Absence of Uniform Progressive Growth of Long-Term Transplants of Rat Liver Neoplastic Nodules 1,2,3
|
|
|
- Gwen Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Absence of Uniform Progressive Growth of Long-Term Transplants of Rat Liver Neoplastic Nodules 1,2,3 Takaaki Ohmori, 4,5 Kenshi Watanabe, 4,6 and Gary M. Williams 4,7, e, 9 ABSTRACT-Fragments of normal rat liver and neoplastic nodules induced by feeding 0.02% N-2-f1uorenylacetamide for 20 weeks were transplanted into the inguinal mammary fat pads of syngeneic rats. All animals were Charles River inbred male albino rats of the CD F strain derived from the F344 strain. Normal liver transplants and neoplastic nodule transplants were detected histologically in the transplant site up to 24 and 66 weeks of survival, respectively. Of 30 nodule transplants followed up to 121 weeks, only 1 neoplastic nodule developed progressive neoplastic growth. The tumor that arose in the transplant site from this nodule was a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma with mucin production. Thus rat liver neoplastic nodules lack the high frequency of progressive growth previously demonstrated for carcinomas.-jnci 65: , The nodular lesions that arise in the livers of rats exposed to chemical carcinogens have been considered by some investigators to be hyperplastic (1-5) and by others to be neoplastic (6-8). In a study specifically designed to examine this question (8), we reported that these nodules persisted and grew progressively following cessation of carcinogen exposure. Therefore, we have interpreted these lesions as being neoplastic (8, 9), which is in accordance with the recommendations of several recent working groups (10, 11). One of the means for establishment of the neoplastic nature of cellular lesions is the demonstration of the ability to form tumors upon transplantation. Earlier studies on the transplantation of rat liver nodules revealed no tumor development (12, 13). These findings were confirmed when fragments of liver, liver hyperplastic nodules, and hepatocellular carcinomas were transplanted into the inguinal fat pad in which longterm survival of transplanted fragments was obtained (14). Subsequently, we demonstrated that transplanted cells from nodules retained their phenotypic abnormalities but did not grow progressively during 8 months of observation (15). Although transplanted carcinomas formed tumors in the mammary fat pad within 16 weeks (14, 15), 8 months may not have been a sufficient time to allow for development of tumors from liver nodules, inasmuch as well-differentiated mouse liver tumors require up to 545 days for growth in this site (16). Therefore, we transplanted nodules into rats and observed these rats for their lifetimes. Here we show that rat liver neoplastic nodules have little tumor-forming capacity when transplanted into the mammary fat pads of intact syngeneic male rats maintained 121 weeks. MATERIALS AND METHODS The animals were 6- to 8-week-old Charles River inbred male albino rats of the CD F strain derived from the F344 strain (Charles River Breeding Laboratories, North Wilmington, Mass.). The basal diet was Purina Laboratory Chow (Ralston Purina Co., St. Louis, Mo.). To induce liver nodules, we fed 20 donor rats 0.02% 2-FAA in the diet for 20 weeks. The 90 recipient rats were divided into 2 groups. The transplantation procedure was the same as that in previous studies (14, 15). In the first group, 30 rats were given transplants in the inguinal mammary fat pad of one small fragment (=1 mm") of normal liver from 10 healthy donor rats. Three recipients were killed every 4 weeks from 8 to 28 weeks after transplantation. In the second group, 60 rats were given transplants of fragments of macroscopic liver lesions from the 20 donor rats fed 2-FAA. Microscopic examination of tissue from the lesions used for transplantation confirmed 41 neoplastic nodules according to the criteria of the Institute for Laboratory Animal Resources (11). Eleven recipients from group 2 were killed at intervals of 8, 16, 52, 56, and 66 weeks after transplantation. The remaining recipients of both groups were kept for their lifetimes or until a tumor appeared at the transplant site. All recipients were examined at the transplant sites by palpation monthly at the time of ABBREVIATIONS USED, 2-FAA =N -2-f1uorenylacetamide; PAS =periodic acid-schiff. 1 Received January 9, 1980; accepted March 17, Supported by Public Health Service grants CAI2376 and CAI7613 from the National Cancer Institute. 3 Animals were maintained under guidelines set forth by the Naylor Dana Institute. 4 Division of Experimental Pathology and Toxicology, Naylor Dana Institute for Disease Prevention, American Health Foundation, I Dana Rd., Valhalla, N.Y S Visiting Scientist from the Department of Pathology, Nara Medical University, 840 Shijo-cho, Kashihara City, Nara 634, Japan. 6 Present address: The Department of Pathology, Kagoshirna University, School of Medicine, Kagoshima 890, Japan. 7 Department of Pathology, New York Medical College, Valhalla, N.Y Address reprint requests to Dr. Williams at the Division of Experimental Pathology and Toxicology, Naylor Dana Institute for Disease Prevention. 9 We thank Ms. Ellen Sestrom of the Research Animal Facility, Naylor Dana Institute for Disease Prevention, and Ms. Carol Meyer of the Division of Experimental Pathology and Toxicology, Naylor Dana Institute for Disease Prevention, for their excellent technical assistance. We also thank Ms. Bette Meyer for preparing this manuscript. 485 JNCI, VOL. 65, NO.2, AUGUST 1980
2 486 Ohmori, Watanabe, and Williams weighing. At necropsy if a transplant was not identified by gross observation, the entire inguinal fat pad at the transplant site was examined microscopically by subserial sections. To evaluate the stability of resistance to iron accumulation of neoplastic nodules (17, 18) after transplantation, as was done in (15), we iron loaded all recipients by feeding them 0.8% 8-hydroxyquinoline and 2.19% ferrous gluconate (17) in the diet from 1 week to 30 weeks in the normal liver transplant group and for 13 weeks in the nodule transplant group. The histologically identified transplants were examined histochemically by the Prussian blue reaction for iron or PAS staining for glycogen. RESULTS TABLE Of 18 normal liver transplants, 8 were histologically detected as clusters or nests of cells up to 24 weeks after transplantation. The iron-loading regimen produced iron deposition in macrophages in the mammary fat pad, and surviving liver cells contained different degrees of cytoplasmic iron granules (fig. 1) as well as PAS-positive granules (table 1). No mitotic figures were found. Of the 60 carcinogen-induced lesions used for transplantation, 41 were histologically confirmed to be neoplastic nodules by examination of the remaining tissue. Of 11 transplants examined at 8, 16, 52, 56, and 66 weeks after transplantation, only 2 were histologically identified, 1 at week 16 and the other at week 66 after transplantation. Compared with the original tissue used for transplantation, these 2 surviving nodule transplants showed the persistence of phenotypic characteristics and also some degree of increased abnormality. Mitotic figures were seen in both transplants. The transplanted nodule examined at 16 weeks showed some acinar arrangements of slightly basophilic cells (fig. 2). The other transplanted nodule found at 66 weeks represented the longest documented period of survival at the transplant site. It also showed increased morphologic abnormalities. The nodule was encapsulated by a rim of connective tissue (fig. 3). The cells within the nodule were arranged in acinar structures composed of highly basophilic cells that occupied more than two-thirds of the nodule and compressed slightly the other less atypical cells. The original nodule used for this transplant contained an area of atypical basophilic cells (fig. 4). Thirty transplanted neoplastic nodules were followed for more than 66 weeks, but only 1 developed a tumor at approximately 71 weeks after transplantation. When the rat bearing this tumor was killed at 75 weeks after receiving the transplant, the tumor was found to be 6.5X4.5X6.0 cm in size and showed central necrosis and metastasis to neighboring lymph nodes. It was a welldifferentiated adenocarcinoma consisting of tubular and/or transitional to trabecular patterns with mucin production and a variable amount of fibrous stroma (fig. 5). The residual portion of the original lesion used for transplantation had a focus of cells arranged in an acinar pattern (fig. 6). All remaining rats in both the normal liver and the neoplastic nodule transplant groups were observed for their lifetimes and killed when moribund. The last animal was killed at 121 weeks after receiving the transplant. All tumors that developed at or around the transplant sites were examined histologically. In a normal liver recipient, 1 mammary adenocarcinoma and 1 fibroadenoma of the mammary gland were found. No other hepatocellular tumors were observed. I.-Behavior and phenotypic characteristics of transplants of normal liver and neoplastic nodulesa Transplants Period of No. of No. of transplants No. of Iron Ini- No. of transplants transplan- transplants Status Mitoses followed tumors examined accumu- Donor tial tation, wk identified lation No. at interim Normal liver Nest of cells Cluster of cells Cluster of cells Cluster of cells Cluster of cells NA NA NA NA NA NA NA Neoplastic nodule NA NA NA Nests b of cells + -/ NA NA NA NA NA NA Nodule" of cells d 1 1 Adenocarcinoma" +++ a -=Negative; +=found in a rare cell; ++=strongly positive; NA=not applicable; -/+=weakly positive; +++=found frequently. b Glandular structures present. C Tubular structures present. d Original transplant was a neoplastic nodule with atypical features. e Well-differentiated adenocarcinoma with tubular, cystic, and papillary patterns. JNCI, VOL. 65. NO.2, AUGUST 1980
3 Transplanted Liver Neoplastic Nodules 487 DISCUSSION In the present study we demonstrated that transplants of carcinogen-induced liver nodules persisted for long periods in the transplant site and retained their phenotypic abnormalities but did not often give rise to progressive neoplastic growth. Of the 41 nodules transplanted, II were examined at intervals during the first 66 weeks of the experiment. Of these, 2 were identified histologically and both displayed the morphologic abnormalities of nodule cells that we have described in a previous study (15). In addition, the first nodule transplant examined during the period of iron administration remained resistant to iron accumulation, characteristic of neoplastic nodules in situ (17, 18) and as previously described for transplants (15). Thus 30 nodule transplants were maintained for weeks and, among these, only I transplant gave rise to a hepatocellular adenocarcinoma in the transplant site. The results of this experiment can be interpreted in several ways. First, neoplastic nodules, as shown in previous studies (14, 15), do not give rise to rapid tumor development in high incidence as do hepatocellular carcinomas. Thus neoplastic nodules are clearly a biologically different lesion, as we have previously suggested (9, 15). Another issue addressed by this experiment is whether these nodules are neoplastic. Our results provide only indirect evidence in support of this interpretation. The nodule transplants that were recovered and examined histologically had retained their phenotypic abnormalities and had even greater abnormalities not seen in transplants of the normal liver. Thus as we reported previously (8, 15), the phenotypic abnormalities in nodules appear to be highly stable. This observation is consistent with nodules' being a permanently altered neoplastic population. However, with the exception of I transplant, the nodules did not show progressive growth in the transplant site. This negative finding must be interpreted cautiously. In a similar study of the transplantability of mouse liver nodules (16), we observed progressive growth of both type A and type B nodules, the neoplastic nature of which had been disputed. Thus this transplantation system can be considered to be reasonably supportive for the growth of neoplastic lesions. Therefore, the failure of rat liver nodules to display a uniform progressive growth suggests that these nodules may depend on some factors in the liver that are not available or operative in the transplant site. The final point of interest in this study is the development after 71 weeks of transplantation of I adenocarcinoma from a transplanted nodule. The first consideration in the interpretation of this finding is whether the original lesion used for transplantation was already a carcinoma. The residual tissue at the periphery of the primary lesion did not display the morphologic aspects of a carcinoma, although it did have some minor atypical features. Regardless, transplantation of carcinomas in this system has generally resulted in tumor growth in the transplant site within much shorter periods (14, 15). Therefore, we believe, as the histology shows, that the primary lesion in this instance was not a carcinoma. Thus the development of a tumor may be due to a very minor component of neoplastic cells in the transplant or may reflect the evolution of a carcinoma from a transplanted neoplastic nodule. The association of carcinoma with nodules in vivo has been illustrated (2, 5, 6, 19). However, several lines of evidence indicate that transition of nodules to carcinoma under most circumstances must occur only at low frequency (9). The present finding, if indicative of transition at all, conforms with this concept. The tumor that developed in the transplant site had the histologic characteristics usually considered to suggest origin from bile ducts. The transplanted fragment may have contained a minor cell type not apparent in the residual tissue available for histologic study. Nevertheless, we (15) previously found that such tumors can arise from transplanted hepatocellular adenocarcinomas or cultured liver epithelial cells with hepatocellular properties. Therefore, we favor the possibility that this tumor arose from neoplastic hepatocytes that, as discussed, may have been present in the transplant fragment or may have evolved from nodule cells. This experiment provides evidence that liver nodules have the phenotypic stability of neoplasms but lack a major capability for independent progressive growth in a transplant site. Furthermore, if nodules give rise to carcinomas, they do so only in low frequency. REFERENCES (l) FIRM INGER HI. Histopathology of carcinogenesis and tumors of liver in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst 1955;15: (2) POPPER H, STERNBERG SS, OSER BL, OSER M. The carcinogenic effect of aramite in rats: A study of hepatic nodules. Cancer 1960;13: (3) REUBER MD. Development of preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions of the liver in male rats given percent N-2-fluorenyldiacetamide. J Nat! Cancer Inst 1965;34: (4) NEWBERNE PM, WOGAN GN. Sequential morphologic changes in aflatoxin B 1 carcinogenesis in the rat. Cancer Res 1968;28: (5) FARBER E. Hyperplastic liver nodules. Methods Cancer Res 1973; 7: (6) SASAKI T, YOSHIDA T. Experimentelle erzeugung des Lebercarcinoms durch Fiitterung met o-amidoazotoluol. Virchows Arch [pathol Anat] 1935;295: (7) BANNASCH P. Cytology and cytogenesis of neoplastic (hyperplastic) hepatic nodules. Cancer Res 1976;36: (8) HIROTA N, WILLIAMS GM. Persistence and growth of rat liver neoplastic nodules following cessation of carcinogen exposure. JNCI 1979;63: (9) WILLIAMS GM. The pathogenesis of rat liver cancer caused by chemical carcinogens. Biochim Biophys Acta 1980;605: (10) SQUIRE RA, LEVITT MH. Report of a workshop on classification of specific hepatocellular lesions in rats. Cancer Res 1975;35: (11) Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources, National Research Council, National Academy of Sciences. Histologic typing of liver tumors of the rat. JNCI 1980;64: (12) REUBER MD, FIRMINGER HI. Morphologic and biologic correla- JNCI. VOL. 65, NO.2, AUGUST 1980
4 488 Ohmori, Watanabe, and Williams tion of lesions obtained in hepatic carcinogenesis in A X C rats given percent N-2-fluorenyldiacetamide. J Natl Cancer Inst 1963;31: (13) REUBER MD, ODASHIMA S. Further studies on the transplantation of lesions obtained in hepatic carcinogenesis in rats given 2-(diacetamidofluoren). Gan 1967;58: (14) WILLIAMS GM, KLAIBER M, FARBER E. Differences in growth of transplants of liver, liver hyperplastic nodules and hepatocellular carcinomas in the mammary fat pad. Am J Pathol 1977;89: (15) WILLIAMS GM, OHMORI T, WATANABE K. Persistence and phenotypic stability of transplanted rat liver neoplastic nodules. Am J Pathol 1980;99:1-12. (16) WILLIAMS GM, HIROTA N, RICE JM. The resistance of spontaneous mouse hepatocellular neoplasms to iron accumulation during rapid iron loading by parenteral administration and their transplantability. Am J Pathol 1979;94: (17) WILLIAMS GM, YAMAMOTO RS. Absence of stainable iron from preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions in rat liver with 8-hydroxyquinoline-induced siderosis. J Natl Cancer Inst 1972;49: (18) WILLIAMS GM. Functional markers and growth behavior of preneoplastic hepatocytes. Cancer Res 1976;36: (19) WILLIAMS GM, WATANABE K. Quantitative kinetics of development of N-2-fluorenylacetamide-induced, altered (hyperplastic) hepatocellular foci resistant to iron accumulation and of their reversion or persistence following removal of carcinogen. JNCI 1978;61: FIGURE I.-Normal liver transplant at 16 wk after transplantation. A cluster of hepatocytes situated in dense connective tissue contains fine PAS-positive material and also some brown ferritin granules (arrow). PAS reaction and hematoxylin. Bar = 50!Lm. X 240 FIGURE 2.-Neoplastic nodule transplant at 16 wk after transplantation. Three different-sized clusters of nodule cells display persistence of the characteristic morphology of neoplastic nodule cells and resistance to iron accumulation. Acinar arrangements of slightly basophilic cells can be seen (arrows). Prussian blue and hematoxylin. Bar=50!Lm. X 240 FIGURE 3.-Neoplastic nodule transplant tissue at 66 wk after transplantation. Highly basophilic neoplastic cells occupy the greater part of the cell mass and form acinar structures (arrows) that slightly compress adjacent cells. Hematoxylin and eosin. Bar =100!Lm. X 120 FIGURE 4.-Residual liver tissue surrounding the tissue used for the transplant shown in fig. 3. Cells surrounding the vacant space (lower two-thirds) include a region of basophilic cells. 'Hematoxylin and eosin. Bar = 100!Lm. X 120 JNCI, VOL. 65, NO.2, AUGUST 1980
5 Transplanted Liver Neoplastic Nodules 489 JNCI, VOL. 65, NO.2, AUG UST 1980
6 490 Ohmori, Watanabe, and Williams FIGURE 5.-Adenocarcinoma that appeared 71 wk after transplantation of a neoplastic nodule. Tumor cells form cystic, tubular, and papillary structures within a fibrous stroma. Occasional transition to a trabecular pattern is apparent. Hematoxylin and eosin. Bar= 100 }.'m. X 120 FIGURE 6.-Residual liver tissue surrounding the tissue used for the transplant shown in fig. 5. Upper left part delineated by a fibrous band is the remaining portion of the neoplastic nodule used lor transplantation. Acinar arrangement of cells is present (arrow). Hematoxylin and eosin. Bar= 100 }.'m. X 120 JNCI, VOL. 65, NO.2, AUGUST 1980
Hyperplastic Nodules and Adenomas of Exocrine Pancreas in Azaserine-Treated Rats 1, 2
 Hyperplastic Nodules and Adenomas of Exocrine Pancreas in Azaserine-Treated Rats 1, 2 Daniel S. Longnecker 3 and Barbara G. Crawford 3.4 SUMMARY-Long-term studies of the carcinogenicity of azaserine in
Hyperplastic Nodules and Adenomas of Exocrine Pancreas in Azaserine-Treated Rats 1, 2 Daniel S. Longnecker 3 and Barbara G. Crawford 3.4 SUMMARY-Long-term studies of the carcinogenicity of azaserine in
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1
 TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1 Hidehiko ISAKA, Hirooki YOSHII, Akinobu OTSUJI, Masao KOIKE, Yuichiro NAGAI, Masatoshi KOURA, Koichiro SUGIYASU, and Teruhiko
TUMORS OF SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RATS INDUCED BY LONG-TERM FEEDING OF PHENACETIN*1 Hidehiko ISAKA, Hirooki YOSHII, Akinobu OTSUJI, Masao KOIKE, Yuichiro NAGAI, Masatoshi KOURA, Koichiro SUGIYASU, and Teruhiko
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2
 Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR )
 ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
Proliferative Lesions of the Exocrine Pancreas in Male F344/N Rats
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 56, pp. 213-217, 1984 Proliferative Lesions of the Exocrine Pancreas in Male F344/N Rats By Gary A. Boorman* and Scot L. Eustis* While the rat pancreas is susceptible
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 56, pp. 213-217, 1984 Proliferative Lesions of the Exocrine Pancreas in Male F344/N Rats By Gary A. Boorman* and Scot L. Eustis* While the rat pancreas is susceptible
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE. (Plates I-V)
 [GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
[GANN, 57, 1-7; February, 1966] UDC 616-006-021.6[616.24]:547.831.6-31:616.24-006-031.6 ORIGIN OF PULMONARY TUMORS IN RATS INDUCED BY 4-NITROQUINOLINE 1-OXIDE (Plates I-V) Kazuo MORI, Jo HIRATSUKA, Shuhei
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND DIAGNOSIS OF COMBINED HEPATOCELLULAR AND CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA
 Chinese Journal ofcancer Researeh 8(1):67-71, 1996. CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND DIAGNOSIS OF COMBINED HEPATOCELLULAR AND CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA LuJianping ~t:~ CaiWeimin* ~)~,/L~ HayashiKeiki I ~)~:i~n
Chinese Journal ofcancer Researeh 8(1):67-71, 1996. CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND DIAGNOSIS OF COMBINED HEPATOCELLULAR AND CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA LuJianping ~t:~ CaiWeimin* ~)~,/L~ HayashiKeiki I ~)~:i~n
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions
 Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver:
 Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Presentations Session II: Histopathology Diagnosis and Criteria
 Presentations Session II: Histopathology Diagnosis and Criteria Dr. John (Jack) Fournie - Importance of Specific Diagnostic Criteria for Non- Neoplastic and Neoplastic Lesions in Fishes Dr. Fournie discussed
Presentations Session II: Histopathology Diagnosis and Criteria Dr. John (Jack) Fournie - Importance of Specific Diagnostic Criteria for Non- Neoplastic and Neoplastic Lesions in Fishes Dr. Fournie discussed
(Iteceived for publication December 3, 1915)
 TRANSPLANTABLE SARCOMATA OF THE RAT LIVER ARISING IN THE WALLS OF PARASITIC CYSTS G. L. ROHDENBURG, M.D., AND F. D. BULLOCK, M.D. From Colurnbia University, George Crocker Special Re-search Fund, F. C.
TRANSPLANTABLE SARCOMATA OF THE RAT LIVER ARISING IN THE WALLS OF PARASITIC CYSTS G. L. ROHDENBURG, M.D., AND F. D. BULLOCK, M.D. From Colurnbia University, George Crocker Special Re-search Fund, F. C.
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology. Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016
 Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS
 BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
A Canine Case of Complex Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland with Metastasis to the Axillary Lymph Node
 A Canine Case of Complex Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland with Metastasis to the Axillary Lymph Node Kenjiro Hashimoto 1), Atsushi Kawabata 1), Tamio Ohmuro 2), Kinji Shirota 1, 3) * 1) Research Institute
A Canine Case of Complex Carcinoma of the Mammary Gland with Metastasis to the Axillary Lymph Node Kenjiro Hashimoto 1), Atsushi Kawabata 1), Tamio Ohmuro 2), Kinji Shirota 1, 3) * 1) Research Institute
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS
 7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy.
 November 2015 Case of the Month A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy. Contributed by: Rasha Salama, M.D., IU Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
November 2015 Case of the Month A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy. Contributed by: Rasha Salama, M.D., IU Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
(CYLINDROMA) ATLAS OF HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA
 (CYLINDROMA) This malignant tumor is poorly encapsulated and while seemingly well defined within the affected gland, there is usually infiltration of surrounding tissue on closer examination. The cut surface
(CYLINDROMA) This malignant tumor is poorly encapsulated and while seemingly well defined within the affected gland, there is usually infiltration of surrounding tissue on closer examination. The cut surface
Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system
 XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d
 هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase
 Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
PRELIMINARY CYTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Suspicious for Acinic Cell Carcinoma. Cell Block: Immunohistochemical Studies CYTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS:
 1 PRELIMINARY CYTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Suspicious for Acinic Cell Carcinoma. Cell Block: Immunohistochemical Studies GCDFP-15 S-100 CYTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Consistent with mammary analogue secretory carcinoma.
1 PRELIMINARY CYTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Suspicious for Acinic Cell Carcinoma. Cell Block: Immunohistochemical Studies GCDFP-15 S-100 CYTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Consistent with mammary analogue secretory carcinoma.
A CYSTICERCUS CARCINO-OSTEOCHONDRO- SARCOMA OF THE RAT LIVER WITH MULTIPLE CYSTICERCUS SARCOMATA
 A CYSTICERCUS CARCINO-OSTEOCHONDRO- SARCOMA OF THE RAT LIVER WITH MULTIPLE CYSTICERCUS SARCOMATA 1. D. BUIJIJOCK AND M. 11. CUIlTIs (Proin fhe Ztulitute of Cancor Research, Francis C. Wood, Director) It
A CYSTICERCUS CARCINO-OSTEOCHONDRO- SARCOMA OF THE RAT LIVER WITH MULTIPLE CYSTICERCUS SARCOMATA 1. D. BUIJIJOCK AND M. 11. CUIlTIs (Proin fhe Ztulitute of Cancor Research, Francis C. Wood, Director) It
A neoplasm is defined as "an abnormal tissue proliferation, which exceeds that of adjacent normal tissue. This proliferation continues even after
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid.
 Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Variability in Weight and Histological Appearance of the Prostate of Beagle Dogs Used in Toxicology Studies
 Toxicologic Pathology, 36: 917-925, 2008 Copyright 2008 by Society of Toxicologic Pathology ISSN: 0192-6233 print / 1533-1601 online DOI: 10.1177/0192623308324958 Variability in Weight and Histological
Toxicologic Pathology, 36: 917-925, 2008 Copyright 2008 by Society of Toxicologic Pathology ISSN: 0192-6233 print / 1533-1601 online DOI: 10.1177/0192623308324958 Variability in Weight and Histological
FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT
 I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice
 Summary of Drinking Water Carcinogenicity Study of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice July 2012 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Summary of Drinking Water Carcinogenicity Study of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice July 2012 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Histogenesis of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid
 J. clin. Path., (1966), 19, 114 E. D. WILLIAMS1 From the Institute ofpathology, The London Hospital SYNOPSIS Thirty-one dog thyroid tumours and 28 spontaneous rat thyroid tumours were studied histologically
J. clin. Path., (1966), 19, 114 E. D. WILLIAMS1 From the Institute ofpathology, The London Hospital SYNOPSIS Thirty-one dog thyroid tumours and 28 spontaneous rat thyroid tumours were studied histologically
Lesions Induced in Rodent Pancreas
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 56, pp. 245-251, 1984 Lesions Induced in Rodent Pancreas by Azaserine and Other Pancreatic Carcinogens by Daniel S. Longnecker* Focal proliferative changes in the
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 56, pp. 245-251, 1984 Lesions Induced in Rodent Pancreas by Azaserine and Other Pancreatic Carcinogens by Daniel S. Longnecker* Focal proliferative changes in the
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES
 DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions
 2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
CHOLANGIOFIBROSIS INDUCED BY SHORT-TERM FEEDING OF 3'-METHYL- 4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)AZOBENZENE: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVA- TION
 [GANN, 65, 249-260; June, 1974] CHOLANGIOFIBROSIS INDUCED BY SHORT-TERM FEEDING OF 3'-METHYL- 4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)AZOBENZENE: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVA- TION Kiyoshi TERAO*1 and Masayuki NAKANO*2 Research
[GANN, 65, 249-260; June, 1974] CHOLANGIOFIBROSIS INDUCED BY SHORT-TERM FEEDING OF 3'-METHYL- 4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)AZOBENZENE: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVA- TION Kiyoshi TERAO*1 and Masayuki NAKANO*2 Research
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
(a), in a discussion of Paget s disease of the nipple, has expressed
 SKIN INVOLVEMENT IN BREAST CANCER WITH REFERENCE TO ITS BEARING ON THE INTERPRE- TATION OF APPEARANCES OF TRANSITION BE- TWEEN NORMAL EPITHELIUM AND CANCER ALSON R. KILGORE From tlw Surgiral Pathology
SKIN INVOLVEMENT IN BREAST CANCER WITH REFERENCE TO ITS BEARING ON THE INTERPRE- TATION OF APPEARANCES OF TRANSITION BE- TWEEN NORMAL EPITHELIUM AND CANCER ALSON R. KILGORE From tlw Surgiral Pathology
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver
 Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver Noboru Terayama, Tadashi Terada and Yasuni Nakanuma Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, Kanazawa One
Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver Noboru Terayama, Tadashi Terada and Yasuni Nakanuma Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, Kanazawa One
Endosalpingiosis. Case report
 Case report Endosalpingiosis Michael D. Holmes, M.D. Howard S. Levin M.D. Department of Pathology Lester A. Ballard, Jr., M.D. Department of Gynecology Endosalpingiosis, a term referring to tuballike epithelium
Case report Endosalpingiosis Michael D. Holmes, M.D. Howard S. Levin M.D. Department of Pathology Lester A. Ballard, Jr., M.D. Department of Gynecology Endosalpingiosis, a term referring to tuballike epithelium
ONCOLOGY. Csaba Bödör. Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research november 19., ÁOK, III.
 ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
Enterprise Interest None
 Enterprise Interest None What are triple negative breast cancers? A synopsis of their histological patterns Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology,
Enterprise Interest None What are triple negative breast cancers? A synopsis of their histological patterns Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology,
Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer 2 The So Called Pre-Neoplastic Lesions and Carcinoma In Situ
 Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
Hemosiderin. Livia Vida 2018
 Hemosiderin Livia Vida 2018 Questions Histochemical caracteristics of the different pigments. Exogenous pigments. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Causes and forms of jaundice. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Pathological
Hemosiderin Livia Vida 2018 Questions Histochemical caracteristics of the different pigments. Exogenous pigments. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Causes and forms of jaundice. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Pathological
Muco-epidermoid tumours of the anal canal
 J. clin. Path. (1963), 16, 200 Muco-epidermoid tumours of the anal canal B. C. MORSON AND H. VOLKSTADT From the Research Department, St. Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology of 21 cases of muco-epidermoid
J. clin. Path. (1963), 16, 200 Muco-epidermoid tumours of the anal canal B. C. MORSON AND H. VOLKSTADT From the Research Department, St. Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology of 21 cases of muco-epidermoid
Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology. Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD
 Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD Too many or... Tumour herniation through a torn capsule simulating capsular invasion fibrous capsule with a sharp discontinuity, suggestive
Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD Too many or... Tumour herniation through a torn capsule simulating capsular invasion fibrous capsule with a sharp discontinuity, suggestive
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation
 Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation Disclosure: Overview D Prognostic features in assessment of post treatment specimens: Tumor size Cellularity Grade Receptors LN Neoadjuvant chemotherapy:
Post Neoadjuvant therapy: issues in interpretation Disclosure: Overview D Prognostic features in assessment of post treatment specimens: Tumor size Cellularity Grade Receptors LN Neoadjuvant chemotherapy:
Lung tumors & pleural lesions
 Lung tumors & pleural lesions A brief introduction 95% of lung tumors are carcinomas Among the remaining 5%, we will discuss: -Hamartoma the most common benign lung tumor spherical, coin lesion on x-rays
Lung tumors & pleural lesions A brief introduction 95% of lung tumors are carcinomas Among the remaining 5%, we will discuss: -Hamartoma the most common benign lung tumor spherical, coin lesion on x-rays
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers.!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1
 !! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
!! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
Multiple Primary Quiz
 Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Giant Ulcerative Lactating Nodule of Ectopic Breast Mimicking Malignancy.
 57 Giant Ulcerative Lactating Nodule of Ectopic Breast Mimicking Malignancy. I. Roy 1 FRCS(C), E Othieno 2 MMed (Path), R Ssentongo 3 FCS (ECSA) 1 Department of Pathology, St. Raphael of St. Francis Hospital,
57 Giant Ulcerative Lactating Nodule of Ectopic Breast Mimicking Malignancy. I. Roy 1 FRCS(C), E Othieno 2 MMed (Path), R Ssentongo 3 FCS (ECSA) 1 Department of Pathology, St. Raphael of St. Francis Hospital,
Interface between adaptive and neoplastic growth in
 Gut, 1987, 28, SI, 253-258 Interface between adaptive and neoplastic growth in the pancreas D S LONGNECKER From the Dartmouth Medical School, Hanover, NH, USA SUMMARY The adaptive changes of hypertrophy
Gut, 1987, 28, SI, 253-258 Interface between adaptive and neoplastic growth in the pancreas D S LONGNECKER From the Dartmouth Medical School, Hanover, NH, USA SUMMARY The adaptive changes of hypertrophy
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares
 Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR
 BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007
 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
DISCUSSION: PLGA accounts for about 2% of all salivary gland tumours and occurs almost exclusively in the minor salivary glands.
 SWELLING ON THE HARD PALATE PRESENTING AS POLYMORPHOUS LOW GRADE ADENOCARCINOMA: A AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Swapnil D. Chandekar 1, Sunita S. Dantkale 2, Rahul R. Narkhede 3, Snehal V. Chavhan 4, Khushboo
SWELLING ON THE HARD PALATE PRESENTING AS POLYMORPHOUS LOW GRADE ADENOCARCINOMA: A AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Swapnil D. Chandekar 1, Sunita S. Dantkale 2, Rahul R. Narkhede 3, Snehal V. Chavhan 4, Khushboo
Malignant Phyllodes tumor with necrosis a rare case report
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 1 ~ Issue 1 (2014) pp: 01-06 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Malignant Phyllodes
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 1 ~ Issue 1 (2014) pp: 01-06 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Malignant Phyllodes
Fig. 59 Malignant phaeochromocytoma, hepatic metastasis.
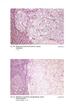 Fig. 59 Malignant phaeochromocytoma, hepatic metastasis. X 120 Hyperte nsion Fig. 60 Malignant sympathetic paraganglioma, lymph node metastasis Primary in bladder. x 1 20 Hypertension Fig. 61 Malignant
Fig. 59 Malignant phaeochromocytoma, hepatic metastasis. X 120 Hyperte nsion Fig. 60 Malignant sympathetic paraganglioma, lymph node metastasis Primary in bladder. x 1 20 Hypertension Fig. 61 Malignant
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
Invited Re vie W. Analytical histopathological diagnosis of small hepatocellular nodules in chronic liver diseases
 Histol Histopathol (1 998) 13: 1077-1 087 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Invited Re vie W Analytical histopathological diagnosis of small hepatocellular nodules in chronic
Histol Histopathol (1 998) 13: 1077-1 087 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Invited Re vie W Analytical histopathological diagnosis of small hepatocellular nodules in chronic
Dimethyihydrazine-induced colon tumors in rats fed diets containing beef fat or corn oil with and without wheat bran1 2
 Dimethyihydrazine-induced colon tumors in rats fed diets containing beef fat or corn oil with and without wheat bran1 2 Robert B. Wilson, David P. Hutcheson, and Linda Wideman ABSTRACT Male rats of the
Dimethyihydrazine-induced colon tumors in rats fed diets containing beef fat or corn oil with and without wheat bran1 2 Robert B. Wilson, David P. Hutcheson, and Linda Wideman ABSTRACT Male rats of the
USCAP 2012: Companion Meeting of the AAOOP. Update on lacrimal gland neoplasms: Molecular pathology of interest
 USCAP 2012: Companion Meeting of the AAOOP Vancouver BC, Canada, March 17, 2012 Update on lacrimal gland neoplasms: Molecular pathology of interest Valerie A. White MD, MHSc, FRCPC Department of Pathology
USCAP 2012: Companion Meeting of the AAOOP Vancouver BC, Canada, March 17, 2012 Update on lacrimal gland neoplasms: Molecular pathology of interest Valerie A. White MD, MHSc, FRCPC Department of Pathology
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches
 Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches Christopher C. Griffith, MD, PhD Raja R. Seethala, MD 1. Salivary gland tumor cytology: A
Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches Christopher C. Griffith, MD, PhD Raja R. Seethala, MD 1. Salivary gland tumor cytology: A
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
NOTE. [GANN, 65, ; August, 1974]
![NOTE. [GANN, 65, ; August, 1974] NOTE. [GANN, 65, ; August, 1974]](/thumbs/83/88553148.jpg) NOTE [GANN, 65, 371-376; August, 1974] COMBINED EFFECT OF VARIOUS SURFACTANTS ON GASTRIC CARCINO- GENESIS IN RATS TREATED WITH N-METHYL-N'-NITRO-N-NITROSOGUANI- DINE*1 Shoji FUKUSHIMA, Masae TATEMATSU,
NOTE [GANN, 65, 371-376; August, 1974] COMBINED EFFECT OF VARIOUS SURFACTANTS ON GASTRIC CARCINO- GENESIS IN RATS TREATED WITH N-METHYL-N'-NITRO-N-NITROSOGUANI- DINE*1 Shoji FUKUSHIMA, Masae TATEMATSU,
ACCME/Disclosures. Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate. Case
 Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
AN OBSERVATION OF PRIMARY TUMORS OF THE PITUITARY, OVARIES, AND MAMMARY GLANDS IN A MOUSE
 AN OBSERVATION OF PRIMARY TUMORS OF THE PITUITARY, OVARIES, AND MAMMARY GLANDS IN A MOUSE W. U. GARDNER,' L. C. STRONG,' AND G. M. SMITH (Front the Department of Anatomy, Yale Univerdy School of Medicine)
AN OBSERVATION OF PRIMARY TUMORS OF THE PITUITARY, OVARIES, AND MAMMARY GLANDS IN A MOUSE W. U. GARDNER,' L. C. STRONG,' AND G. M. SMITH (Front the Department of Anatomy, Yale Univerdy School of Medicine)
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland
 Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum
 2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
NODULAR CYSTIC HIDRADENOMA OVER THE GLUTEAL REGION: A RARE CYTOMORPHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS
 NODULAR CYSTIC HIDRADENOMA OVER THE GLUTEAL REGION: A RARE CYTOMORPHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS Abstract: The primary as well as metastatic tumours of the skin can be diagnosed by fine needle aspiration cytology
NODULAR CYSTIC HIDRADENOMA OVER THE GLUTEAL REGION: A RARE CYTOMORPHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS Abstract: The primary as well as metastatic tumours of the skin can be diagnosed by fine needle aspiration cytology
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
hyperplastic parathyroid glands
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 626-632 A histological comparison of adenomatous and hyperplastic parathyroid glands D. A. S. LAWRENCE From the Department of Histopathology, Royal Free Hospital,
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 626-632 A histological comparison of adenomatous and hyperplastic parathyroid glands D. A. S. LAWRENCE From the Department of Histopathology, Royal Free Hospital,
Case: The patient is a 24 year- old female who was found to have multiple mural nodules within the antrum. Solid and cystic components were noted on
 Case: The patient is a 24 year- old female who was found to have multiple mural nodules within the antrum. Solid and cystic components were noted on imaging. There is no significant past medical history.
Case: The patient is a 24 year- old female who was found to have multiple mural nodules within the antrum. Solid and cystic components were noted on imaging. There is no significant past medical history.
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated. FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia.
 DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation
 168 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 91 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data The first oral hormonal contraceptives that were found to inhibit both ovulation and implantation were developed
168 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 91 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data The first oral hormonal contraceptives that were found to inhibit both ovulation and implantation were developed
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) has been used increasingly
 Worrisome Histologic Alterations Following Fine-Needle Aspiration of Benign Parotid Lesions Shiyong Li, MD, PhD; Zubair W. Baloch, MD, PhD; John E. Tomaszewski, MD; Virginia A. LiVolsi, MD Objective. To
Worrisome Histologic Alterations Following Fine-Needle Aspiration of Benign Parotid Lesions Shiyong Li, MD, PhD; Zubair W. Baloch, MD, PhD; John E. Tomaszewski, MD; Virginia A. LiVolsi, MD Objective. To
O Farrell Legacy UPDATE ON WHO NOMENCLATURE. World Health Organization, 2010 DISCLOSURES WITH EMPHASIS ON PROBLEM HEPATOCELLULAR TUMORS
 O Farrell Legacy UPDATE ON WHO NOMENCLATURE WITH EMPHASIS ON PROBLEM HEPATOCELLULAR TUMORS Linda Ferrell, MD University of California San Francisco Vice Chair, Director of Surgical Pathology World Health
O Farrell Legacy UPDATE ON WHO NOMENCLATURE WITH EMPHASIS ON PROBLEM HEPATOCELLULAR TUMORS Linda Ferrell, MD University of California San Francisco Vice Chair, Director of Surgical Pathology World Health
