Current status of breast reconstruction in China: an experience of 951 breast reconstructions from a single institute
|
|
|
- Stewart Boone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Current status of breast reconstruction in China: an experience of 95 breast reconstructions from a single institute Nai-Si Huang,, Chen-Lian Quan,, Lin-Xiao-Xi Ma,, Jing Si,, Jia-Jian Chen,, Ben-Long Yang,, Xiao-Yan Huang,, Guang-Yu Liu,, Zhen-Zhou Shen,, Zhi-Min Shao,, Jiong Wu,,3 Department of Breast Surgery, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai 3, China; Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 3, China; 3 Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou 56, China Contributions: (I) Conception and design: J Wu, NS Huang; (II) Administrative support: XY Huang, GY Liu, ZZ Shen, ZM Shao, J Wu; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: NS Huang, JJ Chen, BL Yang, XY Huang; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: NS Huang, CL Quan, LX Ma, J Si, JJ Chen, BL Yang; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: NS Huang, CL Quan, LX Ma, J Si; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. Correspondence to: Jiong Wu. No.7 Dongan Rd., Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai 3, China. wujiong@vip.sina.com. Background: Since mastectomy remained the primary strategy for treating breast cancer in China, postmastectomy reconstruction is of great importance in the Chinese population. The current study aimed to assess the current status of breast reconstruction in China. Methods: We reviewed all patients who received breast reconstruction from August to July 5 in the Department of Breast Surgery in our institute. Patients baseline characteristics, reconstruction strategy, final pathology and loco-regional recurrence (LRR) information were collected. Results: A total of 95 breast reconstructions were conducted during the past 5 years, among which 47 (7.%) were abdominal flap reconstruction; 47 (5.5%) were latissimus dorsi myocutaneous ± implant; and 33 (5.5%) were prosthesis-based reconstruction. The majority of cases (78.%) were invasive breast cancer and up to 894 cases (94.%) were immediate reconstruction. Prosthesis-based reconstruction rapidly increased in recent years, and was associated with bilateral reconstruction, contralateral augmentation and higher complications. 8 patients (.%) developed local-regional recurrence at the median follow-up time of 6.6 months (range, months). A total of 66 nipple-areolar complex-sparing mastectomies (NSMs) (6.9%) were performed, none of which developed recurrence. Conclusions: Breast reconstruction cases increased over the 5 years with the change of paradigm. Most strikingly, prosthesis-based reconstruction rapidly gained its prevalence and became the most common strategy. NSM was only performed for highly selected patients. Patients with breast reconstruction were able to achieve satisfactory loco-regional control in our cohort. Keywords: Breast reconstruction; breast cancer; China; current status Submitted Feb, 6. Accepted for publication Feb 9, 6. doi:.37/gs.6.3. View this article at: Introduction With the improvement of systemic treatment, the surgical management of breast cancer experienced substantial revolution over the years. Although breast-conserving therapy (BCT) has become the primary surgical treatment for breast cancer worldwide, and approximately 6 7% of stage II patients in the United States undergo BCT (), a multi-center retrospective study in China indicated that modified radical mastectomy remained the primary strategy for treating breast cancer (). Thus, post-mastectomy reconstruction is of great Gland Surg 6;5(3):78-86
2 Gland Surgery, Vol 5 No 3 June 6 79 importance in the Chinese population. In recent years, attentions have been focused on this field, which would significantly improve aesthetic outcome for breast cancer patients on the basis of not affecting the oncological results. Multiple mastectomy techniques, such as skinsparing mastectomy (SSM) and nipple-areolar complexsparing mastectomy (NSM), combined with immediate breast reconstruction, were adopted for patients with reconstruction demand. Also, various techniques were performed for reconstruction, including pedicle transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap reconstruction, free-tram flap reconstruction, latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap (LDMF) reconstruction and prosthesis-based reconstruction. The current study aimed to assess the current status of breast reconstruction in China, by reviewing 95 breast reconstruction cases over the past 5 years in Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center (FUSCC). We also described the paradigm change and local-regional control of these patients. Materials and methods Patients We reviewed all patients who received breast reconstruction from August to July 5 in the Department of Breast Surgery FUSCC. The following inclusion criteria were applied: (I) female patients who received reconstruction after mastectomy; (II) therapeutic and prophylactic cases; (III) unilateral and bilateral patients with breast reconstruction; (IV) immediate and delayed reconstruction. However, patients with breast-conserving surgery and partial reconstruction were excluded. Patients baseline characteristics, reconstruction strategy, final pathology and loco-regional recurrence (LRR) information were collected. The 7 th edition of the AJCC TNM was utilized to stage the patients. The protocol for the present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of FUSCC. Reconstruction methods The surgical management of the patients was grouped as follows: LDMF flap reconstruction (including extended LDMF flap reconstruction and LDMF + implant reconstruction), abdominal flap reconstruction (pedicle- TRAM and free-tram reconstruction), and prosthesisbased reconstruction (direct to implant reconstruction and two-stage reconstruction). In the two-stage prosthesisbased reconstruction, patients were implanted with a soft-tissue expander immediately after mastectomy. After inflating the expander with saline over a period of time, the expander is then replaced with a permanent implant. Nipple reconstruction, return to operation room (OR) complications, contralateral breast aesthetic surgeries, and ipsilateral breast modification were also included into analysis. Follow-up The follow-up data on the breast cancer patients were acquired from the Department of Clinical Statistics of FUSCC. LRR was defined as any progression in the ipsilateral breast, skin, muscles of the chest wall and/or axillary/supraclavicular lymph nodes (LNs). Survival was calculated from the date of surgery to the date of clinical relapse. Patients whose last follow-up was 3 months after surgery were regarded as lost to follow-up and were excluded from analysis. Results Baseline characteristics of patients From August to July 5, a total of 95 breast reconstructions were conducted in our institute. Among these cases, 885 patients had unilateral breast reconstruction; 3 patients had bilateral breast reconstruction; one patient had bilateral reconstruction while received a third reconstruction after flap loss of her right breast. The median age of patients to have breast reconstruction was 39 years old (range, 9 77 years old). In 3 bilateral reconstruction patients, 3 suffered from bilateral breast cancer, and 8 had unilateral breast cancer and contralateral prophylactic mastectomy. The clinical pathological characteristics of patients primary breast disease were demonstrated in Table. The majority of cases (78.%) were invasive breast cancer and breast cancer in situ (7.%). The median size for invasive breast cancer was. cm (IQR:.5 3. cm), for breast cancer in situ was. cm (IQR:..5 cm) and for other breast tumor was 4.5 cm (IQR: cm), respectively. Of all patients, 6 had previous breast-conserving surgery and developed ipsilateral breast recurrence. They subsequently had mastectomy and breast reconstruction; 39 cases received neo-adjuvant chemotherapy prior to surgery Gland Surg 6;5(3):78-86
3 8 Huang et al. Current status of breast reconstruction in China and reconstruction, seven of which achieved pathological complete remission (pcr). Current status and trend of breast reconstruction in FUSCC In 95 cases, 47 (7.%) were abdominal flap reconstruction; 47 (5.5%) were LDMF ± implant reconstruction; and 33 (5.5%) were prosthesis-based reconstruction, among which 88 were expander-implant reconstruction and 45 were direct-to-implant reconstruction. In terms of timing, 894 cases (94.%) were immediate reconstruction; 5 cases (5.4%) were delayed reconstruction; and six cases were delayedimmediate reconstruction. The trend of breast reconstruction by year was illustrated in Table and Figure. There was a significant Table Baseline clinical-pathological characteristics of patients primary breast disease according to final pathology Pathology N (%) Invasive breast cancer 743 (78.) Stage I 77 (37.3) Stage II 75 (37.) Stage III 79 (.6) In situ breast cancer 63 (7.) Ductal carcinoma in situ 56 (95.7) Lobular carcinoma in situ 7 (4.3) Phyllodes tumor 8 (.9) Other malignant breast tumor 7 (.7) Prophylactic mastectomy 8 (.8) Unknown 3 (.3), seven patients received neo-adjuvant achieved pathological complete remission and staged. change in breast reconstruction strategy over the years. Notably, although the total breast reconstruction cases increased steadily, the percentile of reconstruction strategies varied. LDMF ± implant (Figure ) had remained most common method until 4, while prosthesis-based reconstruction rose rapidly from eight cases in to 6 cases in 5, increased more than -fold during this short period (Figure 3). Pedicle-TRAM reconstruction was gradually replaced by free-tram reconstruction since (Figure 4). Nevertheless, free abdominal flap reconstruction decreased gently in recent years. Among all reconstructions, cases failed to complete reconstruction, including total flap loss in three cases of free TRAM reconstruction, 6 cases of expander or implant loss in prosthesis-based reconstruction, and one case in LDMF + implant reconstruction due to implant exposure. Most interestingly, 3 out of 6 (8.%) cases in the prosthesisbased group lost their expander/implant without specific complications, except for patients regretting their decision to receive reconstruction. Two patients lost their expander/ Breast reconstruction cases 5 5 All Abdominal flap Prosthesis-based LDMF ± implant Year Figure Trend of breast reconstruction in FUSCC. FUSCC, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. Table Breast reconstruction trends in different surgical groups Year LDMF ± implant, N (%) Prosthesisbased, N (%) Pedicle-TRAM, N (%) Free-TRAM, N (%) (5.) (33.3) 4 (.) (.) (.) (.) (.) (.) (5.) (.) (.) (66.7) (.) (.) (.) (.) (89.7) (3.4) (6.9) (.) (88.5) (.) 3 (.5) (.) (73.) (3.8) (7.7) 4 (5.4) (74.4) (4.7) 7 (6.3) (4.7) (63.5) (.4) 3 (3.) 3 (4.) 9 54 (65.9) (.4) 3 (8.) 3 (3.7) 4 (47.) (.4) 7 (7.9) 9 (3.6) 54 (47.8) 8 (7.) 7 (6.) 44 (38.9) 3 53 (4.4) 3 (5.) (7.8) 33 (5.8) (37.9) 69 (49.3) 4 (.9) 4 (.) (7.) 6 (59.6) (.) 4 (3.5) Total , time interval was calculated from August of the prior year to July of the next year. Total 47 (49.5) 33 (4.5) 9 (9.6) 56 (6.4) Gland Surg 6;5(3):78-86
4 Gland Surgery, Vol 5 No 3 June 6 8 A B C D Figure LDMF flap breast reconstruction. (A,B) Pre-operative pictures; (C,D) postoperative pictures with reconstructed breast and donor site scar. LDMF, latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap. A B C D Figure 3 Expander-implant two stage breast reconstructions. (A) Pre-operative pictures; (B) after skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate expander reconstruction, the patient s expander was injected with saline bi-weekly with satisfied appearance; (C) the patient s expander was replaced by permanent implant; (D) the patient received nipple reconstruction and tattoo of nipple-areolar complex (NAC). implant because of post-operative infection; and one patient required her implant removal due to discomfort. Moreover, three patients (two unilateral cases and one bilateral case) failed to turn up in our institute for permanent implant placement after expander reconstruction for more than years, indicating they probably did not complete the twostage reconstructive surgery. Thirty-eight cases (4.%) developed post-operative complications that required re-operation. In prosthesisbased reconstruction, 5 cases returned to operation room with varied reasons, such as infection, expander rupture and expander/implant exposure. Prosthesis-based reconstruction also had more contralateral breast surgery than other reconstructive surgeries, the majority of which were contralateral breast reconstruction (5.9%) and contralateral breast augmentation (9.9%). In the meantime, abdominal flap group had the most contralateral breast reduction/ mastopexy cases (4.9%) (Figure 5). Abdominal flap reconstruction also had the most percentiles of ipsilateral breast modification (5.7%) and nipple reconstruction (4.7%) among three reconstruction surgeries (Table 3). NSM in breast reconstruction For reconstructive patients, we routinely performed SSM. A total of 66 NSMs (6.9%) were performed in 6 patients, of which in LDM ± implant group and 55 in prosthesisbased group. The breast diseases for these cases were as follows: 34 (6.8%) were invasive breast cancer; 4 (5.4%) were in situ breast cancer; (.8%) were phyllodes Gland Surg 6;5(3):78-86
5 8 Huang et al. Current status of breast reconstruction in China A C E B D F Figure 4 Muscle-sparing free TRAM flap reconstruction. (A,B) Pre-operative pictures; (C,D) 3 months after skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstructive surgery; (E,F) year after initial breast reconstruction followed by second-stage nipple reconstruction and tattoo of nipple-areolar complex (NAC). tumor; five for prophylactic mastectomy; and one for other malignant breast tumor. One case received intra-operative single-dose nipple-areola complex (NAC) radiotherapy; in another case, the patient required to resect the NAC because of concerns of NAC recurrence. None of the patients developed NAC, other loco-regional or distant recurrence in our cohort. local-regional recurrence only (Table 4). In terms of the site of local-regional recurrence, 9 out of 8 patients developed breast/chest wall recurrence, four patients had supra-clavicle LN recurrence, two had axillary LN recurrence, two had internal mammary LN recurrence and one patient was not documented the specific site of recurrence. None of these patients died in our cohort. Loco-regional control of breast cancer patients with reconstruction A total of 887 cases were more than three months. The median follow-up time was 8. months (range, months). Eighteen patients (.%) developed local-regional recurrence at the median follow-up time of 6.6 months (range, months). Eight patients developed distant metastasis prior to or at the same time of local-regional recurrence. Two patients developed local-regional recurrence prior to distant metastasis and seven patients developed Discussion The current study revealed a significant trend of increase in breast reconstruction cases in FUSCC. However, compared with the great amount of mastectomies performed in China, breast reconstruction stays at a rather stable low rate of % over the past 5 years (3,4). Several reasons were thought to contribute to the low rate of reconstruction in China. Firstly, traditional Chinese women have low demand for their body image, and many of them are unaware of the possibility of breast reconstruction, especially for the older Gland Surg 6;5(3):78-86
6 Gland Surgery, Vol 5 No 3 June 6 83 generations, which explained why the median age for breast reconstruction was 39 years old while the median age for breast surgery was around 5 in our institute (5). Secondly, the heavy workload hampered the generalized application of reconstruction techniques. As reported by previous studies, there was a 4-fold increase of breast surgeries between 6 A C Figure 5 Free abdominal flap reconstruction with immediate contralateral breast reduction. (A,B) Pre-operative pictures; (C,D) postoperative pictures. B D and 4 while the number of breast surgeons increased from 3 to 5 in FUSCC (3). Next, the dramatic increase of prophylactic mastectomy in Western countries increased reconstruction rate (6,7), while in China, this has little impact since such procedures are rarely performed. Lastly, limited patient education resulted that some patients were not aware of the option of breast reconstruction. Significant shift in breast reconstruction paradigm was observed in our cohort. Prosthesis-based reconstruction displayed a more than ten-fold increase from to 5, which echo with the worldwide transformation. In US, prosthesis-based reconstruction rates increased on average % per year from 8.5% in 998 to 5.8% in 8, surpassing autologous reconstruction to be the leading reconstructive method (8). The use of prosthesis can achieve aesthetical symmetrical appearance in bilateral reconstruction patients, especially in slim women whose autologous tissue may not be abundant enough for reconstruction. In our cohort, up to 5.9% patients had bilateral reconstruction in the prosthesisbased reconstruction group, much higher than other modalities; and another 9.9% patients had contralateral breast augmentation. In sum, up to 5% patients had bilateral implants placed. Notably, despite the advantages of short operation time and in-hospital time, prosthesisbased reconstruction had the highest fail-to-completereconstruction rate and return-to-operation room rate. Most surprisingly, the majority of patients had their implant/expander removed because that they regretted their decision to have prosthesis-based reconstruction. Further investigations are awaited to explore the reason behind this phenomenon. For autologous reconstruction, on the other hand, our data suggested that pedicle-tram reconstruction Table 3 Comparisons of other surgical conditions besides reconstruction in different surgical groups Surgical conditions Total, N=95 (%) Abdominal flap, N=47 (%) LDM ± implant, N=47 (%) Prosthesis-based, N=33 (%) Fail to complete surgery (.) 3 (.) (.) 6 (6.9) Return to OR complications 38 (4.) 3 (5.3) (.) 5 (6.4) Contralateral breast surgery 8 (.4) (8.5) 8 (3.8) 69 (9.6) Reconstruction 53 (5.6) 7 (.8) 9 (.9) 37 (5.9) Reduction/mastopexy 44 (4.6) (4.9) 9 (.9) 9 (3.9) Augmentation (.) (.8) (.) 3 (9.9) Ipsilateral breast modification 9 (.) 4 (5.7) (.4) 3 (.3) Nipple reconstruction (.7) 6 (4.7) 34 (7.) 7 (3.), biopsy and breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy of the contralateral breast were excluded. OR, operation room. Gland Surg 6;5(3):78-86
7 84 Huang et al. Current status of breast reconstruction in China Table 4 Characteristics of breast reconstruction patients who developed LRR prior to distant metastasis or LRR only No. Age Reconstruction Pathology Stage LRR time (mo) LRR site Status (mo) 3 LDMF IDC IIB 37.5 Chest DRFS LDMF + implant IDC pcr 37.6 Chest Bone m at Pedicled TRAM IDC IIB 4. Chest DRFS Free TRAM IDC IIA 6.9 Supra-clavicle LN DRFS LDMF IDC IIB 5.6 Axillary LN DRFS Free TRAM DCIS + micro invasion IIA 9.6 Chest DRFS LDMF + implant DCIS + micro invasion IA 36. Chest DRFS Free TRAM IDC IIA 8. Internal mammary LN Lung m at LDMF + implant DCIS + micro invasion IIA 8.9 Chest DRFS Prosthesis-based IDC IIA.5 IMLN DRFS 6.6 LRR, loco-regional recurrence; LDMF, latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap; IDC, invasive ductal carcinoma; pcr, pathological complete remission; m, metastasis; DRFS, distant recurrence-free survival; TRAM, transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous; DCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ; LN, lymph node; met, metastasis; mo, months. was gradually replaced by free-tram reconstruction since. Compared with pedicle-tram, free- TRAM has significantly lower rate of the complication including abdominal bulge, abdominal strength weaken and hernia, with improved blood supply (9,). Despite all the advantages, the application of free-tram was largely restricted by professional microsurgery skills and techniques as well as a much longer learning curve (). As a typical cancer center in mainland China, there is no Department of Plastics and Reconstructive Surgery in FUCSS and all free-tram cases were performed by one single surgeon, which explained why LDMF reconstruction remained the most common method of autologous reconstruction. Furthermore, patients with abdominal flap reconstruction were more likely to have ipilateral breast modification surgeries and nipple reconstruction than other reconstruction modalities, which implied these patients might have a higher demand for breast symmetry and selfimage. Although SSM is routinely performed for patients who received breast reconstruction in our institute, the use of NSM is still limited. In our cohort, there are 6.9% NSMs performed, all of which are highly selected cases no suspected cancer infiltration to NAC measured by imaging techniques, phyllodes tumor and prophylactic mastectomy. NSM, with preservation of the NAC, is reported to improve patients satisfaction, body image, and psychological adjustment (,3). However, the indication of NSM is still under debate. Multiple studies have demonstrated that tumor size, tumor location, LN metastasis, lymphovascular invasion, histologic type, immunological characteristics like HER should be taken into consideration when propose NSM to breast cancer patients (4-6). In terms of LRR of NSM, none of our cases developed loco-regional or distant recurrence because of relative short follow-up time and highly selective cases. According to previous studies, Orzalesi et al. reported loco-regional, NAC, systemic recurrence accounting for.9%,.7% and.% respectively, with.7% death record among a 6-year study in Italy (7). NAC recurrence cases could be treated with NAC removal and had good prognoses, which suggested that NSM might be a safe procedure after selecting proper patients (8). Despite NSM, same concerns was raised for all patients with breast reconstruction, that residual mammary tissue might be present and that breast reconstruction could negatively affected adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy, especially in loco-regional control. Some study demonstrated that immediate breast reconstruction was associated with delay of adjuvant chemotherapy for women under the age of 6 (9); while another debated that immediate breast reconstruction did not delay adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with patients with no reconstruction (4 vs. 4 days, P=.6) (). As for postmastectomy radiotherapy, Liljegren et al. found that the delivery of radiation was compromised in more than half of the patients underwent prosthesis-based immediate breast reconstruction, however the time from mastectomy to the start of radiotherapy was similar in reconstruction group versus non-reconstruction group (). Kronowitz suggested Gland Surg 6;5(3):78-86
8 Gland Surgery, Vol 5 No 3 June 6 85 that immediate breast reconstruction did not pose negative impact on recurrence free survival in patients who received post-mastectomy radiotherapy in neither autologous tissuebased reconstruction nor implant-based reconstruction (,3). In the current study, at a median follow-up time of 8. months, only.% patients developed LRR, suggesting a satisfactory loco-regional control. Nevertheless, the interaction between breast reconstruction and adjuvant therapy was beyond the scope of our study. Conclusions The current study described a 5-year study of 95 breast reconstruction cases in FUSCC. The reconstruction cases increased over the years with the change of paradigm. Most strikingly, prosthesis-based reconstruction rapidly gained its prevalence and became the most common strategy in last year. Prosthesis-based reconstruction was associated with bilateral reconstruction, contralateral augmentation and higher complications. SSM was routinely performed for all reconstruction patients while NSM was only performed for highly selected patients. Patients with breast reconstruction were able to achieve satisfactory loco-regional control in our cohort. Acknowledgements None. Footnote Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. References. McGuire KP, Santillan AA, Kaur P, et al. Are mastectomies on the rise? A 3-year trend analysis of the selection of mastectomy versus breast conservation therapy in 5865 patients. Ann Surg Oncol 9;6: Zhang B, Song Q, Zhang B, et al. A -year (999 ~ 8) retrospective multi-center study of breast cancer surgical management in various geographic areas of China. Breast 3;: Jia-jian C, Nai-si H, Jing-yan X, et al. Current Status of Breast Reconstruction in Southern China: A 5 Year, Single Institutional Experience of,55 Breast Cancer Patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 5;94:e Chen Y, Chen J, Chen J, et al. Current trends of breast reconstruction after mastectomy for breast cancer patients in China: a survey report. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 4;36: Wang XL, Liu LB, Song FM, et al. Meta-analysis of the safety and factors contributing to complications of MS- TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA flaps for breast reconstruction. Aesthetic Plast Surg 4;38: Tuttle TM, Jarosek S, Habermann EB, et al. Increasing rates of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy among patients with ductal carcinoma in situ. J Clin Oncol 9;7: Cemal Y, Albornoz CR, Disa JJ, et al. A paradigm shift in U.S. breast reconstruction: Part. The influence of changing mastectomy patterns on reconstructive rate and method. Plast Reconstr Surg 3;3:3e-6e. 8. Albornoz CR, Bach PB, Mehrara BJ, et al. A paradigm shift in U.S. Breast reconstruction: increasing implant rates. Plast Reconstr Surg 3;3: Hartrampf CR, Scheflan M, Black PW. Breast reconstruction with a transverse abdominal island flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 98;69:6-5.. Grotting JC. Immediate breast reconstruction using the free TRAM flap. Clin Plast Surg 994;:7-.. Gurunluoglu R, Gurunluoglu A, Williams SA, et al. Current trends in breast reconstruction: survey of American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Ann Plast Surg 3;7:3-.. Wellisch DK, Schain WS, Noone RB, et al. The psychological contribution of nipple addition in breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 987;8: Didier F, Radice D, Gandini S, et al. Does nipple preservation in mastectomy improve satisfaction with cosmetic results, psychological adjustment, body image and sexuality? Breast Cancer Res Treat 9;8: Shimo A, Tsugawa K, Tsuchiya S, et al. Oncologic outcomes and technical considerations of nipple-sparing mastectomies in breast cancer: experience of 45 cases from a single institution. Breast Cancer 5. [Epub ahead of print]. 5. Lohsiriwat V, Martella S, Rietjens M, et al. Paget's disease as a local recurrence after nipple-sparing mastectomy: clinical presentation, treatment, outcome, and risk factor analysis. Ann Surg Oncol ;9: Huang NS, Wu J. Nipple-sparing Mastectomy in Breast Cancer: From an Oncologic Safety Perspective. Chin Med J (Engl) 5;8: Orzalesi L, Casella D, Santi C, et al. Nipple sparing Gland Surg 6;5(3):78-86
9 86 Huang et al. Current status of breast reconstruction in China mastectomy: Surgical and oncological outcomes from a national multicentric registry with 93 patients (6 cases) over a six year period. Breast 6;5: Petit JY, Veronesi U, Orecchia R, et al. Risk factors associated with recurrence after nipple-sparing mastectomy for invasive and intraepithelial neoplasia. Ann Oncol ;3: Alderman AK, Collins ED, Schott A, et al. The impact of breast reconstruction on the delivery of chemotherapy. Cancer ;6: Eck DL, McLaughlin SA, Terkonda SP, et al. Effects of immediate reconstruction on adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Ann Plast Surg 5;74 Suppl 4:S-3.. Liljegren A, Unukovych D, Gagliardi G, et al. No difference in dose distribution in organs at risk in postmastectomy radiotherapy with or without breast implant reconstruction. Radiat Oncol 4;9:4.. Kronowitz SJ. Current status of autologous tissue-based breast reconstruction in patients receiving postmastectomy radiation therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg ;3: Kronowitz SJ. Current status of implantbased breast reconstruction in patients receiving postmastectomy radiation therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg ;3:53e-53e. Cite this article as: Huang NS, Quan CL, Ma LX, Si J, Chen JJ, Yang BL, Huang XY, Liu GY, Shen ZZ, Shao ZM, Wu J. Current status of breast reconstruction in China: an experience of 95 breast reconstructions from a single institute. Gland Surg 6;5(3): doi:.37/gs.6.3. Gland Surg 6;5(3):78-86
Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate surgical options
 A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks
 Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction
 Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities
 Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy. Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD
 How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Breast Reconstruction
 Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications
 Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
The evolution of mastectomies in the oncoplastic breast surgery era
 Perspective The evolution of mastectomies in the oncoplastic breast surgery era Gustavo Zucca-Matthes 1,2, Andrea Manconi 3, Rene Aloísio da Costa Viera 1,2, Rodrigo Augusto Depieri Michelli 2, Angelo
Perspective The evolution of mastectomies in the oncoplastic breast surgery era Gustavo Zucca-Matthes 1,2, Andrea Manconi 3, Rene Aloísio da Costa Viera 1,2, Rodrigo Augusto Depieri Michelli 2, Angelo
Skin sparing mastectomy: Technique and suggested methods of reconstruction
 Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2014) 26, 153 159 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Full Length Article Skin
Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2014) 26, 153 159 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Full Length Article Skin
Predictors of Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy and the Impact on Breast Reconstruction
 CLINICAL PAPER Predictors of Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy and the Impact on Breast Reconstruction Ximena A. Pinell-White, MD, Keli Kolegraff, MD, and Grant W. Carlson, MD Background: Contralateral
CLINICAL PAPER Predictors of Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy and the Impact on Breast Reconstruction Ximena A. Pinell-White, MD, Keli Kolegraff, MD, and Grant W. Carlson, MD Background: Contralateral
National Mastectomy & Breast Reconstruction Audit Datasheet - Mastectomy +/- Immediate Reconstruction
 Patient Registration data Surname Forename NHS/Private Hospital Number Date of birth Postcode Ethnicity Patient-reported outcomes consent Has this patient consented to being sent outcome questionnaires?
Patient Registration data Surname Forename NHS/Private Hospital Number Date of birth Postcode Ethnicity Patient-reported outcomes consent Has this patient consented to being sent outcome questionnaires?
Breast Reconstruction Surgery
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Reconstructive Breast Surgery following Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: A Review
 Research Article http://www.alliedacademies.org/advanced-surgical-research/ Reconstructive Breast Surgery following Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: A Review Gurnam Virdi* Department of surgery, Queen Elizabeth
Research Article http://www.alliedacademies.org/advanced-surgical-research/ Reconstructive Breast Surgery following Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: A Review Gurnam Virdi* Department of surgery, Queen Elizabeth
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy PRE-DETERMINATION
Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy PRE-DETERMINATION
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Breast Cancer Reconstruction
 Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni
 SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy Version 2002: Brunnert Version
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy Plastic Reconstructive Aspects after Mastectomy Version 2002: Brunnert Version
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER
 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: September 2013 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: September 2013 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial
Nipple Sparing Mastectomy: Tips & Tricks. Rebecca Nelson, MD MSc FRCSC Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon, Burnaby Hospital
 Nipple Sparing Mastectomy: Tips & Tricks Rebecca Nelson, MD MSc FRCSC Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon, Burnaby Hospital Nipple Sparing Mastectomy (NSM) Introduction & Technique Safety Evidence Indications/Contraindications
Nipple Sparing Mastectomy: Tips & Tricks Rebecca Nelson, MD MSc FRCSC Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon, Burnaby Hospital Nipple Sparing Mastectomy (NSM) Introduction & Technique Safety Evidence Indications/Contraindications
MASTECTOMY AND IMMEDIATE BREAST RECONSTRUCTION IN INVASIVE CARCINOMA
 MASTECTOMY AND IMMEDIATE BREAST RECONSTRUCTION IN INVASIVE CARCINOMA Node-postive breast cancer Delayed-immediate reconstruction versus delayed reconstruction DBCG RT Recon-Protocol Tine Engberg Damsgaard
MASTECTOMY AND IMMEDIATE BREAST RECONSTRUCTION IN INVASIVE CARCINOMA Node-postive breast cancer Delayed-immediate reconstruction versus delayed reconstruction DBCG RT Recon-Protocol Tine Engberg Damsgaard
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Updates in Breast Care. Truth or Hype. History of Breast Cancer Surgery. Dr Karen Barbosa 5/3/2017 4/20/2017
 Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap?
 Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap? Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, George Collis, MD, and Dustin Eck, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence:
Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap? Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, George Collis, MD, and Dustin Eck, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence:
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
Partial Breast Reconstruction Using Various Oncoplastic Techniques for Centrally Located Breast Cancer
 Partial Breast Reconstruction Using Various Oncoplastic Techniques for Centrally Located Breast Cancer Original Article Hyo Chun Park 1, Hong Yeul Kim 1, Min Chul Kim 2, Jeong Woo Lee 2, Ho Yun Chung 2,
Partial Breast Reconstruction Using Various Oncoplastic Techniques for Centrally Located Breast Cancer Original Article Hyo Chun Park 1, Hong Yeul Kim 1, Min Chul Kim 2, Jeong Woo Lee 2, Ho Yun Chung 2,
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.10 Skin Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.10 Skin Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate
Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries
 Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Effective Date: November 8, 2016 Subject: Breast Surgeries Policy: HPHC covers medically necessary breast surgeries including mastectomy, breast reconstruction,
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Effective Date: November 8, 2016 Subject: Breast Surgeries Policy: HPHC covers medically necessary breast surgeries including mastectomy, breast reconstruction,
The Use of the Latissimus dorsi Flap in Breast Reconstruction of Post-Mastectomy Patients: Is Superior to the Use of Expander / Prosthesis?
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Aesthetic & Reconstructive Surgery DOI: 10.4172/2472-1905.100014 The Use of the Latissimus dorsi Flap in Breast Reconstruction of Post-Mastectomy
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Aesthetic & Reconstructive Surgery DOI: 10.4172/2472-1905.100014 The Use of the Latissimus dorsi Flap in Breast Reconstruction of Post-Mastectomy
Surgical Advances in the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Laura Kruper, MD, MSCE Chief, Breast Surgery
 Surgical Advances in the Treatment of Breast Cancer Laura Kruper, MD, MSCE Chief, Breast Surgery Nothing to disclose DISCLOSURE LESS IS MORE Radiation Lymph nodes Reconstruction Less is More! Radiation
Surgical Advances in the Treatment of Breast Cancer Laura Kruper, MD, MSCE Chief, Breast Surgery Nothing to disclose DISCLOSURE LESS IS MORE Radiation Lymph nodes Reconstruction Less is More! Radiation
Classification System
 Classification System A graduate of the Breast Oncology training program should be able to care for all aspects of disease and/or provide comprehensive management. When referring to a discipline of training
Classification System A graduate of the Breast Oncology training program should be able to care for all aspects of disease and/or provide comprehensive management. When referring to a discipline of training
The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative
 Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander.
 Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction. Westmead Breast Cancer Institute
 Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Oncoplastic breast surgery in a Danish perspective II: Reconstructive strategy in oncoplastic breast surgery
 Oncoplastic breast surgery in a Danish perspective II: Reconstructive strategy in oncoplastic breast surgery Michael Rose, MD Department of Surgery and Plastic Surgery, Hospital of Southwest Jutland, Denmark
Oncoplastic breast surgery in a Danish perspective II: Reconstructive strategy in oncoplastic breast surgery Michael Rose, MD Department of Surgery and Plastic Surgery, Hospital of Southwest Jutland, Denmark
Goals of Care. Restore shape and function after cancer
 Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
COPE Library Sample
 Breast Anatomy LOBULE LOBE ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) NIPPLE AREOLA COMPLEX ENLARGEMENT OF DUCT AND LOBE LOBULE SUPRACLAVICULAR NODES INFRACLAVICULAR NODES DUCT DUCT ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) 8420
Breast Anatomy LOBULE LOBE ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) NIPPLE AREOLA COMPLEX ENLARGEMENT OF DUCT AND LOBE LOBULE SUPRACLAVICULAR NODES INFRACLAVICULAR NODES DUCT DUCT ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) 8420
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: Page 1 of 8
 Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Surgical treatment of BRCA mutated patients. Viviana Galimberti MD European Institute of Oncology Milan, Italy
 Surgical treatment of BRCA mutated patients Viviana Galimberti MD European Institute of Oncology Milan, Italy No pharmaceutical company funding was used I declare I have no conflicts of interest as regards
Surgical treatment of BRCA mutated patients Viviana Galimberti MD European Institute of Oncology Milan, Italy No pharmaceutical company funding was used I declare I have no conflicts of interest as regards
Recent Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment
 Recent Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment Pornchai O-charoenrat MD, PhD, FRCST, FICS Professor Chief, Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery, Siriraj Hospital, THAILAND Recent Advances
Recent Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment Pornchai O-charoenrat MD, PhD, FRCST, FICS Professor Chief, Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery, Siriraj Hospital, THAILAND Recent Advances
Mitchell Buller, MEng, a Adee Heiman, BA, a Jared Davis, MD, b ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Nicolás Ajkay, MD, FACS, c and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD, FACS b
 Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries
 Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Subject: Breast Surgeries Authorization: Prior authorization is required for the following procedures requested for members enrolled in HPHC commercial (HMO, POS,
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Subject: Breast Surgeries Authorization: Prior authorization is required for the following procedures requested for members enrolled in HPHC commercial (HMO, POS,
complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative
 Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
LIPOFILLING AND ONCOPLASTIC BREAST SURGERY : oncologic safety
 LIPOFILLING AND ONCOPLASTIC BREAST SURGERY : oncologic safety JY Petit IEO Milan December 13-15, 2012 29 th Annual New York Controversies, Problems & Techniques in Surgery SYMPOSIUM COURSE DIRECTORS Robert
LIPOFILLING AND ONCOPLASTIC BREAST SURGERY : oncologic safety JY Petit IEO Milan December 13-15, 2012 29 th Annual New York Controversies, Problems & Techniques in Surgery SYMPOSIUM COURSE DIRECTORS Robert
Outcome of Management of Local Recurrence after Immediate Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap Breast Reconstruction
 Outcome of Management of Local Recurrence after Immediate Transverse Rectus bdominis Myocutaneous Flap reast Reconstruction Taik Jong Lee 1, Wu Jin Hur 1, Eun Key Kim 1, Sei Hyun hn 2 1 Department of Plastic
Outcome of Management of Local Recurrence after Immediate Transverse Rectus bdominis Myocutaneous Flap reast Reconstruction Taik Jong Lee 1, Wu Jin Hur 1, Eun Key Kim 1, Sei Hyun hn 2 1 Department of Plastic
Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps Albert Losken, MD, FACS, Claire S. Nicholas, MD, Ximena A. inell, MD, and Grant W.
BREAST SURGERY Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps Albert Losken, MD, FACS, Claire S. Nicholas, MD, Ximena A. inell, MD, and Grant W.
The decision to repair a partial mastectomy CME. State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction.
 CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
Incorporating Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Into Your Practice. Michael Howard, MD, FACS Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS
 Incorporating Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Into Your Practice Michael Howard, MD, FACS Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS 1 Disclosures Michael Howard, MD Scientific Advisor, EO2 Concepts Karol Gutowski, MD Speaker's
Incorporating Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Into Your Practice Michael Howard, MD, FACS Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS 1 Disclosures Michael Howard, MD Scientific Advisor, EO2 Concepts Karol Gutowski, MD Speaker's
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Classifying breast cancer surgery: a novel, complexity-based system for oncological, oncoplastic and reconstructive procedures, and proof of principle by analysis of
Author's response to reviews Title: Classifying breast cancer surgery: a novel, complexity-based system for oncological, oncoplastic and reconstructive procedures, and proof of principle by analysis of
Breast Surgery: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
 Breast Surgery: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow Baptist Hospital Gladys L. Giron, MD, FACS October 11,2014 Homestead Hospital Baptist Children s Hospital Doctors Hospital Baptist Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Breast Surgery: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow Baptist Hospital Gladys L. Giron, MD, FACS October 11,2014 Homestead Hospital Baptist Children s Hospital Doctors Hospital Baptist Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Current Approaches to Managing Partial Breast Defects: The Role of Conservative Breast Surgery Reconstruction
 Review Current Approaches to Managing Partial Breast Defects: The Role of Conservative Breast Surgery Reconstruction ALEXANDRE MENDONÇA MUNHOZ 1, EDUARDO MONTAG 2, JOSÉ ROBERTO FILASSI 3 and ROLF GEMPERLI
Review Current Approaches to Managing Partial Breast Defects: The Role of Conservative Breast Surgery Reconstruction ALEXANDRE MENDONÇA MUNHOZ 1, EDUARDO MONTAG 2, JOSÉ ROBERTO FILASSI 3 and ROLF GEMPERLI
Breast reconstruction has an important role BREAST. A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions
 BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
The biplanar oncoplastic technique case series: a 2-year review
 Original Article The biplanar oncoplastic technique case series: a 2-year review Alexander J. Kaminsky 1, Ketan M. Patel 2, Costanza Cocilovo 1, Maurice Y. Nahabedian 2, Reza Miraliakbari 3 1 INOVA Fairfax
Original Article The biplanar oncoplastic technique case series: a 2-year review Alexander J. Kaminsky 1, Ketan M. Patel 2, Costanza Cocilovo 1, Maurice Y. Nahabedian 2, Reza Miraliakbari 3 1 INOVA Fairfax
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts. Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA
 The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
Breast Reconstruction: Patient Information Document
 breastreconstructioncanada.ca Breast Reconstruction: Patient Information Document By Dr. Nicolas Guay Dr. Haemi Lee STANDARDIZED BREAST RECONSTRUCTION PATIENT INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Glossary...
breastreconstructioncanada.ca Breast Reconstruction: Patient Information Document By Dr. Nicolas Guay Dr. Haemi Lee STANDARDIZED BREAST RECONSTRUCTION PATIENT INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Glossary...
Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer
 BREAST Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer Edward I. Chang, M.D. Eric I. Chang, M.D. Ran Ito, M.D., Ph.D.
BREAST Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer Edward I. Chang, M.D. Eric I. Chang, M.D. Ran Ito, M.D., Ph.D.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap
 Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER
 Page 1 of 44 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: February, 2017 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the
Page 1 of 44 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION FOLLOWING PROPHYLACTIC OR THERAPEUTIC MASTECTOMY FOR BREAST CANCER Effective Date: February, 2017 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the
PAPER. Impact of Chemotherapy on Postoperative Complications After Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 PAPER Impact of Chemotherapy on Postoperative Complications After Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Anne Warren Peled, MD; Kaoru Itakura, BA; Robert D. Foster, MD; Debby Hamolsky, RN, MS;
PAPER Impact of Chemotherapy on Postoperative Complications After Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Anne Warren Peled, MD; Kaoru Itakura, BA; Robert D. Foster, MD; Debby Hamolsky, RN, MS;
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer
 Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
Locally-Advanced Ulcerative T4b Breast Cancer; Are Reconstructive Attempts Feasible?
 Locally-Advanced Ulcerative T4b Breast Cancer; Are Reconstructive Attempts Feasible? Aditya Sood MD, MBA, Lily Daniali, MD, Kameron Razzedah BS, Edward S. Lee MD, Jonathan Keith MD *Nothing to disclose
Locally-Advanced Ulcerative T4b Breast Cancer; Are Reconstructive Attempts Feasible? Aditya Sood MD, MBA, Lily Daniali, MD, Kameron Razzedah BS, Edward S. Lee MD, Jonathan Keith MD *Nothing to disclose
A Combined Practice. Why Its Worked. Barriers to Breast Reconstruction. As a breast oncologist the patient gets seemless care
 A Combined Practice A Combined Breast Oncology and Plastic Surgery Practice Why It Works Anne M. Wallace, MD, FACS Director, Comprehensive Breast Health Center Professor of Clinical Surgery, Surgical Oncology
A Combined Practice A Combined Breast Oncology and Plastic Surgery Practice Why It Works Anne M. Wallace, MD, FACS Director, Comprehensive Breast Health Center Professor of Clinical Surgery, Surgical Oncology
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Versions 2002 2012: Audretsch / Blohmer / Brunnert
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Versions 2002 2012: Audretsch / Blohmer / Brunnert
INSPIRE INTERNATIONAL NIPPLE SPARING MASTECTOMY REGISTRY
 INSPIRE INTERNATIONAL NIPPLE SPARING MASTECTOMY REGISTRY an EURECCA project Riccardo A. Audisio and Isabel T. Rubio Principal Investigators 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Background... 2 2. Rationale 2 3. Registry
INSPIRE INTERNATIONAL NIPPLE SPARING MASTECTOMY REGISTRY an EURECCA project Riccardo A. Audisio and Isabel T. Rubio Principal Investigators 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Background... 2 2. Rationale 2 3. Registry
Breast Cancer Update 2018 The Latest in Diagnosis and Treatment SARATH K, PALAKODETI, DO, FAACS GENERAL, BREAST, AND COSMETIC SURGEON TOLEDO CLINIC
 Breast Cancer Update 2018 The Latest in Diagnosis and Treatment SARATH K, PALAKODETI, DO, FAACS GENERAL, BREAST, AND COSMETIC SURGEON TOLEDO CLINIC Objectives Identify breast lesions and masses, and know
Breast Cancer Update 2018 The Latest in Diagnosis and Treatment SARATH K, PALAKODETI, DO, FAACS GENERAL, BREAST, AND COSMETIC SURGEON TOLEDO CLINIC Objectives Identify breast lesions and masses, and know
Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction
 893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
The use of postmastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) to prevent
 NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
NIPPLE SPARING MASTECTOMY
 NIPPLE SPARING MASTECTOMY 29th Annual Montefiore-Einstein Controversies in Surgery Symposium Virgilio Sacchini, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Professor of Clinical Surgery Weill Cornell Medical
NIPPLE SPARING MASTECTOMY 29th Annual Montefiore-Einstein Controversies in Surgery Symposium Virgilio Sacchini, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Professor of Clinical Surgery Weill Cornell Medical
Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy
 Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy Kseniya Roudakova, MD A CASE FROM SUNY DOWNSTATE 60F who presented for right mastectomy with immediate TRAM flap reconstruction for recurrent breast cancer Oncologic
Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy Kseniya Roudakova, MD A CASE FROM SUNY DOWNSTATE 60F who presented for right mastectomy with immediate TRAM flap reconstruction for recurrent breast cancer Oncologic
Patients with Nipple-Areola Paget s Disease and Underlying Invasive Breast Carcinoma Have Very Poor Survival: A Matched Cohort Study
 Patients with Nipple-Areola Paget s Disease and Underlying Invasive Breast Carcinoma Have Very Poor Survival: A Matched Cohort Study Hong Ling 1,2., Xin Hu 1,2., Xiao-Li Xu 1,3., Zhe-Bin Liu 1,2, Zhi-Min
Patients with Nipple-Areola Paget s Disease and Underlying Invasive Breast Carcinoma Have Very Poor Survival: A Matched Cohort Study Hong Ling 1,2., Xin Hu 1,2., Xiao-Li Xu 1,3., Zhe-Bin Liu 1,2, Zhi-Min
Breast cancer: an update
 Breast cancer: an update Dr. Sanjeewa Seneviratne M.D, MRCS, Ph.D. Senior Lecturer and Honorary Consultant Surgeon Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Colombo Plan The problem Screening & early
Breast cancer: an update Dr. Sanjeewa Seneviratne M.D, MRCS, Ph.D. Senior Lecturer and Honorary Consultant Surgeon Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Colombo Plan The problem Screening & early
Node nega)ve breast cancer: Immediate breast reconstruc)on - An op)on for every pa)ent? Peer Chris)ansen
 Node nega)ve breast cancer: Immediate breast reconstruc)on - An op)on for every pa)ent? Peer Chris)ansen Barriers to immediate breast reconstruc)on Concerns about the increased risks of local recurrence
Node nega)ve breast cancer: Immediate breast reconstruc)on - An op)on for every pa)ent? Peer Chris)ansen Barriers to immediate breast reconstruc)on Concerns about the increased risks of local recurrence
Current perspectives on radiation therapy in autologous and prosthetic breast reconstruction
 Review Article Current perspectives on radiation therapy in autologous and prosthetic breast reconstruction Mark W. Clemens, Steven J. Kronowitz Department of Plastic Surgery, The University of Texas M.D.
Review Article Current perspectives on radiation therapy in autologous and prosthetic breast reconstruction Mark W. Clemens, Steven J. Kronowitz Department of Plastic Surgery, The University of Texas M.D.
The Use of Vertical Scar Techniques in Reconstructive Surgery
 The Use of Vertical Scar Techniques in Reconstructive Surgery 12 Moustapha Hamdi, Phillip Blondeel, Koenraad Van Landuyt, Stan Monstrey H e who does not possess a thing cannot give it. Folk tradition Introduction
The Use of Vertical Scar Techniques in Reconstructive Surgery 12 Moustapha Hamdi, Phillip Blondeel, Koenraad Van Landuyt, Stan Monstrey H e who does not possess a thing cannot give it. Folk tradition Introduction
Skin Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 14, No. 4, December: 259-266, 2002 Skin Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction OMAYA NASSAR, M.D. The Department of Surgical Oncology, National
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 14, No. 4, December: 259-266, 2002 Skin Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction OMAYA NASSAR, M.D. The Department of Surgical Oncology, National
Figure 1. Anatomy of the breast
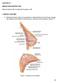 CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
Repeating Conservative Surgery after Ipsilateral Breast Tumor Reappearance: Criteria for Selecting the Best Candidates
 Ann Surg Oncol (2012) 19:3771 3776 DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2404-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Repeating Conservative Surgery after Ipsilateral Breast Tumor Reappearance: Criteria for Selecting the
Ann Surg Oncol (2012) 19:3771 3776 DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2404-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Repeating Conservative Surgery after Ipsilateral Breast Tumor Reappearance: Criteria for Selecting the
Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer.
 Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer. Goal of the study: 1.To assess whether patients at Truman
Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer. Goal of the study: 1.To assess whether patients at Truman
Radiotherapy Management of Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Julia White MD Professor, Radiation Oncology
 Radiotherapy Management of Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Julia White MD Professor, Radiation Oncology Agenda Efficacy of radiotherapy in the management of breast cancer in the Adjuvant
Radiotherapy Management of Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Julia White MD Professor, Radiation Oncology Agenda Efficacy of radiotherapy in the management of breast cancer in the Adjuvant
Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients
 236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
236 Paget's Disease of the Breast: Clinical Analysis of 45 Patients Mingfian Yang Hao Long Jiehua He Xi Wang Zeming Xie Department of Thoracic Oncology, Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou
Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction
 Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
Reconstructive Breast Surgery and Management of Breast Implants
 Reconstructive Breast Surgery and Management of Breast Implants Policy Number: 7.01.22 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 3/1993 Next Review: 1/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Reconstructive Breast Surgery and Management of Breast Implants Policy Number: 7.01.22 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 3/1993 Next Review: 1/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014). Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health?
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
Methods of autologous tissue breast reconstruction BREAST
 BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
BREAST MRI. Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
BREAST MRI Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School BREAST MRI Any assessment of the breast parenchyma requires the administration
Radiotherapy and Oncology
 Radiotherapy and Oncology xxx (2008) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Radiotherapy and Oncology journal homepage: www.thegreenjournal.com Original article Incidence of severe capsular
Radiotherapy and Oncology xxx (2008) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Radiotherapy and Oncology journal homepage: www.thegreenjournal.com Original article Incidence of severe capsular
