Protein oxidation: concepts, mechanisms and new insights. Michael J. Davies The Heart Research Institute Sydney
|
|
|
- Jasmin Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Protein oxidation: concepts, mechanisms and new insights Michael J. Davies The eart Research Institute Sydney
2 utline of talk Mechanisms of oxidation of proteins by radical oxidants. Mechanisms of oxidation of proteins by non-radical oxidants Secondary reactions of reactive protein oxidation intermediates. Products of protein oxidation. Protein oxidation products as potential markers of disease.
3 Reactions of oxidants with biological targets xidants can damage virtually all biological molecules: DA, RA, cholesterol, lipids, carbohydrates, proteins and antioxidants. Extent of damage to particular targets depends on a number of factors including: concentration of target, rate constant for reaction of oxidant with target location of target versus oxidant occurrence of secondary damaging events occurrence of transfer reactions repair and scavenging reactions Biochem. J., 1997, 324, 1-18; Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2001, 1504,
4 Why concentrate on proteins? 1) Concentration of target Proteins are major components of most biological systems: rgan level (liver, per kg wet weight): 146 g protein, 2.6 g DA, 49 g total lipid, 3.9 g cholesterol. Cellular level (per leukocytes): 100 g protein, 6.9 g DA, 8.2 g RA, 15.6 g total lipid, 2 g cholesterol. Plasma (per dm 3 ): 73 g protein, 0.4 g free amino acids, 0.5 g total lipid, 1 g carbohydrates, g cholesterol. Low-density lipoproteins (molecules per particle): 1 protein (4535 amino acids), 1600 cholesterol esters, 700 phospholipids, 600 free cholesterol, 26 free fatty acids, 9 tocopherol.
5 Why concentrate on proteins? 2) Rate constants for reaction Rate constants for reaction of? with macromolecules: DA 8 x 10 8 dm 3 mol -1 s -1 RA 1 x 10 9 dm 3 mol -1 s -1 yaluronan 7 x 10 8 dm 3 mol -1 s -1 Linoleic acid 9 x 10 9 dm 3 mol -1 s -1 Collagen 4 x dm 3 mol -1 s -1 Albumin 8 x dm 3 mol -1 s -1 Antioxidants: Ascorbate 1 x dm 3 mol -1 s -1, GS 1.4 x dm 3 mol -1 s -1, Trolox C 6.9 x 10 9 dm 3 mol -1 s -1
6 Why concentrate on proteins? Kinetic and abundance data can be used to predict sites of damage. For leukocytes: Singlet oxygen? 19% 6% 7% 18% 6% 7% 0% DA RA Protein Lipids thers 0% 68% 69% Such data needs to be treated with great caution!
7 Protein versus DA versus lipid oxidation Medline / Pubmed searches DA oxidation Lipid peroxidation Protein oxidation xidation of proteins studied to a much lesser extent than other targets
8 Protein oxidation in the 1960 s Protein X? Damaged protein ne radical = one damaged amino acid residue Degradation
9 Why is protein oxidation the poor cousin? ot due to a late start - first reports around 1900 First volume of J. Biol. Chem. Dakin,.D. (1906) The oxidation of amido-acids with the production of substances of biological importance J. Biol. Chem., 1, Follow-up papers in 1908, occupied approximately half of the total page-count of J. Biol. Chem. for the entire year.
10 Why is protein oxidation the poor cousin? Complexity of targets? Complexity of products? Complexity of mechanisms? Lack of sensitive, stable, readily detectable markers of damage?
11 Sites of oxidant damage on proteins Backbone - primarily hydrogen atom abstraction at alpha carbon R R - can result in backbone fragmentation Side-chains - 20 different types (excluding unusual amino acids and any post-translational modifications). hydrogen abstraction - primarily with aliphatic addition - primarily with aromatic. - usually results in the formation of altered side-chains Chem Rev, 1987, 87, ; Free Rad Biol Med, 1990, 9, ; J Biol Chem, 1987, 262, R R.
12 Selectivity of damage by different oxidants The most reactive radicals tend to be the least selective e.g? - difference in rate constants is relatively small Most reactive: Trp, Tyr, is, Met, Cys, Phe, Arg: k ca dm 3 mol -1 s -1 Least reactive: Ala, Asp, Asn: k ca dm 3 mol -1 s -1 Result - most side-chains are oxidised Reaction with backbone sites k ca dm 3 mol -1 s -1 Significant backbone fragmentation as well as side-chain oxidation Less reactive radicals tend to be more selective e.g. CCl 3? - difference in value of rate constants between most reactive side-chain (Trp k ca. 9 x 10 7 dm 3 mol -1 s -1 ) and least (aliphatic side-chains - no measurable reaction) very large. Many radicals are electron-deficient (electrophilic) and hence react most rapidly with electron-rich side-chains (Trp, Tyr, is, Met, Cys, Phe). Few nucleophilic oxidants (e -, Ph?, C 2?- ).
13 Sources of kinetic and associated data Compilations of kinetic data:? and? J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1988, 17, ? / 2?- J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1988, 17, Inorganic radicals (e.g. 2?, C 2?-, C 3?-, Br 2?-, 3? ) J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data,, 1990, 19, R? J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1990, 19, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1995, 24, Cl Chem. Res. Toxicol, 2001, 14, Chem. Res. Toxicol, 2003, 16, Website: DRL/IST Solution Kinetics Database - 14,000 rate constants Reduction potentials for one-electron reactions involving radicals J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1989, 18,
14 Selectivity of damage between different sites by a single oxidant Kinetic data does not usually yield information on selectivity of damage at different sites, unless specific absorptions are monitored - usually only possible for aromatic and sulfurcontaining residues. umber of factors influence which sites are most favored - Stability of incipient radical (tertiary > secondary > primary; delocalisation on to other atoms) - Statistics - number of available C- bonds / sites of addition - Accessibility (buried versus exposed; steric and charge interactions)
15 Backbone fragmentation induced by radicals Common intermediate implicated in majority of mechanisms Formation of? -carbon radical via direct, or indirect reaction - detection by EPR spin trapping (e.g. Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2000, 13, ). Subsequent formation of peroxyl radical in presence of 2. Little backbone fragmentation in absence of 2. R. R. - 2 R - R. R R reduction R R R R. 2 R 2 + R R R +.
16 Mechanisms of side-chain oxidation by radicals: aliphatic residues ydrogen atom abstraction gives common intermediates but ratio of intermediates formed at different C- positions varies with attacking radical. C 3 C 3 C 2 3 C 3 C + 3 C Valine side-chain Via primary carbon- centered radical Via tertiary carboncentered radical Direct, rapid-flow, EPR spectroscopy studies can give information on selectivityof initial radical attack for amino acids and peptides. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1998, ; Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2001, 1504,
17 Mechanisms of side-chain oxidation by radicals: aliphatic residues Initial carbon-centred radicals undergo rapid reaction with 2 to give peroxyl radicals. Dimers formed in absence of 2. R? + 2 R? or R? + R? R-R Fate of peroxyl radicals Reaction with another peroxyl radical to give R-X (X = R, ). ydrogen atom abstraction - gives hydroperoxide: R? + X X? + R R + carbonyls Elimination reactions - special case for Ser, Thr and few other residues -C-? -C= +? / Major products from aliphatic side-chains: peroxides, alcohols and carbonyls. Biochem J, 1995, 305, ; Arch Biochem Biophys, 1996, 336, ; Biochem. J. 1997, 324, 1-18
18 Specific aliphatic side-chain oxidation products Glutamic acid hydroperoxides Lysine hydroperoxides alcohols Leucine hydroperoxides alcohols carbonyl compounds? -ketoisocaproic acid isovaleric acid isovaleraldehyde isovaleraldehyde oxime Proline hydroperoxides alcohols 5-hydroxy-2-aminovaleric acid carbonyl compounds carbonyl compounds Glycine Aminomalonic acid Arginine hydroperoxides 5-hydroxy-2-aminovaleric acid Valine hydroperoxides alcohols Isoleucine hydroperoxides, alcohols, carbonyl compounds carbonyl compounds Free Radic. Biol. Med., 1999, 27, Methionine Cysteine Methionine sulphoxide Cystine, xy acids
19 Peroxides are major initial products of? attack on amino acids, peptides and proteins in the presence of 2 Substrate % yield of hydroperoxide groups formed from initial. -Ac-Lys Gly-Lys-Gly 34 Poly-lysine 64 Melittin 16 Protamine 33 Insulin 12 Rase A 53 BSA 36
20 Formation of peroxides on proteins Does it matter what the attacking radical is? - igh energy radiation (?- or X-rays, UV, visible light with sensitizer) Metal ions / ascorbate Metal ions / peroxide systems (?, R? ) Thermo-labile azo compounds + 2 (R? ) Peroxynitrite Activated white cells emoprotein / peroxide systems Does it matter what the amino acid / peptide / protein is? - Formed on most amino acids, and all peptides and proteins tested Detected on both isolated proteins and proteins in cells Yield and exact structure of peroxides formed is dependent on target, the attacking radical, 2 concentration, presence of reductants / antioxidants / metal ions (etc ) Redox Rep, 1997, 3, ; Biochem J, 1997, 324, 1-18; Biochim Biophys Acta, 2001, 1504,
21 Fate of protein peroxides Protein- + 2e -? Protein- Protein- + M n+? Protein-? + M (n+1)+ + - Protein- + UV / heat? Protein-? +? Protein-?? Protein-C? (1,2 hydrogen atom shifts) Protein-?? Protein-carbonyl + R? (? -scission reactions) or Protein-C? + released carbonyl Protein-C? + 2? Protein-? Protein-? + R? Protein- + R? Biochem. J., 1995, 305, ; Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 1996, 336, ; Chem. Res. Toxicol, 2000, 13, ; Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2002, 32,
22 Transfer of damage within proteins Evidence for radical transfer from side-chains sites to backbone via mediation of alkoxyl radicals Favorable process due - to stability of? -carbon radical - relief of steric crowding - stability of carbonyl product R2 R1 X. / 2 R2 R1. Detected by Quantified EPR spin by PLC trapping Results in loss of side-chain group as reactive aldehyde / ketone and formation of backbone radical -> backbone cleavage Similar reactions with thiyl radical from cysteine? Chem Res Toxicol, 2000, 13, 1087; Free Radic Biol Med, 2002, 32, 1171, J Am Chem Soc, 2003, 125, R1 R2
23 ccurrence of chain reactions umber of reactions of protein radicals that give rise to other radicals: 1) Decomposition of dimers formed between two peroxyl radicals R-R 2R? + 2 2) ydrogen atom abstraction by an initial peroxyl radical R? + X R + X? 3) Fragmentation reactions of? -hydroxperoxy radicals on Ser and Thr 4) Decomposition of hydroperoxides to alkoxyl radicals All of these reactions give rise to further radicals and hence either - chain reactions on proteins, or - damage to other biomolecules
24 xidation of Cys, cystine and Met residues Important targets: rapid reaction with range of oxidants (both radical and non-radical) and easily oxidised. Met converted to sulfoxide: -S- -S(=)- -S( 2 )- Cys oxidised via two major pathways: RS RSSR (cystine) via thiyl radical RS RS-X RS 2 + RS 3 (X=, Cl, etc) RSSR Cystine can be oxidised to RSS(=)R Both Met sulfoxide and cystine can be repaired nly major examples of repair of oxidised amino acid residues on proteins Free Radic Biol Med, 1995, 18, 93; PAS, 2001, 98, 12920, Free Radic Biol Med, 1995, 31, 1432; Int J Radiat Biol, 1989, 55, 539; von Sonntag - The Chemical Basis of Radiation Biology
25 Mechanisms of side-chain oxidation by radicals: aromatic residues Major reaction is addition, though electron abstraction can also occur. Electron abstraction reactions usually yield hydroxylated products. Addition reactions tend to yield a greater diversity of products as this depends on the added species. Similar products tend to be formed in presence and absence of 2.
26 Specific aromatic side-chain oxidation products Phenylalanine o-, m-tyrosine dimers Phenylalanine ortho-tyrosine (o-tyr) Tyrosine meta-tyrosine (m-tyr) DPA di-tyrosine Tryptophan -formylkynurenine, kynurenine, Tyrosine 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DPA) 5-hydroxytryptophan, 7-hydroxytryptophan istidine di-tyrosine (di-tyr) 2-oxo-histidine Free Radic. Biol. Med., 1999, 27,
27 Transfer of damage within proteins Evidence for long range transfer of radical sites within proteins: transfer from initial site to a readily oxidised residue (Trp, Tyr, Met, Cys) to give more stable radical - can be equilibria. can occur over very large distances, but depends on protein structure occurs in competition with reaction of initial radical with 2 most common when initial radical is poorly, or unreactive, with 2 examples: Trp <-> Tyr, Trp <-> Cys, Tyr <-> Cys xidised porphyrin ring from Trp, Tyr, Cys J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, ; J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, ; Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 1989, 55, ; J. Biol. Chem., 1997, 272,
28 Mechanisms of protein oxidation by non-radical oxidants Species such as 1 2, Cl, Br, peroxynitrite, 3, UV light Reactions can be very selective and generally on side-chains Little fragmentation, but considerable aggregation damage to Cys, Met, Trp, Tyr and is. Cl / Br - primarily damage to Cys, Met, is, Lys, Trp,? - amino group. Peroxynitrite - damage to Cys, Tyr, Trp. UV light - damage to cystine, Trp, Tyr and is. Some products well-defined - e.g. 3-chloroTyr, 3-nitroTyr, methionine sulfoxide, disulphides. Some poorly defined -> peroxides generated by 1 2 and 3.
29 Aromatic side-chain oxidation products generated by non-radical oxidants Chlorinating species Cl Tyrosine 3-chloroTyrosine (3-ClTyr) itrating species 2 Tyrosine 3-nitroTyrosine (3-2 Tyr) 1 2 Free Radic. Biol. Med., 1999, 27, ; Photochem. Photobiol, 2002, 76, 35-46
30 Damage to other targets induced by reactive intermediates of protein oxidation Protein peroxides can induce damage to other proteins by: on-radical reactions (oxidation of Cys and Met residues) Radical-mediated reactions Biochem. J., 1999, 338, ; Biochem. J., 1999, 344, ; Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2000, 13, ; Biogerentology, 2002, 3, ; Eur. J. Biochem., 2002, 269, ; FEBS Lett., 2002, 527,
31 xidation of other residues by non-radical reactions Evidence for oxidation of cysteine residues by peroxides Protein thiols, peroxides and enzyme activity lost concurrently Cysteine oxidised to disulphide and oxy acids Evidence for oxidation of methionine residues by peroxides Evidence for the generation of methionine sulfoxide Inactivation of methionine-dependent enzymes? Eur. J. Biochem., 2002, 269, ; FEBS Lett., 2002, 527, ; Redox Rep., 2003, 8, 81-86
32 Damage to other targets induced by reactive intermediates of protein oxidation Protein peroxides can induce damage to other proteins by: on-radical reactions (oxidation of susceptible thiols) Radical-mediated reactions Protein peroxides and DPA can induce damage to DA via radical-mediated reactions xidation of bases (e.g. 8-oxodG) Induction of strand breaks Formation of protein-da cross-links Protein peroxides can induce lipid oxidation via radicalmediated reactions Biochem. J., 1999, 338, ; Biochem. J., 1999, 344, ; Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2000, 13, ; Biogerentology, 2002, 3, ; Eur. J. Biochem., 2002, 269, ; FEBS Lett., 2002, 527,
33 X? or nonradical oxidant Consequences of oxidation of proteins Protein xidation of side-chains - some of which can be used as damage markers Backbone fragmentation Formation of new reactive species (peroxides, DPA) Release of further radicals and occurrence of chain reactions Dimerization or aggregation Unfolding or conformational changes Loss of structural or functional activity Alterations in cellular handling / turnover Induction of apoptosis and necrosis Effects on gene regulation and expression Modulation of cell signalling Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2001, 1504, ; J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, 2001, 63,
34 X? X Aromatic side-chain products Stable markers of protein damage Protein Protein radicals 2 Backbone peroxyl radicals 2 Side-chain peroxyl radicals Protein-bound peroxides 1 2 Protein Side-chain oxidation products Secondary radicals Backbone fragmentation Stable markers of protein damage Further damage: Proteins - enzyme inactivation DA - oxidised bases, strand breaks, protein-da cross-links Lipids - induction of peroxidation
35 Acknowledgments Group members: Dr. Clare awkins Dr. Dave Pattison Dr. enri eadlam Dr. Cathy Luxford Dr. Alan Woods Dr. Stuart Linton Dr. Adam Wright Martin Rees Bronwyn Brown Vanessa Policarpio Philip Morgan icole Parker Jingmin Zeng Collaborators: Prof. Roger Dean (Univ of Canberra) Dr. Bill Bubb (Univ of Sydney) Dr. Mark ampton (Christchurch) Prof. Jan Gebicki (Macquarie Univ) Prof. Roger Truscott (Univ of Wollongong) Prof. Chris Easton (Australian ational Univ) Funding from: Australian Research Council ational ealth and Medical Research Council Association for International Cancer Research UK The Wellcome Trust UK
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Enzyme Catalytic Mechanisms. Dr. Kevin Ahern
 Enzyme Catalytic Mechanisms Dr. Kevin Ahern Cleave Peptide Bonds Specificity of Cutting Common Active Site Composition/Structure Mechanistically Well Studied Chymotrypsin Chymotrypsin Catalysis H2O Chymotrypsin
Enzyme Catalytic Mechanisms Dr. Kevin Ahern Cleave Peptide Bonds Specificity of Cutting Common Active Site Composition/Structure Mechanistically Well Studied Chymotrypsin Chymotrypsin Catalysis H2O Chymotrypsin
Introduction to Peptide Sequencing
 Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination #5: Section Five December 7, Name: (print) Section:
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Maha AbuAjamieh. Tamara Wahbeh. Mamoon Ahram
 12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
PROTEINS. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Acid L-form * * Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 O = N -C -C-O.
 Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
 Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011
 Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Amino Acids. Lecture 4: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where?
 Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
Lecture 4: Amino Acids Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 Swiss-prot database: How many proteins? From where? 1986 Use http://us.expasy.org to get to swiss-prot database Proteins are the workhorses of the
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
Chymotrypsin Lecture. Aims: to understand (1) the catalytic strategies used by enzymes and (2) the mechanism of chymotrypsin
 Chymotrypsin Lecture Aims: to understand (1) the catalytic strategies used by enzymes and (2) the mechanism of chymotrypsin What s so great about enzymes? They accomplish large rate accelerations (10 10-10
Chymotrypsin Lecture Aims: to understand (1) the catalytic strategies used by enzymes and (2) the mechanism of chymotrypsin What s so great about enzymes? They accomplish large rate accelerations (10 10-10
PROTEINS. Building blocks, structure and function. Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties
 PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Macromolecules Structure and Function
 Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
2. Which of the following amino acids is most likely to be found on the outer surface of a properly folded protein?
 Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Introduction to proteins and protein structure
 Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Polypeptides. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection
 Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Chemical Mechanism of Enzymes
 Chemical Mechanism of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 5.2 Definition of the mechanism 1. The sequence from substrate(s) to product(s) : Reaction steps 2. The rates at which the complex are interconverted 3.
Chemical Mechanism of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 5.2 Definition of the mechanism 1. The sequence from substrate(s) to product(s) : Reaction steps 2. The rates at which the complex are interconverted 3.
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay
 Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Cells N5 Homework book
 1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
Fatty acids and phospholipids
 PYS 4xx Intro 2 1 PYS 4xx Intro 2 - Molecular building blocks We now describe in more detail the nomenclature and composition of several classes of compounds of relevance to the cell, including: membrane
PYS 4xx Intro 2 1 PYS 4xx Intro 2 - Molecular building blocks We now describe in more detail the nomenclature and composition of several classes of compounds of relevance to the cell, including: membrane
Lecture 4. Grouping Amino Acid 7/1/10. Proteins. Amino Acids. Where Are Proteins Located. Nonpolar Amino Acids
 Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Raghad Abu Jebbeh. Amani Nofal. Mamoon Ahram
 ... 14 Raghad Abu Jebbeh Amani Nofal Mamoon Ahram This sheet includes part of lec.13 + lec.14. Amino acid peptide protein Terminology: 1- Residue: a subunit that is a part of a large molecule. 2- Dipeptide:
... 14 Raghad Abu Jebbeh Amani Nofal Mamoon Ahram This sheet includes part of lec.13 + lec.14. Amino acid peptide protein Terminology: 1- Residue: a subunit that is a part of a large molecule. 2- Dipeptide:
Practice Problems 3. a. What is the name of the bond formed between two amino acids? Are these bonds free to rotate?
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
AA s are the building blocks of proteins
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Effects of Diet, Packaging and Irradiation on Protein Oxidation, Lipid Oxidation of Raw Broiler Thigh Meat
 AS 659 ASL R26 203 Effects of Diet, Packaging and Irradiation on Protein Oxidation, Lipid Oxidation of Raw Broiler Thigh Meat Shan Xiao Iowa State University Wan Gang Zhang Iowa State University Eun Joo
AS 659 ASL R26 203 Effects of Diet, Packaging and Irradiation on Protein Oxidation, Lipid Oxidation of Raw Broiler Thigh Meat Shan Xiao Iowa State University Wan Gang Zhang Iowa State University Eun Joo
Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids.
 Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels. Supplementary Information
 Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
Date: EXERCISE 4. Figure 1. Amino acid structure.
 Student s name: Date: Points: Assistant s signature: Index numer: /6 EXERISE 4 AMIN AIDS AND PRTEINS. Amino acids are structural units (monomers) of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids coded for
Student s name: Date: Points: Assistant s signature: Index numer: /6 EXERISE 4 AMIN AIDS AND PRTEINS. Amino acids are structural units (monomers) of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids coded for
9/16/15. Properties of Water. Benefits of Water. More properties of water
 Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH CHEM 4540 ENZYMOLOGY Winter 2005 Quiz #2: March 24, 2005, 11:30 12:50 Instructor: Prof R. Merrill ANSWERS
 UNIVERSITY F GUELPH CHEM 4540 ENZYMLGY Winter 2005 Quiz #2: March 24, 2005, 11:30 12:50 Instructor: Prof R. Merrill ANSWERS Instructions: Time allowed = 80 minutes. Total marks = 30. This quiz represents
UNIVERSITY F GUELPH CHEM 4540 ENZYMLGY Winter 2005 Quiz #2: March 24, 2005, 11:30 12:50 Instructor: Prof R. Merrill ANSWERS Instructions: Time allowed = 80 minutes. Total marks = 30. This quiz represents
CHAPTER 29 HW: AMINO ACIDS + PROTEINS
 CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
PAPER No. : 16, Bioorganic and biophysical chemistry MODULE No. : 22, Mechanism of enzyme catalyst reaction (I) Chymotrypsin
 Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES
 3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Name. The following exam contains 44 questions, valued at 2.6 points/question. 2. Which of the following is not a principal use of proteins?
 Chemistry 131 Exam 3 Practice Proteins, Enzymes, and Carbohydrates Spring 2018 Name The following exam contains 44 questions, valued at 2.6 points/question 1. Which of the following is a protein? a. Amylase
Chemistry 131 Exam 3 Practice Proteins, Enzymes, and Carbohydrates Spring 2018 Name The following exam contains 44 questions, valued at 2.6 points/question 1. Which of the following is a protein? a. Amylase
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
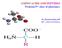 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a Novel Mixed-Mode HPLC Column
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth 2 points.
 MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
Previous Class. Today. Term test I discussions. Detection of enzymatic intermediates: chymotrypsin mechanism
 Term test I discussions Previous Class Today Detection of enzymatic intermediates: chymotrypsin mechanism Mechanistic Understanding of Enzymemediated Reactions Ultimate goals: Identification of the intermediates,
Term test I discussions Previous Class Today Detection of enzymatic intermediates: chymotrypsin mechanism Mechanistic Understanding of Enzymemediated Reactions Ultimate goals: Identification of the intermediates,
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
PHAR3316 Pharmacy biochemistry Exam #2 Fall 2010 KEY
 1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
Distribution of the amino acids in Nature Frequency in proteins (%)
 Distribution of the amino acids in ature Amino Acid Frequency in proteins (%) Leucine Alanine Glycine erine Valine Glutamic acid Threonine Arginine Lysine Aspartic acid Isoleucine Proline Asparagine Glutamine
Distribution of the amino acids in ature Amino Acid Frequency in proteins (%) Leucine Alanine Glycine erine Valine Glutamic acid Threonine Arginine Lysine Aspartic acid Isoleucine Proline Asparagine Glutamine
PROTEIN. By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM
 PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL
 Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 11 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush July 3 rd 2013 Marah Dannoun Continuation of amino acids applications in life other than tryptophan and tyrosine: 1. Glutamate (glutamic acid): it s modified to give monosodium
11 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush July 3 rd 2013 Marah Dannoun Continuation of amino acids applications in life other than tryptophan and tyrosine: 1. Glutamate (glutamic acid): it s modified to give monosodium
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS
 AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam )ومن أحياها(
 Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
Introduction to Biochemistry Midterm exam 2016-2017 )ومن أحياها( 1. Which of the following amino (in a peptide chain) would probably be found at a beta bend or turn? a. lysine * b. Gly c. arg d. asn 2.
2. Which of the following is NOT true about carbohydrates
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Examination #5 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response questions
Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Examination #5 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response questions
Levels of Protein Structure:
 Levels of Protein Structure: PRIMARY STRUCTURE (1 ) - Defined, non-random sequence of amino acids along the peptide backbone o Described in two ways: Amino acid composition Amino acid sequence M-L-D-G-C-G
Levels of Protein Structure: PRIMARY STRUCTURE (1 ) - Defined, non-random sequence of amino acids along the peptide backbone o Described in two ways: Amino acid composition Amino acid sequence M-L-D-G-C-G
CHAPTER 9: CATALYTIC STRATEGIES. Chess vs Enzymes King vs Substrate
 CHAPTER 9: CATALYTIC STRATEGIES Chess vs Enzymes King vs Substrate INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 9 What are the sources of the catalytic power and specificity of enzymes? Problems in reactions in cells Neutral
CHAPTER 9: CATALYTIC STRATEGIES Chess vs Enzymes King vs Substrate INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 9 What are the sources of the catalytic power and specificity of enzymes? Problems in reactions in cells Neutral
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology:
 The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
Lecture 3: 8/24. CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids
 Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Human Biochemistry Option B
 Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
