Role of nuclear bile acid receptor FXR in intestinal bacterial overgrowth and translocation
|
|
|
- Gloria Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Role of nuclear bile acid receptor FXR in intestinal bacterial overgrowth and translocation Antonio Moschetta University of Bari, Consorzio Mario Negri Sud, Santa Maria Imbaro (Chieti), Italy
2 Plan Bile acids and the gut microbiota Nuclear bile acid receptor FXR FXR and mucosal defense Regulation of intestinal FXR
3 Physiologic Functions of Bile Acids CO 2 H OH CO 2 H HO OH H CDCA HO H CA OH liver Absorption of lipids Elimination of cholesterol gall bladder stomach small intestine ileum
4 Bile Acids Protect Intestine Biliary obstruction in rats causes bacterial overgrowth and translocation, which are reversed by oral bile acids (Ding et al., Eur Surg Res 25: 11; Lorenzo-Zuniga et al., Hepatology 37: 551) In humans, biliary obstruction increases susceptibility to bacterial overgrowth and sepsis Preoperative administration of sodium deoxycholate prevents postoperative endotoxaemia in patients with obstructive jaundice (Cahill et al., Surg Gynecol Obstet 165:519) Does bile nuclear receptor FXR protect against bacterial overgrowth and translocation?
5 Bile Acid Receptor, FXR Highly expressed in liver and intestine Binds DNA to IR-1 motifs as RXR heterodimer Activated by primary bile acids FXR-KO mice have elevated CYP7A1 and bile acid synthesis
6 FXR Target Genes in Ileum Fold Gene +83 fibroblast growth factor orphan nuclear receptor SHP +4. inducible nitric oxide synthase +2.3 angiogenin +2.2 interleukin ileal bile acid binding protein -3.7 MHC Q1 BA homeostasis Mucosal defense
7 Bile Duct Ligation Experiments Day 1: Begin treatment with vehicle or GW464 liver Day 3: Perform or sham operation Day 8: Kill mice and quantitate bacteria in ileum, cecum, and mesenteric lymph nodes gall bladder ileum cecum
8 GW464 Blocks Bacterial Overgrowth in presence of FXR wild type FXRKO 3 4 ileum CFU/ml (x 1 7 ) 2 1 a b a CFU/ml (x 1 7 ) Sham GW464 Sham GW cecum CFU/g (x 1 8 ) 8 4 a Sham b a GW464 CFU/g (x 1 8 ) Sham GW464
9 anti-occludin immunostaining FXR Promotes Barrier Integrity Wild type FXR-KO Sham GW464 Sham
10 FXR-KO Sham Bacterial Translocation in FXR-KO
11 Why Link FXR to Mucosal Defense? 1. Bile acids are strong detergents FXR serves as a rheostat to prevent damage to the mucosal barrier 2. Bile acids are released into the intestine after a meal; since food is an important source of microbes, FXR ensures that appropriate levels of antimicrobial proteins are produced inos IL18 angiogenin mucosal protection inflammatory disease FXR agonists may be useful to treat intestinal disease
12 Intestinal Mucosa Architecture Villus Surface Epithelium Differentiation Differentiation Proliferative progenitors Crypt Proliferative progenitors Crypt Stem cells Stem cells Ileum Colon Clevers H. Cell 26
13 FXR expression increases during crypt-to-villus differentiation merge Anti-FXR DAPI protein Reaching confluence
14 FXR expression increases during crypt-to-villus differentiation 12 1 FXRα1/α2 pre-confluence confluence post-confluence mrna
15 FXR disappears in APCm-driven tumors APC min/+ mice FAP patients normal tumor P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 FXRα1/α2 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 FXRα3/α4
16 Induction of WT APC via tet-on system in APCmHT29 restores FXR expression 1 FXRα1/α ZnCl2 +ZnCl2 4 2
17 Thanks Salvatore Modica, PhD student Giuseppe Losasso, PhD student Michele Petruzzelli, PhD student Ilenia D Errico, Postdoc fellow Stefania Murzilli, Research Tech Lorena Salvatore, Research Tech Filomena Cinalli, Lab Manager Jean-Noel Freund, Strasbourg, Fr Ken Kinzler & Bert Vogelstein, Baltimore US Davo Mango and Steven Kliewer Center, Dallas US Giuseppe Palasciano & Piero Portincasa, Bari, It Italian Association for Cancer Research, University of Bari, EU
XV Jornada de Avances en Hepatología Málaga 20 y 21 de Mayo de Barrera intestinal en la cirrosis. Agustín Albillos
 XV Jornada de Avances en Hepatología Málaga 20 y 21 de Mayo de 2016 Barrera intestinal en la cirrosis Agustín Albillos Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Universidad de Alcalá, Ciberehd Madrid, Spain
XV Jornada de Avances en Hepatología Málaga 20 y 21 de Mayo de 2016 Barrera intestinal en la cirrosis Agustín Albillos Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Universidad de Alcalá, Ciberehd Madrid, Spain
Bile acid receptor FXR: metabolic regulator in the gut. Sungsoon Fang
 Bile acid receptor FXR: metabolic regulator in the gut Sungsoon Fang Nuclear hormone receptor 1905: Ernest Starling coined hormone 1929: Estrogen structure 1958: Estrogen receptor by Elwood Jensen 1985:
Bile acid receptor FXR: metabolic regulator in the gut Sungsoon Fang Nuclear hormone receptor 1905: Ernest Starling coined hormone 1929: Estrogen structure 1958: Estrogen receptor by Elwood Jensen 1985:
Gut Microbiota and IBD. Vahedi. H M.D Associate Professor of Medicine DDRI
 Gut Microbiota and IBD Vahedi. H M.D Associate Professor of Medicine DDRI 1393.3.1 2 GUT MICROBIOTA 100 Trillion Microbes - 10 times more than cells in our body Collective weight of about 1kg in human
Gut Microbiota and IBD Vahedi. H M.D Associate Professor of Medicine DDRI 1393.3.1 2 GUT MICROBIOTA 100 Trillion Microbes - 10 times more than cells in our body Collective weight of about 1kg in human
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury. Journal Club December 16, 2004
 Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Bile acids are amphipathic cholesterol metabolites that are
 Regulation of antibacterial defense in the small intestine by the nuclear bile acid receptor Takeshi Inagaki*, Antonio Moschetta, Youn-Kyoung Lee*, Li Peng*, Guixiang Zhao*, Michael Downes, Ruth T. Yu,
Regulation of antibacterial defense in the small intestine by the nuclear bile acid receptor Takeshi Inagaki*, Antonio Moschetta, Youn-Kyoung Lee*, Li Peng*, Guixiang Zhao*, Michael Downes, Ruth T. Yu,
Studies on probiotics effects on innate immune functions in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicks (SUMMARY)
 Doctoral Thesis Studies on probiotics effects on innate immune functions in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicks (SUMMARY) ELSAYED SEDDEK IBRAHEM MOHAMMED Department of Bioresource Science Graduate
Doctoral Thesis Studies on probiotics effects on innate immune functions in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicks (SUMMARY) ELSAYED SEDDEK IBRAHEM MOHAMMED Department of Bioresource Science Graduate
Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease
 Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease February 27, 2015 Master s Course in Gastroenterology Prof. Kathy McCoy 1 Overview Overview of Gut Microbiota Microbiota in Health Microbiota in Disease 2 Gut
Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease February 27, 2015 Master s Course in Gastroenterology Prof. Kathy McCoy 1 Overview Overview of Gut Microbiota Microbiota in Health Microbiota in Disease 2 Gut
Commensal Bacteria at the Crossroad Between Cholesterol Homeostasis and Chronic Inflammation. in Atherosclerosis
 Supplementary Information Commensal Bacteria at the Crossroad Between Cholesterol Homeostasis and Chronic Inflammation in Atherosclerosis Kazuyuki Kasahara 1,, Takeshi Tanoue 3, Tomoya Yamashita 1,*, Keiko
Supplementary Information Commensal Bacteria at the Crossroad Between Cholesterol Homeostasis and Chronic Inflammation in Atherosclerosis Kazuyuki Kasahara 1,, Takeshi Tanoue 3, Tomoya Yamashita 1,*, Keiko
Digestive System. Part 3
 Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
Cormac Gahan APC, University College Cork, Ireland
 Valencia, 2015 Bile Research Group http://apc.ucc.ie Bacterial Bile Salt Hydrolase in the Regulation of Host Lipid Metabolism & Circadian Rhythm: A Role in Probiotic Function? Cormac Gahan APC, University
Valencia, 2015 Bile Research Group http://apc.ucc.ie Bacterial Bile Salt Hydrolase in the Regulation of Host Lipid Metabolism & Circadian Rhythm: A Role in Probiotic Function? Cormac Gahan APC, University
Regulating Hepatic Cellular Cholesterol
 Under circumstances of cholesterol deficiency, Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Proteins (SREBPs) via binding to DNA nuclear response elements set off genomic production of proteins and enzymes that induce
Under circumstances of cholesterol deficiency, Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Proteins (SREBPs) via binding to DNA nuclear response elements set off genomic production of proteins and enzymes that induce
Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by
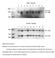 Supplemental Figure 1 Selected ES cell clones show a correctly recombined conditional Ngn3 allele Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by hybridization with
Supplemental Figure 1 Selected ES cell clones show a correctly recombined conditional Ngn3 allele Genotype analysis by Southern blots of nine independent recombinated ES cell clones by hybridization with
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
University of Groningen. Cholesterol, bile acid and triglyceride metabolism intertwined Schonewille, Marleen
 University of Groningen Cholesterol, bile acid and triglyceride metabolism intertwined Schonewille, Marleen IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Cholesterol, bile acid and triglyceride metabolism intertwined Schonewille, Marleen IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
Dysbiosis & Inflammation
 MASTERING THE MICROBIOME: Dysbiosis & Inflammation 2017 Tom Fabian, PhD It is reasonable to propose that the composition of the microbiome and its activities are involved in most, if not all, of the biological
MASTERING THE MICROBIOME: Dysbiosis & Inflammation 2017 Tom Fabian, PhD It is reasonable to propose that the composition of the microbiome and its activities are involved in most, if not all, of the biological
Effect of sow antibiotic treatment and offspring diet on microbiota and gut barrier throughout life
 EAAP Meeting, Nantes, August 29, 2013 Interplay EU Project Workshop 2 Effect of sow antibiotic treatment and offspring diet on microbiota and gut barrier throughout life J.P. Lallès 1, M.E. Arnal 1, G.
EAAP Meeting, Nantes, August 29, 2013 Interplay EU Project Workshop 2 Effect of sow antibiotic treatment and offspring diet on microbiota and gut barrier throughout life J.P. Lallès 1, M.E. Arnal 1, G.
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
 GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS
 1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Tissues and organs PART 1
 Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Hepatic Transporter Proteins involved in Bile Formation
 Bile salt synthesis Hepatic Transporter Proteins involved in Bile Formation Basolateral membrane transporter proteins fx: NTCP uptake of bile salts OATP bulky organic anions Canalicular membrane transporter
Bile salt synthesis Hepatic Transporter Proteins involved in Bile Formation Basolateral membrane transporter proteins fx: NTCP uptake of bile salts OATP bulky organic anions Canalicular membrane transporter
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifthmost
 HEPATOBILIARY MALIGNANCIES Prevention of Spontaneous Hepatocarcinogenesis in Farnesoid X Receptor Null Mice by Intestinal-Specific Farnesoid X Receptor Reactivation Chiara Degirolamo, 1,2 Salvatore Modica,
HEPATOBILIARY MALIGNANCIES Prevention of Spontaneous Hepatocarcinogenesis in Farnesoid X Receptor Null Mice by Intestinal-Specific Farnesoid X Receptor Reactivation Chiara Degirolamo, 1,2 Salvatore Modica,
Bile-acid synthesis is the major mechanism to
 AUTOIMMUNE, CHOLESTATIC AND BILIARY DISEASE Mechanism of Tissue-Specific Farnesoid X Receptor in Suppressing the Expression of Genes in Bile-Acid Synthesis in Mice Bo Kong, 1 Li Wang, 2 John Y.L. Chiang,
AUTOIMMUNE, CHOLESTATIC AND BILIARY DISEASE Mechanism of Tissue-Specific Farnesoid X Receptor in Suppressing the Expression of Genes in Bile-Acid Synthesis in Mice Bo Kong, 1 Li Wang, 2 John Y.L. Chiang,
Physiological processes in the GI tract:
 Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Vitamin D in Cattle: Calcium and Beyond. Corwin D. Nelson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Physiology Department of Animal Sciences
 OH HO OH Vitamin D in Cattle: Calcium and Beyond Corwin D. Nelson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Physiology Department of Animal Sciences Seminar Outline 1. Basics of vitamin D metabolism and genomic actions
OH HO OH Vitamin D in Cattle: Calcium and Beyond Corwin D. Nelson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Physiology Department of Animal Sciences Seminar Outline 1. Basics of vitamin D metabolism and genomic actions
The Small Intestine. The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine.
 The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment
 BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
HOW THE MICROBIOME AFFECTS OUR HEALTH
 HOW THE MICROBIOME AFFECTS OUR HEALTH THE INTESTINAL BARRIER AND INTESTINAL PERMEABILITY Intestinal Barrier: a functional body Defense from translocation of dietary antigens, bacteria or bacterial endotoxins
HOW THE MICROBIOME AFFECTS OUR HEALTH THE INTESTINAL BARRIER AND INTESTINAL PERMEABILITY Intestinal Barrier: a functional body Defense from translocation of dietary antigens, bacteria or bacterial endotoxins
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35
 Biology Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35 Digestion The breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino acids
Biology Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35 Digestion The breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino acids
Holistic Healing Professional Practitioner Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
 The last phase is called the intestinal phase and takes place about four hours after the gastric phase. The chyme passes through the small intestine, or duodenum, through the pyloric sphincter. This is
The last phase is called the intestinal phase and takes place about four hours after the gastric phase. The chyme passes through the small intestine, or duodenum, through the pyloric sphincter. This is
Animal Nutrition. Key Concepts. Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms. What do animals get from food?
 Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts. Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory
 Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012
 17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Inhibition of Human Hepatic Bile Acid Transporters as Contributing Factors to Drug-Induced Liver Injury
 Inhibition of Human Hepatic Bile Acid Transporters as Contributing Factors to Drug-Induced Liver Injury Kenneth R. Brouwer, Ph.D., RPh Chief Scientific Officer DDI Meeting June 2017 Seattle, Washington
Inhibition of Human Hepatic Bile Acid Transporters as Contributing Factors to Drug-Induced Liver Injury Kenneth R. Brouwer, Ph.D., RPh Chief Scientific Officer DDI Meeting June 2017 Seattle, Washington
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
Felix Yarovinsky. Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii
 Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Meeting nutritional needs of acute care patients Feeding acute pancreatitis patients J. Luttikhold (NL) FEEDING ACUTE PANCREATITIS PATIENTS Joanna Luttikhold, MD PhD Registrar
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Meeting nutritional needs of acute care patients Feeding acute pancreatitis patients J. Luttikhold (NL) FEEDING ACUTE PANCREATITIS PATIENTS Joanna Luttikhold, MD PhD Registrar
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
1. Digestion of foods and absorption of nutrients takes place in stomach and small bowel in only 2-3 h.
 1. Digestion of foods and absorption of nutrients takes place in stomach and small bowel in only 2-3 h. 2. The waste is then stored for 2 days in the large bowel. 3. Do modern humans need a large bowel?
1. Digestion of foods and absorption of nutrients takes place in stomach and small bowel in only 2-3 h. 2. The waste is then stored for 2 days in the large bowel. 3. Do modern humans need a large bowel?
THBA Platform - Bile acid imbalance
 - Bile acid imbalance Bile acids play an important role in maintaining human health by means of signaling molecules in the regulation of bile formation, liver function and metabolism. The detergent effect
- Bile acid imbalance Bile acids play an important role in maintaining human health by means of signaling molecules in the regulation of bile formation, liver function and metabolism. The detergent effect
Pathophysiology of Bile Secretion
 Pathophysiology of Bile Secretion Martin C. Carey, D.Sc., M.D. Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women s Hospital and Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, U.S.A. Functions
Pathophysiology of Bile Secretion Martin C. Carey, D.Sc., M.D. Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women s Hospital and Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, U.S.A. Functions
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis
 Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis John C. Marshall, MD FRCSC St. Michael s Hospital Critical Care Canada Forum 2012 Toronto, Canada October 29, 2012 University of Toronto Thanks to Songhui Jia
Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis John C. Marshall, MD FRCSC St. Michael s Hospital Critical Care Canada Forum 2012 Toronto, Canada October 29, 2012 University of Toronto Thanks to Songhui Jia
Bile Acid Receptor Farnesoid X Receptor: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases
 Review J Lipid Atheroscler 2017 June;6(1):1-7 https://doi.org/10.12997/jla.2017.6.1.1 pissn 2287-2892 eissn 2288-2561 JLA Bile Acid Receptor Farnesoid X Receptor: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Metabolic
Review J Lipid Atheroscler 2017 June;6(1):1-7 https://doi.org/10.12997/jla.2017.6.1.1 pissn 2287-2892 eissn 2288-2561 JLA Bile Acid Receptor Farnesoid X Receptor: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Metabolic
Murine Models of. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Outline. Laura P. Hale, M.D. Ph.D. Professor of Pathology Duke University Medical Center
 Murine Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Laura P. Hale, M.D. Ph.D. Professor of Pathology Duke University Medical Center September 19, 2017 Outline Review of IBD in humans Murine models of IBD Tissue
Murine Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Laura P. Hale, M.D. Ph.D. Professor of Pathology Duke University Medical Center September 19, 2017 Outline Review of IBD in humans Murine models of IBD Tissue
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD. Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany
 Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FXR agonists and FGF15 reduce fecal bile acid excretion in a mouse model of bile acid malabsorption
 FXR agonists and FGF15 reduce fecal bile acid excretion in a mouse model of bile acid malabsorption Diana Jung,* Takeshi Inagaki,*, Robert D. Gerard,, Paul A. Dawson,** Steven A. Kliewer,*, David J. Mangelsdorf,
FXR agonists and FGF15 reduce fecal bile acid excretion in a mouse model of bile acid malabsorption Diana Jung,* Takeshi Inagaki,*, Robert D. Gerard,, Paul A. Dawson,** Steven A. Kliewer,*, David J. Mangelsdorf,
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 7 PRINCIPLES OF DISEASE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? How diseases are caused (etiology), how they can be characterized, and the concepts of sepsis and shock are important for developing an in-depth understanding
CHAPTER 7 PRINCIPLES OF DISEASE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? How diseases are caused (etiology), how they can be characterized, and the concepts of sepsis and shock are important for developing an in-depth understanding
ROLE OF THE GUT BACTERIA
 ROLE OF THE GUT BACTERIA Our Good Bacteria In a perfect world, we would all have a proper ratio of good bacteria And what could this proper ratio do for us? The knowledge of the connections between our
ROLE OF THE GUT BACTERIA Our Good Bacteria In a perfect world, we would all have a proper ratio of good bacteria And what could this proper ratio do for us? The knowledge of the connections between our
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
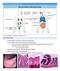 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Dairy Products and Cancer: A Review of the Evidence
 Micro-Nutrients in Milk and Dairy Products: New Insights and Health Benefits CERIN Symposium May 12, 2011 Paris, France Dairy Products and Cancer: A Review of the Evidence Johanna W. Lampe, PhD, RD Division
Micro-Nutrients in Milk and Dairy Products: New Insights and Health Benefits CERIN Symposium May 12, 2011 Paris, France Dairy Products and Cancer: A Review of the Evidence Johanna W. Lampe, PhD, RD Division
SCFA in gut health. Kristin Verbeke. On behalf of the Prebiotic Task Force of ILSI Europe
 SCFA in gut health Kristin Verbeke Translational Research in Gastrointestinal Disorders KU Leuven On behalf of the Prebiotic Task Force of ILSI Europe Acetic acid Major anions in the large intestine Propionic
SCFA in gut health Kristin Verbeke Translational Research in Gastrointestinal Disorders KU Leuven On behalf of the Prebiotic Task Force of ILSI Europe Acetic acid Major anions in the large intestine Propionic
Targeting the cgmp Pathway to Treat Colorectal Cancer
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Faculty Papers Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 29 Targeting the cgmp
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Faculty Papers Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 29 Targeting the cgmp
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption. Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs
 Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Gut microbiota: importance
 Gut microbiota: importance Gut microbiota: importance BACTERIA IN THE GUT SYNTHESIZE SEVERAL HUNDRED GRAMS OF ESSENTIAL AMINO-ACIDS EVERY DAY PROKARYOTES (Bacteria) capability to synthesize essential compounds
Gut microbiota: importance Gut microbiota: importance BACTERIA IN THE GUT SYNTHESIZE SEVERAL HUNDRED GRAMS OF ESSENTIAL AMINO-ACIDS EVERY DAY PROKARYOTES (Bacteria) capability to synthesize essential compounds
Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology
 By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
Innate lymphoid cells
 Innate lymphoid cells Cording et al. FEBS 2014 Retioic acid (RA) is a vitamine A metabolite that control early vertebrate development. RA mediates CXCL13 expression in fetal mesenchyal cells, cytokine
Innate lymphoid cells Cording et al. FEBS 2014 Retioic acid (RA) is a vitamine A metabolite that control early vertebrate development. RA mediates CXCL13 expression in fetal mesenchyal cells, cytokine
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Cholesterol Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels
 Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels David E. Cohen, MD, PhD Director of Hepatology, Gastroenterology Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital
Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels David E. Cohen, MD, PhD Director of Hepatology, Gastroenterology Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism
 Supplementary Information The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism Address correspondence to Yong Li (yongli@xmu.edu.cn, Tel: 86-592-218151) GW464 CDCA Supplementary
Supplementary Information The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism Address correspondence to Yong Li (yongli@xmu.edu.cn, Tel: 86-592-218151) GW464 CDCA Supplementary
Activation of Bile Acid Signaling Shapes the Gut Microbiota to Improve Diabetes and Fatty Liver Disease
 Activation of Bile Acid Signaling Shapes the Gut Microbiota to Improve Diabetes and Fatty Liver Disease John Chiang, Ph.D. Northeast Ohio Medical University Rootstown, OH, USA International Conference
Activation of Bile Acid Signaling Shapes the Gut Microbiota to Improve Diabetes and Fatty Liver Disease John Chiang, Ph.D. Northeast Ohio Medical University Rootstown, OH, USA International Conference
BACTERIAL TRANSLOCATION AND INTESTINAL PERMEABILITY IN PRETERM INFANTS
 BACTERIAL TRANSLOCATION AND INTESTINAL PERMEABILITY IN PRETERM INFANTS Dr Paul Fleming Consultant Neonatal Medicine Homerton University Hospital Honorary Research Fellow Barts and the London School of
BACTERIAL TRANSLOCATION AND INTESTINAL PERMEABILITY IN PRETERM INFANTS Dr Paul Fleming Consultant Neonatal Medicine Homerton University Hospital Honorary Research Fellow Barts and the London School of
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Severe sepsis and Diarrhea : a Case Report
 Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Severe sepsis and Diarrhea : a Case Report Qiurong Li Institute of General Surgery, Jinling Hospital Nanjing Univeristy Gut Microbiota 100 trillion cells 10-fold of
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Severe sepsis and Diarrhea : a Case Report Qiurong Li Institute of General Surgery, Jinling Hospital Nanjing Univeristy Gut Microbiota 100 trillion cells 10-fold of
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology. Robin Lorenz
 Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
The Digestive system
 The Digestive system Question Paper 1 Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet GCSE Biology CCE Enzymes and digestion The digestive system Question Paper Time llowed: Score: Percentage: 67 minutes
The Digestive system Question Paper 1 Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet GCSE Biology CCE Enzymes and digestion The digestive system Question Paper Time llowed: Score: Percentage: 67 minutes
BIOH122 Session 8 Non-Specific Disease Resistance
 BIOH122 Session 8 Non-Specific Disease Resistance To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Disease Resistance Activity: Animations Title: Non-Specific Disease Resistance Introduction 1. Name five general
BIOH122 Session 8 Non-Specific Disease Resistance To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Disease Resistance Activity: Animations Title: Non-Specific Disease Resistance Introduction 1. Name five general
Principles of Toxicology: The Study of Poisons
 Principles of Toxicology: The Study of Poisons Elizabeth Casarez Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University it of Arizona The study of the adverse effects of a toxicant on living organisms Adverse
Principles of Toxicology: The Study of Poisons Elizabeth Casarez Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University it of Arizona The study of the adverse effects of a toxicant on living organisms Adverse
GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA IN THE ILEUM WITH ULCERATION AND CHRONIC BLEEDING
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 66: 113-117, 1974 Copyright 1974 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 66, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA IN THE ILEUM WITH ULCERATION AND CHRONIC BLEEDING KARIM
GASTROENTEROLOGY 66: 113-117, 1974 Copyright 1974 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 66, No.1 Printed in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS GASTRIC HETEROTOPIA IN THE ILEUM WITH ULCERATION AND CHRONIC BLEEDING KARIM
Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis
 Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis Haim Belinson,, Richard M. Locksley, Ophir D. Klein JCI Insight. 2016;1(10):e85395. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.85395.
Dual epithelial and immune cell function of Dvl1 regulates gut microbiota composition and intestinal homeostasis Haim Belinson,, Richard M. Locksley, Ophir D. Klein JCI Insight. 2016;1(10):e85395. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.85395.
Prevention of cholesterol gallstone disease by FXR agonists in a mouse model
 24 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/naturemedicine Prevention of cholesterol gallstone disease by FXR agonists in a mouse model Antonio Moschetta, Angie L Bookout & David J Mangelsdorf Cholesterol
24 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/naturemedicine Prevention of cholesterol gallstone disease by FXR agonists in a mouse model Antonio Moschetta, Angie L Bookout & David J Mangelsdorf Cholesterol
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Supplementary Figure 1. ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons
 Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
The Gut Microbiota: Evidence For Gut Microbes as Contributors to Weight Gain
 The Gut Microbiota: Evidence For Gut Microbes as Contributors to Weight Gain Michael T. Bailey, Ph.D. Center for Microbial Pathogenesis The Research Institute, Nationwide Children s Hospital Department
The Gut Microbiota: Evidence For Gut Microbes as Contributors to Weight Gain Michael T. Bailey, Ph.D. Center for Microbial Pathogenesis The Research Institute, Nationwide Children s Hospital Department
PXR Prevents Cholesterol Gallstone Disease by Regulating Biosynthesis and Transport of Bile Salts
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:2095 2106 PXR Prevents Cholesterol Gallstone Disease by Regulating Biosynthesis and Transport of Bile Salts JINHAN HE,* SHIGERU NISHIDA, MEISHU XU,* MAKOTO MAKISHIMA, and WEN
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:2095 2106 PXR Prevents Cholesterol Gallstone Disease by Regulating Biosynthesis and Transport of Bile Salts JINHAN HE,* SHIGERU NISHIDA, MEISHU XU,* MAKOTO MAKISHIMA, and WEN
Understandings, Applications & Skills
 D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! )
 POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM THE FOUR STEPS OF DIGESTION
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WHAT IS THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? the digestive system is a long, muscular tube The entire system is approximately 9m in length and is usually a one way tract WHY DO WE NEED A DIGESTIVE
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WHAT IS THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? the digestive system is a long, muscular tube The entire system is approximately 9m in length and is usually a one way tract WHY DO WE NEED A DIGESTIVE
Accepted Manuscript. Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development. Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo
 Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR, NR1H4) belongs to
 Genomic Analysis of Hepatic Farnesoid X Receptor Binding Sites Reveals Altered Binding in Obesity and Direct Gene Repression by Farnesoid X Receptor in Mice Jiyoung Lee, 1 * Sunmi Seok, 1 * Pengfei Yu,
Genomic Analysis of Hepatic Farnesoid X Receptor Binding Sites Reveals Altered Binding in Obesity and Direct Gene Repression by Farnesoid X Receptor in Mice Jiyoung Lee, 1 * Sunmi Seok, 1 * Pengfei Yu,
Digestive Tract. Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. stomach small intestine large intestine - anus
 Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Digestion Review V1 /36
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Supplemental Data Tamoxifen administration to Vil-Scap- mice.
 Supplemental Data FIGURE S1. Tamoxifen administration to Vil-Scap - mice. In the experiments shown in Fig. 1 to Fig. 5, tamoxifen (2 mg per dose) was dissolved in corn oil and administered by orogastric
Supplemental Data FIGURE S1. Tamoxifen administration to Vil-Scap - mice. In the experiments shown in Fig. 1 to Fig. 5, tamoxifen (2 mg per dose) was dissolved in corn oil and administered by orogastric
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
