezQorani 3, Hilal Kazan 4 1 Department of Electric-Electronics Engineering,
The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative
 Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis
 5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
Reevaluating the prognostic significance of male gender for papillary thyroid carcinoma and microcarcinoma: a SEER database analysis
 www.nature.com/scientificreports Received: 1 May 2017 Accepted: 30 August 2017 Published: xx xx xxxx OPEN Reevaluating the prognostic significance of male gender for papillary thyroid carcinoma and microcarcinoma:
www.nature.com/scientificreports Received: 1 May 2017 Accepted: 30 August 2017 Published: xx xx xxxx OPEN Reevaluating the prognostic significance of male gender for papillary thyroid carcinoma and microcarcinoma:
TITLE: Unique Genomic Alterations in Prostate Cancers in African American Men
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0046 TITLE: Unique Genomic Alterations in Prostate Cancers in African American Men PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Ittmann, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0046 TITLE: Unique Genomic Alterations in Prostate Cancers in African American Men PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Ittmann, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser
 Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
Molecular signature for management of hepatocellular carcinoma
 Molecular signature for management of hepatocellular carcinoma Yujin Hoshida, MD, PhD Liver Cancer Program, Tisch Cancer Institute Division of Liver Diseases, Department of Medicine Icahn School of Medicine
Molecular signature for management of hepatocellular carcinoma Yujin Hoshida, MD, PhD Liver Cancer Program, Tisch Cancer Institute Division of Liver Diseases, Department of Medicine Icahn School of Medicine
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
S1 Appendix: Figs A G and Table A. b Normal Generalized Fraction 0.075
 Aiello & Alter (216) PLoS One vol. 11 no. 1 e164546 S1 Appendix A-1 S1 Appendix: Figs A G and Table A a Tumor Generalized Fraction b Normal Generalized Fraction.25.5.75.25.5.75 1 53 4 59 2 58 8 57 3 48
Aiello & Alter (216) PLoS One vol. 11 no. 1 e164546 S1 Appendix A-1 S1 Appendix: Figs A G and Table A a Tumor Generalized Fraction b Normal Generalized Fraction.25.5.75.25.5.75 1 53 4 59 2 58 8 57 3 48
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
APPLICATION NOTE. Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices
 APPLICATION NOTE Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices INTRODUCTION Preservation of tissue biopsies is a critical step to This
APPLICATION NOTE Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices INTRODUCTION Preservation of tissue biopsies is a critical step to This
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3): /ISSN: /IJCEP
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):3430-3435 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0019237 Original Article Down-regulation of mir-182 and mir-183 acts as potential predictor biomarkers in progression, metastasis,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):3430-3435 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0019237 Original Article Down-regulation of mir-182 and mir-183 acts as potential predictor biomarkers in progression, metastasis,
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity
 Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Identification of novel gene expression signature in lung adenocarcinoma by using next-generation sequencing data and bioinformatics analysis
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 62), pp: 104831-104854 Identification of novel gene expression signature in lung adenocarcinoma by using next-generation sequencing data and bioinformatics analysis Ya-Ling Hsu 1,*,
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 62), pp: 104831-104854 Identification of novel gene expression signature in lung adenocarcinoma by using next-generation sequencing data and bioinformatics analysis Ya-Ling Hsu 1,*,
Correlation between serum level of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 and poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Correlation between serum level of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 and poor prognosis in breast cancer J.H. Sun 1, N. Fan 2 and Y. Zhang 1 1 Xianyang Hospital of Yan an University Clinical Laboratory,
Correlation between serum level of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 and poor prognosis in breast cancer J.H. Sun 1, N. Fan 2 and Y. Zhang 1 1 Xianyang Hospital of Yan an University Clinical Laboratory,
Reviews in Clinical Medicine
 Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS) Reviews in Clinical Medicine Clinical Research Development Center Ghaem Hospital Prognostic value of HER2/neu expression in patients with prostate cancer:
Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS) Reviews in Clinical Medicine Clinical Research Development Center Ghaem Hospital Prognostic value of HER2/neu expression in patients with prostate cancer:
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva
 Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Negative impact of low body mass index on liver cirrhosis patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
 Li et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:294 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0713-4 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Negative impact of low body mass index on liver cirrhosis
Li et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:294 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0713-4 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Negative impact of low body mass index on liver cirrhosis
FOR REVIEW. BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission. Manuscript Draft. Manuscript Number: BMB
 BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine. Bei Li, Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club
 Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine Bei Li, 23.08.2016 Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club The top ten highest-grossing drugs in the United States help between 1 in 25 and 1 in
Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine Bei Li, 23.08.2016 Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club The top ten highest-grossing drugs in the United States help between 1 in 25 and 1 in
Long non-coding RNA CCHE1 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for cervical cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 20: 479-483 Long non-coding RNA CCHE1 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for cervical cancer Y. CHEN, C.-X. WANG, X.-X. SUN, C. WANG,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 20: 479-483 Long non-coding RNA CCHE1 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for cervical cancer Y. CHEN, C.-X. WANG, X.-X. SUN, C. WANG,
How Many Diseases in Carcinoma in situ?
 How Many Diseases in Carcinoma in situ? Eva Compérat La Pitié Salpêtrière Assistance Publique Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris VI Carcinogenesis of Bladder Cancer (BC) BC is a panurothelial disease
How Many Diseases in Carcinoma in situ? Eva Compérat La Pitié Salpêtrière Assistance Publique Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris VI Carcinogenesis of Bladder Cancer (BC) BC is a panurothelial disease
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9497-9501 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis of relevant risk factor and recurrence prediction model construction of thyroid cancer after surgery. Shuai Lin 1#,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9497-9501 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis of relevant risk factor and recurrence prediction model construction of thyroid cancer after surgery. Shuai Lin 1#,
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3967
 Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
Original Article microrna-217 was downregulated in ovarian cancer and was associated with poor prognosis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(8):8555-8559 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0026997 Original Article microrna-217 was downregulated in ovarian cancer and was associated with poor prognosis Qiong Pan,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(8):8555-8559 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0026997 Original Article microrna-217 was downregulated in ovarian cancer and was associated with poor prognosis Qiong Pan,
Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung
 Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung immortalized broncho-epithelial cells (AALE cells) expressing
Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung immortalized broncho-epithelial cells (AALE cells) expressing
Inactivation of Hippo Pathway Is Significantly Associated with Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Biology of Human Tumors Inactivation of Hippo Pathway Is Significantly Associated with Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Bo Hwa Sohn 1,2, Jae-Jun Shim 1,2,3, Sang-Bae Kim 1,2, Kyu Yun Jang 4,
Biology of Human Tumors Inactivation of Hippo Pathway Is Significantly Associated with Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Bo Hwa Sohn 1,2, Jae-Jun Shim 1,2,3, Sang-Bae Kim 1,2, Kyu Yun Jang 4,
Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers
 Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers Sung-Hou Kim University of California Berkeley, CA Global Bio Conference 2017 MFDS, Seoul, Korea June 28, 2017 Cancer
Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers Sung-Hou Kim University of California Berkeley, CA Global Bio Conference 2017 MFDS, Seoul, Korea June 28, 2017 Cancer
Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning
 Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning Adriana Birlutiu (1),(2), Paul Bulzu (1), Irina Iereminciuc (1), and Alexandru Floares (1) (1) SAIA & OncoPredict, Cluj-Napoca,
Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning Adriana Birlutiu (1),(2), Paul Bulzu (1), Irina Iereminciuc (1), and Alexandru Floares (1) (1) SAIA & OncoPredict, Cluj-Napoca,
Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008
 Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Characterizing an EMT Signature in Breast Cancer. PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Melanie C.
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0306 TITLE: Characterizing an EMT Signature in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Melanie C. Bocanegra CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Leland Stanford Junior University Stanford,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0306 TITLE: Characterizing an EMT Signature in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Melanie C. Bocanegra CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Leland Stanford Junior University Stanford,
Does the lung nodule look aggressive enough to warrant a more extensive operation?
 Accepted Manuscript Does the lung nodule look aggressive enough to warrant a more extensive operation? Michael Kuan-Yew Hsin, MBChB, MA, FRCS(CTh), David Chi-Leung Lam, MD, PhD, FRCP (Edin, Glasg & Lond)
Accepted Manuscript Does the lung nodule look aggressive enough to warrant a more extensive operation? Michael Kuan-Yew Hsin, MBChB, MA, FRCS(CTh), David Chi-Leung Lam, MD, PhD, FRCP (Edin, Glasg & Lond)
Module 3: Pathway and Drug Development
 Module 3: Pathway and Drug Development Table of Contents 1.1 Getting Started... 6 1.2 Identifying a Dasatinib sensitive cancer signature... 7 1.2.1 Identifying and validating a Dasatinib Signature... 7
Module 3: Pathway and Drug Development Table of Contents 1.1 Getting Started... 6 1.2 Identifying a Dasatinib sensitive cancer signature... 7 1.2.1 Identifying and validating a Dasatinib Signature... 7
HepaRG LX2. HepaRG HepaRG LX2 LX2
 C Supporting Figure 1. Experimental design of s between and cells. (A) -hepatocytes were isolated from a 30 days of -progenitors. Differentiation into mature hepatocytes was achieved following a 2-weeks
C Supporting Figure 1. Experimental design of s between and cells. (A) -hepatocytes were isolated from a 30 days of -progenitors. Differentiation into mature hepatocytes was achieved following a 2-weeks
A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
