RESEARCH ARTICLE. Diagnostic Accuracy of Axillary Ultrasonography Compared with Intra-operative Pathological Findings in Patients with Breast Cancer
|
|
|
- Phillip Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: /APJCP RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:06/09/2018 Acceptance:10/13/2018 Diagnostic Accuracy of Axillary Ultrasonography Compared with Intra-operative Pathological Findings in Patients with Breast Cancer Alireza Rezvani 1, Aryan Zahergivar 2 *, Pooya Iranpour 3, Majid Akrami 1, Sepehr Kazemi 1 Abstract Objective: Breast cancer is the most common cancer and leading cause of mortality in women worldwide. Diagnosis of axillary lymph node involvement, frequently by axillary ultrasonography (AUS), is an important step in patients with primary breast cancer, while the gold standard pathological examination is only applicable during surgery. Thus, we aimed to evaluate the predictive value of AUS in detection of lymph node involvement. Methods: A total of 56 patients with primary breast cancer, who were candidate of mastectomy were included in this study. A single radiologist performed pre-operative axillary sonography for all the patients and reported the results in a checklist. The results were then compared with intra-operative pathological results of lymph node dissection to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of AUS in detection of the disease. Result: The results showed that pre-operative AUS had a sensitivity of 63.3%, specificity of 84.6%, positive predictive value of 82.6%, and negative predictive value of 66.6%. Correlation between axillary lymph node characteristics revealed that the absence of fatty hilum, cortical thickness, and loss of ovality of the lymph nodes were the most specific factors in detection of lymph nodes involvement. Conclusion: AUS has a low sensitivity and cannot determine the presence of micro-metastases and suspicious lymph nodes accurately in early stages of the disease, and it seems that defining new parameters may help for increasing the sensitivity and specificity of the axillary lymph node sonography. Apparently, pathological examination remains the gold standard diagnostic method. Keywords: Breast neoplasms- ultrasonography- lymph nodes- Axilla Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 19 (12), Introduction Breast cancer is the most common malignancy in women worldwide (Ghoncheh et al., 2016) with an estimated lifetime chance of 1 in every 8 women in the United States (DeSantis et al., 2014). The lifestyle change and increased life expectancy led to a dramatic increase in the incidence of breast cancer worldwide, while more than half of new cases rise from developing countries (Ngoma, 2006). Furthermore, the peak age of the disease is younger in Asian countries than Western countries (40-50 vs years) (Leong et al., 2010). In Iran, breast cancer accounts for about 25% of all cancers with an incidence of 22.6, prevalence of 120 (Mousavi et al., 2007), and age-standardized rate of 27.4 per 100,000 women in 2015 (Jazayeri et al., 2015). The 5-year survival rate depends on the stage of the disease, varying from 99% in localized stages and 84% in regional disease to 23% in metastatic breast cancer (Shah and Guraya, 2017). The preventive measures have substantially increased the survival rate of patients with breast cancer in the United States to about 90% (Siegel et al., 2018), while it remains at 57% in developing countries (da Costa Vieira et al., 2017). Axillary ultrasonography (AUS) has increased the diagnostic accuracy, especially if it is combined with routine mammography (Berg et al., 2008). It is highly suggested for palpable breast mass in young women with dense breasts or breast implants, differentiation between cystic or solid mass, assessment of peripheral masses, and axillary lymph nodes (Pan, 2016). In addition to diagnostic value of axillary nodes fine needle biopsy under ultrasonography guide (Jung et al., 2010), AUS is suggested as a useful diagnostic tool for patients with breast cancer and palpable mass (Ertan et al., 2013) that can also reduce the number of sentinel node procedures (Deurloo et al., 2003). However, the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography differs based on the operator s skills and experience, ultrasound equipment, and examination procedures with limited standardization 1 Breast Cancer Research Center, 2 School of Medicine, 3 Imaging Research Center, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran. *For Correspondence: aryan_zaher123@yahoo.com Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
2 Alireza Rezvani et al (Ohuchi et al., 2009). Therefore, pathological examination of the breast and axillary lymph nodes during surgery remains the gold standard diagnostic method for tumor, node, metastasis (TNM) staging (Petropoulou et al., 2017). In the present study, we aimed to determine the diagnostic accuracy of pre-operational AUS in our clinical setting on this population, by comparing the results with the pathological results, obtained during surgery. We hypothesized that AUS could be an alternative for diagnosis of patients with breast cancer as a non-invasive, less expensive, more accessible tool, than surgical pathological examination. Materials and Methods Study design In this cross-sectional study, approved by Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (code:12190), patients who were referred to the clinic of the hospital from 28th June 2017 to 24th February 2018 were selected as the study population. Among the patients who referred to the center during the study period, those who were diagnosed as having primary breast cancer based on physical examination, mammographic and sonographic results, indicative of suspicious tumor were referred for pathological examination, and in cases with positive results in the primary pathological examination, surgery was indicated, (mastectomy + sentinel lymph node biopsy based on their physician s order). At last 56 patients who did not have a locally-advanced disease or history of previous chemotherapy were included in the study. First, the patients were asked to read and sign the written informed consent form for their participation in this study. The patients participation was voluntarily, and they were ensured that their information would be recorded by codes, and be used only for the purpose of this study. All the included patients were scheduled for pre-operative axillary ultrasonography of the ipsilateral side of the involvement. Ultrasonography was performed in a supine or contralateral-side-down oblique position with Samsung ultrasound (WS 80) unit by using a 5-10 MHz linear transducer. The radiologist performing the AUS had 7 years experience in breast and axillary sonography, and recorded the results in the checklist, designed for this study. He started the scanning from the lowest part of the axilla and continued upward toward the axillary fossa to find all probable reactive or involved lymph nodes. Cortical thickening of the lymph node (defined as thickness equal to or greater than the width of the fatty hilum), loss of fatty hilum, and morphologic grade of lymph nodes [divided into 6 grades (Pinheiro et al., 2014)], and presence of non-hilar blood flow were findings in favor of metastatic involvement of the lymph node. As loss of ovality of lymph nodes in AUS had a predictive value in diagnosis of lymph node involvement, the ratio of the largest to the smallest diameter of the lymph node was defined as lymph node ovality and shown as K in this study. So 1/K ratio indicated the loss of lymph node ovality as it gets closer to Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 19 Doppler sonography was also used to evaluate the vascular pattern of the nodes and distinguish between reactive and normal lymph nodes, by hilar vascularity, while malignant lymph nodes usually have a peripheral or mixed (hilar + peripheral) vascularity (Ying et al., 2013). Finally, resistance index (RI), pulsatility index (PI), and systolic and diastolic velocity of the lymph node cortical vasculature were measured to find any probable relation between these factors and lymph node involvement. Color Doppler study was done using Samsung (WS 80) ultrasound system (L 3-8 MHZ linear array transducer). The setting for color Doppler sonography was optimized for each patient and wall filters, pulse repetition frequency, color gain, and focusing depth were adjusted accordingly. Then the patients underwent mastectomy + sentinel lymph node biopsy by the breast surgeon, who determined the sentinel node by dye, and took an intra-operative specimen of that lymph node for pathological examination. The specimens were kept in metal tissue disk, and they were transferred to freezer with -20 o C to -30 o C immediately, and sent to the hospital s laboratory in the shortest time possible, and then assessed and reported by a single pathologist. The initial results were reported to the surgeon during surgery, and if the results of frozen sections were positive, the surgeon would perform axillary lymph node dissection, and preserved the lymph nodes in formalin for 24 hours at room temperature. Then, they were transferred to the laboratory, and slides were taken from them for further examination. The researcher compared the reported results of pathology with AUS for evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of AUS. Statistical analysis The data recorded in the study checklist were input into MATLAB software (version 2014b) for comparison of the results and statistical analyses. The lymph node with the highest number of factors in favor of malignancy was selected for comparison with pathological results. We gave priority to the absence of fatty hilum and cortical thickening for the mentioned selection. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were determined for the overall evaluation of AUS and histopathological results. Predictive value of lymph node size (overall and cortical size of the lymph node), width to height ratio, morphological grade, vascular grade and pattern (mild, moderate and severe), the absence of fatty hilum, and the correlation between the number of involved lymph nodes in pathological reports with the probability of the diagnosis of metastasis were compared with pathological results, and reported by receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve and the area under curve (AUC) after exclusion of the patients with missing axillary lymph nodes in AUS (except in morphological grade, where missing axillary lymph nodes were considered as grade 0). Results A total of 56 patients with age of 47.58±12.28 years (range 24-90) were involved in this study. Based on the pathological reports, lymph node involvement was
3 DOI: /APJCP Figure 1. Receiver-operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Calculation Containing X- axis for False Positive Rate (1-specificity) and Y-axis for True Positive Rate (sensitivity); a. Relation between lymph node size in sonography and pathology results (n=56); b. Relation between lymph node cortex size in sonography and pathology results (n=30); c. Relation between cortex size/lymph node diameter ratio in sonography and pathology results (n=30). detected in 26 patients with benign and 30 with malignant disease, while based on ultrasonography results, 33 were diagnosed as having benign (58.9%) and 23 (41.1%) had malignant diseases, resulting in the sensitivity of 63.3%, specificity of 84.6%, PPV of 82.6%, and NPV of 66.6% (Table 1). Correlation between diagnostic features of lymph node involvement in AUS (explained in the method section) and pathology results revealed an AUC of 72.2% for lymph node size (95% CI 59.2; 89.2) (Figure 1A). Assessing the correlation between the lymph node cortical thickness and probability of lymph node involvement in pathology showed a predictive accuracy of 89% (95% CI 99; 77) with marked point of the cortical thickness at 3.7 mm after exclusion of patients with missing axillary lymph nodes in AUS (Figure 1B). Assessing the correlation between the ratio of cortex size/lymph node diameter (in its short axis) and pathological results showed an AUC of 85% (95% CI 95; 70) with marked point at 0.53 mm (Figure 1C). Assessing the correlation between the lymph node sphericity in AUS and the pathological results showed increased risk of lymph node involvement as 1/K approaches 1 (that shows the lymph node is more spherical) with AUC of 82% (95% CI 97; 64) and marked point at 0.41 (Figure 2). The correlation between lymph node morphological grade, considering that missed lymph nodes were as Figure 2. Receiver-operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Calculation for the Relation between Lymph Node Sphericity in Sonography and Pathology Results Applied to Our Study Population (n=30). Table 1. Pathology * Sonography Findings Cross Tabulation Sonography Total Benign Malignant Count benign Pathology Percent within Pathology Count malignant Percent within Pathology Total Count Percent within Pathology Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
4 Alireza Rezvani et al Figure 3. Receiver-operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Calculation for a- relation between Lymph Node Morphologic Grade in Sonography and Pathology Results (n=56); b- Relation between Shape of Lymph Node Hilum in Sonography and Pathology Results (n, 30). Figure 4. Receiver-operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Calculation for a- Relation between Lymph Node Vascular Pattern in Sonography and Pathology Results (n=30); b- Relation between systolic/diastolic flow in Doppler sonography and pathology (n=30); c- Relation between Resistive index (RI) in Doppler sonography and pathology results (n=30); d- Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve calculation for the relation between Pulsatility index (PI) in Doppler sonography and pathology results (n=30). grade 0, revealed an AUC of 81% (95% CI 93; 70) with the marked point at grade 1 (Figure 3A). Assessing the predictive value of the lymph node hilum shape in sonography revealed an AUC of 78% (95% CI 87; 69) with the most specific point marked at the absent fatty hilum (Figure 3B). The correlation between lymph node non-hilar blood flow revealed an AUC of 71% (95% CI 81; 63). The AUC of Resistive index (RI) and Pulsatility index (PI) indices were 62% (95% CI 81; 43) and 57% (95% CI 69; 36), respectively, and were not valuable predictive factors for diagnosis of axillary lymph node involvement. The AUC of systolic/diastolic flow (S/D) ratio was 78% (95% CI 94; 59) (Figure 4 A-D). Finally, studying the correlation between the diagnosis of lymph node involvement in AUS and number of involved lymph nodes in pathological findings revealed that the probability of diagnosis of lymph node involvement in AUS increased by more lymph nodes 3618 Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 19 involved in pathological results. The sensitivity of AUS was >93% in the involvement of two lymph nodes and Figure 5. Receiver-operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Calculation for Correlation between the Diagnosis of Lymph Node Involvement in Sonography and number of Involved Lymph Nodes in Pathology Results (n=56).
5 >97% in the involvement of 3 lymph nodes. The AUC of this figure is 92% (95% CI 94; 59) (Figure 5). Discussion The results of the present study, which aimed to determine the predictive value of AUS and lymph node characteristic in diagnosis of axillary lymph node involvement in patients with primary breast cancer, compared with the intra-operative pathological results, showed an overall sensitivity of 63.3%, specificity of 84.6%, PPV of 82.6%, and NPV of 66.6% for AUS. These results indicate that AUS failed to diagnose all patients with lymph node involvement, as among 30 patients with malignancy according to pathological reports, only 19 patients were diagnosed appropriately. Nevertheless, further analyses showed that the sensitivity of AUS varied based on separated characteristics and increased to >90%, in some cases, as discussed further. Although our limitations in sampling lead to wide confidence intervals, the significance of the results shows that the mentioned factors role in the sonographic evaluation of axillary lymph nodes is not ignorable and further studies with greater sample size will strengthen the concluded results of this study. Breast cancer staging (TNM) requires determination of lymph node involvement and as pathological examination is invasive, several researchers have been looking for non-invasive alternatives, including imaging modalities (Kumar et al., 2003). Hackney et al., (2013) reported the general sensitivity of 65% and specificity of 81% for AUS, which is close to the present study. But different studies have reported different sensitivity values for AUS, ranging from 23% to 97% (Bedrosian et al., 2003; Stachs et al., 2013). This variation among studies is generally based on the fact that the accuracy of ultrasonography depends highly on the operator s skills and experience and different accuracy of devices used that limits its standardization (Ohuchi et al., 2009). Therefore, in this study, AUS was performed by a single radiologist who had 7 years of experience in AUS and used an appropriate device to minimize this confounder. In addition, as the results of the present study indicated, the number of lymph nodes involved had a direct association with the sensitivity of AUS and increased the sensitivity to >93% for the involvement of two lymph nodes and >97% for the involvement of 3 lymph nodes. These results show that AUS can be a more accurate diagnostic tool in advanced stages, but not in early stages, which are consistent with the results of the study by Dihge et al., (2016) that determined the accuracy of AUS associated with metastatic size (OR=1.11), obesity (OR=2.46), and histological grade (OR=4.43). Therefore, not only patients characteristics such as obesity, which limits the detection of lymph node involvement due to axillary fat mass (Shah et al., 2014), disease characteristics such as tumor type and lymph node size also play a role in the variable sensitivity (Rotim et al., 2017). As to the results of the present study, lymph node size had a predictive value of 72% and was not a definite factor in the distinction between reactive DOI: /APJCP and involved lymph nodes, while disease stage, indicated by the number of lymph nodes involved, was associated with AUS sensitivity. These results are in line with what found in the study by Hackney et al., (2013) who reported that the sensitivity of AUS was related to the histological tumor type and decreased to 36% in lobular breast cancers. Other lymph node characteristics were analyzed separately in the present study, which indicated that the cortical thickness and the hilum shape were the most reliable ultrasonography factors in diagnosis of axillary lymph node involvement in primary breast cancer. A lymph node cortex size of 3.7 mm had 81% sensitivity and 85% specificity and absent fatty hilum is the most specific factor for the diagnosis of lymph node involvement. Morphologic grade 1 had also a sensitivity of 66% and specificity of 88%. These results are consistent with the results of Briton and colleagues, who indicated that AUS morphological characteristics, including absence of a hilum and a cortical thickness >4 mm were associated with malignancy (Britton et al., 2009). In the study by Rotim et al., (2017), malignant lymph nodes had a higher maximal cortical thickness and the sensitivity of AUS exceeded 80% at cortical thickness of 5.1 mm. In the present study, the ratio of lymph node cortex size to the whole width of the lymph node in its shortest axis had the highest predictive value (83%), sensitivity of 72%, and specificity of 85% at 0.53, though it is only seen in high stages of the disease. These results are in line with the results of the study by Bedi and colleagues, who reported sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and overall accuracy of cortical shape in AUS at 77%, 80%, 36%, 96%, and 80%, respectively, for prediction of metastatic involvement of axillary nodes (Bedi et al., 2008). Therefore, the diagnostic accuracy of AUS is higher in some characteristics of the lymph node and combination of these morphological characteristics can be used for a more accurate diagnosis by AUS. The highest specificity (100%) in our study was related to 1/K ratio, indicating lymph node sphericity (measured as the ratio of the longest to the shortest diameter of the lymph node), and the risk of lymph node involvement increases as 1/K ratio approaches 1 (that shows the lymph node is more spherical) with predictive value of 82% at 0.41, while the sensitivity was not high (76%). As far as the authors are concerned, this is the first time that lymph node sphericity is reported as a sign, increasing the diagnostic value of AUS. Lymph node Doppler sonography has been suggested by various studies for the assessment of the distribution of intranodal vascular pattern and resistance of lymph nodes (Ying et al., 2013) and has been reported to have high sensitivity and specificity for differentiating metastatic and reactive nodes (Gupta et al., 2011). In the present study, the results showed a positive correlation between lymph node non-hilar blood flow and lymph node involvement. It is noticeable that this factor could not distinguish involved and reactive lymph nodes precisely. The ratio of the systolic to diastolic blood flow also showed a positive correlation with pathological results, though it had a large confidence interval; while the other two vascular factors (RI and PI) showed no correlation with pathological Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
6 Alireza Rezvani et al results. There seems to be much controversy about the diagnostic value of RI and PI in the literature; some suggest higher RI and PI in metastatic than reactive nodes (Cui et al., 2013), while others suggest lower or similar RI and PI in metastatic than benign nodes (Moritz et al., 2000). Accordingly, these indices are considered with limited application in routine clinical practice. The results of the present study could be limited by various aspects. First, any diagnostic errors of the radiologist performing the AUS or the ultrasound device could have affected the results. Second, we could not compare the lymph node characteristics with pathological results, as the aspects recorded were dissimilar in some cases. Therefore, it is suggested to compare the results of preoperative AUS with intra-operative AUS for better assessment and comparison. In conclusion, as our results revealed, AUS is a valuable but not a definite tool for determination of axillary lymph involvement in primary breast cancer and has a high sensitivity at high disease stages with macro-metastases. Therefore, it is suggested to use AUS for general assessment, but not for definite diagnosis. It seems like sensitivity and specificity of the AUS could be raised by adding new parameters like lymph node sphericity to the diagnostic criteria. The operator dependency of ultrasonography is undeniably influences the results, and the similarity between involved and reactive lymph nodes is another challenging part of the diagnosis. For better evaluation of this issue, further studies with a larger population and intra-operative AUS are recommended for comparison of the characteristics of each lymph node detected with pathological evaluation of the same lymph node. Funding Statement The present study was financially supported as M.D thesis by Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (code: 12190). Acknowledgements The authors of the present study sincerely thank Dr. S. Tahmasbi for her kind cooperation in case preparation. References Abe H, Schmidt RA, Kulkarni K, et al (2009). Axillary lymph nodes suspicious for breast cancer metastasis: sampling with US-guided 14-gauge core-needle biopsy-clinical experience in 100 patients. Radiology, 250, Bedi DG, Krishnamurthy R, Krishnamurthy S, et al (2008). Cortical morphologic features of axillary lymph nodes as a predictor of metastasis in breast cancer: in vitro sonographic study. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 191, Bedrosian I, Bedi D, Kuerer HM, et al (2003). Impact of clinicopathological factors on sensitivity of axillary ultrasonography in the detection of axillary nodal metastases in patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol, 10, Berg WA, Blume JD, Cormack JB, et al (2008). Combined screening with ultrasound and mammography vs mammography alone in women at elevated risk of breast cancer. JAMA, 299, Britton PD, Goud A, Godward S, et al (2009). Use of ultrasound-guided axillary node core biopsy in staging of early breast cancer. Eur Radiol, 19, Cui XW, Jenssen C, Saftoiu A, et al (2013). New ultrasound techniques for lymph node evaluation. World J Gastroenterol, 19, da Costa Vieira RA, Biller G, Uemura G, et al (2017). Breast cancer screening in developing countries. Clinics, 72, DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, et al (2014). Breast cancer statistics, CA Cancer J Clin, 64, Deurloo E, Tanis P, Gilhuijs K, et al (2003). Reduction in the number of sentinel lymph node procedures by preoperative ultrasonography of the axilla in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer, 39, Diepstraten SC, Sever AR, Buckens CF, et al (2014). Value of preoperative ultrasound-guided axillary lymph node biopsy for preventing completion axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol, 21, Dihge L, Grabau DA, Rasmussen RW, et al (2016). The accuracy of preoperative axillary nodal staging in primary breast cancer by ultrasound is modified by nodal metastatic load and tumor biology. Acta Oncol, 55, Ertan K, Linsler C, Di Liberto A, et al (2013). Axillary ultrasound for breast cancer staging: an attempt to identify clinical/ histopathological factors impacting diagnostic performance. Breast Cancer Basic Clin Res, 7, S Ghoncheh M, Pournamdar Z, Salehiniya H (2016). Incidence and mortality and epidemiology of breast cancer in the world. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 17, Gupta A, Rahman K, Shahid M, et al (2011). Sonographic assessment of cervical lymphadenopathy: Role of high-resolution and color Doppler imaging. Head Neck, 33, Hackney L, Williams S, Bajwa S, et al (2013). Influence of tumor histology on preoperative staging accuracy of breast metastases to the axilla. Breast J, 19, Houssami N, Ciatto S, Turner RM, et al (2011). Preoperative ultrasound-guided needle biopsy of axillary nodes in invasive breast cancer: meta-analysis of its accuracy and utility in staging the axilla. Ann Surg, 254, Jazayeri SB, Saadat S, Ramezani R, et al (2015). Incidence of primary breast cancer in Iran: Ten-year national cancer registry data report. Cancer Epidemiol, 39, Jung J, Park H, Park J, et al (2010). Accuracy of preoperative ultrasound and ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology for axillary staging in breast cancer. ANZ J Surg, 80, Kumar R, Jana S, Heiba SI, et al (2003). Retrospective analysis of sentinel node localization in multifocal, multicentric, palpable, or nonpalpable breast cancer. J Nucl Med, 44, Leong SP, Shen ZZ, Liu TJ, et al (2010). Is breast cancer the same disease in Asian and Western countries?. World J Surg, 34, Moritz JD, Ludwig A, Oestmann JW (2000). Contrast-enhanced color Doppler sonography for evaluation of enlarged cervical lymph nodes in head and neck tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 174, Mousavi SM, Montazeri A, Mohagheghi MA, et al (2007). Breast cancer in Iran: an epidemiological review. Breast J, 13, Ngoma T (2006). World Health Organization cancer priorities in developing countries. Ann Oncol, 17, Ohuchi N, Suzuki A, Sakurai Y, et al (2009). Current status and problems of breast cancer screening. JMAJ, 52, Pan HB (2016). The role of breast ultrasound in early cancer 3620 Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 19
7 detection. J Med Ultrason, 24, Petropoulou T, Kapoula A, Mastoraki A, et al (2017). Imprint cytology versus frozen section analysis for intraoperative assessment of sentinel lymph node in breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press), 9, 325. Pinheiro DJPdC, Elias S, Nazário ACP (2014). Axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients: sonographic evaluation. Radiol Bras, 47, Rotim T, Kristek B, Turk T, et al (2017). Measurable and unmeasurable features of ultrasound lymph node images in detection of malignant infiltration. Acta Clin Croat, 56, Schwartz TL, Margenthaler JA (2017). Axillary ultrasound before neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: Don t discount the benefits yet!. Ann Surg Oncol, 24, Shah AR, Glazebrook KN, Boughey JC, et al (2014). Does BMI affect the accuracy of preoperative axillary ultrasound in breast cancer patients?. Ann Surg Oncol, 21, Shah TA, Guraya SS (2017). Breast cancer screening programs: Review of merits, demerits, and recent recommendations practiced across the world. J Microsc Ultrast, 5, Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018). Cancer statistics, CA cancer J Clin, 68, Stachs A, Göde K, Hartmann S, et al (2013). Accuracy of axillary ultrasound in preoperative nodal staging of breast cancer-size of metastases as limiting factor. SpringerPlus, 2, 350. Ying M, Bhatia K, Lee Y, et al (2013). Review of ultrasonography of malignant neck nodes: greyscale, Doppler, contrast enhancement and elastography. Cancer Imaging, 13, 658. DOI: /APJCP This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- Non Commercial 4.0 International License. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary Lymph Node Involvement In Breast Carcinoma
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II. (Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II. (Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary
J.N., PRADHAN A.K., KUSTA M.K. ABSTRACT
 Axillary Ultrasound Examination in the Selection of Carcinoma of Breast Patients for Sentinel Node Biopsy - A Prospective Study MISRA J.N., PRADHAN A.K., KUSTA M.K. ABSTRACT Background: Axillary lymph
Axillary Ultrasound Examination in the Selection of Carcinoma of Breast Patients for Sentinel Node Biopsy - A Prospective Study MISRA J.N., PRADHAN A.K., KUSTA M.K. ABSTRACT Background: Axillary lymph
The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes
 Yonsei Med J 49(2):249-254, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.249 The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes Ki Hong Kim, 1 Eun Ju Son, 1 Eun-Kyung Kim,
Yonsei Med J 49(2):249-254, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.249 The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes Ki Hong Kim, 1 Eun Ju Son, 1 Eun-Kyung Kim,
The Clinical Value of Axillary Ultrasonography for Detection of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Cases with Breast Cancer
 Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; October 2014; 5(4): 215-220 The Clinical Value of Axillary Ultrasonography for Detection of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Cases with Breast Cancer Sedigheh
Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; October 2014; 5(4): 215-220 The Clinical Value of Axillary Ultrasonography for Detection of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Cases with Breast Cancer Sedigheh
Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer
 Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer Chiun Sheng Huang, MD, PhD, MPH Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Director of Breast Care Center National Taiwan University Hospital
Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer Chiun Sheng Huang, MD, PhD, MPH Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Director of Breast Care Center National Taiwan University Hospital
EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES AFTER NEOADJUVANT SYSTEMIC THERAPY KIM, MIN JUNG SEVERANCE HOSPITAL, YONSEI UNIVERSITY
 EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES AFTER NEOADJUVANT SYSTEMIC THERAPY KIM, MIN JUNG SEVERANCE HOSPITAL, YONSEI UNIVERSITY AXILLARY LYMPH NODE METASTASIS Axillary lymph node metastasis is one of the most
EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES AFTER NEOADJUVANT SYSTEMIC THERAPY KIM, MIN JUNG SEVERANCE HOSPITAL, YONSEI UNIVERSITY AXILLARY LYMPH NODE METASTASIS Axillary lymph node metastasis is one of the most
Original Article. J Fac Med Baghdad 193. Introduction:
 Original Article The value of Gray scale, color doppler and ultrasound guided- FNA in detection metastasis to the axillary lymph node in patient with primary breast cancer. * Qusay A. Fahad* Enam A.Al
Original Article The value of Gray scale, color doppler and ultrasound guided- FNA in detection metastasis to the axillary lymph node in patient with primary breast cancer. * Qusay A. Fahad* Enam A.Al
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Mainiero et al. Ultrasound-Guided FN in Breast Cancer Patients Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Martha B. Mainiero 1 Christina M. Cinelli 2 Susan L. Koelliker
Women s Imaging Original Research Mainiero et al. Ultrasound-Guided FN in Breast Cancer Patients Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Martha B. Mainiero 1 Christina M. Cinelli 2 Susan L. Koelliker
Feasibility of Preoperative Axillary Lymph Node Marking with a Clip in Breast Cancer Patients before Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study
 [ABS-0078] GBCC 2018 Feasibility of Preoperative Axillary Lymph Node Marking with a Clip in Breast Cancer Patients before Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study Eun Young Kim 1, Kwan Ho Lee 1, Yong
[ABS-0078] GBCC 2018 Feasibility of Preoperative Axillary Lymph Node Marking with a Clip in Breast Cancer Patients before Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study Eun Young Kim 1, Kwan Ho Lee 1, Yong
Malignant Breast Masses Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 4-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad
 ACCURACY OF THE DOPPLER RESISTIVE INDEX IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALIGNANT BREAST MASSES Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad Combined Military Hospital Khuzdar, *AFIRI Rawalpindi ABSTRACT Objective:
ACCURACY OF THE DOPPLER RESISTIVE INDEX IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALIGNANT BREAST MASSES Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad Combined Military Hospital Khuzdar, *AFIRI Rawalpindi ABSTRACT Objective:
Utility of Preoperative Ultrasound for Predicting pn2 or Higher Stage Axillary Lymph Node Involvement in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer
 Women s Imaging Original Research Abe et al. Preoperative Ultrasound to Predict Axillary Lymph Node Involvement Women s Imaging Original Research Hiroyuki Abe 1 David Schacht Charlene A. Sennett Gillian
Women s Imaging Original Research Abe et al. Preoperative Ultrasound to Predict Axillary Lymph Node Involvement Women s Imaging Original Research Hiroyuki Abe 1 David Schacht Charlene A. Sennett Gillian
Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm
 Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm Belinda Curpen, MD, FRCPC; Tetyana Dushenkovska; Mia Skarpathiotakis MD, FRCPC; Carrie Betel, MD, FRCPC; Kalesha Hack, MD, FRCPC; Lara Richmond,
Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm Belinda Curpen, MD, FRCPC; Tetyana Dushenkovska; Mia Skarpathiotakis MD, FRCPC; Carrie Betel, MD, FRCPC; Kalesha Hack, MD, FRCPC; Lara Richmond,
The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1
 The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1 Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Asiry Hwang, M.D., Hye-Young Choi, M.D., Seung Yon Baek, M.D. Purpose: We evaluated the
The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1 Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Asiry Hwang, M.D., Hye-Young Choi, M.D., Seung Yon Baek, M.D. Purpose: We evaluated the
Axillary ultrasound in patients with breast cancer: which lymph nodes should be targeted for fine needle aspiration?
 Axillary ultrasound in patients with breast cancer: which lymph nodes should be targeted for fine needle aspiration? Poster No.: C-0289 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. J. Diaz-Ruiz,
Axillary ultrasound in patients with breast cancer: which lymph nodes should be targeted for fine needle aspiration? Poster No.: C-0289 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. J. Diaz-Ruiz,
Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Cytological Correlation
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/74 Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Cytological Correlation Suresh Kumar 1, Sonjjay Pande
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/74 Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Cytological Correlation Suresh Kumar 1, Sonjjay Pande
The Efficacy of Axillary Ultrasound in the Detection of Nodal Metastasis in Breast Cancer
 Women s Imaging Original Research Lee et al. Ultrasound Detection of Nodal Metastasis Women s Imaging Original Research Belinda Lee 1 Adrian K. Lim 2 Jonathan Krell 1 Keshthra Satchithananda 2 R. Charles
Women s Imaging Original Research Lee et al. Ultrasound Detection of Nodal Metastasis Women s Imaging Original Research Belinda Lee 1 Adrian K. Lim 2 Jonathan Krell 1 Keshthra Satchithananda 2 R. Charles
Differentiating Benign from Malignant Cervical Lymph Nodes with Sonoelastography
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2017; 5(4): 42-46 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20170504.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Differentiating
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2017; 5(4): 42-46 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20170504.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Differentiating
Evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumor and axillary lymph nodes in locally advanced breast cancer: a study of 50 patients
 Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-0005-4 Evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumor and axillary lymph nodes in locally advanced breast cancer: a study of 50 patients
Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-0005-4 Evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumor and axillary lymph nodes in locally advanced breast cancer: a study of 50 patients
Consensus Guideline on Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Palpable and Nonpalpable Breast Lesions
 Consensus Guideline on Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Palpable and Nonpalpable Breast Lesions Purpose: To outline the use of minimally invasive biopsy techniques (MIBT) for palpable and nonpalpable
Consensus Guideline on Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Palpable and Nonpalpable Breast Lesions Purpose: To outline the use of minimally invasive biopsy techniques (MIBT) for palpable and nonpalpable
Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer
 - Official Statement - Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for the
- Official Statement - Position Statement on Management of the Axilla in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) for the
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 39/ May 14, 2015 Page 6787
 ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology in staging clinically node-negative invasive breast cancer
 Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:185 191 DOI 10.1007/s10397-011-0712-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology in staging clinically node-negative invasive breast cancer Daniela Huber &
Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:185 191 DOI 10.1007/s10397-011-0712-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology in staging clinically node-negative invasive breast cancer Daniela Huber &
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
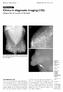 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
The American Society of Breast Surgeons
 The American Journal of Surgery (2008) 196, 477 482 The American Society of Breast Surgeons Scientific Presentation Award: The combination of axillary ultrasound and ultrasound-guided biopsy is an accurate
The American Journal of Surgery (2008) 196, 477 482 The American Society of Breast Surgeons Scientific Presentation Award: The combination of axillary ultrasound and ultrasound-guided biopsy is an accurate
Donna Plecha, MD 1, Shiyu Bai, BS 2, Helen Patterson 3, Cheryl Thompson, PhD 4, and Robert Shenk, MD 5
 Ann Surg Oncol DOI 10.1245/s10434-015-4527-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Improving the Accuracy of Axillary Lymph Node Surgery in Breast Cancer with Ultrasound-Guided Wire Localization of Biopsy Proven
Ann Surg Oncol DOI 10.1245/s10434-015-4527-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Improving the Accuracy of Axillary Lymph Node Surgery in Breast Cancer with Ultrasound-Guided Wire Localization of Biopsy Proven
ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes
 ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes Poster No.: B-0158 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper F. Houari, O. Lucidarme, J. Gabarre, F. Charlotte, C. Pellot- Barakat, M. Lefort,
ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes Poster No.: B-0158 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper F. Houari, O. Lucidarme, J. Gabarre, F. Charlotte, C. Pellot- Barakat, M. Lefort,
Lymph Node Hilus. Gray Scale and Power Doppler Sonography of Cervical Nodes. Article
 Article Lymph Node Hilus Gray Scale and Power Doppler Sonography of Cervical Nodes Anil Ahuja, FRCR, Michael Ying, MPhil, Ann King, FRCR, Hok Yuen Yuen, FRCR Objective. To investigate the difference in
Article Lymph Node Hilus Gray Scale and Power Doppler Sonography of Cervical Nodes Anil Ahuja, FRCR, Michael Ying, MPhil, Ann King, FRCR, Hok Yuen Yuen, FRCR Objective. To investigate the difference in
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Management of Palpable Abnormalities in the Breast Katerina Dodelzon, MD July 31, 2018, 7:00pm ET
 Management of Palpable Abnormalities in the Breast Katerina Dodelzon, MD July 31, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions 1. 21 year old female presenting with left breast palpable mass, what is the most appropriate
Management of Palpable Abnormalities in the Breast Katerina Dodelzon, MD July 31, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions 1. 21 year old female presenting with left breast palpable mass, what is the most appropriate
Cervical Lymph Nodes
 Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Ductal carcinoma in situ, underestimation, ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy
 Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM am am : Clinician s requirements from breast imaging
 Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 Day one, 2 nd November BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 9.00 AM 9.10 am Introduction 9.10 am - 9.30 am : Clinician
Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 Day one, 2 nd November BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 9.00 AM 9.10 am Introduction 9.10 am - 9.30 am : Clinician
Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer: Preoperative Imaging and Localization
 Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer: Preoperative Imaging and Localization Debra Monticciolo, MD Professor of Radiology Texas A&M University no disclosures Debra Monticciolo, MD Professor of Radiology Texas
Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer: Preoperative Imaging and Localization Debra Monticciolo, MD Professor of Radiology Texas A&M University no disclosures Debra Monticciolo, MD Professor of Radiology Texas
Fine needle aspiration cytology guided by ultrasound of suspicious axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients
 Hematology & Medical Oncology Research Article ISSN: 2398-8495 Fine needle aspiration cytology guided by ultrasound of suspicious axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients Waldeir de Almeida Júnior
Hematology & Medical Oncology Research Article ISSN: 2398-8495 Fine needle aspiration cytology guided by ultrasound of suspicious axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients Waldeir de Almeida Júnior
Angela Gilliam, MD University of Colorado Surgical Grand Rounds November 3, 2008
 Angela Gilliam, MD University of Colorado Surgical Grand Rounds November 3, 2008 Breast Cancer Most common cancer in American women 180,000 new cases per year Second most common cause of cancer death 44,000
Angela Gilliam, MD University of Colorado Surgical Grand Rounds November 3, 2008 Breast Cancer Most common cancer in American women 180,000 new cases per year Second most common cause of cancer death 44,000
PROTOCOL SENTINEL NODE BIOPSY (NON OPERATIVE) BREAST CANCER - PATHOLOGY ASSESSMENT
 PROTOCOL SENTINEL NODE BIOPSY (NON OPERATIVE) BREAST CANCER - PATHOLOGY ASSESSMENT Author: Dr Sally Ann Hales On behalf of the Breast and pathology CNGs Written: March 2005 Reviewed by CNG: June 2009 &
PROTOCOL SENTINEL NODE BIOPSY (NON OPERATIVE) BREAST CANCER - PATHOLOGY ASSESSMENT Author: Dr Sally Ann Hales On behalf of the Breast and pathology CNGs Written: March 2005 Reviewed by CNG: June 2009 &
Journal of Breast Cancer
 Journal of Breast Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Cancer 2012 March; 15(1): 65-70 Classification of Metastatic versus Non-Metastatic Axillary Nodes in Breast Cancer Patients: Value of Cortex-Hilum Area
Journal of Breast Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Cancer 2012 March; 15(1): 65-70 Classification of Metastatic versus Non-Metastatic Axillary Nodes in Breast Cancer Patients: Value of Cortex-Hilum Area
Preoperative axillary lymph node staging by ultrasound-guided cytology using a four-level sonographic score
 De Coninck et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2016) 16:13 DOI 10.1186/s12880-016-0116-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Preoperative axillary lymph node staging by ultrasound-guided cytology using a four-level sonographic
De Coninck et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2016) 16:13 DOI 10.1186/s12880-016-0116-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Preoperative axillary lymph node staging by ultrasound-guided cytology using a four-level sonographic
ULTRASOUND GUIDED FNA: WHEN, HOW, AND WHY
 ULTRASOUND GUIDED FNA: WHEN, HOW, AND WHY Marika Russell, MD, FACS Assistant Professor, UCSF OHNS Disclosures: none Overview Background Indications Technique Outcomes Survey Office-based ultrasound? USG-FNA?
ULTRASOUND GUIDED FNA: WHEN, HOW, AND WHY Marika Russell, MD, FACS Assistant Professor, UCSF OHNS Disclosures: none Overview Background Indications Technique Outcomes Survey Office-based ultrasound? USG-FNA?
ELIZABETH CEDARS DR. KOREY HOOD Available September 29
 ELIZABETH CEDARS DR. KOREY HOOD Available September 29 Title and Investigators Optimizing Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer: Using Surgeon-performed Ultrasound to Predict Extrathyroidal Extension of
ELIZABETH CEDARS DR. KOREY HOOD Available September 29 Title and Investigators Optimizing Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer: Using Surgeon-performed Ultrasound to Predict Extrathyroidal Extension of
Risk of Malignancy Index in the Preoperative Evaluation of Patients with Adnexal Masses among Women of Perimenopausal and Postmenopausal Age Group
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 9 Ver. 8 (September. 2018), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org Risk of Malignancy Index in the Preoperative
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 9 Ver. 8 (September. 2018), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org Risk of Malignancy Index in the Preoperative
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography
 Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Clinical Study Ultrasound Guided Core Biopsy versus Fine Needle Aspiration for Evaluation of Axillary Lymphadenopathy in Patients with Breast Cancer
 ISRN Oncology, Article ID 703160, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/703160 Clinical Study Ultrasound Guided Core Biopsy versus Fine Needle Aspiration for Evaluation of Axillary Lymphadenopathy in
ISRN Oncology, Article ID 703160, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/703160 Clinical Study Ultrasound Guided Core Biopsy versus Fine Needle Aspiration for Evaluation of Axillary Lymphadenopathy in
Diagnosis and staging of breast cancer and multidisciplinary team working
 1 Diagnosis and staging of breast cancer and multidisciplinary team working Common symptoms and signs Over 90% of breast cancers (BCs) are local or regional when first detected. At least 60% of patients
1 Diagnosis and staging of breast cancer and multidisciplinary team working Common symptoms and signs Over 90% of breast cancers (BCs) are local or regional when first detected. At least 60% of patients
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
 Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
THE BREAST CENTER AT MONTEFIORE NYACK HOSPITAL
 THE BREAST CENTER AT MONTEFIORE NYACK HOSPITAL COMPLETE BREAST CARE FROM THE TEAM THAT CARES I don t think I could get better care, more support, or encouragement at any of the bigger hospitals or cancer
THE BREAST CENTER AT MONTEFIORE NYACK HOSPITAL COMPLETE BREAST CARE FROM THE TEAM THAT CARES I don t think I could get better care, more support, or encouragement at any of the bigger hospitals or cancer
Tips and Tricks to performing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Breast Interventional Procedures Habib Rahbar, MD, FSBI October 23, 2018, 7:00pm ET
 Tips and Tricks to performing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Breast Interventional Procedures Habib Rahbar, MD, FSBI October 23, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions/Answers/Rationales/References 1. Below
Tips and Tricks to performing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Breast Interventional Procedures Habib Rahbar, MD, FSBI October 23, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions/Answers/Rationales/References 1. Below
Role of spectral doppler in the differentiation of benign and malignant cervical lymphadenopathy
 Al Am een J Med Sci 2014; 7(4):291-298 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Role of spectral doppler in the differentiation of benign
Al Am een J Med Sci 2014; 7(4):291-298 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Role of spectral doppler in the differentiation of benign
Pre- operative staging of the axilla
 Pre- operative staging of the axilla Anthony J Maxwell University Hospital of South Manchester Outline Why stage the axilla? Optimising conventional US & needle sampling Other imaging and needle sampling
Pre- operative staging of the axilla Anthony J Maxwell University Hospital of South Manchester Outline Why stage the axilla? Optimising conventional US & needle sampling Other imaging and needle sampling
High thyroglobulin (Tg) in a lymph node indicates metastatic
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Optimized Cutoff Value and Indication for Washout Thyroglobulin Level According to Ultrasound Findings in Patients with Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer J.Y. Jung, J.H.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Optimized Cutoff Value and Indication for Washout Thyroglobulin Level According to Ultrasound Findings in Patients with Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer J.Y. Jung, J.H.
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound
 Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Feasibility of using negative ultrasonography results of axillary lymph nodes to predict sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients
 Received: 21 April 2018 Revised: 14 May 2018 DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1606 Accepted: 14 May 2018 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Feasibility of using negative ultrasonography results of axillary lymph nodes to predict sentinel
Received: 21 April 2018 Revised: 14 May 2018 DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1606 Accepted: 14 May 2018 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Feasibility of using negative ultrasonography results of axillary lymph nodes to predict sentinel
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Complete breast care from the team that cares. Breast Center
 Breast Center Complete breast care from the team that cares. Imaging Appointment: 845.348.8551 Surgical Consultation: 845.348.8507 nyackhospital.org/breastcenter 1 Complete breast care from the team that
Breast Center Complete breast care from the team that cares. Imaging Appointment: 845.348.8551 Surgical Consultation: 845.348.8507 nyackhospital.org/breastcenter 1 Complete breast care from the team that
ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form
 S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
Targeting Surgery for Known Axillary Disease. Abigail Caudle, MD Henry Kuerer, MD PhD Dept. Surgical Oncology MD Anderson Cancer Center
 Targeting Surgery for Known Axillary Disease Abigail Caudle, MD Henry Kuerer, MD PhD Dept. Surgical Oncology MD Anderson Cancer Center Nodal Ultrasound at Diagnosis Whole breast and draining lymphatic
Targeting Surgery for Known Axillary Disease Abigail Caudle, MD Henry Kuerer, MD PhD Dept. Surgical Oncology MD Anderson Cancer Center Nodal Ultrasound at Diagnosis Whole breast and draining lymphatic
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
ROLE OF MRI IN SCREENING, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF BREAST CANCER. B.Zandi Professor of Radiology
 ROLE OF MRI IN SCREENING, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF BREAST CANCER B.Zandi Professor of Radiology Introduction In the USA, Breast Cancer is : The Most Common Non-Skin Cancer The Second Leading cause of
ROLE OF MRI IN SCREENING, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF BREAST CANCER B.Zandi Professor of Radiology Introduction In the USA, Breast Cancer is : The Most Common Non-Skin Cancer The Second Leading cause of
Axillary ultrasound is frequently used to assess axillary nodes at
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification and Resection of Clipped Node Decreases the False-negative Rate of Sentinel Lymph Node Surgery in Patients Presenting With Node-positive Breast Cancer (T0 T4, N1 N2) Who
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification and Resection of Clipped Node Decreases the False-negative Rate of Sentinel Lymph Node Surgery in Patients Presenting With Node-positive Breast Cancer (T0 T4, N1 N2) Who
Assessment of Ultrasound Features Predicting Axillary Nodal Metastasis in Breast Cancer: The Impact of Cortical Thickness
 THIEME E19 Assessment of Ultrasound Features Predicting Axillary Nodal Metastasis in Breast Cancer: The Impact of Cortical Thickness Authors A. Stachs 1, A. Tra-Ha Thi 1, M. Dieterich 1, J. Stubert 1,
THIEME E19 Assessment of Ultrasound Features Predicting Axillary Nodal Metastasis in Breast Cancer: The Impact of Cortical Thickness Authors A. Stachs 1, A. Tra-Ha Thi 1, M. Dieterich 1, J. Stubert 1,
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Amlendu Nagar
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS
 Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Clinical Study Accuracy of Individual Descriptors and Grading of Nodal Involvement by Axillary Ultrasound in Patients of Breast Cancer
 International Breast Cancer Volume 2013, Article ID 930596, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/930596 Clinical Study Accuracy of Individual Descriptors and Grading of Nodal Involvement by Axillary
International Breast Cancer Volume 2013, Article ID 930596, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/930596 Clinical Study Accuracy of Individual Descriptors and Grading of Nodal Involvement by Axillary
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer
 Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
16/09/2015. ACOSOG Z011 changing practice. Presentation outline. Nodal mets #1 prognostic tool. Less surgery no change in oncologic outcomes
 ACOSOG Z011 changing practice The end of axillary US/FNA? Preoperative staging of the axilla in the era of Z011 Adena S Scheer MD MSc FRCSC Surgical Oncologist, St. Michael s Hospital Assistant Professor,
ACOSOG Z011 changing practice The end of axillary US/FNA? Preoperative staging of the axilla in the era of Z011 Adena S Scheer MD MSc FRCSC Surgical Oncologist, St. Michael s Hospital Assistant Professor,
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
«àπ π â Õ μ «å «π Áß μâ π π ßæ π ª
 «æ å μ Ù-ı ªï Ë Ûapple Ë Ù μ.. -.. ÚııÙ Reg 4-5 Med J Vol. 30 No. 4 Oct - Dec 2011 π æπ åμâπ Original Article «μ»ÿ º æ.., Cheerawan Tansupaphon M.D., «.«. ß «π Thai Board of Diagnostic Radiology ÿà ß π
«æ å μ Ù-ı ªï Ë Ûapple Ë Ù μ.. -.. ÚııÙ Reg 4-5 Med J Vol. 30 No. 4 Oct - Dec 2011 π æπ åμâπ Original Article «μ»ÿ º æ.., Cheerawan Tansupaphon M.D., «.«. ß «π Thai Board of Diagnostic Radiology ÿà ß π
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
COMPARISON OF MAMMOGRAPHY AND ULTRASOUND COMBINED VERSUS ULTRASOUND ALONE IN EARLY EVALUATION OF SYMPTOMATIC BREAST CANCERS IN PAKISTAN
 COMPARISON OF MAMMOGRAPHY AND ULTRASOUND COMBINED VERSUS ULTRASOUND ALONE IN EARLY EVALUATION OF SYMPTOMATIC BREAST CANCERS IN PAKISTAN Razia Bano 1, Huma M. Khan 2, Ayesha Ehsan 1, Awais A. Malik 2, Shahper
COMPARISON OF MAMMOGRAPHY AND ULTRASOUND COMBINED VERSUS ULTRASOUND ALONE IN EARLY EVALUATION OF SYMPTOMATIC BREAST CANCERS IN PAKISTAN Razia Bano 1, Huma M. Khan 2, Ayesha Ehsan 1, Awais A. Malik 2, Shahper
Role of sonographic elastography in the differential diagnosis of axillary lymph nodes
 Role of sonographic elastography in the differential diagnosis of axillary lymph nodes Poster No.: C-0438 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Breast Authors: J. J. Choi, B. J. Kang, S. H.
Role of sonographic elastography in the differential diagnosis of axillary lymph nodes Poster No.: C-0438 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Breast Authors: J. J. Choi, B. J. Kang, S. H.
Role of positron emission mammography (PEM) for assessment of axillary lymph node status in patients with breast cancer
 Role of positron emission mammography (PEM) for assessment of axillary lymph node status in patients with breast cancer Poster No.: C-1260 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: K. M. Kulkarni,
Role of positron emission mammography (PEM) for assessment of axillary lymph node status in patients with breast cancer Poster No.: C-1260 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: K. M. Kulkarni,
NICE diagnostics guidance on intraoperative tests (RD 100i OSNA system and Metasin test) for detecting sentinel lymph node metastases in breast cancer
 NICE diagnostics guidance on intraoperative tests (RD 100i OSNA system and Metasin test) for detecting sentinel lymph node metastases in breast cancer NICE provided the content for this booklet which is
NICE diagnostics guidance on intraoperative tests (RD 100i OSNA system and Metasin test) for detecting sentinel lymph node metastases in breast cancer NICE provided the content for this booklet which is
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
4/22/2010. Hakan Korkmaz, MD Assoc. Prof. of Otolaryngology Ankara Dıșkapı Training Hospital-Turkey.
 Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Head Neck Surgeon Perspective Hakan Korkmaz, MD Assoc. Prof. of Otolaryngology Ankara Dıșkapı Training Hospital-Turkey Thyroid gland Small endocrine gland:
Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Head Neck Surgeon Perspective Hakan Korkmaz, MD Assoc. Prof. of Otolaryngology Ankara Dıșkapı Training Hospital-Turkey Thyroid gland Small endocrine gland:
Clinical Study B-Mode and Elastosonographic Evaluation to Determine the Reference Elastosonography Values for Cervical Lymph Nodes
 ISRN Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 895287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.5402/2013/895287 Clinical Study B-Mode and Elastosonographic Evaluation to Determine the Reference Elastosonography Values for
ISRN Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 895287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.5402/2013/895287 Clinical Study B-Mode and Elastosonographic Evaluation to Determine the Reference Elastosonography Values for
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging
 Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
CURRENT METHODS IN IMAGE GUIDED BREAST BIOPSY
 CURRENT METHODS IN IMAGE GUIDED BREAST BIOPSY Stuart Silver April 24, 2004 OBJECTIVES Review development of current techniques Discuss stereotactic breast biopsy Discuss US guided breast biopsy 1 OBJECTIVES
CURRENT METHODS IN IMAGE GUIDED BREAST BIOPSY Stuart Silver April 24, 2004 OBJECTIVES Review development of current techniques Discuss stereotactic breast biopsy Discuss US guided breast biopsy 1 OBJECTIVES
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Woo Jung Choi, Joo Hee Cha*, Hak Hee Kim, Hee Jung Shin, Hyunji Kim, Eun Young Chae, Min Ji Hong. Abstract.
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.21.9101 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparison of Automated Breast Volume Scanning and Hand- Held Ultrasound in the Detection of Breast Cancer: an Analysis of 5,566 Patient
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.21.9101 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparison of Automated Breast Volume Scanning and Hand- Held Ultrasound in the Detection of Breast Cancer: an Analysis of 5,566 Patient
Role of high-resolution colored-doppler ultrasound in the differentiation between benign and malignant cervical lymphadenopathy
 Role of high-resolution colored-doppler ultrasound in the differentiation between benign and malignant cervical lymphadenopathy Shahad D. Ali (1) *, Taghreed F. Zaidan (2), Fadhil Al-Janabi (3) 1 Department
Role of high-resolution colored-doppler ultrasound in the differentiation between benign and malignant cervical lymphadenopathy Shahad D. Ali (1) *, Taghreed F. Zaidan (2), Fadhil Al-Janabi (3) 1 Department
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CAE of Malignancy with MRI of the Breast Page 1 of 9 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See also: Computer-Aided Evaluation of Malignancy with Magnetic
CAE of Malignancy with MRI of the Breast Page 1 of 9 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See also: Computer-Aided Evaluation of Malignancy with Magnetic
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 SAM - Breast MRI 1
 National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
Does elastography change the indication to biopsy? IBDC
 Does elastography change the indication to biopsy? A LEXANDRA A THANASIOU, M D DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY CURIE INSTITUTE PARIS, FRANCE IBDC Ultrasound Detected Cancers Physician-performed ultrasound increases
Does elastography change the indication to biopsy? A LEXANDRA A THANASIOU, M D DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY CURIE INSTITUTE PARIS, FRANCE IBDC Ultrasound Detected Cancers Physician-performed ultrasound increases
Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): 321-326 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info The logistic regression analysis of ultrasonographic features in differential diagnosis of cervical lymph nodes metastasis
Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): 321-326 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info The logistic regression analysis of ultrasonographic features in differential diagnosis of cervical lymph nodes metastasis
PET CT for Staging Lung Cancer
 PET CT for Staging Lung Cancer Rohit Kochhar Consultant Radiologist Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have financial relationships with commercial organizations that may have a direct
PET CT for Staging Lung Cancer Rohit Kochhar Consultant Radiologist Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have financial relationships with commercial organizations that may have a direct
Ultrasound and MRI evaluation of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE ISSN: 2455-944X www.darshanpublishers.com Volume 3, Issue 12-2018 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrbm.2018.03.12.002
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE ISSN: 2455-944X www.darshanpublishers.com Volume 3, Issue 12-2018 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrbm.2018.03.12.002
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Case Scenario 1. 2/15/2011 The patient received IMRT 45 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction for 25 fractions.
 Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
5/18/2013. Most thyroid nodules are benign. Thyroid nodules: new techniques in evaluation
 Most thyroid nodules are benign Thyroid nodules: new techniques in evaluation Incidence Etiology Risk factors Diagnosis Gene classification system Treatment Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Jessica
Most thyroid nodules are benign Thyroid nodules: new techniques in evaluation Incidence Etiology Risk factors Diagnosis Gene classification system Treatment Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Jessica
Mammography and Subsequent Whole-Breast Sonography of Nonpalpable Breast Cancers: The Importance of Radiologic Breast Density
 Isabelle Leconte 1 Chantal Feger 1 Christine Galant 2 Martine Berlière 3 Bruno Vande Berg 1 William D Hoore 4 Baudouin Maldague 1 Received July 11, 2002; accepted after revision October 28, 2002. 1 Department
Isabelle Leconte 1 Chantal Feger 1 Christine Galant 2 Martine Berlière 3 Bruno Vande Berg 1 William D Hoore 4 Baudouin Maldague 1 Received July 11, 2002; accepted after revision October 28, 2002. 1 Department
A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS
 A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS Hideaki Shirai M.D., M. Sakurai M.D., K. Yoshida M.D., N. Usuda M.D., H. Masuoka M.D., I. Shimokawara M.D, K. Asaishi M.D. Sapporo Kotoni Breast Clinic,
A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS Hideaki Shirai M.D., M. Sakurai M.D., K. Yoshida M.D., N. Usuda M.D., H. Masuoka M.D., I. Shimokawara M.D, K. Asaishi M.D. Sapporo Kotoni Breast Clinic,
BREAST MRI. Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
Diagnostic value of preoperative axillary lymph node ultrasound assessment in patients with breast cancer qualified for sentinel lymph node biopsy
 Original paper Videosurgery Diagnostic value of preoperative axillary lymph node ultrasound assessment in patients with breast cancer qualified for sentinel lymph node biopsy Tomasz Nowikiewicz 1, Adam
Original paper Videosurgery Diagnostic value of preoperative axillary lymph node ultrasound assessment in patients with breast cancer qualified for sentinel lymph node biopsy Tomasz Nowikiewicz 1, Adam
The Use of Unenhanced Doppler Sonography in the Evaluation of Solid Breast Lesions
 Unenhanced Doppler Sonography of Solid Breast Lesions Jose L. del Cura 1 Elena Elizagaray Rosa Zabala Ana Legórburu Domingo Grande del Cura JL, Elizagaray E, Zabala R, Legórburu A, Grande D Received July
Unenhanced Doppler Sonography of Solid Breast Lesions Jose L. del Cura 1 Elena Elizagaray Rosa Zabala Ana Legórburu Domingo Grande del Cura JL, Elizagaray E, Zabala R, Legórburu A, Grande D Received July
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Role of Ultrasonography And Doppler in Evaluation of Neck Nodes And Differentiating Benign from Malignant Nodes
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IX (November. 2016), PP 71-80 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Ultrasonography And Doppler
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IX (November. 2016), PP 71-80 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Ultrasonography And Doppler
Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonographic features for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a singlecenter retrospective study
 Liu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:32 DOI 10.1186/s12957-017-1099-2 RESEARCH Open Access Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonographic features for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid
Liu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:32 DOI 10.1186/s12957-017-1099-2 RESEARCH Open Access Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonographic features for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid
