CHAPTER 1. The in-betweeners: a short introduction
|
|
|
- Luke Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 CHAPTER 1 The in-betweeners: a short introduction Adapted from: Bispecific antibody platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Lameris R, de Bruin RC, Schneiders FL, van Bergen en Henegouwen PM, Verheul HM, de Gruijl TD, van der Vliet HJ. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol Dec;92(3):153-65
3 1CHAPTER 1 Traditionally, immune responses were categorized into two types: innate and adaptive. The traditional opinion that innate immunity is nonspecific and lacks immunologic memory whereas adaptive immunity is characterized by specific antigen recognition and immunologic memory is no longer accurate or sufficient. Innate-like lymphocytes, also called in-betweeners, including γδ T cells and NKT cells, combine conventional adaptive features with rapid, innate-like responses, and thereby play an important role in initiating and orchestrating immune responses [1 3]. Invariant Natural killer T (inkt) cells Invariant natural killer T (inkt) cells represent a distinctive population of lymphocytes characterized by a (semi-)invariant TCR. Unlike conventional T-cells, inkt cells recognize (glyco-)lipids presented by non-polymorphic CD1d molecules. Upon stimulation, inkt cells rapidly secrete a wide range of cytokines and induce activation of effector cells (e.g. NK and CTL) in an IFN-γ dependent manner. [4 6] inkt cells were shown to contribute to immune surveillance in early-stage tumors and chemically induced cancers and appear to play a pivotal role in controlling different forms of cancer, at least in mice. [7,8] Moreover, inkt cells from patients with advanced cancer display quantitative and qualitative defects and circulating numbers correlate with patient survival. [7 10] Reciprocal interactions between dendritic cells (DC) and inkt cells can reverse defects in the inkt cell population. Indeed, in vitro results indicate rehabilitation of inkt cell function after stimulation with monocyte derived DC (modc) pulsed with the agonistic CD1d ligand α-galactosylceramide (α-galcer) and exogenous IL- 12. [11,12] It was shown that sustained activation of inkt cells at the tumor site could be induced after systemic treatment with α-galcer loaded on soluble CD1d fused to an anti-tumor scfv. Potent tumor inhibition of aggressive tumor grafts expressing the targeted antigen was observed in mice. [13,14] Although less clear than in mice, clinical studies evaluating injection of α-galcer-pulsed modc with or without adoptive transfer of ex vivo expanded inkt cells have reported objective tumor regressions in several patients. [15 18] In patients with recurrent HNSCC, nasal submucosal administration of αgalcer-pulsed APCs combined with intra-arterial infusion of activated inkt cells via tumorfeeding arteries produced an objective response in 5 out of 10 patients. [15] The number of infiltrating inkt cells in extirpated tumor tissue correlated with clinical outcome. [18] The precise role of inkt cells in human cancer treatment still has to be determined, however, clinical data underscore their role in tumor immune-surveillance and indicate beneficial effects with low toxicity in cancer 12
4 The In-betweeners: a short introduction treatment. Figure 1. inkt cells are activated by lipid antigens presented in the context of a CD1d antigen presenting molecule. Activation of Vγ9Vδ2-T cells is initiated by conformational changes of CD277 upon intracellular phosphoantigen accumulation (isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP)). Adapted from [19]. Vγ9Vδ2T-cells γδ T-cells, once regarded an evolutionary redundant T-cell subset en route to extinction, have recently been demonstrated to hold a unique position in the immune system. They can directly lyse stressed or infected cells, produce a diversified set of cytokines and chemokines to regulate both immune and nonimmune cells, and can present antigens for αβ T-cell priming. [2] Vγ9Vδ2-T cells constitute the predominant γδ-t cell subset in human peripheral blood and account for 1 5% of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of healthy adults. Vγ9Vδ2-T cells can be activated and expanded by non-peptidic pyrophosphate antigens (pag), of which there are both host and microbe-derived counterparts, typified by isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and hydroxymethyl-but-2-enylpyrophosphate (HMBPP) respectively. Furthermore, aminobisphosphonate compounds (e.g. zoledronic acid and pamidronate) sensitize target cells to Vγ9Vδ2-T cell killing by promoting the intracellular accumulation of endogenous IPP by inhibiting mevalonate metabolism. [20] Recently, it was reported that CD277/ butyrophilin (BTN) 3A1 is required for the presentation of pag to 13
5 CHAPTER 1 1Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. [21,22] In stressed/malignant cells pag production is frequently upregulated allowing discrimination from normal tissue. Indeed, Vγ9Vδ2Tcells have been shown to be able to recognize and eliminate malignant cells from multiple tumors types, including multiple myeloma (MM), NHL, prostate-, renal cell- and colon cancer. Of interest, quantitative and qualitative defects in the Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell population have been observed in various malignancies [20] and negatively impact disease-free survival, e.g. in ovarian carcinoma. [23] Importantly however, these functional Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell defects are reversible. [20] In patients with various metastatic cancers treatment with zoledronic acid and IL-2 promoted the differentiation of peripheral blood Vγ9Vδ2 T-cells toward an effector/memory-like phenotype with augmented numbers correlating with arrested disease progression. Observed toxicities were minor and limited to transient flu-like symptoms. [24,25] Adoptive transfer of Vγ9Vδ2 T-cells following ex vivo expansion by pag, aminobisphosphonates or mabs combined with IL- 2, in patients with various types of metastatic cancer resulted in some clinical responses. [20] Of interest, Vγ9Vδ2T-cell mediated lysis of hepatic tumor cell lines could be significantly enhanced by an anti-epcam-anti-cd3 BiTE in vitro. [26] Although clinical data are still scarce, preliminary findings clearly indicate that exploiting the natural abilities of Vγ9Vδ2 T-cells in cancer immunotherapy is feasible and carries low toxicity. Introduction to the chapters Both inkt cells and Vγ9Vδ2-T cells have shown great promise in anti-tumor immune responses and interest in exploiting these lymphocyte subsets for the induction of potent and enduring antitumor immune responses has grown rapidly. Moreover, given the current spectacular results of immune checkpoint inhibitors and the rising interest in bispecific targeting constructs, specific activation of inkt and Vγ9Vδ2-T cells has more potential than ever before. Multiple studies have shown immunological, biochemical and even clinical responses in patients treated with specific activating ligands, underscoring their role in anti-tumor immunity. However, results lack consistency and many challenges remain to be overcome, since both inkt and Vγ9Vδ2-T cells can be influenced greatly by the environment in which they are in. In this dissertation we have studied inkt and Vγ9Vδ2-T cells in detail and investigated cross-talk between these subsets, evaluating whether their reciprocal interactions can interfere or enhance anti-tumor immune responses. 14
6 The In-betweeners: a short introduction Chapters 1 and 2 provide an introduction to inkt and Vγ9Vδ2-T cells and review the clinical experience that has been obtained in the field of cancer immunotherapy. In Chapter 3 we provide a detailed description of how immature and mature modc can be generated from peripheral blood and are optimally exposed to α-galcer to allow activation and biased cytokine production in responding inkt. Chapter 4 provides an updated analysis of a study in which circulating inkt cell numbers were assessed in a group of HNSCC patients before the start of curative intent radiotherapy. It was shown that patients with HNSCC that have a severe deficiency of inkt cells have a strikingly poor clinical outcome. We studied the effects of inkt cell activation on Vγ9Vδ2-T cells in Chapter 5, and found that co-activation of inkt cells enhanced the IFN-γ production as well as the cytolytic potential of phosphoantigen-activated Vγ9Vδ2-T cells and that this effect was mediated via the production of TNF-α. In Chapter 6 we explored the capacity of Vγ9Vδ2-T cells to act as antigen presenting cells and present glycolipid antigen to inkt cells. Vγ9Vδ2-T APC were indeed found to be able to present α-galcer to inkt cells resulting in their activation. However, glycolipid antigen presentation was shown not to result from the de novo synthesis of CD1d by Vγ9Vδ2-T cells, but depends on trogocytosis of CD1d-containing membrane fragments from pag-expressing cells with which Vγ9Vδ2-T cells interact. We further discuss the role of Vγ9Vδ2-T cells in cancer immunotherapy in Chapter 7, focusing on their putative use as a novel APCplatform for potentiation of inkt cell based cancer immunotherapy. In Chapter 8 we investigated the effect of NBP on glycolipid Ag presentation by modc and found that treatment of modc with NBP during DC maturation resulted in a striking inhibition of inkt cell activation. This inhibitory effect was found to be caused by a reduction in modc apolipoprotein E (apoe, a known facilitator of trans-membrane transport of exogenously derived glycolipids) production and could be relieved by supplementing apoe in the culture medium. Chapter 9 describes the studied effects of intravenous administration of NBP and statins on circulating Vγ9Vδ2-T cells in advanced cancer patients. We found that administration of NBP resulted in the rapid activation of 15
7 CHAPTER 1 1circulating Vγ9Vδ2-T cells, with circulating numbers dropping immediately after infusion and recovering within the next week. Pretreatment of patients with statins did not significantly reduce the observed activation nor did it prevent the occurrence of an acute phase response (APR). References 1. L.L. Lanier, Shades of grey the blurring view of innate and adaptive immunity, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13 (2013) P. Vantourout, A. Hayday, Six-of-the-best: unique contributions of γδ T cells to immunology., Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13 (2013) J. a Walker, J.L. Barlow, A.N.J. McKenzie, Innate lymphoid cells--how did we miss them?, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13 (2013) H.J. van der Vliet, J.W. Molling, B.M.E. von Blomberg, N. Nishi, W. Kölgen, A.J.M. Van Den Eertwegh, et al., The immunoregulatory role of CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells in disease., Clin Immunol. 112 (2004) D.I. Godfrey, M. Kronenberg, Review series Going both ways : immune regulation via CD1d-dependent NKT cells, J Clin Invest. 114 (2004) D.I. Godfrey, H.R. MacDonald, M. Kronenberg, M.J. Smyth, L. Van Kaer, Opinion: NKT cells: what s in a name?, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4 (2004) M. Bellone, M. Ceccon, M. Grioni, E. Jachetti, A. Calcinotto, A. Napolitano, et al., inkt cells control mouse spontaneous carcinoma independently of tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells, PLoS One. 5 (2010). 8. J.B. Swann, A.P. Uldrich, S. Van Dommelen, J. Sharkey, W.K. Murray, D.I. Godfrey, et al., Type I natural killer T cells suppress tumors caused by p53 loss in mice, Blood. 113 (2009) M.A. Exley, L. Lynch, B. Varghese, M. Nowak, N. Alatrakchi, S.P. Balk, Developing understanding of the roles of CD1d-restricted T cell subsets in cancer: Reversing tumor-induced defects, Clin. Immunol. 140 (2011) J.W. Molling, J.A.E. Langius, J.A. Langendijk, C.R. Leemans, H.J. Bontkes, H.J.J. van der Vliet, et al., Low levels of circulating invariant natural killer T cells predict poor clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma., J. Clin. Oncol. 25 (2007) S.M. Tahir, O. Cheng, A. Shaulov, Y. Koezuka, G.J. Bubley, S.B. Wilson, et al., Loss of IFN-gamma production by invariant NK T cells in advanced cancer., J. Immunol. 167 (2001) H.J. van der Vliet, J.W. Molling, N. Nishi, A.J. Masterson, W. Kölgen, S.A. Porcelli, et al., Polarization of Valpha24+ Vbeta11+ natural killer T cells of healthy volunteers and cancer patients using alpha-galactosylceramide-loaded and environmentally instructed dendritic cells., Cancer Res. 63 (2003) K. Stirnemann, J.F. Romero, L. Baldi, B. Robert, V. Cesson, G.S. Besra, et al., Sustained activation and tumor targeting of NKT cells using a CD1d anti-her2 scfv fusion 16
8 The In-betweeners: a short introduction protein induce antitumor effects in mice, J Clin Invest. 118 (2008) S. Corgnac, R. Perret, L. Derré, L. Zhang, K. Stirnemann, M. Zauderer, et al., CD1dantibody fusion proteins target inkt cells to the tumor and trigger long-term therapeutic responses, Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 62 (2013) T. Uchida, S. Horiguchi, Y. Tanaka, H. Yamamoto, N. Kunii, S. Motohashi, et al., Phase I study of alpha-galactosylceramide-pulsed antigen presenting cells administration to the nasal submucosa in unresectable or recurrent head and neck cancer., Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII. 57 (2008) D.H. Chang, K. Osman, J. Connolly, A. Kukreja, J. Krasovsky, M. Pack, et al., Sustained expansion of NKT cells and antigen-specific T cells after injection of α-galactosylceramide loaded mature dendritic cells in cancer patients, J Exp Med. 201 (2005) M. Nieda, M. Okai, A. Tazbirkova, H. Lin, A. Yamaura, K. Ide, et al., Therapeutic activation of Valpha24+Vbeta11+ NKT cells in human subjects results in highly coordinated secondary activation of acquired and innate immunity., Blood. 103 (2004) K. Yamasaki, S. Horiguchi, M. Kurosaki, N. Kunii, K. Nagato, H. Hanaoka, et al., Induction of NKT cell-specific immune responses in cancer tissues after NKT celltargeted adoptive immunotherapy, Clin. Immunol. 138 (2011) J. Rossjohn, D.G. Pellicci, O. Patel, L. Gapin, D.I. Godfrey, Recognition of CD1drestricted antigens by natural killer T cells., Nat. Rev. Immunol. 12 (2012) M.S. Braza, B. Klein, Anti-tumour immunotherapy with Vgamma9Vdelta2 T lymphocytes: from the bench to the bedside, Br J Haematol. (2012). 21. S. Vavassori, A. Kumar, G.S. Wan, G.S. Ramanjaneyulu, M. Cavallari, S. El Daker, et al., Butyrophilin 3A1 binds phosphorylated antigens and stimulates human γδ T cells., Nat. Immunol. 14 (2013) C. Harly, Y. Guillaume, S. Nedellec, C.-M. Peigné, H. Mönkkönen, J. Mönkkönen, et al., Key implication of CD277/butyrophilin-3 (BTN3A) in cellular stress sensing by a major human γδ T-cell subset., Blood. 120 (2012) A. Thedrez, V. Lavoué, B. Dessarthe, P. Daniel, S. Henno, I. Jaffre, et al., A Quantitative Deficiency in Peripheral Blood Vγ9Vδ2 Cells Is a Negative Prognostic Biomarker in Ovarian Cancer Patients, PLoS One. 8 (2013). 24. F. Dieli, D. Vermijlen, F. Fulfaro, N. Caccamo, S. Meraviglia, G. Cicero, et al., Targeting human {gamma}delta} T cells with zoledronate and interleukin-2 for immunotherapy of hormone-refractory prostate cancer., Cancer Res. 67 (2007) S. Meraviglia, M. Eberl, D. Vermijlen, M. Todaro, S. Buccheri, G. Cicero, et al., In vivo manipulation of V9V2 T cells with zoledronate and low-dose interleukin-2 for immunotherapy of advanced breast cancer patients, Clin. Exp. Immunol. 161 (2010) A. Hoh, A. Dewerth, F. Vogt, J. Wenz, P.A. Baeuerle, S.W. Warmann, et al., The activity of γδ T cells against paediatric liver tumour cells and spheroids in cell culture, Liver Int. 33 (2013)
Circulating invariant natural killer T-cell numbers predict outcome in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Updated analysis with 10-year follow-up
 Chapter Circulating invariant natural killer T-cell numbers predict outcome in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Updated analysis with 10-year follow-up Famke L. Schneiders, Renée C.G. de Bruin, Fons
Chapter Circulating invariant natural killer T-cell numbers predict outcome in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Updated analysis with 10-year follow-up Famke L. Schneiders, Renée C.G. de Bruin, Fons
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL: CLINICAL ASPECTS OF inkt CELL BIOLOGY
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL: CLINICAL ASPECTS OF inkt CELL BIOLOGY Injection of α-galcer in Phase I Clinical Trials The first in-human study was a Phase I trial using intravenous injection of α-galcer at a range
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL: CLINICAL ASPECTS OF inkt CELL BIOLOGY Injection of α-galcer in Phase I Clinical Trials The first in-human study was a Phase I trial using intravenous injection of α-galcer at a range
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation. Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
 New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies
 NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
Tumor Immunology. Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant
 Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates
 Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
Ex-Vivo heat shock protein 70-peptide-activated, autologous natural killer cells adoptive therapy: from the bench to the clinic
 Ex-Vivo heat shock protein 70-peptide-activated, autologous natural killer cells adoptive therapy: from the bench to the clinic isbtc 10-13 November 2005 Valeria Milani, MD, PhD Munich Agenda 1. NK ligands
Ex-Vivo heat shock protein 70-peptide-activated, autologous natural killer cells adoptive therapy: from the bench to the clinic isbtc 10-13 November 2005 Valeria Milani, MD, PhD Munich Agenda 1. NK ligands
γδ T Cell Immunotherapy A Review
 Pharmaceuticals 2015, 8, 40-61; doi:10.3390/ph8010040 Review OPEN ACCESS pharmaceuticals ISSN 1424-8247 www.mdpi.com/journal/pharmaceuticals γδ T Cell Immunotherapy A Review Hirohito Kobayashi 1, * and
Pharmaceuticals 2015, 8, 40-61; doi:10.3390/ph8010040 Review OPEN ACCESS pharmaceuticals ISSN 1424-8247 www.mdpi.com/journal/pharmaceuticals γδ T Cell Immunotherapy A Review Hirohito Kobayashi 1, * and
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16
 COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
Role of Innate Immunity in Hepatitis B Virus Infection Adam J. Gehring, Ph.D.
 Role of Innate Immunity in Hepatitis B Virus Infection Adam J. Gehring, Ph.D. Biology Lead Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Toronto General Hospital Research Institute University Health Network (UHN) HBV
Role of Innate Immunity in Hepatitis B Virus Infection Adam J. Gehring, Ph.D. Biology Lead Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Toronto General Hospital Research Institute University Health Network (UHN) HBV
08/02/59. Tumor Immunotherapy. Development of Tumor Vaccines. Types of Tumor Vaccines. Immunotherapy w/ Cytokine Gene-Transfected Tumor Cells
 Tumor Immunotherapy Autologous virus Inactivation Inactivated virus Lymphopheresis Culture? Monocyte s Dendritic cells Immunization Autologous vaccine Development of Tumor Vaccines Types of Tumor Vaccines
Tumor Immunotherapy Autologous virus Inactivation Inactivated virus Lymphopheresis Culture? Monocyte s Dendritic cells Immunization Autologous vaccine Development of Tumor Vaccines Types of Tumor Vaccines
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON. Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust
 IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Lecture outline. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation. Central and peripheral tolerance. Inhibitory receptors of T cells. Regulatory T cells
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK
 08 April, 2018 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 90.41 KB 0 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Natural killer T cells (NK T cells) are a type of lymphocyte, or white blood cell. Natural killer
08 April, 2018 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 90.41 KB 0 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Natural killer T cells (NK T cells) are a type of lymphocyte, or white blood cell. Natural killer
Immunotherapy on the Horizon: Adoptive Cell Therapy
 Immunotherapy on the Horizon: Adoptive Cell Therapy Joseph I. Clark, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Maywood, IL June 23, 2016 Conflicts of Interest
Immunotherapy on the Horizon: Adoptive Cell Therapy Joseph I. Clark, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Maywood, IL June 23, 2016 Conflicts of Interest
Immunity and Cancer. Doriana Fruci. Lab di Immuno-Oncologia
 Immunity and Cancer Doriana Fruci Lab di Immuno-Oncologia Immune System is a network of cells, tissues and organs that work together to defend the body against attacks of foreign invaders (pathogens, cancer
Immunity and Cancer Doriana Fruci Lab di Immuno-Oncologia Immune System is a network of cells, tissues and organs that work together to defend the body against attacks of foreign invaders (pathogens, cancer
Micro 204. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier
 Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
CD40L TCR IL-12 TLR-L
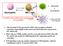 CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
Tumor Immunology. Tumor (latin) = swelling
 Tumor Immunology Tumor (latin) = swelling benign tumor malignant tumor Tumor immunology : the study of the types of antigens that are expressed by tumors how the immune system recognizes and responds to
Tumor Immunology Tumor (latin) = swelling benign tumor malignant tumor Tumor immunology : the study of the types of antigens that are expressed by tumors how the immune system recognizes and responds to
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
Cell-mediated Immunity
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Exploring Immunotherapies: Beyond Checkpoint Inhibitors
 Exploring Immunotherapies: Beyond Checkpoint Inhibitors Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics (Now part of BioTelemetry Research) jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com +1 585 249 6231 Introduction
Exploring Immunotherapies: Beyond Checkpoint Inhibitors Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics (Now part of BioTelemetry Research) jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com +1 585 249 6231 Introduction
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: The New Breakout Stars in Cancer Treatment
 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: The New Breakout Stars in Cancer Treatment 1 Introductions Peter Langecker, MD, PhD Executive Medical Director, Global Oncology Clinipace Worldwide Mark Shapiro Vice President
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: The New Breakout Stars in Cancer Treatment 1 Introductions Peter Langecker, MD, PhD Executive Medical Director, Global Oncology Clinipace Worldwide Mark Shapiro Vice President
Lecture 4. T lymphocytes
 Lecture 4 T lymphocytes Objectives Mention the types of T cells List the Types of T helper cell (CD4+) Discuss the Activation of T cells Define Interleukins Distinguish the Super Ag from ordinary Ag Show
Lecture 4 T lymphocytes Objectives Mention the types of T cells List the Types of T helper cell (CD4+) Discuss the Activation of T cells Define Interleukins Distinguish the Super Ag from ordinary Ag Show
Synergistic combinations of targeted immunotherapy to combat cancer
 Synergistic combinations of targeted immunotherapy to combat cancer Myung Ah Lee, M.D., Ph. D Division of Medical Oncology, Hepato-biliary pancreatic cancer center Seoul St. Mary s hospital, The Catholic
Synergistic combinations of targeted immunotherapy to combat cancer Myung Ah Lee, M.D., Ph. D Division of Medical Oncology, Hepato-biliary pancreatic cancer center Seoul St. Mary s hospital, The Catholic
Immune surveillance hypothesis (Macfarlane Burnet, 1950s)
 TUMOR-IMMUNITÄT A.K. Abbas, A.H. Lichtman, S. Pillai (6th edition, 2007) Cellular and Molecular Immunology Saunders Elsevier Chapter 17, immunity to tumors Immune surveillance hypothesis (Macfarlane Burnet,
TUMOR-IMMUNITÄT A.K. Abbas, A.H. Lichtman, S. Pillai (6th edition, 2007) Cellular and Molecular Immunology Saunders Elsevier Chapter 17, immunity to tumors Immune surveillance hypothesis (Macfarlane Burnet,
Masashi Takahara,* Manami Miyai,* Mai Tomiyama,* Masato Mutou,* Andrew J. Nicol, and Mie Nieda*,1
 Copulsing tumor antigen-pulsed dendritic cells with zoledronate efficiently enhance the expansion of tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells via V 9 T cell activation Masashi Takahara,* Manami Miyai,* Mai Tomiyama,*
Copulsing tumor antigen-pulsed dendritic cells with zoledronate efficiently enhance the expansion of tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells via V 9 T cell activation Masashi Takahara,* Manami Miyai,* Mai Tomiyama,*
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
The Immune System. Innate. Adaptive. - skin, mucosal barriers - complement - neutrophils, NK cells, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils
 Objectives - explain the rationale behind cellular adoptive immunotherapy - describe methods of improving cellular adoptive immunotherapy - identify mechanisms of tumor escape from cellular adoptive immunotherapy
Objectives - explain the rationale behind cellular adoptive immunotherapy - describe methods of improving cellular adoptive immunotherapy - identify mechanisms of tumor escape from cellular adoptive immunotherapy
Immunotherapy: The Newest Treatment Route
 Immunotherapy: The Newest Treatment Route IWMF Patient Forum, Phoenix, AZ Madhav Dhodapkar, MD Professor of Medicine and Immunobiology Chief, Section of Hematology Yale University or the Oldest William
Immunotherapy: The Newest Treatment Route IWMF Patient Forum, Phoenix, AZ Madhav Dhodapkar, MD Professor of Medicine and Immunobiology Chief, Section of Hematology Yale University or the Oldest William
Adoptive T Cell Therapy TILs & TCRs & CARs
 Adoptive T Cell Therapy TILs & TCRs & CARs Inge Marie Svane CCIT DENMARK Professor, MD Center for Cancer Immune Therapy Department of Oncology, Herlev Hospital Copenhagen University Denmark Therapeutic
Adoptive T Cell Therapy TILs & TCRs & CARs Inge Marie Svane CCIT DENMARK Professor, MD Center for Cancer Immune Therapy Department of Oncology, Herlev Hospital Copenhagen University Denmark Therapeutic
Immunology Lecture 4. Clinical Relevance of the Immune System
 Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Engineered Immune Cells for Cancer Therapy : Current Status and Prospects
 When Engineering Meets Immunology Engineered Immune Cells for Cancer Therapy : Current Status and Prospects Yong Taik Lim, Ph.D. Nanomedical Systems Laboratory (http://www.nanomedicalsystems.org) SKKU
When Engineering Meets Immunology Engineered Immune Cells for Cancer Therapy : Current Status and Prospects Yong Taik Lim, Ph.D. Nanomedical Systems Laboratory (http://www.nanomedicalsystems.org) SKKU
Therapeutic activation of V 24 V 11 NKT cells in human subjects results in highly coordinated secondary activation of acquired and innate immunity
 Plenary paper Therapeutic activation of V 24 V 11 NKT cells in human subjects results in highly coordinated secondary activation of acquired and innate immunity Mie Nieda, Miki Okai, Andrea Tazbirkova,
Plenary paper Therapeutic activation of V 24 V 11 NKT cells in human subjects results in highly coordinated secondary activation of acquired and innate immunity Mie Nieda, Miki Okai, Andrea Tazbirkova,
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach
 Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach Oncolytic immunotherapy Oncolytic immunotherapy the use of a genetically modified virus to attack tumors and induce a systemic immune response
Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach Oncolytic immunotherapy Oncolytic immunotherapy the use of a genetically modified virus to attack tumors and induce a systemic immune response
The Adaptive Immune Response. T-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology
 Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Personalized medicine - cancer immunotherapy
 Personalized medicine - cancer immunotherapy Özcan Met, PhD Senior Staff Scientist, Cell Therapy Director Center for Cancer Immune Therapy Department of Hematology Department of Oncology University Hospital
Personalized medicine - cancer immunotherapy Özcan Met, PhD Senior Staff Scientist, Cell Therapy Director Center for Cancer Immune Therapy Department of Hematology Department of Oncology University Hospital
Immune surveillance: The immune system can recognize and destroy nascent malignant cells
 Immune surveillance: The immune system can recognize and destroy nascent malignant cells Control Escape APC T C T H B NKT NK Innate Tumor T cells are believed to play a major role in controlling tumor
Immune surveillance: The immune system can recognize and destroy nascent malignant cells Control Escape APC T C T H B NKT NK Innate Tumor T cells are believed to play a major role in controlling tumor
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology
 Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Interleukin-2 Single Agent and Combinations
 Interleukin-2 Single Agent and Combinations Michael K Wong MD PhD Norris Cancer Center University of Southern California mike.wong@med.usc.edu Disclosures Advisory Board Attendance Merck Bristol Myers
Interleukin-2 Single Agent and Combinations Michael K Wong MD PhD Norris Cancer Center University of Southern California mike.wong@med.usc.edu Disclosures Advisory Board Attendance Merck Bristol Myers
Immune Checkpoints. PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich
 Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Third line of Defense
 Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
The g c Family of Cytokines Prof. Warren J. Leonard M.D.
 The Family of Cytokines Chief, Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Director, Immunology Center National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
The Family of Cytokines Chief, Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Director, Immunology Center National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
DEVELOPMENT OF CELLULAR IMMUNOLOGY
 DEVELOPMENT OF CELLULAR IMMUNOLOGY 1880 s: Antibodies described (dominated studies of immunology until 1960 s) 1958: Journal of Immunology (137 papers) lymphocyte not listed in index Two papers on transfer
DEVELOPMENT OF CELLULAR IMMUNOLOGY 1880 s: Antibodies described (dominated studies of immunology until 1960 s) 1958: Journal of Immunology (137 papers) lymphocyte not listed in index Two papers on transfer
The presence of CD8 + invariant NKT cells in mice
 EXPERIMENTAL and MOLECULAR MEDICINE, Vol. 41, No. 12, 866-872, December 2009 The presence of CD8 + invariant NKT cells in mice Hyunji Lee 1, Changwan Hong 1, Junghoon Shin 1, Soohwan Oh 1, Sundo Jung 1,
EXPERIMENTAL and MOLECULAR MEDICINE, Vol. 41, No. 12, 866-872, December 2009 The presence of CD8 + invariant NKT cells in mice Hyunji Lee 1, Changwan Hong 1, Junghoon Shin 1, Soohwan Oh 1, Sundo Jung 1,
Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D.
 Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Reprogramming Tumor Associated Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy
 Reprogramming Tumor Associated Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy Edgar Engleman, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Medicine Stanford University Disclosures: Founder of Dendreon, a biotechnology company that
Reprogramming Tumor Associated Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy Edgar Engleman, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Medicine Stanford University Disclosures: Founder of Dendreon, a biotechnology company that
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Practical Solution: presentation to cytotoxic T cells. How dendritic cells present antigen. How dendritic cells present antigen
 Christian Kurts Institutes of Molecular Medicine and Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany - presentation and (CTL) activation - I presentation and CD4 + T cell (Th cell) activation Different
Christian Kurts Institutes of Molecular Medicine and Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany - presentation and (CTL) activation - I presentation and CD4 + T cell (Th cell) activation Different
ACTR (Antibody Coupled T-cell Receptor): A universal approach to T-cell therapy
 ACTR (Antibody Coupled T-cell Receptor): A universal approach to T-cell therapy European Medicines Agency Workshop on Scientific and Regulatory Challenges of Genetically Modified Cell-based Cancer Immunotherapy
ACTR (Antibody Coupled T-cell Receptor): A universal approach to T-cell therapy European Medicines Agency Workshop on Scientific and Regulatory Challenges of Genetically Modified Cell-based Cancer Immunotherapy
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, and Applications to Human Disease Dr. Michael A. Caligiuri
 Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy
 Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Developing Novel Immunotherapeutic Cancer Treatments for Clinical Use
 Developing Novel Immunotherapeutic Cancer Treatments for Clinical Use Oncology for Scientists March 8 th, 2016 Jason Muhitch, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Urology Email: jason.muhitch@roswellpark.org
Developing Novel Immunotherapeutic Cancer Treatments for Clinical Use Oncology for Scientists March 8 th, 2016 Jason Muhitch, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Urology Email: jason.muhitch@roswellpark.org
Cell Mediated Immunity CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY. Basic Elements of Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI) Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
 Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Posters and Presentations
 Posters and Presentations June 2017: American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual - Preliminary Correlative Analysis of PD-L1 expression from the SUNRISE Study. View April 2017: American Association
Posters and Presentations June 2017: American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual - Preliminary Correlative Analysis of PD-L1 expression from the SUNRISE Study. View April 2017: American Association
BASIC MECHANISM OF TUMOR IMMUNE SUPPRESSION
 BASIC MECHANISM OF TUMOR IMMUNE SUPPRESSION Zihai Li, M.D., Ph.D. Leader, Cancer Immunology Program Hollings Cancer Center Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) DISCLOSURE GOALS Understand that immune
BASIC MECHANISM OF TUMOR IMMUNE SUPPRESSION Zihai Li, M.D., Ph.D. Leader, Cancer Immunology Program Hollings Cancer Center Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) DISCLOSURE GOALS Understand that immune
Adaptive Immune System
 Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE
 CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
Tumor Associated Macrophages as a Novel Target for Cancer Therapy
 Tumor mass Tumor Associated Macrophage Tumor Associated Macrophages as a Novel Target for Cancer Therapy This booklet contains forward-looking statements that are based on Amgen s current expectations
Tumor mass Tumor Associated Macrophage Tumor Associated Macrophages as a Novel Target for Cancer Therapy This booklet contains forward-looking statements that are based on Amgen s current expectations
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do? Monoclonal antibody approach
 How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about T cell function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified
How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about T cell function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified
A second type of TCR TCR: An αβ heterodimer
 How s recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified Recall
How s recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified Recall
Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology
 By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2018
 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2018 Arunika Mukhopadhaya The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the year 2018 was awarded to James P Allison of the United States and Tasuku Honjo of Japan
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2018 Arunika Mukhopadhaya The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the year 2018 was awarded to James P Allison of the United States and Tasuku Honjo of Japan
Dendritic Cell Based Immunotherapy for Cancer. Edgar G. Engleman, M.D.
 Dendritic Cell Based Immunotherapy for Cancer Edgar G. Engleman, M.D. Two main DC subsets Myeloid (mydc) Derived from monocytes Capture/process/present Ag to T cells Activate NK cells and B cells Plasmacytoid
Dendritic Cell Based Immunotherapy for Cancer Edgar G. Engleman, M.D. Two main DC subsets Myeloid (mydc) Derived from monocytes Capture/process/present Ag to T cells Activate NK cells and B cells Plasmacytoid
0105) at the day 15, respectively1 In contrast, the percentages of CD3 + CD4 + and NK cells displayed no
 2003 12 10 83 23 Natl Med J China, December 10,2003,Vol 83, No. 23 2049 (CIK ), T, CIK 13 (PBMC),,4 7 10 13 15 ;CIK, (DC1) (CD2),CD3 + CD8 +, CD3 + CD56 +, CD25 +, 3315 % 1011 % 717 % 218 %1213 % 415 %,3616
2003 12 10 83 23 Natl Med J China, December 10,2003,Vol 83, No. 23 2049 (CIK ), T, CIK 13 (PBMC),,4 7 10 13 15 ;CIK, (DC1) (CD2),CD3 + CD8 +, CD3 + CD56 +, CD25 +, 3315 % 1011 % 717 % 218 %1213 % 415 %,3616
Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation. mammary cancer model. Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler
 Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation in a spontaneous mammary cancer model Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler Goal of Immunotherapy Boosting the low level anti-tumor immune
Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation in a spontaneous mammary cancer model Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler Goal of Immunotherapy Boosting the low level anti-tumor immune
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. for both infectious diseases and malignancies. Immunity is known as the innate
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1.1. Background of Study The immune system s function is to provide defense of the human body for both infectious diseases and malignancies. Immunity is known as the innate immunity
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1.1. Background of Study The immune system s function is to provide defense of the human body for both infectious diseases and malignancies. Immunity is known as the innate immunity
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response
 chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY. Cancer Research Center, Dpt. of Medicine & Service of Cytometry University of Salamanca. IBSAL
 FARMAFORUM 2015 FACULTAD FARMACIA CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Cancer Research Center, Dpt. of Medicine & Service of Cytometry University of Salamanca. IBSAL The immune response to tumors Oncogenic event The immune
FARMAFORUM 2015 FACULTAD FARMACIA CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Cancer Research Center, Dpt. of Medicine & Service of Cytometry University of Salamanca. IBSAL The immune response to tumors Oncogenic event The immune
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer
 Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer Jason Muhitch, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Urology Department of Immunology Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center Oncology for Scientists March 15,
Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Cancer Jason Muhitch, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Urology Department of Immunology Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center Oncology for Scientists March 15,
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore, MD 21205
 AD Award Number: DAMD7---7 TITLE: Development of Artificial Antigen Presenting Cells for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan P. Schneck, M.D., Ph.D. Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: DAMD7---7 TITLE: Development of Artificial Antigen Presenting Cells for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan P. Schneck, M.D., Ph.D. Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Enhancing the Clinical Activity of HER2/neu Specific T Cells. William Gwin, MD Internal Medicine, Resident University of Washington
 Enhancing the Clinical Activity of HER2/neu Specific T Cells William Gwin, MD Internal Medicine, Resident University of Washington Immunotherapy and Cancer Cancer vaccines were originally used in melanoma
Enhancing the Clinical Activity of HER2/neu Specific T Cells William Gwin, MD Internal Medicine, Resident University of Washington Immunotherapy and Cancer Cancer vaccines were originally used in melanoma
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Priming the Immune System to Kill Cancer and Reverse Tolerance. Dr. Diwakar Davar Assistant Professor, Melanoma and Phase I Therapeutics
 Priming the Immune System to Kill Cancer and Reverse Tolerance Dr. Diwakar Davar Assistant Professor, Melanoma and Phase I Therapeutics Learning Objectives Describe the role of the immune system in cancer
Priming the Immune System to Kill Cancer and Reverse Tolerance Dr. Diwakar Davar Assistant Professor, Melanoma and Phase I Therapeutics Learning Objectives Describe the role of the immune system in cancer
Immune response. This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it.
 Immune response This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it. It s highly recommended to watch Dr Najeeb s lecture that s titled T Helper cells and
Immune response This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it. It s highly recommended to watch Dr Najeeb s lecture that s titled T Helper cells and
Primer on Tumor Immunology. International Society for Biological Therapy of Cancer. C. H. June, M.D. November 10, 2005
 Primer on Tumor Immunology International Society for Biological Therapy of Cancer C. H. June, M.D. November 10, 2005 Outline: Primer on Tumor Immunology T Cell Receptors T Cell Biology Tumor immunology
Primer on Tumor Immunology International Society for Biological Therapy of Cancer C. H. June, M.D. November 10, 2005 Outline: Primer on Tumor Immunology T Cell Receptors T Cell Biology Tumor immunology
Immune Regulation and Tolerance
 Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
