Tumour-infiltrating CD8 to FOXP3 lymphocyte ratio in predicting treatment responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy of aggressive breast cancer
|
|
|
- Randall Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article Tumour-infiltrating CD8 to FOXP3 lymphocyte ratio in predicting treatment responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy of aggressive breast cancer Y. Asano 1, S. Kashiwagi 1,W.Goto 1,K.Kurata 1,S.Noda 1, T. Takashima 1, N. Onoda 1, S. Tanaka 2, M. Ohsawa 2 and K. Hirakawa 1 Departments of 1 Surgical Oncology and 2 Diagnostic Pathology, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan Correspondence to: Dr S. Kashiwagi, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, Asahi-machi, Abeno-ku, Osaka , Japan ( spqv9ke9@view.ocn.ne.jp) Background: Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) can be used to monitor the immune response, and are important in predicting treatment responses and outcomes for various types of cancer. Recently, specific TIL subsets have been reported to be clinically useful in predicting treatment responses. The CD8+/FOXP3+ TIL ratio (CFR) may be a more sensitive indicator for monitoring immune function. This study investigated the clinical significance and value of CFR as a biomarker to predict treatment responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Methods: Patients with resectable early-stage breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy at Osaka City University Hospital, Japan, between 07 and 13 were included. Oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) 2, Ki-67, CD8 and FOXP3 status were assessed by immunohistochemistry, and correlated with pathological complete response (pcr). Results: A total of 177 patients were included, of whom 90 had a high CFR and 87 a low CFR. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) was more common in the high-cfr group than in the low-cfr group (46 versus 23 per cent; P = 0 002), as was HER2-enriched breast cancer (HER2BC) (27 versus 14 per cent; P = 0 033). Among these patients, the pcr rate was significantly higher in the high-cfr group than in the low-cfr group (TNBC: P = 0 022; HER2BC: P < 0 001). In multivariable analysis high-cfr status was an independent predictor of a favourable prognosis: hazard ratio 0 (95 per cent c.i to 0 72; P = 0 015) for TNBC and 0 10 (0 10 to 0 90; P = 0 041) for HER2BC. Conclusion: The CFR may be a useful biomarker to predict treatment response to neoadjuvant therapy in aggressive breast cancer subtypes, such as TNBC and HER2BC. Paper accepted 8 January 16 Published online 8 March 16 in Wiley Online Library ( DOI: /bjs Introduction Cancer cells have gained the capacity to proliferate autonomously and survive owing to gene mutations, but it is evident that the tumour microenvironment also greatly influences tumour progression 1. The immune cells of the tumour microenvironment influence not only the response to immunotherapy, but also the response to, and outcomes after, other anticancer therapies. The importance of regulating and improving the cancer immune microenvironment can therefore play an important role in predicting treatment responses and outcomes 2,3. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) can be used to monitor the immune response and are important in predicting treatment responses in many cancers 4 6.TILs include various cells of the immune system. There are cells involved in eradication of cancer cells such as CD8+ T lymphocytes, natural killer cells, dendritic cells and macrophages. Other cell types, such as regulatory T (Treg) cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, on the other hand, promote survival and proliferation of cancer cells 7. Morphological evaluation of TILs is attracting attention as they are potentially clinically useful biomarkers in breast cancer. Phase III trials including BIG 02/98, Finland Herceptin (FinHER), Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 2197 and ECOG1199 have all shown the value of TILs in predicting treatment responses in patients with highly malignant breast cancer, including triple-negative 16 The Authors. BJS published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd BJS 16; 103: This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
2 846 Y. Asano, S. Kashiwagi, W. Goto, K. Kurata, S. Noda, T. Takashima et al. breast cancer (TNBC) and human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) 2-enriched breast cancer (HER2BC) Recently, specific TIL subsets have been reported to be clinically significant and useful in predicting treatment responses. High pathological complete response (pcr) rates after neoadjuvant chemotherapy have now been reported occasionally in patients with high levels of expression of subsets of TILs such as CD3, CD4, CD8 and Forkhead box 3 (FOXP3) 6, High pcr rates in TNBC have also been reported with ahighcd8+/foxp3+ TIL ratio (CFR) 15,16. Cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes selectively recognize and have the ability to destroy cancer cells. FOXP3, a marker of Treg cells, is a gene that regulates Treg cell generation and function. Treg cells inactivate CD8+ T lymphocytes, which subsequently reduces the function of co-stimulatory proteins on antigen-presenting cells. In other words, Treg cells suppress the induction of cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes in response to cancer cells. The CFR is the ratio of CD8+ to FOXP3+ TILs. Therefore, the CFR may be a more sensitive indicator for monitoring immune function in a cancer. The present study investigated the clinical significance and value of the CFR as a biomarker to predict treatment responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. The results were analysed with stratification for breast cancer subtypes. Changes in the CFR after breast cancer recurrence were also examined. Methods This study was conducted at Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan, according to the REporting recommendations for tumour MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK) guidelines 17,andaretrospectively written research, pathological evaluation and statistical plan. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. This research conformed to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Osaka City University (no. 926). Patients with resectable, early-stage, primary infiltrating ductal breast cancer diagnosed as stage IIA (T1 N1 M0 or T2 N0 M0), IIB (T2 N1 M0 or T3 N0 M0) or IIIA (T1 2 N2 M0 or T3 N1 2 M0), treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy between 07 and 13, were included. Tumour staging was based on the International Union Against Cancer (UICC) TNM classification, seventh edition 18. Breast cancer was confirmed histologically by core needle biopsy and staged by systemic imaging studies using CT, ultrasonography and bone scintigraphy. Breast cancer was classified into molecular subtypes according to the immunohistochemical expressions of oestrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR), HER2 and Ki-67. Neoadjuvant therapy regimens and surgery All patients underwent core needle biopsy before neoadjuvant chemotherapy. A standard protocol was used for neoadjuvant chemotherapy, consisting of four courses of FEC100 (500 mg/m 2 5-fluorouracil, 100 mg/m 2 epirubicin and 500 mg/m 2 cyclophosphamide) every 3 weeks, followed by 12 courses of 80 mg/m 2 paclitaxel administered weekly 19,. Patients with HER2BC also received trastuzumab weekly (2 mg/kg) or triweekly (6 mg/kg) during paclitaxel treatment 21. All patients underwent chemotherapy as outpatients. Patients underwent mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. All patients who had breast-conserving surgery received postoperative radiotherapy to the remnant breast. All patients were followed up by physical examination every 3 months, ultrasonography every 6 months, and CT and bone scintigraphy annually. Clinical endpoints Therapeutic antitumour effects were assessed according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours (RECIST) 22. A pcr was defined as the complete disappearance of the invasive compartment of the lesion with or without intraductal components, including the lymph nodes. Overall survival time was the interval from the date of primary surgery to the time of death from any cause. Disease-free interval (DFS) was defined as the interval from the date of primary surgery to the first local recurrence, distant recurrence or death from any cause. Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical studies were performed as described previously on core needle biopsy specimens 23. Tumour specimens were fixed in 10 per cent formaldehyde solution and embedded in paraffin, and sections 4 μm thick were mounted on glass slides. Slides were deparaffinized in xylene and heated for min (105 C, 0 4 kg/m 2 )inan autoclave in Target Retrieval Solution (Dako, Carpinteria, California, USA). Specimens were incubated with 3 per cent hydrogen peroxide in methanol for 15 min to block endogenous peroxidase activity, then in 10 per cent normal goat or rabbit serum to block non-specific reactions. Primary monoclonal antibodies directed against ER (clone 1D5, dilution 1 : 80; Dako, Cambridge, UK),
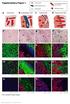
3 Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes as predictors of response to chemotherapy in breast cancer 847 PgR (clone PgR636, dilution 1 : 100; Dako), HER2 (HercepTest ; Dako), Ki-67 (clone MIB-1, dilution 1 : 00; Dako), CD8 (clone C8/144B, dilution 1 : 100; Dako) and FOXP3 (clone 236A/E7, dilution 1 : 100; Abcam, Cambridge, UK) were used. Tissue sections were incubated with each antibody for 70 min at room temperature or overnight at 4 C, then with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antirabbit or antimouse Ig secondary antibodies (HISTOFINE (PO) kit; Nichirei, Tokyo, Japan). Slides were subsequently treated with streptavidin peroxidase reagent and incubated in phosphate-buffered saline diaminobenzidine and 1 per cent hydrogen peroxide (v/v), followed by counterstaining with Mayer s haematoxylin. Positive and negative controls for each marker were used according to the supplier s data sheet. Immunohistochemical scoring Immunohistochemical scoring was performed by two breast pathologists. The cut-off value for ER and PgR positivity was set at at least 1 per cent in accordance with previous studies 23. HER2 expression was scored according to the accepted grading system (0, no reactivity or membranous reactivity in less than 10 per cent of cells; 1+, faint/barely perceptible membranous reactivity in at least 10 per cent of cells or reactivity in only part of the cell membrane; 2+, weak to moderate complete or basolateral membranous reactivity in at least 10 per cent of tumour cells; or 3+, strong complete or basolateral membranous reactivity in at least 10 per cent of tumour cells). HER2 expression was considered positive if the immunostaining score was 3+, or where the score was 2+ and included gene amplification via fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). For FISH analyses, each copy of the HER2 gene and its centromere 17 (CEP17) reference were counted. The interpretation followed the criteria of the American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP) guidelines,25 for HER2 immunohistochemical classification for breast cancer: positive if the HER2/CEP17 ratio was higher than 2 0. A Ki-67 labelling index with 14 per cent or more of tumour cells with nuclear staining was considered positive 26. Histopathological analysis of the percentage of TILs was evaluated on a single haematoxylin and eosin-stained tumour section using criteria described by Salgado and colleagues 7. TILs were defined as the infiltrating lymphocytes within the tumour stroma and the tumour, and expressed in terms of the proportion of the field a TNBC, CD8+ b HER2BC, CD8+ c HRBC, CD8+ d TNBC, FOXP3+ e HER2BC, FOXP3+ f HRBC, FOXP3+ Fig. 1 CD8 and FOXP3 expression in stroma surrounding cancer cells: a c CD8+ cells in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) (a), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-enriched breast cancer (HER2BC) (b) and hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (HRBC) (c); d f FOXP3+ cells in TNBC (d), HER2BC (e) andhrbc(f) (original magnification 400, Mayer s haematoxylin counterstain)
4 848 Y. Asano, S. Kashiwagi, W. Goto, K. Kurata, S. Noda, T. Takashima et al FOXP3+ (per field) FOXP3+ (per field) CD8+ (per field) CD8+ (per field) a Stromal compartment b Intratumoural compartment Fig. 2 Correlation between infiltrating CD8+ and FOXP3+ lymphocytes in a stromal compartment and b intratumoural compartment. a r = 0 676, P < 0 001; b r = 0 657, P < Table 1 Correlation between clinicopathological features and CD8+/FOXP3+ tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte ratio in 177 patients with breast cancer High CFR Low CFR (n = 90) (n = 87) P * Age at operation (years) (49) 43 (49) > (51) 44 (51) In menopause No 36 (40) 36 (41) Yes 54 (60) 51 (59) Tumour size (cm) 2 12 (13) 12 (14) > 2 78 (87) 75 (86) Lymph node status Negative (22) 21 () Positive 70 (78) 66 (76) Nuclear grade (71) 73 (84) 3 26 (29) 14 (16) Ki-67 (%) (31) 46 (53) > (69) 41 (47) Intrinsic subtype TNBC Yes 41 (46) (23) No 49 (54) 67 (77) Intrinsic subtype HER2BC Yes (27) 12 (14) No 66 (73) 75 (86) Intrinsic subtype HRBC Yes 25 (28) 55 (63) No 65 (72) 32 (37) Pathological response pcr 44 (49) 23 (26) Non-pCR 46 (51) 64 (74) < Values in parentheses are percentages. CFR, CD8+/FOXP3+ tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte ratio; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; HER2BC, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-enriched breast cancer; HRBC, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer; pcr, pathological complete response. *χ 2 test. investigated 27,28. To evaluate CD8 and FOXP3 expression, five stained areas were selected, and the number of TILs in stroma surrounding the stained cancer cells was measured quantitatively in each field under 400 magnification (Fig. 1) 29. The cut-off levels for high or low infiltration were based on the mean number of infiltrating cells per field. The CFR was defined as the number of CD8+ TILs divided by the number of FOXP3+ TILs. The cut-off value, based on previous reports, was a CFR of at least Statistical analysis The associations between CFR and clinicopathological variables were examined by χ 2 test. The Kaplan Meier method was used to estimate DFS and overall survival, and the log rank test for comparison of the results between groups. Cut-off values for different biomarkers included in this study were chosen before statistical analysis. Multivariable analysis of prognostic factors was carried out using a Cox regression model. P < was considered significant. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 19.0 statistical software (IBM, Armonk, New York, USA). Results Responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy A total of 177 patients were included in the study. The distribution of breast cancer subtypes was: TNBC in 61 patients (34 5 per cent), HER2BC in 36 ( 3 per cent)
5 Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes as predictors of response to chemotherapy in breast cancer 849 Table 2 Univariable and multivariable Cox regression analysis with respect to disease-free survival in breast cancer subtypes Univariable analysis Multivariable analysis Hazard ratio P Hazard ratio P All breast cancers (n = 177) Tumour size ( 2 versus > 2cm) 1 06 (0 37, 3 05) Lymph node status (negative versus positive) 4 16 (0 99, 17 46) Nuclear grade (1 2 versus 3) 1 03 (0 44, 2 39) Ki-67 ( 140 versus >140) 0 65 (0 32, 1 33) Pathological response (pcr versus non-pcr) 0 61 (0 28, 1 34) (0 34, 1 66) CFR (high versus low) 0 35 (0 16, 0 76) (0 16, 0 81) TNBC (n = 61) Tumour size ( 2 versus > 2cm) 0 55 (0 12, 2 55) Lymph node status (negative versus positive) 0 94 (0, 4 36) Nuclear grade (1 2 versus 3) 1 55 (0 46, 5 31) Ki-67 ( 140 versus >140) 0 74 (0 22, 2 53) Pathological response (pcr versus non-pcr) 0 23 (0 05, 1 08) (0 08, 1 90) 0 2 CFR (high versus low) 0 14 (0 04, 0 53) (0 05, 0 72) HER2BC (n = 36) Tumour size ( 2 versus > 2cm) 0 69 (0 08, 6 30) Lymph node status (negative versus positive) 3 73 (0 07, 5 05) Nuclear grade (1 2 versus 3) 0 04 (0 01, 5 22) Ki-67 ( 140 versus >140) 0 44 (0 07, 2 62) Pathological response (pcr versus non-pcr) 0 48 (0 08, 2 85) (0 15, 12 91) CFR (high versus low) 0 12 (0 18, 0 73) (0 10, 0 90) HRBC (n = 80) Tumour size ( 2 versus > 2cm) 2 46 (0 32, 18 84) Lymph node status (negative versus positive) 3 68 (0 15, 10 38) 0 5 Nuclear grade (1 2 versus 3) 1 06 (0 30, 3 81) Ki-67 ( 140 versus >140) 0 60 (0 21, 1 74) Pathological response (pcr versus non-pcr) 1 33 (0 44, 3 97) (0 42, 3 97) CFR (high versus low) 0 85 (0 27, 2 70) (0 27, 2 91) Values in parentheses are 95 per cent confidence intervals. pcr, pathological complete response; CFR, CD8+/FOXP3+ tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte ratio; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer. HER2BC, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-enriched breast cancer; HRBC, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. and hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (HRBC) in 80 (45 2 per cent). A pcr was achieved in 67 patients (37 9 per cent), a partial response in 84 (47 5 per cent) and stable disease in 19 (10 7 per cent), whereas seven patients (4 0 per cent) had progressive disease. Stratified by subtype, a pcr was achieved in 28 (46 per cent) of 61 patients with TNBC, 18 (50 per cent) of 36 with HER2BC and 21 (26 per cent) of 80 with HRBC. Correlation between stromal and intratumoural tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes Among all 177 patients, the stromal TILs were CD8+ in 91 (51 4 per cent) and 89 patients were FOXP3+ (50 3per cent). The intratumoural TILs were CD8+ in 89 patients (50 3 per cent) and 80 patients were FOXP3+ (45 2 per cent). A positive correlation was observed between CD8+ and FOXP3+ lymphocyte infiltration, both in the stroma (r = 0 676, P < 0 001) (Fig. 2a) and in the intratumoural compartment (r = 0 657, P < 0 001) (Fig. 2b). CFR in stromal tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and outcome of neoadjuvant therapy in all breast cancers Patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy were divided into high- and low-cfr groups, and their clinicopathological features compared. There were 90 patients (50 8 per cent) in the high-cfr group and 87 (49 2 per cent) in the low-cfr group (Table 1). TNBC (P = 0 002) and HER2BC (P = 0 033) were significantly more common, and HRBC was significantly less common (P < 0 001), in the high-cfr group than in the low-cfr group. In addition, nuclear grade (P = 0 042), Ki-67 (P = 0 003) andthe pcrrate (P = 0 002) were significantly higher in the high-cfr group. No correlations between the CFR and other clinicopathological features were found.
6 850 Y. Asano, S. Kashiwagi, W. Goto, K. Kurata, S. Noda, T. Takashima et al. Table 3 Correlations between tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinicopathological parameters in triple-negative, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-enriched and luminal-type breast cancers TNBC HER2BC HRBC High CFR Low CFR High CFR Low CFR High CFR Low CFR (n = 41) (n = ) P* (n = ) (n = 12) P* (n = 25) (n = 55) P* Age at operation (years) (44) 10 (50) 11 (46) 5 (42) 16 (64) 27 (49) > (56) 10 (50) 13 (54) 7 (58) 9 (36) 28 (51) In menopause No 13 (32) 9 (45) 10 (42) 4 (33) 13 (52) 23 (42) Yes 28 (68) 11 (55) 14 (58) 8 (67) 12 (48) 32 (58) Tumour size (cm) (12) 2 (10) 4 (17) 2 (17) 3 (12) 8 (15) > 2 36 (88) 18 (90) (83) 10 (83) 22 (88) 47 (85) Lymph node status Negative 6 (15) 5 (25) 7 (29) 4 (33) 7 (28) 12 (22) Positive 35 (85) 15 (75) 17 (71) 8 (67) 18 (72) 43 (78) Nuclear grade (66) 17 (85) 17 (71) 11 (92) (80) 45 (82) 3 14 (34) 3 (15) 7 (29) 1 (8) 5 () 10 (18) Ki-67 (%) () 8 (40) 8 (33) 9 (75) 10 (40) 29 (53) > (76) 12 (60) 16 (67) 3 (25) 15 (60) 26 (47) Pathological response < pcr 23 (56) 5 (25) 17 (71) 1 (8) 4 (16) 17 (31) Non-pCR 18 (44) 15 (75) 7 (29) 11 (92) 21 (84) 38 (69) Values in parentheses are percentages. TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; HER2BC, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-enriched breast cancer; HRBC, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer; CFR, CD8+/FOXP3+ tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte ratio; pcr, pathological complete response. *χ 2 test. Median follow-up for the assessment of DFS was 3 1 (range ) years and that for overall survival was 3 4 ( ) years. DFS was significantly longer in the high-cfr group than in the low-cfr group (P = 0 005), but overall survival was not significantly different (P = 0 057) (Fig. S1a,b, supporting information). In univariable analysis for recurrence, a high CFR was found to be a favourable prognostic factor (hazard ratio 0 35, 95 per cent c.i to 0 76; P = 0 008) (Table 2). Multivariable analysis showed that a high CFR was an independent favourable prognostic factor (HR 0 37, 0 16 to 0 81; P = 0 013) CFR in stromal tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and outcome in triple-negative breast cancer Of the 61 patients with TNBC, 41 (67 per cent) were in the high-cfr group, and (33 per cent) in the low-cfr group. The pcr rate was significantly higher in the high-cfr group than in the low-cfr group (P = 0 022) (Table 3). Outcome analysis showed significantly longer DFS (P = 0 001) and overall survival (P = 0 003) in the high-cfr group (Fig. 3a,b). Patients in the high-cfr group had a significantly lower rate of recurrence in univariable (HR 0 14, 95 per cent c.i to 0 53; P = 0 004) and multivariable (0, 0 05 to 0 72; P = 0 015) analyses (Table 2). CFR of stromal tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and outcome in HER2-enriched breast cancers Of the 36 patients with HER2BC, (67 per cent) were in the high-cfr group and 12 (33 per cent) were in the low-cfr group. The Ki-67 rate (P = 0 022) and pcr rate (P < 0 001) were significantly higher in the high-cfr group than in the low-cfr group (Table 3). DFS was significantly longer in the high-cfr group (P = 0 006), but overall survival was not (P = 0 611) (Fig. 3c,d). In univariable analysis for recurrence, high-cfr status was a good prognostic factor (HR 0 12, 95 per cent c.i to 0 73; P = 0 021). Multivariable analysis revealed high-cfr status as an independent good prognostic factor (HR 0 10, 0 10 to 0 90; P = 0 041) (Table 2). CFR in stromal tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and outcome in hormone receptor-positive breast cancers Of the 80 patients with HRBC, 25 (31 per cent) were in the high-cfr group and 55 (69 per cent) were in
7 Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes as predictors of response to chemotherapy in breast cancer Survival rate High CFR Low CFR Survival rate Time after surgery (years) Time after surgery (years) No. at risk No. at risk High CFR Low CFR High CFR Low CFR a Disease-free survival in TNBC b Overall survival in TNBC Survival rate Survival rate Time after surgery (years) Time after surgery (years) No. at risk No. at risk High CFR Low CFR High CFR Low CFR c Disease-free survival in HER2BC d Overall survival in HER2BC Fig. 3 Analysis of CD8+/FOXP3+ tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte ratio (CFR) status and outcome in patients with a,b triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and c,d human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-enriched breast cancer (HER2BC): a,c disease-free survival and b,d overall survival. a P = 0 001, b P = 0 003, c P = 0 006, d P = (log rank test) the low-cfr group. No correlation was found between CFR and any clinicopathological variable in these patients (Table 3). There was no correlation between CFR and outcomes (Table 2; Fig. S1c,d, supporting information). Changes in CFR at breast cancer recurrence among patients with high CFR Thirty patients (16 9 per cent) in this study had postoperative recurrence of breast cancer, of whom nine were in the high-cfr group and 21 in the low-cfr group. In the high-cfr group of patients with recurrence (TNBC 3, HER2BC 2, HRBC 4), three (TNBC 1, HER2BC 1, HRBC 1) had a pcr after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Needle biopsy specimens before neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgical specimens after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and needle biopsy specimens after recurrence (available for 7 patients) were reviewed. There were no changes in the CFR in three patients with HRBC. However, in patients with highly malignant breast cancer (TNBC 2, HER2BC 2), the CFR was decreased in needle biopsy specimens after recurrence in both intratumoural and stromal TILs.
8 852 Y. Asano, S. Kashiwagi, W. Goto, K. Kurata, S. Noda, T. Takashima et al. Discussion TILs serve as an indicator for regulation of the tumour immune microenvironment in the host in response to a cancer. TIL subsets include cells such as CD8+ T lymphocytes that eradicate cancer cells, and those such as Treg cells that promote survival and proliferation of cancer cells 7. FOXP3 expression is induced upon activation of naive CD4+ T cells. Previous studies have shown by double staining that almost all FOXP3+ cells were CD4+, and FOXP3+ cells were counted as Treg 30. An experimental study 31 in mice with FOXP3-specific depletion of Treg cells showed that, by decreasing Treg cells, the antitumour immune response by CD8+ T lymphocytes was increased, and tumour proliferation suppressed. This indicates that a large number of Treg cells in the tumour microenvironment leads to an immunosuppressive effect that inhibits the function of CD8+ T lymphocytes. Therefore, to improve the tumour immune microenvironment, the number and function of Treg cells must be controlled. The CFR, as an indicator of the balance between CD8+ TILs and Treg cells in a tumour, may be useful for predicting the response to treatment with chemotherapy. Among patients with breast cancer who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the present study, the pcr rate was significantly higher in the high-cfr group than in the low-cfr group, and this translated into a longer DFS. Analysis of TIL subsets in patients with breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy has shown higher pcr rates, with high levels of expression of CD3, CD4, CD8 and FOXP3, and higher pcr rates with a high CFR have also been reported in TNBC 12,13,32. However, there have been few studies with stratification for intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. In the present study, a pcr was significantly more common in patients with aggressive subtypes and a high CRF, but this was not observed for HRBC. In the patients with aggressive breast cancer subtypes, lymphocytes such as CD8+ TILs that function in tumour immunity have already infiltrated the tumour, and these are controlled by antitumour immunity through Treg cells. Many anticancer drugs have immunosuppressive effects but, depending on their mode of administration, enhancement of the immune activity or reversal of immunosuppression is possible 3,33. Improvement in immunoescape on the cancer cell side and host side is involved in the mechanism of enhancement of antitumour immunity with anticancer drugs. In the present study, a regimen of FEC followed by paclitaxel ± trastuzumab, 5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel has been shown to improve immunoescape by improving the decreased sensitivity of CD8+ T cells 3,33. In addition, paclitaxel also improves immunoescape by inhibiting Treg cells 3,34. The present study also examined CFR changes in needle biopsy tissue samples of lesions after a local recurrence to investigate the relationship between CFR and postoperative recurrence. The CFR decreased in recurrent TNBC and HER2BC, but remained unchanged in the HRBC subtype. This suggests that a decreased CFR may be involved in recurrences of highly malignant breast cancers, and that reduced tumour immunity in the cancer microenvironment plays a role in recurrence. As the numbers of recurrences were low in the present cohort, this finding should, however, be interpreted with caution and replicated in larger studies. Acknowledgements The authors thank Y. Matsukiyo and T. Ohkawa (Department of Surgical Oncology, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine) for helpful advice regarding data management. This study was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI, nos and ) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, Culture and Technology of Japan. Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest. References 1 Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 11; 144: Fridman WH, Pages F, Sautes-Fridman C, Galon J. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat Rev Cancer 12; 12: Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Kroemer G. Immune parameters affecting the efficacy of chemotherapeutic regimens. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 11; 8: Liu H, Zhang T, Ye J, Li H, Huang J, Li X et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes predict response to chemotherapy in patients with advance non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 12; 61: Kocián P, Šedivcová M, Drgáč J, Cerná K, Hoch J, Kodet R et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and dendritic cells in human colorectal cancer: their relationship to KRAS mutational status and disease recurrence. Hum Immunol 11; 72: Lee WS, Kang M, Baek JH, Lee JI, Ha SY. Clinical impact of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes for survival in curatively resected stage IV colon cancer with isolated liver or lung metastasis. Ann Surg Oncol 13; : Salgado R, Denkert C, Demaria S, Sirtaine N, Klauschen F, Pruneri G et al. The evaluation of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 14. Ann Oncol 15; 26: Adams S, Gray RJ, Demaria S, Goldstein L, Perez EA, Shulman LN et al. Prognostic value of tumour-infiltrating
9 Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes as predictors of response to chemotherapy in breast cancer 853 lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers from two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG J Clin Oncol 14; 32: Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, Sinn BV, Gade S, Kronenwett R et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without carboplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive and triple-negative primary breast cancers. JClin Oncol 15; 33: Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F, Salgado R, Viale G, Van Eenoo F et al. Prognostic and predictive value of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG J Clin Oncol 13; 31: Loi S, Michiels S, Salgado R, Sirtaine N, Jose V, Fumagalli D et al. Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: results from the FinHER trial. Ann Oncol 14; 25: Seo AN, Lee HJ, Kim EJ, Kim HJ, Jang MH, Lee HE et al. Tumour-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes as an independent predictive factor for pathological complete response to primary systemic therapy in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 13; 109: Hornychova H, Melichar B, Tomsova M, Mergancova J, Urminska H, Ryska A. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer Invest 08; 26: Oda N, Shimazu K, Naoi Y, Morimoto K, Shimomura A, Shimoda M et al. Intratumoural regulatory T cells as an independent predictive factor for pathological complete response to neoadjuvant paclitaxel followed by 5-FU/epirubicin/cyclophosphamide in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 12; 136: Miyashita M, Sasano H, Tamaki K, Chan M, Hirakawa H, Suzuki A et al. Tumour-infiltrating CD8+ and FOXP3+ lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer: its correlation with pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 14; 148: Nabholtz JM, Abrial C, Mouret-Reynier MA, Dauplat MM, Weber B, Gligorov J et al. Multicentric neoadjuvant phase II study of panitumumab combined with an anthracycline/taxane-based chemotherapy in operable triple-negative breast cancer: identification of biologically defined signatures predicting treatment impact. Ann Oncol 14; 25: McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM. Reporting recommendations for tumour marker prognostic studies (REMARK). J Natl Cancer Inst 05; 97: Greene FL. Breast tumours. In TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours (7th edn), Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK,Wittekind C (eds). Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, 09; Mauri D, Pavlidis N, Ioannidis JP. Neoadjuvant versus adjuvant systemic treatment in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 05; 97: Mieog JS, van der Hage JA, van de Velde CJ. Preoperative chemotherapy for women with operable breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 07; (2)CD Buzdar AU, Valero V, Ibrahim NK, Francis D, Broglio KR, Theriault RL et al. Neoadjuvant therapy with paclitaxel followed by 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy and concurrent trastuzumab in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive operable breast cancer: an update of the initial randomized study population and data of additional patients treated with the same regimen. Clin Cancer Res 07; 13: Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, SargentD,FordRet al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 09; 45: Kashiwagi S, Yashiro M, Takashima T, Aomatsu N, Kawajiri H, Ogawa Y et al. c-kit expression as a prognostic molecular marker in patients with basal-like breast cancer. Br J Surg 13; 100: Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 13; 31: Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. Arch Pathol Lab Med 14; 138: Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ. Strategies for subtypes dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 11. Ann Oncol 11; 22: Ono M, Tsuda H, Shimizu C, Yamamoto S, Shibata T, Yamamoto H et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes are correlated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 12; 132: Mao Y, Qu Q, Zhang Y, Liu J, Chen X, Shen K. The value of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) for predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 14; 9: e Ibrahim EM, Al-Foheidi ME, Al-Mansour MM, Kazkaz GA. The prognostic value of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 14; 148:
10 854 Y. Asano, S. Kashiwagi, W. Goto, K. Kurata, S. Noda, T. Takashima et al. 30 Hasita H, Komohara Y, Okabe H, Masuda T, Ohnishi K, Lei XF et al. Significance of alternatively activated macrophages in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Sci 10; 101: Teng MW, Ngiow SF, von Scheidt B, McLaughlin N, Sparwasser T, Smyth MJ. Conditional regulatory T-cell depletion releases adaptive immunity preventing carcinogenesis and suppressing established tumour growth. Cancer Res 10; 70: Lee HJ, Seo JY, Ahn JH, Ahn SH, Gong G. Tumour-associated lymphocytes predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. JBreast Cancer 13; 16: Vacchelli E, Galluzzi L, Fridman WH, Galon J, Sautes-Fridman C, Tartour E et al. Trialwatch: chemotherapy with immunogenic cell death inducers. Oncoimmunology 12; 1: Yaguchi T, Sumimoto H, Kudo-Saito C, Tsukamoto N, Ueda R, Iwata-Kajihara T et al. The mechanisms of cancer immunoescape and development of overcoming strategies. Int J Hematol 11; 93: Supporting information Additional supporting information may be found in the online version of this article: Fig. S1 Analysis of the CD8+/FOXP3+ tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte ratio status and outcome of all patients with breast cancer and those with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (Word document) If you wish to comment on this, or any other article published in the BJS, please visit the online Your Views section of the website (
Predictive value of improvement in the immune tumour microenvironment in patients with breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
 Additional material is published online only. To view, please visit the journal online (http:// dx. doi. org/ 10. 1136/ esmoopen- 2017-000305). To cite: Goto W, Kashiwagi S, Asano Y, et al. Predictive
Additional material is published online only. To view, please visit the journal online (http:// dx. doi. org/ 10. 1136/ esmoopen- 2017-000305). To cite: Goto W, Kashiwagi S, Asano Y, et al. Predictive
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer
 Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer
 Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer Hee Jung Kwon, Nuri Jang, Min Hui Park, Young Kyung Bae Department of Pathology, Yeungnam
Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer Hee Jung Kwon, Nuri Jang, Min Hui Park, Young Kyung Bae Department of Pathology, Yeungnam
Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy
 Case Series Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy Ling Xu 1*, Fang Li 1,2*, Yinhua Liu 1, Xuening Duan 1, Jingming Ye 1,
Case Series Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy Ling Xu 1*, Fang Li 1,2*, Yinhua Liu 1, Xuening Duan 1, Jingming Ye 1,
Prediction of survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer by evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and residual cancer burden
 Asano et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:888 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3927-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Prediction of survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer by evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
Asano et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:888 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3927-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Prediction of survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer by evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Hormonal and Her-2 Receptor Status in Carcinoma Breast
 Original Research Article A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Hormonal and Her-2 Receptor Status in Carcinoma Breast E. Rajesh Goud 1, M. Muralidhar 2*, M. Srinivasulu 3 1Senior
Original Research Article A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Hormonal and Her-2 Receptor Status in Carcinoma Breast E. Rajesh Goud 1, M. Muralidhar 2*, M. Srinivasulu 3 1Senior
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience
 Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Toru Nakamura 1, Takashi Fukutomi 1, Hitoshi Tsuda 2, Sadako Akashi-Tanaka 1, Kaneyuki Matsuo 1, Chikako Shimizu 1 and Kunihisa Miyakawa 3
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 2: JIA YI WU *, WEI GUO CHEN *, XIAO SONG CHEN, OU HUANG, JIAN RONG HE, LI ZHU, YAFEN LI and KUN WEI SHEN
 MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 2: 997-1002 Long term outcomes following adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients with a positive to negative change of hormone receptor status following neoadjuvant
MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 2: 997-1002 Long term outcomes following adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients with a positive to negative change of hormone receptor status following neoadjuvant
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
EGFR as paradoxical predictor of chemosensitivity and outcome among triple-negative breast cancer
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 21: 413-417, 2009 413 EGFR as paradoxical predictor of chemosensitivity and outcome among triple-negative breast cancer HIROKO NOGI 1, TADASHI KOBAYASHI 2, MASAFUMI SUZUKI 3, ISAO TABEI
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 21: 413-417, 2009 413 EGFR as paradoxical predictor of chemosensitivity and outcome among triple-negative breast cancer HIROKO NOGI 1, TADASHI KOBAYASHI 2, MASAFUMI SUZUKI 3, ISAO TABEI
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Lymphocyte density determined by computational pathology validated as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: secondary analysis of the ARTemis
Edinburgh Research Explorer Lymphocyte density determined by computational pathology validated as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: secondary analysis of the ARTemis
Junichi Asano, 1 Akihiro Hirakawa, 2 Chikuma Hamada, 1 Kan Yonemori, 3 Taizo Hirata, 4 Chikako Shimizu, 3 Kenji Tamura, 3 and Yasuhiro Fujiwara 3
 International Journal of Breast Cancer Volume 201, Article ID 54579, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/201/54579 Research Article Use of Cox s Cure Model to Establish Clinical Determinants of Long-Term
International Journal of Breast Cancer Volume 201, Article ID 54579, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/201/54579 Research Article Use of Cox s Cure Model to Establish Clinical Determinants of Long-Term
What to do after pcr in different subtypes?
 What to do after pcr in different subtypes? Luca Moscetti Breast Unit Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia Policlinico di Modena, Italy Aims of neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer Primary
What to do after pcr in different subtypes? Luca Moscetti Breast Unit Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia Policlinico di Modena, Italy Aims of neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer Primary
Breast Cancer Earlier Disease. Stefan Aebi Luzerner Kantonsspital
 Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Stefan Aebi Luzerner Kantonsspital stefan.aebi@onkologie.ch Switzerland Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis Local Therapy Surgery Radiation therapy Adjuvant
Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Stefan Aebi Luzerner Kantonsspital stefan.aebi@onkologie.ch Switzerland Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis Local Therapy Surgery Radiation therapy Adjuvant
Predictive and prognostic impact of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
 Predictive and prognostic impact of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy Carmen Herrero-Vicent 1, Angel Guerrero 1, Joaquin Gavilá 1, Francisco
Predictive and prognostic impact of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy Carmen Herrero-Vicent 1, Angel Guerrero 1, Joaquin Gavilá 1, Francisco
Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for Luminal A-like breast cancer?
 JBUON 2018; 23(4): 877-882 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for Luminal A-like breast cancer?
JBUON 2018; 23(4): 877-882 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for Luminal A-like breast cancer?
Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer. Cheol Min Kang 2018/04/05
 Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
SYSTEMIC TREATMENT OF TRIPLE NEGATIVE BREAST CANCER
 SYSTEMIC TREATMENT OF TRIPLE NEGATIVE BREAST CANCER Sunil Shrestha 1*, Ji Yuan Yang, Li Shuang and Deepika Dhakal Clinical School of Medicine, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, Hubei Province, PR. China Department
SYSTEMIC TREATMENT OF TRIPLE NEGATIVE BREAST CANCER Sunil Shrestha 1*, Ji Yuan Yang, Li Shuang and Deepika Dhakal Clinical School of Medicine, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, Hubei Province, PR. China Department
Biomarkers for HER2-directed Therapies : Past Failures and Future Perspectives
 Biomarkers for HER2-directed Therapies : Past Failures and Future Perspectives Ian Krop Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Inchon 2018 Adjuvant Trastuzumab Improves Outcomes in HER2+ Breast
Biomarkers for HER2-directed Therapies : Past Failures and Future Perspectives Ian Krop Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Inchon 2018 Adjuvant Trastuzumab Improves Outcomes in HER2+ Breast
Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)?
 Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)? Department of General Surgery, Anam Hospital, Korea University, College of Medicine, 126-, Anam-dong
Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)? Department of General Surgery, Anam Hospital, Korea University, College of Medicine, 126-, Anam-dong
Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K)
 Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
Immunohistochemical Expression of Hormone Receptors and The Histological Characteristics of Biochemically Hormone Receptor Negative Breast Cancers
 Breast Cancer Vol. 14 No. 1 January 2007 Original Article Immunohistochemical Expression of Hormone Receptors and The Histological Characteristics of Biochemically Hormone Receptor Negative Breast Cancers
Breast Cancer Vol. 14 No. 1 January 2007 Original Article Immunohistochemical Expression of Hormone Receptors and The Histological Characteristics of Biochemically Hormone Receptor Negative Breast Cancers
The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative
 Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Review of adjuvant and neo-adjuvant abstracts from SABCS 2011 January 7 th 2012
 Review of adjuvant and neo-adjuvant abstracts from SABCS 2011 January 7 th 2012 Ruth M. O Regan, MD Professor and Vice-Chair for Educational Affairs, Department of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Emory
Review of adjuvant and neo-adjuvant abstracts from SABCS 2011 January 7 th 2012 Ruth M. O Regan, MD Professor and Vice-Chair for Educational Affairs, Department of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Emory
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva
 Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer.
 Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer. Goal of the study: 1.To assess whether patients at Truman
Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer. Goal of the study: 1.To assess whether patients at Truman
Sustained benefits for women with HER2-positive early breast cancer JORGE MADRID BIG GOCCHI PROTOCOLO HERA
 Sustained benefits for women with HER2-positive early breast cancer JORGE MADRID BIG GOCCHI PROTOCOLO HERA The fascinating history of Herceptin 1981 1985 1987 1990 1992 1998 2000 2005 2006 2008 2011 Murine
Sustained benefits for women with HER2-positive early breast cancer JORGE MADRID BIG GOCCHI PROTOCOLO HERA The fascinating history of Herceptin 1981 1985 1987 1990 1992 1998 2000 2005 2006 2008 2011 Murine
Modified primary tumour/vessel tumour/nodal tumour classification for patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast
 British Journal of Cancer (2011) 105, 698 708 All rights reserved 0007 0920/11 www.bjcancer.com Modified primary tumour/vessel tumour/nodal tumour classification for patients with invasive ductal carcinoma
British Journal of Cancer (2011) 105, 698 708 All rights reserved 0007 0920/11 www.bjcancer.com Modified primary tumour/vessel tumour/nodal tumour classification for patients with invasive ductal carcinoma
Perspectivas de desarrollo de la inmunoterapia en cáncer de mama hereditario. Luis de la Cruz Merino Oncología Médica HUVMacarena (Sevilla)
 Perspectivas de desarrollo de la inmunoterapia en cáncer de mama hereditario Luis de la Cruz Merino Oncología Médica HUVMacarena (Sevilla) Outline Immunology and breast cancer Clinical trials with modern
Perspectivas de desarrollo de la inmunoterapia en cáncer de mama hereditario Luis de la Cruz Merino Oncología Médica HUVMacarena (Sevilla) Outline Immunology and breast cancer Clinical trials with modern
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Pathology. AGO e. V. in der DGGG e.v. sowie in der DKG e.v.
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Response to Paclitaxel in Node-positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 J Korean Surg Soc 2010;79:173-179 DOI: 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.3.173 원 저 Response to Paclitaxel in Node-positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine,
J Korean Surg Soc 2010;79:173-179 DOI: 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.3.173 원 저 Response to Paclitaxel in Node-positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine,
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Time to Slice and Dice? Carsten Denkert, MD Charité University Hospital Berlin, Germany
 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Time to Slice and Dice? Carsten Denkert, MD Charité University Hospital Berlin, Germany Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) 2018 Presentation Outline The molecular heterogeneity
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Time to Slice and Dice? Carsten Denkert, MD Charité University Hospital Berlin, Germany Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) 2018 Presentation Outline The molecular heterogeneity
Haruo Ohtani, 1,2 Kazuko Mori-Shiraishi, 3 Morio Nakajima 3 and Hamaichi Ueki 3
 bs_bs_banner Pathology International 2015; 65: 644 651 doi:10.1111/pin.12355 Original Article Defining lymphocyte-predominant breast cancer by the proportion of lymphocyte-rich stroma and its significance
bs_bs_banner Pathology International 2015; 65: 644 651 doi:10.1111/pin.12355 Original Article Defining lymphocyte-predominant breast cancer by the proportion of lymphocyte-rich stroma and its significance
Clinical significance and prognostic value of receptor conversion in hormone receptor positive breast cancers after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
 Yang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:51 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1332-7 RESEARCH Open Access Clinical significance and prognostic value of receptor conversion in hormone receptor
Yang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:51 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1332-7 RESEARCH Open Access Clinical significance and prognostic value of receptor conversion in hormone receptor
Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing. Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine)
 Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine) Breast Cancer Theory: Halsted Operative breast cancer is a local-regional disease The positive
Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine) Breast Cancer Theory: Halsted Operative breast cancer is a local-regional disease The positive
Concurrent Analysis of Human Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 1 and Ribonucleotide
 1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Concurrent Analysis of Human Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 1 and Ribonucleotide Reductase Subunit 1 Expression Increases Predictive Value for Prognosis in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Concurrent Analysis of Human Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 1 and Ribonucleotide Reductase Subunit 1 Expression Increases Predictive Value for Prognosis in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients
Validity of St Gallen risk categories in prognostication of breast cancer patients in Southern Sri Lanka
 Peiris et al. BMC Women's Health (2018) 18:30 DOI 10.1186/s12905-018-0524-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Validity of St Gallen risk categories in prognostication of breast cancer patients in Southern Sri
Peiris et al. BMC Women's Health (2018) 18:30 DOI 10.1186/s12905-018-0524-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Validity of St Gallen risk categories in prognostication of breast cancer patients in Southern Sri
Predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes to pathological complete response in neoadjuvant treated triplenegative
 Ruan et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2018) 13:66 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-018-0743-7 RESEARCH Predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes to pathological complete response in neoadjuvant treated
Ruan et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2018) 13:66 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-018-0743-7 RESEARCH Predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes to pathological complete response in neoadjuvant treated
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 335 340 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4435-y Risk factors of recurrence in small-sized, node negative breast cancer in young women: a retrospective
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 335 340 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4435-y Risk factors of recurrence in small-sized, node negative breast cancer in young women: a retrospective
Tumor-infiltrating immune cell profiles and their change after neoadjuvant chemotherapy predict response and prognosis of breast cancer
 García-Martínez et al. Breast Cancer Research 2014, 16:488 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Tumor-infiltrating immune cell profiles and their change after neoadjuvant chemotherapy predict response and prognosis
García-Martínez et al. Breast Cancer Research 2014, 16:488 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Tumor-infiltrating immune cell profiles and their change after neoadjuvant chemotherapy predict response and prognosis
Lecture 5. Primary systemic therapy: clinical and biological endpoints
 Lecture 5 Primary systemic therapy: clinical and biological endpoints Valentina Guarneri, M.D., Ph.D. Primary systemic therapy in breast cancer Firstly introduced d into clinical i l practice in 70s for
Lecture 5 Primary systemic therapy: clinical and biological endpoints Valentina Guarneri, M.D., Ph.D. Primary systemic therapy in breast cancer Firstly introduced d into clinical i l practice in 70s for
Nadia Harbeck Breast Center University of Cologne, Germany
 Evidence in Favor of Taxane Based Combinations and No Anthracycline in Adjuvant and Metastatic Settings Nadia Harbeck Breast Center University of Cologne, Germany Evidence in Favor of Taxane Based Combinations
Evidence in Favor of Taxane Based Combinations and No Anthracycline in Adjuvant and Metastatic Settings Nadia Harbeck Breast Center University of Cologne, Germany Evidence in Favor of Taxane Based Combinations
Abstract. Introduction. imedpub Journals Mohamed L 1*, Elsaka A 2, Zamzam Y 2 and Elkady A 2. Research Article
 Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.21767/2254-6081.100178 Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Tertiary Lymphoid Structure as Prognostic and Predictive Factor for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.21767/2254-6081.100178 Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Tertiary Lymphoid Structure as Prognostic and Predictive Factor for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Clinical Study The Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for HER-2-Positive Locally Advanced Breast Cancer and Survival Analysis
 Hindawi Analytical Cellular Pathology Volume 2017, Article ID 1350618, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1350618 Clinical Study The Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for HER-2-Positive Locally Advanced
Hindawi Analytical Cellular Pathology Volume 2017, Article ID 1350618, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1350618 Clinical Study The Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for HER-2-Positive Locally Advanced
WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER?
 CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
Prognostic implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes in male breast cancer
 JBUON 2017; 22(2): 377-382 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes in male
JBUON 2017; 22(2): 377-382 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes in male
SFSPM Novembre Valeur prédictive et pronostique de l infiltrat immunitaire dans les cancers du sein traités par chimiothérapie néoadjuvante
 SFSPM Novembre 217 Valeur prédictive et pronostique de l infiltrat immunitaire dans les cancers du sein traités par chimiothérapie néoadjuvante Dr Fabien REYAL Service de Chirurgie INSERM U932 Immunity
SFSPM Novembre 217 Valeur prédictive et pronostique de l infiltrat immunitaire dans les cancers du sein traités par chimiothérapie néoadjuvante Dr Fabien REYAL Service de Chirurgie INSERM U932 Immunity
USING OF BINOMINAL METHOD FOR THE PURPOSE OF DETERMINATION OF CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR PREDICTION OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMA METASTASES
 USING OF BINOMINAL METHOD FOR THE PURPOSE OF DETERMINATION OF CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR PREDICTION OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMA METASTASES Alexandr Lazaruk Department of Pathological Anatomy Higher
USING OF BINOMINAL METHOD FOR THE PURPOSE OF DETERMINATION OF CONFIDENCE INTERVALS FOR PREDICTION OF INVASIVE DUCTAL BREAST CARCINOMA METASTASES Alexandr Lazaruk Department of Pathological Anatomy Higher
Impact of BMI on pathologic complete response (pcr) following neo adjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for locally advanced breast cancer
 Impact of BMI on pathologic complete response (pcr) following neo adjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for locally advanced breast cancer Rachna Raman, MD, MS Fellow physician University of Iowa hospitals and clinics
Impact of BMI on pathologic complete response (pcr) following neo adjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for locally advanced breast cancer Rachna Raman, MD, MS Fellow physician University of Iowa hospitals and clinics
The Neoadjuvant Model as a Translational Tool for Drug and Biomarker Development in Breast Cancer
 The Neoadjuvant Model as a Translational Tool for Drug and Biomarker Development in Breast Cancer Laura Spring, MD Breast Medical Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Primary Mentor: Dr. Aditya Bardia
The Neoadjuvant Model as a Translational Tool for Drug and Biomarker Development in Breast Cancer Laura Spring, MD Breast Medical Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Primary Mentor: Dr. Aditya Bardia
Association between tumour infiltrating lymphocytes, histotype and clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian cancer
 James et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:657 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3585-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Association between tumour infiltrating lymphocytes, histotype and clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian
James et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:657 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3585-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Association between tumour infiltrating lymphocytes, histotype and clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian
original articles introduction
 Annals of Oncology 19. List HJ, Reiter R, Singh B et al. Expression of the nuclear coactivator AIB1 in normal and malignant breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2001; 68: 21 28. 20. Jansson A, Delander
Annals of Oncology 19. List HJ, Reiter R, Singh B et al. Expression of the nuclear coactivator AIB1 in normal and malignant breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2001; 68: 21 28. 20. Jansson A, Delander
Clinical Features and Survival Analysis of T1mic, a, bn0m0 Breast Cancer
 Original Articles Jpn J Clin Oncol 2012;42(6)471 476 doi:10.1093/jjco/hys046 Advance Access Publication 3 April 2012 Clinical Features and Survival Analysis of T1mic, a, bn0m0 Breast Cancer Junnan Li,
Original Articles Jpn J Clin Oncol 2012;42(6)471 476 doi:10.1093/jjco/hys046 Advance Access Publication 3 April 2012 Clinical Features and Survival Analysis of T1mic, a, bn0m0 Breast Cancer Junnan Li,
Controversies in Breast Pathology ELENA PROVENZANO ADDENBROOKES HOSPITAL, CAMBRIDGE
 Controversies in Breast Pathology ELENA PROVENZANO ADDENBROOKES HOSPITAL, CAMBRIDGE Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Indications: Management of locally advanced invasive breast cancers including inflammatory breast
Controversies in Breast Pathology ELENA PROVENZANO ADDENBROOKES HOSPITAL, CAMBRIDGE Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Indications: Management of locally advanced invasive breast cancers including inflammatory breast
XII Michelangelo Foundation Seminar
 XII Michelangelo Foundation Seminar The opportunity of the neoadjuvant approach L. Gianni, Milan, I XII Michelangelo Foundation Seminar Milano, October 12, 2012 The opportunity of the neoadjuvant approach
XII Michelangelo Foundation Seminar The opportunity of the neoadjuvant approach L. Gianni, Milan, I XII Michelangelo Foundation Seminar Milano, October 12, 2012 The opportunity of the neoadjuvant approach
Adjuvan Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
 Adjuvan Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Prof Dr Adnan Aydıner Istanbul University, Oncology Institute aa1 Slide 1 aa1 adnan aydiner; 17.02.2008 15-Year Reductions in Recurrence and Disease-Specific Mortality
Adjuvan Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Prof Dr Adnan Aydıner Istanbul University, Oncology Institute aa1 Slide 1 aa1 adnan aydiner; 17.02.2008 15-Year Reductions in Recurrence and Disease-Specific Mortality
Author(s) Emi; Hatanaka, Yutaka; Matsuno, Yoshihiro; Yamashita. The final publication is available at link.springer. Instructions for use
 Title Prognostic significance of pathologic complete respo cancer Yoshioka, Tatsuya; Hosoda, Mitsuchika; Yamamoto, Mit Author(s) Emi; Hatanaka, Yutaka; Matsuno, Yoshihiro; Yamashita CitationBreast Cancer,
Title Prognostic significance of pathologic complete respo cancer Yoshioka, Tatsuya; Hosoda, Mitsuchika; Yamamoto, Mit Author(s) Emi; Hatanaka, Yutaka; Matsuno, Yoshihiro; Yamashita CitationBreast Cancer,
Novel Preoperative Therapies for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Debu Tripathy, MD University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center
 Novel Preoperative Therapies for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Debu Tripathy, MD University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center Key Findings to Date in the Neoadjuvant Therapy of HER2+
Novel Preoperative Therapies for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Debu Tripathy, MD University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center Key Findings to Date in the Neoadjuvant Therapy of HER2+
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
Neo-adjuvant and adjuvant treatment for HER-2+ breast cancer
 Neo-adjuvant and adjuvant treatment for HER-2+ breast cancer Angelo Di Leo «Sandro Pitigliani» Medical Oncology Unit Hospital of Prato Istituto Toscano Tumori Prato, Italy NOAH: Phase III, Open-Label Trial
Neo-adjuvant and adjuvant treatment for HER-2+ breast cancer Angelo Di Leo «Sandro Pitigliani» Medical Oncology Unit Hospital of Prato Istituto Toscano Tumori Prato, Italy NOAH: Phase III, Open-Label Trial
International Society of Breast Pathology. Immune Targeting in Breast Cancer. USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting
 International Society of Breast Pathology USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Immune Targeting in Breast Cancer Ashley Cimino-Mathews, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology and Oncology The Johns Hopkins Hospital
International Society of Breast Pathology USCAP 2017 Annual Meeting Immune Targeting in Breast Cancer Ashley Cimino-Mathews, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology and Oncology The Johns Hopkins Hospital
Systemic Therapy Considerations in Inflammatory Breast Cancer
 Systemic Therapy Considerations in Inflammatory Breast Cancer Shani Paluch-Shimon, MBBS, MSc Director, Breast Oncology Unit Shaare Zedek Medical Centre, Jerusalem Israel Disclosures Roche: Speakers bureau,
Systemic Therapy Considerations in Inflammatory Breast Cancer Shani Paluch-Shimon, MBBS, MSc Director, Breast Oncology Unit Shaare Zedek Medical Centre, Jerusalem Israel Disclosures Roche: Speakers bureau,
How to Use MRI Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NAC) in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
 Global Breast Cancer Conference 2016 & 5 th International Breast Cancer Symposium April 29 th 2016, 09:40-10:50 How to Use MRI Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NAC) in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
Global Breast Cancer Conference 2016 & 5 th International Breast Cancer Symposium April 29 th 2016, 09:40-10:50 How to Use MRI Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NAC) in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
Neoadjuvant therapy a new pathway to registration?
 Neoadjuvant therapy a new pathway to registration? Graham Ross, FFPM Clinical Science Leader Roche Products Ltd Welwyn Garden City, UK (full time employee) Themes Neoadjuvant therapy Pathological Complete
Neoadjuvant therapy a new pathway to registration? Graham Ross, FFPM Clinical Science Leader Roche Products Ltd Welwyn Garden City, UK (full time employee) Themes Neoadjuvant therapy Pathological Complete
Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients
 BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
The Oncotype DX Assay A Genomic Approach to Breast Cancer
 The Oncotype DX Assay A Genomic Approach to Breast Cancer Pathology: 20 th and 21 st Century Size Age Phenotype Nodal status Protein/Gene Genomic Profiling Prognostic & Predictive Markers Used in Breast
The Oncotype DX Assay A Genomic Approach to Breast Cancer Pathology: 20 th and 21 st Century Size Age Phenotype Nodal status Protein/Gene Genomic Profiling Prognostic & Predictive Markers Used in Breast
* * * * Supplementary Figure 1. DS Lv CK HSA CK HSA. CK Col-3. CK Col-3. See overleaf for figure legend. Cancer cells
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples
 Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer
 Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data
 Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Herceptin Pivotal Studies
 Herceptin Pivotal Studies Nuhad K Ibrahim, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine Breast Medical Oncology Department MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX, USAE-mail: nibrahim@mdanderson.org Herceptin
Herceptin Pivotal Studies Nuhad K Ibrahim, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine Breast Medical Oncology Department MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX, USAE-mail: nibrahim@mdanderson.org Herceptin
Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy
 Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium. Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin
 UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Eight Year Survival Analysis of Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer in India
 APJCP.2016.17.6.2995 RESEARCH ARTICLE Eight Year Survival Analysis of Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer in India Dinesh Chandra Doval 1,2 *, P Suresh 1, Rupal Sinha 2, Saud Azam 2, Ullas Batra
APJCP.2016.17.6.2995 RESEARCH ARTICLE Eight Year Survival Analysis of Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer in India Dinesh Chandra Doval 1,2 *, P Suresh 1, Rupal Sinha 2, Saud Azam 2, Ullas Batra
Residual cancer burden in locally advanced breast cancer: a superior tool
 ABSTRACT Objectives Locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) poses a difficult clinical challenge with an overall poor long-term prognosis. The strength of the association between tumour characteristics,
ABSTRACT Objectives Locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) poses a difficult clinical challenge with an overall poor long-term prognosis. The strength of the association between tumour characteristics,
Ki-67 is a biological tumor marker that reflects tumor
 Evaluation of Ki-67 Index in Core Needle Biopsies and Matched Breast Cancer Surgical Specimens Soomin Ahn, MD; Junghye Lee, MD; Min-Sun Cho, MD, PhD; Sanghui Park, MD, PhD; Sun Hee Sung, MD, PhD Context.
Evaluation of Ki-67 Index in Core Needle Biopsies and Matched Breast Cancer Surgical Specimens Soomin Ahn, MD; Junghye Lee, MD; Min-Sun Cho, MD, PhD; Sanghui Park, MD, PhD; Sun Hee Sung, MD, PhD Context.
DRAFT GUIDANCE. This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only.
 Guidance for Industry Pathologic Complete Response in Neoadjuvant Treatment of High-Risk Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Use as an Endpoint to Support Accelerated Approval DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document
Guidance for Industry Pathologic Complete Response in Neoadjuvant Treatment of High-Risk Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Use as an Endpoint to Support Accelerated Approval DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document
Disclosures. Outline. What IS tumor budding?? Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How. I have nothing to disclose
 Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Bioscore: A Staging System for Breast Cancer Patients that Reflects the Prognostic Significance of Underlying Tumor Biology
 Ann Surg Oncol DOI./s-7-9-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Bioscore: A Staging System for Breast Cancer Patients that Reflects the Prognostic Significance of Underlying Tumor Biology Elizabeth A. Mittendorf,
Ann Surg Oncol DOI./s-7-9-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE BREAST ONCOLOGY Bioscore: A Staging System for Breast Cancer Patients that Reflects the Prognostic Significance of Underlying Tumor Biology Elizabeth A. Mittendorf,
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours
 Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer
 Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
TNBC: What s new Déjà vu All Over Again? Lucy R. Langer, MD MSHS Compass Oncology - SABCS 2016 Review February 21, 2017
 TNBC: What s new Déjà vu All Over Again? Lucy R. Langer, MD MSHS Compass Oncology - SABCS 2016 Review February 21, 2017 The problem with TNBC 1. Generally more aggressive 2. ONLY chemotherapy 3. No other
TNBC: What s new Déjà vu All Over Again? Lucy R. Langer, MD MSHS Compass Oncology - SABCS 2016 Review February 21, 2017 The problem with TNBC 1. Generally more aggressive 2. ONLY chemotherapy 3. No other
Medical Treatment of Early Breast Cancer
 J KMA Pharmacotherapeutics Medical Treatment of Early Breast Cancer Soon beom Kang, MD Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Seoul National University College of Medicine E mail : ksboo308@plaza.snu.ac.kr
J KMA Pharmacotherapeutics Medical Treatment of Early Breast Cancer Soon beom Kang, MD Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Seoul National University College of Medicine E mail : ksboo308@plaza.snu.ac.kr
Accuracy of MRI in the Detection of Residual Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 4, June: 1411-1416, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Accuracy of MRI in the Detection of Residual Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy MONA A. ABUL-ENEIN,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 4, June: 1411-1416, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Accuracy of MRI in the Detection of Residual Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy MONA A. ABUL-ENEIN,
J Clin Oncol 24: by American Society of Clinical Oncology INTRODUCTION
 VOLUME 24 NUMBER 36 DECEMBER 20 2006 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Locoregional Relapse and Distant Metastasis in Conservatively Managed Triple Negative Early-Stage Breast Cancer
VOLUME 24 NUMBER 36 DECEMBER 20 2006 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Locoregional Relapse and Distant Metastasis in Conservatively Managed Triple Negative Early-Stage Breast Cancer
Non-Anthracycline Adjuvant Therapy: When to Use?
 Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Non-Anthracycline Adjuvant Therapy: When to Use? William J. Gradishar MD Betsy Bramsen Professor of Breast Oncology Director, Maggie Daley Center for
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Non-Anthracycline Adjuvant Therapy: When to Use? William J. Gradishar MD Betsy Bramsen Professor of Breast Oncology Director, Maggie Daley Center for
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Fumagalli D, Venet D, Ignatiadis M, et al. RNA Sequencing to predict response to neoadjuvant anti-her2 therapy: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO randomized clinical trial.
Supplementary Online Content Fumagalli D, Venet D, Ignatiadis M, et al. RNA Sequencing to predict response to neoadjuvant anti-her2 therapy: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO randomized clinical trial.
Good Old clinical markers have similar power in breast cancer prognosis as microarray gene expression profilers q
 European Journal of Cancer 40 (2004) 1837 1841 European Journal of Cancer www.ejconline.com Good Old clinical markers have similar power in breast cancer prognosis as microarray gene expression profilers
European Journal of Cancer 40 (2004) 1837 1841 European Journal of Cancer www.ejconline.com Good Old clinical markers have similar power in breast cancer prognosis as microarray gene expression profilers
Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease
 Should gene array assays be routinely used in node positive disease? Yes Christy A. Russell, MD University of Southern California Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease 1 Validity of the Oncotype
Should gene array assays be routinely used in node positive disease? Yes Christy A. Russell, MD University of Southern California Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease 1 Validity of the Oncotype
Evaluation of the prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers
 /, Vol. 7, No. 28 Evaluation of the prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers Tian Tian 1,2, Miao Ruan 1,2, Wentao Yang 1,2, Ruohong Shui 1,2 1 Department of
/, Vol. 7, No. 28 Evaluation of the prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers Tian Tian 1,2, Miao Ruan 1,2, Wentao Yang 1,2, Ruohong Shui 1,2 1 Department of
Emerging Approaches for (Neo)Adjuvant Therapy for ER+ Breast Cancer
 Emerging Approaches for (Neo)Adjuvant Therapy for E+ Breast Cancer Cynthia X. Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Outline Current status of adjuvant endocrine
Emerging Approaches for (Neo)Adjuvant Therapy for E+ Breast Cancer Cynthia X. Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Outline Current status of adjuvant endocrine
Immunohistochemistry in Breast Pathology- Brief Overview of the Technique and Applications in Breast Pathology
 SMGr up Immunohistochemistry in Breast Pathology- Brief Overview of the Technique and Applications in Breast Pathology Bhanumathi K Rao 1 * 1 Department of Biochemistry, JSS Medical College, a constituent
SMGr up Immunohistochemistry in Breast Pathology- Brief Overview of the Technique and Applications in Breast Pathology Bhanumathi K Rao 1 * 1 Department of Biochemistry, JSS Medical College, a constituent
Background: Case Report: Conclusions: Neoplasm Metastasis Breast Neoplasms therapy Aromatase Inhibitors. MeSH Keywords:
 ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.890023 Received: 2013.11.11 Accepted: 2013.12.08 Published: 2014.02.24 Long-term complete remission of metastatic breast cancer, induced by a steroidal aromatase inhibitor
ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.890023 Received: 2013.11.11 Accepted: 2013.12.08 Published: 2014.02.24 Long-term complete remission of metastatic breast cancer, induced by a steroidal aromatase inhibitor
Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
