Non Clinical Toxicology of Nicotine and Aerosol from a Heated Tobacco Product. Patrick Vanscheeuwijck, PhD Director Pre-Clinical Toxicology
|
|
|
- Prudence Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Non Clinical Toxicology of Nicotine and Aerosol from a Heated Tobacco Product Patrick Vanscheeuwijck, PhD Director Pre-Clinical Toxicology
2 PMI s Goal for Harm Reduction Offering adult smokers satisfying products that reduce risk Smoking is addictive and causes a number of serious diseases Worldwide it is estimated that more than one billion people will continue to smoke in the foreseeable future* PRODUCT REDUCED-RISK ACCEPTANCE AND PRODUCT X = USAGE HARM REDUCTION Successful harm reduction requires that current adult smokers be offered a range of Reduced Risk Products (RRPs) so that consumer acceptance can be best fulfilled Our Heated Tobacco Product (HTP) is a RRP. * The Tobacco Atlas 3 rd Edition. American Cancer Society, 2009 Figure adapted from Clive Bates presentation to E-Cigarette Summit (19 Nov 2013) Page: 2
3 Reduced-Risk Products ( RRPs ) is the term the company uses to refer to products with the potential to reduce individual risk and population harm in comparison to smoking cigarettes. PMI s RRPs are in various stages of development and commercialization, and we are conducting extensive and rigorous scientific studies to determine whether we can support claims for such products of reduced exposure to harmful and potentially harmful constituents in smoke, and ultimately claims of reduced disease risk, when compared to smoking cigarettes. Before making any such claims, we will rigorously evaluate the full set of data from the relevant scientific studies to determine whether they substantiate reduced exposure or risk. Any such claims may also be subject to government review and authorization as is the case in the US today. Page: 3
4 Outline & Scope Short description of design and methods used in a series of in vivo inhalation studies assessing the effects of nicotine aerosol, conventional cigarette smoke and aerosols from potentially Risk- Reduced Product (prrp) [or candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product] Heated Tobacco Product Description of effects of nicotine (in combination with pyruvic acid) using pre-clinical and systems toxicology endpoints Toxicity of cigarette smoke exposure and the effect of a HTP interpretation of findings using nicotine-exposure knowledge Application of a mouse disease model for cardiovascular and respiratory disease effects of cigarette smoke exposure, switching to HTP aerosol exposure and cessation HTP: Heated Tobacco Product Page: 4
5 Methods in vivo studies Regulatory rat inhalation studies (OECD protocols; 28-day, 90-day*, OECD GLP) Aerosol generation: using appropriate standards Smoking machines: conventional cigarettes, reduced risk products Collison nebulizers: nicotine/salt solution, nicotine containing liquids Aerosol characterization: demonstrate that aerosol is representative and follows guidelines Determination of aerosol markers (e.g. TPM, CO, carbonyls), breathing zone Particle size distribution Bio-monitoring: demonstrate that exposure is representative Respiratory physiology Urinary particulate and gas phase biomarkers of exposure (e.g. nicotine metabolites, mercapturic acid metabolites from acrolein, benzene, acrylonitrile, NNK) blood carboxyhemoglobin) *OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4. Test No. 413: Subchronic Inhalation Toxicity: 90-day Study, OECD 2009 Test No. 412: Subacute Inhalation Toxicity: 28-Day Study, OECD 2009 Page: 5
6 Methods design Endpoints: OECD TG 412/413 Endpoints Standard Toxicology 1. In-life observations 2. Hematology 3. Clinical chemistry 4. Organ weights 5. Inflammatory cells in BALF 6. Histopathology Systemic toxicity OECD Plus - Systems Toxicology 1. Transcriptomics 2. Genomics 3. Lipidomics 4. Proteomics Subset of data Eg Histopathology or Inflammatory Data Computational analysis Computational Network Biology Biological Impact Factor Analysis Executed according to OECD GLPs Test atmospheres presented in low/medium/high concentration: up to MTD: 50 µg Nicotine/l* for nicotine-containing aerosols 23 µg Nicotine/l for cigarette smoke; concentration-response *50 µg/l nic corresponds to 13.6 mg/kg, daily dose; way above acute toxicity levels- or the nicotine amount from approx. 130 cig/day for a 60 kg human Page: 6
7 Methods Exposure nebulized nicotine nicotine salt solutions Exhaled Air Fresh Aerosol Page: 7
8 Effects of nicotine 28 day inhalation study (OECD TG 412) Exposure and Bio monitoring Urinary nicotine metabolites demonstrate appropriate exposure to respirable aerosol Test atmosphere concentrations Particle size determination Urinary nicotine metabolites Means ± SEM; ***p Means ± SD Page: 8
9 Effects of nicotine 28 day inhalation study (OECD TG 412) Systemic effects Nicotine concentration-dependent changes in: Body weight development (approx. 5% body weight gain reduction in high concentration group) Organ weights (relative to body weight): Liver, higher than controls; Spleen, lower Clinical chemistry: Alkaline phosphatase and alanine aminotransferase: higher than controls; cholesterol and glucose: lower than controls all in normal ranges Hematology: neutrophils, higher than controls; lymphocytes, lower all in normal ranges Means ±SEM; *p 0.05, r**p 0.01, ***p relative to control Page: 9
10 Effects of nicotine 28 day inhalation study (OECD TG 412) Histopathology of non respiratory tract organs Liver effects: nicotine concentration-dependent cytoplasmic vacuolation vacuoles contain PAS-positive material, likely to consist of glycogen granules Means ±SEM; *p 0.05, r**p 0.01, ***p relative to control Page: 10
11 Effects of nicotine 28 day inhalation study (OECD TG 412) Summary & Conclusion Exposure to nicotine aerosols, alone or in combination with pyruvic acid, results in mild changes in toxicity in a 28-day inhalation toxicology study with respect to: Systemic effects: increased liver weight, blood neutrophil counts, activity of liver enzymes and decreased blood levels of cholesterol and glucose Histopathological effects: increased vacuolation of and glycogen content in hepatocytes Changes in liver gene expression and lipidomics provide mechanistic explanation for the changes observed, i.e. alterations in xenobioitic and lipid metabolism Toxicity of aerosols of nicotine and pyruvic acid (separate and combined) in Sprague Dawley rats in a 28-day OECD 412 inhalation study and assessment of systems toxicology. Blaine Phillips, Marco Esposito, Jan Verbeeck, Stephanie Boue, Anita Iskandar, Gregory Vuillaume, Patrice Leroy, Subash Krishnan, Ulrike Kogel, Aneli Utan, Walter K. Schlage, Monali Bera, Emilija Veljkovic, Julia Hoeng, Manuel C. Peitsch, and Patrick Vanscheeuwijck. Inhalation toxicology 2015 Aug;27(9):405-31, PMID Page: 11
12 Methods Conventional cigarette smoke and aerosol from a HTP 90 day inhalation study (OECD TG 413) Approximately 3.9m Control room Assessment of smoke/aerosol Health Canada Intense smoke protocol Approximately 1.2m Exposure room Clean corridor Exhaled Air Fresh Aerosol BV1" WASTE Conventional cigarettes: Smoke from University of Kentucky Standard Reference Cigarette 3R4F Potentially Reduced-Risk product: Aerosol from Heatsticks and Tobacco Heating System, HTP, commercialized as iqos (also designated as P1 or THS 2.2) Page: 12
13 Smoke chemistry determination of 58 constituents in conventional cigarette smoke and HTP (THS2.2) aerosol Smoke chemistry data shows a strong reduction of HPHC* in THS2.2 relative to 3R4F (data per mg nicotine, 100 % is data from 3R4F) *HPHC: Harmful or Potentially Harmful Constituents Page: 13
14 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study (OECD TG 413) Exposure Test atmosphere characterization gas phase and particulate matter markers indicate that: Target nicotine concentrations met HPHCs in test atmospheres reflect aerosol chemistry data CO concentrations in test 400 atmospheres mean concentration of nicotine ( g/l +/- SD) Sham Nicotine concentrations in test atmospheres 3R4F_L_8 3R4F_M_15 3R4F_H_23 THS2.2_L_15 THS2.2_M_23 THS2.2_H_50 mean concentration of CO (ppm +/- SD) mean concentration of acrolein ( g/l +/- SD) test atmosphere concentration of nicotine ( g/l) Acrolein concentrations in test atmospheres test atmosphere concentration of nicotine ( g/l) Sham 3R4F THS2.2 3R4F THS2.2 Page: 14
15 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study (OECD TG 413) Biomarkers of exposure Bio-monitoring parameters indicate that: Urinary biomarkers of nicotine correlate with nicotine levels in test atmosphere Urinary biomarkers of HPHC correlate with chemical composition of aerosols The HTP causes much less upper respiratory tract irritation resulting in higher uptake of aerosol total nicotine metabolites (nmol, mean +/- SD) Urinary nicotine metabolites Sham 3R4F THS2.2 concentration of SPMA (ng/ml, mean +/- SD) Urinary benzene metabolite Sham 3R4F THS2.2 test atmosphere concentration of nicotine ( g/l) test atmosphere concentration of nicotine ( g/l) respiratory minute volume ( ml/ min, mean +/- SEM) Respiratory Minute Volume Sham 3R4F THS2.2 concentration of HPMA (ng/ml, mean +/- SD) Urinary acrolein metabolite Sham 3R4F THS2.2 test atmosphere concentration of nicotine ( g/l) test atmosphere concentration of nicotine ( g/l) Data for male rats only, after 4 weeks of exposure. The data for female rats and different collection time points are very similar. Page: 15
16 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study (OECD TG 413) Systemic toxicity No remarkable toxic effects in THS 2.2 Body weight effect in males only Nicotine concentration-related increases in Neutrophil count in blood Relative weight of liver Liver enzyme activity (normal range) Mild liver effects mean body weight (g) Body weight development, male rats < >< > 90d exposure Study Days 90d exposure + 42d recovery Sham 3R4F_L_8 3R4F_M_15 3R4F_H_23 THS2.2_L_15 THS2.2_M_23 THS2.2_H_50 Alkaline phosphatase activity, female rats Effects similar to those of nicotine exposure * p < 0.05 as compared with SHAM at a given time point, # p < 0.05 as compared with 3R4F at target nicotine 15 g/l at a given time point, p < 0.05 as compared with 3R4F at target nicotine 23 g/l at a given time point, and + p < 0.05 as compared with the same group at the 90-day exposure time point Page: 16
17 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study (OECD TG 413) Lung inflammation Very low numbers of inflammatory cells are recruited in the lungs (BALF) of THS2.2 aerosol-exposed rats Remarks: Data for male rats; the data for female rats are very similar. * p < 0.05 as compared with SHAM at a given time point, # p < 0.05 as compared with 3R4F at target nicotine 15 g/l at a given time point, p < 0.05 as compared with 3R4F at target nicotine 23 g/l at a given time point, and + p < 0.05 as compared with the same group at the 90-day exposure time point Means ± SEM Page: 17
18 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study (OECD TG 413) Histopathology of respiratory tract organs Relative Severity Page: 18
19 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study (OECD TG 413) Histopathology of respiratory tract organs Nose Page: 19
20 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study (OECD TG 413) Histopathology of respiratory tract organs Bronchi and lungs Page: 20
21 Methods design Endpoints: OECD TG 412/413 Endpoints Standard Toxicology 1. In-life observations 2. Hematology 3. Clinical chemistry 4. Organ weights 5. Inflammatory cells in BALF 6. Histopathology Systemic toxicity OECD Plus - Systems Toxicology 1. Transcriptomics 2. Genomics 3. Lipidomics 4. Proteomics Subset of data Eg Histopathology or Inflammatory Data Computational analysis Computational Network Biology Biological Impact Factor Analysis Executed according to OECD GLPs Test atmospheres presented in low/medium/high concentration: up to MTD: 50 µg Nicotine/l* for nicotine-containing aerosols 23 µg Nicotine/l for cigarette smoke; concentration-response *50 µg/l nic corresponds to 13.6 mg/kg, daily dose; way above acute toxicity levels- or the nicotine amount from approx. 130 cig/day for a 60 kg human Page: 21
22 System Toxicology Research Identify and Represent Disease Mechanisms Understanding of disease onset and progression Chronic Cigarette Smoke Exposure Molecular changes Disruption of Biological Mechanism Cell / Tissue Changes Physiological changes Disease (CVD, COPD, Lung cancer) Analytical Chemistry Biological Networks Systems Biology/Toxicology Medicine Chronic exposure to cigarette smoke affects a number of biological networks associated with smoking-related diseases in a causal chain of Key Events known as Adverse Outcome Oxidative Pathways Apoptotic Literature-derived phosphorylation β-adrenergic signaling signaling angiogenesis knowledge SMC differentiation regulation Cigarette smoke Hypoxia-induced taof(snai1) Fhit β-catenin signaling ROS Response to oxidative stress NFKB signaling Gh Fgf2 PDGF family catof(sod1) Data-derived knowledge Identify & Build Biological Network models DNA damage taof(nrf2) Cytokine signaling Inflammation kaof(pi3k) taof(myc) taof(mycn) gtpof(kras) gtpof(hras) Hoeng et al., Case Study: The Role of Mechanistic Network Models in Systems Toxicology. Drug DiscoveryToday, 2013, 19: (PMID: ) Page: 22 22
23 Methods Systems Toxicology Assessment Use Disease Mechanism Understanding for Product Assessment Inflammation Cell Proliferation Sham Cell Stress 3R4F Apoptosis Autophagy prrp DNA Damage Necroptosis Senescense Exposure Multi-Omics Data Systems Response Profile Hoeng J et al. A network-based approach to quantifying the impact of biologically active substances. Drug Discovery Today, 2012, 17: (PMID: ) Previously Built Biological Network models Network Perturbation Amplitudes Page: 23 23
24 Methods From Gene Expression Profiles to Biological Impact Factor Page: 24
25 Effects of nicotine 28 day inhalation study (OECD TG 412) Application of systems toxicology on liver changes System response profile of liver transcriptomics reveal up- and down-regulated gene expression Up-regulated: Xenobiotic metabolism Oxidative phosphorylation Fatty acid/cholesterol metabolism Cell cycle Down-regulated: Intracellular signaling Lipidomics confirm downregulated glycerolipids and sterols Page: 25
26 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study Systems biology evaluation Systems Response Profile analysis of lung (90 days) Page: 26
27 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study Systems biology evaluation Network Perturbation Analysis of lung (90 days) Page: 27
28 Cigarette smoke and HTP aerosol 90 day inhalation study Summary and conclusions Pre-clinical toxicology: Exposure of rats to aerosol from THS2.2 even at a multiple of the aerosol concentration - results in a dramatically lower biological effects as compared to exposure to 3R4F in Systemic toxicity; where effects were observed, they are related to nicotine exposure Lung inflammation Histopathology of respiratory tract organs Systems toxicology: Exposure of rats to aerosol from THS2.2 results in a dramatically lower biological network perturbations in the transcriptomes of the nasal epithelium and lung tissue Page: 28
29 Methods Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease cardiovascular disease/emphysema Comparing switching to the HTP P1* with ongoing smoking and benchmarking against cessation Non-clinical study Point of intervention [Disease Risk] ApoE-P1 Switching Study Design [Time] Groups Point of intervention Inhalation Combustible Cigarette: 3R4F SWITCHING 3R4F HTP CESSATION 3R4F Fresh Air Control: Sham/Air Fresh Air Mice: HTP HTP - ApoE -/- mice: animal model for aspects of CVD and COPD Start Month 2 Month 8 Exposure: - 8 months with dissections at 1,2,3,6 and 8 months - Test atmosphere nicotine concentrations: approx. 30 µg/l *P1: or iqos - Whole body, 3 x 1 h/day Page: 29 3R4F
30 Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Result Summary: Disease Endpoint Lung function and Lung Volume Month 1 Month 2 Month 3 Groups 3R4F Cessation Switching HTP Air Month 6 Month 8 Means ± SEM Displaced liquid weight (g) Lung volume (absolute, measured) Sham 3R4F ZRH Switch Cessation Month Page: 30
31 Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Result Summary: Tissue changes Lung Emphysema Histopathology Score *: Statistically significant compared to sham *: Statistically significant compared to 3R4F:CONT at DT2 Page: 31
32 Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Result Summary: Disease Mechanism Lung Inflammation Free lung cells in Broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) 0 1 Total cells absolute Total Cells (x 10 5 ) +/- SEM Sham 3R4F THS 2.2 Cessation Switch Study month 8 Differential counts Alveolar macrophages (x 10 5 ) +/- SEM Neutrophils (x 10 5 ) +/- SEM Alveolar macrophages absolute Sham 3R4F 2 4 THS 2.2 Cessation 6 Neutrophils absolute Sham 3R4F 2 4 THS 2.2 Cessation 6 Switch 8 Switch Alveolar dendritic cells (x 10 5 ) +/- SEM Lymphocytes (x 10 5 ) +/- SEM Alveolar dendritic cells absolute Sham 3R4F 2 4 THS 2.2 Cessation 6 Lymphocytes absolute Sham 3R4F Switch Study month THS 2.2 Cessation 6 Switch 8 Groups 3R4F Cessation Switching HTP Air Page: 32
33 Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Result Summary: Disease Mechanism Lung Inflammation Multiple analyte profiling in Broncho-alveolar Lavage Fluid 3R4F P1 Cess. Switch. MMP activity (mu/ml) +/- SD Sham 3R4F MMP activity THS 2.2 Cessation Switch Groups 3R4F Cessation Switching P1 Air Month Page: 33
34 Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Result Summary: Differential Gene Expression Lung 3R4F Cessation Switch P1 Page: 34
35 Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Result Summary: Disease Mechanisms Network Perturbations Lung Page: 35
36 Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Result Summary: Disease Endpoint Aortic Plaque Growth Image analysis of stained atherosclerotic plaques Different from sham: * : p<0.05 **: p<0.01 Different from 3R4F: # : p<0.05 ##: p<0.01 ** ## ## ## ## Sham 25.0 % Aortic Arches at month 8 3R4F 38.5 % # * ## # ## HTTP: P % Cessation 28.1 % Switch 29.9 % Air 3R4F P1 Cess. Swit. Air 3R4F P1 Cess. Swit. Page: 36
37 Plaque Volume (mm 3 ) Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Result Summary: Disease Endpoint Aortic Plaque size at Month 8 3D Reconstruction from High Resolution micro-computed Tomography Plaque Volume Aortic Arch Occlusion Plaque Surface Mean Occlusion (%) Air 3R4F P1 Cess. Swit. Air 3R4F P1 Cess. Swit. Air 3R4F P1 Cess. Swit. Plaque Surface (mm 2 ) Means ± SEM Means ± SEM 3D-Reconstructions Means ± SEM Page: 37
38 Switching Study in an Animal Model of Disease Summary and Conclusions The ApoE -/- mouse model is suitable for studying smoke-related aspects of cardiovascular disease and COPD Continuous exposure to aerosol from a prrp for up to 8 months does not increase cardiovascular disease, inflammation and emphysema Switching from cigarette smoke exposure after 2 months to fresh air exposure reverses the onset of disease as measured in apical, functional, and molecular endpoints Switching from cigarette smoke exposure to prrp aerosol exposure reverses the onset of disease in a similar manner as cessation Use of Apoe / Mice in an 8-Month Systems Toxicology Inhalation/Cessation Study to Investigate Cardiovascular and Respiratory Exposure Effects of a Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product, THS 2.2, Compared with Conventional Cigarettes Phillips B, Veljkovic E, Boué S, Schlage WK, Vuillaume G, Martin F, Titz B, Leroy P, Buettner A, Elamin A, Oviedo A, Cabanski M, Guedj E, Schneider T, Talikka M, Ivanov NV, Vanscheeuwijck P, Peitsch MC, Hoeng J. Toxicological Sciences (2016) 149, (PMID ) Page: 38
39 Overall conclusion Exposure of rodents to cigarette smoke results in clear toxicological effects and development of known diseases Nicotine, when administered via inhalation exposure, causes limited toxicological effects after 28 or 90 days Aerosol from a prrp, HTP elicits much lower toxicity (overall more than 80%) than cigarette smoke, even at a multiple of the nicotine exposure concentration. Most effects can be attribute to nicotine Aerosol from a prrp, HTP does not lead to smoke-related disease and switching from smoke to prrp aerosol exposure is almost identical to cessation. Page: 39
40 THANK YOU! Page: 40
Philip Morris International R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Switzerland. 2
 Comparative assessment of lung inflammation, pulmonary function and emphysema caused by the aerosol from potential Reduced Risk Products and cigarette smoke in mouse models of COPD. 11 July, 216 COPD-216
Comparative assessment of lung inflammation, pulmonary function and emphysema caused by the aerosol from potential Reduced Risk Products and cigarette smoke in mouse models of COPD. 11 July, 216 COPD-216
Tobacco Heating System 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment
 Tobacco Heating System 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment Global Forum on Nicotine 2016 Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International R&D June 17th
Tobacco Heating System 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment Global Forum on Nicotine 2016 Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International R&D June 17th
Heat-not-Burn Products: Scientific Assessment of Risk Reduction
 Heat-not-Burn Products: Scientific Assessment of Risk Reduction Tobacco Merchants Association 2015 Annual Meeting Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International R&D May 20th 2015 The Objective is Harm
Heat-not-Burn Products: Scientific Assessment of Risk Reduction Tobacco Merchants Association 2015 Annual Meeting Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International R&D May 20th 2015 The Objective is Harm
Assessment of the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: From Concept to Early Clinical Data
 Assessment of the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: From Concept to Early Clinical Data Global Forum on Nicotine 2015 Bruce D. Clark PhD Philip Morris International
Assessment of the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, A Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product: From Concept to Early Clinical Data Global Forum on Nicotine 2015 Bruce D. Clark PhD Philip Morris International
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING
 CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING Athens, Greece Dr. Patrick Picavet, M.D., on behalf of: Baker, Gizelle; Haziza, Christelle; Hoeng, Julia;
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING Athens, Greece Dr. Patrick Picavet, M.D., on behalf of: Baker, Gizelle; Haziza, Christelle; Hoeng, Julia;
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING
 CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING Athens, Greece Dr. Patrick Picavet, M.D., on behalf of: Baker, Gizelle; Haziza, Christelle; Hoeng, Julia;
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF THE TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS) 2.2 COMPARED WITH CONTINUED SMOKING Athens, Greece Dr. Patrick Picavet, M.D., on behalf of: Baker, Gizelle; Haziza, Christelle; Hoeng, Julia;
Heated Tobacco Technology: Science, Behavior and Avoiding Unintended Consequences
 Heated Tobacco Technology: Science, Behavior and Avoiding Unintended Consequences Global Forum on Nicotine 2017 Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International June 16th 2017 Important Information Reduced-Risk
Heated Tobacco Technology: Science, Behavior and Avoiding Unintended Consequences Global Forum on Nicotine 2017 Moira Gilchrist PhD Philip Morris International June 16th 2017 Important Information Reduced-Risk
TOBACCO HARM REDUCTION:
 TOBACCO HARM REDUCTION: An Overview of PMI s Scientific Approach & Main Results for the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, a Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product Tunis, Tunisia Dr. Nuno Fazenda, on behalf
TOBACCO HARM REDUCTION: An Overview of PMI s Scientific Approach & Main Results for the Tobacco Heating System (THS) 2.2, a Candidate Modified Risk Tobacco Product Tunis, Tunisia Dr. Nuno Fazenda, on behalf
The importance of offering adult smokers a portfolio of potentially less harmful products
 The importance of offering adult smokers a portfolio of potentially less harmful products International Symposium on Nicotine Technology June 15 th 2017 Thomas Mc Grath, PhD PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products
The importance of offering adult smokers a portfolio of potentially less harmful products International Symposium on Nicotine Technology June 15 th 2017 Thomas Mc Grath, PhD PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products
Cancer and its Causes in Korea
 Cancer and its Causes in Korea Prof. Dr. David Khayat, MD, PhD Former Head of Medical Oncology at Pitié-Salpêtrière in Paris Former President of the National Cancer Institute in France Harm Reduction Consultant
Cancer and its Causes in Korea Prof. Dr. David Khayat, MD, PhD Former Head of Medical Oncology at Pitié-Salpêtrière in Paris Former President of the National Cancer Institute in France Harm Reduction Consultant
How innovation will deliver a smokefree
 How innovation will deliver a smokefree future Innovation and Good Practices in the Health Sector Rui Minhos Head of Regional Scientific Engagement Philip Morris International 6th November 2018 Our contact
How innovation will deliver a smokefree future Innovation and Good Practices in the Health Sector Rui Minhos Head of Regional Scientific Engagement Philip Morris International 6th November 2018 Our contact
The IQOS Heating System
 The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee January 24, 2018 CC-1 Introduction Moira Gilchrist, PhD Vice President Scientific and Public Communications Philip Morris International
The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee January 24, 2018 CC-1 Introduction Moira Gilchrist, PhD Vice President Scientific and Public Communications Philip Morris International
The IQOS Heating System
 Script and Slides of Philip Morris International s Presentation before the Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee (TPSAC) 24 January 2018 Slide 1 The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific
Script and Slides of Philip Morris International s Presentation before the Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee (TPSAC) 24 January 2018 Slide 1 The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific
Summary of Evidence on the Cytotoxic Effects on Bronchial Epithelial Cells of IQOS
 Summary of Evidence on the Cytotoxic Effects on Bronchial Epithelial Cells of IQOS Response to the article entitled Cytotoxic effects of heated tobacco products (HTP) on human bronchial epithelial cells
Summary of Evidence on the Cytotoxic Effects on Bronchial Epithelial Cells of IQOS Response to the article entitled Cytotoxic effects of heated tobacco products (HTP) on human bronchial epithelial cells
Biomarker of Exposure Reductions Upon Switching for 5 Days from Cigarettes to a Carbon Heated Tobacco Product (CHTP 1.0)
 Biomarker of Exposure Reductions Upon Switching for Days from to a Carbon Heated Tobacco Product () A. Donelli, C. Tran, C. Haziza, J. Ancerewicz, G. de La Bourdonnaye, R. Weitkunat, and F. Lüdicke 8 healthy
Biomarker of Exposure Reductions Upon Switching for Days from to a Carbon Heated Tobacco Product () A. Donelli, C. Tran, C. Haziza, J. Ancerewicz, G. de La Bourdonnaye, R. Weitkunat, and F. Lüdicke 8 healthy
A study to examine changes in exposure to cigarette smoke chemicals when a smoker switches to using a tobacco heating product. Part I: Study Design.
 A study to examine changes in exposure to cigarette smoke chemicals when a smoker switches to using a tobacco heating product. Part I: Study Design. Nathan Gale 1, Mike McEwan 1, Alison Eldridge 1, Neil
A study to examine changes in exposure to cigarette smoke chemicals when a smoker switches to using a tobacco heating product. Part I: Study Design. Nathan Gale 1, Mike McEwan 1, Alison Eldridge 1, Neil
The IQOS Heating System
 The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee January 24, 2018 CC-1 Introduction Moira Gilchrist, PhD Vice President Scientific and Public Communications Philip Morris International
The IQOS Heating System Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee January 24, 2018 CC-1 Introduction Moira Gilchrist, PhD Vice President Scientific and Public Communications Philip Morris International
Smoking and Non-Communicable Diseases in Hong Kong
 Smoking and Non-Communicable Diseases in Hong Kong Current Status and the Way Forward Prof. David Khayat Former Head of Medical Oncology at the Pitié-Salpêtrière in Paris Former President of the National
Smoking and Non-Communicable Diseases in Hong Kong Current Status and the Way Forward Prof. David Khayat Former Head of Medical Oncology at the Pitié-Salpêtrière in Paris Former President of the National
Modelling the effects of user exposure to harmful emissions across the spectrum of nicotine delivery
 Global Nicotine Forum 2018 Modelling the effects of user exposure to harmful emissions across the spectrum of nicotine delivery Ed Stephens University of St Andrews Declaration: No conflicts of interest
Global Nicotine Forum 2018 Modelling the effects of user exposure to harmful emissions across the spectrum of nicotine delivery Ed Stephens University of St Andrews Declaration: No conflicts of interest
Scientific Evidence for Evaluating Modified Risk Tobacco Products
 Scientific Evidence for Evaluating Modified Risk Tobacco Products Presented to the IOM Committee on Scientific Standards for Modified Risk Tobacco Products May 9 th 2011, Washington DC 1 l Altria Client
Scientific Evidence for Evaluating Modified Risk Tobacco Products Presented to the IOM Committee on Scientific Standards for Modified Risk Tobacco Products May 9 th 2011, Washington DC 1 l Altria Client
UK E-Cigarette Summit Relative risks of cancer posed by combustible and vapourising forms of nicotine delivery: Evidence from chemical exposures
 UK E-Cigarette Summit 2017 Relative risks of cancer posed by combustible and vapourising forms of nicotine delivery: Evidence from chemical exposures Ed Stephens University of St Andrews Scope of presentation
UK E-Cigarette Summit 2017 Relative risks of cancer posed by combustible and vapourising forms of nicotine delivery: Evidence from chemical exposures Ed Stephens University of St Andrews Scope of presentation
Tobacco Control Research and Education, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA
 The Difference between IQOS and Continued Smoking Response to the article entitled PMI s own in vivo clinical data on biomarkers of potential harm in Americans show that IQOS is not detectably different
The Difference between IQOS and Continued Smoking Response to the article entitled PMI s own in vivo clinical data on biomarkers of potential harm in Americans show that IQOS is not detectably different
Reduced-Risk Products Science Update
 Reduced-Risk Products Science Update Dr. Ian Jones, PhD JTI VP, Reduced-Risk Products Science Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements. These statements appear in
Reduced-Risk Products Science Update Dr. Ian Jones, PhD JTI VP, Reduced-Risk Products Science Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements. These statements appear in
Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2
 Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2 THS 2.2. is commercialized under the IQOS brand name Dr Catherine Goujon Ginglinger - Philip Morris International Research & Development,
Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2 THS 2.2. is commercialized under the IQOS brand name Dr Catherine Goujon Ginglinger - Philip Morris International Research & Development,
In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS. Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program
 In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program 1 Outline: 1. In Vitro Toxicology Approach at IIVS 1. Science, Education, & Outreach
In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program 1 Outline: 1. In Vitro Toxicology Approach at IIVS 1. Science, Education, & Outreach
In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS. Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program
 In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program 1 Outline: 1. In Vitro Toxicology Approach at IIVS 1. Science, education, & outreach
In Vitro Models Available for Testing of ENDS Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Respiratory Toxicology Program 1 Outline: 1. In Vitro Toxicology Approach at IIVS 1. Science, education, & outreach
What is combustion and why is the absence of combustion important for heat not burn products
 What is combustion and why is the absence of combustion important for heat not burn products Global Forum on Nicotine 2017 June 16 th 2017 Thomas Mc Grath PhD PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Quai
What is combustion and why is the absence of combustion important for heat not burn products Global Forum on Nicotine 2017 June 16 th 2017 Thomas Mc Grath PhD PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Quai
Electronic Cigarettes, Nicotine and Policy Implications
 Electronic Cigarettes, Nicotine and Policy Implications Neal L Benowitz MD University of California San Francisco The E-Cigarette Summit The Royal Society London November 17, 2016 Disclosures Dr Benowitz
Electronic Cigarettes, Nicotine and Policy Implications Neal L Benowitz MD University of California San Francisco The E-Cigarette Summit The Royal Society London November 17, 2016 Disclosures Dr Benowitz
A. Incorrect! The alveolus is where gas exchange takes place. B. Correct! Surfactant is the lipid-rich material that permits lung inflation.
 Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Cardiovascular effects of nicotine vs. cigarette smoke
 Cardiovascular effects of nicotine vs. cigarette smoke Dr Konstantinos Farsalinos Researcher Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center, Greece University of Patras, Greece National School of Public Health, Athens-Greece
Cardiovascular effects of nicotine vs. cigarette smoke Dr Konstantinos Farsalinos Researcher Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center, Greece University of Patras, Greece National School of Public Health, Athens-Greece
E-Cigarettes: Current Perspective
 E-Cigarettes: Current Perspective Aruni Bhatnagar, Ph.D. Professor of Medicine University of Louisville Louisville, KY Electronic Cigarettes E-cigarettes are electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS),
E-Cigarettes: Current Perspective Aruni Bhatnagar, Ph.D. Professor of Medicine University of Louisville Louisville, KY Electronic Cigarettes E-cigarettes are electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS),
Carl D. D Ruiz 1*, Donald W. Graff 2 and Edward Robinson 3
 D Ruiz et al. BMC Public Health (2016) 16:543 DOI 10.1186/s12889-016-3236-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Reductions in biomarkers of exposure, impacts on smoking urge and assessment of product use and
D Ruiz et al. BMC Public Health (2016) 16:543 DOI 10.1186/s12889-016-3236-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Reductions in biomarkers of exposure, impacts on smoking urge and assessment of product use and
InhalT 90 Current Project Status
 InhalT 90 Current Project Status 90-Day Nose-Only Inhalation Toxicity Study of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Female Wistar Rats with subsequent Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles Sponsor s Study Monitor
InhalT 90 Current Project Status 90-Day Nose-Only Inhalation Toxicity Study of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Female Wistar Rats with subsequent Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles Sponsor s Study Monitor
Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2
 Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2 THS 2.2. is commercialized under the IQOS brand name Maya Mitova, Catherine Goujon Ginglinger, Michel Rotach, Serge Maeder Philip
Air Quality assessment during indoor use of the Tobacco Heating System 2.2 THS 2.2. is commercialized under the IQOS brand name Maya Mitova, Catherine Goujon Ginglinger, Michel Rotach, Serge Maeder Philip
A Primer on Acute Inhalation Toxicity Testing
 A Primer on Acute Inhalation Toxicity Testing Where do Alternative Methods Fit? Jon A. Hotchkiss, PhD Toxicology and Environmental Research and Consulting The Dow Chemical Company 1 Outline Why do we test?
A Primer on Acute Inhalation Toxicity Testing Where do Alternative Methods Fit? Jon A. Hotchkiss, PhD Toxicology and Environmental Research and Consulting The Dow Chemical Company 1 Outline Why do we test?
ICAP 2017, 3rd - 6th July 2017, Caparica, Portugal Philip Morris International is the sole source of funding and sponsor of this project.
 Thomas Schneider PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Quai Jeanrenaud 5, CH-2000 Neuchâtel, Switzerland (Part of Philip Morris International group of companies) ICAP 2017, 3rd - 6th July 2017, Caparica,
Thomas Schneider PMI R&D, Philip Morris Products S.A., Quai Jeanrenaud 5, CH-2000 Neuchâtel, Switzerland (Part of Philip Morris International group of companies) ICAP 2017, 3rd - 6th July 2017, Caparica,
Experimental trial on the effectiveness of IQOS compared to e-cigarettes and regular tobacco cigarettes
 Global Forum on Nicotine Rethinking Nicotine 2018 Experimental trial on the effectiveness of IQOS compared to e-cigarettes and regular tobacco cigarettes Effects on acute craving, withdrawal, positive
Global Forum on Nicotine Rethinking Nicotine 2018 Experimental trial on the effectiveness of IQOS compared to e-cigarettes and regular tobacco cigarettes Effects on acute craving, withdrawal, positive
ΕΝΑΛΛΑΚΤΙΚΕΣ ΜΟΡΦΕΣ ΚΑΠΝΙΣΜΑΤΟΣ
 ΕΝΑΛΛΑΚΤΙΚΕΣ ΜΟΡΦΕΣ ΚΑΠΝΙΣΜΑΤΟΣ E CIGARETTE ENDS:ELECTRONIC NICOTINE DELIVERY S Y S TEM) ΗΕΑΤ-ΝΟΤ-ΒURN CIGARETTES (IQOS) Κουρέα Καλλιρρόη Καρδιολόγος NICOTINE DELIVERY SYSTEMS NICOTINE DELIVERY SYSTEMS
ΕΝΑΛΛΑΚΤΙΚΕΣ ΜΟΡΦΕΣ ΚΑΠΝΙΣΜΑΤΟΣ E CIGARETTE ENDS:ELECTRONIC NICOTINE DELIVERY S Y S TEM) ΗΕΑΤ-ΝΟΤ-ΒURN CIGARETTES (IQOS) Κουρέα Καλλιρρόη Καρδιολόγος NICOTINE DELIVERY SYSTEMS NICOTINE DELIVERY SYSTEMS
E-Cigarette Update: Secondhand Vapour
 E-Cigarette Update: Secondhand Vapour Toxicity and Health Effects The popularity of e-cigarettes continues to increase, with more Canadians than ever using them indoors and out. The scientific evidence
E-Cigarette Update: Secondhand Vapour Toxicity and Health Effects The popularity of e-cigarettes continues to increase, with more Canadians than ever using them indoors and out. The scientific evidence
R. Balansky 1,2, F. D Agostini 2, A. Izzotti 2, P. Kalpakam 3, V.E. Steele 4, S. De Flora 2
 INCON / 10 ICMAA, Guarujà, Brazil, September 26-29, 2010 MECHANISMS OF INHIBITION OF CIGARETTE SMOKE GENOTOXICITY AND CARCINOGENICITY 1 2 3 4 R. Balansky 1,2, F. D Agostini 2, A. Izzotti 2, P. Kalpakam
INCON / 10 ICMAA, Guarujà, Brazil, September 26-29, 2010 MECHANISMS OF INHIBITION OF CIGARETTE SMOKE GENOTOXICITY AND CARCINOGENICITY 1 2 3 4 R. Balansky 1,2, F. D Agostini 2, A. Izzotti 2, P. Kalpakam
4. Other Data Relevant to an Evaluation of Carcinogenicity and its Mechanisms
 212 4. Other Data Relevant to an Evaluation of Carcinogenicity and its Mechanisms 4.1 Deposition, retention, clearance and metabolism The absorption and distribution of indium is highly dependent on its
212 4. Other Data Relevant to an Evaluation of Carcinogenicity and its Mechanisms 4.1 Deposition, retention, clearance and metabolism The absorption and distribution of indium is highly dependent on its
Evaluation of the Potential for Second-hand Exposure to E-cigarette Aerosol in an Office Environment
 Evaluation of the Potential for Second-hand Exposure to E-cigarette Aerosol in an Office Environment Edward A. Robinson, Robert D. Leverette, and Manoj Misra Lorillard Tobacco Company 68 th TSRC Charlottesville,
Evaluation of the Potential for Second-hand Exposure to E-cigarette Aerosol in an Office Environment Edward A. Robinson, Robert D. Leverette, and Manoj Misra Lorillard Tobacco Company 68 th TSRC Charlottesville,
PROCEDURE FOR GENERATION AND TESTING OF MAINSTREAM TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS or IQOS) AEROSOL USING A LINEAR SMOKING MACHINE
 PROCEDURE FOR GENERATION AND TESTING OF MAINSTREAM TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS or IQOS) AEROSOL USING A LINEAR SMOKING MACHINE 1 P age Table of contents / Table des matières 1 Introduction...3 1 Scope...3
PROCEDURE FOR GENERATION AND TESTING OF MAINSTREAM TOBACCO HEATING SYSTEM (THS or IQOS) AEROSOL USING A LINEAR SMOKING MACHINE 1 P age Table of contents / Table des matières 1 Introduction...3 1 Scope...3
Review of Histopathological Changes in the Respiratory Tract of Rat Induced by Inhalation of the Mainstream Smoke of Standard Reference Cigarette 1R4F
 Review of Histopathological Changes in the Respiratory Tract of Rat Induced by Inhalation of the Mainstream Smoke of Standard Reference Cigarette 1R4F A. Teredesai LSRO Meeting, Dec., 13, 2001 Slide 1
Review of Histopathological Changes in the Respiratory Tract of Rat Induced by Inhalation of the Mainstream Smoke of Standard Reference Cigarette 1R4F A. Teredesai LSRO Meeting, Dec., 13, 2001 Slide 1
Investor Day Reduced-Risk Products Lausanne, September 29, 2016
 Investor Day Reduced-Risk Products Lausanne, September 29, 2016 Manuel Peitsch Chief Scientific Officer, Reduced-Risk Products Mirek Zielinski President, Reduced-Risk Products Investor Day Reduced-Risk
Investor Day Reduced-Risk Products Lausanne, September 29, 2016 Manuel Peitsch Chief Scientific Officer, Reduced-Risk Products Mirek Zielinski President, Reduced-Risk Products Investor Day Reduced-Risk
Assessing the impact of Ploom TECH use on indoor air quality (IAQ)
 Assessing the impact of Ploom TECH use on indoor air quality (IAQ) ISoNTech June 14, 2018 Dr. Ian Jones VP Reduced-Risk Products Science, JTI Reduce- Risk Products RRP Science Source reference for the
Assessing the impact of Ploom TECH use on indoor air quality (IAQ) ISoNTech June 14, 2018 Dr. Ian Jones VP Reduced-Risk Products Science, JTI Reduce- Risk Products RRP Science Source reference for the
Biomarker (BMK) Sub-Group 2017 Report
 Biomarker (BMK) Sub-Group 2017 Report Kitzbühel, Austria October 10, 2017 Coordinator: G. L. Prasad Secretary: Kirk Newland Scientific Commission Liaison: Paul Harp Biomarker Sub-Group Objectives Objective
Biomarker (BMK) Sub-Group 2017 Report Kitzbühel, Austria October 10, 2017 Coordinator: G. L. Prasad Secretary: Kirk Newland Scientific Commission Liaison: Paul Harp Biomarker Sub-Group Objectives Objective
Responsible Practice in E-Vapour Products (EVP) Product Stewardship
 Responsible Practice in E-Vapour Products (EVP) Product Stewardship Tanvir Walele, MSc, ERT 11 October 2016 1 Responsible Practice Responsible practice can be divided in to 3 areas: Pre-market product
Responsible Practice in E-Vapour Products (EVP) Product Stewardship Tanvir Walele, MSc, ERT 11 October 2016 1 Responsible Practice Responsible practice can be divided in to 3 areas: Pre-market product
The concept that not all tobacco and nicotine products
 A Model Risk Continuum for Tobacco and Nicotine Products by Chris Proctor, Sudhanshu Patwardhan, and James Murphy The concept that not all tobacco and nicotine products present the same risks to human
A Model Risk Continuum for Tobacco and Nicotine Products by Chris Proctor, Sudhanshu Patwardhan, and James Murphy The concept that not all tobacco and nicotine products present the same risks to human
Read Across with Metabolomics for Phenoxy Herbicides a Case Study with MCPP BASF SE
 Read Across with Metabolomics for Phenoxy Herbicides a Case Study with MCPP BASF SE Prof. Dr. Bennard van Ravenzwaay, BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany Experimental Toxicology and Ecology 1 Introduction: Case
Read Across with Metabolomics for Phenoxy Herbicides a Case Study with MCPP BASF SE Prof. Dr. Bennard van Ravenzwaay, BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany Experimental Toxicology and Ecology 1 Introduction: Case
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Challenges in Nonclinical Development of Inhalation Drug Products
 Challenges in Nonclinical Development of Inhalation Drug Products Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Senior Pharmacologist DPARP, CDER August 6, 2015 Rockville, MD Disclaimer This speech reflects the views of the speaker
Challenges in Nonclinical Development of Inhalation Drug Products Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Senior Pharmacologist DPARP, CDER August 6, 2015 Rockville, MD Disclaimer This speech reflects the views of the speaker
Analysis and Evaluation of a Cross-Sectional Study IEA World Congress of Epidemiology 20 th August Saitama, Japan
 Analysis and Evaluation of a Cross-Sectional Study IEA World Congress of Epidemiology 20 th August Saitama, Japan A van der Plas, L Prieto, D Skiada, M Dobrynina, G Baker, F Ludicke PMI R&D, Philip Morris
Analysis and Evaluation of a Cross-Sectional Study IEA World Congress of Epidemiology 20 th August Saitama, Japan A van der Plas, L Prieto, D Skiada, M Dobrynina, G Baker, F Ludicke PMI R&D, Philip Morris
Evaluation of Nicotine Pharmacokinetics and Subjective Effects following Use of a Novel Nicotine Aerosol System
 Evaluation of Nicotine Pharmacokinetics and Subjective Effects following Use of a Novel Nicotine Aerosol System A. Teichert 1, P. Brossard 1, L. Felber Medlin 1, L. Sandalic 1, J. Ancerewicz 1, M. Franzon
Evaluation of Nicotine Pharmacokinetics and Subjective Effects following Use of a Novel Nicotine Aerosol System A. Teichert 1, P. Brossard 1, L. Felber Medlin 1, L. Sandalic 1, J. Ancerewicz 1, M. Franzon
CULTEX RFS. CULTEX Technology an innovation for in vitro cell exposure. about us. products. Kazuo Kanazawa. Inhalation Toxicity Testing
 an innovation for in vitro cell exposure Hario Science Co., Ltd. about us Tokyo, Japan Scientific branch of Hario Glass Corporation Kazuo Kanazawa Hario Science Co., Ltd. 2/34 Laboratory glassware Hario
an innovation for in vitro cell exposure Hario Science Co., Ltd. about us Tokyo, Japan Scientific branch of Hario Glass Corporation Kazuo Kanazawa Hario Science Co., Ltd. 2/34 Laboratory glassware Hario
3D Reconstructed Human Airway Models: Effect of Acclimation Conditions on Biomarker and Inflammatory Response Following Tissue Challenge
 3D Reconstructed Human Airway Models: Effect of Acclimation Conditions on Biomarker and Inflammatory Response Following Tissue Challenge Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Inhalation Toxicology
3D Reconstructed Human Airway Models: Effect of Acclimation Conditions on Biomarker and Inflammatory Response Following Tissue Challenge Holger P. Behrsing, Ph.D. Principal Scientist Inhalation Toxicology
Might Smoking Rates go up in Flames? Dr John Schoonbee, Chief Medical Officer, Swiss Re
 Might Smoking Rates go up in Flames? Dr John Schoonbee, Chief Medical Officer, Swiss Re 2 Agenda Smoking is still a problem Stopping is hard Electronic cigarettes Reduced Risk tobacco products Males >15yr
Might Smoking Rates go up in Flames? Dr John Schoonbee, Chief Medical Officer, Swiss Re 2 Agenda Smoking is still a problem Stopping is hard Electronic cigarettes Reduced Risk tobacco products Males >15yr
Next Generation Products Sandra Costigan, Marianna Gaca, ChuanLiu, Kevin McAdam, James J. Murphyand Christopher Proctor British American Tobacco 21
 Next Generation Products Sandra Costigan, Marianna Gaca, ChuanLiu, Kevin McAdam, James J. Murphyand Christopher Proctor British American Tobacco 21 st October 2015 Contents Evolution of products across
Next Generation Products Sandra Costigan, Marianna Gaca, ChuanLiu, Kevin McAdam, James J. Murphyand Christopher Proctor British American Tobacco 21 st October 2015 Contents Evolution of products across
The decision on actual implementation depends on the results of a further consequence analysis.
 00- allylamine interim TSD Probit function technical support document Date: February 0 Document id: 00-allylamine-interim Status: interim Author: drs. W. ter Burg, RIVM substance name CAS number Allylamine
00- allylamine interim TSD Probit function technical support document Date: February 0 Document id: 00-allylamine-interim Status: interim Author: drs. W. ter Burg, RIVM substance name CAS number Allylamine
Healthy Lungs. Presented by: Brandi Bishop, RN and Patty Decker, RRT, RCP
 Healthy Lungs Presented by: Brandi Bishop, RN and Patty Decker, RRT, RCP Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease includes 1. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2. Asthma
Healthy Lungs Presented by: Brandi Bishop, RN and Patty Decker, RRT, RCP Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease includes 1. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2. Asthma
Science, Hazard and Risk in the European Union: The Case of TiO 2 Exposures
 Science, Hazard and Risk in the European Union: The Case of TiO 2 Exposures David B. Warheit Ph.D, Chemours Company, Wilmington, Delaware USA Inhaled Particles XII Meeting, Glasgow, UK September 25, 2017
Science, Hazard and Risk in the European Union: The Case of TiO 2 Exposures David B. Warheit Ph.D, Chemours Company, Wilmington, Delaware USA Inhaled Particles XII Meeting, Glasgow, UK September 25, 2017
Risks of smoking on health: Long-term impact
 Risks of smoking on health: Long-term impact Ahmed Basheer Alazmi Family Medicine Specialist, e-mail: dr.aazmi@yahoo.com Abstract Risk of smoking is increasing day by day; cigarettes contain toxic chemicals
Risks of smoking on health: Long-term impact Ahmed Basheer Alazmi Family Medicine Specialist, e-mail: dr.aazmi@yahoo.com Abstract Risk of smoking is increasing day by day; cigarettes contain toxic chemicals
Exploring five common claims about e-cigarette use. Lion Shahab, PhD University College
 Exploring five common claims about e-cigarette use Lion Shahab, PhD University College London @LionShahab Claim 1: Renormalisation Claim 1: Renormalisation A priori predictions for impact on population
Exploring five common claims about e-cigarette use Lion Shahab, PhD University College London @LionShahab Claim 1: Renormalisation Claim 1: Renormalisation A priori predictions for impact on population
RE: Docket No. FDA-2014-N , Electronic Cigarettes and the Public Health
 VIA ELECTRONIC SUBMISSION June 30, 2015 Division of Dockets Management (HFA-305) Food and Drug Administration 5630 Fishers Lane, Rm. 1061 Rockville, MD 20852 RE: Docket No. FDA-2014-N-1936-0001, Electronic
VIA ELECTRONIC SUBMISSION June 30, 2015 Division of Dockets Management (HFA-305) Food and Drug Administration 5630 Fishers Lane, Rm. 1061 Rockville, MD 20852 RE: Docket No. FDA-2014-N-1936-0001, Electronic
BELL WORK. Today we start a new chapter, tobacco. What are some of the health risk you think you would have if you were to use tobacco.
 BELL WORK Today we start a new chapter, tobacco. What are some of the health risk you think you would have if you were to use tobacco. TOBACCO FACTS ABOUT TOBACCO OBJECTIVES recognize the various forms
BELL WORK Today we start a new chapter, tobacco. What are some of the health risk you think you would have if you were to use tobacco. TOBACCO FACTS ABOUT TOBACCO OBJECTIVES recognize the various forms
CHARACTERIZING PASSIVE EXPOSURE TO TOBACCO SMOKE
 this Paper, the health effects literature is described and evaluated using conventional standards of evidence accepted by the scientific community, and in relation to any specific standards that have been
this Paper, the health effects literature is described and evaluated using conventional standards of evidence accepted by the scientific community, and in relation to any specific standards that have been
Data and Knowledge Fusion: Supporting Toxicology, Health Effects Endpoints Analysis & Human Health Risk Assessment
 Data and Knowledge Fusion: Supporting Toxicology, Health Effects Endpoints Analysis & Human Health Risk Assessment OpenTox Asia May 17-18, 2017 Asish Mohapatra Health Canada Disclaimer This presentation
Data and Knowledge Fusion: Supporting Toxicology, Health Effects Endpoints Analysis & Human Health Risk Assessment OpenTox Asia May 17-18, 2017 Asish Mohapatra Health Canada Disclaimer This presentation
Electronic cigarettes: Pre-clinical and clinical assessment
 Disclaimer: The information in these materials is a formal dissemination of information by BAT and issues discussed in my presentation are not in any official manner related to/voiced by EUROTOX or its
Disclaimer: The information in these materials is a formal dissemination of information by BAT and issues discussed in my presentation are not in any official manner related to/voiced by EUROTOX or its
Diseases caused by Smoking
 Name: Class: Date: Diseases caused by Smoking Biology Gr11A Diseases caused by Smoking Unless you're living in a cave under the heart of Kentucky tobacco country, you know that smoking isn't exactly the
Name: Class: Date: Diseases caused by Smoking Biology Gr11A Diseases caused by Smoking Unless you're living in a cave under the heart of Kentucky tobacco country, you know that smoking isn't exactly the
Analysis of 18 Urinary Mercapturic Acids by two Multiplex-LC-MS/MS Methods
 Analysis of 18 Urinary Mercapturic Acids by two Multiplex-LC-MS/MS Methods Nikola Pluym, Gerhard Gilch, Gerhard Scherer, Max Scherer ABF, Analytisch-Biologisches Forschungslabor GmbH, München, Germany
Analysis of 18 Urinary Mercapturic Acids by two Multiplex-LC-MS/MS Methods Nikola Pluym, Gerhard Gilch, Gerhard Scherer, Max Scherer ABF, Analytisch-Biologisches Forschungslabor GmbH, München, Germany
Harmful and potentially harmful constituents in e-cigarettes
 Harmful and potentially harmful constituents in e-cigarettes Prof. Riccardo Polosa Institute of Internal Medicine Centre for the Prevention and Cure of Tabagism University of Catania - ITALY Global Forum
Harmful and potentially harmful constituents in e-cigarettes Prof. Riccardo Polosa Institute of Internal Medicine Centre for the Prevention and Cure of Tabagism University of Catania - ITALY Global Forum
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
AsiaTIDES 2012: Formulation and Delivery of Peptides and Oligonucleotides Strategies for Delivery of RNAi Therapeutics. March 1, 2012 Akin Akinc, PhD
 AsiaTIDES 2012: Formulation and Delivery of Peptides and Oligonucleotides Strategies for Delivery of RNAi Therapeutics March 1, 2012 Akin Akinc, PhD Lead Selection Alnylam RNAi Product Platform Turning
AsiaTIDES 2012: Formulation and Delivery of Peptides and Oligonucleotides Strategies for Delivery of RNAi Therapeutics March 1, 2012 Akin Akinc, PhD Lead Selection Alnylam RNAi Product Platform Turning
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Biomarkers in Public Health: Development and Applications
 Biomarkers in Public Health: Development and Applications Irina Stepanov, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Division of Environmental Health Sciences and Masonic Cancer Center University of Minnesota Biomarker
Biomarkers in Public Health: Development and Applications Irina Stepanov, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Division of Environmental Health Sciences and Masonic Cancer Center University of Minnesota Biomarker
Nonclinical Safety Evaluation of Inhalation Drug Products
 Nonclinical Safety Evaluation of Inhalation Drug Products February 13, 2002 Life Science Research Organization Bethesda, Maryland Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Drug Products Center
Nonclinical Safety Evaluation of Inhalation Drug Products February 13, 2002 Life Science Research Organization Bethesda, Maryland Luqi Pei, Ph.D. Division of Pulmonary and Allergy Drug Products Center
HHS Public Access Author manuscript J Patient Cent Res Rev. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2016 February 04.
 In adult smokers unwilling or unable to quit, does changing from tobacco cigarettes to electronic cigarettes decrease the incidence of negative health effects associated with smoking tobacco? A Clin-IQ
In adult smokers unwilling or unable to quit, does changing from tobacco cigarettes to electronic cigarettes decrease the incidence of negative health effects associated with smoking tobacco? A Clin-IQ
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Physical and chemical properties of cigarette, heated tobacco and e-cigarette aerosols
 SPS3 N2ff Physical and chemical properties of cigarette, heated tobacco and e-cigarette aerosols Caner U Yurteri, Jennifer Margham, Kevin McAdam, Mark Forster, Chuan Liu, Chris Wright, Derek Mariner, Chris
SPS3 N2ff Physical and chemical properties of cigarette, heated tobacco and e-cigarette aerosols Caner U Yurteri, Jennifer Margham, Kevin McAdam, Mark Forster, Chuan Liu, Chris Wright, Derek Mariner, Chris
Kevin Walton, Ph.D. Chief, Clinical Research Grants Branch Division of Therapeutics and Medical Consequences NIDA. No disclosures
 Kevin Walton, Ph.D. Chief, Clinical Research Grants Branch Division of Therapeutics and Medical Consequences NIDA No disclosures NIDA Organizational Chart Office of Diversity & Health Disparities Office
Kevin Walton, Ph.D. Chief, Clinical Research Grants Branch Division of Therapeutics and Medical Consequences NIDA No disclosures NIDA Organizational Chart Office of Diversity & Health Disparities Office
In vitro macrophage assays for selection of drug candidates for preclinical development. Philippa Allen GSK
 In vitro macrophage assays for selection of drug candidates for preclinical development. Philippa Allen GSK Role of macrophages in the lung First line of host defence to inhaled matter. Regulate immune
In vitro macrophage assays for selection of drug candidates for preclinical development. Philippa Allen GSK Role of macrophages in the lung First line of host defence to inhaled matter. Regulate immune
SAFETY E-CIGS: CLINICAL STUDIES
 SAFETY E-CIGS: CLINICAL STUDIES SAFETY ECIGS: clinical studies Source: Safety evaluation and risk assessment of electronic cigarettes as tobacco cigarette substitutes: A systematic review. Ther Adv Drug
SAFETY E-CIGS: CLINICAL STUDIES SAFETY ECIGS: clinical studies Source: Safety evaluation and risk assessment of electronic cigarettes as tobacco cigarette substitutes: A systematic review. Ther Adv Drug
ELECTRONIC CIGARETTES WHAT S THE BOTTOM LINE?
 ELECTRONIC CIGARETTES WHAT S THE BOTTOM LINE? E-cigarettes have the potential to benefit adult smokers who are not pregnant if used as a complete substitute for regular cigarettes and other smoked tobacco
ELECTRONIC CIGARETTES WHAT S THE BOTTOM LINE? E-cigarettes have the potential to benefit adult smokers who are not pregnant if used as a complete substitute for regular cigarettes and other smoked tobacco
Aerosol Characterisation of e-cigarettes. Ross Cabot, Anna Koc, Caner U. Yurteri & John McAughey
 Aerosol Characterisation of e-cigarettes Ross Cabot, Anna Koc, Caner U. Yurteri & John McAughey European Aerosol Conference, Prague 2-6 September 2013 1 Organisation Background Description History Regulation
Aerosol Characterisation of e-cigarettes Ross Cabot, Anna Koc, Caner U. Yurteri & John McAughey European Aerosol Conference, Prague 2-6 September 2013 1 Organisation Background Description History Regulation
BIOM5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam Fall 2013 page 1/5
 BIOM5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam Fall 2013 page 1/5 BIOM 5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam, Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University, December 12, 2013 Instructions: - This exam has 5 pages and 11
BIOM5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam Fall 2013 page 1/5 BIOM 5010 / BMG 5112: Final Exam, Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University, December 12, 2013 Instructions: - This exam has 5 pages and 11
Material Safety Data Sheet 47Industrial Park, Lilydale, Victoria 3140 Phone: Fax:
 This substance is classified as Hazardous according to the criteria of Worksafe Australia. Not classified as Dangerous Goods according to the criteria of ADG code. 1. MATERIAL AND SUPPLY COMPANY IDENTIFICATION
This substance is classified as Hazardous according to the criteria of Worksafe Australia. Not classified as Dangerous Goods according to the criteria of ADG code. 1. MATERIAL AND SUPPLY COMPANY IDENTIFICATION
ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY
 ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY Chapter 4 Toxicokinetics Mohd Amir Bin Arshad Toxicokinetics study on how a substance gets into the body and what happens to it in the body" The kinetics (movement) of substances
ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY Chapter 4 Toxicokinetics Mohd Amir Bin Arshad Toxicokinetics study on how a substance gets into the body and what happens to it in the body" The kinetics (movement) of substances
The effect of active and passive smoking on inhaled drugs in respiratory patients
 CHAPTER 12 The effect of active and passive smoking on inhaled drugs in respiratory patients G. Invernizzi*, A. Ruprecht*, P. Paredi #, R. Mazza*, C. De Marco*, R. Boffi* *Tobacco Control Unit, National
CHAPTER 12 The effect of active and passive smoking on inhaled drugs in respiratory patients G. Invernizzi*, A. Ruprecht*, P. Paredi #, R. Mazza*, C. De Marco*, R. Boffi* *Tobacco Control Unit, National
The Respiratory System
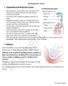 I. Organization of the Respiratory System The Respiratory System The respiratory system allows the circulation of air and the gas exchange between the body and the outside environment. It consists of the
I. Organization of the Respiratory System The Respiratory System The respiratory system allows the circulation of air and the gas exchange between the body and the outside environment. It consists of the
Regulatory Support for Tobacco Products. Feeling daunted by the regulatory process for tobacco products? Don t worry Battelle can help.
 Regulatory Support for Tobacco Products Feeling daunted by the regulatory process for tobacco products? Don t worry Battelle can help. PREMARKET TOBACCO (PMTA) HUMAN FACTORS STUDIES SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE
Regulatory Support for Tobacco Products Feeling daunted by the regulatory process for tobacco products? Don t worry Battelle can help. PREMARKET TOBACCO (PMTA) HUMAN FACTORS STUDIES SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE
Risk Assessment Report on styrene. Human Health Part
 Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks SCHER Risk Assessment Report on styrene Human Health Part CAS No.: 100-42-6 EINECS no.: 202-851-5 SCHER adopted this opinion at its 23 rd plenary
Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks SCHER Risk Assessment Report on styrene Human Health Part CAS No.: 100-42-6 EINECS no.: 202-851-5 SCHER adopted this opinion at its 23 rd plenary
Exhaled Biomarkers Asthma & COPD. AS Paul DM Seminar 30 March 07
 Exhaled Biomarkers Asthma & COPD AS Paul DM Seminar 30 March 07 Introduction Diagnosis and course of COPD/Asthma Clinical information Pulmonary function tests Arterial blood gases Chest X-raysX No direct
Exhaled Biomarkers Asthma & COPD AS Paul DM Seminar 30 March 07 Introduction Diagnosis and course of COPD/Asthma Clinical information Pulmonary function tests Arterial blood gases Chest X-raysX No direct
Changes in Biological and Functional Markers after Six Months, in Three Populations: THS 2.2 (IQOS ) Users, Continued Smokers, and Smoking Abstinence
 Changes in Biological and Functional Markers after Six Months, in Three Populations: THS 2.2 (IQOS ) Users, Continued Smokers, and Smoking Abstinence Christelle Haziza, PhD Manager Clinical Science Philip
Changes in Biological and Functional Markers after Six Months, in Three Populations: THS 2.2 (IQOS ) Users, Continued Smokers, and Smoking Abstinence Christelle Haziza, PhD Manager Clinical Science Philip
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
In Vitro Disease Model Development Current Challenges
 Advances in In Vitro Cell Culture, 22-23 May 2012, Utrecht, The Netherlands In Vitro Disease Model Development Current Challenges Damien Breheny British American Tobacco, Group Research and Development,
Advances in In Vitro Cell Culture, 22-23 May 2012, Utrecht, The Netherlands In Vitro Disease Model Development Current Challenges Damien Breheny British American Tobacco, Group Research and Development,
Ian Indans Regulatory scientist Chemicals Regulation Directorate (CRD)
 Health and Safety Executive Ian Indans Regulatory scientist Chemicals Regulation Directorate (CRD) Health and Safety Executive Acute Inhalation Toxicity testing; The 3Rs, Current needs and Future Prospects
Health and Safety Executive Ian Indans Regulatory scientist Chemicals Regulation Directorate (CRD) Health and Safety Executive Acute Inhalation Toxicity testing; The 3Rs, Current needs and Future Prospects
ABSTRACT TOXICOLOGICAL SCIENCES, 149(2), 2016,
 TOXICOLOGICAL SCIENCES, 149(2), 2016, 441 457 doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv244 Advance Access Publication Date: November 17, 2015 Research Article Effects of Cigarette Smoke, Cessation, and Switching to Two
TOXICOLOGICAL SCIENCES, 149(2), 2016, 441 457 doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv244 Advance Access Publication Date: November 17, 2015 Research Article Effects of Cigarette Smoke, Cessation, and Switching to Two
Smoking, e-cigs and reduced risk products. Dr John Schoonbee, IMS November 2017
 Smoking, e-cigs and reduced risk products Dr John Schoonbee, IMS November 2017 2 The storyline smoking is bad yet many folks still smoke because quitting is very hard is it better, if one cannot quit,
Smoking, e-cigs and reduced risk products Dr John Schoonbee, IMS November 2017 2 The storyline smoking is bad yet many folks still smoke because quitting is very hard is it better, if one cannot quit,
00:08 For decades our scientists have endeavoured to reduce the risks of tobacco use and continue to do so today. 00:15
 00:00 British American Tobacco 00:02 00:03 The Electronic Cigarette 00:07 00:08 For decades our scientists have endeavoured to reduce the risks of tobacco use and continue to do so today. 00:15 00:15 Our
00:00 British American Tobacco 00:02 00:03 The Electronic Cigarette 00:07 00:08 For decades our scientists have endeavoured to reduce the risks of tobacco use and continue to do so today. 00:15 00:15 Our
