Methods of autologous tissue breast reconstruction BREAST
|
|
|
- Dominick Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Background: Breast reconstruction is best accomplished with lower abdominal tissue, but this results in abdominal donor-site morbidity. The superficial inferior epigastric artery (SIEA) flap is the least invasive method of lower abdominal flap breast reconstruction; however, there are no published data comparing the donor-site morbidity of SIEA flaps to that of transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) or deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) flaps. Methods: The authors used a 12-question patient survey and retrospective chart review to compare donor-site function, pain, and aesthetics in 179 patients who had unilateral or bilateral breast reconstruction with 47 SIEA flaps, 49 DIEP flaps, and 136 muscle-sparing free TRAM flaps during a 5-year period. Results: Unilateral SIEA flap patients scored higher on 10 of the 12 survey questions compared with unilateral muscle-sparing TRAM flap patients, including reporting significantly better postoperative lifting function (p 0.02) and nearly significantly shorter duration of abdominal pain (p 0.06). Bilateral reconstruction patients with at least one SIEA flap scored higher on all 12 survey questions, including reporting significantly better ability to get out of bed (sit-up motion) compared with patients with bilateral muscle-sparing TRAM or DIEP flaps (p 0.02). Conclusions: Breast reconstruction using SIEA flaps results in significantly less abdominal donor-site morbidity than DIEP flaps in bilateral cases and free muscle-sparing TRAM flaps in unilateral and bilateral cases. These are clinically relevant differences that are perceived by patients and lead to the authors recommendation to use SIEA flaps for breast reconstruction when possible to minimize abdominal donor-site morbidity. (Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 122: 702, 2008.) From the Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center. Received for publication August 20, 2007; accepted February 4, Copyright 2008 by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons DOI: /PRS.0b013e c15 Methods of autologous tissue breast reconstruction have evolved in an effort to minimize donor-site morbidity. The transverse paddle of lower abdominal tissue remains unmatched in quality and quantity for breast reconstruction. However, harvest of this abdominal donor tissue can result in motor weakness, prolonged pain, functional disturbance, and formation of bulges or hernias. Techniques used to harvest this transverse paddle of lower abdominal tissue include the pedicled transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap, 1 the free TRAM flap, 2 the musclesparing free TRAM flap, the deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) flap, 3,4 and the superficial inferior epigastric artery (SIEA) flap. 5 7 Each successive technique involves decreased excision and decreased incision of rectus abdominis muscle and fascia. The SIEA flap technique is the only one that involves neither incision nor excision of any rectus abdominis muscle or fascia. One would expect patients who undergo breast reconstruction using a SIEA flap to experience less donor-site morbidity than patients whose reconstructions use TRAM or DIEP flaps, but no published reports of which we are aware have explored this possibility. Disclosure: None of the authors has any commercial associations or financial relationships that might pose or create a conflict of interest with the information presented in this article
2 Volume 122, Number 3 Flap Donor-Site Morbidity We therefore sought to determine whether SIEA flap reconstructions resulted in less donorsite morbidity than reconstructions using musclesparing free TRAM or DIEP flaps. We compared patients perceptions of their abdominal donor site following unilateral and bilateral breast reconstruction with SIEA, DIEP, and muscle-sparing free TRAM flaps, and found that the SIEA flap patients have clinically significant decreased abdominal donor-site morbidity. PATIENTS AND METHODS We studied patients who had breast reconstruction using free SIEA flaps, free DIEP flaps, and free muscle-sparing TRAM flaps at the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center during the 5-year period from January 1, 1999, through December 31, All 41 patients who had had at least one SIEA flap breast reconstruction were included in the study. Although 10 different attending surgeons performed the reconstructions, the majority (26 patients, 66 percent) were performed by the senior author (P.M.C.). The 138 patients who had breast reconstruction using only free muscle-sparing TRAM and/or DIEP flaps were limited to those operated on by the two senior authors (D.W.C. and P.M.C.). This was done to minimize the possibility that different outcomes were attributable to variations in surgical technique of free muscle-sparing TRAM flap and DIEP flap harvest. 8 Flap selection was as previously described. 6 8 Eight patients who had died were excluded from the study. The 179 patients included in the final study group were sent a survey consisting of 12 multiplechoice questions regarding abdominal donor-site aesthetics, pain, and function (Table 1). Patients who did not return the initial survey were mailed a second survey and then called by one of the junior authors (L.C.W. and A.K.B.) who then, if the patient was willing, obtained the responses to the questions over the telephone. The surveys were mailed a mean of 1.8 years (range, 6 weeks to 4.7 years) after the participants breast reconstruction surgery. Survey responses were converted to a graded score, with lower scores corresponding to more favorable outcomes. Responses to all questions were scored from 1 to 4 except for question 1, which was scored from 1 to 3, and question 7, which was scored as a 1 or 2. These graded scores were then weighted by multiplying each score by the percentage of respondents who responded with that grade. A single weighted score for each question was obtained by adding together the weighted graded scores for each possible response. Lower weighted scores indicated a more favorable clinical outcome. A weighted score was calculated for responses to each question to obtain a single numerical value that summarized the responses to that question. The weighted scores were used to determine whether the responses of one study group were more or less clinically favorable compared with the responses of another study group. The statistical analysis, in contrast, was used to determine whether responses of one study group differed significantly from another study group but could not judge whether any such difference indicated a more or less favorable clinical outcome. Accordingly, the statistical analysis was performed using the raw number of times each response to a question was given and did not use the weighted scores. The charts of all 179 patients were reviewed retrospectively, and demographic and treatment data were extracted. This study was approved by the institutional review board at the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center. Standard descriptive statistics using the mean and SD were used to summarize continuous variables such as patient age. The Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to compare continuous or graded ordinal variables between reconstruction types. The chi-square test or Fisher s exact test where appropriate was used to compare categorical variables between patient groups. All tests were twosided. Values of p 0.05 were considered statistically significant. RESULTS Of the 179 patients sent surveys, 112 completed them, for a response rate of 63 percent. There was no statistically significant difference between patients who completed the survey (responders) and patients who did not complete the survey (nonresponders) with respect to length of time between surgery and survey mailing, body mass index, timing of breast reconstruction (immediate or delayed), flap type, smoking history, or laterality of the breast reconstruction (right side, left side, or bilateral) (Table 2). The mean age of the responders was 3 years older than the nonresponders (p 0.04), but we judged this difference not to have clinical relevance. Unilateral SIEA versus Unilateral Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps There were 23 unilateral SIEA flap and 79 unilateral muscle-sparing TRAM flap breast re- 703
3 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery September 2008 Table 1. Patient Responses by Survey Question and Weighted Score* Unilateral Bilateral Questions and Response Choices 1. Which best describes your lower abdominal contour? SIEA (%) Muscle-Sparing TRAM (%) p Value SIEA (%) DIEP (%) p Value with SIEA (%) without SIEA (%) p Value (1) Firm and flat 11 (65) 29 (66) 11 (65) 9 (60) 10 (71) 11 (50) (2) Has a bulge on one side 0 (0) 7 (16) 0 (0) 1 (7) 2 (14) 6 (27) (3) Has a generalized bulge 6 (35) 8 (18) 6 (35) 5 (33) 2 (14) 5 (23) Weighted score How do you feel about your abdominal contour? (1) Very satisfied 7 (41) 19 (43) 7 (41) 8 (53) 9 (64) 10 (45) (2) Satisfied 5 (29) 19 (43) 5 (29) 4 (27) 3 (21) 6 (27) (3) Acceptable 4 (24) 4 (9) 4 (24) 1 (7) 2 (14) 6 (27) (4) Not satisfied 1 (6) 2 (5) 1 (6) 2 (13) 0 (0) 0 (0) Weighted score Which best describes your abdominal pain after the 0.26 surgery? (1) No pain 4 (24) 5 (11) 4 (24) 1 (7) 2 (14) 3 (14) (2) Minimally painful 5 (29) 10 (23) 5 (29) 6 (40) 5 (36) 3 (14) (3) Painful but well tolerated 4 (24) 20 (45) 4 (24) 5 (33) 4 (29) 8 (36) (4) Very painful 4 (24) 9 (20) 4 (24) 3 (20) 3 (21) 8 (36) Weighted score How long did abdominal pain associated with your 0.77 surgery last? (1) Few days 9 (53) 12 (25) 9 (53) 4 (27) 4 (29) 9 (41) (2) Few weeks 5 (29) 20 (45) 5 (29) 9 (60) 8 (57) 5 (23) (3) Few months 3 (18) 10 (23) 3 (18) 1 (7) 2 (14) 7 (32) (4) Over a year 0 (0) 3 (7) 0 (0) 1 (7) 0 (0) 1 (5) Weighted score Which best describes your low back pain after 0.39 surgery? (1) No low back pain before or after surgery 11 (65) 24 (56) 11 (65) 10 (67) 11 (79) 13 (59) (2) Same low back pain before and after surgery 4 (24) 7 (26) 4 (24) 2 (13) 2 (14) 4 (18) (3) Low back pain before, and worse after surgery 1 (6) 11 (16) 1 (6) 2 (13) 1 (7) 5 (23) (4) Low back pain after, but not before surgery 1 (6) 1 (2) 1 (6) 1 (7) 0 (0) 0 (0) Weighted score Which of the following best describes your ability to lift, in comparison with your ability to lift prior to surgery? (1) Improved 2 (12) 0 (0) 2 (12) 1 (7) 1 (7) 0 (0) (2) No difference 10 (59) 19 (43) 10 (59) 10 (67) 8 (57) 9 (41) (3) Somewhat less but acceptable 5 (29) 21 (48) 5 (29) 3 (20) 5 (36) 9 (41) (4) Significantly less 0 (0) 4 (9) 0 (0) 1 (7) 0 (0) 4 (18) Weighted score Have you returned to the same job as before surgery? (1) Yes 10 (100) 23 (92) 10 (100) 7 (88) 6 (100) 14 (88) (2) No 0 (0) 2 (8) 0 (0) 1 (12) 0 (0) 2 (13) Weighted score
4 Volume 122, Number 3 Flap Donor-Site Morbidity Table 1. Continued Unilateral Bilateral Questions and Response Choices SIEA (%) Muscle-Sparing TRAM (%) p Value SIEA (%) DIEP (%) p Value with SIEA (%) without SIEA (%) p Value 8. Which of the following best describes your ability to perform your job, in comparison with your ability prior to surgery? (1) Improved 1 (10) 0 (0) 1 (10) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) (2) No difference 8 (80) 19 (76) 8 (80) 5 (71) 6 (100) 9 (64) (3) Somewhat less but acceptable 1 (10) 5 (20) 1 (10) 1 (14) 0 (0) 3 (21) (4) Significantly less 0 (0) 1 (4) 0 (0) 1 (14) 0 (0) 2 (14) Weighted score Which of the following best describes your ability to perform housework, in comparison with your ability prior to surgery? (1) Improved 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) (2) No difference 12 (71) 31 (70) 12 (71) 12 (80) 12 (86) 15 (68) (3) Somewhat less but acceptable 5 (29) 12 (27) 5 (29) 2 (13) 1 (7) 6 (27) (4) Significantly less 0 (0) 1 (2) 0 (0) 1 (7) 1 (7) 1 (5) Weighted score Which of the following best describes your ability to participate in sporting activities, in comparison with your ability prior to surgery? (1) Improved 1 (6) 0 (0) 1 (6) 2 (13) 0 (0) 0 (0) (2) No difference 11 (65) 27 (61) 11 (65) 11 (73) 10 (71) 11 (52) (3) Somewhat less but acceptable 5 (29) 14 (32) 5 (29) 1 (7) 3 (21) 7 (33) (4) Significantly less 0 (0) 3 (7) 0 (0) 1 (7) 1 (7) 3 (14) Weighted score Which of the following best describes your ability to participate in your favorite activities, in comparison with your ability prior to surgery? (1) Improved 2 (12) 1 (2) 2 (12) 1 (7) 1 (7) 0 (0) (2) No difference 11 (65) 33 (75) 11 (65) 11 (73) 11 (79) 17 (77) (3) Somewhat less but acceptable 4 (24) 8 (18) 4 (24) 2 (13) 1 (7) 3 (14) (4) Significantly less 0 (0) 2 (5) 0 (0) 1 (7) 1 (7) 2 (9) Weighted score Which of the following best describes your ability to get out of bed in comparison with your ability prior to surgery? (1) Absolutely no difficulty 3 (18) 0 (0) 3 (18) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) (2) Need to rotate upper body 10 (59) 30 (68) 10 (59) 12 (80) 11 (79) 8 (36) (3) Need to support with one or both arms 4 (24) 13 (30) 4 (24) 2 (13) 3 (21) 14 (64) (4) Need another person s assistance 0 (0) 1 (2) 0 (0) 1 (7) 0 (0) 0 (0) Weighted score *Although 112 patients returned questionnaires, not all patients answered every question. The weighted scores were calculated using percentages carried to one decimal place, not using the percentages rounded to the nearest integer as shown in the table. Please see the Materials and Methods section for an explanation of the purpose for, and method of, calculation of the weighted scores. Fisher s exact test was used to compare the categorical responses of questions 5 and 7. The Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to compare the ordinal responses in questions 1 4, 6, and Statistically significant, and nearly statistically significant p values, and the lower weighted score in each pairwise comparison. 705
5 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery September 2008 Table 2. Comparison of Survey Responders and Nonresponders Characteristic Responders Nonresponders p Value Total No. of patients NA 179 Mean SD age (yr) (8.6) 0.04* Mean SD BMI (kg/m 2 ) (4.9) 0.43* Mean SD days between surgery and survey (median) (589) (728) 0.35* (645) Timing of reconstruction, immediate/delayed/both (%) 76/20/4 70/27/ /22/4 Smoking, current/never/past (%) 13/71/17 7/78/ /73/16 Laterality of reconstruction, right/left/bilateral (%) 33/35/32 30/45/ /39/30 Type of flap(s) 0.68 BMI, body mass index; NA, not applicable;, not shown (the nine possible combinations of unilateral and bilateral breast reconstructions using different combinations of SIEA, DIEP, and muscle-sparing TRAM flaps). *Wilcoxon rank sum test. Fisher s exact test. 2 test. construction patients. These two groups did not differ significantly with regard to age, time between surgery and survey mailing, timing of breast reconstruction, or smoking status (Table 3). However, the unilateral SIEA flap patients had a mean body mass index that was 3.3 kg/m 2 greater than the unilateral muscle-sparing TRAM flap patients, and this was a significant difference (p 0.001). The SIEA flap patients had significantly better ability to lift objects after surgery compared with the muscle-sparing TRAM flap patients (p 0.02). Seventy-one percent of the SIEA flap patients reported that their ability to lift was the same or improved after surgery, compared with 43 percent of the muscle-sparing TRAM flap patients (question 6) (Table 1). The SIEA flap patients reported overall shorter duration of postoperative abdominal pain, with 53 percent reporting that postsurgical pain lasted only a few days, compared with 25 percent of the muscle-sparing TRAM flap patients. Conversely, 30 percent of the muscle-sparing TRAM flap patients reported that their abdominal pain lasted a few months to over a year, compared with only 18 percent of the SIEA flap patients (question 4) (Table 1). These differences were nearly statistically significant (p 0.06). Overall, the SIEA flap patients gave more favorable responses than the muscle-sparing TRAM flap patients on 10 of the 12 survey questions. The lower mean body mass index of the muscle-sparing TRAM flap patients may account for the more favorable responses of this group to the two remaining questions, which dealt with abdominal donor-site contour. Unilateral SIEA versus Unilateral DIEP Flaps There were 23 unilateral SIEA flap and 24 unilateral DIEP flap breast reconstruction patients. These two groups did not differ significantly with regard to age, body mass index, time between surgery and survey mailing, timing of breast reconstruction, or smoking status (Table 3). The unilateral SIEA flap patients gave more favorable responses (lower weighted scores) to nine of the 12 survey questions. However, none of these differences was statistically significant (Table 1). Bilateral with at Least One SIEA Flap versus Bilateral without a SIEA Flap Eighteen patients had bilateral breast reconstruction with at least one SIEA flap (six SIEA plus SIEA, five SIEA plus DIEP, and seven SIEA plus muscle-sparing TRAM flaps), and 35 patients had bilateral breast reconstruction that did not include a SIEA flap (eight DIEP plus DIEP, four DIEP plus muscle-sparing TRAM, and 23 musclesparing TRAM plus muscle-sparing TRAM flaps). The differences in age, body mass index, time between surgery and survey mailing, and timing of breast reconstruction between these two groups were not significant (Table 3). However, the two groups differed significantly with regard to smoking status, with 77 percent of the non-siea flap patients not having smoked, compared with 56 percent of the group who had at least one SIEA flap (p 0.01). The bilateral breast reconstruction patients who had at least one SIEA flap gave more favorable responses to all 12 of the survey questions (Table 1). The responses to question 12 showed that bilateral breast reconstruction patients with at least one SIEA flap were statistically significantly better able to get out of bed compared with bilateral breast reconstruction patients who did not have a SIEA flap (p 0.02). DISCUSSION The SIEA flap harvest is the least invasive method of obtaining lower abdominal tissue for 706
6 Volume 122, Number 3 Flap Donor-Site Morbidity Table 3. Comparison of Breast Reconstruction Patients by Flap Type Unilateral Bilateral Muscle-Sparing TRAM p Value SIEA DIEP p Value With SIEA Without SIEA p Value Characteristic SIEA No. patients NA NA NA Mean age (yr) * * * Mean BMI (kg/m 2 ) * * * Mean days between surgery and survey (median) (497) (706) 0.30* (497) (648) 0.81* (756) (500) 0.27* Timing, immediate/ delayed/both (%) 61/39/0 77/23/ /39/0 67/33/ /11/22 83/9/ Smoking, current/ never/past (%) 4/70/26 11/73/ /70/26 8/83/ /56/39 17/77/ BMI, body mass index. *Wilcoxon rank sum test. Fisher s exact test. 2 test. breast reconstruction, as it involves neither incision nor excision of rectus abdominis muscle or fascia. In addition, the deep inferior epigastric vessels, the dominant blood supply to the rectus abdominis muscle, are not removed as they are in all types of free TRAM flap and DIEP flap harvest. It is therefore reasonable to believe that abdominal donor-site morbidity is minimized when a SIEA flap can be used for breast reconstruction. However, to our knowledge, there are no prior studies published examining abdominal donorsite function of patients who have had breast reconstruction with SIEA flaps. We have previously reported that patients do not perceive a significant difference between abdominal donor-site morbidity of free muscle-sparing TRAM flap and DIEP flap reconstructions. 8 Another recent study did not detect a significant difference in the ability of patients who had free muscle-sparing TRAM or DIEP flaps to perform a sit-up. 9 Two other studies comparing the abdominal donor-site morbidity of free TRAM flap and free DIEP flap harvest have demonstrated statistically significant greater measured abdominal strength in patients who had breast reconstruction with free DIEP flaps. 10,11 However, these quantitative differences were detected using a dynamometer and were not differences that the patients themselves noticed. In fact, no previous studies comparing free TRAM and free DIEP flaps have detected any statistically significant differences in abdominal donor-site morbidity based on patient self-assessments. 8,10 12 This suggests that although DIEP flap patients have measurably greater abdominal donor-site strength compared with free TRAM flap patients, this difference is subclinical and not evident to the patients. We compared the abdominal donor-site function of SIEA flap patients with free muscle-sparing TRAM and DIEP flap patients. We found that patients who have breast reconstruction using a SIEA flap have significantly decreased donor-site morbidity compared with patients having unilateral breast reconstruction with muscle-sparing TRAM flaps or bilateral breast reconstruction with DIEP flaps and muscle-sparing TRAM flaps. Our findings are significant because the patients notice these differences in abdominal donor-site function in their everyday lives. In other words, these findings are clinically relevant and provide evidence on which clinical decisions can be made with a rational basis. Patients with a unilateral SIEA flap breast reconstruction had significantly better ability to lift 707
7 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery September 2008 objects postoperatively and nearly significantly shorter duration of postoperative pain compared with patients who had a unilateral muscle-sparing TRAM flap (questions 4 and 6) (Table 1). Patients with a unilateral SIEA flap also responded more favorably in 10 of the 12 survey questions. Unilateral SIEA flap patients had a significantly higher mean body mass index than unilateral muscle-sparing TRAM flap patients (Table 3). This difference probably exists because we believe patients with a higher body mass index tend to have a larger abdominal pannus and therefore tend to have larger SIEA vessels when they are present, and in turn are more likely to have a SIEA flap used for breast reconstruction. Similarly, patients with higher body mass indexes are more likely to have one or more large vessels perforating the rectus abdominis muscle and are therefore more likely, in our hands, to have a DIEP flap used for breast reconstruction. This could explain why SIEA flap patients did not have a significantly higher mean body mass index than DIEP flap patients (Table 3). Our analyses also revealed a significantly greater incidence of smoking in bilateral breast reconstruction patients having at least one SIEA flap versus those who did not have a SIEA flap (Table 3) (p 0.01). Even though these differences in body mass index and smoking status would presumably decrease the likelihood that benefits from using SIEA flaps would be obvious, we still detected a benefit in patients who underwent a SIEA flap procedure. The two questions that unilateral SIEA flap patients answered less favorably than other groups concerned abdominal contour (questions 1 and 2) (Table 1). This could be explained by considering that the significantly higher mean body mass index of the SIEA flap patients probably reflects a greater degree of intraabdominal fat and a more protruding abdomen. This results in a relative lack of a flat abdomen, a greater propensity for abdominal bulging postoperatively, and likely less favorable perception of the abdominal donor-site contour. The greatest advantage of using a SIEA flap occurs in the case of bilateral breast reconstruction where two hemi lower abdominal flaps are used. If one of the two flaps is a SIEA flap, the donor site is effectively converted from a bilateral to a unilateral free muscle-sparing TRAM flap or DIEP flap donor site. Indeed, bilateral breast reconstruction patients who had at least one SIEA flap found it easier to get out of bed than patients without a SIEA flap (question 12) (Table 1), and there was a trend toward patients with at least one SIEA flap reporting better lifting ability (question 6) (Table 1). We found no statistically significant differences between patients with unilateral SIEA flaps and DIEP flaps with regard to postoperative abdominal contour, pain, or function. However, the SIEA flap patients answered three-quarters of the survey questions more favorably than the DIEP flap patients. CONCLUSIONS We conclude that breast reconstruction with SIEA flaps results in significantly less abdominal donor-site morbidity than unilateral breast reconstruction with free muscle-sparing TRAM flaps or bilateral breast reconstruction with DIEP and/or free muscle-sparing TRAM flaps. We advocate the use of SIEA flaps when possible, especially in bilateral breast reconstruction patients, to minimize abdominal donor-site morbidity. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Plastic Surgery, Unit 443 University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center 1515 Holcombe Boulevard Houston, Texas pchevray@mdanderson.org ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors thank Suyu Liu, M.S., and Gregory D. Ayers, M.S., for statistical analysis. REFERENCES 1. Hartrampf, C. R., Scheflan, M., and Black, P. W. Breast reconstruction with a transverse abdominal island flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 69: 216, Holmstrom, H. The free abdominoplasty flap and its use in breast reconstruction. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 13: 423, Allen, R. J., and Treece, P. Deep inferior epigastric perforator flap for breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 32: 32, Koshima, I., and Soeda, S. Inferior epigastric artery skin flaps without rectus abdominis muscle. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 42: 645, Arnez, Z. M., Khan, U., Pogorelec, D., and Planinsek, F. Breast reconstruction using the free superficial inferior epigastric artery (SIEA) flap. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 52: 276, Chevray, P. M. Breast reconstruction with superficial inferior epigastric artery (SIEA) flaps: A prospective comparison with TRAM and DIEP flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 114: 1077, Chevray, P. M. Update on breast reconstruction using free TRAM, DIEP and SIEA flaps. Semin. Plast. Surg. 18: 97, Bajaj, A. K., Chevray, P. M., and Chang, D. W. Comparison of donor-site complication and functional outcomes in free muscle-sparing TRAM flap and free DIEP flap breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 117: 737,
8 Volume 122, Number 3 Flap Donor-Site Morbidity 9. Nahabedian, M. Y., Tsangaris, T., and Momen, B. Breast reconstruction with the DIEP flap or the muscle-sparing (MS-2) free TRAM flap: Is there a difference? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 115: 436, Blondeel, P. N., Vanderstraeten, G. G., Monstrey, S. J., et al. The donor site morbidity of free DIEP flaps and free TRAM flaps for breast reconstruction. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 50: 322, Futter, C. M., Webster, M. H. C., Hagen, S., and Mitchell, S. L. A retrospective comparison of abdominal muscle strength following breast reconstruction with a free TRAM or DIEP flap. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 53: 578, Nahabedian, M. Y., Momen, B., Galdino, G., and Manson, P. N. Breast reconstruction with the free TRAM or DIEP flap: Patient selection, choice of flap, and outcome. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 110: 466, Online CME Collections This partial list of titles in the developing archive of CME article collections is available online at www. PRSJournal.com. These articles are suitable to use as study guides for board certification, to help readers refamiliarize themselves on a particular topic, or to serve as useful reference articles. Articles less than 3 years old can be taken for CME credit. Breast Current Trends in Breast Reduction David A. Hidalgo et al. Benign Tumors of the Teenage Breast Mary H. McGrath Breast Reconstruction with Implants and Expanders Scott L. Spear and Christopher J. Spittler Breast Cancer: Advances in Surgical Management Alan R. Shons and Charles E. Cox Breast Reconstruction with Free Tissue Transfer Michael S. Beckenstein and James C. Grotting Recurrent Mammary Hyperplasia: Current Concepts Rod J. Rohrich et al. Evolution of the Vertical Reduction Mammaplasty Scott L. Spear and Michael A. Howard Breast Augmentation Cancer Concerns and Mammography: A Literature Review Michael G. Jakubietz et al. Breast Augmentation Scott L. Spear et al. 709
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps
 Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Breast reconstruction using autologous tissue is commonly accomplished using the transverse
Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Breast reconstruction using autologous tissue is commonly accomplished using the transverse
Comparing the donor-site morbidity using DIEP, SIEA or MS-TRAM flaps for breast reconstructive surgery: A meta-analysis
 Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2012) 65, 1474e1480 REVIEW Comparing the donor-site morbidity using DIEP, SIEA or MS-TRAM flaps for breast reconstructive surgery: A meta-analysis
Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2012) 65, 1474e1480 REVIEW Comparing the donor-site morbidity using DIEP, SIEA or MS-TRAM flaps for breast reconstructive surgery: A meta-analysis
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Few would deny that lower abdominal tissue BREAST. An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction.
 BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014). Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health?
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
Breast reconstruction has an important role BREAST. A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions
 BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography
 BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
Reconstruction with autologous tissue remains a
 Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
Abdominal perforator vs. muscle sparing flaps for breast reconstruction
 Review Article Abdominal perforator vs. muscle sparing flaps for breast reconstruction Paris D. Butler, Liza C. Wu Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, University of Pennsylvania Health
Review Article Abdominal perforator vs. muscle sparing flaps for breast reconstruction Paris D. Butler, Liza C. Wu Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, University of Pennsylvania Health
Medical Journal of the Volume 20 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 1385 November Original Articles
 Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction
 Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction
 Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities
 Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
Breast reconstruction following mastectomy has
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: Microsurgical methods Venkat Ramakrishnan, Makarand Tare St. Andrew s Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery, BroomÞ eld Hospital, Chelmsford,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: Microsurgical methods Venkat Ramakrishnan, Makarand Tare St. Andrew s Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery, BroomÞ eld Hospital, Chelmsford,
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
Achieving ideal donor site aesthetics with autologous breast reconstruction
 Review Article Achieving ideal donor site aesthetics with autologous breast reconstruction Maurice Y. Nahabedian Department of Plastic Surgery, Georgetown University, Washington, DC 20007, USA Correspondence
Review Article Achieving ideal donor site aesthetics with autologous breast reconstruction Maurice Y. Nahabedian Department of Plastic Surgery, Georgetown University, Washington, DC 20007, USA Correspondence
Anterolateral Thigh Flap for Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction
 Anterolateral Thigh Flap for Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Fu-chan Wei, M.D., Sinikka Suominen, M.D., Ph.D., Ming-huei Cheng, M.D., Naci Celik, M.D., and Yung-lung Lai, M.D. Taipei, Taiwan Most
Anterolateral Thigh Flap for Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Fu-chan Wei, M.D., Sinikka Suominen, M.D., Ph.D., Ming-huei Cheng, M.D., Naci Celik, M.D., and Yung-lung Lai, M.D. Taipei, Taiwan Most
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
The progress in microsurgical procedures has led
 Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate surgical options
 A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni
 SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction
 Case Report Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction Warren Matthew Rozen 1,2, Nakul Gamanlal Patel 1, Venkat V.
Case Report Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction Warren Matthew Rozen 1,2, Nakul Gamanlal Patel 1, Venkat V.
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications
 Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty?
 Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
INTRODUCTION. Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2, Kazunori Yasumura 1, Taro Mikami 2, Shinji Kobayashi 3, Jiro Maegawa 2. Idea and Innovation
 Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
In autogenous breast reconstruction, traditional SPECIAL TOPIC
 SPECIAL TOPIC Wall following Free TRAM or DIEP Flap Reconstruction: A Meta-Analysis and Critical Review Li-Xing Man, M.D., M.Sc. Jesse C. Selber, M.D., M.P.H. Joseph M. Serletti, M.D. Pittsburgh and Philadelphia,
SPECIAL TOPIC Wall following Free TRAM or DIEP Flap Reconstruction: A Meta-Analysis and Critical Review Li-Xing Man, M.D., M.Sc. Jesse C. Selber, M.D., M.P.H. Joseph M. Serletti, M.D. Pittsburgh and Philadelphia,
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flap and its Relevant Vascular Anatomy in Korean Women
 The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flap and its Relevant Vascular Anatomy in Korean Women Original Article Byung Jun Kim, Jun Ho Choi, Tae Hoon Kim, Ung Sik Jin, Kyung Won Minn, Hak Chang Department
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flap and its Relevant Vascular Anatomy in Korean Women Original Article Byung Jun Kim, Jun Ho Choi, Tae Hoon Kim, Ung Sik Jin, Kyung Won Minn, Hak Chang Department
Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices
 20 Original Article Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices Katie E. Weichman, MD 1 Neil Tanna, MD, MBA 1 P. Niclas Broer, MD 1 Stelios Wilson, MD 1 Hamdan
20 Original Article Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices Katie E. Weichman, MD 1 Neil Tanna, MD, MBA 1 P. Niclas Broer, MD 1 Stelios Wilson, MD 1 Hamdan
Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
Michael A. Howard a, Babak Mehrara b, * REVIEW. Introduction
 International Journal of Surgery (2005) 3, 53e60 www.int-journal-surgery.com REVIEW Emerging trends in microsurgical breast reconstruction: Deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) and the superior
International Journal of Surgery (2005) 3, 53e60 www.int-journal-surgery.com REVIEW Emerging trends in microsurgical breast reconstruction: Deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) and the superior
Breast Reconstruction
 Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction
 A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction
 The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction Zachary Menn and Aldona Spiegel Weill Cornell Medical College, The Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas,
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction Zachary Menn and Aldona Spiegel Weill Cornell Medical College, The Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas,
Glasgow G4 0SF, UK b Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, University Hospital Gent, De Pintelaan 185, 2K12C, B-9000 Gent, Belgium
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 674 683 Do pre-operative abdominal exercises prevent post-operative donor site complications for women undergoing DIEP flap breast reconstruction?
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 674 683 Do pre-operative abdominal exercises prevent post-operative donor site complications for women undergoing DIEP flap breast reconstruction?
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: Page 1 of 8
 Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
The most common type of breast reconstruction
 BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast reconstruction: an analysis of perioperative factors and complications
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
Breast Cancer Reconstruction
 Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps
 Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer
 BREAST Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer Edward I. Chang, M.D. Eric I. Chang, M.D. Ran Ito, M.D., Ph.D.
BREAST Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer Edward I. Chang, M.D. Eric I. Chang, M.D. Ran Ito, M.D., Ph.D.
More women are surviving breast cancer BREAST
 BREAST Patient-Reported Aesthetic Satisfaction with Breast Reconstruction during the Long-Term Survivorship Period Emily S. Hu, M.D. Andrea L. Pusic, M.D. Jennifer F. Waljee, M.D., M.P.H. Latoya Kuhn,
BREAST Patient-Reported Aesthetic Satisfaction with Breast Reconstruction during the Long-Term Survivorship Period Emily S. Hu, M.D. Andrea L. Pusic, M.D. Jennifer F. Waljee, M.D., M.P.H. Latoya Kuhn,
In a second stage or a second operation that tissue expander is removed through the same incision and the implant is placed within the chest pocket.
 Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Goals of Care. Restore shape and function after cancer
 Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Breast Reconstruction. Westmead Breast Cancer Institute
 Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
B11 Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal Tissue Flap
 B11 Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal Tissue Flap Issued March 2011 You can get more information about this procedure from www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org
B11 Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal Tissue Flap Issued March 2011 You can get more information about this procedure from www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org
Since originally described by Hartrampf et al. BREAST
 BREAST Assessment of Zonal Perfusion Using Intraoperative Angiography during Abdominal Flap Breast Reconstruction Albert Losken, M.D. Michael R. Zenn, M.D. Josh A. Hammel, M.D. Mark W. Walsh, M.D. Grant
BREAST Assessment of Zonal Perfusion Using Intraoperative Angiography during Abdominal Flap Breast Reconstruction Albert Losken, M.D. Michael R. Zenn, M.D. Josh A. Hammel, M.D. Mark W. Walsh, M.D. Grant
Cost-utility analysis comparing free and pedicled TRAM flap for breast reconstruction Thoma A, Khuthaila D, Rockwell G, Veltri K
 Cost-utility analysis comparing free and pedicled TRAM flap for breast reconstruction Thoma A, Khuthaila D, Rockwell G, Veltri K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that
Cost-utility analysis comparing free and pedicled TRAM flap for breast reconstruction Thoma A, Khuthaila D, Rockwell G, Veltri K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that
Factors Associated with Anastomotic Failure after Microvascular Reconstruction of the Breast
 Factors Associated with Anastomotic Failure after Microvascular Reconstruction of the Breast Maurice Y. Nahabedian, M.D., Bahram Momen, Ph.D., and Paul N. Manson, M.D. Baltimore and College Park, Md. The
Factors Associated with Anastomotic Failure after Microvascular Reconstruction of the Breast Maurice Y. Nahabedian, M.D., Bahram Momen, Ph.D., and Paul N. Manson, M.D. Baltimore and College Park, Md. The
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
Reconstructive Breast Surgery and Management of Breast Implants
 Reconstructive Breast Surgery and Management of Breast Implants Policy Number: 7.01.22 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 3/1993 Next Review: 1/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Reconstructive Breast Surgery and Management of Breast Implants Policy Number: 7.01.22 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 3/1993 Next Review: 1/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
MAASTRO- CLINIC More than just an institute for radiotherapy Patientcare research training & education
 MAASTRO- CLINIC More than just an institute for radiotherapy Patientcare research training & education Breast reconstruction: Before or after post mastectomy radiotherapy? Prof. dr. Liesbeth Boersma May
MAASTRO- CLINIC More than just an institute for radiotherapy Patientcare research training & education Breast reconstruction: Before or after post mastectomy radiotherapy? Prof. dr. Liesbeth Boersma May
Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap?
 Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap? Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, George Collis, MD, and Dustin Eck, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence:
Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap? Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, George Collis, MD, and Dustin Eck, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence:
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
The use of postmastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) to prevent
 NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
FREE DIEP-FLAP RECONSTRUCTION OF TUMOUR RELATED DEFECTS IN HEAD AND NECK
 JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2008, 59, Suppl 5, 59 67 www.jpp.krakow.pl H. LEONHARDT 1, R. MAI 1, W. PRADEL 1, J. MARKWARDT 1, T. PINZER 2, A. SPASSOV 3, G. LAUER 1 FREE DIEP-FLAP RECONSTRUCTION
JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2008, 59, Suppl 5, 59 67 www.jpp.krakow.pl H. LEONHARDT 1, R. MAI 1, W. PRADEL 1, J. MARKWARDT 1, T. PINZER 2, A. SPASSOV 3, G. LAUER 1 FREE DIEP-FLAP RECONSTRUCTION
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Breast reconstruction with abdominal tissue flap Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every
Procedure Information Guide Breast reconstruction with abdominal tissue flap Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks
 Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
Breast Reconstruction Surgery
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
can see several late effects. Asymmetry is probably the most common and the thing that patients notice the most. We can also see implant wrinkling or
 Hello, I am Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor with the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. And today I m going to talk to you
Hello, I am Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor with the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. And today I m going to talk to you
Does the use of an acellular dermal graft in abdominal closure after rectus flap harvest impact the occurrence of post-operative hernia?
 DOI 10.1007/s10006-015-0498-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does the use of an acellular dermal graft in abdominal closure after rectus flap harvest impact the occurrence of post-operative hernia? Masoud Saman 1 &
DOI 10.1007/s10006-015-0498-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does the use of an acellular dermal graft in abdominal closure after rectus flap harvest impact the occurrence of post-operative hernia? Masoud Saman 1 &
Early Experience With Barbed Sutures for Abdominal Closure in Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction
 Early Experience With Barbed Sutures for Abdominal Closure in Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction Catherine de Blacam, MB, BCh, a Salih Colakoglu, MD, a Adeyiza O. Momoh, MD,
Early Experience With Barbed Sutures for Abdominal Closure in Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction Catherine de Blacam, MB, BCh, a Salih Colakoglu, MD, a Adeyiza O. Momoh, MD,
Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction
 893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
Case Study. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis.
 Case Study TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication Challenge Insulin-dependent diabetes
Case Study TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication Challenge Insulin-dependent diabetes
Awareness and provision of reconstruction. Breast
 Original Article Breast Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction without Microsurgery Fellowship Training Hakan Orbay, MD, PhD* Brittany K. Busse, MD* Thomas R. Stevenson,
Original Article Breast Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction without Microsurgery Fellowship Training Hakan Orbay, MD, PhD* Brittany K. Busse, MD* Thomas R. Stevenson,
Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Successful Simultaneous Breast and Chest Wall Reconstruction in a Poland Anomaly Patient
 CASE REPORT Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Successful Simultaneous Breast and Chest Wall Reconstruction in a Poland Anomaly Patient Han-Tsung Liao, MD, Ming-Huei Cheng, MD, Betul Gozel Ulusal,
CASE REPORT Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Successful Simultaneous Breast and Chest Wall Reconstruction in a Poland Anomaly Patient Han-Tsung Liao, MD, Ming-Huei Cheng, MD, Betul Gozel Ulusal,
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts. Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA
 The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
breast reconstruction
 2.0 ANCC CONTACT HOURS Autologous microvascular breast reconstruction Postoperative strategies to improve outcomes By Maurice Y. Nahabedian, MD, FACS, and Anissa G. Nahabedian, BSN, RN BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
2.0 ANCC CONTACT HOURS Autologous microvascular breast reconstruction Postoperative strategies to improve outcomes By Maurice Y. Nahabedian, MD, FACS, and Anissa G. Nahabedian, BSN, RN BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
Samer Saour, Guido Libondi, Venkat Ramakrishnan. Introduction
 Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
The anatomy of superficial inferior epigastric artery flap 1. Anatomia do retalho com a artéria epigástrica superficial
 7 - ORIGINAL ARTICLE Plastic Surgery The anatomy of superficial inferior epigastric artery flap Anatomia do retalho com a artéria epigástrica superficial Mahdi Fathi I, Ebrahim Hatamipour I, Hamid Reza
7 - ORIGINAL ARTICLE Plastic Surgery The anatomy of superficial inferior epigastric artery flap Anatomia do retalho com a artéria epigástrica superficial Mahdi Fathi I, Ebrahim Hatamipour I, Hamid Reza
Alexis Laungani MD, Erik L Ritman MD PhD, Nirusha Lachman PhD, Jodie Christner PhD, Andrew Vercnocke Medical Imaging Analyst, Steven Jorgensen
 Alexis Laungani MD, Erik L Ritman MD PhD, Nirusha Lachman PhD, Jodie Christner PhD, Andrew Vercnocke Medical Imaging Analyst, Steven Jorgensen Engineer, Jill Anderson Research Technologist, Terry Regnier
Alexis Laungani MD, Erik L Ritman MD PhD, Nirusha Lachman PhD, Jodie Christner PhD, Andrew Vercnocke Medical Imaging Analyst, Steven Jorgensen Engineer, Jill Anderson Research Technologist, Terry Regnier
Planning and optimising DIEP flaps with virtual surgery: the Navarra experience
 Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2010) 63, 289e297 Planning and optimising DIEP flaps with virtual surgery: the Navarra experience Warren Matthew Rozen a, *, Emilio Garcia-Tutor
Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery (2010) 63, 289e297 Planning and optimising DIEP flaps with virtual surgery: the Navarra experience Warren Matthew Rozen a, *, Emilio Garcia-Tutor
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Postoperative Pain Management in DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction: Identification of Patients With Poor Pain Control
 Postoperative Pain Management in DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction: Identification of Patients With Poor Pain Control The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Postoperative Pain Management in DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction: Identification of Patients With Poor Pain Control The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap
 Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Despite breast reduction being one of the BREAST. Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction?
 BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
Figure 1. Anatomy of the breast
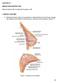 CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
Abdominal-based reconstruction is considered
 Original Article Salvage of Intraoperative Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Venous Congestion with Augmentation of Venous Outflow: Flap Morbidity and Review of the Literature Oscar Ochoa, MD Steven
Original Article Salvage of Intraoperative Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Venous Congestion with Augmentation of Venous Outflow: Flap Morbidity and Review of the Literature Oscar Ochoa, MD Steven
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy. Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD
 How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
Barbed Sutures in Progressive Tension Suture Technique Abdominoplasty. Karol A Gutowski, MD
 Barbed Sutures in Progressive Tension Suture Technique Abdominoplasty Karol A Gutowski, MD 1 Disclosures Speakers Bureau for AngioTech since April 2011 (Makers of Quill bi-directional barbed sutures) Technique
Barbed Sutures in Progressive Tension Suture Technique Abdominoplasty Karol A Gutowski, MD 1 Disclosures Speakers Bureau for AngioTech since April 2011 (Makers of Quill bi-directional barbed sutures) Technique
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects
 Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
rupture, you may notice silicone in their lymph nodes on radiographs. This may be seen and help us detect that there is a rupture.
 Hello. I m Melissa Crosby. I m an Associate Professor at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in the Department of Plastic Surgery. I d like to discuss with you the Late Effects of Breast
Hello. I m Melissa Crosby. I m an Associate Professor at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in the Department of Plastic Surgery. I d like to discuss with you the Late Effects of Breast
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
Plastic surgery of the breast includes; augmentation, reduction, Plastic Surgery of the Breast. Abstract. Continuing Education Column
 Plastic Surgery of the Breast Keuk Shun Shin, M.D. Keuk SHUN SHIN s Asthetic Plastic Surgery E mail: drsks@drsks.co.kr Abstract Plastic surgery of the breast includes; augmentation, reduction, reconstruction
Plastic Surgery of the Breast Keuk Shun Shin, M.D. Keuk SHUN SHIN s Asthetic Plastic Surgery E mail: drsks@drsks.co.kr Abstract Plastic surgery of the breast includes; augmentation, reduction, reconstruction
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Classifying breast cancer surgery: a novel, complexity-based system for oncological, oncoplastic and reconstructive procedures, and proof of principle by analysis of
Author's response to reviews Title: Classifying breast cancer surgery: a novel, complexity-based system for oncological, oncoplastic and reconstructive procedures, and proof of principle by analysis of
Clinical Accuracy of Portrait 3D Surgical Simulation Platform in Breast Augmentation. Ryan K. Wong MD, David T Pointer BS, Kamran Khoobehi MD FACS
 Clinical Accuracy of Portrait 3D Surgical Simulation Platform in Breast Augmentation Ryan K. Wong MD, David T Pointer BS, Kamran Khoobehi MD FACS Division of Plastic, Reconstructive & Reconstructive Surgery,
Clinical Accuracy of Portrait 3D Surgical Simulation Platform in Breast Augmentation Ryan K. Wong MD, David T Pointer BS, Kamran Khoobehi MD FACS Division of Plastic, Reconstructive & Reconstructive Surgery,
Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
