THE HISTOLOGICAL OVERVIEW TO MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES: EVALUATION OF BONE MARROW SMEARS AND BIOPSIES
|
|
|
- Helena Caldwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Disease and Global Health 6(3): , 2016 ISSN: International Knowledge Press THE HISTOLOGICAL OVERVIEW TO MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES: EVALUATION OF BONE MARROW SMEARS AND BIOPSIES YELDA DERE 1*, VOLKAN KARAKUŞ 2, ÖZGÜR ĐLHAN ÇELĐK 1, SERKAN YAŞAR ÇELĐK 1 AND ERDAL KURTOĞLU 3 1 Department of Pathology, Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University, Faculty of Medicine Training and Research Hospital, Muğla, Turkey. 2 Department of Hematology, Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University, Training and Research Hospital, Muğla, Turkey. 3 Department of Hematology, Antalya Ataturk Training and Research Hospital, Antalya, Turkey. AUTHORS CONTRIBUTIONS This work was carried out in collaboration between all authors. Authors YD, VK and OIC designed the study, wrote the protocol and interpreted the data. Authors YD and VK anchored the field study, gathered the initial data and performed preliminary data analysis. Authors SYC and EK managed the literature searches and produced the initial draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Received: 12 th November 2015 Accepted: 8 th December 2015 Published: 17 th December 2015 Original Research Article ABSTRACT Objectıve: Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are clonal haematopoietic stem cell diseases characterized by one/multilineage cytopenias and dysplasia in one or more of cell lineages. The common pathological manifestations of dysplasia are nuclear fragments and multinuclearity of erythroid cells, hypogranulation/ hyposegmentation of the granulocytes, and micromegakaryocytes. We aimed to group the dysplastic features in MDS to organize a useful,schematic approach for pathologists to achieve the accurate diagnosis. Methods: The demographical and histomorphological features of BM aspirates and BM biopsies of 40 MDS cases diagnosed according to WHO criteria were revised and regrouped. The cellularity of BM biopsy and the percentage of blasts in aspirates and biopsies, confirmed by CD34 immunostaining, were compared and noted. Results: Twenty two female (55%) and 18 male (45%) patients with a mean age of were included. The mean cellularity of biopsies was 49.2%. The highest dysplastic lineage was erythroid lineage (75%, n:30) in aspirates and the most common dysplastic features were nuclear abnormalities and binuclear erythroid cells. However, megacaryocytic lineage was the highest dysplastic lineage in biopsies (70%, n:28) and the most common dysplastic feature was found as hypolobulation/ monolobulation. The mean percentage of blastic cells was 2.55 in aspirates and 3.62 in biopsies. Conclusıon: The most common dysplastic lineages and features should be remembered and investigated on every BM aspirate and biopsy by every hematologist and hematopathologist in order to reach an accurate diagnosis of MDS. Keywords: Dysmegakaryopoesis; diserytropoesis; disgranulopoesis; myelodysplastic syndrome; CD34. *Corresponding author: yeldamorgul@gmail.com, yeldadere@mu.edu.tr;
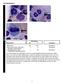
2 1. INTRODUCTION MDS are a group of hematopoietic neoplasms which are being classified according to cytogenetic and morphologic features [1]. The most common presentation of MDS is cytopenias of different lineages [2,3]. The diagnostic approach for MDS is composed of cytologic evaluation of bone marrow (BM) smears, BM biopsies and karyotype analysis [4,5]. The most important role of histopathology in MDS is differentiating from other diseases mimicking MDS such as leukemic infiltrations especially acute myeloid leukemia (AML), hairy cell leukemia or systemic mastocytosis [3]. Among many criteria, the presence of hematopoetic cells with abnormal morphology and localization in addition to the minimally increased (2-3%) number of progenitor / precursor cells showing CD34 positivity remains the most important ones supporting diagnosis of MDS [3]. The BM smears or biopsies are the only was of morphologic examination of hematopoetic cells. The determination of blastic cell percentage is another important step of diagnosis in MDS because of the strict limits of blastic cells in subgroups of MDS, refractory anemia excess blast and in AML. Thus, immunohistochemical analysis, especially anti-cd34 and anti-cd117, is almost always needed to evaluate the blastic cell percentage in MDS. In this study, we aimed to put forth the most common dysplastic features of our MDS patients seen in BM smears and biopsies in addition to the blastic cell percentages evaluated by immunohistochemistry of anti-cd MATERIALS AND METHODS This is a retrospective study of 40 patients diagnosed with MDS between July 2014 and March 2015 in Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University Training and Research Hospital. Bone marrow biopsy was performed by the same hematologist on patients with Hb <11 mg/dl, PLT< X10 9 /mm 3, PNL < 1500/mm 3 for over 6 months with a preliminary diagnosis of suspicious for MDS. These cases were evaluated by bone marrow smears and bone marrow biopsy. Bone marrow smears were observed by both hematologist and hematopathologist. The bone marrow biopsy was evaluated by routine pathologic examination in addition to the automated immunohistochemical procedure of CD 34 staining. Cases were all then established according to WHO criteria [1] for diagnosis. Dysplasia was defined when seen in >10% of the cells. Patients were accepted as sideroblastic when sideroblasts were observed over %15. MDS cases were diagnosed according to the WHO criteria [1] Patients transformed to AML and KMML were excluded from the study. Demographic data of the cases were obtained from hospital records. The pathology reports and hematoxylen eosin slides of all cases were revised in case of the missing data. All cases were already stained with CD34 antibody by automated immunohistochemical staining with Leica Bond Max. The antibodies used for staining were CD34 (Leica ). The cellularity of BM biopsies were noted and the average cellularity was calculated in addition to the minimum and maximum levels. The dysplastic features were subgrouped if they were seen in BM smears or in biopsies for determining the most common dysplastic features seen in each group. Also, if detected, the hyperplastic lineage was noted. The slides were immunohistochemically stained by Leica Bond-Max automated system using anti-cd34 (Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody) antibody and observed under Olympus BX46 microscope. Then, the blastic cell percentage was counted excluding CD34 (+) endothelial cells. Descriptive statistics, frequencies and Chi-Square tests for non parametric correlations were used in statistical analysis of the data by SPSS 15.0 Package Programme for Windows. 3. RESULTS Among 40 patients with a mean age of 69.17; 22 were female whilst 18 were male. The average cellularity of the biopsies was 49.20% with a minimum of 20% and a maximum of 80% (Fig. 1). In the 57,5% (n:23) of the cases erythroid hyperplasia was found in addition to that megakaryocytic hyperplasia was observed in 37,5% (n:15) and myeloid hyperplasia in 10% (n:4) of the cases. The most common dysplastic lineage was erythroid followed by megakaryocytic and myeloid lineages. Cases with triple lineage dysplasia forms 32,5%(n:13) of all. In the bone marrow smears, the most common dysplastic features can be counted as nuclear irregularities in erythroid cells (55%) (n:22) (Fig. 2a), followed by hypogranulation (27,5%) (n:11) and hypersegmentation (25%) (n:10) in myeloid cells (Fig. 2b). Ringed sideroblasts were observed in 15% of the cases. The megakaryocytic lineage was dysplastic in most of the cases (70%) (n:28) showing hypolobulated and hyperchromatic megakaryocytes 103
3 (40%) (n:16) and micromegakaryocytes (10%) (n:4) as the most common dysplastic forms of megakaryocytic lineage (Figs. 3a and 3b). Atypic localization of immature precursors (ALIP) was seen in only 3 cases (7,5%). These 3 cases also showed high blastic cell counts as 6%, 8% and 10% concordant with RAEB. In BM smears the average percentage of blastic cells was 2,55%. In biopsies the average of progenitor / precursor cells with CD34 (+) was found as 2.62%. Six cases showed a rate of CD34 positive progentior/precursor cells over 4% and accepted as compatible with refractory anemia excess blasts (RAEB). Fig. 1. Hypercellular bone marrow with 90% cellularity, HE, X200 Fig. 2. Dyserythropoesis characterized with nuclear irregularities (2a and 2b), bone marrow smear, Giemsa, X400. Dysgranulopoesis with hypersegmentation (2b, arrow), bone marrow smear, Giemsa, X400 Fig. 3. Dysmegakaryopoesis with hyperchromatic and small megakaryocytes, bone marrow biopsy, HE, X200 (3a), bone marrow smear, HE, X400 (3b) 104
4 4. DISCUSSION The diagnosis of MDS depends on morphological evaluation of BM cells which can be applied with BM smears, BM biopsies in addition to karyotypic analysis [4,5]. BM smears can be observed by hematologists and pathologists however BM biopsy is one of the most important material because it can be stored as paraffine blocks and additional analysis can be made on these biopsies [1]. The evaluation of BM biopsy on MDS cases is a multi-step approach beginning with the assessment of the cellularity. The cellularity can be assessed only by BM biopsy so that in hypoplastic MDS cases the evaluation of the cellularity in biopsy gets more important because of the inefficient BM smears [6]. The BM cellularity is generally subgouped as hypocellular, normocellular and hypercellular. The limits of cellularity were reported different in the literature however cellularity usually can be grouped as <20% as hypocellular, 20-70% as normocellular and over 70% as hypercellular in adults however the age of the patient is one of the most important factors effecting BM cellularity [7,8]. According to these criteria, hypocellularity is seen in 10-20% of MDS cases [9]. Our cases mostly were normocellular with an average of 49.20%. Among them, only two cases (5%) were hypocellular. The second step is the evaluation of morphological characteristics of dysplasia and to assess the dysplastic lineages. The morphological abnormalities supporting the diagnosis of MDS can be counted as multinuclearity of the erythroblasts, chromatin bridging, ringed sideroblasts, pseudo-pelger neutrophils, hypogranulated or agranulated neutrophils, micromegakaryocytes, binuclear or hyperchromatic megakaryocytes according to the report of International Working Group on Morphology of MDS [10]. Dysplastic features of different lineages can be observed in both smears and biopsies. However, dyserythropoiesis is generally observed in smears and dysplasia in other lineages in both smears and biopsies [1]. The common characteristics of erithyroid dysplasia are nuclear fragmentation, megaloblastoid changes, nuclear irregularities, chromatin bridging. Among our cases the most common dyserythropoetic features were nuclear irregularities and multinuclearity. Xiong et al. [11] also reported that the dysplastic features in mature erythrocytes such as poikilocytosis and gigantocytes were concordant with the diagnosis of MDS however the accurate value of these features remain unclear. In myeloid cells the major dysplastic features were hypogranulation and hypersegmentation. A specialized form of hypolobulation, Pseudo-Pelger neutrophils is one of the most important features especially in cases showing transformation to AML however this may also can be seen due to many different reasons like transplantation drugs or other medications [12]. In our cases the most common abnormalities of myeloid cells were also hypogranulation and hypersegmentation. Abnormal localized immature precursors, ALIP, defined as small clusters of immature cells located in the central marrow places rather than paratrabecular region and originated from the precursors of all the lineages shows a significant relation to cases with high risk of AML [9]. We observed this in 3 of the cases and these cases showed high rates of blastic cells. The megakaryocytic lineage is the most easily defined precursor cell group due to the larger size of the cells. Abnormal megakaryocytes are usually seen as micromegakaryocytes generally associated with isole del 5q MDS in addition to mononuclear and hyperchromatic forms [9,13]. We observed dysmegakaryopoiesis in 28 cases (70%) and the most common dysplastic features were hypolobulation and hyperchromasia seen in 16 cases (40%). The immunohistochemistry is an easy way to define the percentage of progenitor/precursor cells showing CD34 positivity in MDS [3]. Also this process helps to specify the presence of ALIP, the subgroups of MDS, the high risk MDS patients and transformations to AML. The most important step of detecting the real percentage of CD34 positive progenitor / precursor cells is the exclusion of CD34 positive endothelial cells [3]. We detected CD34 positive progenitor / precursor cells with an average of 2.62% in our cases with only six cases over 4%. The accurate diagnosis of MDS depends on morphological evaluation of hematopoetic cells in addition to specific genetic studies. However it it important to remember that these dysplastic features should be observed in >10% of the cells for accepting as real dysplasia [14]. 5. CONCLUSION Additional studies for BM biopsies especially immunohistochemical detection of CD34 positive progenitor/precursor cells is a major step of the evaluation of these cases. Therefore, a combined evaluation of bone marrow smears, biopsies and genetic studies were needed to make an accurate diagnosis of MDS. 105
5 CONSENT All authors declare that written informed consent was obtained from the patient (or other approved parties) for publication of this case report and accompanying images. ETHICAL APPROVAL All authors hereby declare that all experiments have been examined and approved by the appropriate ethics committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. COMPETING INTERESTS Authors have declared that no competing interests exist. REFERENCES 1. Brunning RD, Bennett JM, Flandrin G. Myelodysplastic syndromes; in Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (eds): World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon, IARC. 2001;1: Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 1982;51: Horny HP, Sotlar K, Valent P. Diagnostic value of histology and immunohistochemistry in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res. 2007;31: Bennett JM. A comparative review of classification systems in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Semin Oncol. 2005;32: Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997;89: Lambertenghi-Deliliers G, Annaloro C, Oriani A, Soligo D. Myelodysplastic syndrome associated with bone marrow fibrosis. Leuk Lymphoma. 1992;8: Hartsock RJ, Smıth EB, Petty CS. Normal variations with aging of the amount of hematopoietic tissue in bone marrow from the anterior iliac crest. A study made from 177 cases of sudden death examined by necropsy. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965;43: Tuzuner N, Cox C, Rowe JM, Bennett JM. Bone marrow cellularity in myeloid stem cell disorders: Đmpact of age correction. Leuk Res. 1994;18(8): Brunning RD, Germing U: Myelodysplastic syndromes; in Attilio Orazi, Lawrence M Weiss, Kathy Foucar, Daniel M Knowles, (ed). Neoplastic hematopathology. Wolters Kluwer Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 3 rd Edition. 2013; Mufti GJ, Bennett JM, Goasguen J, Bain BJ, Baumann I, Brunning R, et al. Diagnosis and classification of myelodysplastic syndrome: International working group on morphology of myelodysplastic syndrome (IWGM-MDS) consensus proposals for the definition and enumeration of myeloblasts and ring sideroblasts. Haematologica. 2008;93: Xiong B, Tang ZH, Zou P, Qing F, Yue QF, Chen WX, Liu XY. Dysplasia features of myelodysplastic syndrome in ethnically chinese people. Acta Haematol. 2014;131: Wang E, Boswell E, Siddigi I, Lu CM, Sebastian S, Rehder C, et al. Pseudo-Pelger Huët anomaly induced by medications. A clinicopathologic study in comparison with myelodysplastic syndrome-related Pseudo- Pelger Huët anomaly. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011; 135: Mathew P, Tefferi A, Dewald GW, Goldberg SL, Su J, Hoagland HC et al. The 5qsyndrome: A single-institution study of 43 consecutive patients. Blood. 1993;81(4): Camitta BM, Rappeport JM, Parkman R, Nathan DG. Selection of patients for bone marrow transplantation in severe aplastic anemia. Blood. 1975;45: Copyright International Knowledge Press. All rights reserved. 106
Published Ahead of Print on January 14, 2009, as doi: /haematol Copyright 2009 Ferrata Storti Foundation.
 Published Ahead of Print on January 14, 2009, as doi:10.3324/haematol.13755. Copyright 2009 Ferrata Storti Foundation. DECISION MAKING AND PROBLEM SOLVING Diagnostic criteria to distinguish hypocellular
Published Ahead of Print on January 14, 2009, as doi:10.3324/haematol.13755. Copyright 2009 Ferrata Storti Foundation. DECISION MAKING AND PROBLEM SOLVING Diagnostic criteria to distinguish hypocellular
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Everyday Challenges and Pitfalls
 Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Everyday Challenges and Pitfalls Kathryn Foucar, MD kfoucar@salud.unm.edu Henry Moon lecture May 2007 Outline Definition Conceptual overview; pathophysiologic mechanisms Incidence,
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Everyday Challenges and Pitfalls Kathryn Foucar, MD kfoucar@salud.unm.edu Henry Moon lecture May 2007 Outline Definition Conceptual overview; pathophysiologic mechanisms Incidence,
INTRODUCTION TO CYTOGENETICS AND MOLECULAR TESTING IN MDS
 INTRODUCTION TO CYTOGENETICS AND MOLECULAR TESTING IN MDS Saturday, September 29, 2018 Cyrus C. Hsia, HBSc, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor of Medicine, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry, Western
INTRODUCTION TO CYTOGENETICS AND MOLECULAR TESTING IN MDS Saturday, September 29, 2018 Cyrus C. Hsia, HBSc, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor of Medicine, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry, Western
Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material
 Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Case Presentation No. 075
 Case Presentation No. 075 Session 4. Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cristina Montalvo, MD Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology
Case Presentation No. 075 Session 4. Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cristina Montalvo, MD Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES
 MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra university hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences Key Features ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Cytopenias
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra university hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences Key Features ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Cytopenias
Myelodysplastic syndromes
 Myelodysplastic syndromes Robert P Hasserjian Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Dr. Hasserjian declares he has no conflict(s) of interest to disclose.
Myelodysplastic syndromes Robert P Hasserjian Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Dr. Hasserjian declares he has no conflict(s) of interest to disclose.
APPROACH TO MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES IN THE ERA OF PRECISION MEDICINE
 APPROACH TO MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES IN THE ERA OF PRECISION MEDICINE Rashmi Kanagal-Shamanna, MD Assistant Professor Hematopathology & Molecular Diagnostics Department of Hematopathology The University
APPROACH TO MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES IN THE ERA OF PRECISION MEDICINE Rashmi Kanagal-Shamanna, MD Assistant Professor Hematopathology & Molecular Diagnostics Department of Hematopathology The University
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/
 Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
RAEB-2 2 Transforming to Acute Erythroleukemia Case # 165
 RAEB-2 2 Transforming to Acute Erythroleukemia Case # 165 Sebastian J. Sasu, M.D. UCLA Medical Center, Hematopathology Los Angeles, CA and Saint John s s Health Center Santa Monica, CA Clinical History
RAEB-2 2 Transforming to Acute Erythroleukemia Case # 165 Sebastian J. Sasu, M.D. UCLA Medical Center, Hematopathology Los Angeles, CA and Saint John s s Health Center Santa Monica, CA Clinical History
Etiology. Definition MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES. De novo. Secondary MDS (10 years earlier than primary) transformation
 MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Rashmi Kanagal-Shamanna, MD Assistant Professor Hematopathology & Molecular Diagnostics The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas No relevant COIs to
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Rashmi Kanagal-Shamanna, MD Assistant Professor Hematopathology & Molecular Diagnostics The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas No relevant COIs to
A prospective, multicenter European Registry for newly diagnosed patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes of IPSS low and intermediate-1 subtypes.
 Protocol Synopsis Study Title A prospective, multicenter European Registry for newly diagnosed patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes of IPSS low and intermediate-1 subtypes. Short Title European MDS
Protocol Synopsis Study Title A prospective, multicenter European Registry for newly diagnosed patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes of IPSS low and intermediate-1 subtypes. Short Title European MDS
Evaluation of Bone Marrow Biopsies and Aspirates ANNA PORWIT DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, LUND UNIVERSITY
 Evaluation of Bone Marrow Biopsies and Aspirates ANNA PORWIT DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, LUND UNIVERSITY DISCLOSURES NONE Learning objectives To review the rules of BMA evaluation To review the main issues
Evaluation of Bone Marrow Biopsies and Aspirates ANNA PORWIT DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, LUND UNIVERSITY DISCLOSURES NONE Learning objectives To review the rules of BMA evaluation To review the main issues
Bone Marrow Mast Cell Morphologic Features and Hematopoietic Dyspoiesis in Systemic Mast Cell Disease
 Hematopathology / SYSTEMIC MAST CELL DISEASE Bone Marrow Mast Cell Morphologic Features and Hematopoietic Dyspoiesis in Systemic Mast Cell Disease Eric C. Stevens, MD, and Nancy S. Rosenthal, MD Key Words:
Hematopathology / SYSTEMIC MAST CELL DISEASE Bone Marrow Mast Cell Morphologic Features and Hematopoietic Dyspoiesis in Systemic Mast Cell Disease Eric C. Stevens, MD, and Nancy S. Rosenthal, MD Key Words:
Study of diagnostic features of bone marrow in aplastic anaemia
 Original article: Study of diagnostic features of bone marrow in aplastic anaemia 1Dr. Poonam Nanwani, 2 Dr. Sativan Khatri* 1MD Pathologist, Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, M.G.M. Medical
Original article: Study of diagnostic features of bone marrow in aplastic anaemia 1Dr. Poonam Nanwani, 2 Dr. Sativan Khatri* 1MD Pathologist, Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, M.G.M. Medical
ACCME/Disclosures. History. Hematopathology Specialty Conference Case #4 4/13/2016
 Hematopathology Specialty Conference Case #4 Sherrie L. Perkins MD, PhD University of Utah ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose
Hematopathology Specialty Conference Case #4 Sherrie L. Perkins MD, PhD University of Utah ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose
Border between aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome
 Int J Hematol (2013) 97:558 563 DOI 10.1007/s12185-013-1324-x PROGRESS IN HEMATOLOGY Advances in the management of acquired aplastic anemia (AA) Border between aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome
Int J Hematol (2013) 97:558 563 DOI 10.1007/s12185-013-1324-x PROGRESS IN HEMATOLOGY Advances in the management of acquired aplastic anemia (AA) Border between aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome
DECISION MAKING AND PROBLEM SOLVING ABSTRACT
 DECISION MAKING AND PROBLEM SOLVING Diagnosis and classification of myelodysplastic syndrome: International Working Group on Morphology of myelodysplastic syndrome (IWGM-MDS) consensus proposals for the
DECISION MAKING AND PROBLEM SOLVING Diagnosis and classification of myelodysplastic syndrome: International Working Group on Morphology of myelodysplastic syndrome (IWGM-MDS) consensus proposals for the
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228
 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology & European Association for Hematopathology Indianapolis, IN, USA Case # 228 Vishnu V. B Reddy, MD University of Alabama at Birmingham Birmingham, AL USA 11/03/07
Ordering Physician CLIENT,CLIENT. Collected REVISED REPORT
 HPWET Hematopathology Consultation, MML Embed Client Hematopathology Consult REVISED INAL DIAGNOSIS Interpretation Peripheral blood, bone marrow aspirate and biopsies, bilateral iliac crests: 1. Normocellular
HPWET Hematopathology Consultation, MML Embed Client Hematopathology Consult REVISED INAL DIAGNOSIS Interpretation Peripheral blood, bone marrow aspirate and biopsies, bilateral iliac crests: 1. Normocellular
Morfologia normale e patologica
 Morfologia normale e patologica Gina Zini Centro di Ricerca ReCAMH Dpt. Ematologia Università Cattolica S. Cuore - Roma EMATOLOGIA DI LABORATORIO: percorsi diagnostici e obiettivi clinici. Milano 11-12
Morfologia normale e patologica Gina Zini Centro di Ricerca ReCAMH Dpt. Ematologia Università Cattolica S. Cuore - Roma EMATOLOGIA DI LABORATORIO: percorsi diagnostici e obiettivi clinici. Milano 11-12
Bone marrow pathology. October 2013 BHS Educational Course
 Bone marrow pathology October 2013 BHS Educational Course Technical aspects Interpretation of BMB Introduction: technical aspects of histology Identification of a disease process or a diagnosis By tissue
Bone marrow pathology October 2013 BHS Educational Course Technical aspects Interpretation of BMB Introduction: technical aspects of histology Identification of a disease process or a diagnosis By tissue
ML Amigo, MC del Cañizo, A Rios, MA Garcia, MD Caballero, A Martin, N Bermejo, P Vilches and JF San Miguel. Summary:
 Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1999) 23, 997 1002 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0268 3369/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bmt Diagnosis of secondary myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) following
Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1999) 23, 997 1002 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0268 3369/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bmt Diagnosis of secondary myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) following
Changes to the 2016 WHO Classification for the Diagnosis of MDS
 Changes to the 2016 WHO Classification for the Diagnosis of MDS Welcome to Managing MDS. I am Dr. Ulrich Germing, and today, I will provide highlights from the 14th International Symposium on MDS in Valencia,
Changes to the 2016 WHO Classification for the Diagnosis of MDS Welcome to Managing MDS. I am Dr. Ulrich Germing, and today, I will provide highlights from the 14th International Symposium on MDS in Valencia,
Case Report. Introduction. Mastocytosis associated with CML Hematopathology - March K. David Li 1,*, Xinjie Xu 1, and Anna P.
 Mastocytosis associated with CML Hematopathology - March 2016 Case Report Systemic mastocytosis with associated clonal hematologic non-mast cell lineage disease (SM-AHNMD) involving chronic myelogenous
Mastocytosis associated with CML Hematopathology - March 2016 Case Report Systemic mastocytosis with associated clonal hematologic non-mast cell lineage disease (SM-AHNMD) involving chronic myelogenous
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: WHO 2008
 Myelodysplastic Syndromes: WHO 2008 Attilio Orazi, M.D., FRCPath. (Engl.) Weill Medical College of Cornell University New York, NY Congresso Nazionale SIE - Società Italiana di Ematologia - MIC Milano
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: WHO 2008 Attilio Orazi, M.D., FRCPath. (Engl.) Weill Medical College of Cornell University New York, NY Congresso Nazionale SIE - Società Italiana di Ematologia - MIC Milano
New system for assessing the prognosis of refractory anemia patients
 Leukemia (1999) 13, 1727 1734 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0887-6924/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/leu New system for assessing the prognosis of refractory anemia patients A Matsuda
Leukemia (1999) 13, 1727 1734 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0887-6924/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/leu New system for assessing the prognosis of refractory anemia patients A Matsuda
Hematology Measure #1: Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Leukemias: Baseline Cytogenetic Testing Performed on Bone Marrow
 Hematology Measure #1: Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Leukemias: Baseline Cytogenetic Testing Performed on Bone Marrow This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Clinical Performance
Hematology Measure #1: Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Leukemias: Baseline Cytogenetic Testing Performed on Bone Marrow This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Clinical Performance
Histopathology in the diagnosis of high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes
 Journal of clinical and experimental hematopathology Vol. 58 No.2, 51-60, 2018 JC lin EH xp ematopathol Review Article Histopathology in the diagnosis of high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes Hidekazu Kayano
Journal of clinical and experimental hematopathology Vol. 58 No.2, 51-60, 2018 JC lin EH xp ematopathol Review Article Histopathology in the diagnosis of high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes Hidekazu Kayano
Myelodysplastic scoring system with flow cytometry. G Detry B Husson
 Myelodysplastic scoring system with flow cytometry G Detry B Husson Myelodysplastic syndroms Clonal haematopoietic stem cell disease characterized by dysplasia in one or more of the myeloid cell lines
Myelodysplastic scoring system with flow cytometry G Detry B Husson Myelodysplastic syndroms Clonal haematopoietic stem cell disease characterized by dysplasia in one or more of the myeloid cell lines
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML)
 Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML) JMML: Definition Monoclonal hematopoietic disorder of childhood characterized by proliferation of the granulocytic and monocytic lineages Erythroid and megakaryocytic
Bone Marrow Morphology after Therapy and Stem Cell Transplantation. Arash Mohtashamian, MD Naval Medical Center, San Diego
 Bone Marrow Morphology after Therapy and Stem Cell Transplantation Arash Mohtashamian, MD Naval Medical Center, San Diego Objectives Bone marrow findings after myeloablative therapy. Effects of recombinant
Bone Marrow Morphology after Therapy and Stem Cell Transplantation Arash Mohtashamian, MD Naval Medical Center, San Diego Objectives Bone marrow findings after myeloablative therapy. Effects of recombinant
Leukaemia Section Review
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Review Classification of myelodysplasic syndromes Georges Flandrin Laboratoire d'hématologie,
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Review Classification of myelodysplasic syndromes Georges Flandrin Laboratoire d'hématologie,
Myelodysplastic syndromes in adults aged less than 50 years: Incidence and clinicopathological data
 JBUON 2014; 19(4): 999-1005 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Myelodysplastic syndromes in adults aged less than 50 years: Incidence
JBUON 2014; 19(4): 999-1005 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Myelodysplastic syndromes in adults aged less than 50 years: Incidence
Myelodysplastic syndromes: revised WHO classification and distinction from non-neoplastic conditions
 Myelodysplastic syndromes: revised WHO classification and distinction from non-neoplastic conditions Robert P Hasserjian, MD Associate Professor Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School
Myelodysplastic syndromes: revised WHO classification and distinction from non-neoplastic conditions Robert P Hasserjian, MD Associate Professor Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School
Pathology. #11 Acute Leukemias. Farah Banyhany. Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16
 35 Pathology #11 Acute Leukemias Farah Banyhany Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16 1 Salam First of all, this tafreegh is NOT as long as you may think. If you just focus while studying this, everything will
35 Pathology #11 Acute Leukemias Farah Banyhany Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16 1 Salam First of all, this tafreegh is NOT as long as you may think. If you just focus while studying this, everything will
Bone Marrow. Procedures Blood Film Aspirate, Cell Block Trephine Biopsy, Touch Imprint
 Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Case Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology
 Case 148 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology Robert P Hasserjian Department of Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA Clinical history
Case 148 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology Robert P Hasserjian Department of Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA Clinical history
NOVEL APPROACHES IN THE CLASSIFICATION AND RISK ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS WITH MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES-CLINICAL IMPLICATION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES NOVEL APPROACHES IN THE CLASSIFICATION AND RISK ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS WITH MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES-CLINICAL IMPLICATION Ilina Micheva 1, Rosen Rachev 1, Hinco Varbanov 1, Vladimir
ORIGINAL ARTICLES NOVEL APPROACHES IN THE CLASSIFICATION AND RISK ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS WITH MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES-CLINICAL IMPLICATION Ilina Micheva 1, Rosen Rachev 1, Hinco Varbanov 1, Vladimir
CASE REPORT Myelodysplastic syndrome with fibrosis and complex karyotype arising in a patient with essential thrombocythaemia
 Malaysian J Pathol 2018; 40(2) : 191 197 CASE REPORT Myelodysplastic syndrome with fibrosis and complex karyotype arising in a patient with essential thrombocythaemia Nor Ainiza MANSOR 1, Nurasyikin YUSOF
Malaysian J Pathol 2018; 40(2) : 191 197 CASE REPORT Myelodysplastic syndrome with fibrosis and complex karyotype arising in a patient with essential thrombocythaemia Nor Ainiza MANSOR 1, Nurasyikin YUSOF
June 11, Ella Noel, D.O., FACOI 1717 West Broadway Madison, WI
 June 11, 2018 Ella Noel, D.O., FACOI 1717 West Broadway Madison, WI 53713 policycomments@wpsic.com RE: Draft Local Coverage Determination: MolDX: MDS FISH (DL37772) Dear Dr. Noel Thank you for the opportunity
June 11, 2018 Ella Noel, D.O., FACOI 1717 West Broadway Madison, WI 53713 policycomments@wpsic.com RE: Draft Local Coverage Determination: MolDX: MDS FISH (DL37772) Dear Dr. Noel Thank you for the opportunity
BONE MARROW EXAMINATION FINDINGS OF A SINGLE CENTRE- AN ORIGINAL ARTICLE.
 BONE MARROW EXAMINATION FINDINGS OF A SINGLE CENTRE- AN ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ISHRAT JAHAN SHIMU¹, M. MEHFUZ-E- KHODA², M. A. SATTAR SARKER 3, FATEMA AHMED 4, PALASH MITRA 5, FAKHRUDDIN BHUIYAN 6, ALAMGIR
BONE MARROW EXAMINATION FINDINGS OF A SINGLE CENTRE- AN ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ISHRAT JAHAN SHIMU¹, M. MEHFUZ-E- KHODA², M. A. SATTAR SARKER 3, FATEMA AHMED 4, PALASH MITRA 5, FAKHRUDDIN BHUIYAN 6, ALAMGIR
Mast Cell Disease Case 054 Session 7
 Mast Cell Disease Case 054 Session 7 Rodney R. Miles, M.D., Ph.D. Lauren B. Smith, M.D. Cem Akin, M.D. Diane Roulston,, Ph.D. Charles W. Ross, M.D. Departments of Pathology and Internal Medicine University
Mast Cell Disease Case 054 Session 7 Rodney R. Miles, M.D., Ph.D. Lauren B. Smith, M.D. Cem Akin, M.D. Diane Roulston,, Ph.D. Charles W. Ross, M.D. Departments of Pathology and Internal Medicine University
Myelodysplastic Syndrome Case 158
 Myelodysplastic Syndrome Case 158 Dong Chen MD PhD Division of Hematopathology Mayo Clinic Clinical History 86 year old man Persistent borderline anemia and thrombocytopenia. His past medical history was
Myelodysplastic Syndrome Case 158 Dong Chen MD PhD Division of Hematopathology Mayo Clinic Clinical History 86 year old man Persistent borderline anemia and thrombocytopenia. His past medical history was
myelodysplastic syndrome MDS MDS MDS
 myelodysplastic syndrome MDS MDS 15 10 3 2004 15 MDS 400 2 65 61 70 MDS MDS 1 1 2 3 3 4 1 4 2 3 4 MDS 1982 Bennett French- American-BritishFAB 1 2 WHO 1999 3 2001 4 2002 Vardiman MDS 5 2WHO FAB refractory
myelodysplastic syndrome MDS MDS 15 10 3 2004 15 MDS 400 2 65 61 70 MDS MDS 1 1 2 3 3 4 1 4 2 3 4 MDS 1982 Bennett French- American-BritishFAB 1 2 WHO 1999 3 2001 4 2002 Vardiman MDS 5 2WHO FAB refractory
Bone Marrow Specimen (Aspirate and Trephine Biopsy) Proforma
 Bone Marrow Specimen (Aspirate and Trephine Biopsy) Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.03). Family name Given name(s) Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate Date
Bone Marrow Specimen (Aspirate and Trephine Biopsy) Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.03). Family name Given name(s) Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate Date
Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation
 Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies. Patricia Aoun MD MPH
 Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
BLASTIC CRISIS AND MYELOFIBROSIS SIMULTANEOUS COMPLICATIONS IN A CASE OF CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
 BLASTIC CRISIS AND MYELOFIBROSIS SIMULTANEOUS COMPLICATIONS IN A CASE OF CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 151 To 153 Khalid Hassan ( Department of Pathology (Haematology)
BLASTIC CRISIS AND MYELOFIBROSIS SIMULTANEOUS COMPLICATIONS IN A CASE OF CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 151 To 153 Khalid Hassan ( Department of Pathology (Haematology)
ADx Bone Marrow Report. Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information
 ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
MORPHOLOGY AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES AND THEIR PATHOLOGIC VARIANTS
 MORPHOLOGY AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES AND THEIR PATHOLOGIC VARIANTS Historical Background/Introduction Peter A. Kouides and John M. Bennett Despite the suffix -dysplastic, the
MORPHOLOGY AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES AND THEIR PATHOLOGIC VARIANTS Historical Background/Introduction Peter A. Kouides and John M. Bennett Despite the suffix -dysplastic, the
Myelodysplastic Syndromes Myeloproliferative Disorders
 Myelodysplastic Syndromes Myeloproliferative Disorders Myelodysplastic Syndromes characterized by maturation defects that are associated with ineffective hematopoiesis and a high risk of transformation
Myelodysplastic Syndromes Myeloproliferative Disorders Myelodysplastic Syndromes characterized by maturation defects that are associated with ineffective hematopoiesis and a high risk of transformation
Reproducibility of Histologic Classification in Nonfibrotic Myeloproliferative Neoplasia
 Hematopathology / Morphologic Features in MPN Reproducibility of Histologic Classification in Nonfibrotic Myeloproliferative Neoplasia Suzanne M. Koopmans, MD, 1 Freek J. Bot, MD, PhD, 1,2 King H. Lam,
Hematopathology / Morphologic Features in MPN Reproducibility of Histologic Classification in Nonfibrotic Myeloproliferative Neoplasia Suzanne M. Koopmans, MD, 1 Freek J. Bot, MD, PhD, 1,2 King H. Lam,
Better Prognosis for Patients With Del(7q) Than for Patients With Monosomy 7 in Myelodysplastic Syndrome
 Better Prognosis for Patients With Del(7q) Than for Patients With Monosomy 7 in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Iris Cordoba, MD 1 ; José R. González-Porras, MD 1 ; Benet Nomdedeu, MD 2 ; Elisa Luño, MD 3 ; Raquel
Better Prognosis for Patients With Del(7q) Than for Patients With Monosomy 7 in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Iris Cordoba, MD 1 ; José R. González-Porras, MD 1 ; Benet Nomdedeu, MD 2 ; Elisa Luño, MD 3 ; Raquel
SH A CASE OF PERSISTANT NEUTROPHILIA: BCR-ABL
 SH2017-0124 A CASE OF PERSISTANT NEUTROPHILIA: BCR-ABL NEGATIVE John R Goodlad 1, Pedro Martin-Cabrera 2, Catherine Cargo 2 1. Department of Pathology, NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde, QEUH, Glasgow 2. Haematological
SH2017-0124 A CASE OF PERSISTANT NEUTROPHILIA: BCR-ABL NEGATIVE John R Goodlad 1, Pedro Martin-Cabrera 2, Catherine Cargo 2 1. Department of Pathology, NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde, QEUH, Glasgow 2. Haematological
Concise Review for Primary-Care Physicians
 Concise Review for Primary-Care Physicians Myelodysplastic (Preleukemia) Syndromes: The Bone Marrow Factory Failure Problem H. CLARK HOAGLAND, M.D. The myelodysplastic syndromes are a group of hematologic
Concise Review for Primary-Care Physicians Myelodysplastic (Preleukemia) Syndromes: The Bone Marrow Factory Failure Problem H. CLARK HOAGLAND, M.D. The myelodysplastic syndromes are a group of hematologic
The histopathology of bone marrow failure in children
 Journal of clinical and experimental hematopathology Vol. 58 No.2, 68-86, 2018 JC lin EH xp ematopathol Review Article The histopathology of bone marrow failure in children Hideto Iwafuchi Bone marrow
Journal of clinical and experimental hematopathology Vol. 58 No.2, 68-86, 2018 JC lin EH xp ematopathol Review Article The histopathology of bone marrow failure in children Hideto Iwafuchi Bone marrow
Mast Cell Disease. Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University, Stanford CA
 Mast Cell Disease Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University, Stanford CA Mast cell disease, or mastocytosis, includes a variety of disorders that are characterized by the presence of mast cell aggregates
Mast Cell Disease Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University, Stanford CA Mast cell disease, or mastocytosis, includes a variety of disorders that are characterized by the presence of mast cell aggregates
CD34 positive dysplastic giant platelets masquerading as blasts on flow cytometry
 CD34+ Giant Platelets Hematopathology - September 2016 Case Study CD34 positive dysplastic giant platelets masquerading as blasts on flow cytometry Anmaar Abdul-Nabi 1,*, Yvette Reese 2, Susan Treese 2,
CD34+ Giant Platelets Hematopathology - September 2016 Case Study CD34 positive dysplastic giant platelets masquerading as blasts on flow cytometry Anmaar Abdul-Nabi 1,*, Yvette Reese 2, Susan Treese 2,
Case Presentation. Attilio Orazi, MD
 Case Presentation Attilio Orazi, MD Weill Cornell Medical College/ NYP Hospital Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine New York, NY United States History 60 year old man presented with anemia
Case Presentation Attilio Orazi, MD Weill Cornell Medical College/ NYP Hospital Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine New York, NY United States History 60 year old man presented with anemia
NUMERATOR: Patients who had baseline cytogenetic testing performed on bone marrow
 Quality ID #67 (NQF 0377): Hematology: Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Leukemias: Baseline Cytogenetic Testing Performed on Bone Marrow National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
Quality ID #67 (NQF 0377): Hematology: Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Leukemias: Baseline Cytogenetic Testing Performed on Bone Marrow National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
Myeloid neoplasms. Early arrest in the blast cell or immature cell "we call it acute leukemia" Myoid neoplasm divided in to 3 major categories:
 Myeloid neoplasms Note: Early arrest in the blast cell or immature cell "we call it acute leukemia" Myoid neoplasm divided in to 3 major categories: 1. AML : Acute myeloid leukemia(stem cell with myeloid
Myeloid neoplasms Note: Early arrest in the blast cell or immature cell "we call it acute leukemia" Myoid neoplasm divided in to 3 major categories: 1. AML : Acute myeloid leukemia(stem cell with myeloid
Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms
 Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms The minimum number of blasts to diagnose acute myeloid leukemia is 5% 10% 20% 50% 80% AML with the best prognosis is AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormality AML with myelodysplasia
Heme 9 Myeloid neoplasms The minimum number of blasts to diagnose acute myeloid leukemia is 5% 10% 20% 50% 80% AML with the best prognosis is AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormality AML with myelodysplasia
NUP214-ABL1 Fusion: A Novel Discovery in Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia
 Case 0094 NUP214-ABL1 Fusion: A Novel Discovery in Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia Jessica Snider, MD Medical University of South Carolina Case Report - 64 year old Caucasian Male Past Medical History Osteoarthritis
Case 0094 NUP214-ABL1 Fusion: A Novel Discovery in Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia Jessica Snider, MD Medical University of South Carolina Case Report - 64 year old Caucasian Male Past Medical History Osteoarthritis
WHO Update to Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
 WHO Update to Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Archana M Agarwal, MD, Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah Department of Pathology/ARUP Laboratories Myeloproliferative Neoplasms The categories
WHO Update to Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Archana M Agarwal, MD, Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah Department of Pathology/ARUP Laboratories Myeloproliferative Neoplasms The categories
Bone Marrow. Procedures Blood Film Aspirate, Cell Block Trephine Biopsy, Touch Imprint
 Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Conditions that mimic neoplasia in the bone marrow. Kaaren K. Reichard Mayo Clinic Rochester
 Conditions that mimic neoplasia in the bone marrow Kaaren K. Reichard Mayo Clinic Rochester reichard.kaaren@mayo.edu Nothing to disclose Conflict of Interest Learning Objectives Multiple conditions in
Conditions that mimic neoplasia in the bone marrow Kaaren K. Reichard Mayo Clinic Rochester reichard.kaaren@mayo.edu Nothing to disclose Conflict of Interest Learning Objectives Multiple conditions in
Myelodysplastic syndromes
 Haematology 601 Myelodysplastic syndromes The myelodysplastic syndromes are a group of disorders predominantly affecting elderly people, leading to ineffective haematopoiesis, and they have the potential
Haematology 601 Myelodysplastic syndromes The myelodysplastic syndromes are a group of disorders predominantly affecting elderly people, leading to ineffective haematopoiesis, and they have the potential
Bone marrow histology 3: Value of bone marrow. syndromes, and chronic myeloid leukaemia. core biopsy in acute leukaemia, myelodysplastic
 J Clin Pathol 1992;45:855-859 855 Haematology Department, Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield S10 2JF D A Winfield Department of Pathology, University of Sheffield Medical School S V Polacarz Correspondence
J Clin Pathol 1992;45:855-859 855 Haematology Department, Royal Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield S10 2JF D A Winfield Department of Pathology, University of Sheffield Medical School S V Polacarz Correspondence
2013 AAIM Pathology Workshop
 2013 AAIM Pathology Workshop John Schmieg, M.D., Ph.D. None Disclosures 1 Pathology Workshop Objectives Define the general philosophy of reviewing pathology reports Review the various components of Bone
2013 AAIM Pathology Workshop John Schmieg, M.D., Ph.D. None Disclosures 1 Pathology Workshop Objectives Define the general philosophy of reviewing pathology reports Review the various components of Bone
Hematology 101. Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD
 Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
Hematology 101 Blanche P Alter, MD, MPH, FAAP Clinical Genetics Branch Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics Bethesda, MD Hematocrits Plasma White cells Red cells Normal, Hemorrhage, IDA, Leukemia,
Overview of guidelines on iron chelation therapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and transfusional iron overload
 Int J Hematol (2008) 88:24 29 DOI 10.1007/s12185-008-0118-z PROGRESS IN HEMATOLOGY Transfusional iron overload and iron chelation therapy Overview of guidelines on iron chelation therapy in patients with
Int J Hematol (2008) 88:24 29 DOI 10.1007/s12185-008-0118-z PROGRESS IN HEMATOLOGY Transfusional iron overload and iron chelation therapy Overview of guidelines on iron chelation therapy in patients with
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. E Verburgh 1, R Achten 2, VJ Louw 1, C Brusselmans 1, M Delforge 1, M Boogaerts 1, A Hagemeijer 3, P Vandenberghe 3 and G Verhoef 1
 (2007) 21, 668 677 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0887-6924/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/leu ORIGINAL ARTICLE A new disease categorization of low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes based on
(2007) 21, 668 677 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0887-6924/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/leu ORIGINAL ARTICLE A new disease categorization of low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes based on
Bone marrow morphology in reactive conditions. Kaaren K. Reichard, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester
 Bone marrow morphology in reactive conditions Kaaren K. Reichard, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester reichard.kaaren@mayo.edu Nothing to disclose Conflict of Interest Outline of Presentation Brief introduction General
Bone marrow morphology in reactive conditions Kaaren K. Reichard, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester reichard.kaaren@mayo.edu Nothing to disclose Conflict of Interest Outline of Presentation Brief introduction General
Primary myelofibrosis
 - It s a bone marrow fibrosis Primary myelofibrosis - It's type of myeloproliferative disease i.e. neoplastic proliferation of mature cell of myloid linage. - Its similar to chronic myloid leukemia (CML).
- It s a bone marrow fibrosis Primary myelofibrosis - It's type of myeloproliferative disease i.e. neoplastic proliferation of mature cell of myloid linage. - Its similar to chronic myloid leukemia (CML).
Leukaemia Section Review
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Review Classification of acute myeloid leukemias Georges Flandrin Laboratoire d'hématologie,
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Review Classification of acute myeloid leukemias Georges Flandrin Laboratoire d'hématologie,
Integrated Diagnostic Approach to the Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms. Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University
 Integrated Diagnostic Approach to the Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University What is an integrated approach? What is an integrated approach? Incorporating all diagnostic
Integrated Diagnostic Approach to the Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms Daniel A. Arber, MD Stanford University What is an integrated approach? What is an integrated approach? Incorporating all diagnostic
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED
 Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
Approaching myeloid neoplasms: diagnostic algorithms
 Approaching myeloid neoplasms: diagnostic algorithms Alexandar Tzankov Histopathology Pathology Content Integration of clinical and laboratory data Bone marrow evaluation approaching Myeloproliferative
Approaching myeloid neoplasms: diagnostic algorithms Alexandar Tzankov Histopathology Pathology Content Integration of clinical and laboratory data Bone marrow evaluation approaching Myeloproliferative
Myelodysplastic syndromes and the new WHO 2016 classification
 Myelodysplastic syndromes and the new WHO 2016 classification 32nd General Annual Meeting of the Belgian Hematology Society 10-11 February 2017 Gregor Verhoef, Departement of Hematology, University Hospital
Myelodysplastic syndromes and the new WHO 2016 classification 32nd General Annual Meeting of the Belgian Hematology Society 10-11 February 2017 Gregor Verhoef, Departement of Hematology, University Hospital
Aplastic Anemia and Monosomy 7 Associated Dysmegakaryocytopoiesis
 Hematopathology / APLASTIC ANEMIA AND DYSMEGAKARYOCYTOPOIESIS Aplastic Anemia and Monosomy 7 Associated Dysmegakaryocytopoiesis Michelle M. Dolan, MD, 1 Timothy P. Singleton, MD, 1 Joseph Neglia, MD, MPH,
Hematopathology / APLASTIC ANEMIA AND DYSMEGAKARYOCYTOPOIESIS Aplastic Anemia and Monosomy 7 Associated Dysmegakaryocytopoiesis Michelle M. Dolan, MD, 1 Timothy P. Singleton, MD, 1 Joseph Neglia, MD, MPH,
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History An 11-year-old girl presented to the emergency room with wheezing and was diagnosed as having asthma. Her CBC showed WBC = 12.5 x 10 9 /L; Hgb = 12.4g/dL;
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History An 11-year-old girl presented to the emergency room with wheezing and was diagnosed as having asthma. Her CBC showed WBC = 12.5 x 10 9 /L; Hgb = 12.4g/dL;
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD. Part 4 MYELOID NEOPLASMS
 HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 4 MYELOID NEOPLASMS Introduction: o Myeloid neoplasms are divided into three major categories: o Acute
HENATOLYMPHOID SYSTEM THIRD YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS- UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN AHMAD T. MANSOUR, MD Part 4 MYELOID NEOPLASMS Introduction: o Myeloid neoplasms are divided into three major categories: o Acute
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES WITH MONOCYTIC COMPONENT: HEMATOLOGIC AND CYTOGENETIC CHARACTERIZATION
 original paper Haematologica 1997; 82:25-30 Advances in the Cytobiology of Leukemias* MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES WITH MONOCYTIC COMPONENT: HEMATOLOGIC AND CYTOGENETIC CHARACTERIZATION GIAN MATTEO RIGOLIN,
original paper Haematologica 1997; 82:25-30 Advances in the Cytobiology of Leukemias* MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES WITH MONOCYTIC COMPONENT: HEMATOLOGIC AND CYTOGENETIC CHARACTERIZATION GIAN MATTEO RIGOLIN,
Bone Marrow Biopsy in Myelodysplastic Syndromes & Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. A Review for Anatomic Pathologists.
 Bone Marrow Biopsy in Myelodysplastic Syndromes & Myeloproliferative Neoplasms A Review for Anatomic Pathologists Bakul I. Dalal MD FRCPC DABP FACP FASCP Clinical Professor, Department of Pathology, UBC
Bone Marrow Biopsy in Myelodysplastic Syndromes & Myeloproliferative Neoplasms A Review for Anatomic Pathologists Bakul I. Dalal MD FRCPC DABP FACP FASCP Clinical Professor, Department of Pathology, UBC
HEMATOPATHOLOGY (SHANDS HOSPITAL AT THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA): Rotation Director: Ying Li, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY (SHANDS HOSPITAL AT THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA): Rotation Director: Ying Li, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor I. Description of the rotation: During this rotation, the resident will gain
HEMATOPATHOLOGY (SHANDS HOSPITAL AT THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA): Rotation Director: Ying Li, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor I. Description of the rotation: During this rotation, the resident will gain
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(1):23 27 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Acute leukemia with erythroid hyperplasia. Our experience on a series of cases
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(1):23 27 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Acute leukemia with erythroid hyperplasia. Our experience on a series of cases
Bone Marrow. Procedures Blood Film Aspirate, Cell Block Trephine Biopsy, Touch Imprint
 Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Bone Marrow Protocol applies to acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative disorders, chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, malignant lymphomas, plasma cell dyscrasias, histiocytic
Practical Diagnosis of Hematologic Disorders. Vol 2 Malignant Disorders
 5 th ed Practical Diagnosis of Hematologic Disorders Vol 2 Malignant Disorders Vol2_FrontMatter_v03_0804 final.indd i 8/6/2009 10:00:11 PM Authors Carl R Kjeldsberg, MD Professor of Pathology, University
5 th ed Practical Diagnosis of Hematologic Disorders Vol 2 Malignant Disorders Vol2_FrontMatter_v03_0804 final.indd i 8/6/2009 10:00:11 PM Authors Carl R Kjeldsberg, MD Professor of Pathology, University
Introduction. Indications for bone marrow examination. Obtaining the bone marrow biopsy
 1 Introduction Indications for bone marrow examination Bone marrow examination, including both aspiration and biopsy sampling, can be performed on virtually any patient. However, patients with coagulation
1 Introduction Indications for bone marrow examination Bone marrow examination, including both aspiration and biopsy sampling, can be performed on virtually any patient. However, patients with coagulation
2 nd step do Bone Marrow Study If possible both the aspiration and
 Blood Malignancies-I Prof. Herman Hariman,SpPK a (KH). Ph.D.(U.K) Prof. Dr. Adikoesoema Aman, SpPK (KH) Dept. Clinpath, FK-USU First do the Full Blood Count Hb, WBCS, Platelets Morphology!! Such as blasts,
Blood Malignancies-I Prof. Herman Hariman,SpPK a (KH). Ph.D.(U.K) Prof. Dr. Adikoesoema Aman, SpPK (KH) Dept. Clinpath, FK-USU First do the Full Blood Count Hb, WBCS, Platelets Morphology!! Such as blasts,
What is MDS? Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Classification & Risk Stratification
 What is MDS? Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Classification & Risk Stratification Rami Komrokji, MD Clinical Director Malignant Hematology Moffitt Cancer Center Normal Blood and Bone Marrow What is MDS Myelodysplastic
What is MDS? Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Classification & Risk Stratification Rami Komrokji, MD Clinical Director Malignant Hematology Moffitt Cancer Center Normal Blood and Bone Marrow What is MDS Myelodysplastic
Collected: , PM Sent: , PM Received: , PM Preliminary: , PM. Notification Status: COMPREHENSIVE DIAGNOSIS
 PATIENT Name:HIPAA, Compliant DOB: 03-25-1945 (60 yr) ID#: xxx-xx-0000 Sex: M Tel: xxx-xxx-xxxx SPECIMEN Your No:WS05-xxxx Case No:C05-00xxx Req. No:Txxxxx Collected: 06-08-05, PM Sent: 06-09-05, PM Received:
PATIENT Name:HIPAA, Compliant DOB: 03-25-1945 (60 yr) ID#: xxx-xx-0000 Sex: M Tel: xxx-xxx-xxxx SPECIMEN Your No:WS05-xxxx Case No:C05-00xxx Req. No:Txxxxx Collected: 06-08-05, PM Sent: 06-09-05, PM Received:
Hematopathology Lab. Third year medical students
 Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) & Myeloproliferative neoplasms
 Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) & Myeloproliferative neoplasms Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) A multipotent stem cell that can differentiate into any of the myeloid lineage cells (RBCs, granulocytes, megakaryocytes)
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) & Myeloproliferative neoplasms Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) A multipotent stem cell that can differentiate into any of the myeloid lineage cells (RBCs, granulocytes, megakaryocytes)
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Treatment of low risk MDS
 Treatment of low risk MDS Matteo G Della Porta Cancer Center IRCCS Humanitas Research Hospital & Humanitas University Rozzano Milano, Italy matteo.della_porta@hunimed.eu International Prognostic Scoring
Treatment of low risk MDS Matteo G Della Porta Cancer Center IRCCS Humanitas Research Hospital & Humanitas University Rozzano Milano, Italy matteo.della_porta@hunimed.eu International Prognostic Scoring
Clinical Prognostic Factors in 86 Chinese Patients with Primary Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Trisomy 8: A Single Institution Experience
 Original Article Yonsei Med J 2016 Mar;57(2):358-364 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Clinical Prognostic Factors in 86 Chinese Patients with Primary Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Trisomy 8: A Single
Original Article Yonsei Med J 2016 Mar;57(2):358-364 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Clinical Prognostic Factors in 86 Chinese Patients with Primary Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Trisomy 8: A Single
CASE 106. Pancytopenia in the setting of marrow hypoplasia, a PNH clone, and a DNMT3A mutation
 CASE 106 Pancytopenia in the setting of marrow hypoplasia, a PNH clone, and a DNMT3A mutation Gabriel C. Caponetti, MD University of Pennsylvania, US Clinical history 69, F peripheral neuropathy, refractory
CASE 106 Pancytopenia in the setting of marrow hypoplasia, a PNH clone, and a DNMT3A mutation Gabriel C. Caponetti, MD University of Pennsylvania, US Clinical history 69, F peripheral neuropathy, refractory
