Chemoprevention Strategies in Lung Carcinogenesis*
|
|
|
- Wesley Martin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemoprevention Strategies in Lung Carcinogenesis* Scott M. Lippman, M.D.; Steven E. Benner M.D.; and Waun Ki Hong, M.D. Chemoprevention entails using specific agents to suppress carcinogenesis and thereby prevent the development of primary or second primary cancers. Because the concept of chemoprevention in patients with or at risk of lung cancer is new, ongoing clinical trials are based on data from epidemiologic and preclinical research, as well as on results of chemoprevention studies in head and neck cancer. The latter studies have provided a model for such studies in lung cancer, considering the two diseases have a similar etiology and biology of field carcinogenesis. Beta-carotene, natural vitamin A, and the retinoids may be effective chemopreventive agents. However, chronic administration of such agents may be required to prevent the development of cancer. Results of chemoprevention trials in head and neck cancer have demonstrated effective inhibition of the development of second primary tumors with the synthetic retinoid 13-cis-retinoic acid; investigators are hopeful this will be repeated in patients with lung cancer. Results of ongoing phase ifi trials and continued advances in the epidemiologic and biologic study of lung carcinogenesis should contribute to future research in this area. (Chest 1993; 103:15S-19S) ung, head and neck, and esophageal cancers are the devastating aerodigestive tract cancers. Lung cancer is the major cancer-related cause of death among both men and women in the United States. Three principal modalities are currently used to control this disease: (1) smokingcessation programs as primary prevention; (2) local therapy for early and locally advanced disease; and (3) chemotherapy for advanced disease. Smoking-cessation programs have begun to reduce the incidence of smoking in developed countries; however, the rate of reduction has been gradual and is irrelevant to the millions of cases of lung cancer that will occur in the coming decades. Although patients with early stage lung cancer can be treated successfully with local therapy, they face an approximately 4 percent per year risk of developing second primary tumors (SPTs), the leading cause of death in early stage disease. The low survival rate in late-stage disease has been improved only negligibly by primary chemotherapy. The few long-term survivors of late-stage disease are also subject to development of SFFs.2 Clearly, new strategies are needed to control lung neoplasms. One new approach is chemoprevention, the intervention with specific agents to suppress carcinogenesis and thereby prevent the development of primary or second primary cancers.4 Chemoprevention is not only an important new approach to lung cancer, it is also being investigated extensively in other epithelial tumors, including head and neck, 5From the Department of Medical Oncology, The University of Texas, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. colon, and breast cancers, which remain major public health hazards despite advances in cancer control and therapy 4.8 Chemoprevention trials differ from standard chemotherapy trials in many respects, including actual and perceived risks, adherence, recruitment, and diet. There are two pivotal differences, however, one of which is toxicity. Patients at risk of SPT are generally willing to accept toxicities that would not be acceptable to the general population. The other pivotal difference is the choice of study end points, which directly affects both sample size and study duration able 1). Standard primary lung cancer chemoprevention studies require follow-up of many thousands of subjects for at least 5 and up to 10 years. The use of intermediate end points (eg, cytologic atypia, bronchial metaplasia, and more sensitive and specific biochemical and molecular markers) would greatly enhance statistical power by reducing sample size and study duration, #{176} but no such end points have been validated prospectively to correlate with cancer incidence in the context of a chemoprevention trial. BIOLOGY The primary biologic rationale for chemoprevention in the aerodigestive tract comprises the concepts of multistep epithelial cancer development and field carcinogenesis.4518 The development of squamous cell carcinoma in the lung is histologically characterized by the multistep progression from hyperplasia through metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma in situ to invasive cancer.48 The histologic sequence of the development of lung cancer is not clear. Alterations in specffic oncogenes (eg, ras, myc, and erb-b gene families), tumor suppressor genes (eg, retinoblastoma, p53), and cytogenetic structures (involving chromosomes ip, 3p, 6q, 7, 9p, lip, i5p, l 7p) have been reported in lung cancer. 5 Studies of nonmalignant highrisk tissue, premalignant tissue, and tissue adjacent to lung cancer have identified genotypic and phenotypic changes that support the concept of multistep field carcinogenesis. #{176} Phenotypic alterations associated with lung carcinogenesis include altered cell differentiation markers (eg, cytokeratins and surface glycoproteins) and proliferative patterns (eg, as measured by proliferating cell nuclear antigen). Although the precise sequence of genotypic and phenotypic alterations in early- and late-stage carcinogenesis is currently unclear, this multistep process of carcinogenesis provides an opportunity to intervene phannacologically to prevent the development of invasive cancer. Field carcinogenesis describes the diffuse, fleldwide mucosal carcinogenic effects of tobacco and alcohol. This hypothesis is supported by recent studies in humans that document the existence of clinical, histologic, biochemical, and molecular signs of premalignancy within the epithelium at risk, and by the higher risk of synchronous and metachronous SPT within the aerodigestive tract.#{176}in high- CHEST / 103 / 1/ JANUARY, 1993 / Supplement 15$
2 Table i-current National Cancer institute-funded Primary Lung Chemoprevention Trials* Study (Principal) Investigators) Agent Dose Population End Point Sample Size CARETt Retinyl palmitate 25,000 lu/day (1) Smokers Cancer (1) 13,000 (Goodman/Omenn) Beta-carotene 30 mg/day (2) Asbestos workers, smokers (2) 4,000 ATBC Alpha tocopherol 50mg/day Smokers Cancer 29,000 (Albanes/Heinonen) Beta-carotene 20 mg/day (2 x 2 factorial) U I Taylor Retinol 25,000 lu every other day Asbestos workers Atypia 600 (McLarty) Beta-carotene 50 mg/day (cytology) UT, MDACC 13-eRA 1 mg/kg/day Smokers Metaplasia 90 (Hong) (histology) 5Adapted from Lippman SM, Hong WK. Chemoprevention strategies in lung carcinogenesis. ASCO Educational Book, Fall Conference, Oct 31-Nov 11992, New Orleans, LA, tcabet=carotene and Retinol Efficiency Trial; ATBC =Alpha-Tocopherol Beta-Carotene Trial (Finland); UT= University of Texas; MDACC = MD Anderson Cancer Center; 13-eRA = cis-retinoic acid. risk patients, various stages of multifocal premalignant foci can be found throughout the lung and other sites of the aerodigestive tract. and synthetic analogues of vitamin A and are potent regulators of normal and malignant cell growth and differentiation. 6 CLINICAL TRIALS Premalignancy Studies Chemoprevention research in the lung is very new, and the vast majority of randomized trials have yet to be completed (Fables 1 and 2).46 Current ongoing randomized trials are based on data from epidemiologic and preclinical research,4.614 and on the results of chemoprevention research in the head and neck. Precinical results suggest that longterm administration of chemopreventive agents may be necessary to prevent the development of cancer. Epidemiologic and head and neck cancer chemoprevention studies suggest that beta-carotene and natural vitamin A may be effective in chemoprevention; combinations of these agents are being tested in three primary lung cancer chemoprevention trials., Recent work in head and neck carcinogenesis has led to the study of synthetic retinoids in lung cancer chemoprevention. This paper will focus on chemoprevention studies in the head and neck region, which provide an excellent model for the design of chemoprevention strategies in the lung. This relationship derives from the similar etiology and biology of field carcinogenesis in the two regions Chemoprevenlion trials in the head and neck have indicated that relinoids have significant activity against oral premalignancy and the development of SPT.7 Retinoids are the natural derivatives Oral leukoplakia, a white patch in the oral cavity that cannot be scraped off or classified clinically as any other disorder is a premalignant precursor of squamous cell carcinoma, tobacco-related, easily monitored, and has preclinical (in vitro and in vivo) models. It is, therefore, an ideal human model for aerodigestive tract carcinogenesis and the study of chemoprevention. Because of field carcinogenesis, results of trials in oral leukoplakia have important implications for cancers in other aerodigestive tract sites, including the lung. Short-term oral leukoplakia chemoprevention trials have been conducted for over 30 years.7 Early trials were not controlled; nonetheless, they made important observations about the activity of supplemental vitamin A (topical or systemic) in reversing oral lesions. Clinical work with synthetic retinoids began over 20 years ago and includes 10 trials (>250 patients). The response rate to retinoid therapy has been >50 percent in every study, and the median response rate for all these studies is >75 percent. The beststudied retinoid is i3-cis-retinoic acid (13-eRA), which has been tested rigorously in two randomized trials. 7. Reported by Hong et al in 1986, the first placebocontrolled phase HI chemoprevention trial in oral leukopla- Table 2-Lung and Head and Neck Second Primary Tumor Chemoprevention: Phase Iii Placebo-Controlled Trials* Study Center Agent Dose/Day Primary End Point MD Anderson 13-cRAt mg/m1 Head and neck SP I recurrence MD AndersonIRTOG/CCOP 13-eRA 30 mg Head and neck SFf NCOG/ECOC 13-eRA 10 mg Head and neck SFI recurrence Yale Beta-carotene 50 mg Head and neck SPT, recurrence NCI (Milan) Retinyl palmitate 300,000 IU NSCLC SFI recurrence EORTC (Euroscan) N-acetyl-cysteine (2 x 2 factorial) Retinyl palmitate 600mg 300,000 lu NSCLC, head and neck SV1 recurrence Intergroup 13-cRA 30 mg NSCLC SPT Adapted from Lippman SM, Hong WK. Chemoprevention strategies in lung carcinogenesis. ASCO Educational Book, Fall Conference, Oct 31-Nov , New Orleans, LA, t13-cra= 13 cis-retinoic acid; SFF= second primary tumor; BTOG= Radiation Therapy Oncology Group; CCOP = Community Clinical Oncology Program; NCOC = Northern California Oncology Group; ECOG = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; NCI = National Cancer Institute; NSCLC = non-small-cell lung cancer; EORTC = European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer. 16$ Chemopmantlon Strategies in Lung Carcinogenesls (Lippman, Benne, Hong)
3 Ida attracted worldwide attention. This study established the activity of high-dose 13-eRA compared with placebo. The trial was short-term, lasting only 3 months, but it revealed two major problems with the retinoid: (1) the relapse rate exceeded 50 percent within 2 to 3 months after stopping therapy, and (2) toxicity was unacceptably high for general chemoprevention study or use. The retinoid response must be maintained, but high-dose toxicity limits the duration of therapy. These problems led to a 12-month randomized trial comparing the ability of low-dose 13-eRA and beta-carotene to maintain remission or nonprogression of oral carcinogenesis after high-dose 13-eRA induction. This trial was conducted in two phases: a 3-month induction phase employing high-dose 13-eRA in all patients and a 9-month maintenance phase in which patients were randomized to receive either low-dose 13-eRA or beta-carotene. Patients whose disease progressed at any time were removed from the study. Prior to randomization in the second phase, patients were stratified into four groups with different histologic and response-to-induction characteristics. This study s use of the retinoid 13-eRA was based on extensive preclinical data demonstrating the retinoid s significant anticarcinogenic activity in many systems, 8 on high-dose 13- era s significant activity in our 1986 trial, and on this agent s dose-related toxicity. The choice of beta-carotene for the maintenance comparison arm was based on several factors, including positive epidemiologic data on its effect on squamous cell malignancy of the aerodigestive tract.46 4 Beta-carotene and other natural, nontoxic, and relatively inexpensive agents would be ideal for long-term chemoprevention if their effectiveness, either alone or in combination, could be established. Seventy patients were registered in this induction/maintenance study. High-dose 13-eRA induction produced a complete plus partial remission rate of 55 percent. Betacarotene was significantly less effective than low-dose 13- era: after the maintenance phase, the progression rate was 8 percent in the low-dose 13-eRA group vs 55 percent in the beta-carotene group. Furthermore, low-dose 13-eRA was well tolerated: toxic effects of grade 3 or greater severity were experienced by 34 percent of those who received highdose 13-eRA compared with only 12 percent of those receiving the lower dose. These two randomized trials established that high-dose 13-eRA and low-dose 13-eRA have significant activity in leukoplakia. Only one third of the established high dose, the maintenance 13-eRA dose (0.5 mg/kg/day) is the lowest dose ever studied in leukoplakia. Low-dose 13-eRA is currently undergoing further chemoprevention study in the aerodigestive tract, including adjuvant trials designed to prevent SPT associated with head and neck and lung cancers, which are discussed later. Retinoids are unquestionably the most studied chemopreventive agents; the next best studied agent in oral leukoplakia is beta-carotene, but no phase III placebo-controlled study data exist for this agent. The only randomized study data addressing beta-carotene use are those from the phase III maintenance trial discussed previously. Stich and col- Ieagues reported the first trials of beta-carotene, each of whom tested 180 mg/wk in unique high-risk populations (eg, Asian betel nut users). Their first trial (10 weeks of therapy) produced no clinical responses in Inuits with visible snuff-related white oral lesions. In a more recent trial from these investigators, conducted in Asian betel nut users and lasting 6 months, beta-carotene produced a 15 percent clinical complete response rate, which was not significantly different from that obtained with placebo.20 Four other single-arm trials employing beta-carotene doses of 30, 60, 90, and 120 mg/day produced respective overall response rates of 71, 61, 27, and 24 percent.7 This inverse relationship between increasing doses and decreasing response rates is unexplained. Phase III placebo-controlled trials are required to clarify this phenomenon. Bronchial metaplasia is related to lung cancer as oral leukoplakia is related to oral cancer. The promising results obtained with 13-eRA in oral premalignancy and with another synthetic retinoid in a European nonrandomized study of bronchial metaplasia2i led to a 4-year placebocontrolled National Cancer Institute phase III trial of 13- era in bronchial metaplasia, which will be completed in Two other randomized studies, one using the retinoid etretinate and the other retinol plus bea-earotene, are attempting to reverse cytologic atypia in sputum.4 5 Second Primary Tumor Prevention A randomized adjuvant trial of high-dose 13-eRA has been conducted in cured head and neck cancer patients. Eligible patients included those with biopsy-proven stages I through IV (MO) disease who were rendered disease-free following surgery or radiation therapy or both. Patients were stratified by tumor site (oral cavity, oropharynx, hypopharynx, or larynx) and previous treatment (radiation, surgery, or both) to receive 13-eRA (50 to 100 mg/me/day) or placebo for 12 months. Treatment was initiated no later than 10 weeks after surgery or 16 weeks after radiation. The study end point was recurrence of primary disease and development of SPT. Initially reported in detail in 1990, this study found, after a median follow-up of 2.5 years, a significant reduction in SPT rates in the high-dose 13-eRA group compared to the placebo group, although primary disease recurrence was not inhibited significantly by the drug. After two years of additional follow-up, primary disease progression rates are now 33 percent in both groups, but SFT rates remain significantly different -8 percent in the 13-eRA group vs 29 percent in the placebo group (p=o.0o7). The apparent persistent anticarcinogenic effect of 13-eRA suggests a several-year increase in the tumor latency period. This differs from the findings of preclinical and short-term oral leukoplakia studies, in which the retinoid chemopreventive effect wore off within months of stopping therapy. The optimal duration of chemopreventive retinoid administration is unclear. Besides the significant reduction in SPT overall, no SPT developed in the retinoid arm within the 12-month therapy period, no lung SPT developed in the retinoid arm both during and following surgery, and multiple SPTs developed only in the placebo group. In a subset analysis excluding non-tobacco-related SPT the difference between SFT rates in the 13-eRA and placebo arms remained highly significant. The clinical data from this adjuvant trial and other studies CHEST / 103 / 1 / JANUARY 1993 / Supplement 17$
4 monitoring patterns of treatment failures in head and neck cancer patients support the concept of field carcinogenesis. In the adjuvant study,n 16 of 19 patients (total from both anns) developed SF! of squamous cell carcinoma type within the field of the upper aerodigestive tract (head and neck, lung, upper two thirds of the esophagus) and in the bladder. Survival was not prolonged in the group that received 13-eRA, probably becauses (1) the rates of primary disease recurrence were identical, or (2) high-dose 13-eRA s significant toxicity kept many patients from completing the full 12 months of therapy. Furthermore, prospective followup with early SF! detection and therapy minimized the impact of SF! on the survival of patients in the placebo arm. As stated above, SPTs are the major cause of death in early stage head and neck cancer and lung cancer patients. 3 The SPTs develop from premalignant foci, either visible or invisible, that remain after local therapy. The adjuvant activity of high-dose 13-eRA against SF1 led to implementation of two multicenter trials of low-dose 13-eRA designed specifically to prevent SF! in early stage disease: one, involving the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Radiation Therapy Oncology Group, and Community Clinical Oncology Program, is treating patients with stage I or II head and neck cancer and began multicenter patient accrual in February 1992; the other, a recently activated intergroup trial, will treat patients with stage I non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) (Table 2). The choices of dose and administration schedule were based on the randomized maintenance trial of 13-eRA in oral leukoplalda. To eliminate the diagnostic and survival problems and statistical issues associated with high competing rates of primary disease failure, both studies are including only patients with early stage disease. The primary end point of these large-scale trials will be SF1 development. Mechanfstic Studies Retinoids are the best studied chemopreventive agents. Major recent advances have been made toward understanding the retinoids mechanism(s) of action. It is now apparent that the nuclear receptors for the retinoids belong to a common superfamily that also includes familiar steroids, such as the glucocorticoids. The two major classes of retinoic acid receptors, the RAR and RXR series, have alpha, beta, and gamma subtypes and multiple isoforms. These receptors are involved in the selective regulation of gene transcription, which in turn regulates cell differentiation and proliferation. CONCLUSION Despite local and systemic therapy and smoking cessation programs, lung cancer remains the major cause of cancerrelated death in the United States. Chemoprevention is an exciting and promising investigational modality for the control of lung carcinogenesis. Future directions for this research will hinge on forthcoming clinical results of ongoing phase I!! trials and continued advances in the epidemiologic and biologic study of lung carcinogenesis. Current and planned lung cancer chemoprevention studies owe their designs in large part to extensive work already completed in the related system of head and neck carcinogenesis. Because of encouraging results in the control of SPT associated with head and neck cancers, hopes are high for controlling SF! in the lung in recently designed phase II! trials. Second primary tumors are now a major problem in early stage disease s and will become an even greater concern as primary therapy advances improve long-term survival rates in patients with later stage disease. Conducted on a multicenter and intergroup basis, these trials are available to early stage NSCLC patients throughout the United States and Europe (Table 2). The results of the current series of SF! lung chemoprevention trials will determine future multimodality strategies in lung cancer, which may include primary and adjuvant therapy followed by long-term chemoprevention. Such an integrated approach may ultimately lead to major improvements in the survival of patients with lung cancer. REFERENCES 1 Boring CL, Squires TS, Tong T Cancer statistics, CA 1992; 42: de Vries N, van Zandwijk N, Pastorino U. The Euroscan study. Br J Cancer 1991; 64: Heyne K, Lippman SM, Lee JJ, et al. The incidence of second primary tumors in long-term survivors of small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 1992; 10: Lippman SM, Spitz MR, eds. Intervention in the premalignant process. Cancer Bull 1991; 43: Benner SE, Lippman SM, Hong WK. Chemoprevention strategies for lung and upper aerodigestive tract cancer. Cancer Res 1992; 52(suppl):2758S-63S 6 Greenwald P, Nixon DW, Malone WF, et a!. Concepts in cancer chemoprevention research. Cancer 1990; 65: Lippman SM, Hong WK. Retinoid chemoprevention of upper aerodigestive tract carcinogenesis. In: DeVita VT, Hellman S. Rosenberg SA, eds. Important advances in oncology. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott, 1992; Boone CW, Kelloff CJ, Steele VE. Natural history of intraepithelial neoplasia in humans with implications for cancer chemoprevention strategy. Cancer Res 1991; 52: Lippman SM, LeeJS, Lotan R, etal. Biomarkers as intermediate endpoints in chemoprevention trials. J NatI Cancer Inst 1990; 82: Lee JS, Lippman SM, Hong WK, et al. Determination of biomarkers for intermediate end points in chemoprevention. Cancer Res 1992; 52(suppl):2707S-1OS 11 Sozzi C, Miozzo M, Tagliabue E, et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities and overexpression of receptors for growth factors in normal bronchial epithelium and tumor samples of lung cancer patients. Cancer Res 1991; 51: Wolf C, Lippman SM, Laramore C, etal. Head and neck cancer. In: Holland JF, Frei E, Bast RC Jr. et al, eds. Cancer medicine. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1992 (In press) 13 Lippman SM, Hong WK. Second malignant tumors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: the overshadowing threat for patients with early stage disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1989; 17: Bertram JS, Kolonel LN, Meyskens FL. Rationale and strategies for chemoprevention of cancer in humans. Cancer Res 1987; 47: Stich HF, Rosin MP, Vallejera MO. Reduction with vitamin A and beta-carotene administration of proportion of micronucleated buccal mucosal cell in Asian betel nut and tobacco chewers. Lancet 1984; 1: Lippman SM, Kessler JF, Meyskens FL. Retinoids as preventive and therapeutic anticancer agents. Cancer Treat Rep 1987; 18$ Chemoprevention Strategies in Lung Carcinogenesis (Lippman, Benne, Hong)
5 71: , Hong WK, Endicott J, Itri LM, eta!. 13-cis-Retinoic acid in the treatment of oral leukoplakia. N EngI J Med 1986; 315: Lippman SM, Toth BB, Batsakis JC, et al. Phase-Ill trial to maintain remission of oral premalignancy: low-dose 13-cisretinoic acid (13cRA) versus beta-carotene [abstract]. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1992; 11: Stich HF, Hornby AP, Dunn BP A pilot beta-carotene intervention trial with Inuits using smokeless tobacco. mt J Cancer 1985; 36: Stieh HF, Rosin MP, Hornby AP et a!. Remission or oral leukoplakias and mieronuclei in tobacco/betel quid chewers treated with beta-carotene and with beta-carotene plus vitamin A. Int J Cancer 1988; 42: Lippman SM, Hong WK. Differentiation therapy for head and neck cancer. In: Snow C, Clark JR, ads. Multimodality therapy for head and neck cancer. New York: Thieme Medical Publishers, 1992; Hong WK, Lippman SM, Itri L, et al. Prevention of second primary tumors with isotretinoin in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N EngI J Med 1990; 323: Smith MA, Parkinson DR, Cheson BD, et al. Retinoids in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 1992; 10: CHEST / 103 / 1 / JANUARY 1993 / Supplement 19$
CHEMOPREVENTION OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER AND PROSTATE CANCER HUSEYIN ABALI, MD BASKENT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL ONCOLOGY ANKARA/TURKEY
 CHEMOPREVENTION OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER AND PROSTATE CANCER HUSEYIN ABALI, MD BASKENT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL ONCOLOGY ANKARA/TURKEY Definition Cancer chemoprevention is defined as the use of natural, synthetic,
CHEMOPREVENTION OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER AND PROSTATE CANCER HUSEYIN ABALI, MD BASKENT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL ONCOLOGY ANKARA/TURKEY Definition Cancer chemoprevention is defined as the use of natural, synthetic,
Cancer Chemoprevention Part 1: Retinoids and Carotenoids and Other Classic Antioxidants
 Cancer Chemoprevention Part 1: Retinoids and Carotenoids and Other Classic Antioxidants Review Article [1] November 01, 1998 By Diljeet K. Singh, MD, MPH [2] and Scott M. Lippman, MD, FACP [3] Cancer chemoprevention
Cancer Chemoprevention Part 1: Retinoids and Carotenoids and Other Classic Antioxidants Review Article [1] November 01, 1998 By Diljeet K. Singh, MD, MPH [2] and Scott M. Lippman, MD, FACP [3] Cancer chemoprevention
Randomized Phase III Intergroup Trial of Isotretinoin to Prevent Second Primary Tumors in Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
 Randomized Phase III Intergroup Trial of Isotretinoin to Prevent Second Primary Tumors in Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Scott M. Lippman, J. Jack Lee, Daniel D. Karp, Everett E. Vokes, Steven E. Benner,
Randomized Phase III Intergroup Trial of Isotretinoin to Prevent Second Primary Tumors in Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Scott M. Lippman, J. Jack Lee, Daniel D. Karp, Everett E. Vokes, Steven E. Benner,
Proliferative Changes in the Bronchial Epithelium of Former Smokers Treated With Retinoids
 ARTICLE Proliferative Changes in the Bronchial Epithelium of Former Smokers Treated With Retinoids Walter N. Hittelman, Diane D. Liu, Jonathan M. Kurie, Reuben Lotan, Jin Soo Lee, Fadlo Khuri, Heladio
ARTICLE Proliferative Changes in the Bronchial Epithelium of Former Smokers Treated With Retinoids Walter N. Hittelman, Diane D. Liu, Jonathan M. Kurie, Reuben Lotan, Jin Soo Lee, Fadlo Khuri, Heladio
Key words: Nasopharynx, oropharyngeal, squamous, carcinomas, epidemiology, snuffed tobacco.
 -(study of 314 cases) Abuidris DO, Elhaj AHA, Eltayeb EA, Elgayli EM and El Mustafa OM ABSTRACT Objective: The objective of this work is to study the patterns of head and neck malignancies (HNM) in central
-(study of 314 cases) Abuidris DO, Elhaj AHA, Eltayeb EA, Elgayli EM and El Mustafa OM ABSTRACT Objective: The objective of this work is to study the patterns of head and neck malignancies (HNM) in central
Adjuvant Therapy in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. Ezra EW Cohen University of Chicago. Financial Support
 Adjuvant Therapy in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Ezra EW Cohen University of Chicago Financial Support This program is made possible by an educational grant from Eli Lilly Oncology, who had no
Adjuvant Therapy in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Ezra EW Cohen University of Chicago Financial Support This program is made possible by an educational grant from Eli Lilly Oncology, who had no
Antioxidants: Are We abusing It?
 10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1319 TG Shrihari et al REVIEW ARTICLE TG Shrihari, Vijeev Vasudevan, S Kailasam, Devaraju Devaiah, V Manjunath, GR Jagadish ABSTRACT Oral cancer holds the eighth position in the
10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1319 TG Shrihari et al REVIEW ARTICLE TG Shrihari, Vijeev Vasudevan, S Kailasam, Devaraju Devaiah, V Manjunath, GR Jagadish ABSTRACT Oral cancer holds the eighth position in the
Predicting Cancer Development in Oral Leukoplakia: Ten Years of Translational Research 1
 1702 Vol. 6, 1702 1710, May 2000 Clinical Cancer Research Predicting Cancer Development in Oral Leukoplakia: Ten Years of Translational Research 1 J. Jack Lee, 2 Waun Ki Hong, Walter N. Hittelman, Li Mao,
1702 Vol. 6, 1702 1710, May 2000 Clinical Cancer Research Predicting Cancer Development in Oral Leukoplakia: Ten Years of Translational Research 1 J. Jack Lee, 2 Waun Ki Hong, Walter N. Hittelman, Li Mao,
Head and Neck Chemoprevention: Recent Advances
 Head and Neck Chemoprevention: Recent Advances Scott M. Lippman, MD Significant clinical advances have been made in understanding the role of retinoids, particularly 13cRA, in the chemoprevention of head
Head and Neck Chemoprevention: Recent Advances Scott M. Lippman, MD Significant clinical advances have been made in understanding the role of retinoids, particularly 13cRA, in the chemoprevention of head
Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Residency Site Director Weill Cornell Medical Center Associate Professor Division of Head
Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Residency Site Director Weill Cornell Medical Center Associate Professor Division of Head
HPV and Head and Neck Cancer: What it means for you and your patients
 HPV and Head and Neck Cancer: What it means for you and your patients Financial Disclosure: None November 8, 2013 Steven J. Wang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
HPV and Head and Neck Cancer: What it means for you and your patients Financial Disclosure: None November 8, 2013 Steven J. Wang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
-RA (1 + AT (1200 IU),
 Treatment of Former Smokers With 9-cis-Retinoic Acid Reverses Loss of Retinoic Acid Receptor- Expression in the Bronchial Epithelium: Results From a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial Jonathan M. Kurie,
Treatment of Former Smokers With 9-cis-Retinoic Acid Reverses Loss of Retinoic Acid Receptor- Expression in the Bronchial Epithelium: Results From a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial Jonathan M. Kurie,
Field Cancerization Of Oral Cavity - A Case Report And An Update
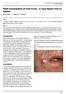 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 1 Field Cancerization Of Oral Cavity - A Case Report And An Update A Mufeed, L Chatra, P Shenai Citation A Mufeed, L Chatra, P Shenai..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 1 Field Cancerization Of Oral Cavity - A Case Report And An Update A Mufeed, L Chatra, P Shenai Citation A Mufeed, L Chatra, P Shenai..
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Epidemiology Clinical presentation
 LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
OUR EXPERIENCES WITH ERLOTINIB IN SECOND AND THIRD LINE TREATMENT PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED STAGE IIIB/ IV NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
 & OUR EXPERIENCES WITH ERLOTINIB IN SECOND AND THIRD LINE TREATMENT PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED STAGE IIIB/ IV NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Interim Data Report of TRUST study on patients from Bosnia and Herzegovina
& OUR EXPERIENCES WITH ERLOTINIB IN SECOND AND THIRD LINE TREATMENT PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED STAGE IIIB/ IV NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Interim Data Report of TRUST study on patients from Bosnia and Herzegovina
Key words: chemoprevention; epidermal growth factor receptor; G1 cyclin; lung cancer; retinoids
 Lung Cancer Prevention* The Guidelines Konstantin H. Dragnev, MD; Diane Stover, MD, FCCP; and Ethan Dmitrovsky, MD Lung carcinogenesis is a chronic and multi-step process resulting in malignant lung tumors.
Lung Cancer Prevention* The Guidelines Konstantin H. Dragnev, MD; Diane Stover, MD, FCCP; and Ethan Dmitrovsky, MD Lung carcinogenesis is a chronic and multi-step process resulting in malignant lung tumors.
Chemoprevention of Lung Cancer
 CHEST Supplement DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER, 3RD ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice
CHEST Supplement DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER, 3RD ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice
eastern cooperative oncology group Michael Williams, Fangxin Hong, Brad Kahl, Randy Gascoyne, Lynne Wagner, John Krauss, Sandra Horning
 Results of E4402 (RESORT): A Randomized Phase III Study Comparing Two Different Rituximab Dosing Strategies for Low Tumor Burden Indolent B-Cell Lymphoma Michael Williams, Fangxin Hong, Brad Kahl, Randy
Results of E4402 (RESORT): A Randomized Phase III Study Comparing Two Different Rituximab Dosing Strategies for Low Tumor Burden Indolent B-Cell Lymphoma Michael Williams, Fangxin Hong, Brad Kahl, Randy
Diseases of oral cavity
 Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
EGFR inhibitors in NSCLC
 Suresh S. Ramalingam, MD Associate Professor Director of Medical Oncology Emory University i Winship Cancer Institute EGFR inhibitors in NSCLC Role in 2nd/3 rd line setting Role in first-line and maintenance
Suresh S. Ramalingam, MD Associate Professor Director of Medical Oncology Emory University i Winship Cancer Institute EGFR inhibitors in NSCLC Role in 2nd/3 rd line setting Role in first-line and maintenance
Chemoprevention of Cancer
 Chemoprevention of Cancer Michael B. Sporn, MD Scott M. Lippman, MD 30 There are two general approaches to the problem of control of cancer. The classic approach, followed for more than a hundred years,
Chemoprevention of Cancer Michael B. Sporn, MD Scott M. Lippman, MD 30 There are two general approaches to the problem of control of cancer. The classic approach, followed for more than a hundred years,
Head and Neck Cancer:
 Head and Neck Cancer: Robert Haddad M.D. Clinical Director Head and Neck Oncology Program Dana Farber Cancer Institute Boston, MA Predictive Biomarkers: HPV Abstract 6003: Survival Outcomes By HPV Status
Head and Neck Cancer: Robert Haddad M.D. Clinical Director Head and Neck Oncology Program Dana Farber Cancer Institute Boston, MA Predictive Biomarkers: HPV Abstract 6003: Survival Outcomes By HPV Status
Immunotherapy in the Adjuvant Setting for Melanoma: What You Need to Know
 Immunotherapy in the Adjuvant Setting for Melanoma: What You Need to Know Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center NYU Langone Medical Center New York, New York What Is the Current
Immunotherapy in the Adjuvant Setting for Melanoma: What You Need to Know Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center NYU Langone Medical Center New York, New York What Is the Current
Biology Based Cancer Interception
 Biology Based Cancer Interception Waun Ki Hong, M.D. American Cancer Society Professor Former Head Division of Cancer Medicine UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosures SAB : Janssen,Medimmune,Molecular
Biology Based Cancer Interception Waun Ki Hong, M.D. American Cancer Society Professor Former Head Division of Cancer Medicine UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosures SAB : Janssen,Medimmune,Molecular
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: New Concepts and Controversies
 Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: New Concepts and Controversies James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine, EVMS Case Presentation
Ductal Carcinoma-in-Situ: New Concepts and Controversies James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine, EVMS Case Presentation
Intermediate Markers and Molecular Genetics of Lung Carcinogenesis
 Similarly in oncology, cervical dysplasia diagnosed by Papanicolaou smear, with its high rate of progression to invasive cancer, has been used as a surrogate for invasive cancer and forms the basis for
Similarly in oncology, cervical dysplasia diagnosed by Papanicolaou smear, with its high rate of progression to invasive cancer, has been used as a surrogate for invasive cancer and forms the basis for
De-Escalate Trial for the Head and neck NSSG. Dr Eleanor Aynsley Consultant Clinical Oncologist
 De-Escalate Trial for the Head and neck NSSG Dr Eleanor Aynsley Consultant Clinical Oncologist 3 HPV+ H&N A distinct disease entity Leemans et al., Nature Reviews, 2011 4 Good news Improved response to
De-Escalate Trial for the Head and neck NSSG Dr Eleanor Aynsley Consultant Clinical Oncologist 3 HPV+ H&N A distinct disease entity Leemans et al., Nature Reviews, 2011 4 Good news Improved response to
Evaluation of Mirror Image Biopsy for Incidence of Multiple Premalignant and Malignant Lesions in Oral Cancer: A Clinical Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1294 Manjula A Hebbale et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Mirror Image Biopsy for Incidence of Multiple Premalignant and Malignant Lesions in Oral Cancer: A Clinical Study Manjula
10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1294 Manjula A Hebbale et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Mirror Image Biopsy for Incidence of Multiple Premalignant and Malignant Lesions in Oral Cancer: A Clinical Study Manjula
Oral Cavity Cancer. Oral Cavity. Disclosures. Screening Methods for Early Oral Cancer
 Screening Methods for Early Oral Cancer M. Boyd Gillespie, M.D., M.Sc. UCSF Head & Neck Cancer Course San Francisco, CA November 8, 2014 Disclosures Paid consultant & Research Support on sleep apnea devices
Screening Methods for Early Oral Cancer M. Boyd Gillespie, M.D., M.Sc. UCSF Head & Neck Cancer Course San Francisco, CA November 8, 2014 Disclosures Paid consultant & Research Support on sleep apnea devices
Who is the Ideal Candidate for PEG Intron?
 Who is the Ideal Candidate for PEG Intron? Sanjiv S. Agarwala, MD Chief, Oncology & Hematology St. Luke s Cancer Center Professor, Temple University School of Medicine Philadelphia, PA, USA Overview Introduction
Who is the Ideal Candidate for PEG Intron? Sanjiv S. Agarwala, MD Chief, Oncology & Hematology St. Luke s Cancer Center Professor, Temple University School of Medicine Philadelphia, PA, USA Overview Introduction
1. Describe the mechanism of carcinogenesis of head and neck cancer. 2. Explain chemoprevention with retinoids and other chemopreventive compounds.
 The Oncologist Head and Neck Cancer Advances in Chemoprevention of Head and Neck Cancer JOHN C. RHEE, a FADLO R. KHURI, b DONG M. SHIN b a Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Oncology, University
The Oncologist Head and Neck Cancer Advances in Chemoprevention of Head and Neck Cancer JOHN C. RHEE, a FADLO R. KHURI, b DONG M. SHIN b a Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology/Oncology, University
Targeted Agents as Maintenance Therapy. Karen Kelly, MD Professor of Medicine UC Davis Cancer Center
 Targeted Agents as Maintenance Therapy Karen Kelly, MD Professor of Medicine UC Davis Cancer Center Disclosures Genentech Advisory Board Maintenance Therapy Defined Treatment Non-Progressing Patients Drug
Targeted Agents as Maintenance Therapy Karen Kelly, MD Professor of Medicine UC Davis Cancer Center Disclosures Genentech Advisory Board Maintenance Therapy Defined Treatment Non-Progressing Patients Drug
TISSUE TUMOR MARKER EXPRESSION IN
 TISSUE TUMOR MARKER EXPRESSION IN NORMAL CERVICAL TISSUE AND IN CERVICAL INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA, FOR WOMEN WHO ARE AT HIGH RISK OF HPV (HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS INFECTION). Raghad Samir MD PhD Verksamhet
TISSUE TUMOR MARKER EXPRESSION IN NORMAL CERVICAL TISSUE AND IN CERVICAL INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA, FOR WOMEN WHO ARE AT HIGH RISK OF HPV (HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS INFECTION). Raghad Samir MD PhD Verksamhet
UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works
 UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works Title Phase II trial of beta-all-trans-retinoic acid for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia delivered via a collagen sponge and cervical cap. Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8533w3p6
UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works Title Phase II trial of beta-all-trans-retinoic acid for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia delivered via a collagen sponge and cervical cap. Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8533w3p6
Sequential Dose-Dense Adjuvant Therapy With Doxorubicin, Paclitaxel, and Cyclophosphamide
 Sequential Dose-Dense Adjuvant Therapy With Doxorubicin, Paclitaxel, and Cyclophosphamide Review Article [1] April 01, 1997 By Clifford A. Hudis, MD [2] The recognition of paclitaxel's (Taxol's) activity
Sequential Dose-Dense Adjuvant Therapy With Doxorubicin, Paclitaxel, and Cyclophosphamide Review Article [1] April 01, 1997 By Clifford A. Hudis, MD [2] The recognition of paclitaxel's (Taxol's) activity
CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS (EPID 770) FALL 2009
 CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS (EPID 770) FALL 2009 Tues/Thurs 12:30 1:45, McGavran Greenberg 1304 Instructor: Office: Melissa Troester, Ph.D., M.P.H. 2104H McGavran Greenberg Phone: (919) 966 7408
CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS (EPID 770) FALL 2009 Tues/Thurs 12:30 1:45, McGavran Greenberg 1304 Instructor: Office: Melissa Troester, Ph.D., M.P.H. 2104H McGavran Greenberg Phone: (919) 966 7408
R. Balansky 1,2, F. D Agostini 2, A. Izzotti 2, P. Kalpakam 3, V.E. Steele 4, S. De Flora 2
 INCON / 10 ICMAA, Guarujà, Brazil, September 26-29, 2010 MECHANISMS OF INHIBITION OF CIGARETTE SMOKE GENOTOXICITY AND CARCINOGENICITY 1 2 3 4 R. Balansky 1,2, F. D Agostini 2, A. Izzotti 2, P. Kalpakam
INCON / 10 ICMAA, Guarujà, Brazil, September 26-29, 2010 MECHANISMS OF INHIBITION OF CIGARETTE SMOKE GENOTOXICITY AND CARCINOGENICITY 1 2 3 4 R. Balansky 1,2, F. D Agostini 2, A. Izzotti 2, P. Kalpakam
Virtual Journal Club: Front-Line Therapy and Beyond Recent Perspectives on ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
 Virtual Journal Club: Front-Line Therapy and Beyond Recent Perspectives on ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Reference Slides ALK Rearrangement in NSCLC ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) is a receptor
Virtual Journal Club: Front-Line Therapy and Beyond Recent Perspectives on ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Reference Slides ALK Rearrangement in NSCLC ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) is a receptor
Heather Wakelee, M.D.
 Heather Wakelee, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine, Oncology Stanford University Sponsored by Educational Grant Support from Adjuvant (Post-Operative) Lung Cancer Chemotherapy Heather Wakelee, M.D.
Heather Wakelee, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine, Oncology Stanford University Sponsored by Educational Grant Support from Adjuvant (Post-Operative) Lung Cancer Chemotherapy Heather Wakelee, M.D.
trial update clinical
 trial update clinical by John W. Mucenski, BS, PharmD, Director of Pharmacy Operations, UPMC Cancer Centers The treatment outcome for patients with relapsed or refractory cervical carcinoma remains dismal.
trial update clinical by John W. Mucenski, BS, PharmD, Director of Pharmacy Operations, UPMC Cancer Centers The treatment outcome for patients with relapsed or refractory cervical carcinoma remains dismal.
Accepted 28 April 2005 Published online 13 September 2005 in Wiley InterScience ( DOI: /hed.
 DEFINING RISK LEVELS IN LOCALLY ADVANCED HEAD AND NECK CANCERS: A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF CONCURRENT POSTOPERATIVE RADIATION PLUS CHEMOTHERAPY TRIALS OF THE EORTC (#22931) AND RTOG (#9501) Jacques Bernier,
DEFINING RISK LEVELS IN LOCALLY ADVANCED HEAD AND NECK CANCERS: A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF CONCURRENT POSTOPERATIVE RADIATION PLUS CHEMOTHERAPY TRIALS OF THE EORTC (#22931) AND RTOG (#9501) Jacques Bernier,
Lung Cancer Update. HARMESH R NAIK, MD. February 28, 2001
 Lung Cancer Update HARMESH R NAIK, MD. February 28, 2001 Progress update Prevention Screening Staging Treatment Epidemiology Estimated 169,500 new cases Estimated 157,400 deaths Second commonest cancer
Lung Cancer Update HARMESH R NAIK, MD. February 28, 2001 Progress update Prevention Screening Staging Treatment Epidemiology Estimated 169,500 new cases Estimated 157,400 deaths Second commonest cancer
Invited Re vie W. Molecular genetics of ovarian carcinomas. Histology and Histo pathology
 Histol Histopathol (1 999) 14: 269-277 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histo pathology Invited Re vie W Molecular genetics of ovarian carcinomas J. Diebold Pathological Institute, Ludwig-Maximilians-University
Histol Histopathol (1 999) 14: 269-277 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histo pathology Invited Re vie W Molecular genetics of ovarian carcinomas J. Diebold Pathological Institute, Ludwig-Maximilians-University
Retinoids as chemoprevention for head and neck cancer: where do we go from here?
 Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 55 (2005) 143 152 Retinoids as chemoprevention for head and neck cancer: where do we go from here? Wade Smith, Nabil Saba Winship Cancer Institute, Hematology Oncology,
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 55 (2005) 143 152 Retinoids as chemoprevention for head and neck cancer: where do we go from here? Wade Smith, Nabil Saba Winship Cancer Institute, Hematology Oncology,
Chemoprevention of Bladder and Prostate Carcinoma
 Primary prevention involves the identification and avoidance of cancer-causing factors. Factors associated with bladder cancer incidence and progression include occupational exposure to chemicals (eg,
Primary prevention involves the identification and avoidance of cancer-causing factors. Factors associated with bladder cancer incidence and progression include occupational exposure to chemicals (eg,
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
8/8/2011. PONDERing the Need to TAILOR Adjuvant Chemotherapy in ER+ Node Positive Breast Cancer. Overview
 Overview PONDERing the Need to TAILOR Adjuvant in ER+ Node Positive Breast Cancer Jennifer K. Litton, M.D. Assistant Professor The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Using multigene assay
Overview PONDERing the Need to TAILOR Adjuvant in ER+ Node Positive Breast Cancer Jennifer K. Litton, M.D. Assistant Professor The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Using multigene assay
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
Radiation and DCIS. The 16 th Annual Conference on A Multidisciplinary Approach to Comprehensive Breast Care and Imaging
 Radiation and DCIS The 16 th Annual Conference on A Multidisciplinary Approach to Comprehensive Breast Care and Imaging Einsley-Marie Janowski, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Oncology
Radiation and DCIS The 16 th Annual Conference on A Multidisciplinary Approach to Comprehensive Breast Care and Imaging Einsley-Marie Janowski, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Oncology
Charles Mulligan, MD, FACS, FCCP 26 March 2015
 Charles Mulligan, MD, FACS, FCCP 26 March 2015 Review lung cancer statistics Review the risk factors Discuss presentation and staging Discuss treatment options and outcomes Discuss the status of screening
Charles Mulligan, MD, FACS, FCCP 26 March 2015 Review lung cancer statistics Review the risk factors Discuss presentation and staging Discuss treatment options and outcomes Discuss the status of screening
LESSONS FROM THE RESULTS OF OBSERVATIONAL STUDIES AND TRIALS OF BETA-CAROTENE AND VITAMIN E?
 LESSONS FROM THE RESULTS OF OBSERVATIONAL STUDIES AND TRIALS OF BETA-CAROTENE AND VITAMIN E? Julie E. Buring, ScD American College if Epidemiology Chicago, September 2003 BETA-CAROTENE AND CANCER At the
LESSONS FROM THE RESULTS OF OBSERVATIONAL STUDIES AND TRIALS OF BETA-CAROTENE AND VITAMIN E? Julie E. Buring, ScD American College if Epidemiology Chicago, September 2003 BETA-CAROTENE AND CANCER At the
IRESSA (Gefitinib) The Journey. Anne De Bock Portfolio Leader, Oncology/Infection European Regulatory Affairs AstraZeneca
 IRESSA (Gefitinib) The Journey Anne De Bock Portfolio Leader, Oncology/Infection European Regulatory Affairs AstraZeneca Overview The Drug The Biomarker and Clinical Trials Sampling Lessons Learned The
IRESSA (Gefitinib) The Journey Anne De Bock Portfolio Leader, Oncology/Infection European Regulatory Affairs AstraZeneca Overview The Drug The Biomarker and Clinical Trials Sampling Lessons Learned The
NCI Precision Medicine Trial Designs
 NCI Precision Medicine Trial Designs Shakun Malik, M.D. Head, Thoracic and Head & Neck Cancer Therapeutics Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program (CTEP) National Cancer institute/nih 1 Outline Background Current
NCI Precision Medicine Trial Designs Shakun Malik, M.D. Head, Thoracic and Head & Neck Cancer Therapeutics Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program (CTEP) National Cancer institute/nih 1 Outline Background Current
The Challenges of Chemoprevention: How Can We Develop Drugs to Treat Cancer Risk Instead of Metastases?
 The Challenges of Chemoprevention: How Can We Develop Drugs to Treat Cancer Risk Instead of Metastases? Moderator: Gary Kelloff, MD, Special Advisor, Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis, National
The Challenges of Chemoprevention: How Can We Develop Drugs to Treat Cancer Risk Instead of Metastases? Moderator: Gary Kelloff, MD, Special Advisor, Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis, National
Smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and p53 mutation as risk factors in oropharyngeal cancer: a case-control study
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and p53 as risk factors in oropharyngeal cancer: a case-control study PKS Chan *, JSY Chor, AC Vlantis, TL
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and p53 as risk factors in oropharyngeal cancer: a case-control study PKS Chan *, JSY Chor, AC Vlantis, TL
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Combined Modality Therapy State of the Art. Everett E. Vokes The University of Chicago
 Combined Modality Therapy State of the Art Everett E. Vokes The University of Chicago What we Know Some patients are cured (20%) Induction and concurrent chemoradiotherapy are each superior to radiotherapy
Combined Modality Therapy State of the Art Everett E. Vokes The University of Chicago What we Know Some patients are cured (20%) Induction and concurrent chemoradiotherapy are each superior to radiotherapy
Patient Selection: The Search for Immunotherapy Biomarkers
 Patient Selection: The Search for Immunotherapy Biomarkers Mark A. Socinski, MD Executive Medical Director Florida Hospital Cancer Institute Orlando, Florida Patient Selection Clinical smoking status Histologic
Patient Selection: The Search for Immunotherapy Biomarkers Mark A. Socinski, MD Executive Medical Director Florida Hospital Cancer Institute Orlando, Florida Patient Selection Clinical smoking status Histologic
PROCARBAZINE, lomustine, and vincristine (PCV) is
 RAPID PUBLICATION Procarbazine, Lomustine, and Vincristine () Chemotherapy for Anaplastic Astrocytoma: A Retrospective Review of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Protocols Comparing Survival With Carmustine
RAPID PUBLICATION Procarbazine, Lomustine, and Vincristine () Chemotherapy for Anaplastic Astrocytoma: A Retrospective Review of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Protocols Comparing Survival With Carmustine
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Implication for second primary cancer from visible oral and oropharyngeal premalignant lesions in betel-nut chewing related oral cancer
 Received: 31 August 2016 Revised: 22 October 2016 Accepted: 10 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/hed.24777 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Implication for second primary cancer from visible oral and oropharyngeal premalignant
Received: 31 August 2016 Revised: 22 October 2016 Accepted: 10 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/hed.24777 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Implication for second primary cancer from visible oral and oropharyngeal premalignant
Lung Cancer in Women: A Different Disease? James J. Stark, MD, FACP
 Lung Cancer in Women: A Different Disease? James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Director of Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical
Lung Cancer in Women: A Different Disease? James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Director of Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical
Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy
 Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences TREATMENT OF ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA WITH ANTIOXIDANTS A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW ABSTRACT
 Review Article Pharmacology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 TREATMENT OF ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA WITH ANTIOXIDANTS A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW T.N. UMA MAHESWARI* Associate Professor,
Review Article Pharmacology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 TREATMENT OF ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA WITH ANTIOXIDANTS A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW T.N. UMA MAHESWARI* Associate Professor,
Early detection and treatment for Esophageal Cancer in Africa
 Early detection and treatment for Esophageal Cancer in Africa Dr Michael Mwachiro Tenwek Hospital NCI-IARC ESCC Tumor Workshop Where is Tenwek Hospital? Tenwek Nairobi Tenwek Hospital Identification of
Early detection and treatment for Esophageal Cancer in Africa Dr Michael Mwachiro Tenwek Hospital NCI-IARC ESCC Tumor Workshop Where is Tenwek Hospital? Tenwek Nairobi Tenwek Hospital Identification of
Chapter 5. Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance Ratio for In Vivo Detection of oral Pre-cancer
 Chapter 5 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance Ratio for In Vivo Detection of oral Pre-cancer This work is published in: JB0 (SPIE) 13(4):041306 (1-10), 2008 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance
Chapter 5 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance Ratio for In Vivo Detection of oral Pre-cancer This work is published in: JB0 (SPIE) 13(4):041306 (1-10), 2008 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance
Leukoplakia is a clinical diagnosis 1 that may represent histologic
 629 Topical Bleomycin for the Treatment of Dysplastic Oral Leukoplakia Joel B. Epstein, D.M.D., M.S.D. 1 Meir Gorsky, D.M.D. 2 Frances L. W. Wong, M.D. Amelia Millner, M.D. 1 British Columbia Cancer Agency,
629 Topical Bleomycin for the Treatment of Dysplastic Oral Leukoplakia Joel B. Epstein, D.M.D., M.S.D. 1 Meir Gorsky, D.M.D. 2 Frances L. W. Wong, M.D. Amelia Millner, M.D. 1 British Columbia Cancer Agency,
CONTRIBUTORS. IngaliIl A vis National Cancer Institute U.S. PHS, Bldg. 8, Rm NNMC 8901 Wisconsin Avenue Bethesda, Maryland
 CONTRIBUTORS IngaliIl A vis Bethesda, Maryland 20814-5101 Michael Birrer Bethesda, Maryland 20814-5 10 I Robert M. Byers Department of Head and Neck, Box 69 The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Houston,
CONTRIBUTORS IngaliIl A vis Bethesda, Maryland 20814-5101 Michael Birrer Bethesda, Maryland 20814-5 10 I Robert M. Byers Department of Head and Neck, Box 69 The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Houston,
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD J M O R G A N
 VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Lung Cancer William N. William Jr.
 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Lung Cancer William N. William Jr. Diretor de Onco-Hematologia Hospital BP, A Beneficência Portuguesa Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in second-line therapy
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Lung Cancer William N. William Jr. Diretor de Onco-Hematologia Hospital BP, A Beneficência Portuguesa Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in second-line therapy
The Association between Vitamin D and Lung Cancer Risk in Finnish Male Smokers. Julia Burkley Briarcliff High School
 The Association between Vitamin D and Lung Cancer Risk in Finnish Male Smokers. Julia Burkley Briarcliff High School 2 Burkley Table of Contents Introduction~ Pg. 2 Methods~ Pg. 4 Ethics Statement~ Pg.
The Association between Vitamin D and Lung Cancer Risk in Finnish Male Smokers. Julia Burkley Briarcliff High School 2 Burkley Table of Contents Introduction~ Pg. 2 Methods~ Pg. 4 Ethics Statement~ Pg.
HDAC Inhibitors and PARP inhibitors. Suresh Ramalingam, MD Associate Professor Chief of Thoracic Oncology Emory University School of Medicine
 HDAC Inhibitors and PARP inhibitors Suresh Ramalingam, MD Associate Professor Chief of Thoracic Oncology Emory University School of Medicine Histone Acetylation HAT Ac Ac Ac Ac HDAC Ac Ac Ac Ac mrna DACs
HDAC Inhibitors and PARP inhibitors Suresh Ramalingam, MD Associate Professor Chief of Thoracic Oncology Emory University School of Medicine Histone Acetylation HAT Ac Ac Ac Ac HDAC Ac Ac Ac Ac mrna DACs
METRIC Study Key Eligibility Criteria
 The METRIC Study METRIC Study Key Eligibility Criteria The pivotal METRIC Study is evaluating glembatumumab vedotin in patients with gpnmb overexpressing metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
The METRIC Study METRIC Study Key Eligibility Criteria The pivotal METRIC Study is evaluating glembatumumab vedotin in patients with gpnmb overexpressing metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Screening for Lung Cancer - State of the Art
 Screening for Lung Cancer - State of the Art Rohit Kumar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Fox Chase Cancer Center Temple University School of Medicine Philadelphia, PA Objectives Review current evidence
Screening for Lung Cancer - State of the Art Rohit Kumar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Fox Chase Cancer Center Temple University School of Medicine Philadelphia, PA Objectives Review current evidence
Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers. Robert F. Taylor, MD Aurora Health Care
 Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers Robert F. Taylor, MD Aurora Health Care Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose I will be discussing non-fda approved indications
Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers Robert F. Taylor, MD Aurora Health Care Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose I will be discussing non-fda approved indications
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Multidisciplinary Role: Role of Medical Oncologist
 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Multidisciplinary Role: Role of Medical Oncologist Vichien Srimuninnimit, MD. Medical Oncology Division Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital Outline Resectable NSCLC stage
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Multidisciplinary Role: Role of Medical Oncologist Vichien Srimuninnimit, MD. Medical Oncology Division Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital Outline Resectable NSCLC stage
Cancer Prevention. Underlying Assumptions. Other Known Risk Factors. Other Known Risk Factors 6/25/2009
 Underlying Assumptions Cancer Prevention Judith A. Luce, M.D. jluce@hemeonc.ucsf.edu The Model of Carcinogenesis Multistep, multiple mutations Takes years: peak annual risk @ 70+ yrs Accelerated by genetic
Underlying Assumptions Cancer Prevention Judith A. Luce, M.D. jluce@hemeonc.ucsf.edu The Model of Carcinogenesis Multistep, multiple mutations Takes years: peak annual risk @ 70+ yrs Accelerated by genetic
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LONDON CANCER NEW DRUGS GROUP RAPID REVIEW. Erlotinib for the third or fourth-line treatment of NSCLC January 2012
 Disease background LONDON CANCER NEW DRUGS GROUP RAPID REVIEW Erlotinib for the third or fourth-line treatment of NSCLC January 2012 Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in the UK (after breast),
Disease background LONDON CANCER NEW DRUGS GROUP RAPID REVIEW Erlotinib for the third or fourth-line treatment of NSCLC January 2012 Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in the UK (after breast),
RETINOIDS, including vitamin A and its analogues,
 Vol. 332 No. 21 RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR b IN PREMALIGNANT ORAL LESIONS 1405 SUPPRESSION OF RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR IN PREMALIGNANT ORAL LESIONS AND ITS UP-REGULATION BY ISOTRETINOIN REUBEN LOTAN, PH.D.,
Vol. 332 No. 21 RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR b IN PREMALIGNANT ORAL LESIONS 1405 SUPPRESSION OF RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR IN PREMALIGNANT ORAL LESIONS AND ITS UP-REGULATION BY ISOTRETINOIN REUBEN LOTAN, PH.D.,
Targeting the Expression of the Angiogenic Phenotype in Head and Neck Cancer
 Targeting the Expression of the Angiogenic Phenotype in Head and Neck Cancer Mark W. Lingen, DDS, PhD, FRCPath Introduction With over 600,000 new cases annually, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and
Targeting the Expression of the Angiogenic Phenotype in Head and Neck Cancer Mark W. Lingen, DDS, PhD, FRCPath Introduction With over 600,000 new cases annually, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and
Maintenance paradigm in non-squamous NSCLC
 Maintenance paradigm in non-squamous NSCLC L. Paz-Ares Hospital Universitario Virgen del Rocío Sevilla Agenda Theoretical basis The data The comparisons Agenda Theoretical basis The data The comparisons
Maintenance paradigm in non-squamous NSCLC L. Paz-Ares Hospital Universitario Virgen del Rocío Sevilla Agenda Theoretical basis The data The comparisons Agenda Theoretical basis The data The comparisons
Laryngeal Preservation Using Radiation Therapy. Chemotherapy and Organ Preservation
 1 Laryngeal Preservation Using Radiation Therapy 1903: Schepegrell was the first to perform radiation therapy for the treatment of laryngeal cancer Conventional external beam radiation produced disappointing
1 Laryngeal Preservation Using Radiation Therapy 1903: Schepegrell was the first to perform radiation therapy for the treatment of laryngeal cancer Conventional external beam radiation produced disappointing
2 nd line Therapy and Beyond NSCLC. Alan Sandler, M.D. Oregon Health & Science University
 2 nd line Therapy and Beyond NSCLC Alan Sandler, M.D. Oregon Health & Science University Treatment options for advanced or metastatic (stage IIIb/IV) NSCLC Suitable for chemotherapy Diagnosis Unsuitable/unwilling
2 nd line Therapy and Beyond NSCLC Alan Sandler, M.D. Oregon Health & Science University Treatment options for advanced or metastatic (stage IIIb/IV) NSCLC Suitable for chemotherapy Diagnosis Unsuitable/unwilling
Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative breast lesions adjacent to malignancy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. IV. (Mar. 2014), PP 84-89 Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. IV. (Mar. 2014), PP 84-89 Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer statistics, CA: Cancer J Clin 59(4):225-49, 2009
 Ovarian cancer 2010-22,500 cases diagnosed per year in the United States and 16,500 deaths per year1. - Most patients are diagnosed in late stages; no screening test exists. - Pathology: 4 different types
Ovarian cancer 2010-22,500 cases diagnosed per year in the United States and 16,500 deaths per year1. - Most patients are diagnosed in late stages; no screening test exists. - Pathology: 4 different types
7/6/2015. Cancer Related Deaths: United States. Management of NSCLC TODAY. Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview
 Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
Adjuvant Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer in 2009: Where Are We? Highlights from the 45 th ASCO Annual Meeting. Orlando, FL, USA. May 29 - June 2, 2009
 HIGHLIGHT ARTICLE - Slide Show Adjuvant Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer in 2009: Where Are We? Highlights from the 45 th ASCO Annual Meeting. Orlando, FL, USA. May 29 - June 2, 2009 Muhammad Wasif Saif
HIGHLIGHT ARTICLE - Slide Show Adjuvant Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer in 2009: Where Are We? Highlights from the 45 th ASCO Annual Meeting. Orlando, FL, USA. May 29 - June 2, 2009 Muhammad Wasif Saif
WELL WOMAN CLINIC-SCREENING PROGRAM FOR CERVICAL CARCINOMAS G. J. Vani Padmaja 1
 WELL WOMAN CLINIC-SCREENING PROGRAM FOR CERVICAL CARCINOMAS G. J. Vani Padmaja 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: G. J. Vani Padmaja. Well Woman Clinic-Screening Program for Cervical Carcinomas. Journal of Evolution
WELL WOMAN CLINIC-SCREENING PROGRAM FOR CERVICAL CARCINOMAS G. J. Vani Padmaja 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: G. J. Vani Padmaja. Well Woman Clinic-Screening Program for Cervical Carcinomas. Journal of Evolution
It s s Always Something!
 It s s Always Something! New Approaches in Brain Tumor Treatment Virginia Stark-Vance, M.D. When Something Is a Brain Tumor Brain tumors aren t rare: there are over 100,000/yr Most originate as other cancers
It s s Always Something! New Approaches in Brain Tumor Treatment Virginia Stark-Vance, M.D. When Something Is a Brain Tumor Brain tumors aren t rare: there are over 100,000/yr Most originate as other cancers
Standard of care for patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who are not eligible for a transplant
 Standard of care for patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who are not eligible for a transplant Pr Philippe Moreau University Hospital, Nantes, France MP: Standard of care until 2007 J Clin Oncol
Standard of care for patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who are not eligible for a transplant Pr Philippe Moreau University Hospital, Nantes, France MP: Standard of care until 2007 J Clin Oncol
The PARADIGM Study: A Phase III Study Comparing Sequential Therapy (ST) to Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer
 The PARADIGM Study: A Phase III Study Comparing Sequential Therapy (ST) to Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Robert I. Haddad, Guilherme Rabinowits, Roy B. Tishler,
The PARADIGM Study: A Phase III Study Comparing Sequential Therapy (ST) to Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Robert I. Haddad, Guilherme Rabinowits, Roy B. Tishler,
Câncer Cervical e Nutrição 21 trabalhos
 Câncer Cervical e Nutrição 21 trabalhos Cervical Cancer cancer showed that frequent consumption of dark green and yellow vegetables and fruit juices was associated with reduced risk of cervical cancer
Câncer Cervical e Nutrição 21 trabalhos Cervical Cancer cancer showed that frequent consumption of dark green and yellow vegetables and fruit juices was associated with reduced risk of cervical cancer
Adjuvant Therapy of High Risk Melanoma
 Adjuvant Therapy of High Risk Melanoma William Sharfman, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Oncology and Dermatology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine July 5, 2012 Adjuvant options for Stage IIB/C
Adjuvant Therapy of High Risk Melanoma William Sharfman, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Oncology and Dermatology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine July 5, 2012 Adjuvant options for Stage IIB/C
Lung Cancer Non-small Cell Local, Regional, Small Cell, Other Thoracic Cancers: The Question Isn t Can We, but Should We
 Lung Cancer Non-small Cell Local, Regional, Small Cell, Other Thoracic Cancers: The Question Isn t Can We, but Should We Edward Garon, MD, MS Associate Professor Director- Thoracic Oncology Program David
Lung Cancer Non-small Cell Local, Regional, Small Cell, Other Thoracic Cancers: The Question Isn t Can We, but Should We Edward Garon, MD, MS Associate Professor Director- Thoracic Oncology Program David
Questions and Answers About Beta Carotene Chemoprevention Trials
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Questions and Answers
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Questions and Answers
