Like any tissue, tumors require blood supply. (1) The vascular
|
|
|
- Clifford Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anti-bevacizumab idiotype antibody vaccination is effective in inducing vascular endothelial growth factor-binding response, impairing tumor outgrowth Jessica de Souza Sanches, 1,3 Rodrigo Barbosa de Aguiar, 1,3 Carolina Bellini Parise, 1,3 Juliana Mayumi Suzuki, 1 Roger Chammas 2 and Jane Zveiter de Moraes 1 1 Department of Biophysics, Escola Paulista de Medicina, Universidade Federal de S~ao Paulo, S~ao Paulo; 2 Department of Radiology, Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade de S~ao Paulo, S~ao Paulo, Brazil Key words Angiogenesis, idiotype, monoclonal antibody, vaccination, vascular endothelial growth factor Correspondence Jane Zveiter de Moraes, Departamento de Biofısica, Escola Paulista de Medicina, Universidade Federal de S~ao Paulo, S~ao Paulo, Brazil. Rua Botucatu, S~ao Paulo, SP, Brazil. Tel.: ext. 2329; Fax: ; janezvmo@gmail.com 3 These authors contributed equally to this work. Funding Information Coordenacß~ao de Aperfeicßoamento de Pessoal de Nıvel Superior, Fundacß~ao de Apoio a Pesquisa do Estado de S~ao Paulo. Received October 29, 2015; Revised January 29, 2016; Accepted January 31, 2016 Cancer Sci 107 (2016) doi: /cas Tumors require blood supply and, to overcome this restriction, induce angiogenesis. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays an important role in this process, which explains the great number of antiangiogenic therapies targeting VEGF. The research and development of targeted therapy has led to the approval of bevacizumab, a humanized anti-vegf monoclonal antibody (mab), in clinical settings. However, side effects have been reported, usually as a consequence of bolus-dose administration of the antibody. This limitation could be circumvented through the use of anti-idiotype (Id) antibodies. In the present study, we evaluated the efficacy of an active VEGF-binding immune response generated by an anti-bevacizumab idiotype mab, 10.D7. The 10.D7 anti-id mab vaccination led to detectable levels of VEGF-binding anti-anti-id antibodies. In order to examine whether this humoral immune response could have implications for tumor development, 10.D7-immunized mice were challenged with B16-F10 tumor cells. Mice immunized with 10.D7 anti-id mab revealed reduced tumor growth when compared to control groups. Histological analyses of tumor sections from 10.D7- immunized mice showed increased necrotic areas, decreased CD31-positive vascular density and reduced CD68-positive cell infiltration. Our results encourage further therapeutic studies, particularly if one considers that the anti-id therapeutic vaccination maintains stable levels of VEGF-binding antibodies, which might be useful in the control of tumor relapse. Like any tissue, tumors require blood supply. (1) The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a key angiogenic factor secreted by several tumors, at least in their initial stages. (2) Thus, therapies targeting angiogenesis have a place in treating human cancer. A humanized anti-vegf monoclonal antibody (mab), bevacizumab, has been approved for use, with other drugs, for certain tumors. (3,4) However, clinical studies show that the use of bevacizumab is associated with some side effects, such as gastrointestinal bleeding, thrombotic events, epistaxis and hypertensive episodes. (3,5) These complications are related to the weekly or the 2-week administrations of antibody in massive doses, which often prevent continuing treatment. (3) Taking into account our experience with anti-idiotype (anti- Id) antibodies, (6,7) we considered that the idiotype network approach could circumvent the need for administration of high doses of anti-vegf antibodies. In contrast to this, therapeutic vaccination with an anti-id mab stimulates an active immune response, usually of low but sustained intensity. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to prove the concept that it is possible to obtain a VEGF mimic anti-id This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes. antibody. For this, we examined whether the anti-id mab immunization triggers a VEGF-binding antibody response able to inhibit angiogenesis and, thereby, interfere with the tumor growth. Materials and Methods Hybridoma, HUVEC and B16-F10 melanoma cells were cultured as described previously. (8) Antibody generation was obtained by hybridoma technology (6) and VEGF-binding antibody detection by ELISA. (9) Detailed procedures are described in Data S1. Results Generation of anti-bevacizumab idiotype monoclonal antibody, 10.D7. To generate an anti-bevacizumab idiotype antibody, four BALB C mice were immunized with KLH-conjugated bevacizumab. Screening was based on the inhibition of biotinylated bevacizumab binding to hvegf in the presence Cancer Sci April 2016 vol. 107 no
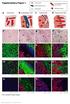
2 Anti-bevacizumab idiotype antibody (a) (b) (c) Fig D7 anti-idiotype (anti-id) antibody vaccination compromises tumor growth. (a) Experimental design. (b) B16-F10 tumor growth curves. Mice were immunized with 10.D7 anti-id monoclonal antibody (mab) (or controls). (c) ELISA detection of VEGF-binding antibodies in 1:100- diluted serum samples from mice 10 days after immunization boost. Adjuvant control, n = 6; isotype control mab-immunized, n = 8; 10.D7 anti- Id mab-immunized group, n = 8. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Mean SD. *P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA Bonferroni s post-test. of immune serum. After limiting dilution cloning, stable antibevacizumab idiotype-secreting hybridoma clone 10.D7 was selected and the secreted antibody was determined to be an IgG1 isotype. Therapeutic vaccination with 10.D7 anti-idiotype monoclonal antibody impairs tumor growth and angiogenesis. We used the B16-10 tumor model to examine the therapeutic potential of our proposed anti-id mab vaccination. Mice were challenged with B16-F10 cells on the 10th day after boost immunization, according to the experimental schedule shown in Figure 1a. Vaccination with 10.D7 anti-id mab resulted in significantly reduced tumor growth, compared to the adjuvant and isotype immunized control groups (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA). Tumor growth curves are plotted in Figure 1b. The presence of detectable levels of hvegf-binding antibodies in serum samples from 10.D7 anti-id mab-immunized mice immediately before B16-F10 cell injection was verified by ELISA (Fig. 1c). It is important to observe here that such immune sera recognize not only hvegf but also the murine form of this factor. Bevacizumab, in comparison, could bind only to hvegf, as expected (Fig. 2). Histological analyses of HE-stained sections revealed an increase of necrotic area in tumors from mice immunized with 10.D7 anti-id mab: the mean percentage of tumor necrotic area was approximately fivefold higher than that observed in the control groups (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA). Representative HE-stained sections and the respective necrosis quantification are shown in Figure 3a. This result was accompanied by a decreased CD31-positive vascular network in subcutaneous tumors excised from the 10.D7 anti-id mab-immunized group, compared to controls (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA; Fig. 3b). In addition, a reduced number of CD68-positive cells were observed in tumors from 10.D7 mab-immunized mice (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA) (Fig. 3c). Furthermore, such angiogenic inhibition was also observed by in vitro tubulogenesis assay. As shown in Figure 4, HUVEC incubation with sera obtained after 10.D7 anti-id mab immunization gave a reduced and poorly organized capillary-like plexus, compared with the serum controls (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA). Discussion The use of anti-id antibodies acting as an internal image of tumor-expressing antigens on vaccination settings offers the opportunity to overcome tolerance to auto-antigens (10) and to control tumor progression, (11,12) with some studies already in clinical development (Table S1). Herein, we show the effectiveness of an anti-bevacizumab idiotype antibody in generating an active VEGF-binding immune response. As far as we know, this is the first time that an anti-id approach has been used to inhibit angiogenesis. The B16-F10 tumor model was chosen to investigate the therapeutic viability of our anti-bevacizumab idiotype mab vaccination approach. Despite clinical studies pointing to the non-responsiveness of melanomas to VEGF-targeting therapies, (13,14) the previous reported impairments of B16-F10 solid tumor growth and vascular density by anti-vegf antibodies (15,16) provide a rationale for the use of this experimental mouse model. The effectiveness of the studied anti-id mab vaccination was revealed by the detection of serum VEGF-binding antibodies, in B16-F10-challenged animals, leading to tumors with reduced size and higher necrotic areas, compared to those obtained in the control groups. The antiangiogenic activity obtained by anti-id vaccination was evidenced by the significantly lower CD31-positive tumor vascular area, as well as by the hampered in vitro formation of tube-like structures of HUVEC, known to secrete VEGF. (17) These results are in Cancer Sci April 2016 vol. 107 no
3 Sanches et al. Fig. 2. Serum from 10.D7 anti-idiotype (anti-id) antibody-immunized mice recognizes murine and human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). VEGF-binding evaluated by ELISA. Fig D7 anti-idiotype (anti-id) monoclonal antibody (mab) vaccination increases necrosis and reduces CD31-positive vessel area and CD68-positive cells in a murine tumor model. (a) Representative HEstained B16-F10 tumor sections from the group immunized with 10.D7 anti-id mab (or controls). Graph shows quantification of % necrosis area. Adjuvant control, n = 6; isotypic control mab-immunized, n = 7; 10.D7 anti-id mab-immunized group, n = 5. (b) Representative images of tumor sections immunolabeled for CD31. Graph shows quantification of %CD31-positive vessels per tumor section area. CD31, green; DAPI, blue. Adjuvant control, n = 5; isotypic control mab-immunized, n = 7; 10.D7 anti-id mab-immunized group, n = 7. (c) Representative images of tumor sections immunolabeled for CD68. Graph shows quantification of %CD68-positive cells per tumor section area. CD68, green; DAPI, blue. Adjuvant control, n = 5; isotypic control mab-immunized, n = 7; 10.D7 anti-id mab-immunized group, n = 7. *P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA Bonferroni s post-test, related to controls. agreement with previous reports stating that VEGF inhibition, mainly in the early stages of tumor growth, impairs tumor angiogenesis and its further progression. (16,18) It is already known that even though bevacizumab seems to interact with degraded products of murine VEGF, (19) it fails in inhibiting mvegf-induced activity and in displaying any effect on murine tumor growth. (20) Despite this, sera from mice immunized with 10.D7 anti-bevacizumab idiotype antibody recognize both murine and human VEGF, which makes it reasonable to assume that the in vivo data presented here might be, at least in part, the result of mvegf immunoneutralization by VEGF-binding antibody serum content. Given that VEGF acts in several processes in the tumor microenvironment, mechanisms other than impairing tumor angiogenesis might be behind our therapeutic findings. Of note, it is known that VEGF blocking strategies led to reduced recruitment and retention of circulating myeloid cells, like monocytes, to the perivascular area, (21) as well as to enhanced activation of dendritic cells. (22) In fact, analyses of tumors from 10.D7 mab-immunized mice pointed in the same direction. In addition, Fc-mediated mechanisms, such as complement- or antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicities, might contribute to the reduced tumor growth observed. Overall, mice immunization with an anti-bevacizumab idiotype antibody was effective in eliciting VEGF-binding humoral IgG antibodies capable of impairing vascular density and tumor growth. The proposed vaccination should be considered as an antiangiogenic therapeutic strategy for controlling the progression of VEGF-dependent tumors, including post-surgical resection relapse scenarios, where VEGF plays an important role. (23,24) Acknowledgments This work was supported by FAPESP ( ; ; ) and CAPES (JSS; CBP; RBA) research grants. Disclosure Statement The authors have no conflict of interest to declare. Cancer Sci April 2016 vol. 107 no
4 Anti-bevacizumab idiotype antibody (a) (b) (c) Fig. 4. Sera from anti-bevacizumab idiotype 10.D7 mab-immunized mice inhibit HUVEC tube-like structure formation on Matrigel. Representative images obtained after HUVEC 6-h incubation with 1:100-diluted pool sera from 10.D7 anti-id mab-immunized mice (or controls). Graph shows quantification of total mesh area, normalized to vehicle control. Assays were performed in duplicate (mean SEM). The data are representative of two independent experiments. Scale bar, 50 lm. *P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA Bonferroni s post-test. References 1 Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000; 407: Ranieri G, Patruno R, Ruggieri E et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a target of bevacizumab in cancer: from the biology to the clinic. Curr Med Chem 2006; 13: Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: Board RE, Thistlewaite FC, Hawkins RE. Anti-angiogenic therapy in the treatment of advanced renal cell cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 2007; 33: Ahmadizar F, Onland-Moret NC, de Boer A, Liu G, Maitland-van der Zee AH. Efficacy and safety assessment of the addition of bevacizumab to adjuvant therapy agents in cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2015; 10: e Moraes JZ, Gesztesi JL, Westermann P, Le Doussal JM, Lopes JD, Mach JP. Anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody AB3, reacting with the primary antigen (CEA), can localize in human colon-carcinoma xenografts as efficiently as AB1. Int J Cancer 1994; 57: Ramos AS, Parise CB, Travassos LR, Han SW, de Campos-Lima PO, de Moraes JZ. The idiotype (Id) cascade in mice elicited the production of anti-r24 Id and anti-anti-id monoclonal antibodies with antitumor and protective activity against human melanoma. Cancer Sci 2011; 102: Aguiar RB, Parise CB, Souza CR et al. Blocking FGF2 with a new specific monoclonal antibody impairs angiogenesis and experimental metastatic melanoma, suggesting a potential role in adjuvant settings. Cancer Lett 2016; 371: Parise CB, Lisboa B, Takeshita D, Sacramento CB, de Moraes JZ, Han SW. Humoral immune response after genetic immunization is consistently improved by electroporation. Vaccine 2008; 26: Cancer Sci April 2016 vol. 107 no
5 Sanches et al. 10 Ladjemi MZ. Anti-idiotypic antibodies as cancer vaccines: achievements and future improvements. Front Oncol 2012; 2: Foon KA, Sen G, Hutchins L et al. Antibody responses in melanoma patients immunized with an anti-idiotype antibody mimicking disialoganglioside GD2. Clin Cancer Res 1998; 4: Vazquez AM, Hernandez AM, Macıas A et al. Racotumomab: an anti-idiotype vaccine related to N-glycolyl-containing gangliosides Preclinical and clinical data. Front Oncol 2012; 2: Varker KA, Biber JE, Kefauver C et al. A randomized phase 2 trial of bevacizumab with or without daily low-dose interferon alfa-2b in metastatic malignant melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2007; 14: Flaherty KT, Hamilton BK, Rosen MA et al. Phase I II trial of imatinib and bevacizumab in patients with advanced melanoma and other advanced cancers. Oncologist 2015; 20: Ghosh S, Maity P. Augmented antitumor effects of combination therapy with VEGF antibody and cisplatin on murine B16F10 melanoma cells. Int Immunopharmacol 2007; 7: Shrimali RK, Yu Z, Theoret MR, Chinnasamy D, Restifo NP, Rosenberg SA. Antiangiogenic agents can increase lymphocyte infiltration into tumor and enhance the effectiveness of adoptive immunotherapy of cancer. Cancer Res 2010; 70: Imaizumi T, Itaya H, Nasu S et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human umbilical vein endothelial cells stimulated with interleukin-1alpha an autocrine regulation of angiogenesis and inflammatory reactions. Thromb Haemost 2000; 83: Liang WC, Wu X, Peale FV et al. Cross-species vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-blocking antibodies completely inhibit the growth of human tumor xenografts and measure the contribution of stromal VEGF. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: Camacho X, Garcia MF, Calzada V et al. [(99 m)tc(co)(3)]-radiolabeled bevacizumab: in vitro and in vivo evaluation in a melanoma model. J Anal Oncol 2014; 3: Yu L, Wu X, Cheng Z et al. Interaction between bevacizumab and murine VEGF-A: a reassessment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008; 49: Grunewald M, Avraham I, Dor Y et al. VEGF-induced adult neovascularization: recruitment, retention, and role of accessory cells. Cell 2006; 124: Osada T, Chong G, Tansik R et al. The effect of anti-vegf therapy on immature myeloid cell and dendritic cells in cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2008; 57: Fondevila C, Metges JP, Fuster J et al. p53 and VEGF expression are independent predictors of tumour recurrence and survival following curative resection of gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 2004; 90: Kottke T, Boisgerault N, Diaz RM et al. Detecting and targeting tumor relapse by its resistance to innate effectors at early recurrence. Nat Med 2013; 19: Supporting Information Additional supporting information may be found in the online version of this article: Data S1. Supplementary Materials and Methods. Table S1. Status of the clinical development of anti-idiotype antibodies for cancer therapy. Cancer Sci April 2016 vol. 107 no
Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach
 Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach Oncolytic immunotherapy Oncolytic immunotherapy the use of a genetically modified virus to attack tumors and induce a systemic immune response
Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach Oncolytic immunotherapy Oncolytic immunotherapy the use of a genetically modified virus to attack tumors and induce a systemic immune response
Chemotherapy of colon cancers
 Chemotherapy of colon cancers Stage distribution Stage I : 15% T 1,2 NO Stage IV: 20 25% M+ Stage II : 20 30% T3,4 NO Stage III N+: 30 40% clinical stages I, II, or III colon cancer are at risk for having
Chemotherapy of colon cancers Stage distribution Stage I : 15% T 1,2 NO Stage IV: 20 25% M+ Stage II : 20 30% T3,4 NO Stage III N+: 30 40% clinical stages I, II, or III colon cancer are at risk for having
Bevacizumab (Avastin)
 Bevacizumab (Avastin) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.001 09/14/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 03/01/2014 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s) of Service:
Bevacizumab (Avastin) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.001 09/14/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 03/01/2014 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s) of Service:
STATE OF THE ART 4: Combination Immune Therapy-Chemotherapy. Elizabeth M. Jaffee (JHU) James Yang (NCI) Jared Gollob (Duke) John Kirkwood (UPMI)
 STATE OF THE ART 4: Combination Immune Therapy-Chemotherapy Elizabeth M. Jaffee (JHU) James Yang (NCI) Jared Gollob (Duke) John Kirkwood (UPMI) Topics for Consideration What are the rules for integrating
STATE OF THE ART 4: Combination Immune Therapy-Chemotherapy Elizabeth M. Jaffee (JHU) James Yang (NCI) Jared Gollob (Duke) John Kirkwood (UPMI) Topics for Consideration What are the rules for integrating
Potentiality of Anti-idiotypic Antibodies Mimicking GD2 to Induce Cellular Immunity
 GD2 Potentiality of Anti-idiotypic Antibodies Mimicking GD2 to Induce Cellular Immunity Yoon-Sun Park and Woon-Seob Shin Department of Microbiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Gangneung,
GD2 Potentiality of Anti-idiotypic Antibodies Mimicking GD2 to Induce Cellular Immunity Yoon-Sun Park and Woon-Seob Shin Department of Microbiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Gangneung,
Avastin. Avastin (bevacizumab) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.04 Subject: Avastin Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: September 20, 2018 Avastin Description Avastin
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.04 Subject: Avastin Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: September 20, 2018 Avastin Description Avastin
Serum IL-8 and IL-12 Levels in Breast Cancer
 Medical Oncology, vol. 24, no. 2, 163 168, 2007 Copyright 2007 by Humana Press Inc. All rights of any nature whatsoever reserved. 1357-0560/(Online)1559-131X/07/24:163 168/$30.00 Original Article Serum
Medical Oncology, vol. 24, no. 2, 163 168, 2007 Copyright 2007 by Humana Press Inc. All rights of any nature whatsoever reserved. 1357-0560/(Online)1559-131X/07/24:163 168/$30.00 Original Article Serum
Engineered Immune Cells for Cancer Therapy : Current Status and Prospects
 When Engineering Meets Immunology Engineered Immune Cells for Cancer Therapy : Current Status and Prospects Yong Taik Lim, Ph.D. Nanomedical Systems Laboratory (http://www.nanomedicalsystems.org) SKKU
When Engineering Meets Immunology Engineered Immune Cells for Cancer Therapy : Current Status and Prospects Yong Taik Lim, Ph.D. Nanomedical Systems Laboratory (http://www.nanomedicalsystems.org) SKKU
LPS CD40 + IL-4. Vorinostat (24 Hours) Vorinostat (24 Hours) Panobinostat (24 Hours) Panobinostat (24 Hours) Romidepsin (48 Hours)
 A) CD + IL- B) LPS ( Hours) ( Hours) Cell number (x1-3 ) 1 1 3.7 M 1. M. M.1 M Cell number (x1 - ) 1 1 3. M 1. M.7 M.38 M Cell number (x1-3 ) Cell number (x1-3 ) 3 1 1 1 ( Hours) 7.nM.nM 1.7nM.nM Romidepsin
A) CD + IL- B) LPS ( Hours) ( Hours) Cell number (x1-3 ) 1 1 3.7 M 1. M. M.1 M Cell number (x1 - ) 1 1 3. M 1. M.7 M.38 M Cell number (x1-3 ) Cell number (x1-3 ) 3 1 1 1 ( Hours) 7.nM.nM 1.7nM.nM Romidepsin
Avastin (bevacizumab)
 Avastin (bevacizumab) Policy Number: 5.02.502 Last Review: 04/2018 Origination: 03/2017 Next Review: 04/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for Avastin
Avastin (bevacizumab) Policy Number: 5.02.502 Last Review: 04/2018 Origination: 03/2017 Next Review: 04/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for Avastin
Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology
 Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology 04-28-2009 Is tumor self or non-self? How are tumor antigens generated? What are they? How does immune system respond? Introduction Tumor Antigens/Categories
Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology 04-28-2009 Is tumor self or non-self? How are tumor antigens generated? What are they? How does immune system respond? Introduction Tumor Antigens/Categories
ANTITUMOR EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ENDOTHELIAL CELL MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY BVE-1 ON SOLID TUMOR XENOGRAFT IN NUDE MICE
 92 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research 11(2): 92 --96, 1999 ANTITUMOR EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ENDOTHELIAL CELL MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY BVE-1 ON SOLID TUMOR XENOGRAFT IN NUDE MICE LI Peiyu z}~r~]~-,1 YUAN Mei 3~'J~,
92 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research 11(2): 92 --96, 1999 ANTITUMOR EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ENDOTHELIAL CELL MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY BVE-1 ON SOLID TUMOR XENOGRAFT IN NUDE MICE LI Peiyu z}~r~]~-,1 YUAN Mei 3~'J~,
Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update
 Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update ASCO 2007: Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update Bevacizumab is effective in combination with XELOX or FOLFOX-4 Bevacizumab
Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update ASCO 2007: Targeted Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Update Bevacizumab is effective in combination with XELOX or FOLFOX-4 Bevacizumab
Tumor Immunology. Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant
 Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
Developing Novel Immunotherapeutic Cancer Treatments for Clinical Use
 Developing Novel Immunotherapeutic Cancer Treatments for Clinical Use Oncology for Scientists March 8 th, 2016 Jason Muhitch, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Urology Email: jason.muhitch@roswellpark.org
Developing Novel Immunotherapeutic Cancer Treatments for Clinical Use Oncology for Scientists March 8 th, 2016 Jason Muhitch, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Urology Email: jason.muhitch@roswellpark.org
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal drainage, after hepatic resection, 159 160 Ablation, radiofrequency, for hepatocellular carcinoma, 160 161 Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic.
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal drainage, after hepatic resection, 159 160 Ablation, radiofrequency, for hepatocellular carcinoma, 160 161 Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic.
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Bevacizumab (Avastin) for glioblastoma multiforme - relapsed. August 2008
 Bevacizumab (Avastin) for glioblastoma multiforme - relapsed August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Bevacizumab (Avastin) for glioblastoma multiforme - relapsed August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Where Are Anti-Angiogenic Agents Positioned Within Cancer Care Guidelines?
 Introduction Additionally, other anti-angiogenic drugs, including sorafenib, sunitinib, axitinib, pazopanib, vandetanib, The development and subsequent use of drugs for treating cancer cabozantinib, and
Introduction Additionally, other anti-angiogenic drugs, including sorafenib, sunitinib, axitinib, pazopanib, vandetanib, The development and subsequent use of drugs for treating cancer cabozantinib, and
Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 SITC Primer on Tumor Immunology and Biological Therapy of Cancer Innate Immunity and Inflammation Willem Overwijk, Ph.D. MD Anderson Cancer Center Center for Cancer Immunology Research Houston, TX www.allthingsbeautiful.com
SITC Primer on Tumor Immunology and Biological Therapy of Cancer Innate Immunity and Inflammation Willem Overwijk, Ph.D. MD Anderson Cancer Center Center for Cancer Immunology Research Houston, TX www.allthingsbeautiful.com
Immune surveillance hypothesis (Macfarlane Burnet, 1950s)
 TUMOR-IMMUNITÄT A.K. Abbas, A.H. Lichtman, S. Pillai (6th edition, 2007) Cellular and Molecular Immunology Saunders Elsevier Chapter 17, immunity to tumors Immune surveillance hypothesis (Macfarlane Burnet,
TUMOR-IMMUNITÄT A.K. Abbas, A.H. Lichtman, S. Pillai (6th edition, 2007) Cellular and Molecular Immunology Saunders Elsevier Chapter 17, immunity to tumors Immune surveillance hypothesis (Macfarlane Burnet,
Reprogramming Tumor Associated Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy
 Reprogramming Tumor Associated Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy Edgar Engleman, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Medicine Stanford University Disclosures: Founder of Dendreon, a biotechnology company that
Reprogramming Tumor Associated Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy Edgar Engleman, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Medicine Stanford University Disclosures: Founder of Dendreon, a biotechnology company that
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
08/02/59. Tumor Immunotherapy. Development of Tumor Vaccines. Types of Tumor Vaccines. Immunotherapy w/ Cytokine Gene-Transfected Tumor Cells
 Tumor Immunotherapy Autologous virus Inactivation Inactivated virus Lymphopheresis Culture? Monocyte s Dendritic cells Immunization Autologous vaccine Development of Tumor Vaccines Types of Tumor Vaccines
Tumor Immunotherapy Autologous virus Inactivation Inactivated virus Lymphopheresis Culture? Monocyte s Dendritic cells Immunization Autologous vaccine Development of Tumor Vaccines Types of Tumor Vaccines
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast
 Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Posters and Presentations
 Posters and Presentations June 2017: American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual - Preliminary Correlative Analysis of PD-L1 expression from the SUNRISE Study. View April 2017: American Association
Posters and Presentations June 2017: American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual - Preliminary Correlative Analysis of PD-L1 expression from the SUNRISE Study. View April 2017: American Association
racotumomab a novel anti-idiotype
 Drugs of Today 2014, 50(4): 301-307 Copyright 2014 prous Science, S.a.U. or its licensors. all rights reserved. CCC: 1699-3993/2014 DoI: 10.1358/dot.2014.50.4.2116670 Monograph racotumomab a novel anti-idiotype
Drugs of Today 2014, 50(4): 301-307 Copyright 2014 prous Science, S.a.U. or its licensors. all rights reserved. CCC: 1699-3993/2014 DoI: 10.1358/dot.2014.50.4.2116670 Monograph racotumomab a novel anti-idiotype
CANCER IMMUNOPATHOLOGY. Eryati Darwin Faculty of Medicine Andalas University
 CANCER IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Eryati Darwin Faculty of Medicine Andalas University Padang 18 Mei 2013 INTRODUCTION Tumor: cells that continue to replicate, fail to differentiate into specialized cells, and become
CANCER IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Eryati Darwin Faculty of Medicine Andalas University Padang 18 Mei 2013 INTRODUCTION Tumor: cells that continue to replicate, fail to differentiate into specialized cells, and become
Releasing the Brakes on Tumor Immunity: Immune Checkpoint Blockade Strategies
 Releasing the Brakes on Tumor Immunity: Immune Checkpoint Blockade Strategies Jason Muhitch, PhD MIR 509 October 1 st, 2014 Email: jason.muhitch@roswellpark.org 0 Holy Grail of Tumor Immunity Exquisite
Releasing the Brakes on Tumor Immunity: Immune Checkpoint Blockade Strategies Jason Muhitch, PhD MIR 509 October 1 st, 2014 Email: jason.muhitch@roswellpark.org 0 Holy Grail of Tumor Immunity Exquisite
Improving experimental cancer therapy through (a better understanding of) tumor physiology
 Improving experimental cancer therapy through (a better understanding of) tumor physiology Laboratório de Oncologia Experimental Faculdade de Medicina da USP and Instituto do Câncer do Estado de São Paulo
Improving experimental cancer therapy through (a better understanding of) tumor physiology Laboratório de Oncologia Experimental Faculdade de Medicina da USP and Instituto do Câncer do Estado de São Paulo
Interpreting Therapeutic Response on Immune Cell Number and Spatial Distribution within the Tumor Microenvironment. Lorcan Sherry, CSO OracleBio
 Interpreting Therapeutic Response on Immune Cell Number and Spatial Distribution within the Tumor Microenvironment Lorcan Sherry, CSO OracleBio Company Overview OracleBio is a specialised CRO providing
Interpreting Therapeutic Response on Immune Cell Number and Spatial Distribution within the Tumor Microenvironment Lorcan Sherry, CSO OracleBio Company Overview OracleBio is a specialised CRO providing
Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy: New Frontiers
 Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy: New Frontiers May 12 th, 2017 Anshu K. Jain, MD Radiation Oncologist, Ashland-Bellefonte and Logan Regional Cancer Centers Assistant Professor of Therapeutic Radiology,
Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy: New Frontiers May 12 th, 2017 Anshu K. Jain, MD Radiation Oncologist, Ashland-Bellefonte and Logan Regional Cancer Centers Assistant Professor of Therapeutic Radiology,
Avastin. Avastin (bevacizumab) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.04.04 Subject: Avastin Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: December 3, 2015 Avastin Description Avastin (bevacizumab)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.04.04 Subject: Avastin Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: December 3, 2015 Avastin Description Avastin (bevacizumab)
Inhibitors of Methionine Aminopeptidase-2 2 in the Treatment of Non-Hodgkin
 Inhibitors of Methionine Aminopeptidase-2 2 in the Treatment of Non-Hodgkin Hodgkin s s Lymphoma Targeted Cancer Therapies William Westlin, Ph.D. Vice President, Preclinical Research Discovery of Fumagillin
Inhibitors of Methionine Aminopeptidase-2 2 in the Treatment of Non-Hodgkin Hodgkin s s Lymphoma Targeted Cancer Therapies William Westlin, Ph.D. Vice President, Preclinical Research Discovery of Fumagillin
NKTR-214 plus NKTR-262, a Scientifically-Guided Rational Combination Approach for Immune Oncology
 plus NKTR-262, a Scientifically-Guided Rational Combination Approach for Immune Oncology Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics World Preclinical Congress, 2017
plus NKTR-262, a Scientifically-Guided Rational Combination Approach for Immune Oncology Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics World Preclinical Congress, 2017
Cytokines: Interferons, Interleukins and Beyond. Michael B. Atkins, MD Georgetown-Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center
 Cytokines: Interferons, Interleukins and Beyond Michael B. Atkins, MD Georgetown-Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center Disclosures Advisory Boards: Bristol-Myers Squibb,Amgen, Novartis, Alkermes, Infinity,
Cytokines: Interferons, Interleukins and Beyond Michael B. Atkins, MD Georgetown-Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center Disclosures Advisory Boards: Bristol-Myers Squibb,Amgen, Novartis, Alkermes, Infinity,
OMP-305B83: A Novel, Potent DLL4 & VEGF Targeting Bispecific Antibody for the Treatment Of Solid Tumors
 OMP-305B83: A Novel, Potent DLL4 & VEGF Targeting Bispecific Antibody for the Treatment Of Solid Tumors Jakob Dupont MD MA CMO, SVP: OncoMed Pharmaceuticals Adjunct Clinical Faculty: Stanford University
OMP-305B83: A Novel, Potent DLL4 & VEGF Targeting Bispecific Antibody for the Treatment Of Solid Tumors Jakob Dupont MD MA CMO, SVP: OncoMed Pharmaceuticals Adjunct Clinical Faculty: Stanford University
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Serum Concentration Changes during Chemotherapy in Patients with Lung Cancer
 Original Article Kurume Medical Journal, 48, 43-47, 2001 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Serum Concentration Changes during Chemotherapy in Patients with Lung Cancer YASU KO KI DO Department
Original Article Kurume Medical Journal, 48, 43-47, 2001 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Serum Concentration Changes during Chemotherapy in Patients with Lung Cancer YASU KO KI DO Department
Avastin. Avastin (bevacizumab) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.04 Subject: Avastin Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Avastin Description Avastin
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.04 Subject: Avastin Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Avastin Description Avastin
Oncologic Applications of Interleukin-2 (Aldesleukin) When Used as Monotherapy. Original Policy Date
 MP 8.01.03 Oncologic Applications of Interleukin-2 (Aldesleukin) When Used as Monotherapy Medical Policy Section Therapy Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with
MP 8.01.03 Oncologic Applications of Interleukin-2 (Aldesleukin) When Used as Monotherapy Medical Policy Section Therapy Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with
Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation. mammary cancer model. Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler
 Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation in a spontaneous mammary cancer model Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler Goal of Immunotherapy Boosting the low level anti-tumor immune
Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation in a spontaneous mammary cancer model Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler Goal of Immunotherapy Boosting the low level anti-tumor immune
Horizon Scanning Technology Briefing. Sutent (Sunitinib) for first-line and adjuvant treatment of renal cell carcinoma
 Horizon Scanning Technology Briefing National Horizon Scanning Centre Sutent (Sunitinib) for first-line and adjuvant treatment of renal cell carcinoma August 2006: Updated October 2006 This technology
Horizon Scanning Technology Briefing National Horizon Scanning Centre Sutent (Sunitinib) for first-line and adjuvant treatment of renal cell carcinoma August 2006: Updated October 2006 This technology
Avastin. Avastin (bevacizumab) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.04 Subject: Avastin Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Avastin Description Avastin (bevacizumab)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.04 Subject: Avastin Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Avastin Description Avastin (bevacizumab)
Immunotherapie: algemene principes
 Immunotherapie: algemene principes Prof. dr. Evelien Smits Tumorimmunologie, UAntwerpen 14 Oktober 2017, IKG evelien.smits@uza.be Concept of immune evasion Finn O. J. Ann Oncol. 2012 Sep; 23(Suppl 8):
Immunotherapie: algemene principes Prof. dr. Evelien Smits Tumorimmunologie, UAntwerpen 14 Oktober 2017, IKG evelien.smits@uza.be Concept of immune evasion Finn O. J. Ann Oncol. 2012 Sep; 23(Suppl 8):
Supplemental Figure 1. Cell-bound Cetuximab reduces EGFR staining intensity. Blood
 Antibody-mediated depletion of CD19-CAR T cells Supplemental 1 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure 1. Supplemental Figure 1. Cell-bound Cetuximab reduces EGFR staining intensity. Blood cells were
Antibody-mediated depletion of CD19-CAR T cells Supplemental 1 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure 1. Supplemental Figure 1. Cell-bound Cetuximab reduces EGFR staining intensity. Blood cells were
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates
 Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy: New Frontiers
 Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy: New Frontiers Nevada Oncology Society Fall Meeting November 16 th, 2017 Anshu K. Jain, MD Radiation Oncologist, Ashland Bellefonte Cancer Center Assistant Clinical
Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy: New Frontiers Nevada Oncology Society Fall Meeting November 16 th, 2017 Anshu K. Jain, MD Radiation Oncologist, Ashland Bellefonte Cancer Center Assistant Clinical
Management of Advanced Colorectal Cancer in Older Patients
 Review Article [1] April 15, 2005 By Stuart M. Lichtman, MD, FACP [2] Many elderly individuals have substantial life expectancy, even in the setting of significant illness. There is evidence to indicate
Review Article [1] April 15, 2005 By Stuart M. Lichtman, MD, FACP [2] Many elderly individuals have substantial life expectancy, even in the setting of significant illness. There is evidence to indicate
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
THE ROLE OF TARGETED THERAPY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF ADVANCED CERVIX CANCER
 Gynecologic Cancer InterGroup Cervix Cancer Research Network THE ROLE OF TARGETED THERAPY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF ADVANCED CERVIX CANCER Linda Mileshkin, Medical Oncologist Peter MacCallum
Gynecologic Cancer InterGroup Cervix Cancer Research Network THE ROLE OF TARGETED THERAPY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF ADVANCED CERVIX CANCER Linda Mileshkin, Medical Oncologist Peter MacCallum
Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers
 Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Biological therapies use the body s immune system to fight cancer or to lessen the side effects that may be caused by some cancer treatments
Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Biological therapies use the body s immune system to fight cancer or to lessen the side effects that may be caused by some cancer treatments
Chapter 7 Conclusions
 VII-1 Chapter 7 Conclusions VII-2 The development of cell-based therapies ranging from well-established practices such as bone marrow transplant to next-generation strategies such as adoptive T-cell therapy
VII-1 Chapter 7 Conclusions VII-2 The development of cell-based therapies ranging from well-established practices such as bone marrow transplant to next-generation strategies such as adoptive T-cell therapy
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer Manuscript Draft. Manuscript Number: IJGC-298
 Manuscript Number: IJGC- Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer Manuscript Draft Title: Low rate of bleeding and absence of perforation in metastatic colorectal cancer [mcrc] patients with unresected primary
Manuscript Number: IJGC- Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer Manuscript Draft Title: Low rate of bleeding and absence of perforation in metastatic colorectal cancer [mcrc] patients with unresected primary
Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Brain Metastases
 Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Brain Metastases Geoffrey T. Gibney, MD Georgetown-Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center Medstar-Georgetown University Hospital
Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Brain Metastases Geoffrey T. Gibney, MD Georgetown-Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center Medstar-Georgetown University Hospital
Cancer Metronomic Therapy Milan, February 26, 2016
 Cancer Metronomic Therapy Milan, February 26, 2016 Metronomic Chemotherapy: Evolution and Development of the Concept Robert S. Kerbel, PhD Senior Scientist Sunnybrook Research Institute Professor, Dept.
Cancer Metronomic Therapy Milan, February 26, 2016 Metronomic Chemotherapy: Evolution and Development of the Concept Robert S. Kerbel, PhD Senior Scientist Sunnybrook Research Institute Professor, Dept.
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON. Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust
 IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Clinical trials which assess vaccine characteristics. ISBT Meeting, San Francisco, CA November 4-8, 2004
 The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Clinical trials which assess vaccine characteristics ISBT Meeting, San Francisco, CA November 4-8, 2004 Ideal cancer vaccine trial 1. An informative immune assay 2. Ability
The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Clinical trials which assess vaccine characteristics ISBT Meeting, San Francisco, CA November 4-8, 2004 Ideal cancer vaccine trial 1. An informative immune assay 2. Ability
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland Approved for public release; distribution unlimited
 AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
Targeted and immunotherapy in RCC
 Targeted and immunotherapy in RCC Treatment options Surgery (radical VS partial nephrectomy) Thermal ablation therapy Surveillance Immunotherapy Molecular targeted therapy Molecular targeted therapy Targeted
Targeted and immunotherapy in RCC Treatment options Surgery (radical VS partial nephrectomy) Thermal ablation therapy Surveillance Immunotherapy Molecular targeted therapy Molecular targeted therapy Targeted
Outcome of rectal cancer after radiotherapy with a long or short waiting period before surgery, a descriptive clinical study
 Original Article Outcome of rectal cancer after radiotherapy with a long or short waiting period before surgery, a descriptive clinical study Elmer E. van Eeghen 1, Frank den Boer 2, Sandra D. Bakker 1,
Original Article Outcome of rectal cancer after radiotherapy with a long or short waiting period before surgery, a descriptive clinical study Elmer E. van Eeghen 1, Frank den Boer 2, Sandra D. Bakker 1,
Basic Principles of Tumor Immunotherapy and Mechanisms of Tumor Immune Suppression. Bryon Johnson, PhD
 Basic Principles of Tumor Immunotherapy and Mechanisms of Tumor Immune Suppression Bryon Johnson, PhD Disclosures There will be discussion about the use of products for non-fda indications in this presentation.
Basic Principles of Tumor Immunotherapy and Mechanisms of Tumor Immune Suppression Bryon Johnson, PhD Disclosures There will be discussion about the use of products for non-fda indications in this presentation.
SPECIAL AUTHORIZATION REQUEST FOR COVERAGE OF HIGH COST CANCER DRUGS
 SPECIAL AUTHORIZATION REQUEST FOR COVERAGE OF HIGH COST CANCER DRUGS (Filgrastim, Capecitabine, Imatinib, Dasatinib, Erolotinib, Sunitinib, Pazopanib, Fludarabine, Sorafenib, Crizotinib, Tretinoin, Nilotinib,
SPECIAL AUTHORIZATION REQUEST FOR COVERAGE OF HIGH COST CANCER DRUGS (Filgrastim, Capecitabine, Imatinib, Dasatinib, Erolotinib, Sunitinib, Pazopanib, Fludarabine, Sorafenib, Crizotinib, Tretinoin, Nilotinib,
Index. neurosurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A A Complimentary Trial of an Immunotherapy Vaccine Against Tumor-specific EGFRvIII (ACTIVATE), 90 91 Active immunotherapy, 5 8, 96. See
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A A Complimentary Trial of an Immunotherapy Vaccine Against Tumor-specific EGFRvIII (ACTIVATE), 90 91 Active immunotherapy, 5 8, 96. See
Immunotherapy in Colorectal cancer
 Immunotherapy in Colorectal cancer Ahmed Zakari, MD Associate Professor University of Central Florida, College of Medicine Medical Director, Gastro Intestinal Cancer Program Florida Hospital Cancer Institute
Immunotherapy in Colorectal cancer Ahmed Zakari, MD Associate Professor University of Central Florida, College of Medicine Medical Director, Gastro Intestinal Cancer Program Florida Hospital Cancer Institute
General Information, efficacy and safety data
 Horizon Scanning in Oncology Horizon Scanning in Oncology 23 rd Prioritization 2 nd quarter 2015 General Information, efficacy and safety data Eleen Rothschedl Anna Nachtnebel Priorisierung XXIII HSS Onkologie
Horizon Scanning in Oncology Horizon Scanning in Oncology 23 rd Prioritization 2 nd quarter 2015 General Information, efficacy and safety data Eleen Rothschedl Anna Nachtnebel Priorisierung XXIII HSS Onkologie
Antiangiogenesis - Immune Therapy Combinations. George Coukos, MD, PhD Heinz Zwierzina, MD
 Antiangiogenesis - Immune Therapy Combinations George Coukos, MD, PhD Heinz Zwierzina, MD Overview Effect of VEGF on antitumor immune response Antigen presentation Effector mechanisms Ying and yang and
Antiangiogenesis - Immune Therapy Combinations George Coukos, MD, PhD Heinz Zwierzina, MD Overview Effect of VEGF on antitumor immune response Antigen presentation Effector mechanisms Ying and yang and
Innate Immunity, Inflammation and Cancer
 Innate Immunity, Inflammation and Cancer Willem Overwijk, Ph.D. Melanoma Medical Oncology Center for Cancer Immunology Research MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX SITC/MDACC -6/14/2013 www.allthingsbeautiful.com
Innate Immunity, Inflammation and Cancer Willem Overwijk, Ph.D. Melanoma Medical Oncology Center for Cancer Immunology Research MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX SITC/MDACC -6/14/2013 www.allthingsbeautiful.com
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Cancer Cell Research 14 (2017)
 Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer Ping Xu, Hongmei Li*, Xiaoyan Zhang Department of
Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer Ping Xu, Hongmei Li*, Xiaoyan Zhang Department of
Tumor Immunology: A Primer
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Discovery And Development Of A Monoclonal Antibody Against A Novel Target For The Treatment Of Colorectal Cancer
 1 Discovery And Development Of A Monoclonal Antibody Against A Novel Target For The Treatment Of Colorectal Cancer Philip M. Arlen, MD 16th Drug Discovery Summit and 3rd Discovery Chemistry & Drug Design
1 Discovery And Development Of A Monoclonal Antibody Against A Novel Target For The Treatment Of Colorectal Cancer Philip M. Arlen, MD 16th Drug Discovery Summit and 3rd Discovery Chemistry & Drug Design
A PHASE 1 STUDY OF TRC105 (ANTI- ADVANCED SOLID TUMORS
 ASCO 2011 Abstract Number: 3073 A PHASE 1 STUDY OF TRC105 (ANTI- CD105 ANTIBODY) IN PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED SOLID TUMORS J. W. Goldman, M. S. Gordon, H. Hurwitz, R. Pili, D. S. Mendelson, B. J. Adams, D.
ASCO 2011 Abstract Number: 3073 A PHASE 1 STUDY OF TRC105 (ANTI- CD105 ANTIBODY) IN PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED SOLID TUMORS J. W. Goldman, M. S. Gordon, H. Hurwitz, R. Pili, D. S. Mendelson, B. J. Adams, D.
Pearson r = P (one-tailed) = n = 9
 8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
Exploring Immunotherapies: Beyond Checkpoint Inhibitors
 Exploring Immunotherapies: Beyond Checkpoint Inhibitors Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics (Now part of BioTelemetry Research) jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com +1 585 249 6231 Introduction
Exploring Immunotherapies: Beyond Checkpoint Inhibitors Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics (Now part of BioTelemetry Research) jennifer_fox@virtualscopics.com +1 585 249 6231 Introduction
CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY
 CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY Policy Name: Avastin (bevacizumab) Policy Number: MP-030-MD-DE Responsible Department(s): Medical Management; Clinical Pharmacy Provider Notice Date: 10/01/2017 Original Effective
CLINICAL MEDICAL POLICY Policy Name: Avastin (bevacizumab) Policy Number: MP-030-MD-DE Responsible Department(s): Medical Management; Clinical Pharmacy Provider Notice Date: 10/01/2017 Original Effective
The Galectin-3 Inhibitor GR-MD-02 for Combination Cancer Immunotherapy
 The Galectin-3 Inhibitor GR-MD-02 for Combination Cancer Immunotherapy Supplemental Information to Corporate Presentation February 6, 2018 NASDAQ: GALT www.galectintherapeutics.com 2018 2017 Galectin Therapeutics
The Galectin-3 Inhibitor GR-MD-02 for Combination Cancer Immunotherapy Supplemental Information to Corporate Presentation February 6, 2018 NASDAQ: GALT www.galectintherapeutics.com 2018 2017 Galectin Therapeutics
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit
 Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest
 Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest Michelle S. Ginsberg, MD Objectives Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest To understand the mechanisms of action of different classes of
Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest Michelle S. Ginsberg, MD Objectives Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest To understand the mechanisms of action of different classes of
Innovations in Immunotherapy - Melanoma. Systemic Therapies October 27, 2018 Charles L. Bane, MD
 Innovations in Immunotherapy - Melanoma Systemic Therapies October 27, 2018 Charles L. Bane, MD Melanoma Prognosis Survival at 10 years Stage I: 90% Stage II: 60% Stage III: 40% Stage IV: 10% 2 Indications
Innovations in Immunotherapy - Melanoma Systemic Therapies October 27, 2018 Charles L. Bane, MD Melanoma Prognosis Survival at 10 years Stage I: 90% Stage II: 60% Stage III: 40% Stage IV: 10% 2 Indications
* * * * Supplementary Figure 1. DS Lv CK HSA CK HSA. CK Col-3. CK Col-3. See overleaf for figure legend. Cancer cells
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression
 Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
The efficacy of bevacizumab in Chinese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and its effect in different line setting*
 Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-1295-2 April 2014, Vol. 13, No. 4, P169 P173 The efficacy of bevacizumab in Chinese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and its effect in different
Chinese-German J Clin Oncol DOI 10.1007/s10330-014-1295-2 April 2014, Vol. 13, No. 4, P169 P173 The efficacy of bevacizumab in Chinese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and its effect in different
Liver Cancer. Su Jong Yu, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Liver Cancer Su Jong Yu, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine Primary Liver Cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) : > 80% Derived
Liver Cancer Su Jong Yu, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine Primary Liver Cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) : > 80% Derived
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Aflibercept (VEGF Trap) for advanced chemo-refractory epithelial ovarian cancer. December 2007
 Aflibercept (VEGF Trap) for advanced chemo-refractory epithelial ovarian cancer December 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature
Aflibercept (VEGF Trap) for advanced chemo-refractory epithelial ovarian cancer December 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature
Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer
 Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER?
 CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY NFORMATON n format provided by Melero et al. (AUGUST 2015) Supplementary nformation S3 Combinations including two or more immunotherapy agents based on PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. (Source: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
SUPPLEMENTARY NFORMATON n format provided by Melero et al. (AUGUST 2015) Supplementary nformation S3 Combinations including two or more immunotherapy agents based on PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. (Source: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
FIRST LINE 5-FU-BASED CHEMOTHERAPY WITH/ WITHOUT BEVACIZUMAB FOR METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: ONE CENTER EXPERIENCE RESULTS
 PROCEEDINGS FIRST LINE 5-FU-BASED CHEMOTHERAPY WITH/ WITHOUT BEVACIZUMAB FOR METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: ONE CENTER EXPERIENCE RESULTS Assia Konsoulova, Ivan Donev, Nikolay Conev, Sonya Draganova, Trifon
PROCEEDINGS FIRST LINE 5-FU-BASED CHEMOTHERAPY WITH/ WITHOUT BEVACIZUMAB FOR METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: ONE CENTER EXPERIENCE RESULTS Assia Konsoulova, Ivan Donev, Nikolay Conev, Sonya Draganova, Trifon
Historical overview of immunotherapy
 Historical overview of immunotherapy Before introduction of immune checkpoint inhibitors John B.A.G. Haanen, MD PhD My Disclosures I have provided consultation, attended advisory boards, and/or provided
Historical overview of immunotherapy Before introduction of immune checkpoint inhibitors John B.A.G. Haanen, MD PhD My Disclosures I have provided consultation, attended advisory boards, and/or provided
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Bevacizumab (Avastin) in combination with non-taxanes for metastatic breast cancer - first line therapy
 Bevacizumab (Avastin) in combination with non-taxanes for metastatic breast cancer - first line therapy December 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and
Bevacizumab (Avastin) in combination with non-taxanes for metastatic breast cancer - first line therapy December 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
The Immune System. Innate. Adaptive. - skin, mucosal barriers - complement - neutrophils, NK cells, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils
 Objectives - explain the rationale behind cellular adoptive immunotherapy - describe methods of improving cellular adoptive immunotherapy - identify mechanisms of tumor escape from cellular adoptive immunotherapy
Objectives - explain the rationale behind cellular adoptive immunotherapy - describe methods of improving cellular adoptive immunotherapy - identify mechanisms of tumor escape from cellular adoptive immunotherapy
Objectives. Briefly summarize the current state of colorectal cancer
 Disclaimer I do not have any financial conflicts to disclose. I will not be promoting any service or product. This presentation is not meant to offer medical advice and is not intended to establish a standard
Disclaimer I do not have any financial conflicts to disclose. I will not be promoting any service or product. This presentation is not meant to offer medical advice and is not intended to establish a standard
DISCLOSURES. Roche/MSD-Merck/Celgene: Research Funding
 DISCLOSURES Roche/MSD-Merck/Celgene: Research Funding Roche/Celgene/AstraZeneca/Amgen/MSD/Novartis/Sanofi- Aventis/Pierre Fabré: Advisory Board or Consultant No conflict of interest with respect to this
DISCLOSURES Roche/MSD-Merck/Celgene: Research Funding Roche/Celgene/AstraZeneca/Amgen/MSD/Novartis/Sanofi- Aventis/Pierre Fabré: Advisory Board or Consultant No conflict of interest with respect to this
ESMO wishes to thank the following companies for supporting this ESMO Preceptorship Programme
 ESMO wishes to thank the following companies for supporting this ESMO Preceptorship Programme Immunotherapy of cancer Some historical background Rolf Stahel University Hospital Zürich, Switzerland Amsterdam,
ESMO wishes to thank the following companies for supporting this ESMO Preceptorship Programme Immunotherapy of cancer Some historical background Rolf Stahel University Hospital Zürich, Switzerland Amsterdam,
Emerging Concepts of Cancer Immunotherapy
 Emerging Concepts of Cancer Immunotherapy Jeffrey Schlom, Ph.D. Laboratory of Tumor Immunology and Biology (LTIB) Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute, NIH Immune Cell Infiltrate in Primary
Emerging Concepts of Cancer Immunotherapy Jeffrey Schlom, Ph.D. Laboratory of Tumor Immunology and Biology (LTIB) Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute, NIH Immune Cell Infiltrate in Primary
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
Herlyn Lab - Monoclonal Antibodies
 Herlyn Lab - Monoclonal Antibodies GI Tract tumors I. Lewis and related antigens 1. 1116-NS-19-9 (CO 19-9), IgG1, Sialylated Le a Koprowski et al. 1979 2. 129-2-C3-9-11 (CO 29.11), IgG1, Sialylated Le
Herlyn Lab - Monoclonal Antibodies GI Tract tumors I. Lewis and related antigens 1. 1116-NS-19-9 (CO 19-9), IgG1, Sialylated Le a Koprowski et al. 1979 2. 129-2-C3-9-11 (CO 29.11), IgG1, Sialylated Le
Cabozantinib for medullary thyroid cancer. February 2012
 Cabozantinib for medullary thyroid cancer February 2012 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to be a definitive
Cabozantinib for medullary thyroid cancer February 2012 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to be a definitive
