Ultrasound and MRI evaluation of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer
|
|
|
- Bernard Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH IN BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE ISSN: X Volume 3, Issue Original Research Article DOI: Ultrasound and MRI evaluation of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer *Ramesh Chander, **Lohit Shivashish, *** Jatinder Pal Singh Multani, **** N.S. Neki * Professor & Head, **Junior Resident, *** Associate Professor, Dept. of Radiodiagnosis, Govt. Medical College, Amritsar, India, ****Professor, Dept of Medicine, Govt. Medical College/Guru Nanak Dev Hospital, Amritsar, India Corresponding Author: Dr. Lohit Shivashish, Junior Resident, Dept. of Radiodiagnosis, Govt. Medical College, Amritsar, India, lohitshivashish7@gmail.com Abstract Aims and objectives: 1. To evaluate the status of axillary lymph nodes by ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in newly diagnosed breast cancer patients. 2. To assess accuracy of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Materials and Methods: 60 patients of biopsy proven breast carcinoma were subjected to clinical examination, ultrasound and multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of axilla for lymph node status and further evaluated by histopathology. Observations : Status of axillary lymph nodes is one of the most important prognostic factors for breast cancer survival and.axillary staging of patients with early-stage breast cancer is essential in the treatment planning. The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of preoperative ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for detection of metastatic axillary lymph node in breast cancer cases. Conclusion: With high sensitivity and specificity, USG and MRI are effective methods to differentiate metastatic axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients, which can provide useful information for surgical procedure selection. Keywords: Usg, MRI, Axillary lymph node metastasis, Breast cancer. Introduction Status of axillary lymph nodes is one of the most important prognostic factors for breast cancer survival and is necessary for making treatment decisions. Another advantage is that, if the surgeon is aware of metastatic axillary nodes prior to surgery, the axillary lymph nodes dissections can be well planned. 1 9 Several imaging techniques are currently available for preoperative assessment of lymph node status including mammography, ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission 2 tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT). Axillary ultrasonography is useful in excluding nodal
2 stage N2 and N3 (according to TNM staging) invasive ductal metastases. 3 Physical examination It is the oldest and simplest non-surgical method for evaluation of Axillary lymph node status. The limitation with physical examination is that it is highly inaccurate and having very low sensitivity and high false positive rate. In few studies, sensitivity and false positive rate are 31.6%, and 53.6% respectively. 4,5 Ultrasonography- Provides the best means to assess the axillary nodes, gives its relatively sensitive and highly specific capabilities. A normal or benignappearing axillary lymph node should have an oval or lobulated shape and a smooth, well-defined margin. The lobulated shape is because of concurrent constrictions and bulges of both the cortex and fatty hilum. The cortex should be slightly hypoechoic and uniformly thin, measuring 3 mm or less. Nodes that meet this description have a very high negative predictive value for excluding metastases. The echogenic hilum should constitute the major part of the node. Arterial flow in the hilum can be demonstrated with colour doppler imaging. Morphologic criteria such as cortical thickening, hilar effacement and non-hilar cortical blood flow are more important than size criteria in the identification of metastases. Characteristics of lymph nodes that are concerning for malignancy besides overall size include round shape, absence of the fatty hilum and increased concentric or focal cortical thickness greater than 3 mm, all being predictors of malignancy. Various studies have shown that axillary ultrasound has a sensitivity and specificity up to 73% and 96% respectively for detecting malignant involvement of nodes. It also helps in guiding biopsies of axillary lymph nodes, if needed Fig showing Normal lymph node: On ultrasound, lymph nodes typically are smooth, gently lobulated ovals with a hypoechoic cortex measuring less than 3 mm in thickness with a central echogenic hilum Fig showing abnormal lymph nodes: characteristics concerning for malignancy: a. absence of the fatty hilum and b. increased focal cortical thickness greater than 3 mm with colour Doppler US that shows hyperaemic blood flow in the hilum and central cortex or abnormal (non-hilar cortical) blood flow. 10
3 USG is the most widely used method for the evaluation of lymph nodes. Moreover, preoperative lymph node staging with US combined with either fine needle aspiration or core needle biopsy can achieve high diagnostic accuracy. The assessment of axillary nodal status, size, morphology, cortical thickness, and vascularity are used as feasible diagnostic criteria. Of these criteria, longitudinal-transverse (LT) axis ratio, concentric or eccentric cortical thickening and absent or displaced fatty hilum on gray scale US and higher peripheral vascularity on power Doppler US are reported as the most reliable criteria for predicting metastatic lymph nodes MRI -The preoperative MR images of patients with diagnosis of breast cancer are evaluated to determine axillary lymph node status. Axillary lymph node size, long axis to short axis ratio, cortical thickness to anteroposterior (AP) diameter ratio, the presence of a fatty hilum and contrast enhancing patterns (homogenous or heterogenous) on postcontrast series are noted. Additionally, the presence of a comet tail sign on postcontrast series is also noted. Comet tail sign was first described for breast lesions by Kaiser. It is a tail extending from an enhancing breast lesion into the parenchyma. The tail is usually directed towards nipple or the ductal system. This sign might represent ductal infiltration or angiogenesis. Diffusion weighted imaging is important predictor of axillary lymphnode metastasis Aims and Objective 1. To evaluate the status of axillary lymph nodes by ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in newly diagnosed breast cancer patients. 2. To assess accuracy of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of axillary node status, in comparison with surgical and histopathological findings. Materials and Methods This study was conducted after taking approval from Institutional Ethics Committee, Govt. medical college, Amritsar. Study design: Observation study Study setting: The proposed study was carried out in the department of Radiodiagnosis and Imaging in collaboration with department of surgery, pathology 11 and radiotherapy, Government Medical College, Amritsar. Subject and inclusion criteria: Ultrasound and MRI study was planned to include 60 patients of FNAC biopsy proven breast cancer for evaluation of axillary lymph node status. Before recruitment in present study written informed consent of patient was taken. Exclusion criteria: 1) Patients with metallic implants and other contraindications of MRI. 2) Patients having allergy to MRI Contrast. 3) Patients not proved breast cancer on histopathology. Methodology: All patients underwent clinical examination, ultrasound and multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of axilla for lymph node status. After clinical palpation patients were categorised into two groups. Those patients who had clinically palpable axillary lymph nodes were categorised as Group A, while those who had clinically non palpable lymph nodes were categorised as Group B. We performed ultrasound and MRI examination of breast and bilateral axilla in all sixty patients. Clinical examination: All enrolled patients underwent clinical evaluation for the breast and the axilla.all palpable axillary lymph nodes on clinical examination were assumed as positive for metastasis. If a node was not palpable, itwas assumed as negative for metastasis. Ultrasound: Ultrasound examination was performed using an US scanner MINDRAY DC-8 Machine and PHILIPS HD 11-XEwith linear array transducers of frequency 9-12 MHz. On ultrasound primary tumour size, shape, margin, echotexture and calcification was evaluated. All the following three levels of axillary lymph nodes were examined bilaterally.
4 Any abnormal lymph node found in these areas was noted as suspicious for metastasis. Lymph node of size < 10 mm in short axis on ultrasound was assumed as negative for metastasis.the criteria for abnormal lymph nodes include round shape, a long to short axis ratio < 1,thickening or asymmetry of cortex, hypoechoic echotexture and loss of central fatty hilum. Magnetic resonance imaging: The magnetic resonance imaging study was performed using a 1.5T MR scanner SEIMENS AERA in our department. All patients were scanned in the standard prone position, using dedicated bilateral breast coil.t1w, T2W, DWI and T2 STIR images of breast and axillary lymph nodes were obtained in transverse and sagittal planes and T2 scan obtained in coronal plane. Following the conventional MRI, post contrast sequence was obtained in axial plane following intravenous administration of Gd-DTPA (0.1 mmol/kg). The study images were taken after contrast. All the three level of axillary lymph nodes were examined and lymph nodes suspicious for metastasis were noted. The criteria of lymph nodes for metastatic involvement included size >10 mm, rounded shape, eccentric cortical hypertrophy, abnormal diffusion and abnormal signal intensity enhancement. All lymph nodes detected as abnormal on ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging were advised for histopathology. Observations Table 1 below depicts the age distribution of the female patients in our study. The majority of the patients in our study belonged to the younger age group. 43 patients (71.6%) of the total 60 patients had age between years. The above table depict that 38 of the total 60 patients (63.34%) had lesion in their right breast, compared to only 22 patients who had a lesion in their left breast (36.66%). None of the 60 patients had bilateral lesions. Table 1 Patient distribution based on age group Age (years) No Table 2 Site No. of patients Right breast 38 Left breast 22 Table 3 Diagnostic performance result of ultrasound in axillary lymph nodes detection in both group A and group B' (clinically palpable and non palpable axilla) patients (n=60) Ultrasound diagnosis of axillary lymph Histopathology positive Histopathology negative node Abnormal Normal
5 In 60 patients including both clinically palpable and non-palpable patients, 30 patients (50.0%) had abnormal axillary nodes on ultrasound. Of these 30 patients, 25 patients (83.34%) had metastatic nodes on histopathology. In 16 patients (26.67%) who had normal axillary nodes on ultrasound, 3 patients (18.75%) had metastatic nodes on histopathology. Table 4 Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound in detection of axillary lymph node metastasis in both in both group a and group b (clinically palpable and non palpable) axillary nodes.(n=60) Sensitivity Specificity Positive predictive value Negative predictive value 89.28% 72.23% 83.34% 81.25% X 2 : 10.8; df: 1; p=0.001 Thus the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and P value of ultrasound in axillary lymph node detection was 89.28%, 72.23%, 83.34%, 81.25% and respectively in both clinically palpable and non palpable axillary node patients. All detected axillary lymph nodes on MRI were sent for histopathology and compare with histopathology diagnosis. Table 5 Diagnostic performance result of MRI in axillary lymph nodes detection m both group a and group b (clinically palpable and non palpable axilla) :(n=60) MRI diagnosis of axillary lymph nodes Histopathology positive Histopathology negative Abnormal Normal In both clinically palpable and non palpable axillary nodes patients, MRI detected abnormal lymph nodes in 32 patients (53.34%). Of these 32 patients, 27 patients (84.37%) had metastatic nodes confirmed on histopathology. In 16 patients (26.67%) with norm al axillary nodes on MRI, 4 patients (25.0%) had metastatic axillary nodes confirmed on histopathology. Table 6 Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detection of axillary lymph node metastasis in both group a and group b (both clinically palpable and non palpable) patients.(n=60) Sensitivity Specificity Positive predictive value Negative predictive value 87.09% 70.58% 84.37% 75.0% X 2 : 16.4; df: 1; p=0.001 Thus sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and p value of MRI in both clinically palpable and clinically non palpable axilla was 87.09%, 70.58%, 84.37%, 75.0 % and respectively as described above. Table 7 Diagnostic performance result of combined ultrasound and MRI in axillary lymph nodes detection in both group A and group B (clinically palpable and non paipable axilla) patients: (n=60) Imaging features of abnormal axillary node Histopathology positive Histopathology negative Positive Negative
6 In both clinically palpable and non palpable axillary nodes patients MRI and ultrasound as a combined modalities detected abnormal lymph nodes in 36 patients (60.0%). Out of 36 patients, 33 patients (91.67%) had metastatic nodes on histopathology. In 14 patients (23.34% ) out of 60 patients with normal axillary nodes, one patient (7.14%) had metastatic axillary node on histopathology. Table 8 Diagnostic accuracy of combined MRI and ultrasound in detection of axillary lymph node metastasis in both group A and group B (clinically palpable and non palpable axillary nodes) patients.(n=60) Sensitivity Specificity Positive predictive value Negative predictive value 97.05% 81.25% 91.67% 92.85% X 2 : 33.1; df: 1; p=0.001 Thus as a combined modalities, ultrasound and MRI had sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and p value of 97.05%, 81.25%, 91.67%, 92.85% and respectively in both clinically palpable and non palpable axillary node patients. Table 9 Comparative diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound, MRI and combined modalities in both group A and group B (clinically palpable and non palpable axillary nodes) patients (n=60) Cases Accuracy Ultrasound MRI Ultrasound +MRI sensitivity % 87.09% 97.05% specificity 72.23% 70.58% 81.25% (a) (b) (c) (d) 70 yr / female with Right breast lump/mass for 6 months.images shows-(a) Ultrasound image of right breast shows a hypoechoic mass lesion in right outer upper quadrant extending to retroareolar region. (b) Ultrasound image of right axilla shows hypoechoic level II axillary lymphnode with loss of central fatty hilum. (c) Breast mass lesion shows homogenous enhancement after contrast administration.(d)axillary lymphnode shows homogenous enhancement after contrast administration. 14
7 (a) (b) (c) (d) 50 yr / female patient with Right breast lump/mass for 1 year. Images shows-(a) Ultrasound image of right breast shows hypoechoic mass lesions seen in retroareolar region. (b) Ultrasound image of right axilla shows hypoechoic level II axillary lymphnode with loss of central fatty hilum. (c) Breast mass lesion shows homogenous enhancement after contrast administration. (d) Axillary lymphnode shows homogenous enhancement after contrast administration. Discussion The present study was conducted on 60 patients who presented with breast cancer in the department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College & Hospital, Amritsar. USG - In our study, we included 60 patients of primary breast cancer. In total of 60 patients (when combined Group A and Group B), 30 patients had abnormal axillary lymph nodes on ultrasound and 16 patients had normal axillary lymph nodes. Of these 30 patients, 25 patients had metastatic nodes confirmed on histopathology, while in 16 patients who had normal axillary nodes on ultrasound, 3 patients had confirmed metastatic nodes on histopathology. Thus sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and p value of diagnosing metastatic lymph nodes on axillary ultrasound was 89.28%, 72.23%, 83.34%, 81.25% and respectively. 15
8 Study done on detection of abnormal axillary lymph node on USG Sensitivity Table 10 Specificity Positive predictive value Negative predictive value Strauss HG et al. 90% 91.7% - - Mainiero MB et al. 59% 100% - - Lee B et al. 53.7% 85.1% 81.0% 60.0% Stachs A et al. 47.6% 95.7% 85.9% 77.0% Koehler KE et al. 53.6% 75.5% 77.3% 51.3% Ha SM et al. 60% 62.4% - - Present Study 89.28% 72.23% 83.34% 81.25% Our study shows comparable or better sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound in detection of axillary nodes metastasis than previous studies done by StachsA et al, Koehler KE et al, Mainiero et al., Lee B et al., Ha SM et al. and similar sensitivity to Strauss HG et al. and specificity shows similar to previous studies by Koehler K et al. MRI -In our study we evaluated axillary nodes with MRI and compared with histological diagnosis. In total group of 60 patients, MRI detected abnormal lymph nodes in 32 patients, of which, 27 patients had metastatic nodes confirmed on histopathology. In 16 patients, who had normal axillary nodes on MRI. A patients had metastatic nodes confirmed on histopathology. Thus, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive valueand p value of MRI in detection of axillary lymph nodes metastasis was 87.09%, 70.58%,84.37%, 75.0% and respectively. Study done on detection of abnormal axillary lymph node on MRI Table 11 Sensitivity Specificity Positive predictive value Negative predictive value Yoshimura G et al. 79% 93% - - Murray AD et al. 100% 56% 38% 100% Memarsadeghi M et al. 100% 98% - - He N et al. 66.4% 94% - - Kim EJ et al. 75.8% 83.9% - - Ha SM et al. 57.3% 72% 78.18% - Zhou P et al. 95% 95% - - Present Study 87.09% 70.58% 84.37% 75.0% Our study shows comparable or better sensitivity and specificity for lymph node metastasis detection to previous studies by Yoshimura G et al., He N et al., Kim EJ et al., Ha SM et al. and specificity shows similar result to Ha SM et al. study. Additionally. Combined USG AND MRI - In all 60 patients (clinically palpable and non-palpable) combined modalities detected abnormal lymph nodes in 36 patients, of which 33 patients had metastatic nodes on histopathology. In our study of the 14 patients, who had normal axillary nodes on combined modalities, only one patient had metastatic nodes on histopathology. Thus, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and p value of combined modalities was 97.05%, %, 91.67%, % and respectively. Thus, the results of our study shows better sensitivity and specificity in comparison to studies done by Valente SA and Ha SMet al. The sensitivity and specificity of combined modalities was better than individual modalities in detection of axillary lymph node metastasis in our study. 16
9 Study done on detection of abnormal axillary lymph node on USG and MRI Table 12 sensitivity specificity positive predictive value negative predictive value Valente SA et al % 89 % - - Ha SM et al. 65.3% 60.4% - - Present Study 97.05% 81.25% 91.67% 92.85% Summary and Conclusions We performed a prospective study in 60 patients with breast cancer and evaluated the role of ultrasound and MRI in detection of axillary node metastasis in breast cancer patients. The accuracy of ultrasound and MRI in detection of axillary node metastases was correlated with surgical and histopathological findings. The majority of the patients in our study belonged to the age group years. 43 of the total 60 patients (71.6%) had age between years. When compared with surgical and histopathological finding, ultrasound had sensitivity and specificity of % and % in detection of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer patient, MRI had sensitivity and specificity of % and % respectively for similar detection. When ultrasound and MRI were used as combine modalities, the sensitivity and specificity of combined modalities was % and % respectively. MRI and ultrasound were found to be equally accurate in detection of axillary node metastasis in breast cancer. When used as combined modalities the accuracy of imaging increases significantly in detection of axillary node metastasis in breast cancer. References 1. Valente SA, Levine GM, Silverstein MJ, Rayhanabad JA, Weng-Grumley JG, LingyunJi et al. Accuracy of predicting axillary lymph node positivity by physical examination, mammography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging. Ann surg oncol. 2012: Choi YJ, Shin YD, Kang YH, Lee MS, Lee MK, Cho BS et al. The effects of preoperative 18F- FDG PET/CT in breast cancer patients in comparison to the conventional imaging study. Journal of breast cancer. 2012;15(4): Neal CH, Daly CP, Nees AV, Helvie MA. Can preoperative axillary US help exclude N2 and N3 metastatic breast cancer?. Radiology. 2010;257(2): Specht MC, Fey JV, Borgen PI, Cody III HS. Is the clinically positive axilla in breast cancer really a contraindication to sentinel lymph node biopsy? Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 2005;200(1): Lanng C, Hoff mann J, Galatius H. Assessment of clinical palpation of the axilla as a criterion for performing the sentinel node procedure in breast cancer. Euro J Surg Oncol. 2007;33(3): Shetty MK, Carpenter WS. Sonographic evaluation of isolated abnormal axillary lymph nodes identified on mammograms. J Ultrasound Med. 2004;23(1): Bedi DG, Krishnamurthy R, Krishnamurthy S, Edeiken BS, Le-Petross H, Fornage BD et al. Cortical morphologic features of axillary lymph nodes as a predictor of metastasis in breast cancer: in vitro sonographic study. American Journal of Roentgenology Sep;191(3): Choi YJ, Ko EY, Han BK, Shin JH, Kang SS, Hahn SY. High-resolution ultrasonographic features of axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer. The Breast. 2009;18(2): Deurloo EE, Tanis PJ, Gilhuijs KG, Muller SH, Kröger R, Peterse JL et al. Reduction in the number of sentinel lymph node procedures by preoperative ultrasonography of the axilla in breast cancer. European Journal of Cancer. 2003;39(8): Gogas J, Markopoulos C, Kouskos E, Gogas H, Mantas D, Antonopoulou Z et al. Granular cell tumor of the breast: a rare lesion resembling breast cancer. European journal of gynaecological oncology. 2002;23(4): Lee MC, Joh JE, Chau A. Axillary staging prior to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The roles of sentinel lymph node biopsy and axillary ultrasonography. Cancer Control. 2012;19(4):
10 12. De Kanter AY, van Eijck CH, van Geel AN, Kruijt RH, Henzen SC, Paul MA et al. Multicentre study of ultrasonographically guided axillary node biopsy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 1999;86: Tate JJ, Lewis V, Archer T, Guyer PG, Royle GT, Taylor I. Ultrasound detection of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1989;15: Damera A, Evans AJ, Cornford EJ, Wilson AR, Burrell HC, James JJ et al. Diagnosis of axillary nodal metastases by ultrasound-guided core biopsy in primary operable breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89: Lernevall A. Imaging of axillary lymph nodes. Acta Oncol. 2000;39: Yang WT, Metreweli C, Lam PK, Chang J. Benign and malignant breast masses and axillary nodes: evaluation with echo-enhanced color power Doppler US. Radiology. 2001;220: Luciani A, Pigneur F, Ghozali F, Dao TH, Cunin P, Meyblum E et al. Ex vivo MRI of axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer. European journal of radiology. 2009;69(1): Chung J, Youk JH, Kim JA, Gweon HM, Kim EK, Ryu YH et al. Role of diffusion-weighted MRI: predicting axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer. Acta Radiologica. 2014;55(8): Quick Response Code Access this Article in Online Website: Subject: Medical Sciences How to cite this article: Ramesh Chander, Lohit Shivashish, Jatinder Pal Singh Multani, N.S. Neki. (2018). Ultrasound and MRI evaluation of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer. Int. J. Curr. Res. Biol. Med. 3(12): DOI: 18
Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary Lymph Node Involvement In Breast Carcinoma
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II. (Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II. (Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary
The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes
 Yonsei Med J 49(2):249-254, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.249 The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes Ki Hong Kim, 1 Eun Ju Son, 1 Eun-Kyung Kim,
Yonsei Med J 49(2):249-254, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.249 The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes Ki Hong Kim, 1 Eun Ju Son, 1 Eun-Kyung Kim,
EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES AFTER NEOADJUVANT SYSTEMIC THERAPY KIM, MIN JUNG SEVERANCE HOSPITAL, YONSEI UNIVERSITY
 EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES AFTER NEOADJUVANT SYSTEMIC THERAPY KIM, MIN JUNG SEVERANCE HOSPITAL, YONSEI UNIVERSITY AXILLARY LYMPH NODE METASTASIS Axillary lymph node metastasis is one of the most
EVALUATION OF AXILLARY LYMPH NODES AFTER NEOADJUVANT SYSTEMIC THERAPY KIM, MIN JUNG SEVERANCE HOSPITAL, YONSEI UNIVERSITY AXILLARY LYMPH NODE METASTASIS Axillary lymph node metastasis is one of the most
Journal of Breast Cancer
 Journal of Breast Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Cancer 2012 March; 15(1): 65-70 Classification of Metastatic versus Non-Metastatic Axillary Nodes in Breast Cancer Patients: Value of Cortex-Hilum Area
Journal of Breast Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Cancer 2012 March; 15(1): 65-70 Classification of Metastatic versus Non-Metastatic Axillary Nodes in Breast Cancer Patients: Value of Cortex-Hilum Area
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Mainiero et al. Ultrasound-Guided FN in Breast Cancer Patients Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Martha B. Mainiero 1 Christina M. Cinelli 2 Susan L. Koelliker
Women s Imaging Original Research Mainiero et al. Ultrasound-Guided FN in Breast Cancer Patients Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Martha B. Mainiero 1 Christina M. Cinelli 2 Susan L. Koelliker
Axillary ultrasound in patients with breast cancer: which lymph nodes should be targeted for fine needle aspiration?
 Axillary ultrasound in patients with breast cancer: which lymph nodes should be targeted for fine needle aspiration? Poster No.: C-0289 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. J. Diaz-Ruiz,
Axillary ultrasound in patients with breast cancer: which lymph nodes should be targeted for fine needle aspiration? Poster No.: C-0289 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. J. Diaz-Ruiz,
Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Cytological Correlation
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/74 Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Cytological Correlation Suresh Kumar 1, Sonjjay Pande
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/74 Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Cytological Correlation Suresh Kumar 1, Sonjjay Pande
Study of validity of ultrasonographic diagnosis in relation to Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) diagnosis
 Original article: Study of validity of ultrasonographic diagnosis in relation to Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) diagnosis *Dr Rajvi Matalia, ** Dr Y.P.Sachdev, ***Dr D.S.Kulkarni *Junior Resident,
Original article: Study of validity of ultrasonographic diagnosis in relation to Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) diagnosis *Dr Rajvi Matalia, ** Dr Y.P.Sachdev, ***Dr D.S.Kulkarni *Junior Resident,
Original Article. J Fac Med Baghdad 193. Introduction:
 Original Article The value of Gray scale, color doppler and ultrasound guided- FNA in detection metastasis to the axillary lymph node in patient with primary breast cancer. * Qusay A. Fahad* Enam A.Al
Original Article The value of Gray scale, color doppler and ultrasound guided- FNA in detection metastasis to the axillary lymph node in patient with primary breast cancer. * Qusay A. Fahad* Enam A.Al
Clinical Study Accuracy of Individual Descriptors and Grading of Nodal Involvement by Axillary Ultrasound in Patients of Breast Cancer
 International Breast Cancer Volume 2013, Article ID 930596, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/930596 Clinical Study Accuracy of Individual Descriptors and Grading of Nodal Involvement by Axillary
International Breast Cancer Volume 2013, Article ID 930596, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/930596 Clinical Study Accuracy of Individual Descriptors and Grading of Nodal Involvement by Axillary
The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1
 The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1 Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Asiry Hwang, M.D., Hye-Young Choi, M.D., Seung Yon Baek, M.D. Purpose: We evaluated the
The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1 Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Asiry Hwang, M.D., Hye-Young Choi, M.D., Seung Yon Baek, M.D. Purpose: We evaluated the
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Role of positron emission mammography (PEM) for assessment of axillary lymph node status in patients with breast cancer
 Role of positron emission mammography (PEM) for assessment of axillary lymph node status in patients with breast cancer Poster No.: C-1260 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: K. M. Kulkarni,
Role of positron emission mammography (PEM) for assessment of axillary lymph node status in patients with breast cancer Poster No.: C-1260 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: K. M. Kulkarni,
Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm
 Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm Belinda Curpen, MD, FRCPC; Tetyana Dushenkovska; Mia Skarpathiotakis MD, FRCPC; Carrie Betel, MD, FRCPC; Kalesha Hack, MD, FRCPC; Lara Richmond,
Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm Belinda Curpen, MD, FRCPC; Tetyana Dushenkovska; Mia Skarpathiotakis MD, FRCPC; Carrie Betel, MD, FRCPC; Kalesha Hack, MD, FRCPC; Lara Richmond,
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 10
 Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography
 Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes
 ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes Poster No.: B-0158 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper F. Houari, O. Lucidarme, J. Gabarre, F. Charlotte, C. Pellot- Barakat, M. Lefort,
ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes Poster No.: B-0158 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper F. Houari, O. Lucidarme, J. Gabarre, F. Charlotte, C. Pellot- Barakat, M. Lefort,
Index. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
 Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer
 Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer Chiun Sheng Huang, MD, PhD, MPH Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Director of Breast Care Center National Taiwan University Hospital
Ultrasound or FNA for Predicting Node Positive in Breast Cancer Chiun Sheng Huang, MD, PhD, MPH Professor and Chairman Department of Surgery Director of Breast Care Center National Taiwan University Hospital
Ductal carcinoma in situ, underestimation, ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy
 Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
J.N., PRADHAN A.K., KUSTA M.K. ABSTRACT
 Axillary Ultrasound Examination in the Selection of Carcinoma of Breast Patients for Sentinel Node Biopsy - A Prospective Study MISRA J.N., PRADHAN A.K., KUSTA M.K. ABSTRACT Background: Axillary lymph
Axillary Ultrasound Examination in the Selection of Carcinoma of Breast Patients for Sentinel Node Biopsy - A Prospective Study MISRA J.N., PRADHAN A.K., KUSTA M.K. ABSTRACT Background: Axillary lymph
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings
 Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Role of ultrasonography in recognition of malignant potential of thyroid nodules on the basis of their internal composition
 Role of ultrasonography in recognition of malignant potential of thyroid nodules on the basis of their internal composition Nodular thyroid is a common clinical entity. All patients were evaluated by grey
Role of ultrasonography in recognition of malignant potential of thyroid nodules on the basis of their internal composition Nodular thyroid is a common clinical entity. All patients were evaluated by grey
The American Society of Breast Surgeons
 The American Journal of Surgery (2008) 196, 477 482 The American Society of Breast Surgeons Scientific Presentation Award: The combination of axillary ultrasound and ultrasound-guided biopsy is an accurate
The American Journal of Surgery (2008) 196, 477 482 The American Society of Breast Surgeons Scientific Presentation Award: The combination of axillary ultrasound and ultrasound-guided biopsy is an accurate
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology
 American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
Evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumor and axillary lymph nodes in locally advanced breast cancer: a study of 50 patients
 Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-0005-4 Evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumor and axillary lymph nodes in locally advanced breast cancer: a study of 50 patients
Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-0005-4 Evaluation of the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on tumor and axillary lymph nodes in locally advanced breast cancer: a study of 50 patients
TÍTULO The role of FUSION between MRI and PET-CT as preoperative staging in breast cancer
 TÍTULO The role of FUSION between MRI and PET-CT as preoperative staging in breast cancer Páramo M, Zalazar R, Elizalde A, Pina-Insausti L, Vigil C, Hernández M, Rodríguez-Fraile M Clínica Universidad
TÍTULO The role of FUSION between MRI and PET-CT as preoperative staging in breast cancer Páramo M, Zalazar R, Elizalde A, Pina-Insausti L, Vigil C, Hernández M, Rodríguez-Fraile M Clínica Universidad
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
ISSN X (Print) Original Research Article
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 17; 5(11D):11-1 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 17; 5(11D):11-1 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 39/ May 14, 2015 Page 6787
 ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
BI-RADS and Breast MRI. Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018
 BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 03 Page March 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i3.135 Diagnosis of Carcinoma Prostate Based
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i3.135 Diagnosis of Carcinoma Prostate Based
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines. Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting
 Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting Approved by Council June 2018 Approved: June 2018 Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting Approved by Council June 2018 Approved: June 2018 Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting
Date of Preparation: December 8, 2017 A. GENERAL INFORMATION. 1. Name: Eun Sook KO Citizenship: Republic of Korea
 Date of Preparation: December 8, 2017 A. GENERAL INFORMATION 1. Name: Eun Sook KO 2. Email: mathilda0330@gmail.com 3. Citizenship: Republic of Korea B. EDUCATIONAL & TRAINING BACKGROUND Degree Institution
Date of Preparation: December 8, 2017 A. GENERAL INFORMATION 1. Name: Eun Sook KO 2. Email: mathilda0330@gmail.com 3. Citizenship: Republic of Korea B. EDUCATIONAL & TRAINING BACKGROUND Degree Institution
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions?
 Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions? Poster No.: C-0332 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Radiologic Findings of Mucocele-like Tumors of the breast: Can we differentiate pure benign from associated with high risk lesions? Poster No.: C-0332 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging
 Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
Ultrasonogrpahic examination of peripheral nerves in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 12-2018 Ultrasonogrpahic
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 12-2018 Ultrasonogrpahic
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Cervical Lymph Nodes
 Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
Cairo/EG, Khartoum/SD, London/UK Biological effects, Diagnostic procedure, Ultrasound, Mammography, Breast /ecr2015/C-0107
 Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS
 A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS Hideaki Shirai M.D., M. Sakurai M.D., K. Yoshida M.D., N. Usuda M.D., H. Masuoka M.D., I. Shimokawara M.D, K. Asaishi M.D. Sapporo Kotoni Breast Clinic,
A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS Hideaki Shirai M.D., M. Sakurai M.D., K. Yoshida M.D., N. Usuda M.D., H. Masuoka M.D., I. Shimokawara M.D, K. Asaishi M.D. Sapporo Kotoni Breast Clinic,
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 09/Jan 29, 2015 Page 1533
 EVALUATION OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES BY ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN CORRELATION WITH FNAC Aaditya Kumar Singh 1, Purnima Hegde 2, Anil Kumar Sakalecha 3, T. N. Suresh 4, P. N. Sreeramulu 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
EVALUATION OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES BY ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN CORRELATION WITH FNAC Aaditya Kumar Singh 1, Purnima Hegde 2, Anil Kumar Sakalecha 3, T. N. Suresh 4, P. N. Sreeramulu 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Diagnosis and staging of breast cancer and multidisciplinary team working
 1 Diagnosis and staging of breast cancer and multidisciplinary team working Common symptoms and signs Over 90% of breast cancers (BCs) are local or regional when first detected. At least 60% of patients
1 Diagnosis and staging of breast cancer and multidisciplinary team working Common symptoms and signs Over 90% of breast cancers (BCs) are local or regional when first detected. At least 60% of patients
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient. Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester
 Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
Radiological assessment of neoadjuvent chemotherapy for breast cancer
 XV th Balkan Congress of Radiology Budapest, Hungary, October 12 15, 2017 Radiological assessment of neoadjuvent chemotherapy for breast cancer V. Bešlagić C l i n i c o f R a d i o l o g y, U n i v e
XV th Balkan Congress of Radiology Budapest, Hungary, October 12 15, 2017 Radiological assessment of neoadjuvent chemotherapy for breast cancer V. Bešlagić C l i n i c o f R a d i o l o g y, U n i v e
Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM am am : Clinician s requirements from breast imaging
 Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 Day one, 2 nd November BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 9.00 AM 9.10 am Introduction 9.10 am - 9.30 am : Clinician
Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 Day one, 2 nd November BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 9.00 AM 9.10 am Introduction 9.10 am - 9.30 am : Clinician
Toru Nakamura 1, Takashi Fukutomi 1, Hitoshi Tsuda 2, Sadako Akashi-Tanaka 1, Kaneyuki Matsuo 1, Chikako Shimizu 1 and Kunihisa Miyakawa 3
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer
 Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach. Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina
 Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS)
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Abbreviated Key Title: Sch. J. App. Med. Sci. Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher A Unit of Scholars Academic and Scientific Society, India www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Abbreviated Key Title: Sch. J. App. Med. Sci. Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher A Unit of Scholars Academic and Scientific Society, India www.saspublisher.com
Evaluation of breast lesions with ultrasonography and colour doppler
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of breast lesions with USG and colour Doppler Evaluation of breast lesions with ultrasonography and colour doppler Falguni Shah 1, Hemangi Patel 2*, Nila Gandhi 3, Sudhir Singh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of breast lesions with USG and colour Doppler Evaluation of breast lesions with ultrasonography and colour doppler Falguni Shah 1, Hemangi Patel 2*, Nila Gandhi 3, Sudhir Singh
Fine needle aspiration cytology guided by ultrasound of suspicious axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients
 Hematology & Medical Oncology Research Article ISSN: 2398-8495 Fine needle aspiration cytology guided by ultrasound of suspicious axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients Waldeir de Almeida Júnior
Hematology & Medical Oncology Research Article ISSN: 2398-8495 Fine needle aspiration cytology guided by ultrasound of suspicious axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients Waldeir de Almeida Júnior
Utility of Preoperative Ultrasound for Predicting pn2 or Higher Stage Axillary Lymph Node Involvement in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer
 Women s Imaging Original Research Abe et al. Preoperative Ultrasound to Predict Axillary Lymph Node Involvement Women s Imaging Original Research Hiroyuki Abe 1 David Schacht Charlene A. Sennett Gillian
Women s Imaging Original Research Abe et al. Preoperative Ultrasound to Predict Axillary Lymph Node Involvement Women s Imaging Original Research Hiroyuki Abe 1 David Schacht Charlene A. Sennett Gillian
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
SBI/ACR Breast Imaging Symposium April 7-10, 2016 Austin, TX
 SBI/ACR Breast Imaging Symposium April 7-10, 2016 Austin, TX SAM Session 2 Friday, April 8 2.5 SAM Credits Thank you for completing this SAM activity. Below you will find correct responses, rationales,
SBI/ACR Breast Imaging Symposium April 7-10, 2016 Austin, TX SAM Session 2 Friday, April 8 2.5 SAM Credits Thank you for completing this SAM activity. Below you will find correct responses, rationales,
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Journal of Breast Cancer
 CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2016 December; 19(4): 459-464 Increased Malignant Microcalcifications after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in dvanced reast Cancer Gi Won Shin, Young Mi Park,
CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2016 December; 19(4): 459-464 Increased Malignant Microcalcifications after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in dvanced reast Cancer Gi Won Shin, Young Mi Park,
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Diagnostic Accuracy of Axillary Ultrasonography Compared with Intra-operative Pathological Findings in Patients with Breast Cancer
 DOI:10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3615 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:06/09/2018 Acceptance:10/13/2018 Diagnostic Accuracy of Axillary Ultrasonography Compared with Intra-operative Pathological
DOI:10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3615 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:06/09/2018 Acceptance:10/13/2018 Diagnostic Accuracy of Axillary Ultrasonography Compared with Intra-operative Pathological
Pre- operative staging of the axilla
 Pre- operative staging of the axilla Anthony J Maxwell University Hospital of South Manchester Outline Why stage the axilla? Optimising conventional US & needle sampling Other imaging and needle sampling
Pre- operative staging of the axilla Anthony J Maxwell University Hospital of South Manchester Outline Why stage the axilla? Optimising conventional US & needle sampling Other imaging and needle sampling
Feasibility of using negative ultrasonography results of axillary lymph nodes to predict sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients
 Received: 21 April 2018 Revised: 14 May 2018 DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1606 Accepted: 14 May 2018 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Feasibility of using negative ultrasonography results of axillary lymph nodes to predict sentinel
Received: 21 April 2018 Revised: 14 May 2018 DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1606 Accepted: 14 May 2018 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Feasibility of using negative ultrasonography results of axillary lymph nodes to predict sentinel
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
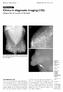 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
Journal of Breast Cancer
 Journal of Breast Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Cancer 2012 June; 15(2): 211-217 Efficiency of Ultrasound and Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Preoperative Assessment of Axillary
Journal of Breast Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Cancer 2012 June; 15(2): 211-217 Efficiency of Ultrasound and Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Preoperative Assessment of Axillary
Case Scenario 1. 2/15/2011 The patient received IMRT 45 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction for 25 fractions.
 Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
CONSENSUS ULTRASOUND SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL AFTER POSITIVE SENTINEL LYMPH NODE BIOPSY FOR MELANOMA
 CONSENSUS ULTRASOUND SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL AFTER POSITIVE SENTINEL LYMPH NODE BIOPSY FOR MELANOMA Created by Drs P. Robins, Z. Al-Ogaili and B. Adler in collaboration with the WA Kirkbride Melanoma Advisory
CONSENSUS ULTRASOUND SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL AFTER POSITIVE SENTINEL LYMPH NODE BIOPSY FOR MELANOMA Created by Drs P. Robins, Z. Al-Ogaili and B. Adler in collaboration with the WA Kirkbride Melanoma Advisory
ULTRASOUND DIFFERENTIATION OF BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 Original Article ULTRASOUND DIFFERENTIATION OF BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CERVICAL LYMPH NODES Md. Mizanur Rahman 1, ASQM Sadeque 2, Eliza Omar 3 and Sonjoy Kumar Bhakta 4 1 Department of Radiology and Imaging,
Original Article ULTRASOUND DIFFERENTIATION OF BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CERVICAL LYMPH NODES Md. Mizanur Rahman 1, ASQM Sadeque 2, Eliza Omar 3 and Sonjoy Kumar Bhakta 4 1 Department of Radiology and Imaging,
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Case series: imaging features of intraductal papillomas in patients presenting as nipple discharge
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Dhull V et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 20 Jul;4():2882882 www.msjonline.org pissn 2200 eissn 22002 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.820/22002.ijrms2099
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Dhull V et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 20 Jul;4():2882882 www.msjonline.org pissn 2200 eissn 22002 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.820/22002.ijrms2099
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience.
 MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules & Guidelines for Management
 Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules & Guidelines for Management Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University,
Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules & Guidelines for Management Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University,
Consensus Guideline on Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Palpable and Nonpalpable Breast Lesions
 Consensus Guideline on Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Palpable and Nonpalpable Breast Lesions Purpose: To outline the use of minimally invasive biopsy techniques (MIBT) for palpable and nonpalpable
Consensus Guideline on Image-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Palpable and Nonpalpable Breast Lesions Purpose: To outline the use of minimally invasive biopsy techniques (MIBT) for palpable and nonpalpable
Primary Breast Liposarcoma
 Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Utility of PET-CT for detection of N2 or N3 nodal mestastases in the mediastinum in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
 Utility of PET-CT for detection of N2 or N3 nodal mestastases in the mediastinum in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Poster No.: C-1360 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Utility of PET-CT for detection of N2 or N3 nodal mestastases in the mediastinum in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Poster No.: C-1360 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Feasibility of Preoperative Axillary Lymph Node Marking with a Clip in Breast Cancer Patients before Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study
 [ABS-0078] GBCC 2018 Feasibility of Preoperative Axillary Lymph Node Marking with a Clip in Breast Cancer Patients before Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study Eun Young Kim 1, Kwan Ho Lee 1, Yong
[ABS-0078] GBCC 2018 Feasibility of Preoperative Axillary Lymph Node Marking with a Clip in Breast Cancer Patients before Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Preliminary Study Eun Young Kim 1, Kwan Ho Lee 1, Yong
Breast Surgery When Less is More and More is Less. E MacIntosh, MD June 6, 2015
 Breast Surgery When Less is More and More is Less E MacIntosh, MD June 6, 2015 Presenter Disclosure Faculty: E. MacIntosh Relationships with commercial interests: None Mitigating Potential Bias Not applicable
Breast Surgery When Less is More and More is Less E MacIntosh, MD June 6, 2015 Presenter Disclosure Faculty: E. MacIntosh Relationships with commercial interests: None Mitigating Potential Bias Not applicable
Preoperative Evaluation
 Preoperative Evaluation Lateral compartment lymph nodes are easier to detect and are amenable to FNA Central compartment lymph nodes are much more difficult to detect and FNA (Tg washout testing is compromised)
Preoperative Evaluation Lateral compartment lymph nodes are easier to detect and are amenable to FNA Central compartment lymph nodes are much more difficult to detect and FNA (Tg washout testing is compromised)
Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks
 Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks Claire McKay, DO M&S Imaging Assoc. San Antonio, TX cmckayhart@juno.com Goals Describe modalities available, old and new Provide understanding of pros and cons
Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks Claire McKay, DO M&S Imaging Assoc. San Antonio, TX cmckayhart@juno.com Goals Describe modalities available, old and new Provide understanding of pros and cons
Role of Ultrasonography And Doppler in Evaluation of Neck Nodes And Differentiating Benign from Malignant Nodes
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IX (November. 2016), PP 71-80 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Ultrasonography And Doppler
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IX (November. 2016), PP 71-80 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Ultrasonography And Doppler
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
What is Cancer? Petra Ketterl, MD Medical Oncology and Functional Medicine
 What is Cancer? Petra Ketterl, MD Medical Oncology and Functional Medicine What is Cancer? Layman s terms: cancer starts when cells grow out of control (in any place in the body) and crowd out normal cells
What is Cancer? Petra Ketterl, MD Medical Oncology and Functional Medicine What is Cancer? Layman s terms: cancer starts when cells grow out of control (in any place in the body) and crowd out normal cells
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report
 Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
