Sputum Screening by Nomarski Interference Contrast
|
|
|
- Abigail Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 1979, p /79/ /05$02.00/0 Vol. 9, No. 4 Sputum Screening by Nomarski Interference Contrast Microscopy DAVID F. WELCH AND MICHAEL T. KELLYt* Veterans Administration Hospital and Department of Pathology, University of Utah College ofmedicine, Salt Lake City, Utah Received for publication 2 January 1979 Gram-stained smears of specirnens submitted for sputum cultures were compared with direct wet mounts examined by Nomarski interference contrast microscopy (NIM) for enumeration of squamous epithelial cells (EPC) and leukocytes (WBC). The results obtained by the two methods were comparable, but specimens were more rapidly screened and cell types were more readily differentiated by NIM. Specimens submitted for sputum culture over a 3-month period were examined for EPC and WBC by NIM. Twenty-two percent of the specimens had >25 EPC/field or a predominance of EPC (class I), 30% had >25 EPC and >25 WBC/field (class II), and 48% had >25 WBC/field or a predominance of WBC (class III). The clinical relevance of the culture results was determined by reviewing the records of patients whose specimens were included in the study. Class I specimens provided only 30% clinically relevant culture results. Specimens in class II provided useful culture results in 63% of the patients, and 96% of those in class III provided clinically relevant information. The results confirm the value of sputum screening and demonstrate that NIM provides a rapid, simple, and accurate method for sputum screening. There are an estimated two million cases of pneumonia per year in the United States (9), and, despite modem diagnostic methods and effective antimicrobial therapy, pneumonia remains a leading cause of death. A factor that may contribute to the continuing morbidity and mortality of pneumonia is the frequently poor quality of expectorated sputum specimens received for culture in clinical microbiology laboratories. For example, Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is the leading cause of bacterial pneumonia, may be recovered in only 50% of expectorated sputum specimens from patients with documented pneumococcal pneumonia (1). Microscopic screening of sputum specimens can improve the reliability of culture results (2, 3, 5, 8, 10). Geckler and co-workers (5) have confirmed the value of sputum screening by their demonstration that expectorated sputum specimens, judged to contain lower respiratory tract secretions, gave culture results comparable to specimens obtained by transtracheal aspiration. Gram-stained smears of sputum specimens are normally employed for screening, but Gram staining is time-consuming and cells are often distorted and difficult to identify. In the present study, we evaluated the use of direct wet mounts t Present address: Department of Pathology, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX examined by Nomarski interference contrast microscopy (NIM) for sputum screening. MATERIALS AND METHODS The study included specimens submitted over a 3- month period to the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory of the Veterans Administration Hospital for routine sputum culture. Single expectorated specimens were collected under the supervision of nursing personnel and transported to the laboratory immediately or after not more than 1 h of refrigeration. The specimens were processed for culture immediately upon receipt in the laboratory. Microscopy was generally done at the same time as the culture. When microscopy could not be done immediately, the specimens were refrigerated for not more than 4 h after collection. Refrigeration for this period of time did not change the cellular composition of the sputum. All specimens, except those that could not be examined within 4 h after collection, were included in the study. The most purulent mucoid or blood-flecked portion of each specimen was carefully selected for culture and microscopy. Direct wet mounts were made by placing a loopful of the selected portion of the specimen on a slide, adding a cover slip, and gently pressing down without allowing the specimen to go beyond the cover slip edges. Gram-stained smears were prepared from the same portions of the specimens. The sputa were cultured on 5% sheep blood agar, colistin-nalidixic acid agar, MacConkey agar, and chocolate agar. Organisms were enumerated semi-quantitatively on streak plate cultures and identified by established procedures. 520
2 VOL. 9, 1979 The direct mounts were examined by NIM (Olympus model BHA), and the Gram-stained smears were observed under normal bright-field optics. All of the microscopic observations were made by the same individual (D.F.W.). In each case the entire slide was first scanned at x125 magnification to determine the distribution of cell types. Leukocytes (WBC) and buccal epithelial cells (EPC) were then counted in 10 representative fields, and the average number of each cell type was determined. Medical records of the patients whose specimens were included in the study were reviewed to determine the clinical correlation of sputum culture results with respect to the quality of specimen provided. Clinical and laboratory evidence of lower-respiratory-tract infection included radiographic findings of pneumonia, elevated WBC count, fever, increased sputum production, and positive blood cultures. Evidence against lower-respiratory-tract infection included absence of the above findings and subsequent diagnosis of other noninfectious pulmonary diseases (e.g., neoplasms). RESULTS Comparison of screening by NIM and Gram stain. In initial studies, specimens were screened by both NIM and Gram stain to determine the comparability of the two methods. Cell counts with the two methods had 96% agreement. The 4% discrepancies encountered were due to more uniform distribution of cells on the wet mount compared with the smear and to easier recognition of cell types by NIM. NIM produces a three-dimensional image that makes recognition of EPC, WBC, and other cell types straightforward (Fig. 1). By NIM, WBC are smaller than EPC, and they appear spherical. Also, lysosomal granules and phagocytic vesicles are apparent on higher magnification. EPC are characteristically large and flat, with a small central nucleus that is readily apparent by NIM. Classification of specimens. Specimens were initially graded by the scheme of Murray and Washington (10). However, several specimens contained fewer than 25 cells per field and thus did not fit into the Murray and Washington scheme. Two additional groups were established to accomodate these specimens (Table 1). Group 0 had a predominance of EPC, and group 6 had a predominance of WBC. To simplify this scheme, classes of sputum specimens were established (Table 1). Class I consisted of groups 0, 1, and 2, and it represented specimens having more than 25 EPC and/or a predominance of EPC. Class II included specimens of group 3 that had more than 25 of both EPC and WBC. Class III included groups 4, 5, and 6, which were those specimens having more than 25 WBC and/or a predominance of WBC. Microbiology of sputum specimens. Normal upper respiratory flora was recovered in 96% NIM AND SPUTUM SCREENING 521 of class I specimens but in only 86% of class II and 81% of class III specimens (Table 2). Thus, nearly 20% of class III specimens yielded only potential pathogens without normal flora. In general, a higher percentage of class II and III specimens yielded enteric bacteria and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. S. pneumoniae was isolated from a total of 30 specimens during the study, and group III specimens accounted for 50% of these isolates. More potential pathogens were isolated from specimens of classes II and III compared with class I. An average of 0.65 potential pathogen was recovered from class I specimens. Cultures of class II specimens had an average of 1.2 potentially pathogenic organisms, and class III specimens yielded an average of 1.0 potential pathogen per specimen. Clinical correlation of culture results. To determine the clinical significance of the sputum culture results, hospital records of 110 patients included in the study were reviewed for evidence of lower-respiratory-tract infection. Clinically relevant culture results were defined as isolation of a potential pathogen in the presence of clinical evidence of infection or as the absence of a potential pathogen with no evidence of infection. Strikingly different results were obtained with sputum specimens of the three classes (Table 3). Class I specimens had 42% false-positive results and 28% false-negative results, providing clinically useful information from only 30% of the specimens. Sputa of class II provided 63% clinically relevant results. Specimens of class III provided 96% clinically relevant culture results, and no false-positive results were encountered with specimens of this class. Therefore, there are marked differences in the clinical validity of culture results from sputum specimens of the three different classes. DISCUSSION Accurate microbiological diagnosis of pneumonia depends upon culture of sputum that represents lower-respiratory-tract secretions. The best methods for obtaining such specimens are transtracheal aspiration (7) or lung biopsy (6). However, because of the invasive nature of these procedures, expectorated sputum is the specimen most often obtained. Microscopic screening of sputum specimens can be used to select for culture those specimens that represent lower-respiratory-tract secretions (5, 8, 10). Previous studies have used Gram-stained smears for such screening, but direct wet mounts, examined under oil immersion by standard light microscopy, have been used to differentiate eosinophilic and neutrophilic WBC in sputum (4). In the present study, we demonstrate that NIM
3 *....S.n.:- ; A v..f a. *C w.:.^ %.t- I 'k 1. I :... t4 a II. ~~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ B '2..l or '. L:..F.~~~~.x.. ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Al 14~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 4!:..., ;..0, " Downloaded from 'I. t.. C..l**L -} X~~~~~~~~..2t~~~~~~0 49f..:,..t '.; 4 AV A44~~~~~~.~~~~ *' in' FIG. 1. Cg.s' t on December 30, 2018 by guest FIG.c of EComandifewofC sputu screeningtainim NIM smand Gramh stain. (A)ien spcie NIM showimng preom-n large numbers of both EPC and WBC; (D) Gram-stained smear of the same specimen; (E) NIM of specimen showingpredominance of WBC and few EPC; (F) Gram-stained smear of the same specimen. x
4 VOL. 9, 1979 TABLE 1. Classification of sputum specimens Class Group EPC'a WBCb I 0 <25 (EPC > <25 WBC) 1 >25 <10 2 > II 3 >25 >25 III >25 5 <10 >25 6 <25 <25 (WBC > EPC) a Number of EPC per x125 field (average of 10 fields). b'number of WBC per X125 field (average of 10 fieldls). TABLE 2. Microbiology of sputum specimens Sputum class (%) a Culture result I II III Normal throat florab Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pyogenes Staphylococcus aureus Haemophilus influenzae Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Enterobacter aerogenes Proteus mirabilis Pseudomonas aeruginosa Candida albicans Other a Percentage of cultures of each sputum class that yielded the indicated organism. Sputum classes are defined as follows: I, >25 EPC or predominance of EPC (57 specimens); II, >25 EPC and >25 WBC (77 specimens); III, >25 WBC or predominance of WBC (122 specimens). b Alpha-hemolytic streptococci, diphtheroids, Neisseria sp., nonhemolytic streptococci, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Hemophilus sp., and yeasts. provides a rapid and accurate method for screening wet mounts of sputum. Examination of wet mounts has the additional advantage that Quellung reactions can be performed, where indicated, by the addition of antiserum. Also, under x450 or x 1,000 magnification, erythrocytes, pulmonary macrophages, ciliated epithelial cells, fungi, parasites (e.g., Trichomonas tenax), and bacteria can be observed. These observations are often difficult to make on Gram-stained preparations. We found that sputum specimens could be divided into three classes based on the relative numbers of EPC and WBC in the specimens, and the culture results varied with the sputum NIM AND SPUTUM SCREENING 523 TABLE 3. Clinical correlation of sputum culture results Clinical correlation' Sputum True True False False Clinically valid recl~a posi- nega- posi- nega- sults (%) tive tive tive tive I II III a Definitions of sputum classes: I, >25 EPC or predominance of EPC (26 specimens); II, >25 EPC and >25 WBC (37 specimens); III, >25 WBC or predominance of WBC (47 specimens). b Percentage of specimens from each class that provided: true-positive results, potential pathogen isolated and evidence of lower-respiratory tract infection; true-negative results, no potential pathogen isolated and no evidence of infection; false-positive results, potential pathogen isolated and no evidence of infection; or false-negative results, no potential pathogen isolated and evidence of infection. ' Percent true-positive results plus percent true-negative results. class. Our results are similar to those of Van Scoy (11) and Murray and Washington (10), which suggest that sputum specimens with a predominance of EPC (class I) have an average of less than one potential pathogen, and specimens with many WBC or a predominance of WBC (classes II and III) average about one potential pathogen per culture. As suggested by Van Scoy (11), these results indicate that class I specimens should be rejected as upper respiratory in origin, and only class II and III specimens should be cultured. This conclusion is further substantiated by our observations that 70% of cultures of class I sputum specimens fail to provide clinically relevant results, but most specimens of classes II and III do provide useful results. These findings support the concept that sputum specimens containing mostly EPC do not provide valid results and that only specimens with many WBC or a predominance of WBC should be cultured. The results of this study demonstrate that microscopic sputum screening is a valuable procedure that can significantly enhance the validity of sputum culture results. Screening of sputa by NIM provides several advantages over the examination of Gram-stained smears, and Nomarski optics can be added to most microscopes at relatively modest cost. Microscopes with Nomarski optics can also be used for routine microscopy and, therefore, need not be dedicated to sputum screening. In addition, NIM is very useful in other areas of clinical microbiology, such as virology, mycology, and parasitology. NIM should be considered as a simple, rapid,
5 524 WELCH AND KELLY and accurate method for determining the cellular composition of sputum specimens. LITERATURE CITED 1. Barret-Conner, E The non-value of sputum culture in the diagnosis of bacterial pneumonia. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 103: Bartlett, R. C p In Medical microbiology: quality, cost and clinical relevance. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York. 3. Chodosh, S Examination of sputum cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 282: Epstein, R. L Constituents of sputum: a simple method. Ann. Intern. Med. 77: Geckler, R. W., D. H. Gremillion, C. K. McAllister, and C. Ellenbogen Microscopic and bacteriological comparison of paired sputa and transtracheal J. CLIN. MICROBIOL. aspirates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 6: Greenman, R. L., P. T. Goodall, and D. King Lung biopsy in immunocompromised hosts. Am. J. Med. 59: Hahn, H. H., and H. N. Beaty Transtracheal aspiration in the evaluation of patients with pneumonia. Ann. Intern. Med. 72: Heineman, H. S., J. K. Chawla, and W. M. Lofton Misinformation from sputum cultures without microscopic examination. J. Clin. Microbiol. 6: Hoeprich, P. D Bacterial pneumonias, p In P. D. Hoeprich (ed.), Infectious diseases. Harper & Row Publishers, Inc., Hagerstown, Md. 10. Murray, P. R., and J. A. Washington II Microscopic and bacteriologic analysis of expectorated sputum. Mayo Clin. Proc. 50: Van Scoy, R. E Bacterial sputum cultures. A clinician's viewpoint. Mayo Clin. Proc. 52: Downloaded from on December 30, 2018 by guest
Acceptability of Sputum Specimens
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1982, p. 627-631 0095-1137/82/100627-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1982, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 4 Comparison of Six Different Criteria for Judging
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1982, p. 627-631 0095-1137/82/100627-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1982, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 4 Comparison of Six Different Criteria for Judging
Work-up of Respiratory Specimens Now you can breathe easier
 34 th Annual Meeting Southwestern Association of Clinical Microbiology Work-up of Respiratory Specimens Now you can breathe easier Yvette S. McCarter, PhD, D(ABMM) Director, Clinical Microbiology Laboratory
34 th Annual Meeting Southwestern Association of Clinical Microbiology Work-up of Respiratory Specimens Now you can breathe easier Yvette S. McCarter, PhD, D(ABMM) Director, Clinical Microbiology Laboratory
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
Correlation of Sputum Gram Stain and Sputum Culture for Respiratory Tract Infections in a Tertiary Care Hospital, Ballari, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 6 (2017) pp. 3008-3012 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.606.357
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 6 (2017) pp. 3008-3012 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.606.357
Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures:
 Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures: Culture work up 2 Systematic approaches 1 Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures Resident flora Colonizing organisms Pathogens 2 Work up of Respiratory & Wound
Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures: Culture work up 2 Systematic approaches 1 Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures Resident flora Colonizing organisms Pathogens 2 Work up of Respiratory & Wound
Comparative Evaluation of the Limulus Assay and the Direct Gram Stain for Detection of Significant Bacteriuria
 Comparative Evaluation of the Limulus Assay and the Direct for Detection of Significant Bacteriuria JAMES H. JORGENSEN, PH.D., AND PAMELA M. JONES, M.T. (ASCP) Departments of Pathology and Microbiology,
Comparative Evaluation of the Limulus Assay and the Direct for Detection of Significant Bacteriuria JAMES H. JORGENSEN, PH.D., AND PAMELA M. JONES, M.T. (ASCP) Departments of Pathology and Microbiology,
Respiratory Tract Infections
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1987, p. 758-762 0095-1137/87/050758-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1987, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 25, No. 5 Nonvalue of Sputum Culture in the Management of Lower
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1987, p. 758-762 0095-1137/87/050758-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1987, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 25, No. 5 Nonvalue of Sputum Culture in the Management of Lower
Babak Valizadeh, DCLS
 Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Respiratory Tract Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1391. 02. 05 2012. 04. 25 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Biological Safety Cabinet Process specimens in biological
Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Respiratory Tract Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1391. 02. 05 2012. 04. 25 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Biological Safety Cabinet Process specimens in biological
Discrepancies in the recovery of bacteria from multiple sinuses in acute and chronic sinusitis
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 879 885 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45655-0 Short Communication Correspondence Itzhak Brook ib6@georgetown.edu Received 1 March 2004 Accepted 18 May 2004 Discrepancies
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 879 885 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45655-0 Short Communication Correspondence Itzhak Brook ib6@georgetown.edu Received 1 March 2004 Accepted 18 May 2004 Discrepancies
Association of Mucoid Encapsulated Moraxella duplex
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1968, p. 315-319 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 2 Prinited int U.S.A. Association of Mucoid Encapsulated Moraxella duplex var. nonliquefaciens
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1968, p. 315-319 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 2 Prinited int U.S.A. Association of Mucoid Encapsulated Moraxella duplex var. nonliquefaciens
INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Lower Respiratory Tract Infection
 Lower Respiratory Tract Infection - Clinical Diseases and etiologic agents -Sample Collection and transport -Direct Smear (interpretation and Report) -Culture methods (interpretation and Report) The culture
Lower Respiratory Tract Infection - Clinical Diseases and etiologic agents -Sample Collection and transport -Direct Smear (interpretation and Report) -Culture methods (interpretation and Report) The culture
Normal Human Flora. (Human Microbiome) Dr.Sarmad M.H. Zeiny Baghdad College of Medicine
 Normal Human Flora (Human Microbiome) Dr.Sarmad M.H. Zeiny Baghdad College of Medicine 2014-2015 Objectives Describe important human normal flora. Demonstrate the epidemiology of human normal flora. Determine
Normal Human Flora (Human Microbiome) Dr.Sarmad M.H. Zeiny Baghdad College of Medicine 2014-2015 Objectives Describe important human normal flora. Demonstrate the epidemiology of human normal flora. Determine
References Required document for Laboratory Accreditation by the College of American Pathologists.
 Subject Culture: Lower Respiratory Tract Index Number Lab-3375 Section Laboratory Subsection Microbiology Category Departmental Contact Sarah Stoner Last Revised 9/11/2017 References Required document
Subject Culture: Lower Respiratory Tract Index Number Lab-3375 Section Laboratory Subsection Microbiology Category Departmental Contact Sarah Stoner Last Revised 9/11/2017 References Required document
Advances in Pathogen Detection and Diagnostic Tools for Infectious Diseases. Maria Rosario Z. Capeding, MD, FPPS, FPIDSP
 Advances in Pathogen Detection and Diagnostic Tools for Infectious Diseases Maria Rosario Z. Capeding, MD, FPPS, FPIDSP The Future of Microbiology The Future (can machine replace human being?) Why do we
Advances in Pathogen Detection and Diagnostic Tools for Infectious Diseases Maria Rosario Z. Capeding, MD, FPPS, FPIDSP The Future of Microbiology The Future (can machine replace human being?) Why do we
Diagnostic Value of Sputum Gram s Stain and Sputum Culture in Lower Respiratory Tract Infections in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 4310-4314 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.448
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 4310-4314 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.448
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.124 COPD: Microbial Pattern in Acute Exacerbation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.124 COPD: Microbial Pattern in Acute Exacerbation
Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples
 Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples Background The VACUETTE Urine CCM tube is for the collection, transport and storage of urine samples
Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples Background The VACUETTE Urine CCM tube is for the collection, transport and storage of urine samples
Quantitation of Microorganisms in Sputum
 APPTED MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1969, p. 214-22 VoL 18, No. 2 Copyright 1969 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Quantitation of Microorganisms in Sputum P. W. MONROE, H. G. MUCHMORE, F. G. FELTON,
APPTED MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1969, p. 214-22 VoL 18, No. 2 Copyright 1969 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Quantitation of Microorganisms in Sputum P. W. MONROE, H. G. MUCHMORE, F. G. FELTON,
Streptococcus(gram positive coccus) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Streptococcus(gram positive coccus) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Streptococci Facultative anaerobe Gram-positive usually chains (sometimes pairs) Catalase negative Non motile Hemolysins Lancefield Groups (C-carbohydrate
Streptococcus(gram positive coccus) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Streptococci Facultative anaerobe Gram-positive usually chains (sometimes pairs) Catalase negative Non motile Hemolysins Lancefield Groups (C-carbohydrate
Original Article Characterization of candida species isolated from cases of lower respiratory tract infection
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 3, Issue 15, 290-294 Original Article Characterization of candida species isolated from cases of lower respiratory tract infection Jha BK 1, Dey
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 3, Issue 15, 290-294 Original Article Characterization of candida species isolated from cases of lower respiratory tract infection Jha BK 1, Dey
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year )
 BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci
 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sprung CL, Annane D, Keh D, et al. Hydrocortisone therapy for
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sprung CL, Annane D, Keh D, et al. Hydrocortisone therapy for
Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory. 11 April 2013
 Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory 11 April 2013 Lecture Plan Revision of infectious disease Triad of infectious disease Interaction between host and infectious agent Pathogenesis Phases
Appropriate utilization of the microbiology laboratory 11 April 2013 Lecture Plan Revision of infectious disease Triad of infectious disease Interaction between host and infectious agent Pathogenesis Phases
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
Bacterial pneumonia with associated pleural empyema pleural effusion
 EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
Staphylococci. Gram stain: gram positive cocci arranged in clusters.
 Microbiology lab Respiratory system Third medical year Lab contents: Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp), two types of filamentous fungi (Aspergillus and Penicillium spp), and
Microbiology lab Respiratory system Third medical year Lab contents: Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp), two types of filamentous fungi (Aspergillus and Penicillium spp), and
Study of etiological factors and sensitivity pattern in CSOM
 Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; December 2015: Vol.-5, Issue- 1, P. 766-770 766-771 Original article: Study of etiological factors and sensitivity pattern in CSOM Paresh Chavan, G
Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; December 2015: Vol.-5, Issue- 1, P. 766-770 766-771 Original article: Study of etiological factors and sensitivity pattern in CSOM Paresh Chavan, G
Healthcare-associated infections acquired in intensive care units
 SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2015 Healthcare-associated infections acquired in intensive care units Key facts In 2015, 11 788 (8.3%) of patients staying in an intensive care unit
SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2015 Healthcare-associated infections acquired in intensive care units Key facts In 2015, 11 788 (8.3%) of patients staying in an intensive care unit
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement
 CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES. Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to:
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to: distinguish three types of hemolysis produced by bacterial colonies. discuss
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to: distinguish three types of hemolysis produced by bacterial colonies. discuss
V. Reporting UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK/MOUNT SINAI HOSPITAL, DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
 Version: 1.0 CURRENT 1 of 26 TABLE OF CONTENTS Urinary Tract Infection Workup I. Introduction... 3 II. Specimen Collection and Transplant... 4 III. Reagents/Materials/Media... 4 IV. Procedure... 4 Asymptomatic
Version: 1.0 CURRENT 1 of 26 TABLE OF CONTENTS Urinary Tract Infection Workup I. Introduction... 3 II. Specimen Collection and Transplant... 4 III. Reagents/Materials/Media... 4 IV. Procedure... 4 Asymptomatic
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Blood Culture What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected into bottles with culture
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Blood Culture What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected into bottles with culture
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Routine endotracheal cultures for the prediction of sepsis in ventilated babies
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 34-38 Routine endotracheal cultures for the prediction of sepsis in ventilated babies T A SLAGLE, E M BIFANO, J W WOLF, AND S J GROSS Department of Pediatrics,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 34-38 Routine endotracheal cultures for the prediction of sepsis in ventilated babies T A SLAGLE, E M BIFANO, J W WOLF, AND S J GROSS Department of Pediatrics,
Lab 4. Blood Culture (Media) MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 1
 Lab 4. Blood Culture (Media) 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 1 Blood Culture 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 2 What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected
Lab 4. Blood Culture (Media) 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 1 Blood Culture 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 2 What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected
Detection of Bacteriuria and Pyuria by URISCREEN, a Rapid Enzymatic Screening Test
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1992, p. 680-684 0095-1137/92/03680-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 30, No. 3 Detection of Bacteriuria and Pyuria by URISCREEN,
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1992, p. 680-684 0095-1137/92/03680-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 30, No. 3 Detection of Bacteriuria and Pyuria by URISCREEN,
Clinical Microbiology CLS 2019 Clinical Microbiology Laboratory Scheme Application Form
 Laboratory Scheme Application Form complete all sections below and return to LGC Standards Proficiency Testing by email, fax or post. Returning customer Lab ID: Purchase order no.: (compulsory) Round Despatch
Laboratory Scheme Application Form complete all sections below and return to LGC Standards Proficiency Testing by email, fax or post. Returning customer Lab ID: Purchase order no.: (compulsory) Round Despatch
JAC Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin versus clarithromycin in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 41, Suppl. B, 69 73 JAC Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin versus clarithromycin in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections G. Tatsis*, G.
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 41, Suppl. B, 69 73 JAC Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin versus clarithromycin in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections G. Tatsis*, G.
Protocols for Laboratory Verification of Performance of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel
 Protocols for Laboratory Verification of Performance of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel Laboratory Protocols for Use with a ZeptoMetrix NATtrol Verification Panel Purpose The Clinical Laboratory
Protocols for Laboratory Verification of Performance of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel Laboratory Protocols for Use with a ZeptoMetrix NATtrol Verification Panel Purpose The Clinical Laboratory
THE USE OF THE PENICILLINASE-RESISTANT
 Therapeutic problems THE USE OF THE PENICILLINASE-RESISTANT PENICILLIN IN THE PNEUMONIAS OF CHILDREN MARTHA D. Yow, MARY A. SOUTH AND CHARLES G. HESS From the Department of Pediatrics, Baylor University
Therapeutic problems THE USE OF THE PENICILLINASE-RESISTANT PENICILLIN IN THE PNEUMONIAS OF CHILDREN MARTHA D. Yow, MARY A. SOUTH AND CHARLES G. HESS From the Department of Pediatrics, Baylor University
Torres, Brian Carlmichael L., Ma. Luisa G. Daroy, Juan s. Lopez, Vanessa Oh, Marie Joan Loy, Prospero ma. Tuaño, and Ronald R. Matias Research and
 Torres, Brian Carlmichael L., Ma. Luisa G. Daroy, Juan s. Lopez, Vanessa Oh, Marie Joan Loy, Prospero ma. Tuaño, and Ronald R. Matias Research and Biotechnology Division and International Eye Institute
Torres, Brian Carlmichael L., Ma. Luisa G. Daroy, Juan s. Lopez, Vanessa Oh, Marie Joan Loy, Prospero ma. Tuaño, and Ronald R. Matias Research and Biotechnology Division and International Eye Institute
Streptococcus pneumonia
 Streptococcus pneumonia The pneumococci (S. pneumoniae) are gram-positive diplococci. Often lancet shaped or arranged in chains, possessing a capsule of polysaccharide that permits typing with specific
Streptococcus pneumonia The pneumococci (S. pneumoniae) are gram-positive diplococci. Often lancet shaped or arranged in chains, possessing a capsule of polysaccharide that permits typing with specific
Guidelines for workup of Throat and Genital Cultures
 Guidelines for workup of Throat and Genital Cultures 1 Acute Pharyngitis By far the most common infection of the upper respiratory tract Viral infection is by far the most common cause of pharyngitis The
Guidelines for workup of Throat and Genital Cultures 1 Acute Pharyngitis By far the most common infection of the upper respiratory tract Viral infection is by far the most common cause of pharyngitis The
Skin reactivity to autologous bacteria isolated from respiratory tract of patients with obstructive pulmonary disease
 Skin reactivity to autologous bacteria 149 Original Article Skin reactivity to autologous bacteria isolated from respiratory tract of patients with obstructive pulmonary disease J. Halasa 1, M. Halasa
Skin reactivity to autologous bacteria 149 Original Article Skin reactivity to autologous bacteria isolated from respiratory tract of patients with obstructive pulmonary disease J. Halasa 1, M. Halasa
Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus from sputum in cystic fibrosis
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 913-918 Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus from sputum in cystic fibrosis P. D. SPARHAM, D. I. LOBBAN, AND D. C. E. SPELLER From the Bacteriology Department, Bristol
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 913-918 Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus from sputum in cystic fibrosis P. D. SPARHAM, D. I. LOBBAN, AND D. C. E. SPELLER From the Bacteriology Department, Bristol
Int.J.Curr.Res.Aca.Rev.2017; 5(9): 10-14
 International Journal of Current Research and Academic Review ISSN: 2347-3215 (Online) Volume 5 Number 9 (September-2017) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcrar.com doi: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcrar.2017.509.002
International Journal of Current Research and Academic Review ISSN: 2347-3215 (Online) Volume 5 Number 9 (September-2017) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcrar.com doi: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcrar.2017.509.002
PULMONARY EMERGENCIES
 EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
II- Streptococci. Practical 3. Objective: Required materials: Classification of Streptococci: Streptococci can be classified according to:
 Practical 3 II- Streptococci Objective: 1. Use of blood agar to differentiate between,, and hemolytic streptococci. 2. To know Gram reaction, shape and arrangement of streptococci. 3. To differentiate
Practical 3 II- Streptococci Objective: 1. Use of blood agar to differentiate between,, and hemolytic streptococci. 2. To know Gram reaction, shape and arrangement of streptococci. 3. To differentiate
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
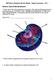 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY
 18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
Received 13 June 1991/Accepted 4 November 1991
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1992, p. 318-322 0095-1137/92/020318-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 30, No. 2 Quantitation of Pneumococcal C Polysaccharide in
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1992, p. 318-322 0095-1137/92/020318-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1992, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 30, No. 2 Quantitation of Pneumococcal C Polysaccharide in
Pathogenic organisms in the sputum of patients
 Thorax (1967), 22, 265. Pathogenic organisms in the sputum of patients with chronic bronchitis 0. L. WADE, P. C. ELMES, AND EILEEN BARTLEY From the Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology and the Department
Thorax (1967), 22, 265. Pathogenic organisms in the sputum of patients with chronic bronchitis 0. L. WADE, P. C. ELMES, AND EILEEN BARTLEY From the Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology and the Department
Urine bench. Urine test for: SARAH Sugar
 Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
1430 West McCoy Lane Santa Maria, CA p:
 091217TR HardyCHROM BluEcoli 1 HardyCHROM Candida 2 HardyCHROM ECC 3 HardyCHROM ESBL 4 HardyCHROM Listeria 5 HardyCHROM MRSA 6 HardyCHROM O157 7 HardyCHROM Salmonella 8 HardyCHROM SS NoPRO 9 HardyCHROM
091217TR HardyCHROM BluEcoli 1 HardyCHROM Candida 2 HardyCHROM ECC 3 HardyCHROM ESBL 4 HardyCHROM Listeria 5 HardyCHROM MRSA 6 HardyCHROM O157 7 HardyCHROM Salmonella 8 HardyCHROM SS NoPRO 9 HardyCHROM
Comparison of Acridine Orange and Gram Stains for
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1981, p. 201-205 0095-1137/81/080201-05$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 2 Comparison of Acridine Orange and Gram Stains for Detection of Microorganisms in Cerebrospinal Fluid
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1981, p. 201-205 0095-1137/81/080201-05$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 2 Comparison of Acridine Orange and Gram Stains for Detection of Microorganisms in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela
 Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Method for studying the role of indigenous cervical
 British Journal of Venereal Diseases, 1978, 54, 386-393 Method for studying the role of indigenous cervical flora in colonisation by Neisseria gonorrhoeae M. E. McBRIDE, W. C. DUNCAN, AND J. M. KNOX From
British Journal of Venereal Diseases, 1978, 54, 386-393 Method for studying the role of indigenous cervical flora in colonisation by Neisseria gonorrhoeae M. E. McBRIDE, W. C. DUNCAN, AND J. M. KNOX From
Protocols for Laboratory Verification of Performance of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel plus
 Protocols for Laboratory Verification of Performance of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel plus Laboratory Protocols for Use with a ZeptoMetrix NATtrol Verification Panel Purpose The Clinical Laboratory
Protocols for Laboratory Verification of Performance of the BioFire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel plus Laboratory Protocols for Use with a ZeptoMetrix NATtrol Verification Panel Purpose The Clinical Laboratory
Culture of Throat, Sputum and Other Respiratory Specimens
 Culture of Throat, Sputum and Other Respiratory Specimens Carol Spiegel, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at the UW School of Medicine and Public Health and Director of Clinical
Culture of Throat, Sputum and Other Respiratory Specimens Carol Spiegel, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at the UW School of Medicine and Public Health and Director of Clinical
INFECTIOUS DISEASE. Page 2
 Infectious disease Advantages OF TESTING INFECTIOUS DISEASE We are in the middle of a paradigm shift in infectious disease diagnostic testing. As we move from targeted infectious disease testing to a syndromic
Infectious disease Advantages OF TESTING INFECTIOUS DISEASE We are in the middle of a paradigm shift in infectious disease diagnostic testing. As we move from targeted infectious disease testing to a syndromic
Diagnostic Considerations and Interpretation of Microbiological Findings for Evaluation of Chronic Prostatitis
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1989, p. 2240-2244 0095-1137/89/102240-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1989, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 27, No. 10 Diagnostic Considerations and Interpretation
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1989, p. 2240-2244 0095-1137/89/102240-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1989, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 27, No. 10 Diagnostic Considerations and Interpretation
Evaluation of a Two-Minute Test for Urine Screening
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1983. p. 697-701 0095-1137/83/090697-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 18, No. 3 Evaluation of a Two-Minute Test for Urine Screening
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1983. p. 697-701 0095-1137/83/090697-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 18, No. 3 Evaluation of a Two-Minute Test for Urine Screening
Labquality External Quality Assesment Programmes General Bacteriology 1 1/2010
 Labquality External Quality Assesment Programmes General Bacteriology 1 1/2010 Photos and text: Markku Koskela, M.D., Ph.D. Clinical microbiology specialist Oulu, Finland Sample 1/2010 Pus from an infected
Labquality External Quality Assesment Programmes General Bacteriology 1 1/2010 Photos and text: Markku Koskela, M.D., Ph.D. Clinical microbiology specialist Oulu, Finland Sample 1/2010 Pus from an infected
Microscopic Examination of Urine
 Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Simplified Microscopy for Rapid Detection of Significant Bacteriuria in Random Urine Specimens
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1978, p. 286-291 0095-1 137/78/0007-0286$02.00/0 Copyright ( 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 7, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Simplified Microscopy for Rapid
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1978, p. 286-291 0095-1 137/78/0007-0286$02.00/0 Copyright ( 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 7, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Simplified Microscopy for Rapid
Aerobic bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds
 Aerobic bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds Eithar Mohammed Mahgoub*, Mohammed Elfatih A. Omer Faculty of Pharmacy, Omdurman Islamic University Department of Pharmaceutical Microbiology, Omdurman
Aerobic bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds Eithar Mohammed Mahgoub*, Mohammed Elfatih A. Omer Faculty of Pharmacy, Omdurman Islamic University Department of Pharmaceutical Microbiology, Omdurman
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Medical Microbiology
 Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
Microbiology products. Liofilchem Chromatic
 ET Microbiology products M IC R O PL A N www.liofilchem.net Liofilchem Chromatic c h ro m o g e n i c c u l t u re m e d i a LIOFILCHEM s.r.l. Via Scozia, Zona Industriale 64026 Roseto degli Abruzzi (Te)
ET Microbiology products M IC R O PL A N www.liofilchem.net Liofilchem Chromatic c h ro m o g e n i c c u l t u re m e d i a LIOFILCHEM s.r.l. Via Scozia, Zona Industriale 64026 Roseto degli Abruzzi (Te)
Bacteriology. Mycology. Patient: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Sex: MRN: Rare. Rare. Positive. Brown. Negative *NG. Negative
 Patient: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Sex: MRN: 3.2 0.9-26.8 U/g 1.2 0.2-3.3 mg/g 2.2 1.3-8.6 micromol/g 1.1 1.3-23.7 mg/g 1.1 0.2-3.5 mg/g Rare 1.0 0.2-8.8 mg/g Rare 4.4 2.6-32.4 mg/g 64.6 >= 13.6 micromol/g Bacteriology
Patient: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Sex: MRN: 3.2 0.9-26.8 U/g 1.2 0.2-3.3 mg/g 2.2 1.3-8.6 micromol/g 1.1 1.3-23.7 mg/g 1.1 0.2-3.5 mg/g Rare 1.0 0.2-8.8 mg/g Rare 4.4 2.6-32.4 mg/g 64.6 >= 13.6 micromol/g Bacteriology
Respiratory Pathogen Panel TEM-PCR Test Code:
 Respiratory Pathogen Panel TEM-PCR Test Code: 220000 Tests in this Panel Enterovirus group Human bocavirus Human coronavirus (4 types) Human metapneumovirus Influenza A - Human influenza Influenza A -
Respiratory Pathogen Panel TEM-PCR Test Code: 220000 Tests in this Panel Enterovirus group Human bocavirus Human coronavirus (4 types) Human metapneumovirus Influenza A - Human influenza Influenza A -
The Clinical Significance of Blood Cultures. Presented BY; Cindy Winfrey, MSN, RN, CIC, DON- LTC TM, VA- BC TM
 The Clinical Significance of Blood Cultures Presented BY; Cindy Winfrey, MSN, RN, CIC, DON- LTC TM, VA- BC TM OVERVIEW Blood cultures are considered an important laboratory tool used to diagnose serious
The Clinical Significance of Blood Cultures Presented BY; Cindy Winfrey, MSN, RN, CIC, DON- LTC TM, VA- BC TM OVERVIEW Blood cultures are considered an important laboratory tool used to diagnose serious
Epidemiology and Etiology of Community-Acquired Pneumonia 761 Lionel A. Mandell
 LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS Preface Thomas M. File, Jr xiii Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Pathophysiology and Host Factors with Focus on Possible New Approaches to Management of Lower Respiratory
LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS Preface Thomas M. File, Jr xiii Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Pathophysiology and Host Factors with Focus on Possible New Approaches to Management of Lower Respiratory
Environmental survival of Neisseria meningitidis
 Environmental survival of Neisseria meningitidis Yih-Ling Tzeng, Emory University L.E. Martin, Emory University David Stephens, Emory University Journal Title: Epidemiology and Infection Volume: Volume
Environmental survival of Neisseria meningitidis Yih-Ling Tzeng, Emory University L.E. Martin, Emory University David Stephens, Emory University Journal Title: Epidemiology and Infection Volume: Volume
Urinary tract infections Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Urinary tract infections Dr. Hala Al Daghistani UTIs are considered to be one of the most common bacterial infections. Diagnosis depends on the symptoms, urinalysis, and urine culture. UTIs occur more
Urinary tract infections Dr. Hala Al Daghistani UTIs are considered to be one of the most common bacterial infections. Diagnosis depends on the symptoms, urinalysis, and urine culture. UTIs occur more
AN IMMUNOASSAY TEST FOR THE QUALITATIVE DETECTION OF STREP A ANTIGEN IN THROAT SWAB SPECIMENS
 CLARITY Strep A Dipsticks FOR LABORATORY AND PROFESSIONAL USE AN IMMUNOASSAY TEST FOR THE QUALITATIVE DETECTION OF STREP A ANTIGEN IN THROAT SWAB SPECIMENS CLIA COMPLEXITY: Waived CLARITY Strep A Dipsticks:
CLARITY Strep A Dipsticks FOR LABORATORY AND PROFESSIONAL USE AN IMMUNOASSAY TEST FOR THE QUALITATIVE DETECTION OF STREP A ANTIGEN IN THROAT SWAB SPECIMENS CLIA COMPLEXITY: Waived CLARITY Strep A Dipsticks:
The Bacteriology of Bronchiectasis in Australian Indigenous children
 The Bacteriology of Bronchiectasis in Australian Indigenous children Kim Hare, Amanda Leach, Peter Morris, Heidi Smith-Vaughan, Anne Chang Presentation outline What is bronchiectasis? Our research at Menzies
The Bacteriology of Bronchiectasis in Australian Indigenous children Kim Hare, Amanda Leach, Peter Morris, Heidi Smith-Vaughan, Anne Chang Presentation outline What is bronchiectasis? Our research at Menzies
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 08 Page August 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i8.09 Original Article Sputum Bacteriology
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i8.09 Original Article Sputum Bacteriology
International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn eissn
 CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION (CAUTI) INDUCED NOSOCOMIAL INFECTION WITH REFERENCE TO INCIDENCE, DURATION AND ORGANISM IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL Dr.Trilok Patil* Associate Professor,
CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION (CAUTI) INDUCED NOSOCOMIAL INFECTION WITH REFERENCE TO INCIDENCE, DURATION AND ORGANISM IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL Dr.Trilok Patil* Associate Professor,
Correlation between the Treatment Result and Causative Bacteria in Amputation of Diabetic Foot
 Correlation between the Treatment Result and Causative Bacteria in Amputation of Diabetic Foot Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A university, Busan, Korea Myoung Jin Lee M.D.,
Correlation between the Treatment Result and Causative Bacteria in Amputation of Diabetic Foot Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A university, Busan, Korea Myoung Jin Lee M.D.,
Kyabaggu D, 2 Ejobi F 3* Olila D
 The sensitivities to first-line antibiotic therapy of the common urinary tract bacterial infections detected in urine samples at a hospital in metropolitan Kampala (Uganda) 1 Kyabaggu D, 2 Ejobi F 3* Olila
The sensitivities to first-line antibiotic therapy of the common urinary tract bacterial infections detected in urine samples at a hospital in metropolitan Kampala (Uganda) 1 Kyabaggu D, 2 Ejobi F 3* Olila
Chapter 19. Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria. Staphylococcus & Streptococcus
 Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE Original Article S o n i c a t e d V a s c u l a r C a t h e t e r T i p C u l t u r e s Quantitative Association With Catheter-related Sepsis and the Non-Utility
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE Original Article S o n i c a t e d V a s c u l a r C a t h e t e r T i p C u l t u r e s Quantitative Association With Catheter-related Sepsis and the Non-Utility
Streptococci facultative anaerobe
 THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
Normal Flora. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Normal Flora CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Relationships between Organisms Symbiosis Permanent association between two different organisms. Neutralism Two organisms living together, and neither is affected
Normal Flora CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Relationships between Organisms Symbiosis Permanent association between two different organisms. Neutralism Two organisms living together, and neither is affected
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM. ITEMS NECESSARY BUT NOT INCLUDED IN THE KIT A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM Reagent (ref ) Mycoplasma Transport Broth (ref.
 A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM ENGLISH System for detection, count and susceptibility test of pathogenic urogenital microorganisms DESCRIPTION A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM is a 24-well system containing desiccated biochemical
A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM ENGLISH System for detection, count and susceptibility test of pathogenic urogenital microorganisms DESCRIPTION A.F. GENITAL SYSTEM is a 24-well system containing desiccated biochemical
Bio Microbiology - Spring 2013 Study Guide 20 Normal Flora - Normal Responses - Disease
 Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2013 Study Guide 20 Normal Flora - Normal Responses - Disease It has been calculated that the normal human houses about 10 12 bacteria on the skin, 10 10 in the mouth, and
Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2013 Study Guide 20 Normal Flora - Normal Responses - Disease It has been calculated that the normal human houses about 10 12 bacteria on the skin, 10 10 in the mouth, and
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS OF THE RABBIT.
 Published Online: 1 February, 1925 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.41.2.275 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 3, 2018 EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS OF THE RABBIT. VI.
Published Online: 1 February, 1925 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.41.2.275 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 3, 2018 EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS OF THE RABBIT. VI.
Comparisons Between Direct Microscopic and Cultural Methods for Recognition of Corynebacterium vaginale in Women with Vaginitis
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1977, p. 268-272 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 5, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Comparisons Between Direct Microscopic and Cultural Methods for
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1977, p. 268-272 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 5, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Comparisons Between Direct Microscopic and Cultural Methods for
Bacteria causing respiratory tract infections
 Editing file Bacteria causing respiratory tract infections Objectives : Recognize signs & symptoms of different bacterial respiratory tract infections Be able to come up with a short differential to relevant
Editing file Bacteria causing respiratory tract infections Objectives : Recognize signs & symptoms of different bacterial respiratory tract infections Be able to come up with a short differential to relevant
Creating a User Defined Pneumonia-Specific Syndrome in ESSENCE. Preventive Medicine Directorate September 2016
 Creating a User Defined Pneumonia-Specific Syndrome in ESSENCE Preventive Medicine Directorate September 2016 0 Pneumonia-Specific Syndrome NMCPHC retrospective analyses suggest that surveillance using
Creating a User Defined Pneumonia-Specific Syndrome in ESSENCE Preventive Medicine Directorate September 2016 0 Pneumonia-Specific Syndrome NMCPHC retrospective analyses suggest that surveillance using
Efficacy of Ceftriaxone in Serious Bacterial Infections
 ANTIMIROBIAL AGENTS AND HEMOTHERAPY, Mar 1982, p 402-406 0066-4804/82/030402-05$0200/0 Vol 21, No 3 Efficacy of eftriaxone in Serious Bacterial Infections JAY S EPSTEIN, SUSAN M HASSELQUIST, AND GARY L
ANTIMIROBIAL AGENTS AND HEMOTHERAPY, Mar 1982, p 402-406 0066-4804/82/030402-05$0200/0 Vol 21, No 3 Efficacy of eftriaxone in Serious Bacterial Infections JAY S EPSTEIN, SUSAN M HASSELQUIST, AND GARY L
Prevalence of Human immunodeficiency virus associated bacterial and fungal respiratory tract infections.
 Original article: Prevalence of Human immunodeficiency virus associated bacterial and fungal respiratory tract infections. *Dr. Meghna S Palewar 1, Dr. A.G Dhanvijay 2, Dr. S.R More 3 1Department of Microbiology,
Original article: Prevalence of Human immunodeficiency virus associated bacterial and fungal respiratory tract infections. *Dr. Meghna S Palewar 1, Dr. A.G Dhanvijay 2, Dr. S.R More 3 1Department of Microbiology,
Visual and Clinical Analysis of Bac-T-Screen Urine Screen Results
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1988, p. 2382-2386 0095-1137/88/112382-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1988, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 26, No. 11 Visual and Clinical Analysis of Bac-T-Screen
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1988, p. 2382-2386 0095-1137/88/112382-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1988, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 26, No. 11 Visual and Clinical Analysis of Bac-T-Screen
Abstract. J Pak Med Assoc
 Intraprostatic Tissue Infection in Catheterised Patients in comparison to Controls A. N. Talpur, A. T. Hasan, M. A. Sheikh Department of Urological Surgery and Transplantation, Jinnah Postraduate Medical
Intraprostatic Tissue Infection in Catheterised Patients in comparison to Controls A. N. Talpur, A. T. Hasan, M. A. Sheikh Department of Urological Surgery and Transplantation, Jinnah Postraduate Medical
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM)
 HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
