Glossary of terms for cancer
|
|
|
- Charlotte Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Glossary of terms for cancer A Adjuvant chemotherapy Adjuvant therapy Alopecia Alveoli Anemia Anesthetic Anorexia Antibiotic Antiemetic Asymptomatic Atypical Axillary node The use of anticancer drugs after surgery to decrease the chance of the cancer coming back or recurring. A treatment method used in addition to the primary therapy; used to improve the chances of curing cancer. Loss of hair, which can include body hair and which is a side effect of some cancer treatments. Tiny air sacs found at the end of the smallest branches of the bronchial tree in the lungs. Oxygen passes through the alveoli and into the bloodstream. Carbon dioxide passes from the bloodstream into the alveoli and is breathed out through the lungs. A condition where the number of red blood cells in the blood is lower than normal. Anemia can occur because of the cancer itself or from the treatments. Symptoms of anemia include fatigue and shortness of breath. A drug that causes a loss of feeling or awareness and that may be used locally or generally, in which case sleep occurs. A lack of appetite for food. A drug that fights bacterial infections by killing or reducing the growth of bacteria. A drug that reduces or prevents nausea or vomiting. Not having the signs or symptoms of a disease. Abnormal or not usual. A lymph node located in the armpit (axilla).
2 - 2 - B Biopsy Blood cells Blood count Bone marrow Bone metastases Bone scan Brachytherapy Brain scan Bronchial carcinoma Bronchiole Bronchoscope Bronchoscopy Bronchus The removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination. General terms describing the three types of cells in blood (white blood cells WBC, red blood cells RBC and platelets), all of which are made in the bone marrow. A routine test that determines the number of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets in a sample of blood. Spongy material found inside some bones that produces blood cells. Tumour cells that have spread from the original (primary) tumour to the bone. A procedure by which an image of the bones is produced after the injection of a radioisotope. A bone scan is used to determine if the cancer has spread to the bones. A type of internal radiation therapy treatment. A radioactive source is placed in the area of the tumour and affects only that local area. A test used to determine if cancer has spread to the brain. Lung cancer. Very small tube(s) in the lungs that are without cartilage and that are at the end of the bronchus before it leads into the alveolus (plural: alveoli). A long thin instrument that is inserted into the throat or nasal passage to examine the larger lung breathing passages; see fibre optic bronchoscopy. The examination of the lung breathing passages with a bronchoscope. Either of the two main breathing tubes (plural: bronchi) branching off from the windpipe (trachea); one bronchus leads to each lung.
3 - 3 - C Cancer cell Carcinoma in situ Carcinogen Capillaries Catheter Cell Central nervous system (CNS) Central venous catheter Chemotherapy Chronic Combination chemotherapy Combined modality therapy Complementary therapy Complete blood count (CBC) A cell that divides and reproduces abnormally and is capable of invading (metastasizing to) other tissues. Early-stage cancer in which the tumour cells have not yet invaded surrounding tissues. A substance that causes cancer. Tiny blood vessels. A flexible tube inserted into the body to transport fluids into or out of the body. The basic building block of all living tissues, a cell is comprised of a nucleus (the brain of the cell), cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus and a cell wall containing the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The control center for the body and made up of the spinal cord and the brain. A special catheter placed in a large vein. It is left in place as long as necessary to deliver and/or withdraw fluids or administer drugs such as chemotherapy drugs. A drug or combination of drugs used to destroy cancer cells. Lasting for a long period of time. Treatment using two or more anticancer medications. Two or more types of cancer treatment given either at the same time or in sequence, and that can include combinations of radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery or other treatments. Techniques or approaches that may be used in addition to a standard treatment. Examples are meditation and changes in types of food eaten. An analysis to determine the quantities of various parts or components of the blood (see Blood count).
4 - 4 - Complete remission Complete response Complications Consent form Cure CT scan or CAT scan (computed axial tomography) Cytology D Diagnostic procedure Diaphragm Dysphagia Dyspnea The disappearance of all signs of cancer in response to treatment. This does not always mean the cancer has been cured. Also called complete response. The disappearance of all signs of cancer in response to treatment. This does not always mean the cancer has been cured. Also called complete remission. Unexpected symptoms or problems resulting from medical treatment such as surgery, chemotherapy or radiotherapy. A hospital or clinic legal form that informs patients about all the potential risks and benefits of any treatment they are to receive. Before a treatment can start, the form must be explained to the patient by the hospital or clinic staff, and the patient then can sign the form if they agree that they understand the risks and benefits and consent to the treatment. No sign of a disease or cancer is present in the body, and sufficient time has passed that the chance of the disease or cancer reoccurring is small. A diagnostic test that uses a combination of x-ray and computers to produce cross-sectional views (or layers) of the inside of the body. The study of cells and their origin, structure and function. A medical method used to identify (diagnose) the type of disease or abnormality and its cause. A major muscle that separates the chest from the abdominal cavity (the stomach and other parts) and helps with breathing. Difficulty in swallowing. Shortness of breath or air hunger.
5 - 5 - E Edema Epithelium Erythema Erythrocyte Erythropoietin Esophagus Excision Expectorant F Fibre optic bronchoscopy Fraction Fractionation G Granulocyte Granulocytopenia Swelling of a body part due to a build up of fluid in the tissue. The covering or lining of organs, glands, or other structures in the body. Cancers of the epithelium are called carcinomas. Redness of the skin. The red blood cell that carries oxygen to the cells and carries carbon dioxide away from them. A hormone that stimulates cells in the bone marrow to produce red blood cells. The part of the body that connects the mouth to the stomach. A common name is the swallowing tube. Removal by surgery. Medicine that helps a person cough up thick fluid (secretions) from the lungs. A procedure, either diagnostic or therapeutic, to examine the breathing passages of the lungs. The dose of radiation for a single treatment. Dividing the total dose of radiation therapy into several smaller, equal doses that are delivered over a period of several days. A type of white blood cell (WBC) that fights bacteria. Having a lower than normal number of granulocytes in the blood, which may reduce the ability of the immune system to fight infection.
6 H Hematologist Hematology Hemoglobin Hemoptysis Hospice Hypercalcemia Hyperfractionated radiation I A doctor who specializes in diseases of the blood. The study of blood, blood-producing organs and blood disorders or diseases. The iron-protein part or component of red blood cells that carries oxygen to body tissues. Coughing or spitting up blood in the sputum (spit). A place or program dedicated to caring for patients and their families near the end of life. Abnormally high concentrations of calcium in the blood, which can cause symptoms of nausea, vomiting, constipation, fatigue, and sleepiness. The total daily dose of radiation divided into smaller doses and given more than once a day. Imaging procedures Methods of producing pictures of areas inside the body that include x-ray, ultrasound, CT scan, MRI and nuclear medicine scans. Immune function Immune response Incision In situ Infection Informed consent The production of cells that fight disease or infection. The activity of the immune system against foreign cells and disease. A cut, usually used in reference to a surgical incision. In place, localized, and confined to one area; a very early stage of cancer. The reaction caused when disease-producing organisms such as viruses and bacteria invade and multiply in the body. Legal procedure conducted to ensure that a patient understands the potential risks and benefits of a treatment before it is started. The patient is informed about the treatment procedure, the potential risks and benefits, and even possible alternative treatments. To give informed consent the patient must be competent to understand the explanations and must give consent voluntarily.
7 - 7 - Intermittent Intravenous Invasive cancer L Larynx Laser treatment Lesion Leukocyte Leukopenia Lobe Lobectomy Local treatment Locally advanced cancer Lymph Lymph node Stopping or ceasing for a time, then beginning again. For example, intermittent pain. When drugs or fluids are put into a vein either by a single injection or continuously through a needle, tubing, and a solution bag; abbreviated as IV. Cancer that has spread beyond where it started and is growing into surrounding, healthy tissues. Also called infiltrating cancer. The voice box, which is located above the windpipe (trachea). The use of an intense narrow beam of laser light to kill cancer cells. An abnormal change in the structure of a tissue due to an injury or disease. A type of white blood cell (WBC) that protects the body against disease. An abnormally low number of leukocytes or WBCs, which decreases a person s ability to fight infection or disease. The division of a body organ such as the lung or liver marked by a surface fissure (crease).there are usually two lobes in the left lung and three lobes in the right lung. Surgical removal of one lobe of the lung. Treatment that affects a tumour and the area close to it. Cancer that has spread only to nearby tissue or lymph nodes, but not to other parts of the body. An almost colourless fluid that travels through the lymph or lymphatic system to help fight infection or disease. A small bean-shaped organ that acts as a filter to collect bacteria and other foreign substances from the lymph or lymphatic system to be processed by the immune system. There are chains of lymph nodes throughout the body.
8 - 8 - Lymphatic (lymph) system Lymphocyte M MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Malignant mesothelioma Mediastinum Medical oncologist Mediastinoscopy Metastasis Metastatic cancer Modality Monoclonal antibody (MoAb) Mucositis Multimodality therapy Myelosuppression The internal body network including the lymph nodes, lymph cells and lymph fluid that drains bacteria and other foreign substances from the body but that can also be an avenue of spread for cancer cells. A type of WBC that fights viruses and other foreign substances. A test that uses a magnetic field to create twodimensional images of the body. A malignant tumour that starts from the lining (pleura) of the chest cavity or covering of the lungs. This type of lung cancer has been linked to exposure to asbestos. The area between the two lungs containing body parts such as the esophagus (feeding or swallowing tube), trachea (windpipe), heart and lymph nodes. A doctor who specializes in the treatment of cancer, including using chemotherapy A surgical procedure that examines the lymph nodes along the trachea (windpipe) behind the breastbone for the presence of cancer or other diseases. The spread of cancer cells from the original tumour to other parts of the body. Cancer that has spread from one part of the body to another. A type or kind of treatment such as surgery. An antibody that recognizes a specific protein on a cancer cell. It attaches to the cancer cell and encourages cell death. Inflammation of the mucous membranes (lining) such as in the mouth or digestive system, which causes pain, soreness and/or excessive mucous production. Therapy that combines more than one method of treatment such as chemotherapy plus radiation. A side effect of chemotherapy that causes a slowed production of blood cells.
9 - 9 - N Nausea Needle aspiration biopsy Neoadjuvant therapy Neurologic(al) Neuropathy Neutropenia Neutrophil Neurotoxicity O Oncologist Oncology P Partial Remission Pathologic fracture Pathology Peripheral neuropathy Feeling sick to your stomach and needing to vomit. The withdrawal of fluid or cells from a part of the tumour for examination under a microscope. Initial treatment, such as chemotherapy, given to reduce the size of a cancerous tumour before surgery or radiation. Involving the nerves or nervous system. Nerve malfunction that may be caused by chemotherapy. Numbness or weakness is a common symptom. An abnormally low number of neutrophils or WBCs that may increase the risk of infection, depending on how low the count is and for how long. A type of WBC that fights bacterial infections. The tendency of some treatments to cause damage to the nervous system. A doctor who specializes in the study, diagnosis and treatment of cancer. The study of the development, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. Some, but not all of the signs and symptoms have disappeared but cancer may still be in the body. A broken bone often caused by metastases to the bone or other disease-related problems. The study of the nature of disease and its causes, processes, development and consequences. Nerve damage resulting from disease of or treatment to nerve endings. Numbness, tingling, and loss of movement may be noticed in the hands and feet.
10 Phase I clinical trial The phase of clinical research in which the safety and dosage of drugs are evaluated for the first time in humans. Because these treatments are new, there may be risks to participants; therefore, these trials are only open to a small number of healthy volunteers. Phase II clinical trial These trials focus on assessing the effectiveness of a treatment in a larger number of patients with the same type and stage of cancer. They help to better determine the potential usefulness of a new treatment in that cancer and to assess side effects that may not have been seen in Phase I trials. Phase III clinical trial Phase IV clinical trial Plasma Platelet Platelet count Platinum-based therapy Pleural effusion Pleurodesis Port Evaluates safety, efficacy, dosing and side effects of a new therapy compared to a standard treatment in a large group of patients in randomized controlled multicentre trials. A postmarketing trial of a drug treatment after its approval by the Health Protection Bureau (HPB) in Canada and its availability for sale in Canada. The liquid part of the blood. A type of blood cell that helps control bleeding by causing clotting and is also called a thrombocyte. The measurement of the number of platelets in the blood. The use of a combination of chemotherapy drugs, one of which contains the drug cisplatinum or carboplatin. Excess (pleural) fluid that collects between the lungs and the lining of the chest wall. A procedure using talcum or chemicals to eliminate the space between the lining of the lungs and the lining of the chest cavity to prevent the build up of pleural fluid within that space. A device placed beneath the skin and connected to a catheter in a vein for the delivery of medication or fluids.
11 Positron emission tomography (PET or PET scan) Primary tumour Psychological support R Radiation oncologist Radiation surgery Radiation therapy Radiologist Recurrent cancer Red blood cell (RBC) Regimen Regional involvement Regression Remission A scanning test that produces images of the inside of the human body and its metabolic functions. The tumour at the original site where the cancer began. Support designed to meet psychological and social needs, particularly those of a patient. A doctor who specializes in the treatment of cancer with radiation therapy. Also known as radiosurgery or stereotactic external beam irradiation or radiotherapy (EBRT); a type of therapy that delivers a single high dose of radiation directly to the tumour, sparing the healthy tissues from the effects of the radiation. X-ray treatment that damages or kills cancer cells. A doctor with training in reading diagnostic x-rays and performing specialized x-ray procedures. Cancer that has come back after treatment. Recurrent cancer may occur in the original site, or it may return elsewhere in the body. A type of blood cell that carries oxygen to the cells of the body and removes carbon dioxide. The plan that outlines the dosage, schedule and duration of treatment. The spread of cancer from its original site to nearby surrounding areas. A reduction in the symptoms or extent of cancer growth and spread. The time when a disease is under control and the person is free from signs and symptoms.
12 S Screening Secondary tumour Segmental resection Side effects Simulation Solid tumour Sputum Sputum cytology Standard treatment Steroid therapy Stomatitis Surgical biopsy A procedure or procedures used to determine if disease is present where there are no symptoms (or a person is asymptomatic). A tumour that develops as a result of metastases or the spread of cancer beyond the original site to another part of the body. If lung cancer cells, for example, metastasize to bone, the secondary tumour in the bone will be made of lung cancer cells. The surgical removal of an anatomic segment of tissue, for example, lung tissue. Lobes of the lung are divided into segments by creases (fissures). An undesirable effect (adverse reaction) in the body caused by the cancer treatment rather than the cancer itself. A process involving the use of special x-ray pictures to plan radiation treatment. A cancer of body tissues other than those of the blood, bone marrow, or lymphatic system. Lung cancer is classified as a solid tumour. Mucus from the bronchial tubes. The examination by microscope of cells in sputum coughed up from the lungs; usually used to look for the presence of cancer cells. Treatment that is commonly used for a condition, because it has been proved effective. The use of drugs that mimic the action of some of the hormones in the body and that may reduce such symptoms of inflammation as swelling and pain. An inflammation of the tissues that line the mouth, a side effect of radiation therapy. Surgical removal of a segment of tissue for examination under a microscope.
13 Surgical resection Systemic disease Systemic treatment T Terminal Therapy Thoracentesis Tunnelled catheter Removal of tissue from the body through a surgical procedure. Disease that affects the whole body rather than only an organ or single site. A treatment that reaches cells all over the body by traveling through the bloodstream. A term used to describe an advanced stage of disease with limited life expectancy. Treatment. The removal of fluid, by a needle, from the space (pleural space) between the lungs and the chest wall. A specialized catheter that is inserted into a large vein near the heart and is used for the delivery of medications, transfusions, and blood sampling. For other terms, search the website Hamilton Health Sciences, 2014 PD /2014 dpc/pted/cancerglossaryterms-th.doc dt/september 4, 2014
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung.
 Lung Cancer Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the
Lung Cancer Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the
Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time.
 Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Esophageal Cancer. Source: National Cancer Institute
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Esophageal cancer. What is esophageal cancer? Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the esophagus.
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) affects 15% of all lung cancer patients. SCLC is the most aggressive type of lung cancer. It may be treated with chemotherapy and radiation. SCLC has
Small Cell Lung Cancer Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) affects 15% of all lung cancer patients. SCLC is the most aggressive type of lung cancer. It may be treated with chemotherapy and radiation. SCLC has
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma
 Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy
 Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracoscopy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem. Or you may
Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracoscopy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem. Or you may
Leukemia. There are different types of leukemia and several treatment options for each type.
 Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Lung Cancer Resection
 Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer
 Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer
 Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program. Patient information for. Last revised: November
 Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
 11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
 SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS Anatomy of the Lungs...2 Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)...3 Risk Factors...3 Your
SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS Anatomy of the Lungs...2 Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)...3 Risk Factors...3 Your
Cancer of the oropharynx
 Cancer of the oropharynx Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly
Cancer of the oropharynx Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly
Pancreatic Cancer. What is pancreatic cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
WELLNESS INITIATIVE NOW
 WELLNESS INITIATIVE NOW To promote personal well-being, fitness and nutrition for all TDCJ employees. November 2008 Lung cancer is cancer that forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining
WELLNESS INITIATIVE NOW To promote personal well-being, fitness and nutrition for all TDCJ employees. November 2008 Lung cancer is cancer that forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining
Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells (lymphocytes) of the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Small cell lung cancer
 understanding SerieS Small cell lung cancer 1-800-298-2436 lungcanceralliance.org a Guide for the patient i table of contents anatomy of the lungs The following image shows different parts that make up
understanding SerieS Small cell lung cancer 1-800-298-2436 lungcanceralliance.org a Guide for the patient i table of contents anatomy of the lungs The following image shows different parts that make up
Chapter 8. Other Important Tests and Procedures. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Lung Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis cancer.ca
 Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed
Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
Tongue cancer. Patient information
 What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This process ensures each part of
What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This process ensures each part of
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer
 Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER
 The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER What is breast cancer? Breast cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the breast. The breast is made up of lobes and ducts.
The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER What is breast cancer? Breast cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the breast. The breast is made up of lobes and ducts.
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
General Information Key Points
 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
What is Thyroid Cancer?
 Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
 Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
Esophageal Cancer. What is esophageal cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
LUNG SURGERY. Treatment for Lung Problems
 LUNG SURGERY Treatment for Lung Problems When You Need Lung Surgery Your doctor is recommending surgery for your lung problem. Surgery alone may treat your problem. Or you may need other treatments as
LUNG SURGERY Treatment for Lung Problems When You Need Lung Surgery Your doctor is recommending surgery for your lung problem. Surgery alone may treat your problem. Or you may need other treatments as
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
What is Thyroid Cancer? Here are four types of thyroid cancer:
 What is Thyroid Cancer? Thyroid cancer is a group of malignant tumors that originate from the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine from the bloodstream
What is Thyroid Cancer? Thyroid cancer is a group of malignant tumors that originate from the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine from the bloodstream
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
What is lung cancer? Contents
 13 11 20 Information and support What is lung cancer? Contents About the lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Different types of lung cancer Causes Symptoms Information reviewed by About the lungs
13 11 20 Information and support What is lung cancer? Contents About the lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Different types of lung cancer Causes Symptoms Information reviewed by About the lungs
If You Have Head or Neck Cancer
 EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Anemia: A condition in which the number of red blood cells is below normal.
 Veterinary Teaching Hospital Oncology Service Virginia-Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine 245 Duck Pond Drive Blacksburg, VA 24061 Phone: 540-231-4621 Definitions This fact sheet is based
Veterinary Teaching Hospital Oncology Service Virginia-Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine 245 Duck Pond Drive Blacksburg, VA 24061 Phone: 540-231-4621 Definitions This fact sheet is based
Pneumonia. Trachea , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Symptoms. Types
 Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect
 Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Head and Neck Cancer. What is head and neck cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that usually originate in the squamous cells that line the mouth, nose and throat. Typical symptoms include a persistent
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that usually originate in the squamous cells that line the mouth, nose and throat. Typical symptoms include a persistent
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
What is head and neck cancer? How is head and neck cancer diagnosed and evaluated? How is head and neck cancer treated?
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
Interventional Oncology Patient Awareness
 Interventional Oncology Patient Awareness Interventional Radiology: your minimally invasive alternative www.cirse.org Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe Cardiovascular and
Interventional Oncology Patient Awareness Interventional Radiology: your minimally invasive alternative www.cirse.org Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe Cardiovascular and
Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. ocf80101 Last reviewed: 06/08/2016 1
 Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
 To the Patient and Family This booklet has been written for people who have received a diagnosis of thyroid cancer or who are being tested for this illness. If you have questions that are not answered
To the Patient and Family This booklet has been written for people who have received a diagnosis of thyroid cancer or who are being tested for this illness. If you have questions that are not answered
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
General information about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Colon Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. oc Last reviewed: 05/17/2017 1
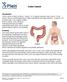 Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Information. about cancer
 1 Information about cancer This chapter may help you answer simple questions about what cancer is and how it is treated. There are more than 200 different types of cancer and a range of treatments. Being
1 Information about cancer This chapter may help you answer simple questions about what cancer is and how it is treated. There are more than 200 different types of cancer and a range of treatments. Being
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood. Functions:
 Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Lung Cancer. Trusted Information to Help Manage Your Care from the American Society of Clinical Oncology
 Lung Cancer Trusted Information to Help Manage Your Care from the American Society of Clinical Oncology ABOUT ASCO The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is the world s leading professional organization
Lung Cancer Trusted Information to Help Manage Your Care from the American Society of Clinical Oncology ABOUT ASCO The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is the world s leading professional organization
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Lung Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center
 LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
 Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Case Scenario 1. The patient agreed to a CT guided biopsy of the left upper lobe mass. This was performed and confirmed non-small cell carcinoma.
 Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Colorectal Cancer Glossary. Colorectal Cancer Glossary
 1 A Abdomen: (AB-do-men) The part of the body between the chest and the pelvis that contains organs including the pancreas, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), liver and gallbladder. Adjuvant
1 A Abdomen: (AB-do-men) The part of the body between the chest and the pelvis that contains organs including the pancreas, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), liver and gallbladder. Adjuvant
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
GCE AS/A level 1661/01-A APPLIED SCIENCE UNIT 1
 GCE AS/A level 1661/01-A APPLIED SCIENCE UNIT 1 S16-1661-01A Pre-release Article for Examination in May 2016 1661 01A001 CJ*(S16-1661-01A) 2 Information for Teachers The pre-release article is intended
GCE AS/A level 1661/01-A APPLIED SCIENCE UNIT 1 S16-1661-01A Pre-release Article for Examination in May 2016 1661 01A001 CJ*(S16-1661-01A) 2 Information for Teachers The pre-release article is intended
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix.
 Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery
 Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT
 UNDERSTANDING SERIES YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...2 The Basics...3 Sections of a Pathology Report...6
UNDERSTANDING SERIES YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...2 The Basics...3 Sections of a Pathology Report...6
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Thoracotomy. Surgery for Lung Problems
 Thoracotomy Surgery for Lung Problems A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracotomy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem.
Thoracotomy Surgery for Lung Problems A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracotomy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem.
What is Esophageal Cancer?
 What is Esophageal Cancer? The esophagus is a hollow, muscular tube, about 10 inches long which connects the throat to the stomach. When a person swallows, the walls of the esophagus contract to push food
What is Esophageal Cancer? The esophagus is a hollow, muscular tube, about 10 inches long which connects the throat to the stomach. When a person swallows, the walls of the esophagus contract to push food
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul. Epidemiology. Risk factors/aetiology
 Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Lung Carcinoid Tumor Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Lung Carcinoid Tumor Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Lung Carcinoid Tumor Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Small Cell Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that
Small Cell Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that
Chapter 16. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
