Neoplastic transformation of epithelial cells in whole mammary gland in vitro
|
|
|
- Eugenia Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 76, No. 11, pp , November 1979 Medical Sciences Neoplastic transformation of epithelial cells in whole mammary gland in vitro (organ culture/7,12-dimethylbenz[alanthracene/carcinogenesis/mammary cells/balb/c mice) NITYANAND T. TELANG, MIHIR R. BANERJEE, ANAND P. IYER, AND AMIT B. KUNDU Tumor Biology Laboratory, School of Life Sciences, University of Nebraska, 201 Lyman Hall, Lincoln, Nebraska Communicated by James A. Miller, July 23, 1979 ABSTRACT Biological characteristics of nodule-like alveolar lesions (NLAL) induced by 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) in organ culture of whole mammary gland (BALB/c female mice) were assessed after transplantation into gland-free mammary fat pads of syngeneic virgin mice. (i)tissue-fragment explants from NLAL areas of the gland produced abnormal lobuloalveolar (LA) outgrowths in 3 of 10 fat pads. (il) Transplantation of dissociated cells of NLAL-derived LA outgrowths into 36 fat pads showed 100% LA outgrowths and 3 (8%) of these 36 outgrowths produced mammary carcinomas. (iii) The explants of dissociated cells from whole mammary glands treated with DMBA in culture produced full or partial LA structures in 2 of 56 outgrowths. (iv) The explants of dissociated cells prepared from outgrowths derived from explants as in iii produced 9 LA outgrowths in 16 instances; mammary tumor incidence in these outgrowths was 3 of 16 (18%). (v) The explants of tissue fragments from LA outgrowths as in iv produced LA outgrowths in 20 of 20 fat pads; mammary carcinomas appeared in 16 of 20 (80%) of these outgrowths. No NLAL was detectable in control glands treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (solvent for DMBA); explants of the control glands consistently produced ductal outgrowths and no tumor. This accomplishment of chemical carcinogen-induced neoplastic transformation of epithelial cells in vitro provides a model for studying carcinogenesis in an entire isolated organ. Use of the in vitro oncogenesis model of fibroblasts has produced impressive advances of knowledge about the pathogenesis of neoplasia (1, 2). Attempts to obtain transformation of epithelial cells in monolayer culture so far have been of limited success (3-5). However, induction of neoplastic transformation of cells in organ culture, in general, has remained a challenge, although 7,12-dimethylbenz[a ]anthracene (DMBA)-induced transformation in rat mammary slices in culture has been reported (6). Because human malignancies in different organs are mostly of epithelial cell origin, the need for an organ culture model for studying carcinogenesis in vitro has been emphasized in several reports (7-9). By using the organ culture model of the whole mammary gland (10-14), it has been found (15-18) that treatment of the gland in culture with hydrocarbon carcinogens (DMBA or 3- methylcholanthrene) induces nodule-like alveolar lesions (NLAL). DMBA also binds to DNA of the mammary cells in culture, indicating that DMBA action in organ culture of the whole mammary gland is consistent with the characteristics associated with most hydrocarbon carcinogen-induced tumorigenesis in vivo and in vitro (2, 19). In this report we present biological characteristics, including tumorigenesis, of mammary epithelial cells treated with DMBA in organ culture. The findings provide a demonstration of neoplastic transformation of epithelial cells in culture of the whole mammary organ in a serum-free medium. The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked "advertisement" in accordance with 18 U. S. C solely to indicate this fact. MATERIALS AND METHODS Animals, Organ Culture, DMBA Treatment, and NLAL Induction. Low-mammary-tumor strain BALB/c female mice free of mouse mammary tumor virus (MuMTV) activity were obtained through the National Cancer Institute. The procedures used for organ culture of the whole mammary gland, DMBA treatment, and NLAL induction were as described (16, 18, 20) Ėnzymatic Dissociation of Mammary Epithelial Cells. For cell dissociation (CD), mammary tissue (minced) was first incubated (370C) in a solution containing 1% collagenase and 1% hyaluronidase in Waymouth's medium, and this was followed by treatments with Pronase and DNase (21). This method of CD yields mostly epithelial cells with about 80-90% viability as monitored by the trypan blue exclusion test (21). In Vivo Transplantation of NLAL and Dissociated Cells. The biological characteristics of the mammary cells treated with DMBA or dimethyl sulfoxide (Me2SO; solvent for DMBA) in organ culture were determined in vivo by transplantation into gland-free mammary fat pads of syngeneic virgin hosts according to the standard procedure (22). Fig. 1 outlines the experimental protocol. Examination of s and Tumors. The outgrowths produced by the explants in the gland-free mammary fat pads at different times after transplantation were initially assessed in anesthetized (Nembutal) animals injected intraperitoneally with 0.75 ml of 0.5% trypan blue solution in 0.9% saline 24 hr before microscopic examination. The trypan blue staining facilitates tentative detection of the outgrowth (21). As needed, small fragments (-1 mm) of the outgrowth were transplanted into gland-free mammary fat pads of another batch of young hosts. The stained preparation of the fat pad was microscopically analyzed to confirm the morphological type of the outgrowth. Animals were palpated regularly for tumors; characteristics of the tumors were assessed by histopathology. Growth potential of tumor samples was tested by transplantation into intact mammary glands (inguinal) and into subcutaneous sites. RESULTS The morphology (Fig. 1) of DMBA-induced NLALs in organ culture of the whole mammary gland was as observed earlier (16, 18). The present experiments also showed that 70-80% of the glands contained NLAL, with an average of eight lesions per gland. No NLAL was observed in control glands treated with Me2SO. A similar high incidence of DMBA-induced NLAL in organ culture of the whole mammary gland also has been recently observed by Tonelli et al. (24). Abbreviations: DMBA, 7,12-dimethylbenzla lanthracene; NLAL, nodule-like alveolar lesion; MuMTV, mouse mammary tumor virus; CD, cell dissociation; Me2SO, dimethyl sulfoxide; Du, ductal; LADu, mixed lobuloalveolar plus ductal; LA, lobuloalveolar; LAT, lobuloalveolar with tumor; HAN, hyperplastic alveolar nodule. 5886
2 Medical Sciences: Telang et al. Series Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76 (1979) 5887 Series II 'p NLAL in regressed gland Culture LA gland Culture NLAL explant Pituitary stimulation CD CD explant CD1 CD1 explant Fragment explant CD1 CD1 explant CD2 CD2 explant Fragment explant FIG. 1. Experimental protocol for assessment of the biological characteristics of the mammary cells treated with DMBA in culture of the whole mammary organ. (Series I) Whole second thoracic mammary glands of 3- to 4-week-old female BALB/c mice were cultivated for 9 days in Waymouth's medium containing insulin, prolactin, and hydrocortisone each at 5 gg/ml and aldosterone at 1 Ag/ml. Between days 3 and 4 of culture the glands were treated for 24 hr with DMBA (7.8 MsM); control glands were treated with Me2SO (0.2% of medium). Subsequent 15-day cultivation in medium with insulin and aldosterone caused alveolar regression, and NLALs (indicated by arrow in the photograph) were present only in DMBA-treated glands (for details see refs. 16 and 20). One tissue fragment (fragment explant, t1 mm) from a NLAL area was transplanted into the right gland-free inguinal mammary fat pad of a syngeneic virgin host; the left side carried the control explant. Host animals bearing primary NLAL explants also carried a pituitary (from syngeneic male) isograft in the right kidney capsule during the initial 6 weeks after transplantation. [Pituitary stimulation during the initial weeks is conducive to expression of transformed cells in DMBA-induced precancerous hyperplastic alveolar nodules (HAN) of mouse mammary gland in vivo (23).] For preparation of CD explants, fat pads carrying NLAL-derived lobuloalveolar (LA) outgrowths (see Table 1) were pooled and subjected to CD. The CD explant containing 5 X 105 cells in 10,l of Waymouth's medium was then injected into one gland-free inguinal mammary fat pad of syngeneic virgin host as described (21). (Series II) The initial 9-day cultivation and DMBA or Me2SO treatments of the glands were as in series I. Whole LA glands (as illustrated) were subjected to CD. The dissociated cells contained in CD1 explants were then injected into the gland-free fat pads as in series I. For preparation of CD2 explants, the outgrowths from CD1 explants were subjected to CD. The CD2 explants containing these outgrowth cells were then injected into gland-free fat pads as in series I. Assessment of NLAL Explants. Table 1 shows the characteristics of NLAL analyzed in series I experiments outlined in Fig. 1. After transplantation into gland-free mammary fat pads, fragment explants of NLAL areas produced ductal (Du), mixed lobuloalveolar plus ductal (LADu), and lobuloalveolar (LA) outgrowths in generation 1 (Fig. 2). Fragment explants of LA outgrowth obtained in generation 1 and carried through serial fat pad transplantation continued to produce LA outgrowths (generations 2 and 3A) in virgin hosts. Fragment explants of Me2SO-treated tissue carried in contralateral fat pads of the host animals consistently produced only Du type outgrowth at transplant generations 1, 2, and 3A (Fig. 2c). Mammary fat pad transplantation of dissociated cells of outgrowths derived from DMBA-induced hyperplastic alveolar nodule (HAN) of mouse mammary gland in vivo has been reported to elicit an enhanced expression of the latent neoplastic cells (25, 26). In the present study, CD explants prepared from NLAL-derived generation 2 LA outgrowths were transplanted into 36 gland-free mammary fat pads of virgin hosts. In generation 3B all 36 CD explants produced LA outgrowths, filling the fat pad within 8-10 weeks (Table 1). Mammary carcinomas appeared in three of these outgrowths between 2 and 5 months after transplantation (Fig. 3). CD explants prepared from generation 2 outgrowths produced by fragment explants from Me2SO-treated glands produced only Du outgrowth in contralateral fat pads.
3 5888 Medical Sciences: Telang et al. Table 1. Types of outgrowth derived from DMBA-induced NLAL after mammary fat pad transplantation Host No. of Gener- age, fat type* ation wk pads Du LADu LA LAT it A B * Du, ductal; LADu, mixed ductal and alveolar; LA, lobuloalveolar; LAT, lobuloalveolar with tumor. t Pituitary stimulation during the initial 6 weeks and outgrowth were examined 10 wk after cauterization of the grafted pituitary. Generation 2 outgrowth was obtained from one of the generation 1 LA outgrowths (the remaining two were used for whole-mount preparation). Both 3A and 3B were generation 3- outgrowths, 3A from fragment explants and 3B from CD explants. Sixteen generation 2 LA outgrowths from a different batch of host animals were pooled for CD (for details see Fig. 1).-Me2SO-treated cells, both in fragment and CD explants, consistently produced only Du type outgrowth.. t C re~~~~~~d Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76 (1979) Allq6*IV Assessment of CD1 Explants. Table 2 shows the results of CD1 experiments indicated in series II of Fig. 1. Among the total of 56 outgrowths derived from CD1 explants, 54 were Du, 1 was LADu, and 1 was LA in generation 1. Morphology of the single LA outgrowth was essentially as illustrated in Fig. 2a. Fragments from CDI-derived single LA outgrowth and from the LA region of the LADu outgrowth after retransplantation into gland-free fat pads produced similar LA outgrowth in generation 2 (Fig. 4 a and b). Fig. 4c illustrates a typical Du type outgrowth derived from CDI explant from Me2SO-treated control glands. Assessment of CD2 Explants. As outlined also in series II of Fig.- 1, CD2 explants used in these experiments were prepared a m _ b c _ FIG. 2. Different types of outgrowths derived from NLAL explants. (X1O.) (a) LA outgrowth of NLAL primary explant in virgin host 10 wk after withdrawal of pituitary stimulation. The characteristics are typical of the outgrowth obtained in subsequent transplant generations in virgin hosts. (b) Mixed LADu type outgrowth derived from a primary NLAL explant. The arrow points to the LA area. (c) Typical Du outgrowth derived from a primary explant of Me2SOtreated gland in the contralateral fat pads. FIG. 3. Mammary tumor obtained from outgrowths of CD explant containing cells (X200.) prepared from a NLAL-derived outgrowth line. from outgrowths produced by different batches of CD1 explants of DMBA-treated glands. Table 3 shows that, in experiment I, three of seven CD2 explants of 2 X 105 cells produced LA outgrowths and one of the LA outgrowths produced a rapidly growing mammary carcinoma (of the type shown in Fig. 3), 10 months after transplantation. In experiment II, six of nine CD2 explants of 1 X 105 cells produced dense LA outgrowths. Mammary carcinomas appeared in two of these outgrowths 6-8 months after transplantation. In control experiments, CD2 explants were prepared from outgrowths obtained from CD1 explants of Me2SO-treated glands. The control CD2 explants in experiments I and II produced only Du outgrowths in contralateral fat pads. In experiment III, fragment explants from two of the LA outgrowths obtained in experiment IH were retransplanted, one into the right and the--other into the left gland-free fat pads of another batch of virgin hosts (Table 3). The dense LA structure in 20 of 20 outgrowths filled the fat pads in 8 weeks; within 4-5 months, mammary carcinomas appeared in 16 of these 20 outgrowths (Fig. 5). Thus, 22 mammary tumors were observed in LA outgrowths produced by the explants of mammary cells treated with DMBA in organ culture. The tumors were transplantable into intact mammary gland as well as into subcutaneous sites. Table 2. Types of outgrowth derived from CD1 explants of DMBA-treated glands Host No. of No. of age, fat cells in type Exp. wk pads explant Du LADu LA LAT I x II X III x An average of DMBA- or Me2SO-treated glands (36.8 mg per gland), pooled for each CD, yielded -4.9 X 106 cells. Me2SO control explants produced only Du type outgrowths in contralateral fat pads (for details see Fig. 1).
4 Medical Sciences: Telang et al. ''"~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~I FIG. 5. Mammary adenocarcinoma in a typical hyperplastic LA Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76 (1979) 5889 outgrowth derived from CD2 explants. (X80.) b~i FIG. 4. s obtained from CD1 explants. Ln, lymph node. (X10.) (a) LADu type mixed outgrowth. The arrow points to the LA area. (b) LA outgrowth derived from explants of LA area of the outgrowth in a. (c) Typical Du outgrowth derived from CD1, Me2SO control explants. DISCUSSION The present findings on the ability of the NLAL explants to produce serially transplantable LA outgrowths in mammary fat pads of virgin host strongly indicate that the nodule transformation, associated with an escape of some mammary epithelial cells in NLAL from "normal" hormonal control, is irreversible and their characteristics appear to be similar to those of outgrowths derived from DMBA-induced HAN of mouse mammary gland in vivo (26, 27). Furthermore, the appearance of several mammary tumors in the LA outgrowths obtained from NLAL-derived CD explants clearly demonstrates that neoplastic transformation of mammary epithelial cells is inducible by DMBA in organ culture of the whole mammary gland. The presence of latent neoplastic cells in NLAL further suggests that at least some of the NLAL induced in culture are potentially carcinogenic. Normal-appearing ductal outgrowths consistently produced by explants of Me2SO-treated glands indicate that the transformation is a consequence of DMBA treatment of the mammary cells in organ culture. In an earlier attempt, intact Table 3. Different types of outgrowths produced by CD2 explants after mammary fat pad transplantation Age of No. of mice, fat Type of type Exp. wk pads explant Du LADu LA LAT CD2 (2 X 105) II CD2 (1 x 105) III Tissue fragment The CD1 explants used in these experiments were prepared from batches of glands different from those in Table 2. In Exp. I and II, 16 and 12 outgrowths, respectively, produced by two different batches of CDl explants were used. In Exp. III, tissue fragments from the two LA outgrowths obtained in Exp. II were transplanted into opposite gland-free fat pads. Me2SO control explants in Exps. I and II produced only Du type outgrowth (for details see Fig. 1). mammary gland (rat) exposed (20 min) to DMBA in culture was found to produce mammary tumor on transplantation in vivo, but carryover of the hydrocarbon into the site of transplantation remained a distinct possibility in this single preliminary experiment (28). In CD1 experiments, only two explants of DMBA-treated glands showed abnormal LA or LADu structures. The LADu type outgrowths obtained from both NLAL and CD1 explants appear to resemble the LADu outgrowths derived from dissociated mammary cells of BALB/cfC3H (MuMTV+) female mice (21). Fragment explants of the LA outgrowth and LA region of the LADu outgrowth obtained from CD1 explants produced LA outgrowth in generation 2, indicating the irreversible nature of the transformation. The CD1 experiments, however, do not provide information as to whether the LA or LADu outgrowths are derived from NLAL or non-nlal areas because the explants represent the total cell population of the glands pooled. Nonetheless, the morphological characteristics of the LA- or LADu-derived LA outgrowths appear to be similar to those derived from NLAL explants. Because CD1 explants of Me2SO-treated glands consistently produced Du outgrowths, LA and LADu type transformations observed in the CD1 experiments again reflect responses of the mammary cells to DMBA action in organ culture. Because the CD procedure is known to favor expression of inapparent transformed cells (21), the occurrence of LA and LADu characteristics in only 2 of 56 outgrowths derived from the CD1 explants appears rather low. However, recent findings (25) have indicated that mixing CD explants of HAN cells with dissociated normal mammary epithelial cells markedly decreases expression of transformed HAN cells, and the effect is directly related to the ratio of normal to HAN cells in the mixture. The CD1 explants in the present study are expected to contain mostly "normal" cells because in these experiments whole lobuloalveolar glands were used for CD (Fig. 1). Therefore, the presence of a vast excess of "normal" mammary cells may mask expression of the transformed cells in CD1 explants. Normal mammary cells are also known to have a finite life expectancy, whereas nodule-transformed (HAN) mammary cells have an unlimited proliferative potential (29). Thus, it is conceivable that the ratio of normal to transformed cells may be decreased during rapid spatial proliferation of the cells in CD1 explants filling the fat pad. Consequently, explants of CD2
5 5890 Medical Sciences: Telang et al. cells may be more conducive to enhanced expression of the transformed cells. The appearance of typical LA outgrowths in 9 of 16 CD2 explants clearly indicates a markedly increased expression of the latent transformed cells, apparently present in outgrowths of CD1 explants. The expression of neoplastic cells is also favored in outgrowths derived from CD2 explants, as evidenced by the appearance of several mammary tumors. Furthermore, fragment explants of CD2-derived LA outgrowths after fat pad transplantation produced mammary tumors in 16 of 20 outgrowths in the following generation. The results of the present studies demonstrate that both nodule and tumor transformation of epithelial cells are inducible by a carcinogenic chemical in culture of the whole mammary gland. The transformation is associated with the occurrence of discrete alveolar lesions (NLAL), some of which produce serially transplantable LA outgrowths having tumorigenic potential. In this respect, the NLAL appears to be analogous to the precancerous HAN induced by MuMTV or carcinogenic chemicals in mouse mammary gland in vivo (26, 30). NLALs detectable within 2-3 weeks after carcinogen treatment in culture thus may provide morphologic criteria useful for bioassay of potential carcinogens and drugs. NLALs are inducible also by carcinogenic aryl amines and amides (24), and a study indicates that retinoid inhibits DMBA-induction of these lesions (31). We thank Dr. M. Rustia for pathologic diagnosis of the tumors, Drs. S. Nandi and K. B. DeOme for helpful discussions, and Ms. Arvilla Kirchhoff for secretarial assistance. This work was supported by Contract N01-CP from the National Cancer Institute. 1. Casto, B. C. & DiPaolo, J. A. (1973) Progr. Med. Virol. 16, Heidelberger, C. (1975) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 44, Yamada, T., Takoka, T., Katsuta, H., Namba, M. & Sato, J. (1972) Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 42, Williams, G. M., Elliott, J. M. & Wiseburger, J. H. (1973) Exp. Cell Res. 69, Richards, J. & Nandi, S. (1978) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, Dao, T. L. & Sinha, D. (1972) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 49, Lasnitzki, I. (1963) Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 12, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76 (1979) 8. Roller, M. R. & Heidelberger, C. (1967) Int. J. Cancer 2, Heidelberger, C. (1973) Adv. Cancer Res. 18, Ichinose, R. R. & Nandi, S. (1966) J. Endocrinol. 35, Mehta, R. G. & Banerjee, M. R. (1975) Acta Endocrinol. 80, Banerjee, M. R., Terry, P. M., Sakai, S. & Lin, F. K. (1977) J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 3, Wood, B. G., Washburn, L. L., Mukherjee, A. S. & Banerjee, M. R. (1975) J. Endocrinol. 65, Terry, P. M., Banerjee, M. R. & Lui, R. M. (1977) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, Banerjee, M. R., Wood, B. G. & Washburn, L. L. (1974) J. NatI. Cancer Inst. 53, Lin, F. K., Banerjee, M. R. & Crump, L. R. (1976) Cancer Res. 36, Banerjee, M. R. (1976) Int. Rev. Cytol. 47, Kundu, A. B., Telang, N. T. & Banerjee, M. R. (1978) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 61, Miller, E. C. & Miller, J. A. (1974) in Molecular Biology of Cancer, ed. Busch, H. (Academic, New York), pp Banerjee, M. R., Wood, B. G., Lin, F. K. & Crump,-L. L. (1976) in Tissue Culture Assoc. Manual, ed. Sanford, K. K. (Tissue Culture Association, Rockville, MD), Vol. 2, pp * 21. DeOme, K. B., Miyamoto, M. J., Osborn, R. C., Guzman, R. C. & Lum, K. (1978) Cancer Res. 38, DeOme, K. B., Faulkin, L. J., Jr., Bern, H. A. & Blair, P. B. (1959) Cancer Res. 19, Medina, D. (1974) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 53, Tonelli, Q. J., Custer, P. R. & Sorof, S. (1979) Cancer Res. 39, Medina, D., Shepherd, F. & Gropp, D. (1978) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 60, Medina, D. (1978) in Breast Cancer, ed. McGuire, W. L. (Plenum, New York), Vol. 2, pp Medina, D. (1974) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 53, Brennan, M. J., Grace, W. H. & Singly, J. A. (1966) Proc. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 6, 9 (abstr.). 29. Daniel, C. W., DeOme, K. B., Young, L. J. T., Blair, P. B. & Faulkin, L. J., Jr. (1968) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 61, Bern, H. A. & Nandi, S. (1961) Progr. Exp. Tumor Res. 2, Dickens, M. S., Custer, P. R. & Sorof, S. (1979) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76,
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Cell Organization and Responsiveness to Hormones in Vitro: Genesis of Domes in Mammary Cell Cultures
 AMER. ZOOL., 15:231-236 (1975). Cell Organization and Responsiveness to Hormones in Vitro: Genesis of Domes in Mammary Cell Cultures CHARLES M. MCGRATH Division of Biology, Michigan Cancer Foundation,
AMER. ZOOL., 15:231-236 (1975). Cell Organization and Responsiveness to Hormones in Vitro: Genesis of Domes in Mammary Cell Cultures CHARLES M. MCGRATH Division of Biology, Michigan Cancer Foundation,
ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC CELLS IN MOUSE LEUKEMIA INDUCED BY N-BUTYLNITROSOUREA*1. ed by cytotoxicity tests. Cells from leukemia without thymus involvement
 [Gann, 66, 37-42; February, 1975] ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC CELLS IN MOUSE LEUKEMIA INDUCED BY N-BUTYLNITROSOUREA*1 Hayase SHISA, Yasue MATSUDAIRA, Hiroshi HIAI, and Yasuaki NISHIZUKA Laboratory of Experimental
[Gann, 66, 37-42; February, 1975] ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC CELLS IN MOUSE LEUKEMIA INDUCED BY N-BUTYLNITROSOUREA*1 Hayase SHISA, Yasue MATSUDAIRA, Hiroshi HIAI, and Yasuaki NISHIZUKA Laboratory of Experimental
tumorigenicity in NIH 3T3 cells
 Proc. Nadl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 87, pp. 10005-10009, December 1990 Cell Biology Physiological induction and reversal of focus formation and tumorigenicity in NIH 3T3 cells (neoplastic transformation/adaptation/progressive
Proc. Nadl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 87, pp. 10005-10009, December 1990 Cell Biology Physiological induction and reversal of focus formation and tumorigenicity in NIH 3T3 cells (neoplastic transformation/adaptation/progressive
XANTHINE OXIDASE ACTIVITY IN PROGRESSIVE SPONTANEOUS MAMMARY CARCINOG ENESIS
 833 XANTHINE OXIDASE ACTIVITY IN PROGRESSIVE SPONTANEOUS MAMMARY CARCINOG ENESIS NANDINI A. SHETH, SUMATI V. BHIDE AND KAMAL J. RANADIVE Biology Division, Cancer Research Institute, Tata Memorial Centre,
833 XANTHINE OXIDASE ACTIVITY IN PROGRESSIVE SPONTANEOUS MAMMARY CARCINOG ENESIS NANDINI A. SHETH, SUMATI V. BHIDE AND KAMAL J. RANADIVE Biology Division, Cancer Research Institute, Tata Memorial Centre,
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
high-tumor-incidence mouse strains (7,12-dimethylbenz[aJanthracene/BALB/c/BALB/cfC3H/molecular hybridization/immunohistochemical staining)
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 76, No. 10, pp. 5360-5364, October 1979 Microbiology Mouse mammary tumor virus genome expression in chemical carcinogen-induced mammary tumors in low- and high-tumor-incidence
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 76, No. 10, pp. 5360-5364, October 1979 Microbiology Mouse mammary tumor virus genome expression in chemical carcinogen-induced mammary tumors in low- and high-tumor-incidence
5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation
 288 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure Oral contraceptives have been used since the early 1960s and are now used by about 90 million women worldwide. The pill is given as a combination
288 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure Oral contraceptives have been used since the early 1960s and are now used by about 90 million women worldwide. The pill is given as a combination
ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE. (Plates I-V)
 [GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
[GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Wnt1 is epistatic to Id2 in modeling mammary gland development and in causing mammary tumors Authors: Susan Marino (smarino@cmgm.stanford.edu) Claire Romelfanger (clairefrog@yahoo.com)
Author's response to reviews Title: Wnt1 is epistatic to Id2 in modeling mammary gland development and in causing mammary tumors Authors: Susan Marino (smarino@cmgm.stanford.edu) Claire Romelfanger (clairefrog@yahoo.com)
Absence of Uniform Progressive Growth of Long-Term Transplants of Rat Liver Neoplastic Nodules 1,2,3
 Absence of Uniform Progressive Growth of Long-Term Transplants of Rat Liver Neoplastic Nodules 1,2,3 Takaaki Ohmori, 4,5 Kenshi Watanabe, 4,6 and Gary M. Williams 4,7, e, 9 ABSTRACT-Fragments of normal
Absence of Uniform Progressive Growth of Long-Term Transplants of Rat Liver Neoplastic Nodules 1,2,3 Takaaki Ohmori, 4,5 Kenshi Watanabe, 4,6 and Gary M. Williams 4,7, e, 9 ABSTRACT-Fragments of normal
Sensitivity and Specificity of Bioassay of Estrogenicity on Mammary Gland and Uterus of Female Mice
 Physiol. Res. 51: 407-412, 2002 Sensitivity and Specificity of Bioassay of Estrogenicity on Mammary Gland and Uterus of Female Mice J. ŠKARDA Institute of Animal Physiology and Genetics, Academy of Sciences
Physiol. Res. 51: 407-412, 2002 Sensitivity and Specificity of Bioassay of Estrogenicity on Mammary Gland and Uterus of Female Mice J. ŠKARDA Institute of Animal Physiology and Genetics, Academy of Sciences
TRANSPLANTATION OF EXPERIMENTAL OVARIAN TUMORS AND THEIR SENSITIVITY TO CARCINOSTATICS
 THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol, 26, No. 2, p.145-151, 1979 TRANSPLANTATION OF EXPERIMENTAL OVARIAN TUMORS AND THEIR SENSITIVITY TO CARCINOSTATICS MICHIAKI YAKUSHIJI, KAIKITSU IDE, HARUO NISHIMURA, TAKASHI
THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol, 26, No. 2, p.145-151, 1979 TRANSPLANTATION OF EXPERIMENTAL OVARIAN TUMORS AND THEIR SENSITIVITY TO CARCINOSTATICS MICHIAKI YAKUSHIJI, KAIKITSU IDE, HARUO NISHIMURA, TAKASHI
creasing the incidence of mammary tumors in C3H mice is unknown. In this paper, we report that the primary effects of a low-calorie
 Proc. NatL Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 79, pp. 7758-7762, December 1982 Cell Biology Low-calorie diet prevents the development of mammary tumors in C3H mice and reduces circulating prolactin level, murine mammary
Proc. NatL Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 79, pp. 7758-7762, December 1982 Cell Biology Low-calorie diet prevents the development of mammary tumors in C3H mice and reduces circulating prolactin level, murine mammary
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
3. Studies of Cancer in Experimental Animals
 364 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 94 3. Studies of Cancer in Experimental Animals 3.1 Pure microcystin-lr (see Table 3.1) 3.1.1 Mouse A group of 13 male ICR mice, 5 weeks of age, received 100 intraperitoneal
364 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 94 3. Studies of Cancer in Experimental Animals 3.1 Pure microcystin-lr (see Table 3.1) 3.1.1 Mouse A group of 13 male ICR mice, 5 weeks of age, received 100 intraperitoneal
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0262 TITLE: Role of CDK4 in Breast Development and Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Haritha Reddy CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University Philadelphia PA 19122-6024 REPORT
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0262 TITLE: Role of CDK4 in Breast Development and Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Haritha Reddy CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University Philadelphia PA 19122-6024 REPORT
5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation
 326 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data Combined estrogen progestogen menopausal therapy involves the co-administration of an estrogen and a progestogen to peri- or postmenopausal
326 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data Combined estrogen progestogen menopausal therapy involves the co-administration of an estrogen and a progestogen to peri- or postmenopausal
IMPLANTATION OF RAT CARCINOMA AND SARCOMA WITHIN BENIGN FIBROADENOMA
 IMPLANTATION OF RAT CARCINOMA AND SARCOMA WITHIN BENIGN FIBROADENOMA JACOB HEIMAN (From the Institute qf Cancer Research, Columbia University, Francis C. Wood, Director) The results of transplanting mixtures
IMPLANTATION OF RAT CARCINOMA AND SARCOMA WITHIN BENIGN FIBROADENOMA JACOB HEIMAN (From the Institute qf Cancer Research, Columbia University, Francis C. Wood, Director) The results of transplanting mixtures
5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation
 168 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 91 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data The first oral hormonal contraceptives that were found to inhibit both ovulation and implantation were developed
168 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 91 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data The first oral hormonal contraceptives that were found to inhibit both ovulation and implantation were developed
of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice
 Summary of Drinking Water Carcinogenicity Study of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice July 2012 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Summary of Drinking Water Carcinogenicity Study of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice July 2012 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
No cases of precocious puberty were reported during clinical trials of risperidone in, cases of precocious puberty have been
 levels than adults. The growth hormone elevations reported for the 12 patients with growth hormone excess were modest and well below levels reported in children with gigantism. 7,8 None of the patients
levels than adults. The growth hormone elevations reported for the 12 patients with growth hormone excess were modest and well below levels reported in children with gigantism. 7,8 None of the patients
ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY TARIFF
 ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY TARIFF A GUIDE TO UTILISATION. The following guidelines have been agreed by consensus of Anatomical Pathologists who are members of the Anatomical Pathologist s Group, or the National
ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY TARIFF A GUIDE TO UTILISATION. The following guidelines have been agreed by consensus of Anatomical Pathologists who are members of the Anatomical Pathologist s Group, or the National
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MAMMARY TUMOURS IN FEMALE RATS TREATED WITH 1-METHYL-1-NITROSOUREA
 ENDOCRINE REGULATIONS, Vol. 34, 91 96, 2000 91 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MAMMARY TUMOURS IN FEMALE RATS TREATED WITH 1-METHYL-1-NITROSOUREA J. LISKA, 1 S. GALBAVY, 2 D. MACEJOVA, 1 J. ZLATOS, 2 J. BRTKO Institute
ENDOCRINE REGULATIONS, Vol. 34, 91 96, 2000 91 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MAMMARY TUMOURS IN FEMALE RATS TREATED WITH 1-METHYL-1-NITROSOUREA J. LISKA, 1 S. GALBAVY, 2 D. MACEJOVA, 1 J. ZLATOS, 2 J. BRTKO Institute
The purpose of this short article is not to provide
 Of Mice and Women: A Short History of Mouse Mammary Cancer Research with an Emphasis on the Paradigms Inspired by the Transplantation Method Daniel Medina Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology,
Of Mice and Women: A Short History of Mouse Mammary Cancer Research with an Emphasis on the Paradigms Inspired by the Transplantation Method Daniel Medina Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology,
Increased risk of cancer with anti-diabetes drugs? : pros
 24 th Spring Congress of Korean Diabetes Association Increased risk of cancer with anti-diabetes drugs? : pros Nan Hee Kim, MD, Ph.D. Professor Korea University Medical School Contents Diabetes and cancer
24 th Spring Congress of Korean Diabetes Association Increased risk of cancer with anti-diabetes drugs? : pros Nan Hee Kim, MD, Ph.D. Professor Korea University Medical School Contents Diabetes and cancer
"Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation during pregnancy, and in adult nulliparous mice, delays the subsequent development of DMBAinduced
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Papers U.S. Environmental Protection Agency 2011 Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Papers U.S. Environmental Protection Agency 2011 Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation
5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation
 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data Static electric and magnetic fields arise from both natural and man-made sources, whereas electric and magnetic fields in the extremely low-frequency
5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data Static electric and magnetic fields arise from both natural and man-made sources, whereas electric and magnetic fields in the extremely low-frequency
TITLE: Investigating the Role of TBX2 in the Inhibition of Senescence in Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0155 TITLE: Investigating the Role of TBX2 in the Inhibition of Senescence in Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Srinivas Nandana CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0155 TITLE: Investigating the Role of TBX2 in the Inhibition of Senescence in Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Srinivas Nandana CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt
5. SUMMARY OF DATA. 5.1 Exposure data
 5. SUMMARY OF DATA 5.1 Exposure data Obesity is the accumulation of excess body fat. Body mass index (BMI) is commonly used as a proxy measure of body fatness, because it correlates strongly with both
5. SUMMARY OF DATA 5.1 Exposure data Obesity is the accumulation of excess body fat. Body mass index (BMI) is commonly used as a proxy measure of body fatness, because it correlates strongly with both
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast
 Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
 AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-05-1-0262 TITLE: Role of CDK4 in Breast Development and Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Haritha Reddy CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19122-6024
AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-05-1-0262 TITLE: Role of CDK4 in Breast Development and Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Haritha Reddy CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19122-6024
Acta Medica Okayama APRIL 1974
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 28, Issue 2 1974 Article 4 APRIL 1974 Carcinogenesis in tissue culture. 22. Malignant transformation of cloned rat liver cells treated in culture with 4-dimethylaminoazobenzene
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 28, Issue 2 1974 Article 4 APRIL 1974 Carcinogenesis in tissue culture. 22. Malignant transformation of cloned rat liver cells treated in culture with 4-dimethylaminoazobenzene
World Congress on Breast Cancer
 World Congress on Breast Cancer 05.08.2015 How pregnancy at early age protects against breast cancer Fabienne Meier-Abt, MD PhD Background: Early age pregnancy protects against breast cancer. MacMahon,
World Congress on Breast Cancer 05.08.2015 How pregnancy at early age protects against breast cancer Fabienne Meier-Abt, MD PhD Background: Early age pregnancy protects against breast cancer. MacMahon,
Immunologically Induced and Elicited Local
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1970, p. 757-761 Copyright 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 2, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Immunologically Induced and Elicited Local Resistance to Staphylococcus aureus
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1970, p. 757-761 Copyright 1970 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 2, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Immunologically Induced and Elicited Local Resistance to Staphylococcus aureus
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study. of Tetrachloroethylene. in BDF 1 Mice
 Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Tetrachloroethylene in BDF 1 Mice March 1993 Japan Bioassay Laboratory Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Tetrachloroethylene in BDF 1 Mice March 1993 Japan Bioassay Laboratory Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and
ARTICLES. Rajendra G. Mehta, Robert M. Moriarty, Rajeshwari R. Mehta, Raju Penmasta, Gianluca Lazzaro, Andreas Constantinou, Liang Guo*
 ARTICLES Prevention of Preneoplastic Mammary Lesion Development by a Novel Vitamin D Analogue, 1 -Hydroxyvitamin D 5 Rajendra G. Mehta, Robert M. Moriarty, Rajeshwari R. Mehta, Raju Penmasta, Gianluca
ARTICLES Prevention of Preneoplastic Mammary Lesion Development by a Novel Vitamin D Analogue, 1 -Hydroxyvitamin D 5 Rajendra G. Mehta, Robert M. Moriarty, Rajeshwari R. Mehta, Raju Penmasta, Gianluca
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Weighing Evidence from National Toxicology Program Cancer Bioassays
 Weighing Evidence from National Toxicology Program Cancer Bioassays John Bucher, PhD, DABT National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Breast Cancer and the Environment IOM July 6-7, 2010 Topics
Weighing Evidence from National Toxicology Program Cancer Bioassays John Bucher, PhD, DABT National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Breast Cancer and the Environment IOM July 6-7, 2010 Topics
By Soha Mohamed Hamdy (1),Abdelkarim Mohamed Abdellatif (2) and Rania Mortada Mahmuod (1)
 BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF TURMERIC ON BREAST CANCER OF RATS By Soha Mohamed Hamdy (1),Abdelkarim Mohamed Abdellatif (2) and Rania Mortada Mahmuod (1) 1) Biochemistry Div. Chemistry Dep. Faculty
BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF TURMERIC ON BREAST CANCER OF RATS By Soha Mohamed Hamdy (1),Abdelkarim Mohamed Abdellatif (2) and Rania Mortada Mahmuod (1) 1) Biochemistry Div. Chemistry Dep. Faculty
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-6-1-628 TITLE: Novel Transgenic Mouse Model for Testing the Effect of Circulating IGF-I on Mammary Stem/Progenitor Cell Number and Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Adrian V.
AD Award Number: W81XWH-6-1-628 TITLE: Novel Transgenic Mouse Model for Testing the Effect of Circulating IGF-I on Mammary Stem/Progenitor Cell Number and Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Adrian V.
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Targeting Inflammation in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis
 Targeting Inflammation in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis Clifford Hudis, M.D. Chief, Breast Cancer Medicine Service Attending Physician, MSKCC Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College August 7,
Targeting Inflammation in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis Clifford Hudis, M.D. Chief, Breast Cancer Medicine Service Attending Physician, MSKCC Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College August 7,
Histological Typing Of Cancer And Precancer Of The Oral Mucosa
 Histological Typing Of Cancer And Precancer Of The Oral Mucosa 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Histological Typing Of Cancer And Within the last decade, histologic grading has become widely accepted as a powerful indicator
Histological Typing Of Cancer And Precancer Of The Oral Mucosa 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Histological Typing Of Cancer And Within the last decade, histologic grading has become widely accepted as a powerful indicator
Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis
 Nagoya Med. J., 107 Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis AYA NAIKI-ITO Department of experimental pathology and tumor biology Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
Nagoya Med. J., 107 Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis AYA NAIKI-ITO Department of experimental pathology and tumor biology Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
LONG TERM OBSERVATION AFTER CULTURED HUMAN PARATHYROID CELLS ALLOTRANSPLANTATION WITHOUT IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
 LONG TERM OBSERVATION AFTER CULTURED HUMAN PARATHYROID CELLS ALLOTRANSPLANTATION WITHOUT IMMUNOSUPPRESSION Nawrot I, Tołłoczko T, Szmidt J, Woźniewicz B, Migaj M, Górski A, Sawicki A, Zawitkowska T, Pietrasik
LONG TERM OBSERVATION AFTER CULTURED HUMAN PARATHYROID CELLS ALLOTRANSPLANTATION WITHOUT IMMUNOSUPPRESSION Nawrot I, Tołłoczko T, Szmidt J, Woźniewicz B, Migaj M, Górski A, Sawicki A, Zawitkowska T, Pietrasik
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16
 COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
AACR Launches the First English-Language Cancer Journal, The Journal of Cancer Research
 1916 AACR Launches the First English-Language Cancer Journal, The Journal of Cancer Research RICHARD WEIL, MD, EDITOR, 1916-1917 THE JOURNAL OF CANCER RESEARCH CONTENTS Early in his short career, Dr. Weil
1916 AACR Launches the First English-Language Cancer Journal, The Journal of Cancer Research RICHARD WEIL, MD, EDITOR, 1916-1917 THE JOURNAL OF CANCER RESEARCH CONTENTS Early in his short career, Dr. Weil
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Effects of Age and Parity on Mammary Gland Lesions and Progenitor Cells in the FVB/N-RC Mice
 Effects of Age and Parity on Mammary Gland Lesions and Progenitor Cells in the FVB/N-RC Mice Ahmed Raafat 1, Luigi Strizzi 2, Karim Lashin 1, Erika Ginsburg 3, David McCurdy 1, David Salomon 4, Gilbert
Effects of Age and Parity on Mammary Gland Lesions and Progenitor Cells in the FVB/N-RC Mice Ahmed Raafat 1, Luigi Strizzi 2, Karim Lashin 1, Erika Ginsburg 3, David McCurdy 1, David Salomon 4, Gilbert
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
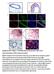 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
Effect of Thyroid Status on Development of Spontaneous Mammary Tumors in Primiparous C3H Mice
 [CANCER RESEARCH 42, 4553-4561, November 1982] Effect of Thyroid Status on Development of Spontaneous Mammary Tumors in Primiparous C3H Mice Barbara K. Vonderhaar1 and Antoinette E. Greco Laboratory of
[CANCER RESEARCH 42, 4553-4561, November 1982] Effect of Thyroid Status on Development of Spontaneous Mammary Tumors in Primiparous C3H Mice Barbara K. Vonderhaar1 and Antoinette E. Greco Laboratory of
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Evidence That an Early Pregnancy Causes a Persistent Decrease in the Number of Functional Mammary Epithelial Stem Cells Implications for Pregnancy-Induced Protection Against
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Evidence That an Early Pregnancy Causes a Persistent Decrease in the Number of Functional Mammary Epithelial Stem Cells Implications for Pregnancy-Induced Protection Against
Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation
 Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation Disclosure: Overview D Prognostic features in assessment of post treatment specimens: Tumor size Cellularity Grade Receptors LN Neoadjuvant chemotherapy:
Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation Disclosure: Overview D Prognostic features in assessment of post treatment specimens: Tumor size Cellularity Grade Receptors LN Neoadjuvant chemotherapy:
BIOLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF CELL LINES ESTABLISHED FROM Mc29-VIRUS INDUCED TRANSPLANTABLE CHICKEN HEPATOMA
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 34 40 ) BIOLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION
PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 34 40 ) BIOLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION
MORPHOLOGY, GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS AND
 Br. J. Cancer (1977) 35, 602 MORPHOLOGY, GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS AND OESTROGEN-BINDING CAPACITY OF DMBA-INDUCED MAMMARY TUMOURS FROM OVARIECTOMIZED RATS E. S. BOYLAN, E. H. FOWLER AND J. L. WITTLIFF From
Br. J. Cancer (1977) 35, 602 MORPHOLOGY, GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS AND OESTROGEN-BINDING CAPACITY OF DMBA-INDUCED MAMMARY TUMOURS FROM OVARIECTOMIZED RATS E. S. BOYLAN, E. H. FOWLER AND J. L. WITTLIFF From
hemagglutinin and the neuraminidase genes (RNA/recombinant viruses/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis/genetics)
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 73, No. 6, pp. 242-246, June 976 Microbiology Mapping of the influenza virus genome: Identification of the hemagglutinin and the neuraminidase genes (RNA/recombinant viruses/polyacrylamide
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 73, No. 6, pp. 242-246, June 976 Microbiology Mapping of the influenza virus genome: Identification of the hemagglutinin and the neuraminidase genes (RNA/recombinant viruses/polyacrylamide
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0618 TITLE: Are Breast Tumor Stem Cells Responsible for Metastasis and Angiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Quintin Pan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0618 TITLE: Are Breast Tumor Stem Cells Responsible for Metastasis and Angiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Quintin Pan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy. Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI
 A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
CERVIX. MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb.
 CERVIX MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb. CERVIX Most cervical lesions are: Most are Cervicitis. cancers ( common in women worldwide). CERVICITIS Extremely
CERVIX MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb. CERVIX Most cervical lesions are: Most are Cervicitis. cancers ( common in women worldwide). CERVICITIS Extremely
Molecular and genetic analysis of stromal fibroblasts in prostate cancer
 Final report ESMO Translational Research Fellowship 2010-2011 Molecular and genetic analysis of stromal fibroblasts in prostate cancer Michalis Karamouzis Host Institute Department of Biological Chemistry,
Final report ESMO Translational Research Fellowship 2010-2011 Molecular and genetic analysis of stromal fibroblasts in prostate cancer Michalis Karamouzis Host Institute Department of Biological Chemistry,
Mitotic Blockage at G 2 After Partial Hepatectomy During 4-Dlmethylamlnoazobenzene Hepatocarclnogenesls I, 2
 Mitotic Blockage at G 2 After Partial Hepatectomy During 4-Dlmethylamlnoazobenzene Hepatocarclnogenesls I, 2 M. R. BANERJEE,.. Institute lor Cancer Research, PhilacJelphia, Pennsylvania SUMMARY-Under the
Mitotic Blockage at G 2 After Partial Hepatectomy During 4-Dlmethylamlnoazobenzene Hepatocarclnogenesls I, 2 M. R. BANERJEE,.. Institute lor Cancer Research, PhilacJelphia, Pennsylvania SUMMARY-Under the
Mammary Gland Whole Mount Round Robin Summary Suzanne Fenton, NIEHS, NTP December 4, 2009
 Mammary Gland Whole Mount Round Robin Summary Suzanne Fenton, NIEHS, NTP December 4, 2009 In order to improve reliability and standardization of mammary gland whole mount assessments, directors and staff
Mammary Gland Whole Mount Round Robin Summary Suzanne Fenton, NIEHS, NTP December 4, 2009 In order to improve reliability and standardization of mammary gland whole mount assessments, directors and staff
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer 2 The So Called Pre-Neoplastic Lesions and Carcinoma In Situ
 Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
ENHANCING EFFECT OF COENZYME Q10 ON IMMUNORESTORATION WITH MYCOBACTERIUM BOVIS BCG IN TUMOR-BEARING MICE*1
 ENHANCING EFFECT OF COENZYME Q10 ON IMMUNORESTORATION WITH MYCOBACTERIUM BOVIS BCG IN TUMOR-BEARING MICE*1 Ichiro KAWASE, Hisanobu NIITANI, Nagahiro SAIJO, Haruo SASAKI, and Tatsuhide MORITA National Cancer
ENHANCING EFFECT OF COENZYME Q10 ON IMMUNORESTORATION WITH MYCOBACTERIUM BOVIS BCG IN TUMOR-BEARING MICE*1 Ichiro KAWASE, Hisanobu NIITANI, Nagahiro SAIJO, Haruo SASAKI, and Tatsuhide MORITA National Cancer
Downloaded by on April 28, 2018 https://pubs.acs.org Publication Date: April 24, 1984 doi: /bk
 1 Virus-Receptor Interactions BERNARD N. FIELDS Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, Harvard Medical School, and Department of Medicine (Infectious Disease), Brigham and Women's Hospital,
1 Virus-Receptor Interactions BERNARD N. FIELDS Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, Harvard Medical School, and Department of Medicine (Infectious Disease), Brigham and Women's Hospital,
Breast Pathology. Breast Development
 Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1
 TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1 Hidehiko ISAKA, Hirooki YOSHII, Akinobu OTSUJI, Masao KOIKE, Yuichiro NAGAI, Masatoshi KOURA, Koichiro SUGIYASU, and Teruhiko
TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1 Hidehiko ISAKA, Hirooki YOSHII, Akinobu OTSUJI, Masao KOIKE, Yuichiro NAGAI, Masatoshi KOURA, Koichiro SUGIYASU, and Teruhiko
Quantification of early stage lesions for loss of p53 should be shown in the main figures.
 Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Expert in prostate cancer The manuscript "Clonal dynamics following p53 loss of heterozygosity in Kras-driven cancers" uses a number of novel genetically engineered
Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Expert in prostate cancer The manuscript "Clonal dynamics following p53 loss of heterozygosity in Kras-driven cancers" uses a number of novel genetically engineered
4. Other Data Relevant to an Evaluation of Carcinogenicity and its Mechanisms
 550 4. Other Data Relevant to an Evaluation of Carcinogenicity and its Mechanisms 4.1 Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion 4.1.1 Humans The pharmacokinetics of the newer progestogens, desogestrel,
550 4. Other Data Relevant to an Evaluation of Carcinogenicity and its Mechanisms 4.1 Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion 4.1.1 Humans The pharmacokinetics of the newer progestogens, desogestrel,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
A Reappraisal of Progesterone Action in the Mammary Gland
 Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia, Vol. 5, No. 3, 2000 A Reappraisal of Progesterone Action in the Mammary Gland John P. Lydon 1, Lakshmi Sivaraman 1, and Orla M. Conneely 1,2 The ovarian
Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia, Vol. 5, No. 3, 2000 A Reappraisal of Progesterone Action in the Mammary Gland John P. Lydon 1, Lakshmi Sivaraman 1, and Orla M. Conneely 1,2 The ovarian
FILE # WHAT PERCENTAGE OF PANCREATIC TUMORS ARE BENIGN
 14 February, 2018 FILE # WHAT PERCENTAGE OF PANCREATIC TUMORS ARE BENIGN Document Filetype: PDF 95.97 KB 0 FILE # WHAT PERCENTAGE OF PANCREATIC TUMORS ARE BENIGN What is the percentage of lung tumors being
14 February, 2018 FILE # WHAT PERCENTAGE OF PANCREATIC TUMORS ARE BENIGN Document Filetype: PDF 95.97 KB 0 FILE # WHAT PERCENTAGE OF PANCREATIC TUMORS ARE BENIGN What is the percentage of lung tumors being
EDITORIAL EXPERIMENTAL SKIN CANCER
 EDITORIAL EXPERIMENTAL SKIN CANCER THE experimental study of skin cancer is of historical interest in that it was the first type of malignant turnout to be induced by a pure synthetic chemical compound.
EDITORIAL EXPERIMENTAL SKIN CANCER THE experimental study of skin cancer is of historical interest in that it was the first type of malignant turnout to be induced by a pure synthetic chemical compound.
Erbb2 transgenic mice: a tool to evaluate the potential efficacy of vaccination in the prevention and cure of carcinomas
 1 st International MUGEN Conference on Animal Models for Human Immunological Disease Athens, 11 September 2006 Erbb2 transgenic mice: a tool to evaluate the potential efficacy of vaccination in the prevention
1 st International MUGEN Conference on Animal Models for Human Immunological Disease Athens, 11 September 2006 Erbb2 transgenic mice: a tool to evaluate the potential efficacy of vaccination in the prevention
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
ABSTRACTS: FISH OILS AND CANCER
 ABSTRACTS: FISH OILS AND CANCER J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 May;74(5):1145-50. Dietary effects of menhaden oil on the growth and membrane lipid composition of rat mammary tumors. Jurkowski JJ, Cave WT Jr.
ABSTRACTS: FISH OILS AND CANCER J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 May;74(5):1145-50. Dietary effects of menhaden oil on the growth and membrane lipid composition of rat mammary tumors. Jurkowski JJ, Cave WT Jr.
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument. Mikrogeo. com
 SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
The carcinogenicity of benzene. The IARC Monograph Vol 120. Kurt Straif, MD MPH PhD. PSA, Stavanger, 25 October 2018
 The carcinogenicity of benzene. The IARC Monograph Vol 120 Kurt Straif, MD MPH PhD PSA, Stavanger, 25 October 2018 The encyclopaedia of The IARC Monographs evaluate Chemicals Complex mixtures Occupational
The carcinogenicity of benzene. The IARC Monograph Vol 120 Kurt Straif, MD MPH PhD PSA, Stavanger, 25 October 2018 The encyclopaedia of The IARC Monographs evaluate Chemicals Complex mixtures Occupational
Partial Expression of Endogenous Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus in Mammary Tumors Induced in BALB/c Mice by Chemical, Hormonal, and Physical Agents
 JouRNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 1981, p. 571-580 0022-538X/81/050571-10$02.00/0 Vol. 38, No. 2 Partial Expression of Endogenous Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus in Mammary Tumors Induced in BALB/c Mice by Chemical,
JouRNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 1981, p. 571-580 0022-538X/81/050571-10$02.00/0 Vol. 38, No. 2 Partial Expression of Endogenous Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus in Mammary Tumors Induced in BALB/c Mice by Chemical,
Hyperplastic Nodules and Adenomas of Exocrine Pancreas in Azaserine-Treated Rats 1, 2
 Hyperplastic Nodules and Adenomas of Exocrine Pancreas in Azaserine-Treated Rats 1, 2 Daniel S. Longnecker 3 and Barbara G. Crawford 3.4 SUMMARY-Long-term studies of the carcinogenicity of azaserine in
Hyperplastic Nodules and Adenomas of Exocrine Pancreas in Azaserine-Treated Rats 1, 2 Daniel S. Longnecker 3 and Barbara G. Crawford 3.4 SUMMARY-Long-term studies of the carcinogenicity of azaserine in
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2
 Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Muco-epidermoid tumours of the anal canal
 J. clin. Path. (1963), 16, 200 Muco-epidermoid tumours of the anal canal B. C. MORSON AND H. VOLKSTADT From the Research Department, St. Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology of 21 cases of muco-epidermoid
J. clin. Path. (1963), 16, 200 Muco-epidermoid tumours of the anal canal B. C. MORSON AND H. VOLKSTADT From the Research Department, St. Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology of 21 cases of muco-epidermoid
PRINCIPLES OF BREAST SURGERY & COMPLICATIONS
 PRINCIPLES OF BREAST SURGERY & COMPLICATIONS Adam Cichowitz The Royal Melbourne Hospital ANATOMY Lies in subcutaneous tissue Base: midline to midaxillary line, 2nd to 6th rib Overlies pec major, serratus
PRINCIPLES OF BREAST SURGERY & COMPLICATIONS Adam Cichowitz The Royal Melbourne Hospital ANATOMY Lies in subcutaneous tissue Base: midline to midaxillary line, 2nd to 6th rib Overlies pec major, serratus
Proliferative Lesions of the Exocrine Pancreas in Male F344/N Rats
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 56, pp. 213-217, 1984 Proliferative Lesions of the Exocrine Pancreas in Male F344/N Rats By Gary A. Boorman* and Scot L. Eustis* While the rat pancreas is susceptible
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 56, pp. 213-217, 1984 Proliferative Lesions of the Exocrine Pancreas in Male F344/N Rats By Gary A. Boorman* and Scot L. Eustis* While the rat pancreas is susceptible
YOU ARE WHAT YOU EAT: THE ROLE OF DIET IN CANCER PREVENTION
 College of Public Health and Human Sciences Moore Family Center for Whole Grain Foods, Nutrition and Preventive Health YOU ARE WHAT YOU EAT: THE ROLE OF DIET IN CANCER PREVENTION Emily Ho, PhD Director,
College of Public Health and Human Sciences Moore Family Center for Whole Grain Foods, Nutrition and Preventive Health YOU ARE WHAT YOU EAT: THE ROLE OF DIET IN CANCER PREVENTION Emily Ho, PhD Director,
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2697 Figure S1 Cytokeratin 5 is a specific marker for basal and intermediate cells in all mouse prostate lobes. (a) Immunofluorescence staining showing co-localization of YFP with p63 in
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2697 Figure S1 Cytokeratin 5 is a specific marker for basal and intermediate cells in all mouse prostate lobes. (a) Immunofluorescence staining showing co-localization of YFP with p63 in
In the third part of the present study tumours which previous were described as basal cell tumours but now have been reclassified as trichoblastomas
 170 6. SUMMARY Immunhistochemical investigations for identifying the histogenesis of basaloid neoplasias and hyperplasias in the mamma parenchyma of the bitch, for the use of the human nuclear protein
170 6. SUMMARY Immunhistochemical investigations for identifying the histogenesis of basaloid neoplasias and hyperplasias in the mamma parenchyma of the bitch, for the use of the human nuclear protein
AD (Leave blank) PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0254 TITLE: Role of Fetuin-A in Breast Tumor Cell Growth PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Josiah Ochieng, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Meharry Medical College Nashville
AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0254 TITLE: Role of Fetuin-A in Breast Tumor Cell Growth PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Josiah Ochieng, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Meharry Medical College Nashville
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICO-IMAGING STUDY OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMAS CORRELATED TO HORMONAL RECEPTORS AND HER2/NEU ONCOPROTEIN
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICO-IMAGING STUDY OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMAS CORRELATED TO HORMONAL RECEPTORS AND HER2/NEU ONCOPROTEIN
Etoposide sensitivity of human prostatic cancer cell lines PC-3, DU 145 and LNCaP
 Histol Histopathol (1 999) 14: 125-1 34 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-hlstopathol Histology and Histopathology Etoposide sensitivity of human prostatic cancer cell lines PC-3, DU 145 and LNCaP M. Salido, J.
Histol Histopathol (1 999) 14: 125-1 34 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-hlstopathol Histology and Histopathology Etoposide sensitivity of human prostatic cancer cell lines PC-3, DU 145 and LNCaP M. Salido, J.
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3957
 Supplementary Fig. 1. p38 alternative activation, IL-21 expression, and T helper cell transcription factors in PDAC tissue. (a) Tissue microarrays of pancreatic tissue from 192 patients with pancreatic
Supplementary Fig. 1. p38 alternative activation, IL-21 expression, and T helper cell transcription factors in PDAC tissue. (a) Tissue microarrays of pancreatic tissue from 192 patients with pancreatic
THE EFFECT OF ADRENAL STEROIDS AND CORTI- COTROPHIN ON THE GROWTH OF A SARCOMA OF HUMAN ORIGIN IN SMALL LABORATORY ANIMALS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 307. THE EFFECT OF ADRENAL STEROIDS AND CORTI- COTROPHIN ON THE GROWTH OF A SARCOMA OF HUMAN ORIGIN IN SMALL LABORATORY ANIMALS BY G. A. H. BUTTLE, P. F. D'ARCY,* E. M.
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 307. THE EFFECT OF ADRENAL STEROIDS AND CORTI- COTROPHIN ON THE GROWTH OF A SARCOMA OF HUMAN ORIGIN IN SMALL LABORATORY ANIMALS BY G. A. H. BUTTLE, P. F. D'ARCY,* E. M.
The stroma as a crucial target in rat mammary gland carcinogenesis
 Research Article 1495 The stroma as a crucial target in rat mammary gland carcinogenesis Maricel V. Maffini 1, Ana M. Soto 1, *, Janine M. Calabro 1, Angelo A. Ucci 2 and Carlos Sonnenschein 1 1 Department
Research Article 1495 The stroma as a crucial target in rat mammary gland carcinogenesis Maricel V. Maffini 1, Ana M. Soto 1, *, Janine M. Calabro 1, Angelo A. Ucci 2 and Carlos Sonnenschein 1 1 Department
Mousa. Israa Ayed. Abdullah AlZibdeh. 0 P a g e
 1 Mousa Israa Ayed Abdullah AlZibdeh 0 P a g e Breast pathology The basic histological units of the breast are called lobules, which are composed of glandular epithelial cells (luminal cells) resting on
1 Mousa Israa Ayed Abdullah AlZibdeh 0 P a g e Breast pathology The basic histological units of the breast are called lobules, which are composed of glandular epithelial cells (luminal cells) resting on
