Philip Morris International R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Switzerland. 2
|
|
|
- Kellie Lindsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comparative assessment of lung inflammation, pulmonary function and emphysema caused by the aerosol from potential Reduced Risk Products and cigarette smoke in mouse models of COPD. 11 July, 216 COPD Brisbane Patrick Vanscheeuwijck 1, Blaine Phillips 2, Ee Tsin Wong 2, Julia Hoeng 1, Manuel C. Peitsch 1 1 Philip Morris International R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Switzerland. 2 Philip Morris International R&D, Philip Morris International Research Laboratories Pte Ltd, Singapore Philip Morris International is the sole source of funding and sponsor of this project.
2 PMI s Goal for Harm Reduction Offering adult smokers satisfying products that reduce risk Smoking is addictive and causes a number of serious diseases Worldwide it is estimated that more than one billion people will continue to smoke in the foreseeable future PRODUCT REDUCED-RISK ACCEPTANCE AND PRODUCT X = USAGE HARM REDUCTION Successful harm reduction requires that current adult smokers be offered a range of Reduced Risk Products (RRPs) so that consumer acceptance can be best fulfilled The Tobacco Atlas 3 rd Edition. American Cancer Society, 29 Figure adapted from Clive Bates presentation to E-Cigarette Summit (19 Nov 213)
3 Reduced-Risk Products ( RRPs ) is the term the company uses to refer to products with the potential to reduce individual risk and population harm in comparison to smoking cigarettes. PMI s RRPs are in various stages of development and commercialization, and we are conducting extensive and rigorous scientific studies to determine whether we can support claims for such products of reduced exposure to harmful and potentially harmful constituents in smoke, and ultimately claims of reduced disease risk, when compared to smoking cigarettes. Before making any such claims, we will rigorously evaluate the full set of data from the relevant scientific studies to determine whether they substantiate reduced exposure or risk. Any such claims may also be subject to government review and authorization as is the case in the US today.
4 Aim and scope of the presentation Assessment of the effects of cigarette smoke and a RRP (THS2.2), using PMI s Heat-not-Burn technology, in 2 animal models of COPD: ApoE -/- mouse (C57Bl6 background), typically used as model for cardiovascular disease A/J mouse, used as model for lung cancer Both animal models are responsive to cigarette mainstream smoke and develop different pathologies, among which aspects of COPD such as lung inflammation, changed pulmonary function, emphysema Other endpoints, such as general (chronic) toxicity, atherosclerosis, lung tumor development determined in these studies will not be reported here Lo Sasso G, Schlage WK, Boué S, Veljkovic E, Peitsch MC, Hoeng J. (216) The Apoe(-/-) mouse model: a suitable model to study cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in the context of cigarette smoke exposure and harm reduction. J Transl Med (1):146.Epub. Review. PMID Stinn W, Buettner A, Weiler H, Friedrichs B, Luetjen S, van Overveld F, Meurrens K, Janssens K, Gebel S, Stabbert R, Haussmann HJ. (213) Lung inflammatory effects, tumorigenesis, and emphysema development in a long-term inhalation study with cigarette mainstream smoke in mice. Toxicol Sci. 131(2): PMID:
5 Common disease mechanisms in different mouse models, relevance to human situation Possible interrelationships and roles for the identified common mechanisms (HYPs) in five mouse models of emphysema in a framework of classical human COPD mechanisms. transcription factors (black font) inflammatory mediators (orange font) classical pathways of human COPD pathogenesis (black arrows) as depicted, From: Cabanski M, Fields B, Boue S, Boukharov N, DeLeon H, Dror N, Geertz M, Guedj E, Iskandar A, Kogel U, Merg C, Peck MJ, Poussin C, Schlage WK, Talikka M, Ivanov NV, Hoeng J, Peitsch MC. (215): Transcriptional profiling and targeted proteomics reveals common molecular changes associated with cigarette smokeinduced lung emphysema development in five susceptible mouse strains. Inflamm Res.64(7): PMID:
6 Methods Cigarette smoke and aerosol from a RRP Assessment of smoke/aerosol Health Canada Intense smoke protocol Conventional cigarettes: Smoke from University of Kentucky Standard Reference Cigarette Potentially Reduced-Risk product: Aerosol generated by Tobacco Heating System, commercialized as iqos (also designated as THS 2.2)
7 [Disease Risk] ApoE -/- mouse switching study Study design Comparative assessment of effects of THS2.2 and Switching design upon initiation of disease: to assess reversibility (switch to fresh air, i.e. cessation) and To quantify how similar switching to THS2.2 is to cessation Point of intervention Groups SWITCHING CESSATION Control: Sham/Air THS2.2 Start Inhalation THS2.2 Fresh Air Fresh Air THS2.2 Month 2 Month 8 [Time] Dissection time points: Month 1, 2, 3, 6 and 8 7
8 N ic o tin e c o n c e n tr a tio n g /l + /- S D ApoE -/- mouse switching study Methods - Exposure regime Fresh air 4 Nicotine concentration in exposure chamber (study average) THS2.2 or - Animals were exposed 3 hours per day (3 x 1 hour interrupted exposure periods), 5 days per week - Nicotine was measured during every exposure period (3 samples per chamber per day) - Aerosol delivery (nicotine) was within +/- 1% of the targeted 29.9 µg/l nicotine concentration 29.9 µg/l nic corresponds to 6.5 mg/kg, daily dose- or the nicotine amount from approx. 32 cig/day for a 6 kg human, based on body surface comparison, Guidance document Heq dose, FDA R 4 F 8
9 ApoE -/- mouse switching study Aerosol uptake (biomarkers of exposure) Plasma Nicotine (month 8) HPMA (Acrolein metabolite) Urinary Metabolites (months 3, 6, 8) CEMA (Acrylonitrile metabolite) Air THS2.2 Cess. Swit. Means ± SEM NNAL (NNK metabolite) SPMA (Benzene metabolite) Groups Cessation Switching THS2.2 Sham / Air Means ± SEM 9
10 N e u tro p h ils (x 1 5 ) + /- S E M L y m p h o c y te s (x 1 5 ) + /- S E M A lv e o la r m a c ro p h a g e s (x 1 5 ) + /- S E M A lv e o la r d e n d ritic c e lls (x 1 5 ) + /- S E M ApoE -/- mouse switching study Result summary: Disease mechanisms - Lung inflammation Free lung cells in Broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) Total Cells (x 1 5 ) +/- SEM Total cells absolute Sham THS 2.2 Cessation Switch Differential counts A lv e o la r m a c ro p h a g e s a b s o lu te A lv e o la r d e n d ritic c e lls a b s o lu te R 4 F TH S 2.2 C e s s a tio n S w itc h R 4 F TH S 2.2 C e s s a tio n S w itc h N e u tro p h ils a b s o lu te L y m p h o c y te s a b s o lu te 8 5 TH S 2.2 S w itc h S w itc h 3 R 4 F C e s s a tio n 3 R 4 F C e s s a tio n 4 6 Groups Cessation Switching THS2.2 Sham / Air Study month Study month 1
11 U n p ig m e n te d m a c ro p h a g e s in a lv e o la r lu m e n M e a n s c o r e + /- S E M ApoE -/- mouse switching study Result summary: Histopathology of the lung Pulmonary inflammation Results, Lung Inflammation unpigmented macrophages in the alveolar lumen Groups Cessation Switching THS2.2 Sham / Air sham THS2.2 Cessation Switch S tu d y m o n th : Statistically significant compared to sham : Statistically significant compared to :CONT at month 2 Decrease in mean scores after switching to fresh air or THS2.2 (statistically significant from month 6) No statistically significant difference between Cessation group and THS2.2-Switch group at month 3 11
12 M M P a c tiv ity (m U /m l) + /- S D ApoE -/- mouse switching study Result summary: Disease mechanisms - Lung inflammation Multiple analyte profiling in Broncho-alveolar Lavage Fluid THS2.2 Cess. Switch 3 M M P a c tiv ity Groups Cessation Switching THS2.2 Sham / Air M o n th 12
13 V p l (m l) + /- S E M V p l (m l) + /- S E M V p l (m l) + /- S E M V p l (m l) + /- S E M D is p la c e d liq u id w e ig h t (g ) ApoE -/- mouse switching study Result summary: Disease endpoints- Lung function and lung volume Lung function: Pressure Volume Loops (PVsP) (FlexiVent (Scireq)) M o n th 2 3 R 4 FMonth R 4 F M o n th 3 Month 3 C e s s a tio n S w itc h Groups Cessation Switching THS2.2 Sham / Air L u n g v o lu m e (a b s o lu te, m e a s u re d ) S w itc h 3 R 4 F C e s s a tio n R 4F P p l (c m H 2 O ) M o n th 6 C essation S w itc h R 4 F P p l (c m H 2 O ) M o n th 8 Month 6 Month 8 C e s s a tio n S w itc h M o n th P p l (c m H 2 O ) P p l (c m H 2 O ) Means ± SEM 13
14 A lv e o la r e m p h y s e m a + /- S E M Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Result summary: Tissue changes Histopathology Histopathological Assessment emphysema Groups Cessation Switching THS2.2 Sham / Air sham THS2.2 Cessation Switch S tu d y m o n th : Statistically significant compared to sham : Statistically significant compared to :CONT at month 2 14
15 B r o n c h io la r a tta c h m e n ts + /- S E M M e a n c o r d le n g th (u m ) + /- S E M D e s tru c tiv e in d e x (e m p h y s e m a to u s tis s u e (% ) + /- S E M ApoE -/- mouse switching study Result Summary: Lung tissue changes Morphometry Groups Cessation Switching THS2.2 Sham / Air S tu d y m o n th S tu d y m o n th S tu d y m o n th Bronchiolar attachments - Fewer Bronchiolar attachments in -exposed group Mean chord length (MCL) - Mean linear intercept length - Increased MCL in exposed group Destructive index (DI) - Index of parenchymal destruction - Increased DI in -exposed group 15
16 Down regulated -log 1 (p value) Up regulated ApoE -/- mouse switching study Result Summary: Systems response profile: differential gene expression - Lung Cessation Switch q =.5 log 2 (fold change) THS2.2 16
17 ApoE -/- mouse switching study Result Summary: Disease mechanisms - Network perturbations - Lung Cessation Switch Cell proliferation Tissue repair Inflammation Senescence DNA damage Apoptosis Cell stress THS2.2 17
18 Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Summary and Conclusions The ApoE -/- mouse model is suitable for studying smoke-related aspects of COPD Continuous exposure to smoke from causes lung inflammation, lung function and emphysematous changes as of one month of treatment Continuous exposure to aerosol from THS2.2 for up to 8 months does not increase inflammation and emphysema in comparison to Sham group Switching from cigarette smoke exposure after 2 months to fresh air (Sham) exposure reverses the onset of disease as measured in apical, functional, and molecular endpoints Switching from cigarette smoke exposure to THS2.2 aerosol exposure reverses the onset of disease in a similar manner as cessation Phillips B, Veljkovic E, Boué S, Schlage WK, Vuillaume G, Martin F, Titz B, Leroy P, Buettner A, Elamin A, Oviedo A, Cabanski M, De León H, Guedj E, Schneider T, Talikka M, Ivanov NV, Vanscheeuwijck P, Peitsch MC, Hoeng J. (216). An 8-Month Systems Toxicology Inhalation/Cessation Study in Apoe-/- Mice to Investigate Cardiovascular and Respiratory Exposure Effects of a Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product, THS 2.2, Compared With Conventional CigarettesToxicol Sci. 149(2): PMID Titz, B., Boue, S., Phillips, B., Talikka, M., Vihervaara, T., Schneider, T., Nury, C., Elamin, A., Guedj, E., Peck, M.J., Schlage WK, Cabanski M, Leroy P, Vuillaume G, Martin F, Ivanov NV, Veljkovic E, Ekroos K, Laaksonen R, Vanscheeuwijck P, Peitsch MC, Hoeng J.(216). Effects of Cigarette Smoke, Cessation, and Switching to Two Heat-Not-Burn Tobacco Products on Lung Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/6 and Apoe-/- Mice-An Integrative Systems Toxicology Analysis. Toxicol Sci 149, PMID Lo Sasso, G., Titz, B., Nury, C., Boue, S., Phillips, B., Belcastro, V., Schneider, T., Dijon, S., Baumer, K., Peric, D, Dulize R, Elamin A, Guedj E, Buettner A, Leroy P, Kleinhans S, Vuillaume G, Veljkovic E, Ivanov NV, Martin F, Vanscheeuwijck P, Peitsch MC, Hoeng J. (216). Effects of cigarette smoke, cessation and switching to a candidate modified risk tobacco product on the liver in Apoe / mice a systems toxicology analysis. Inhal Toxicol. 28(5): PMID Lo Sasso G, Schlage WK, Boué S, Veljkovic E, Peitsch MC, Hoeng J. (216) The Apoe(-/-) mouse model: a suitable model to study cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in the context of cigarette smoke exposure and harm reduction. J Transl Med (1):146.Epub. Review. PMID
19 A/J mouse study Study design (OECD TG 453 Chronic toxicity) BALF analysis Lung function Biomarkers of exposure, hematology, blood FACS, clinical chemistry, urinalysis Biomarkers of exposure, blood FACS, urinalysis Omics Histopathology Omics Histopathology 19
20 N ic o tin e ( g /l), m e a n + /- S D T o t a l N i c o t i n e M e t a b o l i t e s ( n m o l, m e a n + / - S E M ) A/J mouse study Methods - Exposure and aerosol uptake - Animals were exposed 6 hours per day, 5 days per week - Nicotine was measured 3 samples per chamber per day) - Aerosol delivery (nicotine) was within +/- 1% of the targeted nicotine concentration - Aerosol uptake was in line with test atmosphere nicotine concentration Nicotine concentration in exposure chamber (study average) Nicotine metabolites in urine 3 R 4 F T H S 2. 2 T H S 2. 2 T H S 2. 2 T H S 2. 2 L o w M e d H ig h H ig h L o w M e d H i g h H i g h F e m a le M a l e F e m a l e M a l e 26.8 µg/l nic (high dose) corresponds to 11.6 mg/kg, daily dose- or the nicotine amount from approx. 56 cig/day for a 6 kg human, based on body surface comparison, Guidance document Heq dose, FDA 2
21 T L y m p h o c y t e C o u n t (1 5, m e a n + /-S E M ) B L y m p h o c y t e C o u n t (1 5, m e a n + /-S E M ) T o ta l C e ll C o u n t (1 5, m e a n + /-S E M ) N e u t r o p h il C o u n t (1 5, m e a n + /-S E M ) A/J mouse study Result summary: Inflammation - Free lung cell analysis in BALF exposure-related increases in neutrophil, alveolar macrophage, dendritic cell, and lymphocyte count No obvious increase in the immune cell counts in lungs (BALF) of THS2.2 aerosol-exposed mice M o n th 1 M o n th L o w M e d H ig h L o w M e d H ig h 3.4 M o n th 1 M o n th 1 M o n th 5.3 M o n th R 4F L o w M e d H ig h 3R 4F L o w M e d H ig h 21
22 A/J mouse study Result summary: Lung inflammation BALF cytokines/chemokines Minimal up-regulation of key inflammatory factors in THS2.2 aerosol-exposed mice exposure-related increases in Levels of inflammatory cytokines, e.g. IL-6, TNF-a, IL1-b Levels of chemotactic factors, e.g. MCP1, KC Growth factors, e.g. EGF, VEGF 22
23 A/J mouse study Result summary: Lung function No obvious changes in lung function in THS2.2 aerosol-exposed mice Lung function Flexivent - Pressure- Volume loops Month 1 THS2.2 Month 1 exposure-related changes Leftward & upward shift of the P-V loops for both the inflation and deflation phases Increased lung volumes at specified pressure; greater ease with which the lungs may be extended at a specified pressure Month 5 Month 5 Lower pressure at specified volume of air in the lung THS2.2 23
24 M e a n C h o r d L e n g t h m e a n ± S E M ( m ) D e s t r u c t i v e i n d e x m e a n ± S E M ( % ) B r o n c h i o l a r a t t a c h m. m e a n ± S E M ( n /m m ) S e v e r i t y s c o r e m e a n ± S E M A/J mouse study Result summary: Lung tissue changes Histopathology and morphometry Histopathology - emphysema Histopathological assessment and morphometric analysis shows consistent emphysema in -exposed A/J mice but in THS2.2-exposed animals M o n th 1 M o n th 5 M o n th 1 1 Morphometry Mean Chord Length Month Morphometry Destructive index Month R 4 F 3 R 4 F L o w L o w M e d M e d H ig h Morphometry Bronchiolar attachments Month 5 H ig h R 4 F 3 R 4 F L o w L o w M e d M e d H ig h p<.5; p<.1; p<.1 differences relative to sham H ig h 3 R 4 F 3 R 4 F L o w L o w M e d M e d H ig h H ig h 3 R 4 F 3 R 4 F L o w L o w M e d M e d H ig h H ig h 24
25 A l v. s u r f. d e n s it y s e p t u m (n /m m ) N u m. d e n s. a l v e o li p a r. ( n ) t o t a l n o. a l v e o l i A/J mouse study Result summary: Lung tissue changes Morphometry Supplemental analysis of lung volume-independent state-of-the-art morphometric parameters confirm the emphysematous changes in -exposed but in the THS2.2-exposed mice 4 Morphometry Alveolar surface density in septum Month 5 4 Morphometry Numerical density of alveoli in parenchyma Month 5 4 Morphometry Total number of alveoli Month R 4 F 3 R 4 F L o w L o w M e d M e d H ig h H ig h 3 R 4 F 3 R 4 F L o w L o w M e d M e d H ig h H ig h 3 R 4 F 3 R 4 F L o w L o w M e d M e d H ig h H ig h p<.5; p<.1; p<.1 differences relative to sham 25
26 A/J mouse study Summary and Conclusions The A/J mouse model is suitable for studying smoke-related aspects of COPD After 1 month of exposure to cigarette smoke, lung inflammation is clearly present and changes in lung function are obvious lung emphysema is present at the 5 months time point Exposure to aerosol for THS2.2 doesn t cause any changes in lung inflammation, lung function and emphysema Stinn W, Buettner A, Weiler H, Friedrichs B, Luetjen S, van Overveld F, Meurrens K, Janssens K, Gebel S, Stabbert R, Haussmann HJ. (213) Lung inflammatory effects, tumorigenesis, and emphysema development in a long-term inhalation study with cigarette mainstream smoke in mice. Toxicol Sci. 131(2): PMID:
27 Comparison mouse models Both independent mouse studies have shown that: Lung inflammation and changes in pulmonary function are induced after 1 month of exposure to cigarette smoke Lung emphysema is caused by cigarette smoke and significant after 2 months (or 5 months A/J mice) of exposure to cigarette smoke Aerosol from THS2.2, a RRP, causes only minimal changes in lung inflammation, but no changes in lung function and pulmonary emphysema. 27
28 THANK YOU 28
Non Clinical Toxicology of Nicotine and Aerosol from a Heated Tobacco Product. Patrick Vanscheeuwijck, PhD Director Pre-Clinical Toxicology
 Non Clinical Toxicology of Nicotine and Aerosol from a Heated Tobacco Product Patrick Vanscheeuwijck, PhD Director Pre-Clinical Toxicology PMI s Goal for Harm Reduction Offering adult smokers satisfying
Non Clinical Toxicology of Nicotine and Aerosol from a Heated Tobacco Product Patrick Vanscheeuwijck, PhD Director Pre-Clinical Toxicology PMI s Goal for Harm Reduction Offering adult smokers satisfying
Tobacco Heating System 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment
 Tobacco Heating System 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment Global Forum on Nicotine 2016 Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International R&D June 17th
Tobacco Heating System 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment Global Forum on Nicotine 2016 Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International R&D June 17th
Heat-not-Burn Products: Scientific Assessment of Risk Reduction
 Heat-not-Burn Products: Scientific Assessment of Risk Reduction Tobacco Merchants Association 2015 Annual Meeting Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International R&D May 20th 2015 The Objective is Harm
Heat-not-Burn Products: Scientific Assessment of Risk Reduction Tobacco Merchants Association 2015 Annual Meeting Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International R&D May 20th 2015 The Objective is Harm
Assessment of the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: From Concept to Early Clinical Data
 Assessment of the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: From Concept to Early Clinical Data Global Forum on Nicotine 2015 Bruce D. Clark PhD Philip Morris International
Assessment of the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: From Concept to Early Clinical Data Global Forum on Nicotine 2015 Bruce D. Clark PhD Philip Morris International
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING
 CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING Athens, Greece Dr. Patrick Picavet, M.D., on behalf of: Baker, Gizelle; Haziza, Christelle; Hoeng, Julia;
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING Athens, Greece Dr. Patrick Picavet, M.D., on behalf of: Baker, Gizelle; Haziza, Christelle; Hoeng, Julia;
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING
 CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING Athens, Greece Dr. Patrick Picavet, M.D., on behalf of: Baker, Gizelle; Haziza, Christelle; Hoeng, Julia;
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING Athens, Greece Dr. Patrick Picavet, M.D., on behalf of: Baker, Gizelle; Haziza, Christelle; Hoeng, Julia;
Heated Tobacco Technology: Science, Behavior and Avoiding Unintended Consequences
 Heated Tobacco Technology: Science, Behavior and Avoiding Unintended Consequences Global Forum on Nicotine 2017 Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International June 16th 2017 Important Information Reduced-Risk
Heated Tobacco Technology: Science, Behavior and Avoiding Unintended Consequences Global Forum on Nicotine 2017 Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International June 16th 2017 Important Information Reduced-Risk
TOBACCO HARM REDUCTION:
 TOBACCO HARM REDUCTION: An Overview of PMI s Scientific Approach & Main Results for the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, a Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product Tunis, Tunisia Dr. Nuno Fazenda, on behalf
TOBACCO HARM REDUCTION: An Overview of PMI s Scientific Approach & Main Results for the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, a Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product Tunis, Tunisia Dr. Nuno Fazenda, on behalf
The importance of offering adult smokers a portfolio of potentially less harmful products
 The importance of offering adult smokers a portfolio of potentially less harmful products International Symposium on Nicotine Technology June 15 th 2017 Thomas Mc Grath, PhD PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products
The importance of offering adult smokers a portfolio of potentially less harmful products International Symposium on Nicotine Technology June 15 th 2017 Thomas Mc Grath, PhD PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products
Cancer and its Causes in Korea
 Cancer and its Causes in Korea Prof. Dr. David Khayat, MD, PhD Former Head of Medical Oncology at Pitié-Salpêtrière in Paris Former President of the National Cancer Institute in France Harm Reduction Consultant
Cancer and its Causes in Korea Prof. Dr. David Khayat, MD, PhD Former Head of Medical Oncology at Pitié-Salpêtrière in Paris Former President of the National Cancer Institute in France Harm Reduction Consultant
How innovation will deliver a smokefree
 How innovation will deliver a smokefree future Innovation and Good Practices in the Health Sector Rui Minhos Head of Regional Scientific Engagement Philip Morris International 6th November 2018 Our contact
How innovation will deliver a smokefree future Innovation and Good Practices in the Health Sector Rui Minhos Head of Regional Scientific Engagement Philip Morris International 6th November 2018 Our contact
The IQOS Heating System
 Script and Slides of Philip Morris International s Presentation before the Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee (TPSAC) 24 January 2018 Slide 1 The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific
Script and Slides of Philip Morris International s Presentation before the Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee (TPSAC) 24 January 2018 Slide 1 The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific
Biomarker of Exposure Reductions Upon Switching for 5 Days from Cigarettes to a Carbon Heated Tobacco Product (CHTP 1.0)
 Biomarker of Exposure Reductions Upon Switching for Days from to a Carbon Heated Tobacco Product () A. Donelli, C. Tran, C. Haziza, J. Ancerewicz, G. de La Bourdonnaye, R. Weitkunat, and F. Lüdicke 8 healthy
Biomarker of Exposure Reductions Upon Switching for Days from to a Carbon Heated Tobacco Product () A. Donelli, C. Tran, C. Haziza, J. Ancerewicz, G. de La Bourdonnaye, R. Weitkunat, and F. Lüdicke 8 healthy
The IQOS Heating System
 The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee January 24, 2018 CC-1 Introduction Moira Gilchrist, PhD Vice President Scientific and Public Communications Philip Morris International
The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee January 24, 2018 CC-1 Introduction Moira Gilchrist, PhD Vice President Scientific and Public Communications Philip Morris International
Summary of Evidence on the Cytotoxic Effects on Bronchial Epithelial Cells of IQOS
 Summary of Evidence on the Cytotoxic Effects on Bronchial Epithelial Cells of IQOS Response to the article entitled Cytotoxic effects of heated tobacco products (HTP) on human bronchial epithelial cells
Summary of Evidence on the Cytotoxic Effects on Bronchial Epithelial Cells of IQOS Response to the article entitled Cytotoxic effects of heated tobacco products (HTP) on human bronchial epithelial cells
The IQOS Heating System
 The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee January 24, 2018 CC-1 Introduction Moira Gilchrist, PhD Vice President Scientific and Public Communications Philip Morris International
The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee January 24, 2018 CC-1 Introduction Moira Gilchrist, PhD Vice President Scientific and Public Communications Philip Morris International
A study to examine changes in exposure to cigarette smoke chemicals when a smoker switches to using a tobacco heating product. Part I: Study Design.
 A study to examine changes in exposure to cigarette smoke chemicals when a smoker switches to using a tobacco heating product. Part I: Study Design. Nathan Gale 1, Mike McEwan 1, Alison Eldridge 1, Neil
A study to examine changes in exposure to cigarette smoke chemicals when a smoker switches to using a tobacco heating product. Part I: Study Design. Nathan Gale 1, Mike McEwan 1, Alison Eldridge 1, Neil
Smoking and Non-Communicable Diseases in Hong Kong
 Smoking and Non-Communicable Diseases in Hong Kong Current Status and the Way Forward Prof. David Khayat Former Head of Medical Oncology at the Pitié-Salpêtrière in Paris Former President of the National
Smoking and Non-Communicable Diseases in Hong Kong Current Status and the Way Forward Prof. David Khayat Former Head of Medical Oncology at the Pitié-Salpêtrière in Paris Former President of the National
ICAP 2017, 3rd - 6th July 2017, Caparica, Portugal Philip Morris International is the sole source of funding and sponsor of this project.
 Thomas Schneider PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Quai Jeanrenaud 5, CH-2000 Neuchâtel, Switzerland (Part of Philip Morris International group of companies) ICAP 2017, 3rd - 6th July 2017, Caparica,
Thomas Schneider PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Quai Jeanrenaud 5, CH-2000 Neuchâtel, Switzerland (Part of Philip Morris International group of companies) ICAP 2017, 3rd - 6th July 2017, Caparica,
Might Smoking Rates go up in Flames? Dr John Schoonbee, Chief Medical Officer, Swiss Re
 Might Smoking Rates go up in Flames? Dr John Schoonbee, Chief Medical Officer, Swiss Re 2 Agenda Smoking is still a problem Stopping is hard Electronic cigarettes Reduced Risk tobacco products Males >15yr
Might Smoking Rates go up in Flames? Dr John Schoonbee, Chief Medical Officer, Swiss Re 2 Agenda Smoking is still a problem Stopping is hard Electronic cigarettes Reduced Risk tobacco products Males >15yr
Tobacco Control Research and Education, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
 The Difference between IQOS and Continued Smoking Response to the article entitled PMI s own in vivo clinical data on biomarkers of potential harm in Americans show that IQOS is not detectably different
The Difference between IQOS and Continued Smoking Response to the article entitled PMI s own in vivo clinical data on biomarkers of potential harm in Americans show that IQOS is not detectably different
UPDATE ON PREMARKET TOBACCO PRODUCT AUTHORIZATION PATHWAY
 UPDATE ON PREMARKET TOBACCO PRODUCT AUTHORIZATION PATHWAY Presented by Ii-Lun Chen, M.D Director Division of Individual Health Science Office of Science, CTP, FDA Disclaimer: This is not a formal dissemination
UPDATE ON PREMARKET TOBACCO PRODUCT AUTHORIZATION PATHWAY Presented by Ii-Lun Chen, M.D Director Division of Individual Health Science Office of Science, CTP, FDA Disclaimer: This is not a formal dissemination
Assessing Consumer Responses to RRP: Experience at PMI in Developing Fit-for-Purpose Self-Report Instruments
 Assessing Consumer Responses to RRP: Experience at PMI in Developing Fit-for-Purpose Self-Report Instruments C. Chrea, E. Spies, E. Afolalu, N. Mainy, S. Gallot, P. Binggeli, E. Clerc, R. Weitkunat PMI
Assessing Consumer Responses to RRP: Experience at PMI in Developing Fit-for-Purpose Self-Report Instruments C. Chrea, E. Spies, E. Afolalu, N. Mainy, S. Gallot, P. Binggeli, E. Clerc, R. Weitkunat PMI
Conference Name Start date End date Location Title of presentation Authors Type of presentation
 Philip Morris International Oral and Poster Presentations at Conferences January to December 2016 Conference Name Start date End date Location Title of presentation Authors Type of presentation 47th Tobacco
Philip Morris International Oral and Poster Presentations at Conferences January to December 2016 Conference Name Start date End date Location Title of presentation Authors Type of presentation 47th Tobacco
Scientific Evidence for Evaluating Modified Risk Tobacco Products
 Scientific Evidence for Evaluating Modified Risk Tobacco Products Presented to the IOM Committee on Scientific Standards for Modified Risk Tobacco Products May 9 th 2011, Washington DC 1 l Altria Client
Scientific Evidence for Evaluating Modified Risk Tobacco Products Presented to the IOM Committee on Scientific Standards for Modified Risk Tobacco Products May 9 th 2011, Washington DC 1 l Altria Client
Evaluation of Nicotine Pharmacokinetics and Subjective Effects following Use of a Novel Nicotine Aerosol System
 Evaluation of Nicotine Pharmacokinetics and Subjective Effects following Use of a Novel Nicotine Aerosol System A. Teichert 1, P. Brossard 1, L. Felber Medlin 1, L. Sandalic 1, J. Ancerewicz 1, M. Franzon
Evaluation of Nicotine Pharmacokinetics and Subjective Effects following Use of a Novel Nicotine Aerosol System A. Teichert 1, P. Brossard 1, L. Felber Medlin 1, L. Sandalic 1, J. Ancerewicz 1, M. Franzon
Actual Use Study of the Potential Reduced-Risk Product (RRP): Tobacco Heating System (THS)
 Actual Use Study of the Potential Reduced-Risk Product (RRP): Tobacco Heating System (THS) S. Roulet 1, P. Magnani 1, G. Kallischnigg 2, A. Dugan 3, C. Gage 3, C. Kanitscheider 4, M. Apecechea 4, A. Ramazzotti
Actual Use Study of the Potential Reduced-Risk Product (RRP): Tobacco Heating System (THS) S. Roulet 1, P. Magnani 1, G. Kallischnigg 2, A. Dugan 3, C. Gage 3, C. Kanitscheider 4, M. Apecechea 4, A. Ramazzotti
Modelling the effects of user exposure to harmful emissions across the spectrum of nicotine delivery
 Global Nicotine Forum 2018 Modelling the effects of user exposure to harmful emissions across the spectrum of nicotine delivery Ed Stephens University of St Andrews Declaration: No conflicts of interest
Global Nicotine Forum 2018 Modelling the effects of user exposure to harmful emissions across the spectrum of nicotine delivery Ed Stephens University of St Andrews Declaration: No conflicts of interest
Analysis and Evaluation of a Cross-Sectional Study IEA World Congress of Epidemiology 20 th August Saitama, Japan
 Analysis and Evaluation of a Cross-Sectional Study IEA World Congress of Epidemiology 20 th August Saitama, Japan A van der Plas, L Prieto, D Skiada, M Dobrynina, G Baker, F Ludicke PMI R&D, Philip Morris
Analysis and Evaluation of a Cross-Sectional Study IEA World Congress of Epidemiology 20 th August Saitama, Japan A van der Plas, L Prieto, D Skiada, M Dobrynina, G Baker, F Ludicke PMI R&D, Philip Morris
Changes in Biological and Functional Markers after Six Months, in Three Populations: THS 2.2 (IQOS ) Users, Continued Smokers, and Smoking Abstinence
 Changes in Biological and Functional Markers after Six Months, in Three Populations: THS 2.2 (IQOS ) Users, Continued Smokers, and Smoking Abstinence Christelle Haziza, PhD Manager Clinical Science Philip
Changes in Biological and Functional Markers after Six Months, in Three Populations: THS 2.2 (IQOS ) Users, Continued Smokers, and Smoking Abstinence Christelle Haziza, PhD Manager Clinical Science Philip
The concept that not all tobacco and nicotine products
 A Model Risk Continuum for Tobacco and Nicotine Products by Chris Proctor, Sudhanshu Patwardhan, and James Murphy The concept that not all tobacco and nicotine products present the same risks to human
A Model Risk Continuum for Tobacco and Nicotine Products by Chris Proctor, Sudhanshu Patwardhan, and James Murphy The concept that not all tobacco and nicotine products present the same risks to human
PROCEDURE FOR GENERATION AND TESTING OF MAINSTREAM TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS or IQOS) AEROSOL USING A LINEAR SMOKING MACHINE
 PROCEDURE FOR GENERATION AND TESTING OF MAINSTREAM TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS or IQOS) AEROSOL USING A LINEAR SMOKING MACHINE 1 P age Table of contents / Table des matières 1 Introduction...3 1 Scope...3
PROCEDURE FOR GENERATION AND TESTING OF MAINSTREAM TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS or IQOS) AEROSOL USING A LINEAR SMOKING MACHINE 1 P age Table of contents / Table des matières 1 Introduction...3 1 Scope...3
Cardiovascular effects of nicotine vs. cigarette smoke
 Cardiovascular effects of nicotine vs. cigarette smoke Dr Konstantinos Farsalinos Researcher Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center, Greece University of Patras, Greece National School of Public Health, Athens-Greece
Cardiovascular effects of nicotine vs. cigarette smoke Dr Konstantinos Farsalinos Researcher Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center, Greece University of Patras, Greece National School of Public Health, Athens-Greece
In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS. Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program
 In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program 1 Outline: 1. In Vitro Toxicology Approach at IIVS 1. Science, Education, & Outreach
In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program 1 Outline: 1. In Vitro Toxicology Approach at IIVS 1. Science, Education, & Outreach
Biomarker (BMK) Sub-Group 2017 Report
 Biomarker (BMK) Sub-Group 2017 Report Kitzbühel, Austria October 10, 2017 Coordinator: G. L. Prasad Secretary: Kirk Newland Scientific Commission Liaison: Paul Harp Biomarker Sub-Group Objectives Objective
Biomarker (BMK) Sub-Group 2017 Report Kitzbühel, Austria October 10, 2017 Coordinator: G. L. Prasad Secretary: Kirk Newland Scientific Commission Liaison: Paul Harp Biomarker Sub-Group Objectives Objective
SAFETY E-CIGS: CLINICAL STUDIES
 SAFETY E-CIGS: CLINICAL STUDIES SAFETY ECIGS: clinical studies Source: Safety evaluation and risk assessment of electronic cigarettes as tobacco cigarette substitutes: A systematic review. Ther Adv Drug
SAFETY E-CIGS: CLINICAL STUDIES SAFETY ECIGS: clinical studies Source: Safety evaluation and risk assessment of electronic cigarettes as tobacco cigarette substitutes: A systematic review. Ther Adv Drug
Lung Cancer Epidemiology & Prevention. A/Prof Fraser Brims
 Lung Cancer Epidemiology & Prevention A/Prof Fraser Brims Introduction Lung cancer burden Global, Australia, WA Current smoking rates Other risks and associations Prevention Tobacco control E-cigarettes
Lung Cancer Epidemiology & Prevention A/Prof Fraser Brims Introduction Lung cancer burden Global, Australia, WA Current smoking rates Other risks and associations Prevention Tobacco control E-cigarettes
UK E-Cigarette Summit Relative risks of cancer posed by combustible and vapourising forms of nicotine delivery: Evidence from chemical exposures
 UK E-Cigarette Summit 2017 Relative risks of cancer posed by combustible and vapourising forms of nicotine delivery: Evidence from chemical exposures Ed Stephens University of St Andrews Scope of presentation
UK E-Cigarette Summit 2017 Relative risks of cancer posed by combustible and vapourising forms of nicotine delivery: Evidence from chemical exposures Ed Stephens University of St Andrews Scope of presentation
E-Cigarettes: Current Perspective
 E-Cigarettes: Current Perspective Aruni Bhatnagar, Ph.D. Professor of Medicine University of Louisville Louisville, KY Electronic Cigarettes E-cigarettes are electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS),
E-Cigarettes: Current Perspective Aruni Bhatnagar, Ph.D. Professor of Medicine University of Louisville Louisville, KY Electronic Cigarettes E-cigarettes are electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS),
ELECTRONIC CIGARETTES WHAT S THE BOTTOM LINE?
 ELECTRONIC CIGARETTES WHAT S THE BOTTOM LINE? E-cigarettes have the potential to benefit adult smokers who are not pregnant if used as a complete substitute for regular cigarettes and other smoked tobacco
ELECTRONIC CIGARETTES WHAT S THE BOTTOM LINE? E-cigarettes have the potential to benefit adult smokers who are not pregnant if used as a complete substitute for regular cigarettes and other smoked tobacco
Smoking, e-cigs and reduced risk products. Dr John Schoonbee, IMS November 2017
 Smoking, e-cigs and reduced risk products Dr John Schoonbee, IMS November 2017 2 The storyline smoking is bad yet many folks still smoke because quitting is very hard is it better, if one cannot quit,
Smoking, e-cigs and reduced risk products Dr John Schoonbee, IMS November 2017 2 The storyline smoking is bad yet many folks still smoke because quitting is very hard is it better, if one cannot quit,
In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS. Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program
 In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program 1 Outline: 1. In Vitro Toxicology Approach at IIVS 1. Science, education, & outreach
In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program 1 Outline: 1. In Vitro Toxicology Approach at IIVS 1. Science, education, & outreach
What is combustion and why is the absence of combustion important for heat not burn products
 What is combustion and why is the absence of combustion important for heat not burn products Global Forum on Nicotine 2017 June 16 th 2017 Thomas Mc Grath PhD PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Quai
What is combustion and why is the absence of combustion important for heat not burn products Global Forum on Nicotine 2017 June 16 th 2017 Thomas Mc Grath PhD PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Quai
Exploring five common claims about e-cigarette use. Lion Shahab, PhD University College
 Exploring five common claims about e-cigarette use Lion Shahab, PhD University College London @LionShahab Claim 1: Renormalisation Claim 1: Renormalisation A priori predictions for impact on population
Exploring five common claims about e-cigarette use Lion Shahab, PhD University College London @LionShahab Claim 1: Renormalisation Claim 1: Renormalisation A priori predictions for impact on population
Investor Day Reduced-Risk Products Lausanne, September 29, 2016
 Investor Day Reduced-Risk Products Lausanne, September 29, 2016 Manuel Peitsch Chief Scientific Officer, Reduced-Risk Products Mirek Zielinski President, Reduced-Risk Products Investor Day Reduced-Risk
Investor Day Reduced-Risk Products Lausanne, September 29, 2016 Manuel Peitsch Chief Scientific Officer, Reduced-Risk Products Mirek Zielinski President, Reduced-Risk Products Investor Day Reduced-Risk
Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2
 Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2 THS 2.2. is commercialized under the IQOS brand name Dr Catherine Goujon Ginglinger - Philip Morris International Research & Development,
Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2 THS 2.2. is commercialized under the IQOS brand name Dr Catherine Goujon Ginglinger - Philip Morris International Research & Development,
Diseases caused by Smoking
 Name: Class: Date: Diseases caused by Smoking Biology Gr11A Diseases caused by Smoking Unless you're living in a cave under the heart of Kentucky tobacco country, you know that smoking isn't exactly the
Name: Class: Date: Diseases caused by Smoking Biology Gr11A Diseases caused by Smoking Unless you're living in a cave under the heart of Kentucky tobacco country, you know that smoking isn't exactly the
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment blocks inflammatory pathways and promotes survival and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells
 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment blocks inflammatory pathways and promotes survival and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells Gérald J. Prud homme, MD, FRCPC Keenan Research Centre for Biomedical
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment blocks inflammatory pathways and promotes survival and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells Gérald J. Prud homme, MD, FRCPC Keenan Research Centre for Biomedical
Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2
 Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2 THS 2.2. is commercialized under the IQOS brand name Maya Mitova, Catherine Goujon Ginglinger, Michel Rotach, Serge Maeder Philip
Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2 THS 2.2. is commercialized under the IQOS brand name Maya Mitova, Catherine Goujon Ginglinger, Michel Rotach, Serge Maeder Philip
R. Balansky 1,2, F. D Agostini 2, A. Izzotti 2, P. Kalpakam 3, V.E. Steele 4, S. De Flora 2
 INCON / 10 ICMAA, Guarujà, Brazil, September 26-29, 2010 MECHANISMS OF INHIBITION OF CIGARETTE SMOKE GENOTOXICITY AND CARCINOGENICITY 1 2 3 4 R. Balansky 1,2, F. D Agostini 2, A. Izzotti 2, P. Kalpakam
INCON / 10 ICMAA, Guarujà, Brazil, September 26-29, 2010 MECHANISMS OF INHIBITION OF CIGARETTE SMOKE GENOTOXICITY AND CARCINOGENICITY 1 2 3 4 R. Balansky 1,2, F. D Agostini 2, A. Izzotti 2, P. Kalpakam
1 Natalia Boukharov. 1,4 Emmanuel Guedj. 1 Nikolai V. Ivanov
 Inflamm. Res. (2015) 64:471 486 DOI 10.1007/s00011-015-0820-2 Inflammation Research ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER Transcriptional profiling and targeted proteomics reveals common molecular changes associated
Inflamm. Res. (2015) 64:471 486 DOI 10.1007/s00011-015-0820-2 Inflammation Research ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER Transcriptional profiling and targeted proteomics reveals common molecular changes associated
COPD: Genomic Biomarker Status and Challenge Scoring
 COPD: Genomic Biomarker Status and Challenge Scoring Julia Hoeng, PMI R&D Raquel Norel, IBM Research 3 rd October 2012 COPD: Genomic Biomarker Status Julia Hoeng, Ph.D. Philip Morris International, Research
COPD: Genomic Biomarker Status and Challenge Scoring Julia Hoeng, PMI R&D Raquel Norel, IBM Research 3 rd October 2012 COPD: Genomic Biomarker Status Julia Hoeng, Ph.D. Philip Morris International, Research
3D Reconstructed Human Airway Models: Effect of Acclimation Conditions on Biomarker and Inflammatory Response Following Tissue Challenge
 3D Reconstructed Human Airway Models: Effect of Acclimation Conditions on Biomarker and Inflammatory Response Following Tissue Challenge Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Inhalation Toxicology
3D Reconstructed Human Airway Models: Effect of Acclimation Conditions on Biomarker and Inflammatory Response Following Tissue Challenge Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Inhalation Toxicology
Quantitative Risk Assessment of Tobacco-Burning and Tobacco-Heating Cigarettes
 Quantitative Risk Assessment of Tobacco-Burning and Tobacco-Heating Cigarettes Kristin M. Marano, MS, MPH, CPH Ziad S. Naufal, PhD Michael F. Borgerding, PhD Ryan J. Potts, PhD 66 th TSRC Symposium September
Quantitative Risk Assessment of Tobacco-Burning and Tobacco-Heating Cigarettes Kristin M. Marano, MS, MPH, CPH Ziad S. Naufal, PhD Michael F. Borgerding, PhD Ryan J. Potts, PhD 66 th TSRC Symposium September
Next Generation Products Sandra Costigan, Marianna Gaca, ChuanLiu, Kevin McAdam, James J. Murphyand Christopher Proctor British American Tobacco 21
 Next Generation Products Sandra Costigan, Marianna Gaca, ChuanLiu, Kevin McAdam, James J. Murphyand Christopher Proctor British American Tobacco 21 st October 2015 Contents Evolution of products across
Next Generation Products Sandra Costigan, Marianna Gaca, ChuanLiu, Kevin McAdam, James J. Murphyand Christopher Proctor British American Tobacco 21 st October 2015 Contents Evolution of products across
JUERGEN FROEHLICH, JANICE DAHMS, DAVID CIPOLLA,
 Reduction in Frequency of Pulmonary Exacerbations With Inhaled ARD-315 in Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis (NCFB) Patients is Independent of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Susceptibility at Baseline JUERGEN
Reduction in Frequency of Pulmonary Exacerbations With Inhaled ARD-315 in Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis (NCFB) Patients is Independent of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Susceptibility at Baseline JUERGEN
Supplementary figure 1. Systemic delivery of anti-cd47 antibody controls tumor growth in
 T u m o r v o lu m e (m m 3 ) P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l Supplementary data a 1 8 6 4 2 5 1 1 5 2 2 5 3 3 5 4 T im e a fte r tu m o r in o c u la tio n (d ) b c 1 5 1 1 5 * *
T u m o r v o lu m e (m m 3 ) P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l Supplementary data a 1 8 6 4 2 5 1 1 5 2 2 5 3 3 5 4 T im e a fte r tu m o r in o c u la tio n (d ) b c 1 5 1 1 5 * *
TOBACCO PRODUCT OR MEDICAL PRODUCT?
 TOBACCO PRODUCT OR MEDICAL PRODUCT? Priscilla Callahan-Lyon, MD Deputy Director Division of Individual Health Science Office of Science, CTP Grail Sipes, JD Director Office of Regulatory Policy, CDER Disclaimer:
TOBACCO PRODUCT OR MEDICAL PRODUCT? Priscilla Callahan-Lyon, MD Deputy Director Division of Individual Health Science Office of Science, CTP Grail Sipes, JD Director Office of Regulatory Policy, CDER Disclaimer:
Challenges in Nonclinical Development of Inhalation Drug Products
 Challenges in Nonclinical Development of Inhalation Drug Products Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Senior Pharmacologist DPARP, CDER August 6, 2015 Rockville, MD Disclaimer This speech reflects the views of the speaker
Challenges in Nonclinical Development of Inhalation Drug Products Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Senior Pharmacologist DPARP, CDER August 6, 2015 Rockville, MD Disclaimer This speech reflects the views of the speaker
A. Incorrect! The alveolus is where gas exchange takes place. B. Correct! Surfactant is the lipid-rich material that permits lung inflation.
 Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Smoking vs Smokeless. Tobacco is a plant that contains nicotine. Cigars and pipes contain more tar and other chemicals.
 Tobacco Smoking vs Smokeless Tobacco is a plant that contains nicotine. Cigars and pipes contain more tar and other chemicals. Smoking Tobacco is tobacco that is smoked or inhaled. Smokeless tobacco is
Tobacco Smoking vs Smokeless Tobacco is a plant that contains nicotine. Cigars and pipes contain more tar and other chemicals. Smoking Tobacco is tobacco that is smoked or inhaled. Smokeless tobacco is
Reduced-Risk Products Science Update
 Reduced-Risk Products Science Update Dr. Ian Jones, PhD JTI VP, Reduced-Risk Products Science Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements. These statements appear in
Reduced-Risk Products Science Update Dr. Ian Jones, PhD JTI VP, Reduced-Risk Products Science Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements. These statements appear in
Carl D. D Ruiz 1*, Donald W. Graff 2 and Edward Robinson 3
 D Ruiz et al. BMC Public Health (2016) 16:543 DOI 10.1186/s12889-016-3236-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Reductions in biomarkers of exposure, impacts on smoking urge and assessment of product use and
D Ruiz et al. BMC Public Health (2016) 16:543 DOI 10.1186/s12889-016-3236-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Reductions in biomarkers of exposure, impacts on smoking urge and assessment of product use and
Because PMI application did not report the full range of HPHCs in IQOS aerosol,
 Because PMI application did not report the full range of HPHCs in IQOS aerosol, characterize HPHCs in sidestream emissions, include a non-targeted analysis of chemicals in emissions, or conduct clinical
Because PMI application did not report the full range of HPHCs in IQOS aerosol, characterize HPHCs in sidestream emissions, include a non-targeted analysis of chemicals in emissions, or conduct clinical
ABSTRACT TOXICOLOGICAL SCIENCES, 149(2), 2016,
 TOXICOLOGICAL SCIENCES, 149(2), 2016, 441 457 doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv244 Advance Access Publication Date: November 17, 2015 Research Article Effects of Cigarette Smoke, Cessation, and Switching to Two
TOXICOLOGICAL SCIENCES, 149(2), 2016, 441 457 doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv244 Advance Access Publication Date: November 17, 2015 Research Article Effects of Cigarette Smoke, Cessation, and Switching to Two
Biomarkers in Public Health: Development and Applications
 Biomarkers in Public Health: Development and Applications Irina Stepanov, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Division of Environmental Health Sciences and Masonic Cancer Center University of Minnesota Biomarker
Biomarkers in Public Health: Development and Applications Irina Stepanov, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Division of Environmental Health Sciences and Masonic Cancer Center University of Minnesota Biomarker
BIOM5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam Fall 2013 page 1/5
 BIOM5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam Fall 2013 page 1/5 BIOM 5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam, Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University, December 12, 2013 Instructions: - This exam has 5 pages and 11
BIOM5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam Fall 2013 page 1/5 BIOM 5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam, Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University, December 12, 2013 Instructions: - This exam has 5 pages and 11
Analysis of 18 Urinary Mercapturic Acids by two Multiplex-LC-MS/MS Methods
 Analysis of 18 Urinary Mercapturic Acids by two Multiplex-LC-MS/MS Methods Nikola Pluym, Gerhard Gilch, Gerhard Scherer, Max Scherer ABF, Analytisch-Biologisches Forschungslabor GmbH, München, Germany
Analysis of 18 Urinary Mercapturic Acids by two Multiplex-LC-MS/MS Methods Nikola Pluym, Gerhard Gilch, Gerhard Scherer, Max Scherer ABF, Analytisch-Biologisches Forschungslabor GmbH, München, Germany
Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice
 Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice Vikramaditya Dumpa, MD Lori C Nielsen, MS Huamei Wang, MD Vasanth HS Kumar, MD Supported by AAP Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Grant
Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice Vikramaditya Dumpa, MD Lori C Nielsen, MS Huamei Wang, MD Vasanth HS Kumar, MD Supported by AAP Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Grant
Influenza A virus infection predisposes hosts to secondary infection with different
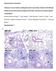 Supplementary information Influenza A virus infection predisposes hosts to secondary infection with different Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes with similar outcome but serotype-specific manifestation.
Supplementary information Influenza A virus infection predisposes hosts to secondary infection with different Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes with similar outcome but serotype-specific manifestation.
Detection of Inflammation and Parenchymal Damage Using Precision-cut Lung Slices
 Detection of Inflammation and Parenchymal Damage Using Precision-cut Lung Slices Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Inhalation Toxicology Program 1 Presentation Outline Disclaimer History and
Detection of Inflammation and Parenchymal Damage Using Precision-cut Lung Slices Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Inhalation Toxicology Program 1 Presentation Outline Disclaimer History and
Comparisons Between Adult Menthol and Non-Menthol Smokers Total Exposure Study. Mohamadi Sarkar, M.Pharm., Ph.D Altria Client Services
 Comparisons Between Adult and Non- Smokers Total Exposure Study ohamadi Sarkar,.Pharm., Ph.D Altria Client Services 1 Altria Client Services (on behalf of Philip orris USA) Presentation to the Tobacco
Comparisons Between Adult and Non- Smokers Total Exposure Study ohamadi Sarkar,.Pharm., Ph.D Altria Client Services 1 Altria Client Services (on behalf of Philip orris USA) Presentation to the Tobacco
Nonclinical Safety Evaluation of Inhalation Drug Products
 Nonclinical Safety Evaluation of Inhalation Drug Products February 13, 2002 Life Science Research Organization Bethesda, Maryland Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Drug Products Center
Nonclinical Safety Evaluation of Inhalation Drug Products February 13, 2002 Life Science Research Organization Bethesda, Maryland Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Drug Products Center
00:08 For decades our scientists have endeavoured to reduce the risks of tobacco use and continue to do so today. 00:15
 00:00 British American Tobacco 00:02 00:03 The Electronic Cigarette 00:07 00:08 For decades our scientists have endeavoured to reduce the risks of tobacco use and continue to do so today. 00:15 00:15 Our
00:00 British American Tobacco 00:02 00:03 The Electronic Cigarette 00:07 00:08 For decades our scientists have endeavoured to reduce the risks of tobacco use and continue to do so today. 00:15 00:15 Our
Science, Hazard and Risk in the European Union: The Case of TiO 2 Exposures
 Science, Hazard and Risk in the European Union: The Case of TiO 2 Exposures David B. Warheit Ph.D, Chemours Company, Wilmington, Delaware USA Inhaled Particles XII Meeting, Glasgow, UK September 25, 2017
Science, Hazard and Risk in the European Union: The Case of TiO 2 Exposures David B. Warheit Ph.D, Chemours Company, Wilmington, Delaware USA Inhaled Particles XII Meeting, Glasgow, UK September 25, 2017
Experimental trial on the effectiveness of IQOS compared to e-cigarettes and regular tobacco cigarettes
 Global Forum on Nicotine Rethinking Nicotine 2018 Experimental trial on the effectiveness of IQOS compared to e-cigarettes and regular tobacco cigarettes Effects on acute craving, withdrawal, positive
Global Forum on Nicotine Rethinking Nicotine 2018 Experimental trial on the effectiveness of IQOS compared to e-cigarettes and regular tobacco cigarettes Effects on acute craving, withdrawal, positive
TGR5 activation induces intestinal growth and improves intestinal mucositis in mice. Hannelouise Kissow
 TGR5 activation induces intestinal growth and improves intestinal mucositis in mice Hannelouise Kissow Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences Faculty Disclosure x No,
TGR5 activation induces intestinal growth and improves intestinal mucositis in mice Hannelouise Kissow Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences Faculty Disclosure x No,
Philip Morris International s Position Statement on the Revision of the Tobacco Excise Directive. 14 February 2017
 Philip Morris International s Position Statement on the Revision of the Tobacco Excise Directive 14 February 2017 1 Contents Introduction... 3 Revision of the Tobacco Excise Directive... 4 Scope of the
Philip Morris International s Position Statement on the Revision of the Tobacco Excise Directive 14 February 2017 1 Contents Introduction... 3 Revision of the Tobacco Excise Directive... 4 Scope of the
The Tobacco Control Act s Premarket Review Authorities: Reports on Substantial Equivalence and Exemption Requests (905(j))
 The Tobacco Control Act s Premarket Review Authorities: Reports on Substantial Equivalence and Exemption Requests (905(j)) January 12, 2011 Cristi Stark, MS Senior Regulatory Health Project Manager Office
The Tobacco Control Act s Premarket Review Authorities: Reports on Substantial Equivalence and Exemption Requests (905(j)) January 12, 2011 Cristi Stark, MS Senior Regulatory Health Project Manager Office
Chapter 3. Regional variability in cigarette smoke-induced lung emphysema in mice. T.J.A van Eijl, C.F. Kuper, F.P. Nijkamp and N.
 Regional variability in cigarette smoke-induced lung emphysema in mice T.J.A van Eijl, C.F. Kuper, F.P. Nijkamp and N. Bloksma in preparation Abstract To validate a mouse model of cigarette smoke-induced
Regional variability in cigarette smoke-induced lung emphysema in mice T.J.A van Eijl, C.F. Kuper, F.P. Nijkamp and N. Bloksma in preparation Abstract To validate a mouse model of cigarette smoke-induced
Peter G. Shields, MD Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee (TPSAC) August 16, 2013
 Peter G. Shields, MD Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee (TPSAC) August 16, 2013 Conceptual Framework for Evaluating MRTPs: Objectives Provide a framework for evaluating all tobacco products
Peter G. Shields, MD Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee (TPSAC) August 16, 2013 Conceptual Framework for Evaluating MRTPs: Objectives Provide a framework for evaluating all tobacco products
Emphysema. Lungs The lungs help us breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Everyone is born with 2 lungs: a right lung and a left lung.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects millions of people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This makes
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects millions of people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This makes
Tobacco-related risk perceptions in the regulation of tobacco products at the FDA Center for Tobacco Products
 Tobacco-related risk perceptions in the regulation of tobacco products at the FDA Center for Tobacco Products David B. Portnoy, PhD, MPH Conrad J. Choiniere, PhD Office of Science FDA, Center for Tobacco
Tobacco-related risk perceptions in the regulation of tobacco products at the FDA Center for Tobacco Products David B. Portnoy, PhD, MPH Conrad J. Choiniere, PhD Office of Science FDA, Center for Tobacco
Defining COPD. Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist
 Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
Modified Risk Tobacco Product Applications A Succinct ENDS Industry Perspective
 Modified Risk Tobacco Product Applications A Succinct ENDS Industry Perspective Patricia I. Kovacevic General Counsel, Chief Compliance Officer Presentation to the Food and Drug Law Institute Tobacco Conference,
Modified Risk Tobacco Product Applications A Succinct ENDS Industry Perspective Patricia I. Kovacevic General Counsel, Chief Compliance Officer Presentation to the Food and Drug Law Institute Tobacco Conference,
The good, the bad and the ugly about the Foundation for a Smoke-Free World
 The good, the bad and the ugly about the Foundation for a Smoke-Free World Pr. Jean-François ETTER, PhD E-cigarette Summit, London November 17, 2017 No competing interests I talked to Derek Yach in preparing
The good, the bad and the ugly about the Foundation for a Smoke-Free World Pr. Jean-François ETTER, PhD E-cigarette Summit, London November 17, 2017 No competing interests I talked to Derek Yach in preparing
Regulatory Support for Tobacco Products. Feeling daunted by the regulatory process for tobacco products? Don t worry Battelle can help.
 Regulatory Support for Tobacco Products Feeling daunted by the regulatory process for tobacco products? Don t worry Battelle can help. PREMARKET TOBACCO (PMTA) HUMAN FACTORS STUDIES SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE
Regulatory Support for Tobacco Products Feeling daunted by the regulatory process for tobacco products? Don t worry Battelle can help. PREMARKET TOBACCO (PMTA) HUMAN FACTORS STUDIES SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE
Electronic cigarettes: Pre-clinical and clinical assessment
 Disclaimer: The information in these materials is a formal dissemination of information by BAT and issues discussed in my presentation are not in any official manner related to/voiced by EUROTOX or its
Disclaimer: The information in these materials is a formal dissemination of information by BAT and issues discussed in my presentation are not in any official manner related to/voiced by EUROTOX or its
David B. Warheit Ph.D, Chemours Company, Wilmington, Delaware USA
 How Does One Interpret the Relevance of Particle Overload/ Rat Lung Tumor Findings in Chronic Inhalation Studies with PSPs for Assessing Human Occupational Health Risks? David B. Warheit Ph.D, Chemours
How Does One Interpret the Relevance of Particle Overload/ Rat Lung Tumor Findings in Chronic Inhalation Studies with PSPs for Assessing Human Occupational Health Risks? David B. Warheit Ph.D, Chemours
Comprehensive systems biology analysis of a 7-month cigarette smoke inhalation study in C57BL/6 mice
 www.nature.com/scientificdata OPEN SUBJECT CATEGORIES» Respiratory system models» Microarray analysis» Systems biology» Lipidomics» Proteomic analysis Received: 29 December 2014 Accepted: 19 November 2015
www.nature.com/scientificdata OPEN SUBJECT CATEGORIES» Respiratory system models» Microarray analysis» Systems biology» Lipidomics» Proteomic analysis Received: 29 December 2014 Accepted: 19 November 2015
Chapter 4. Effects of humic acid deposition on induction of lung emphysema by cigarette smoke in mice
 Effects of humic acid deposition on induction of lung emphysema by cigarette smoke in mice T.J.A. van Eijl, A.F. Ferreira, C.F. Kuper, F.P. Nijkamp and N. Bloksma submitted Abstract Tobacco smoke is the
Effects of humic acid deposition on induction of lung emphysema by cigarette smoke in mice T.J.A. van Eijl, A.F. Ferreira, C.F. Kuper, F.P. Nijkamp and N. Bloksma submitted Abstract Tobacco smoke is the
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
Providing a Science Base for the Evaluation of. Tobacco Products
 Providing a Science Base for the Evaluation of Tobacco Products Peter G. Shields MD, Greg Connolly DMD,MPH, K. Michael Cummings PhD, Mirjana V. Djordjevic PhD, Dorothy K. Hatsukami PhD, Jack E. Henningfield
Providing a Science Base for the Evaluation of Tobacco Products Peter G. Shields MD, Greg Connolly DMD,MPH, K. Michael Cummings PhD, Mirjana V. Djordjevic PhD, Dorothy K. Hatsukami PhD, Jack E. Henningfield
Abhd2 regulates alveolar type Ⅱ apoptosis and airway smooth muscle remodeling: a key target of COPD research
 Abhd2 regulates alveolar type Ⅱ apoptosis and airway smooth muscle remodeling: a key target of COPD research Shoude Jin Harbin Medical University, China Background COPD ------ a silent killer Insidious,
Abhd2 regulates alveolar type Ⅱ apoptosis and airway smooth muscle remodeling: a key target of COPD research Shoude Jin Harbin Medical University, China Background COPD ------ a silent killer Insidious,
PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESS TEMPLATE
 1 PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESS TEMPLATE DISEASE: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) DEFINITION: COPD can be defined as a disease in which there is a significant damage to the lungs thus reducing
1 PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESS TEMPLATE DISEASE: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) DEFINITION: COPD can be defined as a disease in which there is a significant damage to the lungs thus reducing
E-Cigarette Update: Secondhand Vapour
 E-Cigarette Update: Secondhand Vapour Toxicity and Health Effects The popularity of e-cigarettes continues to increase, with more Canadians than ever using them indoors and out. The scientific evidence
E-Cigarette Update: Secondhand Vapour Toxicity and Health Effects The popularity of e-cigarettes continues to increase, with more Canadians than ever using them indoors and out. The scientific evidence
How Might Medicinal Regulators Evolve in their Expectations for ENDS? David M Graham Chief Impact Officer - NJOY
 How Might Medicinal Regulators Evolve in their Expectations for ENDS? David M Graham Chief Impact Officer - NJOY 4 Years Ago The Regulation of Nicotine-Containing Products Jeremy Mean 2015 The fact that
How Might Medicinal Regulators Evolve in their Expectations for ENDS? David M Graham Chief Impact Officer - NJOY 4 Years Ago The Regulation of Nicotine-Containing Products Jeremy Mean 2015 The fact that
Study Summary Study THS-PBA-02-US
 Page 1 Study Summary Study THS-PBA-02-US Study Title: Sponsor: Qualitative Study to Develop THS 2.2 Hypothetical Product Messages Philip Morris International Management S.A. Avenue de Rhodanie, 50 1007
Page 1 Study Summary Study THS-PBA-02-US Study Title: Sponsor: Qualitative Study to Develop THS 2.2 Hypothetical Product Messages Philip Morris International Management S.A. Avenue de Rhodanie, 50 1007
BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SUMMER 2014
 THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SUMMER 2014 Jessica Rose Napolitano PhD Candidate Examination of the role of ZIP8 and cadmium in the development of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SUMMER 2014 Jessica Rose Napolitano PhD Candidate Examination of the role of ZIP8 and cadmium in the development of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
