Aminoglycoside Resistance in Gram-negative Bacilli
|
|
|
- Tobias Vernon Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Korean J Clin Microbiol Vol. 12, No. 2, June, 2009 Aminoglycoside Resistance in Gram-negative Bacilli Yeon-Joon Park Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea Aminoglycosides are one of the clinically relevant antibiotics. They kill bacteria by binding to bacterial 30S subunit of ribosome. Resistance to aminoglycosides occurs by three different mechanisms: 1. Production of an enzyme that modifies aminoglycosides, 2. Impaired entry of aminoglycoside into the cell by altering the OMP permeability, decreasing inner membrane transport, or active efflux, 3. The receptor protein on the 30S ribosomal subunit may be deleted or altered as a result of a mutation. By far, enzymatic modification has been the most important mechanism. In this review, the mechanisms of action and resistance, and the prevalence of resistance due to acquisition of enzymes are briefly described. (Korean J Clin Microbiol 2009;12:57-61) Key Words: Aminoglycoside resistance, Gram negative aerobic rods, 30S ribosome subunits The aminoglycosides/aminocyclitol antibiotics are characterized by two or more amino sugars linked by a glycosidic bond to the aminocyclitol (hexose) ring, which is either streptidine (found in streptomycin) or 2-deoxystreptamine (found in other aminoglycosides) (Fig. 1)[1]. The latter is again classified as 4,5-disubstituted and 4,6-disubstituted. The examples of 4,5-disubstituted are neomycin and paromomycin. Most of other aminoglycosides are 4,6-disubstituted. These are basic, strongly polar compounds that are positively charged (cationic). Because of their positive charge, they are able to bind negatively charged lipopolysaccharide of the bacterial cell wall and a variety of molecules such as DNA, RNA, and phospholipids. The primary mechanism of action of aminoglycosides is a decrease in protein synthesis after the drug has bound to the bacterial 30S subunit of the ribosome. Their polycationic nature allows binding to the polyanionic 16S rrna on the 30S ribosome at the A site (site of codon and anticodon recognition) for trna binding. The aminoglycoside-bound bacterial ribosomes then become unavailable for translation of mrna during protein synthesis, thereby leading to cell death. To reach the intracellular ribosomal binding targets, the initial event is passive diffusion via porin channels across the outer membrane. Drug is then actively transported across the cell membrane into the cytoplasm Received 1 June, 2009, Revised 10 June, 2009, Accepted 15 June, 2009 Correspondence: Yeon-Joon Park, Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary s Hospital, 505, Banpo-dong, Seocho-gu, Seoul , Korea. (Tel) , (Fax) , ( ) yjpk@ catholic.ac.kr by an oxygen-dependent process. Transport may be enhanced by cell wall-active drugs such as penicillin or vancomycin: This enhancement maybe the basis of the synergism of these antibiotics with aminoglycosides[2]. Resistance to aminoglycosides occurs by three different mechanisms: 1. Production of a enzyme that modifies aminoglycosides (aminoglycoside modifying enzymes, AMEs) 2. Impaired entry of aminoglycoside into the cell by altering the OMP permeability, decreasing inner membrane transport, or active efflux 3. The receptor protein on the 30S ribosomal subunit may be deleted or altered as a result of a mutation. By far, enzymatic modification is (has been) the most important mechanism. These enzymes are assigned to three groups: (a) acetyltransferases (acetylation of an aminogroup-aac), (b) phosphotransferases (phosphorylationof a hydroxyl group-aph) and (c) adenyltransferases (adenylation of a hydroxyl group-aad or ANT). These AMEs are often plasmid encoded but are also associated with transposable elements. Sites of AME modification of aminoglycosides are identified by a standard numbering system. The first sugar moiety at the 4 position has positions numbered with a single prime (1' to 6'); the second sugar moiety at the 6 position has positions numbered with a double prime (1'' to 6'') (Fig. 2)[1,3]. Aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms can be ascertained by examining the susceptibility of the strains to a panel of aminoglycosides (phenotypic characterization) (Table 1)[4]. However, in case of harboring more than two enzymes, the phenotype will not match any one of them. 57
2 58 Korean J Clin Microbiol 2009;12(2):57-61 Fig. 1. Backbone structures of the aminoglycosides. Fig. 2. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes and their substrates. A, amikacin; Dbk, dibekacin; G, gentamicin; Gmb, gentamicin B; I, isepamicin; K, kanamycin A; N, netilmicin; S, sisomicin; T, tobramycin. This enzyme is important because it confers resistance to amikacin, netilmicin, kanamycin, and tobramycin and its gene is located within integrons and transposons[5,6]. In Korean isolates of AmpC-producing Enterobacteriaceae, the prevalence of aac(6')-ib was 41.3%, 18.7%, and 6.6%, respectively in Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter freundii and Serratia marcescens[6]. Interestingly, of the aac(6')-ib or aac(6')-ib-cr harboring isolates, only about only 25 30% were nonsusceptible to amikacin[6,7] and this finding needs further investigation. Moreoever, the fact that AAC(6')-I coexists very frequently with other antibiotic-inactivating enzymes such as β- lactamases, carbapenemases or other aminoglycosidases alarms us[7]. For P. aeruginosa, Miller et al.[8] brought together several studies carried out worldwide. Results showed that in Europe, between 1988 and 1993, aac(6')-ii was the most prevalent ( %, avr. 32.5%), followed by ant(2'')-i ( %, avr. 16.9%), and non-enzymatic resistance ( %, average of 14.0%). In a study conducted with P. aeruginosa isolates showing high-level resistance to gentamicin and netilmicin and strains presenting a low-level resistance to all aminoglycosides including apramycin, collected in 2000 from community and private healthcare centers[9], the predominance of the three enzymes (aac(6')-ib, ant(2'')-ia, aac(3)-iic) was observed (36.5%, 21.2%, and 7.7%, respectively), and the non-enzymatic resistance was 34.6%. In addition, the presence of aac(6')-ib, which acetylates kanamycin, tobramycin, netilmicin, amikacin (KTNA), but not gentamicin, was regularly associated with a decreased gentamicin susceptibility. And it was assigned to the amino acid sequence at position 119, a leucine being associated with amikacin resistance and a serine with gentamicin resistance. In Korean nationwide study, of the 250 isolates of P. aerugi-
3 Yeon-Joon Park : Aminoglycoside Resistance in Gram-negative Bacilli 59 Table 1. Phenotypic characteristics of isolates producing aminoglycoside modifying enzymes (cited from EUCAST expert rules in antimicrobial susceptibility testing) Phenotype Enzyme St Sp K A G Nt T Nm St APH(3 ) R S S S S S S S St Sp ANT(3 )(9) R R S S S S S S G AAC(3)-I S S S S R s/r s/r S K APH(3 )-I S S R S S S S R K A APH(3 )-VI S S R R S S S R G T AAC(3)-VI* S S S S R s/r R S T K A ANT(4 )-II S S R R S S R S G T Nt Nm AAC(2 )-I AAC(3)-IV S S S S R R R R K G T ANT(2 )-I S S R S R S r S K T A Nt AAC(6 )-I S S R r S R R S K T G Nt AAC(3)-II S S R S R R R S K T G A Nt Impermeability±different enzymes R R R R R R R R *AAC(3)-IIa. Abbreviations: S, streptomycin; Sp, spectinomycin; K, kanamycin; A, amikacin; G, gentamicin; Nt, netilmicin; T, tobramycin; Nm, neomycin; APH, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase; ANT, aminoglycoside nucleotidyltransferase; AAC, aminoglycoside acetyltransferase; R, resistance; r, reduced zones but likely to remain susceptible at BSAC breakpoints; S, susceptible. nosa collected in 2002, the amikacin resistance rate was 22% (55 isolates), and of them, aph(3')-vi, ant(2'')-i, and aac(6')-i were found in 37, 32, and 18 isolates, respectively, alone or in combination[10]. Thirty-six strains harboured two or more types of enzymes, of which a combination of aac(6')-i and ant(2'')-i was the most frequent (24/36 isolates). The association with class 1 integron was confirmed with all of the ant(2'')-i, 6 of 18 aac(6')-i, but none of the aph(3')-vi. The difference in the enzyme distribution might be derived from the difference in selection of bacterial population and aminoglycoside usage. More recently, 16S rrna methylases (RmtA, RmtB, RmtC, RmtD, ArmA and NpmA) conferring resistance to almost all aminoglycosides, including arbekacin, has emerged and disseminated via mobile elements. Of these, arma gene has been found to be widely disseminated among various species[11], and was found on a large plasmid which carries a type 1 integron that mediates various gene cassettes responsible for multiple antimicrobial resistance[12]. In Korean isolates of Enterobacteriacae collected between 1995 and 1998 and between 2001 and 2006 at a university hospital, arma was first appeared in 1997[13]. Among the E. cloacae, C. freundii, and S. marcescens collected in 2003, amikacin resistance rate was 9.5%, 10.3% and 17.1%, respectively. About 84.5% of the amikacin-resistant isolates showed high-level (MIC>512μg/mL), and almost all of them harboured arma gene[14]. Among arbekacin or amikacin-nonsusceptible K. pneumoniae and A. baumannii, 53.8% and 53.3% harbored arma, respectively, and most arma-harboring A. baumannii were nonsusceptible to carbapenem[15]. rmta gene is likely associated with the mercury-resistant transposon Tn5041[16]; the rmtb gene was found in the flanking region of Tn3-like structure[17]. The rmtc was located downstream of an ISEcpI-like element containing tnpa[18]. NpmA is unique in that it gives resistance to apramycin and neomycin, due to methylation of the A1408 position at the A site of 16S rrna; all other 16S rrna methylases methylate the G1405 position[19]. Aminoglycosides is also the substrates for a number of multidrug efflux pumps, including the resistance nodulation cell division (RND) transporter superfamily, which plays an important role in Gram-negative bacteria. Several RND proteins are involved in aminoglycoside resistance in various Gram-negative pathogens, including P. aeruginosa, Burkholderia pseudomallei, Acinetobacter baumannii, and E. coli[20]. Despite these various resistance mechanisms, aminoglycosides are still valuable weapons in antimicrobial treatment, particularly in the treatment of serious Gram-negative nosocomial infections[5]. To use the aminoglycosides properly, accurate detection of resistance and efforts to prevent the spread of resistant
4 60 Korean J Clin Microbiol 2009;12(2):57-61 isolates are required. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Part of this work was presented at the 10 th anniversary symposium of Yonsei research institute of bacterial resistance. I appreciate the help of Dr. Dong Wook Jekarl and Ms Hyo Jin Park in preparing this manuscript. REFERENCES 1. Jona S and Deb JK. Molecular understanding of aminoglycoside action and resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2006;70: Kasper DL, Braunwald E, et al. eds. Principles of Internal Medicine. 16th ed. New York; McGraw Hill; 2008: Murray PR, Baron EJ, et al. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 9th ed. Washington, D.C.; American Society of Microbiology; 2007: Rafael C. EUCAST interpretive rules in antimicrobial susceptibility testing for fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides and Enterobacteriaceae. EUCAST Educational Workshop. 18th ECCMID Grogan J, Murphy H, Butler K. Extended-spectrum β-lactamaseproducing Klebsiella pneumonia in a Dublin paediatric hospital. Br J Biomed Sci 1998;55: Kim SY, Park YJ, Yu JK, Kim YS, Han K. Prevalence and characteristics of aac(6 )-Ib-cr in AmpC-producing Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter freundii, and Serratia marcescens: a multicenter study from Korea. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2009;63: Sabtcheva S, Kaku M, Saga T, Ishii Y, Kantardjiev T. High prevalence of the aac(6 )-Ib-cr gene and its dissemination among Enterobacteriaceae isolates by CTX-M-15 plasmids in Bulgaria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2009;53: Miller GH, Sabatelli FJ, Hare RS, Glupczynski Y, Mackey P, Shlaes D, et al. The most frequent aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms changes with time and geographic area: a reflection of aminoglycoside usage patterns? Aminoglycoside Resistance Study Groups. Clin Infect Dis 1997;24:S Dubois V, Arpin C, Dupart V, Scavelli A, Coulange L, Andre C, et al. β-lactam and aminoglycoside resistance rates and mechanisms among Pseudomonas aeruginosa in French general practice (community and private healthcare centres). J Antimicrob Chemother 2008;62: Kim JY, Park YJ, Kwon HJ, Han K, Kang MW, Woo GJ. Occurrence and mechanisms of amikacin resistance and its association with β-lactamases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a Korean nationwide study. J Antimicrob Chemother 2008;62: Doi Y and Arakawa Y. 16S ribosomal RNA methylation: emerging resistance mechanism against aminoglycosides. Clin Infect Dis 2007;45: Galimand M, Courvalin P, Lambert T. Plasmid-mediated high-level resistance to aminoglycosides in Enterobacteriaceae due to 16S rrna methylation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2003;47: Kang HY, Kim KY, Kim J, Lee JC, Lee YC, Cho DT, et al. Distribution of conjugative-plasmid-mediated 16S rrna methylase genes among amikacin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates collected in 1995 to 1998 and 2001 to 2006 at a university hospital in South Korea and identification of conjugative plasmids mediating dissemination of 16S rrna methylase. J Clin Microbiol 2008;46: Park YJ, Lee S, Yu JK, Woo GJ, Lee K, Arakawa Y. Co-production of 16S rrna methylases and extended-spectrum β-lactamases in AmpC-producing Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter freundii and Serratia marcescens in Korea. J Antimicrob Chemother 2006;58: Lee H, Yong D, Yum JH, Roh KH, Lee K, Yamane K, et al. Dissemination of 16S rrna methylase-mediated highly amikacinresistant isolates of Klebsiella pneumonia and Acinetobacter baumannii in Korea. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2006;56: Yamane K, Doi Y, Yokoyama K, Yagi T, Kurokawa H, Shibata N, et al. Genetic environments of the rmta gene found in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004;48: Doi Y, Yokoyama K, Yamane K, Wachino J, Shibata N, Yagi T, et al. Plasmid-mediated 16S rrna methylase in Serratia marcescens conferring high-level resistance to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004;48: Wachino J, Yamane K, Shibayama K, Kurokawa H, Shibata N, Suzuki S, et al. Novel plasmid-mediated 16S rrna methylase, RmtC, found in a Proteus mirabilis isolate demonstrating extraordinary high-level resistance against various aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006;50: Wachino J, Shibayama K, Kurokawa H, Kimura K, Yamane K, Suzuki S, et al. Novel plasmid-mediated 16S rrna m1a1408 methyltransferase, NpmA, found in a clinically isolated Escherichia coli strain resistant to structurally diverse aminoglycoside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2007;12: Poole K. Efflux mediated antimicrobial resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother 2005;56:20-51.
5 Yeon-Joon Park : Aminoglycoside Resistance in Gram-negative Bacilli 61 = 국문초록 = 그람음성세균에서의 Aminoglycoside 내성 가톨릭대학교의과대학서울성모병원진단검사의학교실박연준 Aminoglycoside는임상적으로유용한항균제중하나로, 세균의리보솜의 30S subunit에결합함으로써살균작용을보인다. 이약제에대한내성은세가지기전에의해일어난다. 첫째는 aminoglycoside를불활화시키는효소의생성이고, 둘째는세균의세포외막투과성의변화, 능동적유출에의해약제가세균세포내로이동하지못하게되는기전이며, 셋째는리보솜단백질의변화이다. 현재까지는효소에의한내성이가장흔하다. 본종설에서는 aminoglycoside의작용및내성기전, aminoglycoside 불활화효소에의한내성의빈도등에대해간략히살펴보았다. [ 대한임상미생물학회지 2009;12: 57-61] 교신저자 : 박연준, , 서울시서초구반포동 505 가톨릭대학교의과대학서울성모병원진단검사의학교실 Tel: , Fax: yjpk@catholic.ac.kr
The changing nature of aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms and prevalence of newly recognized resistance mechanisms in Turkey
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The changing nature of aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms and prevalence of newly recognized resistance mechanisms in Turkey U. OÈver 1,D.GuÈr 2,S.UÈnal 2, G. H. Miller 3 and the Aminoglycoside
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The changing nature of aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms and prevalence of newly recognized resistance mechanisms in Turkey U. OÈver 1,D.GuÈr 2,S.UÈnal 2, G. H. Miller 3 and the Aminoglycoside
Aminoglycosides. Not orally absorbed. Interact with negatively charged lipopolysaccharide on Gram- cell wall. Aminoglycoside properties
 Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins
 Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
The Most Frequent Aminoglycoside Resistance Mechanisms Changes with Time and Geographic Area: A Reflection of Aminoglycoside Usage Patterns?
 S46 The Most Frequent Aminoglycoside Resistance Mechanisms Changes with Time and Geographic Area: A Reflection of Aminoglycoside Usage Patterns? G. H. Miller, F. J. Sabatelli, R. S. Hare, Y. Glupczynski,
S46 The Most Frequent Aminoglycoside Resistance Mechanisms Changes with Time and Geographic Area: A Reflection of Aminoglycoside Usage Patterns? G. H. Miller, F. J. Sabatelli, R. S. Hare, Y. Glupczynski,
(multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; MDRP)
 220 2009 (multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; MDRP) 21 4 1 21 10 4 amikacin (AMK), imipenem/cilastatin (IPM), ciprofloxacin (CPFX) multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRP) CHROMagar TM
220 2009 (multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; MDRP) 21 4 1 21 10 4 amikacin (AMK), imipenem/cilastatin (IPM), ciprofloxacin (CPFX) multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRP) CHROMagar TM
jmb Research Article Review Semi Kim 1, Ji Youn Sung 2, Hye Hyun Cho 3, Kye Chul Kwon 1, and Sun Hoe Koo 1 *
 J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2014), 24(6), 765 770 http://dx.doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1306.06036 Review Research Article jmb Characterization of CTX-M-14- and CTX-M-15-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella
J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2014), 24(6), 765 770 http://dx.doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1306.06036 Review Research Article jmb Characterization of CTX-M-14- and CTX-M-15-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
ALERT. Clinical microbiology considerations related to the emergence of. New Delhi metallo beta lactamases (NDM 1) and Klebsiella
 ALERT Clinical microbiology considerations related to the emergence of New Delhi metallo beta lactamases (NDM 1) and Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases (KPC) amongst hospitalized patients in South Africa
ALERT Clinical microbiology considerations related to the emergence of New Delhi metallo beta lactamases (NDM 1) and Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases (KPC) amongst hospitalized patients in South Africa
Expert rules in antimicrobial susceptibility testing: State of the art
 Expert rules in antimicrobial susceptibility testing: State of the art ESCMID Postgraduate Education Course Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Surveillance: from Laboratory to Clinic Hospital Universitario
Expert rules in antimicrobial susceptibility testing: State of the art ESCMID Postgraduate Education Course Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Surveillance: from Laboratory to Clinic Hospital Universitario
MHSAL Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Antimicrobial Resistant Organisms (AROs) - Response to Questions
 MHSAL Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Antimicrobial Resistant Organisms (AROs) - Response to Questions Dr. Andrew Walkty Medical Microbiologist, Diagnostic Services Manitoba (DSM) June. 17,
MHSAL Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Antimicrobial Resistant Organisms (AROs) - Response to Questions Dr. Andrew Walkty Medical Microbiologist, Diagnostic Services Manitoba (DSM) June. 17,
Translocation Studies Mid-Term Review (MTR) Meeting Marseille, France
 Marie Curie Actions Research Training Networks (RTN) Translocation Studies Mid-Term Review (MTR) Meeting Marseille, France F. Vidal-Aroca, M.G.P. Page and J. Dreier Background Deteriorating situation regarding
Marie Curie Actions Research Training Networks (RTN) Translocation Studies Mid-Term Review (MTR) Meeting Marseille, France F. Vidal-Aroca, M.G.P. Page and J. Dreier Background Deteriorating situation regarding
Emergence of non-kpc carbapenemases: NDM and more
 Emergence of non-kpc carbapenemases: NDM and more --- David Livermore Health Protection Agency, UK The first acquired carbapenemase to be recognised in gram-negative bacteria was IMP-1, a metallo-type,
Emergence of non-kpc carbapenemases: NDM and more --- David Livermore Health Protection Agency, UK The first acquired carbapenemase to be recognised in gram-negative bacteria was IMP-1, a metallo-type,
Comparison of Aminoglycoside Resistance Patterns in Japan,
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Aug. 1985, p. 282-288 0066-4804/85/080282-07$02.00/0 Copyright 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 28, No. 2 Comparison of Aminoglycoside Resistance Patterns
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Aug. 1985, p. 282-288 0066-4804/85/080282-07$02.00/0 Copyright 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 28, No. 2 Comparison of Aminoglycoside Resistance Patterns
Determining the Optimal Carbapenem MIC that Distinguishes Carbapenemase-Producing
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 8 August 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00838-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 1 2 Determining the
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 8 August 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00838-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 1 2 Determining the
Carbapenemases in Enterobacteriaceae: Prof P. Nordmann Bicêtre hospital, South-Paris Med School
 Carbapenemases in Enterobacteriaceae: 2012 Prof P. Nordmann Bicêtre hospital, South-Paris Med School March 21, 2012 Trends in Molecular Medecine NDM IMP OXA-48 KPC VIM ALERT VI M KPC KPC NDM I MP OXA-
Carbapenemases in Enterobacteriaceae: 2012 Prof P. Nordmann Bicêtre hospital, South-Paris Med School March 21, 2012 Trends in Molecular Medecine NDM IMP OXA-48 KPC VIM ALERT VI M KPC KPC NDM I MP OXA-
First report of the IncI1/ST898 conjugative plasmid encoding rmte2. 16S rrna methyltransferase gene in Escherichia coli
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 21 September 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01235-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. [First Authors Last
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 21 September 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01235-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. [First Authors Last
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 13 October 2008 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi: /aac
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 13 October 2008 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00931-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 13 October 2008 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00931-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics. Question No. 1 of 10. Question. Feedback. Question
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
/01/$ DOI: /JCM Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 2001, p. 183 190 Vol. 39, No. 1 0095-1137/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.1.183 190.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Contemporary
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 2001, p. 183 190 Vol. 39, No. 1 0095-1137/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.1.183 190.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Contemporary
Received 31 January 2011/Returned for modification 2 March 2011/Accepted 15 March 2011
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 2011, p. 1965 1969 Vol. 49, No. 5 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00203-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Comparative
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 2011, p. 1965 1969 Vol. 49, No. 5 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00203-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Comparative
NONFERMENTING GRAM NEGATIVE RODS. April Abbott Deaconess Health System Evansville, IN
 NONFERMENTING GRAM NEGATIVE RODS April Abbott Deaconess Health System Evansville, IN OBJECTIVES Discuss basic limitations to assessing carbapenem resistance in nonfermenting GNRs Discuss antimicrobial
NONFERMENTING GRAM NEGATIVE RODS April Abbott Deaconess Health System Evansville, IN OBJECTIVES Discuss basic limitations to assessing carbapenem resistance in nonfermenting GNRs Discuss antimicrobial
Resistance to Polymyxins in France
 Resistance to Polymyxins in France Paris Prof. Patrice Nordmann NDM producers in Enterobacteriaceae The polymyxins; colistin and polymyxin B Colistin - Synthesis by Bacillus polymyxa spp colistinus -
Resistance to Polymyxins in France Paris Prof. Patrice Nordmann NDM producers in Enterobacteriaceae The polymyxins; colistin and polymyxin B Colistin - Synthesis by Bacillus polymyxa spp colistinus -
Update on CLSI and EUCAST
 Update on CLSI and EUCAST 1 Completed work» Cephalosporin breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae ESBL screens MIC versus resistance mechanism» Carbapenem breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae Modified Hodge Test»
Update on CLSI and EUCAST 1 Completed work» Cephalosporin breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae ESBL screens MIC versus resistance mechanism» Carbapenem breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae Modified Hodge Test»
Discussion points CLSI M100 S19 Update. #1 format of tables has changed. #2 non susceptible category
 Discussion points 2009 CLSI M100 S19 Update Nebraska Public Health Laboratory Changes most important to routine antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Documents available Janet Hindler discussion slide
Discussion points 2009 CLSI M100 S19 Update Nebraska Public Health Laboratory Changes most important to routine antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Documents available Janet Hindler discussion slide
Outpatient treatment in women with acute pyelonephritis after visiting emergency department
 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:369-373 Outpatient treatment in women with acute pyelonephritis after visiting emergency department Hee Kyoung Choi 1,*, Jin-Won Chung 2, Won Sup Oh 3,
LETTER TO THE EDITOR Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:369-373 Outpatient treatment in women with acute pyelonephritis after visiting emergency department Hee Kyoung Choi 1,*, Jin-Won Chung 2, Won Sup Oh 3,
Rapid identification and resistance assessment: The future is mass spectrometry
 Rapid identification and resistance assessment: The future is mass spectrometry Dr Sanmarié Schlebusch Director of Microbiology Mater Pathology Brisbane Outline Introduction Plug and play Pre-prep and
Rapid identification and resistance assessment: The future is mass spectrometry Dr Sanmarié Schlebusch Director of Microbiology Mater Pathology Brisbane Outline Introduction Plug and play Pre-prep and
#Corresponding author: Pathology Department, Singapore General Hospital, 20 College. Road, Academia, Level 7, Diagnostics Tower, , Singapore
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 October 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01754-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Title: Escherichia
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 October 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01754-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Title: Escherichia
Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the
Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the
Antibacterial-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Clinical Impact and Complex Regulation of Chromosomally Encoded Resistance Mechanisms
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 2009, p. 582 610 Vol. 22, No. 4 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00040-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antibacterial-Resistant
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 2009, p. 582 610 Vol. 22, No. 4 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00040-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antibacterial-Resistant
life-threatening infections
 Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Helen Heffernan and Rosemary Woodhouse Antibiotic Reference Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research Limited (ESR); July 2014.
 Annual survey of extended-spectrum -lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae, 2013 Helen Heffernan and Rosemary Woodhouse Antibiotic Reference Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research
Annual survey of extended-spectrum -lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae, 2013 Helen Heffernan and Rosemary Woodhouse Antibiotic Reference Laboratory, Institute of Environmental Science and Research
In Vitro Activity of Ceftazidime-Avibactam Against Isolates. in a Phase 3 Open-label Clinical Trial for Complicated
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 21 November 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01820-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 21 November 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01820-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Carbapenem Disks on MacConkey agar as screening methods for the detection of. Carbapenem-Resistant Gram negative rods in stools.
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 November 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02878-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Carbapenem Disks
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 November 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02878-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Carbapenem Disks
Below is an overview of the oral and poster presentations featuring cefiderocol and S at IDWeek 2017:
 SHIONOGI TO HIGHLIGHT RESEARCH ON CEFIDEROCOL (S-649266), A SIDEROPHORE CEPHALOSPORIN, AND S-033188, A CAP-DEPENDENT ENDONUCLEASE INHIBITOR FOR TREATMENT OF INFLUENZA, AT IDWEEK 2017 OSAKA, Japan and FLORHAM
SHIONOGI TO HIGHLIGHT RESEARCH ON CEFIDEROCOL (S-649266), A SIDEROPHORE CEPHALOSPORIN, AND S-033188, A CAP-DEPENDENT ENDONUCLEASE INHIBITOR FOR TREATMENT OF INFLUENZA, AT IDWEEK 2017 OSAKA, Japan and FLORHAM
Prevalence of Extended Spectrum -Lactamases In E.coli and Klebsiella spp. in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 474-478 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Extended Spectrum -Lactamases In E.coli and Klebsiella spp. in a Tertiary Care Hospital
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 474-478 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Extended Spectrum -Lactamases In E.coli and Klebsiella spp. in a Tertiary Care Hospital
NETILMICIN SUMMARY OF PRECLINICAL MICROBIOLOGICAL STUDIES. G. H. MILLER, R. S. HARE, E. L. Moss, Jr., F. J. SABATELLI and J. A.
 NETILMICIN SUMMARY OF PRECLINICAL MICROBIOLOGICAL STUDIES G. H. MILLER, R. S. HARE, E. L. Moss, Jr., F. J. SABATELLI and J. A. WAITZ Departments of Chemotherapy and Antibiotic Research Schering Corporation
NETILMICIN SUMMARY OF PRECLINICAL MICROBIOLOGICAL STUDIES G. H. MILLER, R. S. HARE, E. L. Moss, Jr., F. J. SABATELLI and J. A. WAITZ Departments of Chemotherapy and Antibiotic Research Schering Corporation
Journal of Infectious Diseases and
 Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy ISSN: 2332-0877 Journal of Infectious Diseases and Therapy Santanirand et al., J Infect Dis Ther 2018, 6:5 DOI: 10.4172/2332-0877.1000378 Research Article Open
Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy ISSN: 2332-0877 Journal of Infectious Diseases and Therapy Santanirand et al., J Infect Dis Ther 2018, 6:5 DOI: 10.4172/2332-0877.1000378 Research Article Open
Phenotypic Detection Methods of Carbapenemase Production in Enterobacteriaceae
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 547-552 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Phenotypic Detection Methods of Carbapenemase Production in Enterobacteriaceae Sathya Pandurangan 1,
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 547-552 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Phenotypic Detection Methods of Carbapenemase Production in Enterobacteriaceae Sathya Pandurangan 1,
Sep Oct Nov Dec Total
 LB PAGE 2 LB PAGE 3 Sep Oct Nov Dec 2007 2007 2007 2007 Total Repeat Information Total Repeats 35 15 17 9 76 Repeat Rate 6.01% 0.17% 1.12% 0.39% 2.07% Repeat Chemistry 25 0 2 0 27 Repeat Extraction 1 0
LB PAGE 2 LB PAGE 3 Sep Oct Nov Dec 2007 2007 2007 2007 Total Repeat Information Total Repeats 35 15 17 9 76 Repeat Rate 6.01% 0.17% 1.12% 0.39% 2.07% Repeat Chemistry 25 0 2 0 27 Repeat Extraction 1 0
Detection of NDM-1, VIM-1, KPC, OXA-48, and OXA-162 carbapenemases by MALDI- TOF mass spectrometry
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 2 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01002-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 2 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01002-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Affinity of Doripenem and Comparators to Penicillin-Binding Proteins in Escherichia coli and ACCEPTED
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Detection of Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacteriacae from Clinical Isolates
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 5 (2016) pp. 864-869 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.505.089
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 5 (2016) pp. 864-869 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.505.089
Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae pathogens isolated from intensive care units and surgical units in Russia
 Feb. 2016 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 69 1 41 41 Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae pathogens isolated from intensive care units and surgical units in Russia IRINA
Feb. 2016 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 69 1 41 41 Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae pathogens isolated from intensive care units and surgical units in Russia IRINA
Analysis of the common opportunistic pathogens
 2009 12 4 4 Journal of Microbes and Infection, December 2009, Vol. 4, No. 4 241 1, 3 1, 2, 3, 1. ( ), 201508; 2., 200040; 3., 200032 :,,,,,,, ;, : ; ; Analysis of the common opportunistic pathogens SUN
2009 12 4 4 Journal of Microbes and Infection, December 2009, Vol. 4, No. 4 241 1, 3 1, 2, 3, 1. ( ), 201508; 2., 200040; 3., 200032 :,,,,,,, ;, : ; ; Analysis of the common opportunistic pathogens SUN
Expert rules. for Gram-negatives
 Academic Perspective in Expert rules Emerging Issues of Resistance in Gram-ve Bacteria for Gram-negatives Trevor Winstanley Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Presented on behalf of David Livermore University
Academic Perspective in Expert rules Emerging Issues of Resistance in Gram-ve Bacteria for Gram-negatives Trevor Winstanley Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Presented on behalf of David Livermore University
Klebsiella pneumoniae 21 PCR
 2011 11 TEM-132 ESBL Klebsiella pneumoniae 1) 2) 1) 1) 3) 2) 1) 2) 3) 19 6 27 22 10 20 2003 4 2004 11 95 ceftazidime (CAZ) Klebsiella pneumoniae 21 PCR b- (ESBL) PCR (PFGE) PCR bla TEM-132 PFGE 19 TEM-132
2011 11 TEM-132 ESBL Klebsiella pneumoniae 1) 2) 1) 1) 3) 2) 1) 2) 3) 19 6 27 22 10 20 2003 4 2004 11 95 ceftazidime (CAZ) Klebsiella pneumoniae 21 PCR b- (ESBL) PCR (PFGE) PCR bla TEM-132 PFGE 19 TEM-132
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets
 Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
Plazomicin Versus Meropenem for the Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Acute Pyelonephritis: Results of the EPIC Study
 Plazomicin Versus Meropenem for the Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Acute Pyelonephritis: Results of the EPIC Study Daniel J. Cloutier 1, Loren G. Miller 2, Allison S. Komirenko 1,
Plazomicin Versus Meropenem for the Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Acute Pyelonephritis: Results of the EPIC Study Daniel J. Cloutier 1, Loren G. Miller 2, Allison S. Komirenko 1,
Emergence of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 with KPC-2 in Hong Kong. Title. Ho, PL; Tse, CWS; Lai, EL; Lo, WU; Chow, KH
 Title Emergence of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 with KPC-2 in Hong Kong Author(s) Ho, PL; Tse, CWS; Lai, EL; Lo, WU; Chow, KH Citation International Journal Of Antimicrobial Agents, 2011, v. 37 n. 4, p.
Title Emergence of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 with KPC-2 in Hong Kong Author(s) Ho, PL; Tse, CWS; Lai, EL; Lo, WU; Chow, KH Citation International Journal Of Antimicrobial Agents, 2011, v. 37 n. 4, p.
Original Article Clinical Microbiology
 Original Article Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 2015;35:212-219 http://dx.doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.212 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Combined Use of the Modified Hodge Test and Carbapenemase Inhibition
Original Article Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 2015;35:212-219 http://dx.doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.212 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Combined Use of the Modified Hodge Test and Carbapenemase Inhibition
ST11 KPC-2 Klebsiella pneumoniae detected in Taiwan
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 January 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.05576-11 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 January 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.05576-11 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5
Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Aminoglycosides Macrolides
 Protein synthesis inhibitors Antimicrobial protein synthesis inhibitors Joseph K. Ritter, PhD Assoc. Prof Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology MSB Room 536 jritter@mail2.vcu.edu 828-1022 Tetracyclines
Protein synthesis inhibitors Antimicrobial protein synthesis inhibitors Joseph K. Ritter, PhD Assoc. Prof Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology MSB Room 536 jritter@mail2.vcu.edu 828-1022 Tetracyclines
Spread of carbapenems resistant Enterobacteriaceae in South Africa; report from National Antimicrobial Resistance Reference Laboratory
 Spread of carbapenems resistant Enterobacteriaceae in South Africa; report from National Antimicrobial Resistance Reference Laboratory Olga Perovic*, Ashika Singh-Moodley, Samantha Iyaloo 5 th November
Spread of carbapenems resistant Enterobacteriaceae in South Africa; report from National Antimicrobial Resistance Reference Laboratory Olga Perovic*, Ashika Singh-Moodley, Samantha Iyaloo 5 th November
K. Lee, Y. S. Lim, D. Yong, J. H. Yum, and Y. Chong*
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 2003, p. 4623 4629 Vol. 41, No. 10 0095-1137/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.10.4623 4629.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 2003, p. 4623 4629 Vol. 41, No. 10 0095-1137/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.10.4623 4629.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology
 University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology This material is supported in part by unrestricted educational
University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology This material is supported in part by unrestricted educational
Sensitivity of Surveillance Testing for Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria in the
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 20 August 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02369-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Sensitivity of Surveillance
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 20 August 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02369-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Sensitivity of Surveillance
Against Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 1979, p. 6-6 0066-0/79/1-06/05$0.00/0 Vol., No. 6 In Vitro Activity of LY17935, a New 1-Oxa Cephalosporin, Against Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli DENNIS G. DELGADO,
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 1979, p. 6-6 0066-0/79/1-06/05$0.00/0 Vol., No. 6 In Vitro Activity of LY17935, a New 1-Oxa Cephalosporin, Against Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli DENNIS G. DELGADO,
First detection of the mcr-1 gene in Escherichia coli isolated from livestock between 2013
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 29 August 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01472-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 First detection of
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 29 August 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01472-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 First detection of
In-House Standardization of Carba NP Test for Carbapenemase Detection in Gram Negative Bacteria
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.342
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.342
Received 30 March 2005; returned 16 June 2005; revised 8 September 2005; accepted 12 September 2005
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
Other β-lactam. A. Carbapenems:
 A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
Enterobacteriaceae with acquired carbapenemases, 2016
 Enterobacteriaceae with acquired carbapenemases, 2016 Background The acquired or transferable (as opposed to chromosomally encoded) carbapenemases found in Enterobacteriaceae belong to three of the four
Enterobacteriaceae with acquired carbapenemases, 2016 Background The acquired or transferable (as opposed to chromosomally encoded) carbapenemases found in Enterobacteriaceae belong to three of the four
Antibiotic Treatment of GNR MDR Infections. Stan Deresinski
 Antibiotic Treatment of GNR MDR Infections Stan Deresinski Kucers: The Use of Antibiotics 1st Edition 1972 392 pages Kucers: The Use of Antibiotics 7 th Edition 2017 5338 pages Carbapenem Susceptibility
Antibiotic Treatment of GNR MDR Infections Stan Deresinski Kucers: The Use of Antibiotics 1st Edition 1972 392 pages Kucers: The Use of Antibiotics 7 th Edition 2017 5338 pages Carbapenem Susceptibility
Guidance on screening and confirmation of carbapenem resistant Enterobacteriacae (CRE) December 12, 2011
 Guidance on screening and confirmation of carbapenem resistant Enterobacteriacae (CRE) December 12, 2011 Objectives: To discuss the guidelines for detection of CRE in the laboratory setting. To review
Guidance on screening and confirmation of carbapenem resistant Enterobacteriacae (CRE) December 12, 2011 Objectives: To discuss the guidelines for detection of CRE in the laboratory setting. To review
Laboratory CLSI M100-S18 update. Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator
 Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
et al.. What remains against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae? Evaluation of chloramphenicol,
 What remains against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae? Evaluation of chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, colistin, fosfomycin, minocycline, nitrofurantoin, temocillin and tigecycline David M. Livermore,
What remains against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae? Evaluation of chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, colistin, fosfomycin, minocycline, nitrofurantoin, temocillin and tigecycline David M. Livermore,
breakpoints, cephalosporins, CLSI, Enterobacteriacae, EUCAST, review Clin Microbiol Infect 2008; 14 (Suppl. 1):
 REVIEW Breakpoints for intravenously used cephalosporins in Enterobacteriaceae EUCAST and CLSI breakpoints G. Kahlmeter Department of Clinical Microbiology, Central Hospital, Växjö, Sweden ABSTRACT It
REVIEW Breakpoints for intravenously used cephalosporins in Enterobacteriaceae EUCAST and CLSI breakpoints G. Kahlmeter Department of Clinical Microbiology, Central Hospital, Växjö, Sweden ABSTRACT It
Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory
 Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory Dr Danièle Meunier, AMRHAI BSAC - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing User Days Oxazolidinone Linezolid
Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory Dr Danièle Meunier, AMRHAI BSAC - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing User Days Oxazolidinone Linezolid
Consultation on the Revision of Carbapenem Breakpoints
 Consultation on the Revision of Carbapenem Breakpoints July 2018 Please send comments to the EUCAST Scientific Secretary at jturnidge@gmail.com by September 15. EUCAST revision of carbapenem breakpoints
Consultation on the Revision of Carbapenem Breakpoints July 2018 Please send comments to the EUCAST Scientific Secretary at jturnidge@gmail.com by September 15. EUCAST revision of carbapenem breakpoints
(Plasmid mediated) Carbapenemases. Timothy R. Walsh, Cardiff University, Wales
 (Plasmid mediated) Carbapenemases Timothy R. Walsh, Cardiff University, Wales What is a carbapenemase? How much carbapenem do they need to breakdown before they are called a carbapenemase? ESBL-enzymes
(Plasmid mediated) Carbapenemases Timothy R. Walsh, Cardiff University, Wales What is a carbapenemase? How much carbapenem do they need to breakdown before they are called a carbapenemase? ESBL-enzymes
Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics
 Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2008 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part V: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis ntroduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2008 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part V: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis ntroduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
High diversity of extended-spectrum b-lactamases among clinical isolates of Enterobacteriaceae from Portugal
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published October 3, 2007 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy doi:10.1093/jac/dkm381 High diversity of extended-spectrum b-lactamases among clinical
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published October 3, 2007 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy doi:10.1093/jac/dkm381 High diversity of extended-spectrum b-lactamases among clinical
Public Health Surveillance for Multi Drug Resistant Organisms in Orange County
 Public Health Surveillance for Multi Drug Resistant Organisms in Orange County Matt Zahn, MD Medical Director Epidemiology and Assessment Orange County Public Health Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Action
Public Health Surveillance for Multi Drug Resistant Organisms in Orange County Matt Zahn, MD Medical Director Epidemiology and Assessment Orange County Public Health Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Action
DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis.
 Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae
 medicaldaily.com http://en.vircell.com/diseases ppcorn.com Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae Robert Nicholas University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill cdc.gov Timeline
medicaldaily.com http://en.vircell.com/diseases ppcorn.com Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae Robert Nicholas University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill cdc.gov Timeline
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate
 Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Identification of a Serratia marcescens clinical isolate with multiple. Serratia marcescens, a Gram-negative bacillus that belongs to the family
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 13 August 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00070-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 13 August 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00070-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6
The Public Health Benefit of CRE Colonization Testing
 The Public Health Benefit of CRE Colonization Testing Allison C Brown, PhD MPH Team Lead, AR Capacities and Special Studies Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion CDC Carbapenem Resistance Serious threat
The Public Health Benefit of CRE Colonization Testing Allison C Brown, PhD MPH Team Lead, AR Capacities and Special Studies Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion CDC Carbapenem Resistance Serious threat
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERNS IN GRAM NEGATIVE URINARY ISOLATES TO CIPROFLOXACIN, CO-TRIMOXAZOLE AND NITROFURANTOIN
 SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERNS IN GRAM NEGATIVE URINARY ISOLATES TO CIPROFLOXACIN, CO-TRIMOXAZOLE AND NITROFURANTOIN Anoop Sinha 1, Benny P V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Anoop Sinha, Benny PV. Susceptibility
SUSCEPTIBILITY PATTERNS IN GRAM NEGATIVE URINARY ISOLATES TO CIPROFLOXACIN, CO-TRIMOXAZOLE AND NITROFURANTOIN Anoop Sinha 1, Benny P V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Anoop Sinha, Benny PV. Susceptibility
A Snapshot of Colistin Use in South-East Europe and Particularly in Greece
 A Snapshot of Colistin Use in South-East Europe and Particularly in Greece Helen Giamarellou 02.05.2013 When Greek Physicians Prescribe Colistin? It is mainly prescribed in the ICU for VAP, bacteremia
A Snapshot of Colistin Use in South-East Europe and Particularly in Greece Helen Giamarellou 02.05.2013 When Greek Physicians Prescribe Colistin? It is mainly prescribed in the ICU for VAP, bacteremia
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Julie Creighton and Clare Tibbs. Canterbury Health Laboratories, Christchurch
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of the MAST indirect carbapenemase test and comparison with a modified carbapenem inactivation method for the detection of carbapenemase enzymes in Gram-negative bacteria Julie
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of the MAST indirect carbapenemase test and comparison with a modified carbapenem inactivation method for the detection of carbapenemase enzymes in Gram-negative bacteria Julie
Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics
 Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2012 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part IV: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis Introduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2012 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part IV: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis Introduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
Cephalosporin, Against Cephalosporin-Resistant Bacteria, and
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Nov. 1979, P. 59-553 Vol. 16, No. 5 66-/79/11-59/$2./ Antibacterial Activity of Ceftizoxime (FK 79), a New Cephalosporin, Against Cephalosporin-Resistant Bacteria,
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Nov. 1979, P. 59-553 Vol. 16, No. 5 66-/79/11-59/$2./ Antibacterial Activity of Ceftizoxime (FK 79), a New Cephalosporin, Against Cephalosporin-Resistant Bacteria,
Downloaded from ismj.bpums.ac.ir at 10: on Friday March 8th 2019
 - ( ) - * :... (MDR) (ESBLs: Extended-Spectrum Beta Lactamases). :.. (CLSI:Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute). ESBL. combined disk method ESBL : / / / / / B / ( /). / / combined disk method.
- ( ) - * :... (MDR) (ESBLs: Extended-Spectrum Beta Lactamases). :.. (CLSI:Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute). ESBL. combined disk method ESBL : / / / / / B / ( /). / / combined disk method.
Differentiation of Carbapenemase producing Enterobacteriaceae by Triple disc Test
 Original article: Differentiation of Carbapenemase producing Enterobacteriaceae by Triple disc Test Manish Bansal 1, Nitya Vyas 2, Babita Sharma 3, R.K.Maheshwari 4 1PG Resident, 2 Professor, 3 Assistant
Original article: Differentiation of Carbapenemase producing Enterobacteriaceae by Triple disc Test Manish Bansal 1, Nitya Vyas 2, Babita Sharma 3, R.K.Maheshwari 4 1PG Resident, 2 Professor, 3 Assistant
Evaluation of Six Phenotypic Methods for the Detection of Carbapenemases in Gram-Negative Bacteria With Characterized Resistance Mechanisms
 Original Article Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 2017;37:305-312 https://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2017.37.4.305 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Evaluation of Six Phenotypic Methods for the Detection of Carbapenemases
Original Article Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 2017;37:305-312 https://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2017.37.4.305 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Evaluation of Six Phenotypic Methods for the Detection of Carbapenemases
International transfer of NDM-1-producing Klebsiella. pneumoniae from Iraq to France
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 18 January 2011 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01761-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 18 January 2011 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01761-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Antibiotics for Research
 Antibiotics for Research Natural antibiotics have existed for centuries prior to scientists identifying and isolating active moieties responsible for antibacterial activity. Today antibiotics are widely
Antibiotics for Research Natural antibiotics have existed for centuries prior to scientists identifying and isolating active moieties responsible for antibacterial activity. Today antibiotics are widely
Adenium Biotech. Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes
 Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Resistance to new anti-grampositive. Roland Leclercq, Microbiology, CHU Cote de Nacre, Caen, France
 Resistance to new anti-grampositive agents Roland Leclercq, Microbiology, CHU Cote de Nacre, Caen, France Recently available antimicrobials against MDR Gram-positive infections Cyclic lipopeptide: daptomycin
Resistance to new anti-grampositive agents Roland Leclercq, Microbiology, CHU Cote de Nacre, Caen, France Recently available antimicrobials against MDR Gram-positive infections Cyclic lipopeptide: daptomycin
Author: Souha Kanj Andrew Whitelaw Michael J. Dowzicky. To appear in: International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
 t Title: In vitro activity of tigecycline and comparators against Gram-positive and Gram-negative isolates collected from the Middle East and Africa between 2004 and 2011 Author: Souha Kanj Andrew Whitelaw
t Title: In vitro activity of tigecycline and comparators against Gram-positive and Gram-negative isolates collected from the Middle East and Africa between 2004 and 2011 Author: Souha Kanj Andrew Whitelaw
Rapid identification of emerging resistance in Gram negatives. Prof. Patrice Nordmann
 Rapid identification of emerging resistance in Gram negatives Prof. Patrice Nordmann Emerging Resistance threats, CDC USA-2013 Enterobacteriaceae producing extendedspectrum β-lactamases (ESBL) Multi-resistant
Rapid identification of emerging resistance in Gram negatives Prof. Patrice Nordmann Emerging Resistance threats, CDC USA-2013 Enterobacteriaceae producing extendedspectrum β-lactamases (ESBL) Multi-resistant
Treatment Options for Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Extended-Spectrum Β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae
 Treatment Options for Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Extended-Spectrum Β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae medicine.missouri.edu/jahm/treatment-options-urinary-tract-infections-caused-extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producingescherichia-coli-klebsiella-pneumoniae/
Treatment Options for Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Extended-Spectrum Β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae medicine.missouri.edu/jahm/treatment-options-urinary-tract-infections-caused-extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producingescherichia-coli-klebsiella-pneumoniae/
EVALUATION OF METHODS FOR AMPC β-lactamase IN GRAM NEGATIVE CLINICAL ISOLATES FROM TERTIARY CARE HOSPITALS
 Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology, (2005) 23 (2):120-124 Brief Communication EVALUATION OF METHODS FOR AMPC β-lactamase IN GRAM NEGATIVE CLINICAL ISOLATES FROM TERTIARY CARE HOSPITALS S Singhal, T
Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology, (2005) 23 (2):120-124 Brief Communication EVALUATION OF METHODS FOR AMPC β-lactamase IN GRAM NEGATIVE CLINICAL ISOLATES FROM TERTIARY CARE HOSPITALS S Singhal, T
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
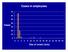 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
This material is supported in part by unrestricted educational grants from: Abbott, Bayer HealthCare, Merck Frosst, Roche Diagnostics, and Wyeth Inc.
 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology University of Alberta Hospital and Stollery Children's Hospital Antibiogram 2006 This material is supported in part by unrestricted
Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology University of Alberta Hospital and Stollery Children's Hospital Antibiogram 2006 This material is supported in part by unrestricted
Screening and detection of carbapenemases
 Screening and detection of carbapenemases For many isolates with carbapenemases the MICs of carbapenems are around the susceptible breakpoint making resistance difficult to detect - particularly with automated
Screening and detection of carbapenemases For many isolates with carbapenemases the MICs of carbapenems are around the susceptible breakpoint making resistance difficult to detect - particularly with automated
Aminoglycosides John A. Bosso, Pharm.D.
 AMINOGLYCOSIDES Therapeutics/PHRMP-73 Aminoglycoside Mechanism of Action Aminoglycosides bind to 30s ribosomal subunit resulting in mistranslation of mrna thus disrupting protein synthesis. They are rapidly
AMINOGLYCOSIDES Therapeutics/PHRMP-73 Aminoglycoside Mechanism of Action Aminoglycosides bind to 30s ribosomal subunit resulting in mistranslation of mrna thus disrupting protein synthesis. They are rapidly
Overcoming the PosESBLities of Enterobacteriaceae Resistance
 Overcoming the PosESBLities of Enterobacteriaceae Resistance Review of current treatment options Jamie Reed, PharmD Pharmacy Grand Rounds August 28, 2018 Rochester, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No
Overcoming the PosESBLities of Enterobacteriaceae Resistance Review of current treatment options Jamie Reed, PharmD Pharmacy Grand Rounds August 28, 2018 Rochester, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No
