OSCE Surgery Dossier. New 2016/2017
|
|
|
- Marybeth Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OSCE Surgery Dssier New 2016/2017
2 # Title OSCE statins (past years) General histry General: cancer staging Lump histry & examinatin The neck & cervical lymph ndes Neck swellings Thyrid histry Thyrid - physical Salivary glands histry & physical exam Breast histry & physical exam GI histry taking Abdmen physical examinatin Biliary disease histry & examinatin Acute appendicitis histry & examinatin Pancreatitis histry & examinatin Diverticulitis histry Intestinal bstructin histry & examinatin Dysphagia histry Histry f fresh bld per rectum Cln cancer histry & examinatin Inguinal hernia examinatin Jaundice Peripheral arterial disease Hx & P/E Peripheral venus disease Hx & P/E Ulcer Ulcer exam Varicse veins Diabetic ft exam Pediatric histry Dne by Yasmin Khundakji *** Old dssier Yasmin Khundakji *** Old dssier *** المحاضرات التي وضعت بجانبها هذه اإلشارة كتبها الطالب التالية أسماؤهم : ميرة يونس/شذى الرخامين/محمود منصور/عبد هللا المصري/إبراهيم صبري/خالد الحمد/مهند أبو حمد
3 The fllwing tpics have been mitted frm the dssier since they rarely cme in OSCE statins as histry taking and physical examinatin. But it is imprtant t study them fr Mini-OSCE. Mini-OSCE files cver mst f these tpics with pictures and cmmn questins. Fr further reading, yu can read frm ld OSCE dssier, surgical recall r any ther surce. - Gastric cancer histry - PUD - Tumr f esphagus - Hydatid cyst - IBD - Lung cancer and pneumthrax - Amputatin - Stma/ trachestmy/ tubes & drains - Aneurysm / AV fistulas/ wund healing/ scars - Skin tumrs/ melanma/ mles/ hemangima/ BCC/ SCC - PNS - Sft tissue sarcma If yu have any prepared material that wuld make this dssier much better please send t this juclinical@gmail.cm
4 OSCE statins st semester - take a hx frm a patient cmplaining f tenesmus (n taking the histry the patient als cmplained f rectal bleeding and weight lss) at the end the dr asks fr a diagnsis (rectal ca) and what the next step is (PR). - A patient had sigmid ca and a sigmidectmy was perfrmed, examine the patient fr signs f distant metastasis: GI exam fcusing n liver, lymph ndes, sister Mary jseph.. Etc - take a fcused histry frm a patient distinguishing whether they have hyp r hyperthyridism. - Peripheral vascular examinatins fr arterial disease f the lwer limbs nd semester 1- Examine neck mass. 2- Histry breast mass. 3- Histry jaundice in elderly and what is the diagnsis "cancer". 4- Abdminal examinatin fr a patient presented with right iliac pain and what is the diagnsis. st semester -P/E fr Patient diagnsed t have Acute appendicitis. -Histry fr patient with thyrid mass with manifestatins f hypthyrid. -Hx fr a patient with Lt lwer abdminal pain Diverticuliti. -P/E fr patient with peripheral arterial disease.
5 nd semester 1. This patient is a 55 year ld male wh came t the ER cmplaining f RUQ pain f 4 hurs duratin. Take relevant histry in 5 minutes then give the prvisinal diagnsis and the diagnstic test. -Acute chlecystitis vs. biliary clic. Abdminal ultrasund. 2. This female patient came t the clinic saying she fund a mass in her right breast incidentally in the shwer, take a prper histry then give yur initial diagnsis and yur recmmended investigatins. -Breast ca, U/S, mammgraphy, FNA and cre needle bipsy. 3. This patient has intermittent right partid gland swelling, perfrm full examinatin f head and neck and cmment. 4. This patient came t the ER with abdminal pain, yur fellw resident says he has small bwel bstructin but yu cmpletely disagree with him. Perfrm a physical examinatin mentining all imprtant negative findings t rule ut intestinal bstructin a patient came t the ER with all the symptms f appendicitis right iliac fssa pain that has started in the para umbulical regin vmiting, fever,... d a prper fcused physical examinatin fr him 2- take a histry frm a patient with inguinal hernia. 3- take a prper fcused histry frm a patient wh's 57 yrs ld came t the ER by a severe chest pain, in the hspital they did cath fr him, after 6 hrs he had a pain n his ankle 4- Take a prper fcused histry frm a patient wh came t the ER with direct flame burn invlving bth arms and face.. It's suspected t be frm the 2nd & 3rd degree.. 5- take a histry frm a patient cming t the clinic cmplaining f neck swelling, & d a prper physical examinatin fr him
6
7
8
9
10 General: Synpsis f a Histry (Brwse) - Patient's Prfile: Name; age; sex; marital status; ccupatin; ethnic grup; admissin. - Chief Cmplaint: Preferably in the patient s wn wrds. - Histry Of Present Cmplaint: Alimentary system and abdmen (AS) Appetite. Diet. Weight. Nausea. Dysphagia. Regurgitatin. Flatulence. Heartburn. Vmiting. Haematemesis. Indigestin pain. Abdminal pain. Abdminal distensin. Bwel habit. Nature f stl. Rectal bleeding. Mucus. Slime. Prlapse. Incntinence. Tenesmus. Jaundice. Respiratry system (RS) Cugh. Sputum. Haemptysis. Dyspnea. Harseness. Wheezing. Chest pain. Exercise tlerance. Cardivascular system (CVS) Dyspnea. Parxysmal ncturnal dyspnea. Orthpnea. Chest pain. Palpitatins. Dizziness. Ankle swelling. Limb pain. Walking distance. Clur changes in hands and feet. Musculskeletal system (MSS) Aches r pains in muscles, bnes r jints. Swelling jints. Limitatin f jint mvements. Lcking. Weakness. Disturbances f gait. Urgenital system (UGS) Lin pain. Frequency f micturitin including ncturnal frequency. Pr stream. Dribbling. Hesitancy. Dysuria. Urgency. Precipitancy. Painful micturitin. Plyuria. Thirst. Haematuria. Incntinence. Men: Prblems with sexual intercurse and imptence. Wmen: Date f menarche r menpause. Frequency. Duratin f menstruatin. Vaginal discharge. Dysmenrrhea. Dyspareunia. Previus pregnancies and their cmplicatins. Prlapse. Urinary incntinence. Breast pain. Nipple discharge. Lumps. Skin changes. Nervus system (CNS) Changes f behaviur r psyche. Depressin. Memry lss. Delusins. Anxiety. Tremr. Syncpal attacks. Lss f cnsciusness. Fits. Muscle weakness. Paralysis. Sensry disturbances. Paraesthesiae. Dizziness. Changes f smell, visin r hearing. Tinnitus. Headaches. - Previus Histry: Previus illnesses. Previus Surgeries r accidents. Diabetes. HTN. Rheumatic fever. Immune Diseases. Bleeding tendencies. Asthma. Allergies. TB etc. - Drug Histry and Immunizatins: Insulin. Sterids. Anti-depressants and the cntraceptive pill. Drug abuse. - Family Histry: Causes f death f clse relatives. Familial illnesses in siblings and ffspring. - Scial Histry and Habits: Marital status. Sexual habits. Living accmmdatin. Occupatin. Expsure t industrial hazards. Travel abrad. Leisure activities. Smking. Drinking. Number f cigarettes smked per day. Units f alchl drunk per week. 2
11 General: Cancer Staging (NMS) Cancer is a grup f diseases caused by unregulated grwth and spread f neplastic cells. Neplasias may be either benign (nninvasive grwth, n metastases) r malignant (invasive grwth, metastases). Types a. Carcinmas are malignancies that arise frm epithelium. b. Adencarcinmas are malignancies that arise frm epithelium and have a glandular cmpnent. c. Sarcmas are malignancies that arise frm mesdermal tissues. Clinical manifestatins f cancer - Seven classic symptms f cancer spell ut the mnemnic "CAUTION:" Change in bwel r bladder habits A sre that des nt heal Unusual bleeding r discharge Thickening r lump in the breast r elsewhere Indigestin r difficulty swallwing Obvius change in a wart r mle Nagging cugh r harseness. Other manifestatins Grwth, causing a mass, bstructin, r neurlgic deficit Grwth int neighbring tissues causing pain, paralysis, fixatin, r immbility f a palpable mass Tumr necrsis causing bleeding r fever Systemic manifestatins such as thrmbphlebitis, endcrine symptms due t hrmnes secreted by the tumr, and cachexia Extreme weight lss ver a shrt perid f time Metastatic spread as the first symptm such as enlarged lymph ndes, neurlgic symptms, r pathlgic bne fractures. The standard staging f mst cancers is based n the tumr, ndes, and metastasis (TNM) system: T describes the primary tumr. N describes the invlvement f lymph ndes with metastatic spread. M describes distant metastases. Stage gruping. Staging is necessary t chse the apprpriate therapy and t assess the prgnsis. Example: TNM Classificatin System and Stage Gruping fur Gastric Adencarcinma Tumr (T) T0 N evidence f primary tumr Tis (in situ) Tumr limited t mucsa T1 Tumr limited t mucsa r submucsa T2 Tumr t but nt thrugh the sersa T3 Tumr thrugh the sersa but nt int adjacent rgans T4 Tumr int adjacent rgans (direct extensin) Ndes (N) N0 N metastases t lymph ndes N1 Only perigastric lymph ndes within 3 cm f the primary tumr N2 Only reginal lymph ndes mre than 3 cm frm tumr but remvable at peratin N3 Other intra-abdminal lymph ndes invlved Metastases (M) M0 N distant metastases M1 Distant metastases Stage gruping Stage 0 Tis Stage 1 T1 Stage 2 T2 r T3 Stage 3 T1-3, N1 r N2, M0 Stage 4 Any T4, any T3, any N3, any M1 3
12 General: Histry And Examinatin Of A Lump Histry Taking: Duratin When was it first nticed? First symptm What brught it t the patient s ntice? (pain, its appearance, was it felt r had smene else nticed it?) Other symptms What symptms des it cause? (usually related t the site f the lump.) Prgressin Hw has it changed since it was first nticed? (any change in size r tenderness) Persistence Has it ever disappeared r healed? (a lump may disappear n lying dwn, r during exercise, and yet be irreducible at the time f yur examinatin.) Multiplicity Has (r had) the patient any ther lumps r ulcers? Cause What des the patient think caused it? (fllw injuries r systemic illnesses knwn nly t the patient) The Examinatin: 1. Site Describe in exact anatmical terms. 3. Shape Shuld be described in 3D: Hemispherical r dme shaped. If asymmetrical, yu may use terms such as 'pear shaped' r 'kidney shaped'. 5. Surface It may be smth r irregular. An irregular surface may be cvered with smth bumps: bsselated; r be irregular r rugh. 7. Tenderness Feel the nn-tender part befre the tender area, and watch the patient s face fr signs f discmfrt. 2. Skin May be disclred and becme smth and shiny r thick and rugh. 4. Size Width, length and height r depth. 6. Temperature Assess the skin temperature with the drsal surfaces f yur fingers. 8. Edge Clearly defined r indistinct. It may have a definite pattern. 9. Cmpsitin Calcified tissues such as bne Hard Tightly packed cells Slid Extravascular fluid: Urine, serum, CSF, synvial fluid r extravascular bld Cystic Gas Intravascular bld 4
13 There are certain physical signs which help yu decide the cmpsitin f a lump, and these are: Cnsistency Stny hard Firm Rubbery Spngy Sft Fluctuatin Can nly be elicited by feeling at least tw ther areas f the lump whilst pressing n a third. It fluctuates and cntains fluid if tw areas n ppsite aspects f the lump bulge ut when a third area is pressed in. This examinatin is best carried ut in tw places, the secnd at right angles t the first. Fluid thrill The presence f a fluid thrill is detected by tapping ne side f the lump and feeling the transmitted vibratin when it reaches the ther side. It can't be felt acrss small lumps. Translucence Psitive fr lumps that cntain water, serum, lymph r plasma, r highly refractile fat. Bld and ther paque fluids d nt transmit light. Transilluminatin requires a bright pinpint light surce and a darkened rm. The light shuld be placed n ne side f the lump, nt directly n tp f it Resnance Slid and fluid-filled lumps sund dull when percussed. A gas-filled lump sunds hllw and resnant. Pulsatility Place a finger f each hand n ppsite sides f the lump and feel fr a pulsatin. If they are pushed utwards and upwards then the lump has an expansile pulsatin (aneurysms and vascular tumrs). When they are pushed in the same directin (usually upwards), the lump has a transmitted pulsatin. Cmpressibility Sme fluid-filled lumps can be cmpressed until they disappear. When the cmpressing hand is remved the lump re-frms spntaneusly. Bruit Always listen t a lump. Vascular lumps that cntain an AV fistula may have a systlic bruit. Hernaie cntaining bwel may have audible bwel sunds. 10. Reducibility A lump which is reducible can be pushed away int anther place but will ften nt reappear spntaneusly withut the stimulus f cughing r gravity. 11. Mbility and Fixity Attachment t the Skin Attachment t Muscle: Underlying muscles must be tensed t see if this reduces the mbility. If this makes it easier t feel the lump: the lump is attached t the fascia cvering the muscle r t the muscle itself. If it becmes less easy t feel: the lump is within r deep t the muscles. Attachment t Bne: Lump mves very little. Attachment t r arising frm Vessels r Nerves: may be mved frm side t side acrss the length f the vessel r nerve, but nt up and dwn alng their length. Lumps in the abdmen that are freely mbile usually arise frm the intestine, its mesentery r the mentum. 12. Reginal Lymph Ndes 13. Examinatins Specific t The Site f The Lump 5
14 The Neck and Cervical Lymph Ndes Familiarity with neck anatmy is critical fr diagnsis and management f disease prcesses affecting this regin. The neck is traditinally divided int the central and the lateral necks, with the lateral neck further subdivided int anterir and psterir triangles. It is imprtant t palpate the head and neck lymph ndes in a systematic way t avid missing any. Occipital ndes: at the base f the skull Psterir auricular ndes: just psterir t the ear, abve the mastid prcess Pre-auricular ndes: just anterir t the ear Submental ndes: just psterir t the tip f the mandible (just belw the chin) Submandibular ndes: alng the bdy f the mandible (the underside f the jaw n either side) Superficial cervical ndes: alng the sternal head f the SCM Psterir cervical ndes: Extend in a line psterir t the SCM but in frnt f the trapezius, frm the level f the mastid bne t the clavicle, alng the clavicular head f the SCM Deep cervical ndes: deeply alng the sternal head f the SCM Supraclavicular ndes: in the hllw abve the clavicle, just lateral t where it jins the sternum Infraclavicular ndes: belw the clavicle 6
15 Neck Swellings Cngenital Inflammatry Neplastic and Others Branchial Cyst: Reactive Viral Metastatic Head and Neck - Presents in late childhd r early Lymphadenpathy: Carcinma: adulthd - Usually asymptmatic, diagnsis is - Behind upper 1/3 rd f SCM cnfirmed with FNA + histlgy - Ovid, 5-10 cm lng - Painless, slw-grwing, stny hard - Painless unless it's infected, and and smth LN, size and shape vary recurrent infectins culd ccur - Hard, dull, fluctuates, nt very mbile Primary Neplasms f Lymph Ndes Thyrglssal Duct Cyst: - A midline mass in the ant neck cm diameter, firm r hard, smth, spherical - Mves up n tngue prtrusin - Becmes infected in the setting f an URTI - Tx: Sistrunk peratin Vascular Anmalies: - Vascular tumrs (hemangima) - Vascular malfrmatins (Lymphatic malfrmatins are the mst likely t present as a neck mass) Laryngcele: - When it extends beynd the larynx it ften presents as an air filled cyst in the anterir neck - Harseness, cugh, and a freign bdy sensatin Ranula: - A muccele arising frm an bstructin in the sublingual glands in the flr f muth - painless and slw-grwing Teratma: - A tumr cmpsed f tissues nt nrmally present at the site Dermid Cyst: - Midline, nn-tender, mbile, submental r sublingual neck masses - Cntent: hair/sebaceus/sweat gland Thymic Cyst: - Between the angle f the mandible and the midline f the neck Cystic Hygrma: - Cmmnly presents in yung children, base f neck, psterir triangle, brilliantly translucent. Sternmastid 'tumr': - In nenates, presents with cngenital trticllis, fusifrm, slid, smth lump in the middle f the SCM. - Arises in the setting f an URTI - Reslves within 1-2 weeks f symptm reslutin (symptms last 1-2 weeks) - Typically tender, < 1 cm - Mnnuclesis: neck ndes are quite large (>2 cm), may als ccur in the psterir triangle and may rutinely take 4-6 weeks t reslve - CT findings: ndes <1cm, blng in shape, with n evidence f central hypdensity, and a preserved vascular hilum Bacterial Lymphadenpathy: - Tuberculus lymphadenitis: islated chrnic nn-tender, usually in upper and middle deep cervical LN, indistinct firm mass, the glands are matted tgether. May develp int a cllar stud abscess in the upper 1/2 f the neck which is tender, firm-rubbery, with reddish-purple verlying skin, and eventually develps int a chrnic sinus. - Cat-scratch disease: submandibular and/r preauricular, caused by Rchalimaea henselae, which is carried by felines, painful and accmpanied by fevers and generalized malaise Parasitic Lymphadenpathy: - Txplasma gndii Ludwig's Angina: - A rapidly swelling cellulitis, caused by dental infectins (strep/staph) at the flr f the muth. Fever, edema, erythema under chin, and causes severe airway impairment due t pressure n larynx, causes suffcatin and death if nt managed Sialadenitis: - Inflammatin f a salivary gland Nninfectius - Difficult t diagnse - e.g. Sarcidsis - Lymphma: Usually vid, smth, nn-tender, slid-rubbery, slwlygrwing, cmmn in children and YA - Sx: Malaise and Weight lss, spread t skin may cause Mycsis Fungides Salivary Gland Neplasms: - Mstly arise in the partid and are mainly benign plemrphic adenmas r warthin tumrs (tail f partid) - Incidence f malignancy in tumrs f the submandibular gland is much higher - Benign: present as asymptmatic enlarging masses. - Pain, cranial nerve deficits, r verlying skin changes usually indicate malignancy Cartid Bdy Tumr: - Highly vascular, typically benign, in the lateral neck, ften pulsatile with a bruit, mbile in a side t side directin but nt in a vertical directin - Diagnsed thrugh an angigram, emblizatin is dne befre surgery Lipma: - Dme shaped, slippery edges, sft but turns hard if fat necrses, n skin changes, nn-tender Schwannma Thyrid Malignancies Others: Benign Skin Cysts: - Sebaceus cysts: dme-shaped, thin shiny hairless verlying skin, may be infected and red, tender, ht. - Attached t the skin. A punctum is usually seen. Culd develp int a sebaceus hrn r cck's peculiar tumr Pharyngeal Puch (Zencker) - Dysphagia + halitsis. Dx: Ba swallw Cervical Rib Giter 7
16 Thyrid - Histry Taking Patient's Prfile Chief Cmplaint: it will mst prbably be a 'neck lump' Histry f Present Cmplaint: 1. Symptms f The Lump Itself: Duratin Site, Size, Shape and Mbility (general) First symptm: Hw it was nticed Other symptms: a. Dysphagia r discmfrt n swallwing b. Dyspnea, SOB n sleeping r Stridr c. Pain, referred t anywhere? d. Harseness r inability t reach high ntes Prgressin Multiplicity Persistence Previus Hx f a similar case Cause: ask the patient what they think may have caused it 2. Symptms Specific t Thyrid diseases: HYPERTHYROIDISM HYPOTHYROIDISM Neurlgical and General Symptms: Fatigue r weakness Insmnia Nervusness, irritability, anxiety Headaches Vertig Tremrs in the hands and tngue Eye symptms: duble visin, bulging, difficulty clsing eyelids r sme eye mvement difficulties Cardivascular Symptms: Palpitatins (missed & irregular beats: A Fib) Shrtness f breath r atypical chest pain n exertin Swelling f the ankles Metablic and Alimentary Symptms: Lss f weight despite a nrmal r increased appetite Diarrhea r hyperdefecatin Excessive sweating Thirst Gyneclgical: amenrrhea r ligmenrrhea Others: Wasting f muscles and prximal muscle mypathies: lifting bjects and climbing stairs may becme increasingly difficult Heat intlerant (prefers cld weather) Neurlgical and General Symptms: Cgnitive: range frm mild lapses in memry with slw thught, speech and actin t delirium, hallucinatins, dementia, seizures and cma Myxedema Madness Depressed md with limited initiative and sciability Fatigue, lethargy, myalgias, arthralgias, parethesias Weakness Cardivascular Symptms: assciated with heart failure Dyspnea Ankle edema Metablic and Alimentary Symptms: Increase in weight despite pr appetite Depsitin f fat mst nticed arund the back f the neck and shulders Cnstipatin Gyneclgical: Menrrhagia (heavy bleeding) Others: Cld intlerant (always cld( Thinning f hair: scalp and lateral eyebrws Dry Skin 8
17 3. Other Symptms: Symptms f inflammatin r infectin (e.g. Fever, recent RTI) Symptms f Metastasis: deep bne pain, pathlgical fractures r sft pulsating tumrs Risk Factrs: Expsure t irradiatin Diet lacking idine: (e.g. Seafd, Dairy prducts) Previus Histry f thyrid disease, any autimmune r liver diseases Family Histry Drug Hx: amidarne, interfern-a, pharmaclgic preparatins f thyrid hrmne Smking Investigatins TSH receptr antibdy: Increased in Graves disease. Thyrid functin tests: Free T3 and T4 levels are mre useful than ttal levels. Thyrid autantibdies: Anti-thyrid perxidase may be increased in Hashimt s and Graves diseases. Its presence in Graves disease signifies an increased likelihd f pst-treatment hypthyridism. Ultrasund scan: Useful t distinguish cystic frm slid lumps (which are mre likely t be malignant). Istpe scan: t differentiate different causes f a giter and identify ectpic thyrid tissue and ht and cld ndules. Cld ndules are much mre likely t be malignant than ht ndules. Bld lipids and glucse: Patients with hypthyridism are at risk f CVD and diabetes. Treatment Hyperthyridism Hypthyridism Drugs: Symptm cntrl: beta-blckers, e.g. prpranll. Mdificatin: Anti thyrid medicatin e.g. carbimazle + thyrxine Radiactive idine: Absrbed by the thyrid gland where it causes it t shrink usually within 3-6 mnths Cntraindicated in active hyperthyridism (due t an increased risk f thyrtxic strm), pregnancy and breast-feeding. Treatment is with Levthyrxine (synthetic thyrid hrmne) but remember that: Enzyme-inducing drugs may increase the breakdwn f Levthyrxine Thyrxine can increase the risk f a mycardial infarctin in patients with ischemic heart disease. Cmplete r partial thyridectmy: This is reserved fr: Cases refractry t medical treatment Cmpressin f imprtant structures Patient preference fr csmetic reasns. Damage t lcal structures, including the recurrent laryngeal nerve and parathyrid glands, is a serius cmplicatin f thyrid surgeries. 9
18 Thyrid Physical Examinatin Always Remember: Intrduce yurself, explain the exam briefly and ask fr permissin. Ensure privacy, warmth and gd lighting. Wash yur hands befre yu start. Psitin and Expsure: The patient must be sitting. The neck shuld be expsed fully. First impressin The patient is cnscius, alert and riented t time, place and persn. D they seem abnrmally hyper- r hypactive? Hyperthyridism: restless and agitated Hypthyridism: slw mtin and apathy Vital signs Pulse: Hyperthyridism: resting tachycardia, there may be irregular irregularity (A Fib). Hypthyridism: bradycardia. Respiratry rate Bld pressure Nte if there is harseness r stridr after talking t the patient Clthing (any suggestin f heat r cld intlerance) Obese r cachectic Obvius tubes r drains BMI: Hypthyridism: increased. Hyperthyridism: decreased. Temperature Hands Palms: Hyperthyridism: Sweaty and warm. Lk fr palmar erythema r thenar muscle wasting. Hypthyridism: Cld and dry. May be carse, yellw and cld due t peripheral vascnstrictin. Thyrid Acrpachy: tender wrist, clubbing and peristeal bne frmatin. Fund in Hyperthyridism. Fine Tremr in hyperthyridism: ask the patient t extend their arms and tngue. Yu may place a paper ver the patient's hand t make it mre visible. Onychlysis in hyperthyridism. Brittle nails may be seen in hypthyridism. Face and Eyes 1. Exphthalms: examine frm abve r the lateral side. Crneal Ulcer: due t prlnged eye pening and infrequent blinking Cnjunctivitis Chemsis (redness and edema) Perirbital edema - The patient may able t lk up withut any frntal wrinkles in severe prptsis and may have prblems with cnvergence. 2. Ophthalmplegia: ask the patient t fllw the letter H; test fr diplpia and nystagmus. 3. Lid lag: ask the patient t fllw yur finger r an bject mving dwn vertically. Occurs in hyperthyridism. Psitive when a rim f sclera is visible between the upper eyelid and the superir iris n dwnward gaze. 4. Lid retractin: the sclera is visible abve the superir crneal limbus. 5. Hair Lss: diffuse thinning f hair in scalp r lateral eyebrws may ccur in hypthyridism. 10
19 The Neck Inspectin: The neck shuld be hyper-extended. Cmment On: Symmetry Masses: Single r Multindular. Size, Site, Shape and verlying Skin changes. Scars: neck cllar scar at the crease f the neck indicates previus thyrid surgery. Vein engrgement, visible pulsatins, edema and redness. Perfrm Fur Maneuvers, ask the patient t: 1) Swallw (yu may give them sme water) and bserve any abnrmalities. A thyrid swelling mves upward n swallwing since it lies in the pretracheal fascia. 2) Prtrude their tngue. A thyrglssal cyst mves upward n swallwing (attached t the hyid bne). 3) Open their muth and use the trch t check fr a lingual thyrid. 4) Raise their arms abve their head and watch fr any flushing: Pembertn s sign (thyrid enlargement can cause SVC bstructin). Palpatin: The neck shuld be slightly flexed. Explain the exam, warm yur hands and ask if there is any pain. - Frm the anterir: Tenderness: Palpate while watching fr any signs f discmfrt - Frm behind the patient: Palpate the entire length f bth lbes as well as the isthmus. Fix ne hand n ne lbe t stabilize it and palpate the ther lbe. Nte any swellings r abnrmal lumps: Examine als while the patient swallws. Cmment n: tenderness, temperature, shape, size, surface, cnsistency and mbility. - Cmment n whether there is a palpable thrill Lymph Ndes: Cervical Supraclavicular Mediastinum: Tracheal tug Tracheal deviatin Cricsternal distance Berry Sign: an absence f a cartid pulsatin as a direct result f a tumr encasing the cartid artery and muffling the pulsatin Percussin: Dwnwards frm the sternal ntch t detect retrsternal extensin f giter: Becmes dull if a giter extends retrsternally r if the whle thyrid is displaced. Auscultatin: Bruit ver the thyrid is characteristic f Graves disease. T reduce transmissin, ask the patient t: Hld his breath Place yur hand n the rt f the neck t reduce transmissin frm the jugular vein At the end f the examinatin, mentin that yu want t examine the fllwing: Lwer Limbs - Pretibial myxedema (pink r brwn scars with thick skin(: Graves disease. - Myxedema (nn-pitting edema): Hypthyridism Deep tendn reflexes - Hyperthyridism: Hyper-reflexia - Hypthyridism: Delayed relaxatin Prximal Mypathy: - Sit the patient n the edge f the cuch, and instruct them t fld their arms and then stand frm the sitting psitin withut using their hands 11
20 Duratin Salivary Glands - Histry Taking Patient's Prfile; Chief Cmplaint: it is cmmnly an asymptmatic mass. Histry f Present Cmplaint: Site, Size, Mbility and Skin changes (general) First Symptm: Hw it was nticed Other Symptms: Pain? If yes, SOCRATES - Relatinship t eating (e.g. citrus), hunger r chewing? These stimulate salivary flw - Des it persist in between meals? - Relatinship t speaking r mving the jaw (any mvement f the tempr-mandibular jint is painful in mumps) - Radiatin: The pain may radiate t the ear and ver the side f the face in partid carcinma. - Symptms may be relieved by pressing n the gland, and this may prduce a ful-tasting fluid in their muth: purulent saliva (Submandibular calculi) Swelling: - Is it increased befre r after eating? (Chrnic Partitis is particularly nticeable befre eating) - Plemrphic adenma f the partid may be mre prminent when the muth is pen, r when eating. Infectin r Inflammatin: Fever, Sweating, Rigrs (e.g. mumps) Discharge frm inside the ral cavity Signs f facial r trigeminal nerve invasin: - Numbness r asymmetry f the muth and difficulty in clsing the eyes Dry eyes and generalized arthritis: Sjögren's syndrme Trismus: usually a late presentatin, extensin t muscles f masticatin Dysphagia: deep lbe tumr Prgressin: - Slw-grwing vs. Rapidly enlarging Multiplicity Persistence Recurrence: Previus Hx Cause: what they think may have caused it Risk factrs include: Oral Hygiene Debility Pst-p Dehydratin Medical and Surgical Hx - Irradiatin expsure Family Histry Drug Hx Scial Hx Differentiating between the different causes: Investigatins: A slwly enlarging, distinct mass: benign r malignant neplasm. A rapidly enlarging, firm distinct mass assciated with firm, ipsilateral adenpathy r a mass assciated with pain r facial nerve paralysis: malignancy. Acute, painful swelling in ne r bth glands, assciated with fever r systemic symptms: inflammatin. Intermittent pain and swelling in the gland suggest calculus sialadenitis. A stne may ccasinally be palpable n intraral examinatin. Metastatic disease in a partid lymph nde (drainage frm the upper 2/3 rd s f the face and the anterir scalp) may present as a mass in r near the partid gland. MRI lets us knw if the superficial r deep lbes are invlved, if suspicius lymphadenpathy is present, and if there is facial nerve invasin. It may als help t differentiate individual histlgic lesins. CT scans nt as successful in differentiating histlgic lesins. Ultrasund can lcalize the lesin t the superficial r deep lbe but therwise adds little infrmatin. Plain radigraphs r Sialgrams may be useful fr imaging stnes. FNA has a gd accuracy rate (87%) and a lw risk f spreading malignant cells. Cre-needle bipsy r pen bipsy carries the risk f spreading tumr cells and generally is nt indicated. Treatment: Ranges frm superficial surgical excisin if benign t lbar r ttal resectin f the gland. Facial nerve resectin, neck dissectin and pst-p raditherapy may be needed in highly invasive malignancies. 12
21 Salivary Glands Physical Examinatin Always Remember: Intrduce yurself, explain the exam briefly and ask fr permissin. Ensure privacy, warmth and gd lighting. Wash yur hands befre yu start. Psitin and Expsure: The patient must be sitting. The neck shuld be expsed fully. Inspectin: Inspect frm the same level as the patient's head. Cmment n: - Overall symmetry: unilateral r bilateral swelling - Site: Partid: lies n the lateral surface f the mandibular ramus and flds itself arund the psterir brder f the mandible. Masses culd be at the angle f the jaw r at the base f the ear pinna (tail f the partid). The mass may bliterate the retrmandibular space. Submandibular: resides just under the inferir brder f the mandibular bdy. Sublingual: lie just beneath the mucsa in the flr f the muth. - Number and Size - Skin Changes - Shape Nte any limitatin in jaw pening Nte any Scars r Fistulae (can fllw partidectmy r lng-standing partid traumatic injury) and skin r scalp lesins suggestive f primary malignancy Intraral inspectin: Use a tngue depressr, lk fr: - Pharyngeal asymmetry r buccal invlvement - Inflammatin, pus r any discharge - Stnes at the flr f the muth: The submandibular gland is mre cmmnly assciated with stne frmatin because the gland's secretin is mre mucid and it lies in a dependent psitin relative t the duct rifice. This leads t stasis f secretins in the prximal duct. - A pharyngeal bulge which is assciated with a deep lbe partid tumr (masses in the deep part f the partid may bulge thrugh the lateral pharyngeal wall) Facial nerve examinatin - Facial symmetry - Present naslabial flds - Frntal wrinkling n raising eyebrws - Able t blink: eyelid clsure - Able t puff ut cheeks - Ask the patient t smile: any muth deviatin Palpatin: Explain the exam, warm yur hands and ask if there is any pain. Features f the lump: - Tenderness - Temperature - Surface and Edge - Cnsistence Mbility and Relatin (Fixatin t verlying skin r t deep structures) - Ask the patient t clench teeth tgether (tenses the masseter muscle) and cmment n mbility - Put the SCM muscle in actin: t see if the mass is superficial r deep t it (LN are deep) Observe the salivary effluent intra rally during palpatin Intra-ral Palpatin: Use a trch and wear glves. - The Partid Duct: (Stensen's) enters the ral cavity in the cheek just ppsite the upper 2 nd mlar tth. Saliva is usually clear, thin, and clrless. - The Submandibular Duct (Whartn's) runs superirly and anterirly t empty adjacent t the frenulum f the tngue. The small duct rifice is visible in the tp f a papilla in this area. - Lk fr pus, mucus, r particulate matter in the secretin. - Nte: The sublingual glands empty directly int the muth r the submandibular duct. Nt discretely palpable, the duct penings are nt usually visible. Palpate the Cervical Lymph Ndes Bi-manual Palpatin: - Palpate the submandibular gland: Feel the lump between the index finger f ne hand in the lateral flr f the muth and the fingers f the ther hand n the uter surface f the lump. It is usually sft and mbile and shuld nt be tender - Palpate the deep lbe f the partid gland bi-manually. 13
22 The Breast Histry Taking Patient's Prfile: - Name - Age: One f the mst imprtant risk factrs fr breast cancer. The risk peaks at ages abve 50 y/. Pts that are 70 and lder have a much higher risk f malignancy. Cancer is very unlikely in yunger ages - Occupatin: Check if the jb invlves expsure t radiatin fr prlnged time perids. - Marital Status: T ask abut parity later n. - Admissin Chief Cmplaint: it will mst prbably be a 'breast lump' Histry f Present Cmplaint: 1. Symptms f The Lump Itself: Duratin: When was it first nticed? Site, Size, Shape, Cnsistency and Mbility First symptm: Hw was it nticed? Other symptms: Skin Changes: Redness, htness, ulceratin Pain Hardening r dimpling f the breast Nipple Changes (7Ds) Nipple discharge: clr, amunt, smell, texture Swelling in the axilla 2. Risk Factrs: Prgressin: Des its size change? Has it becme mre painful? Change in cnsistence? Multiplicity: Are there any ther masses? Persistence: Des it ever disappear? Previus Hx f a similar case Cause: ask the patient what they think may have caused it Recent trauma Hx (fat necrsis) Past Hx and Family Hx - Previus breast r varian cancer? - Previus Hx f a breast mass? - Previus chem r raditherapy? - Any family histry f breast, varian r cln cancer/masses? - Ask abut first degree relatives (mther, daughters, sisters) and secnd degree relatives. Ask abut their age n nset f the disease. Pregnancy and Breast Feeding - Age during first pregnancy? as this age increases, the incidence f breast cancer increases due t increased estrgen expsure. - N. f children? Increased parity is assciated with a decreased incidence f breast cancer. - Hw many f yur children did yu breastfeed? Fr hw lng? (decreases BC incidence) Gyneclgical Hx - Menstrual pattern? Regular vs. Irregular (indicates hrmnal disturbances) - Duratin: early menarche and late menpause are assciated with increased incidence f breast cancer. - Quantity f bleeding during menses - Are the symptms altered with menses? This is very imprtant as it indicates benign disrders usually. Medicatins - Oral Cntraceptive Pills: assciated with an increased risk f breast cancer. - Hrmnal Replacement Therapy: Als assciated with an increased risk f breast cancer. Scial Histry - Smking: assciated with duct ectasia - Alchl 3. Review f Systems and Symptms f Metastasis: General: weight lss, fever, chills, appetite, diet Musculskeletal: deep bne pain, pathlgical fractures, backaches GI: distensin, jaundice, bleeding tendency Neurlgical: fits, vertig, headaches Respiratry: cugh, SOB 14
23 The Breast Physical Examinatin Always Remember: Intrduce yurself, explain the exam briefly and ask fr permissin. Ensure privacy, warmth and gd lighting. Wash yur hands befre yu start. Ask fr a CHAPERONE. Expsure: frm the waist up Inspectin: Stand in frnt f the patient, lk bilaterally t cmpare. While the patient is sitting, ask her t 1. Rest hands n thighs: this relaxes the pectral muscles, cmment n: - Symmetry - Obvius swelling r mass in the breast - Inspect arms, axilla, supraclavicular fssa - Scars - Skin Changes: Erythema Thickening r Ulceratin (eczematus) Paeu d'range (due t bstructin f lymphatics by cancer cells) Dimpling, Puckering, Tethering Dilated veins - Nipple Changes (7Ds): Destructin Disclratin (nte that the clr nrmally darkens during pregnancy) Displacement (elevatin.. etc) Discharge: ask the patient t express it Deviatin Depressin (transverse slit: duct ectasia) r retractin Duplicatin 2. Press hands firmly n hips: this cntracts the pectral muscles and may reveal swellings. 3. Raise arms abve head: this allws skin changes t becme mre apparent, especially tethering. 4. Lean frward with breasts hanging - Cmment n any changes in the previusly described bservatins r any new nes. - Cmment n the presence r absence f visibly enlarged axillary r supraclavicular LN - Dn't frget t inspect the axillary tail and the underside f the breast. Lymph Ndes: Since the patient is already sitting, yu may examine the lymph ndes befre palpating the breast Axillary - While examining the Rt side, stand n the Rt f the patient. Supprt the patient s arm and elbw with the nn-examining hand. Start palpating the central ndes deep in the apex f the axilla. The hand is straight up, deep in the underarm. Mve dwnwards, gently mve the pads f the fingers medially and inside the brder f the pectral muscle t palpate the medial LN. Sweep back up and return t the axilla with the palm facing laterally, feeling inside the muscle f the psterir axillary fld. Check the lateral ndes with the palm f the hand facing the humeral head. Supraclavicular Cervical 15
24 Palpatin: The patient shuld be supine When examining the medial side: ask her t place her arm under her head n the side t be examined. When examining the lateral side: nrmal supine psitin Begin palpating the nn-pathlgical side first. Explain the exam, warm yur hands and ask if there is any pain. Palpate the breast using the pads f yur middle 3 fingers by 'dipping and rlling'. - Palpatin shuld be dne slwly. - It shuld invlve the entire breast area: frm the 2 nd -6 th rib vertically, and frm the sternal edge t the mid-axillary line hrizntally. - Palpatin can be dne in 3 different ways: Circles, Wedges r Lines. Examine the axillary tail (ver the axillary fld) between yur finger and thumb. Elevate the breast t uncver any abnrmalities such as intertrig in bese patients. Palpate the nipple with the index and thumb and try t express any discharge by massaging the breast twards the nipple. Nte clr and cnsistency. Lump Examinatin (If a mass is fund) 1. Site: Which Quadrant 3. Shape: Shuld be described in 3D 5. Surface 7. Tenderness 9. Cnsistency: sft, firm r hard 2. Skin Changes 4. Size 6. Temperature 8. Edge: Regular, well-circumscribed, irregular 10. Mbility - Fixity (Relatin t surrunding structures) - T examine this, ask the patient t place her hands n her hips and hld the mass between yur thumb and frefinger, ask the pt t push int her hips (t cntract the pectral muscles) If the mass is fixed with and withut this maneuver it's fixed t the chest wall If it becmes fixed after perfrming this maneuver it's fixed t the pectral fascia Perfrm a general exam t search fr metastasis: - Palpate fr cervical lymphadenpathy - Auscultate the lung bases fr effusins - Percuss the spine fr tenderness Investigatins: - Neurlgical exam - Abdminal exam fr hepatmegaly and ascites Treatment: Mammgram: shws sft tissue mass r architectural distrtin and clustered micrcalcificatins Ultrasund: differentiates slid frm cystic masses that are palpable r detected mammgraphically MRI: high sensitivity but limited specificity FNA r cre needle bipsy; surgical bipsy Fr metastasis: Bne/Brain CT; PET scan; LFT; CXR Simple mastectmy has been the histric standard treatment fr Paget's disease Breast Cnserving Treatment is preferred fr invasive and in-situ breast carcinma Highly invasive carcinmas may require a radical mastectmy with wide lcal excisin and axillary clearance Chem r raditherapy may be indicated 16
25 General: GI Histry Taking Patient's Prfile: Name; Age; Marital Status; Place f Residence; Occupatin Chief Cmplaint: Acute Pain (f less than a few days duratin that has wrsened prgressively until the time f presentatin.) Histry f Present Cmplaint: 1) Site f Pain RUQ RLQ LUQ LLQ Biliary Tree: - Chlecystitis - Chledchlithiasis - Chlangitis Liver: - Hepatitis - Tumrs - Hepatmegaly Appendicitis during pregnancy Thracic: - Lwer lbe pneumnia - PE - MI (especially inferir) - Dissecting artic aneurysm Peptic Ulcer Disease Esphageal GI: - Gastritis - Cln ca (cecum) Pancreatitis (epigastric) Appendicitis GI: - Gastrenteritis - Cecal diverticulitis - Meckel s diverticulum - Intussusceptins Mesenteric lymphadenitis - usually preceded by an URTI Inferir Epigastric Artery Rupture Urgenital Gyneclgic: - PID - Adnexal Pathlgy - Ovarian cyst - Trsin - Ectpic Pregnancy - Mittelschmerz - Endmetrisis Splenic - Injury - Splenic Artery aneurysm - Abscess r infarctin Peptic Ulcer Disease GI: - Gastritis Thracic Esphageal (als Rt): - Reflux - Hiatal hernia - Berhaave s Syndrme - Mallry-Weiss tear GI: - Diverticulitis - Vlvulus - Perfrated Cln - Cln Cancer - Small Bwel Obstructin - IBD - Crhn's - Ulcerative Clitis Urgenital: - UTI - Bladder distentin - Nephrlithiasis - Pyelnephritis Gyneclgic Central r Epigastric: - Pancreatitis - Dyspepsia - Mycardial infarctin r ischemia - Pain frm midline retrperitneal structures (arta) - Appendicitis: initially epigastric then shifts t RUQ Generalized (Diffuse): - Referred pain - Peritnitis - Mesenteric Ischemia r Infarctin (severe pain withut any significant clinical findings n PE initially) - Ruptured Aneurysm - Intestinal Obstructin: Adhesins - Self-limiting enteritis r clitis; fd pisning 2) Onset and Duratin f Pain Hw des the pain cme abut? Hw lng des it last? Hw des it fade away? Gradually r suddenly? Sudden: - Perfratin peptic ulcer - Rupture AAA - Infarctin MI - Mesenteric cclusin Rapidly Accelerating: - Clicky syndrmes - Inflammatin - Ischemia Gradual: - Inflammatin persist until underlying cause subsides - Obstructin nn-strangulated bwel bstructin, urinary retentin 17
26 3) Character and severity f Pain Describe the pain t me: Is it cntinuus r n and ff? Is it sharp r dull? Severity: Des it vary in severity? Hw did it prgress? Visceral: Dull and aching, can be clicky. Prly lcalized. (distentin r spasm f a hllw rgan) Parietal: Sharp and lcalized. (peritneal irritatin r spread f inflammatin t the parietal peritneum) Referred: Aching and perceived t be near the surface f the bdy Clicky: - Hyperperistalsis f smth muscle against a mechanical site bstructin f a muscular cnducting tube (bwels, ureter) prduces a cramping pain - The pain fluctuates in severity at frequent intervals and described as 'gripping' - The interval between buts helps lcate the cause: Shrt interval: Jejunum, Intermediate: Ileum, Lng: Cln - Muscular dysfunctin - GI mbility disrders (IBD) cause clicky pain but it's nt true clic. - Biliary/Renal clic: shrt peaks f pain which desn't reslve cmpletely in between exacerbatins Persistent: - Sharp, severe - Steadily increases in intensity - Suggests infectin r inflammatin Burning r Gnawing: - GERD and PUD 4) Radiatin Shulder Pain: - Diaphragmatic irritatin - Spleen - Perfrated ulcer r abscess Lin/Grin: - Renal clic 5) Shifting r Migratin Back: - Pancreatic pain - Ruptured r dissecting AAA - Peptic ulcer in psterir wall - Rectal (midline small f back) Uterine (midline small f back Scapula: - Gallbladder (Right) Periumbilical: - Small bwel - Appendicitis Did the pain shift frm its initial site? After hw lng? Did that increase r decrease its severity? Did it becme mre lcalized? Can yu pint ut the pint f maximal pain? 6) Timing (Tempral Sequence) Did yu d anything that may have initiated the pain? - Relatin t fd, meals, alchl r bwel mvements. Recent trauma? 7) Alleviating and Exacerbating Factrs Des anything increase r decrease the severity? Factr Relieves Exacerbates Mvement - Patients with Renal Clic r Breathing Stnes are restless and unable t lie still since they find n psitin cmfrtable Inflammatin: - Diffuse peritnitis (relieved by rest and flexin f knees) - Chlecystitis, Pancreatitis Fd - Dudenal Ulcer - Gastric Ulcer - Chlecystitis; Pancreatitis - Mesenteric Ischemia Sitting up, Leaning Frward - Pancreatitis - Vmiting - Visceral pain in intestinal bstructin (transient) - Gastric Ulcer pain - 18
27 8) Assciated Gastrintestinal Symptms Appetite and Anrexia: - Is it caused by a lack f desire t eat r apprehensin as eating always causes pain? Diet Weight Muth Ulcers (Crhn's, Celiac) Dysphagia and Odynphagia: - Slids, liquids r bth? List in chrnlgical rder - Level at which the fd sticks - Duratin, Onset and Prgressin Regurgitatin - What cmes up? If fd, is it digested r recgnizable and undigested? - Hw ften? Precipitating factrs? Flatulence (Belching) Water r Acid Brash Heartburn: - Burning sensatin behind the sternum caused by the reflux f acid int the esphagus - Hw ften des it ccur and what makes it happen, e.g. lying flat r bending ver? Dyspepsia: - Pain r discmfrt centered in the upper abdmen - 'Fat intlerance': nausea and abdminal fullness which is wrse after fatty r spicy meals. - Culd be Reflux, Ulcer r Dismtility-like Nausea and Vmiting: - Befre r after nset f pain? - Hw ften? Amunt, clr, smell? - Related t meals? Relieves symptms? - Is it recgnizable fd frm previus meals, digested fd, clear acidic fluid, bile-stained fluid r feculent? Hematemesis: - Fresh bld r ld, altered bld cffee grund' - Recent nse bleed? (They may be vmiting swallwed up bld) Indigestin r abdminal pain: - A term cmmnly used fr ill-defined symptms frm the upper GI tract Distensin: - Duratin and Prgressin - Is it cnstant r variable? (Functinal blating is fluctuating distensin that develps during the day and reslves vernight in IBS) - What factrs are assciated with any variatins? - Is it painful? (IBS) - Des it affect their breathing? - Is it relieved by belching, vmiting r defecatin? Altered Bwel Habits: nrmal frequency ranges frm 3 times daily t nce every 3 days. Cnstipatin: infrequent passage f hard stls - Lifelng r recent? - Hw ften d the bwels empty each week? Hw much time is spent straining? - Assciated abdminal pain, anal pain n defecatin r rectal bleeding? Diarrhea: frequent passage f lse stls - Is it acute, chrnic r intermittent? - Is there tenesmus, urgency r incntinence? Defecatin: - Clur: brwn, black, pale, white r silver? - Cnsistence: hard, sft r watery? - Size: bulky, pellets, string r tape like? - Specific gravity: des it flat r sink? - Smell? - Des it cntain mucus r slime? Melena: - Passage f tarry, shiny black stls with a characteristic dr and results frm upper GI bleeding Rectal Bleeding (hematchezia): - Amunt? bright r dark? - Bld may be mixed with stl, cat the surface f therwise nrmal stl, r be seen n the tilet paper r in the pan - Severe upper GI bleeding: bld may pass thrugh the intestine unaltered, causing fresh rectal bleeding - Anal pain? Flatus: - Mre than usual r unable t pass flatus? Prlapse and Incntinence: - Des anything cme ut f the anus n straining? Des it return spntaneusly r have t be pushed back? - Is the patient cntinent f feces and flatus? - Have they had any injuries r anal peratins in the past? Tenesmus: Unprductive desire t pass stl - Usually accmpanied by pain, cramping and invluntary straining effrts - Is it true Tenesmus r nly due t fear f pain? Change f Skin clr r jaundice: - Duratin - Assciated with itching, stl r urine clr changes? 19
28 9) Review f Systems: DDx General Urinary Gyneclgical Neurlgical Respiratry and Cardiac Fever Dysuria Menstrual Fainting r Cugh - any inflamed rgan, high Plyuria pattern: last Dizziness - Symptms f grade if there is Hematuria perid, regularity Altered pneumnia: RUQ perfratin Ncturia Cntraceptives mental pain + cugh + Chills r Rigrs Slw flw, Sexual Hx status fever - Chlangitis; hesitancy r Pregnancies: Vertig Palpitatins Chledclithiasis dribbling nrmal r ectpic Headaches SOB Sweating r thirst Urine Clr Previus Chest pain Arthralgias, weakness, changes gyneclgical r - Symptms f fatigue Pruritis tubal surgeries thracic disease Masses r Lumps recently Ankle Mid-cycle pain nticed in the abdmen r grin? Swelling Vaginal bleeding Dehydratin Anemia Symptms 10) Past Medical, Family and Surgical Histry Chrnic diseases: - Hypertensin - Hyperchlesteremia - GI Diseases - Cardivascular Diseases: Risk f abdminal vascular disease (AAA, mesenteric ischemia) - Diabetes Predispses t mycardial ischemia and sepsis and may mask abdminal pain - Cancer Hx Risk f bwel bstructin and perfratin frm recurrence. - Immune diseases - Liver diseases r prtal hypertensin - Thyrid dyfunctin - Bld disrders - Neurlgical r neurmuscular disrders (GI dysmtility) 11) Medicatins Recent Dietary Hx: fd-brne illness Past Hx - Similar cnditin r symptms - Recent infectins - Previus radiatin r chemtherapy - Previus Bld transfusins Previus prcedures: endscpy; ERCP; clnscpy etc Previus Surgeries: - Adhesins may lead t intestinal bstructin - Previus remval f any rgan excludes it frm cnsideratin Family Hx - Cancer - Chrnic diseases - Celiac disease r IBD 12) Scial NSAIDs: - Risk f peptic ulcer Crticsterids: - May mask signs f inflammatin (fever, peritneal irritatin) Antibitics: - May decrease the pain in pts with peritnitis due t partial treatment. - Als, if a patient has diarrhea suspect ABinduced pseudmembranus clitis. OCP Statins Vitamins and supplements Smking (heartburn, PUD, Crhn's, GI malignancies) Travel Hx Alchl (heartburn, dyspepsia, nausea, diarrhea, chrnic liver disease) Sexual Hx Drug use Obesity Dietary Hx: fiber r fat rich; any fd intlerance Allergies Recent stressrs 20
29 Abdmen Physical Examinatin Always Remember: Intrduce yurself, explain the exam briefly and ask fr permissin. Ensure privacy, warmth and gd lighting. Wash yur hands befre yu start. Expsure: Ideally frm the nipples t the knees, but t preserve dignity, frm the cstal margin t the grin. Psitin f The Patient: - Supine with the head rested n a pillw (~15 ) t relax the abdminal muscles and the arms shuld be n the side. If the abdminal muscles still aren't relaxed, ask the patient t flex their knees Psitin f The Examiner: - Stand at the patient's right the whle time, except during initial inspectin, stand at the ft f the bed. - During palpatin: yu shuld SIT r kneel dwn beside the bed. General Inspectin General Apperance - C, O, A (imprtant fr hepatic encephalpathy) - Is the patient in pain r distressed? (shallw breathing, hyperventilatin, etc) - Cachectic r bese - Obvius Pallr r Jaundice - Obvius tubes r drains - Mving r Lying still; Itching; Sweating; Rigrs Vital Signs + BMI - Pulse, BP, RR, and Temperature. - Measure the weight and height then calculate the BMI, yu may als measure the waist circumference Peripheral Examinatin Hands - Nails: Clubbing (IBD) Kilnychia (ID anemia) Leuknychia (hypalbuminemia, prtein malnutritin, malabsrptin, nephrtic syndrme) - Temperature - Palmar Erythema; Dupuytren's Cntracture (alchlic liver disease) - Tremr: Asterixis - Frearm: bruising, tatts, IVDU signs, fistulae, hair distributin Head and Face - Eyes: Cnjuctival Pallr Scleral Icterus Crneal Arcus Keiser-Fleischer Ring (slit lamp examinatin) Xanthelesma - Muth: Hydratin Cyansis Ulcers r Angular Stmatitis (ID anemia) Tngue: Glssitis (B12 deficiency); Beefy tngue Pr dentitin r Caries - Obvius Smells: Fetr Hepaticus, Alchl, Uremia, r Ketnes - Pallr r Jaundice - Partid gland swelling (alchl) Neck - Supraclavicular LN: Virchw s nde metastatic tumr t Lt supraclavicular nde (classically due t gastric cancer) - JVP: elevated in HF (suggests cause f hepatic cngestin) - Axillary - Inguinal Lymph Ndes Chest and Gnads - Spider Naevi - Gynecmastria and testicular atrphy in men - Breast Atrphy - Hair lss (axillary and pubic) 21
30 Abdminal Inspectin and Examinatin: Inspectin - Frm the ft f the bed, cmment n: Symmetry Shape f The Abdmen (Scaphid, Distended, Flat, Full flanks) Abdminal mvement with respiratin Shape and Site f The Umbilicus - Frm the Rt side f the patient, cmment n: Any masses, hernias r bulges, Sister Mary Jseph Ndule 5Ss: Scars; Striae; Stmas; Sinuses; Scratch marks Disclratin r bruises; Dilated veins r Caput Medusae; Hair lss 2 Ps: Visible Pulsatin r Peristalsis - Perfrm 3 Maneuvers: Cugh Impulse Cugh Tenderness (Dunphy's Sign: increased abdminal pain n cughing) Divaricatin f Recti Palpatin Remember t: - Warm yur hands, ask fr permissin and Maintain EYE CONTACT. - Ask fr a chair and sit r kneel dwn at the Rt side f the patient - The whle hand shuld rest n the abdmen by keeping the hand and frearm hrizntal, in the same plane as the frnt f the abdmen - Ask if there is any pain, begin the exam away frm the area f maximum tenderness Superficial Palpatin - Start at RIF (r mst distal site t pain) and mve systemically arund all 9 regins - Dne t gain the cnfidence f the patient - Cmment n: Tne f abdminal muscles and guarding, tested thrugh light, dipping mvements with the fingers. Superfical Tenderness Superficial masses. If a mass is fund then yu must cmment n it. Deep Palpatin - Repeat the exam with deeper palpatin - Cmment n: Deep Tenderness Deep masses. A mass in a particular abdminal quadrant suggests a specific diagnsis. Rebund tenderness: - Tenderness that ccurs when the examining hand is quickly remved frm the abdminal wall (the sudden withdrawal f manual pressure). It is indicative f acute peritneal irritatin. It culd als be assessed by the patient s respnse t light percussin. 22
31 Palpatin f The Nrmal Slid Viscera 1) The Liver - Place yur Rt hand transversely and flat n the skin f the RIF. Ask the patient t breathe in deeply thrugh the muth and feel fr the liver edge as it descends n inspiratin. Mve yur hand prgressively up the abdmen, 1 cm at a time, between each breath the patient takes, until yu reach the cstal margin r detect the liver edge. - A nrmal edge is smth and smetimes slightly tender if palpated. - Describe the size and surface (smth/ndular) f the liver if palpable, its cnsistency and tenderness. - Percuss fr the upper edge f the liver starting at the middle f the clavicle until yu find dullness. Measure the liver span, it is nrmally 6-12 cm. It may be diminished in a patient with cirrhsis whereas hepatmegaly is detected in hepatic cngestin (due t HF), NAFLD and chlestatic frms f cirrhsis. 2) The Spleen - Start at the RIF and, using the same methd used t palpate the liver, mve diagnally twards the Lt 10 th rib. - If yu cannt feel the splenic edge, ask the patient t rll twards yu and n t his right side and repeat the abve. Palpate with yur right hand, placing yur left hand behind the patient s left lwer ribs, pulling the ribcage frward. - Percuss ver the lateral chest wall (ver 9 th, 10 th and 11 th ribs, midaxillary line) t cnfirm r exclude the presence f splenic dullness. - A palpable spleen tip is highly suggestive f prtal hypertensin in patients with chrnic liver disease. 3) The Kidneys - Place yur Lt hand behind the patient s back belw the lwer ribs and yur Rt hand anterirly n the right side f the abdmen just belw the level f the ASIS. As the patient breathes in and ut, palpate the lin between bth hands. - Feel fr the lwer ple f the kidney mving dwn between yur hands. If this happens, gently push the kidney back and frwards between yur tw hands t demnstrate its mbility. This is balltting, and cnfirms that this structure is the kidney. - Ask the patient t sit up. Palpate the renal angle (between the spine and 12th rib psterirly). - With mderate frce, firmly strike the renal angle nce with the ulnar aspect f yur clsed fist after warning the patient. Nte any discmfrt. - Repeat this n the Lt side. - Percussin f the kidneys is unhelpful. Percuss fr the bladder ver a resnant area in the upper abdmen in the midline and then dwn twards the symphysis pubis. A change t a dull percussin nte indicates the upper brder f the bladder. 23
32 Percussin General percussin ver the 9 regins f the abdmen Test Fr Ascites: Shifting Dullness - Percuss frm the midline (mst resnant area) t the flanks. Nte any change frm resnant t dull. Keep yur finger n the site f dullness in the flank and ask the patient t turn t the ppsite side. Pause fr 10 secnds t allw any ascites t gravitate, then percuss again. - If the area f dullness is nw resnant, shifting dullness is present, indicating ascites. Fluid Thrill - Ask the patient t place the edge f their hand n the midline f the abdmen and place the palm f yur left hand flat against the left side f the patient s abdmen and flick a finger f yur right hand against the right side f the abdmen. - If yu still feel a ripple against yur left hand, a fluid thrill is present (nly detected in grss ascites). Auscultatin Bwel Sunds - Nrmal bwel sunds are lw-pitched gurgles which ccur every few secnds. - Listen at the Rt f the umbilicus fr up t 2 minutes befre cncluding that bwel sunds are absent Bruits (mst imprtant) - Abve the umbilicus at the arta cm abve and lateral t the umbilicus fr bruits frm renal artery stensis. - Listen ver the liver fr bruits Frictin Rubs - Splenic - Hepatic Venus Hum - Over dilated veins Succussin Splash - It sunds like a half-filled water bttle being shaken. Explain the prcedure t the patient, then shake the patient s abdmen by lifting him with bth hands under his pelvis. - An audible splash indicates gastric utlet bstructin r gastric paresis. The patient must nt have eaten anything fr the past 4 hurs. After perfrming the abdminal examinatin, yu must mentin that yu want t examine the fllwing: Hernia rifices Femral pulses Examine the inguinal lymph ndes Genitalia Anal canal and rectum Gyneclgic examinatin Lwer limbs fr edema and Pyderma gangrensum (IBD) Nte that, in sme bks, the examinatin sequence is inspectin, auscultatin, percussin and then palpatin as palpatin may interfere with bwel sunds. But this is nly imprtant in cases f intestinal bstructin. 24
33 Special Signs Psas Sign - Pain in the lwer abdmen and psas regin that is elicited when the thigh is flexed against resistance. - It suggests that an inflammatry prcess, such as appendicitis r perinephric abscess, is in cntact with the psas muscle. Obturatr Sign - Pain elicited when the thigh is flexed and then rtated internally and externally. - It suggests an inflammatry prcess in the regin f the bturatr muscle, such as an bturatr hernia. Als seen in patients with appendicitis/pelvic abscess Rvsing s Sign - Palpatin f the LLQ resulting in pain in the RLQ. Seen in appendicitis McBurney s Sign - Tenderness at McBurney s pint (1/3 rd the distance frm the ASIS t the umbilicus n a line cnnecting the tw) - Seen in patients with appendicitis Murphy's Sign - Elicited by palpating the RUQ during inspiratin: As the gallbladder descends during inspiratin, acute pain is elicited, and inspiratin halts. - It suggests acute chlecystitis. Bas Sign - Hperaesthesia in the regin f the Right subscapula resulting frm chlelithiasis. Cugh Tenderness (Duphny's Sign) - Occurs in the area f maximum tenderness when the patient cughs. The tenderness may als be elicited by shaking the patient r by any ther sudden jarring mvement. Ecchymsis - Culd be in the flank, periumbilical regin, r back and suggests a retrperitneal hemrrhage. (Grey Turner, Cullen and Fx signs) - Pssible causes include trauma, acute hemrrhagic pancreatitis, a leaking abdminal artic aneurysm, and intestinal gangrene. Kehr s Sign - Severe Lt shulder pain - Seen in patients with splenic rupture (as a result f referred pain frm diaphragmatic irritatin) 25
34 Biliary Disease Histry Taking Patient Prfile: Age is usually 30-60, F > M Chief Cmplaint: Abdminal Pain 1. SOCRATES Acute Chlecystitis Biliary clic Chrnic Chlecystitis Acute Chlangitis Due t prlnged r GB cntracts and presses recurrent cystic duct a stne against the blckage leading t ttal utlet r cystic duct bstructin pening - Lasts > 6 hurs - Occurs as severe, sudden, cntinuus pain that reaches a plateau then diminishes gradually - RUQ, radiates t the back and the tip f the Rt scapula - Increased by mvement r breathing and eating fatty meals - Relieved by analgesics. - Assciated with N, V, lwgrade fever and anrexia - Obstructive jaundice: pale stl, dark urine, pruritus. - Cmes in distinct attacks lasting 30 minutes t several hurs - Sudden, deep and gnawing, severe, cnstant, excruciating exacerbatins that may cause the patient t restrict breathing - Desn t remit between buts - RUQ r epigastric, may radiate t the back - Assciated with N and V - Exacerbated by eating fatty meals, awakens patient frm sleep - Nt relieved by analgesics Results frm mechanical irritatin r recurrent attacks f acute chlecystitis leading t fibrsis and thickening f the GB - Begins minutes after a meal and lasts minutes - Indigestin-like and gradual - Usually epigastric, nly mves ver t RUQ when severe - Assciated with eating, (especially fatty meals), belching, dyspepsia, N and V nly in acute exacerbatins - Relieved by analgesics. - Irregular attacks that last fr weeks/mnths with pain free intervals. When a stne becmes impacted in the biliary r hepatic ducts and causes dilatin f the bstructed duct and bacterial superinfectin - Vague, RUQ Pain - Chills and Rigrs, jaundice - Cnfusin and hyptensin can ccur in patients with suppurative chlangitis - If septic shck develps, multirgan failure may be seen 2. Assciated Symptms Gastrintestinal Appetite Masses nticed in Weight abdmen Dyspepsia and Jaundice: Flatulence - Duratin, first symptm, Nausea, Vmiting where is it mst prminent, Altered Bwel is it cnstant, hw has it Habits prgressed? Defecatin: - Itching, Urine r stl clr - Offensive, pale, changes? flating stls that wn't flush Distensin Other Symptms Fever Cancer Symptms: lss f - Chlecystitis (lw appetite, weight lss, altered grade) bwel habits, paleness, Chills r Rigrs tiredness, buts f back pain - Chlangitis; Lethargy r cma Chledclithiasis - Abscess under pressure Sweating Flu-like symptms preceding Dehydratin jaundice (EBV) Dyspnea 3. Medical Histry Same cnditin? Previus admissin? Chrnic GI Diseases DM, HTN 4. Family Histry 5. Medicatins OCP DM medicatins TPN Lipid lwering agents 6. Scial Histry Travel Alchl Smking Bld transfusins Multisexuality 7. Surgeries and Prcedures Endscpy, ERCP Truncal vagtmy (PUD), terminal ileum resectin, bypass 26
35 Biliary Disease Physical Examinatin General Appearance: - Distress - Pattern f breathing: (shallw in acute chlecystitis) - 5Fs - Rigrs - Jaundice - Sweating: acute - Mvement: lying still and unable t mve? Vital Signs - Temperature: Pyrexia (late acute chlecystitis) - Heart rate: Signs f tachycardia Inspectin: - Abdminal mvement with respiratin, Cugh tenderness, Fullness in RH Palpatin: - Tenderness in the RH: palpate just belw tip f 9 th cstal cartilage - Guarding almst always fund - Murphy's sign: ask the patient t inspire deeply while palpating the area f the gallbladder fssa just beneath the liver edge. Deep inspiratin causes the gallbladder t descend tward and press against the examining fingers, which in patients with acute chlecystitis cmmnly leads t increased discmfrt and the patient catching his r her breath. - Ba's sign: as pain radiates t tip f scapula, the affected dermatme may be hyperaesthetic. - A palpable mass culd be: 1. The Gallbladder: may be fund during early stages, befre guarding 2. Empyema (Abscess): A very tender inflammatry mass, mves little with respiratin, fund at a later stage (after several days f inflammatin). 3. Muccele: an verdistended gallbladder filled with mucid r clear and watery cntent. Nn-inflammatry and results frm utlet bstructin (cmmnly caused by an impacted stne in the neck f the gallbladder r in the cystic duct) Percussin - Detects inflammatry masses when guarding impedes palpatin (dullness under the cstal margin) Auscultatin: - Bwel sunds shuld be present unless infectin spreads and causes peritnitis Mentin that yu'd like t perfrm: Gyneclgical and pelvic exams, PR, Check the Pulses Cmplicatins : Patients with cmplicatins may have signs f sepsis (gangrene), generalized peritnitis (perfratin), abdminal crepitus (emphysematus chlecystitis), r bwel bstructin (gallstne ileus) Investigatins: CBC: - Leukcytsis (a left shift) Electrlytes and Enzyme levels: - Elevatin in the serum ttal bilirubin and alkaline phsphatase cncentratins in cmplicated cnditins such as chlangitis, chledchlithiasis, r Mirizzi syndrme. Nuclear chlescintigraphy (HIDA): - In cases in which the diagnsis remains uncertain after ultrasngraphy. Ultrasngraphy: - Usually the first test btained and can ften establish the diagnsis. - Sngraphic features f Chlecystitis include: The presence f stnes in the gallbladder Gallbladder wall thickening r edema A Sngraphic Murphy's sign: the psitive respnse is bserved during palpatin with the ultrasund transducer. MRCP; ERCP (chledchlithiasis; chlangitis) CT 27
36 Acute Appendicitis Histry Taking Patient's Prfile; Chief Cmplaint: Abdminal Pain in the RIF + duratin Histry f Present Illness: Pain: Site, Character and Severity Onset, duratin and ffset Radiatin Timing Exacerbating and relieving factrs Assciated With Unusual presentatins Initially: Shifting: - Initially it's a prgressive, persistent midabdminal (epigastric) discmfrt (visceral pain) - Once the inflammatin extends t the parietal peritneum, the pain becmes sharp and lcalized at the RIF The pain usually shifts after 5-6 hurs but it smetimes takes 2 3 days The nset f symptms t time f presentatin is usually less than 24 hurs fr acute appendicitis and averages several hurs. Des the pain radiate anywhere? What d yu think may have initiated the pain? Peritneal irritatin is assciated with pain n mvement and cughing. Is it relieved by analgesics? Anrexia and lss f appetite, precede pain Cnstipatin: present a few days befre A lw-grade fever (<38.5 C) the pain but a few cmplain f diarrhea Nausea and Vmiting: after the nset f Fever, rigrs and sweating: indicate an pain abscess r generalized peritnitis Retrcecal Appendix: Pelvic appendix: - Desn't cause signs f peritnitis as it may - Can present with urinary symptms such be separated frm the anterir abdminal as urinary frequency and dysuria. peritneum. Irritatin f adjacent - Or it may present with rectal symptms, structures can cause diarrhea, urinary such as tenesmus and diarrhea. frequency, pyuria, r micrscpic - A pre r pst-ileal appendix may present hematuria depending n lcatin. with symptms f intestinal bstructin Other Symptms and DDx: Peptic Ulcer Disease: - Ask abut epigastric pain, related t fd and assciated with heartburn, NSAID use Gyneclgic: - Menstrual irregularities, vaginal discharge (PID). Last menstrual perid (pregnancy). Nte that appendicitis during pregnancy may present as pain in the RUQ. Intestinal bstructin: - Distensin, cnstipatin and inability t pass flatus Urinary: - Ask abut dysuria/ply/hematuria Mesenteric Adenitis: - Was the pain preceded by an URTI? Inferir Epigastric Artery Rupture - Causes hematma: Pain + swelling in the RIF r LIF Past Medical and Surgical Histry Family Histry Medicatins Scial Histry Investigatins: - CBC: leukcytsis (left shift) and neutrphilia - Urinalysis: Pyuria, albuminuria, and hematuria - C-Reactive Prtein - Electrlytes (may be abnrmal due t dehydratin and Vmiting)and a pregnancy test (hcg) are ptinal - Ultrasund: mst useful in wmen f childbearing age and in children - CT scan: superir t U/S, highly sensitive and specific - MRI: pregnant patient whse appendix is nt visualized n U/S 28
37 Acute Appendicitis Physical Examinatin General Appearance: - Distress: lk unwell with flushed cheeks - Pattern f breathing Vital Signs - Lw-grade pyrexia (If high: suggests general peritnitis and a ruptured appendix) - Sweating, Rigrs (peritnitis) - Mvement: lying still and unable t mve? - Fetr ris - Heart rate: pulse rate is usually elevated and rises as the infectin spreads Inspectin f Abdmen: - May be slightly distended. Cmment n abdminal mvement with respiratin. Cugh tenderness. The right hip may be kept slightly flexed if the appendix lies against the psas majr. Palpatin: Tenderness and Guarding: The right iliac fssa (nrmally) Retrcecal appendix: Lateral part f the lumbar regin (the flank), may nt exhibit marked lcalized tenderness in the RIF Subhepatic: Belw the right cstal margin McBurney s Pint: - It is classically the maximum site f tenderness and must be carefully assessed by gentle palpatin. - Tw thirds f the distance frm the umbilicus t the ASIS. A palpable mass: - Uncmmn in the RIF, may suggest a periappendiceal abscess r phlegmn - An appendix mass: usually takes a few days t develp. A tender, indistinct mass felt in the RIF, It is usually impssible t feel belw it because it is fixed psterirly. Dull t percussin. - An appendix abscess: swinging fever and a very tender mass that may fluctuate in late stages and cause edema r reddening f verlying skin. Rsving's Sign: - Pressure n the LIF may cause pain in the RIF. Rebund Tenderness (in RIF) The Obturatr Sign: - While the patient is supine with the knee and hip flexed, the hip is internally and externally rtated. Hypgastric pain indicates that the appendix lies against the bturatr muscle. The Ilpsas Sign: - The patient shuld lie n their left side. With the knee flexed, the thigh is hyperextended. The test is psitive if the patient experiences pain n the right side with this maneuver. Percussin - Causes pain if peritnitis is present. Dullness suggests an underlying mass bscured by guarding. Auscultatin: - Bwel sunds are present unless perfratin and general peritnitis have caused a paralytic ileus. Mentin that yu'd like t perfrm: Gyneclgical and pelvic exams, PR (nt very useful), Check pulses. Cmplicatins : Perfratin is accmpanied by severe pain, fever, tachycardia and generalized peritnitis. Intra-abdminal and pelvic abscesses ccur with perfratin. Culd becme gangrenus. Chrnic Appendicitis: Tw frms f chrnic inflammatin may develp in the appendix: The Muccele and the Empyema. Fllw recurrent acute appendicitis attacks and cause RIF pain that may be clicky. Wrms and fecliths may prduce similar symptms. 29
38 Pancreatitis Histry Taking Patient's Prfile: Age is usually Chief Cmplaint: Epigastric Pain that radiates t the back Histry f Present Illness: Pain: Site, Character and Severity Onset, duratin and ffset Radiatin Timing Exacerbating and relieving factrs Assciated With - Epigastric (in the upper abdmen). It is severe, dull, gnawing and persistently aching. - Gallstne pancreatitis: pain is well lcalized and the nset f pain is rapid (reaches maximum intensity in minutes). - Pancreatitis due t hereditary r metablic causes r alchl: The nset f pain may be less abrupt and the pain may be prly lcalized Sudden nset with severity gradually increasing. The pain lasts days. Its nset is rapid, but nt as abrupt as that with a perfrated viscus Band-like radiatin t mid back, Pancreatic cancer: radiatin t the LH (tumr at the head) r RH (tumr at the tail) What d yu think may have initiated the pain? Eating a large meal r drinking alchl? Des it increase at night (cancer)? D mvement and lying supine increase it? Usually there are n alleviating factrs but bending frward while sitting may relieve it slightly Vmiting: Frequency, clr, smell, amunt and cntent. Any invluntary effrts t vmit withut fruitful vmiting? Nausea: persistent between vmting attacks Dizziness Restlessness and agitatin Patients with fulminant attacks may present in shck r cma Jaundice: Cancer r Chrnic pancreatitis Inability t take full breaths and dyspnea? (diaphragmatic inflammatin secndary t pancreatitis, pleural effusins, r ARDS) Steatrrhea: Fatty and frthy stl that desn't flush (chrnic, cancer) Muscle cramps r spasms (hypcalcemia), in severe cases nly Weight lss: Cancer r Chrnic Other Symptms and DDx: Gallbladder Disease: - Flatulence, dyspepsia, jaundice - Past Hx f biliary tree disease: previus attack f upper indigestin like abdminal pain with flatulence and belching, r jaundice? Other GI Symptms Urinary Symptms Gyneclgic Symptms Pancreatic cancer: - The pain is incessant and bring, accmpanied by gastric discmfrt, anrexia and weight lss - Steatrrhea, epigastric blating, flatulence, altered bwel habits - Vmiting - Obstructive Jaundice: Pale stls, dark urine, itching - Respiratry Symptms (metastasis) Past Medical and Surgical Histry - Previus attacks? Frequency? (2-3 times a year indicate chrnic pancreatitis) - Surgeries: Pancreas, stmach, heart? - Previus Prcedures: Recent ERCP? - Chrnic Diseases: DM; Hyperparathyridism; Hyperlipidemia (increased LDH) Medicatins - OCPs - Diuretics - Crticsterids - AB (tetracycline) - Chemtherapy - Opiate analgesics Scial Histry - Alchl - Smking - Scrpin sting (very rare) - Cntact with a persn that has mumps Family Histry - Of same cnditin 30
39 Pancreatitis Physical Examinatin General Appearance: - Distress - Pattern f breathing: Shallw - If respiratin is impaired: the patient appears apprehensive, dyspnic and cyansed - Pale and Sweating (indicate hypvlemia) - Mvement: the patient lies still - Jaundice: if the cause is a stne ldged in the lwer end f the bile duct r if edema in the head f the pancreas cmpresses it Vital Signs - Temperature: nt usually elevated - Heart rate: Tachycardia - BP: if the patient has becme hypvlemic, the JVP and bld pressure may be lw Inspectin f Abdmen: - Cmment n abdminal mvement with respiratin (usually nne as pain is severe and the tne f the muscles increases). Cugh tenderness. Distentin may be present. Grey Turner and Cullen's Signs: bruising r disclratin in the left flank r periumbilical regin respectively. Thse are late and rare signs that indicate extensive destructin f the gland due t retrperitneal hemrrhage (very severe haemrrhagic pancreatitis). Palpatin: Tenderness and Guarding in the upper abdmen. Pseudcyst: A cllectin f inflammatry exudates that develps in the lesser sac and This is initially suggested by fullness in the epigastrium,which may becme a mre prminent mass if a pseudcyst r abscess develps. Percussin: May cause pain. Dullness may be fund ver a develping pseudcyst. Auscultatin: Bwel sunds present in the first hrs but fade away if a paralytic ileus develps. Mentin that yu'd like t perfrm: Gyneclgical and pelvic exams, PR, Check pulses and LN. Ntes: Yu may find: Hepatmegaly in patients with alchlic pancreatitis, xanthmas in hyperlipidemic pancreatitis, and partid swelling in patients with mumps. Any patient with severe pain but minimal abdminal signs may have acute pancreatitis. Carcinma f the head f the pancreas: Obstructive jaundice, a palpable gallbladder and an enlarged liver. In the early stages there are barely any physical signs. Chrnic pancreatitis can cause thrmbsis f the prtal vein (signs f prtal HTN will be present). There are ften few physical signs. Patients ften lk distraught and disheveled. Assciated with DM. Investigatins (acute pancreatitis): Serum amylase and lipase: elevated ALT: >3x (gallstne pancreatitis) CRP: elevated CBC: leukcytsis Hematcrit: Elevated LFT: increased bilirubin Abdminal X Ray: unremarkable findings in mild Abdminal US: appears diffusely enlarged and hypechic Abdminal CT MRI: higher sensitivity than CT MRCP r ERCP: chledchlithiasis 31
40 Diverticulitis Histry and Examinatin - A diverticulum is a sac-like prtrusin f the clnic wall. Uncmplicated diverticulsis is ften asymptmatic and an incidental finding n clnscpy r sigmidscpy. Sme patients cmplain f cramping, blating, flatulence, and irregular defecatin. - Acute diverticulitis is an inflammatin due t micrperfratin f a diverticulum. It is either simple r cmplicated. Cmplicatins include: bwel bstructin, abscess, fistula, r perfratin. Patient's Prfile: Age is usually Chief Cmplaint: usually presents as abdminal pain in the LLQ Histry f Present Illness: Pain: Site, Character, Shifting and Severity Onset, duratin and ffset Radiatin Timing Exacerbating and relieving factrs Assciated With - The first symptm is ften a mild intermittent lwer abdminal pain which then shifts t the left iliac fssa where it becmes a mre cnstant ache. The pain begins gradually befre becming mre severe and cnstant. The pain is usually in the left lwer quadrant due t invlvement f the sigmid cln. - Much less cmmnly, right-sided (cecal) diverticulitis which has a higher incidence in Asian ppulatins. Pain is usually cnstant and is ften present fr several days prir t presentatin May radiate t the suprapubic area, left grin, r back Sme patients can relate their attacks t the type f fd they have eaten Des anything increase r decrease the pain? Fever: lw grade Altered bwel habits: Mst patients are cnstipated but a few develp diarrhea Nausea Vmiting: rare Lss f appetite Hematchezia: rare Generalized peritnitis: rare and results if diverticular perfratin leads t widespread fecal cntaminatin Urinary urgency: if the cln lies against the vault f the bladder and the bladder wall becmes inflamed, there may be increased frequency f and painful micturitin. Other Symptms and DDx: Generalized Symptms GI Symptms Urinary and Gyneclgic Symptms Past Medical and Surgical Histry - Previus episdes f similar pain - Hx f chrnic diverticular disease, flatulence, distensin and LIF pain. Medicatins, Scial Hx, Family Hx Physical Examinatin: - The mst cmmn finding is lcalized left-lwer-quadrant tenderness. The finding f a mass suggests an abscess r phlegmn (tender, sausage-shaped). Distentin may be present. The patient lies still, is tachycardic and pyrexic. Reversed Rsving's sign may be present. - Patients may have lcalized peritneal signs (guarding, rigidity, and rebund tenderness). - PR: mass r tenderness with a distal sigmid abscess. Stl may be psitive fr ccult bld. Investigatin: - Evaluatin by CT scan and cmplete bld cunt (CBC) is the standard f care. Neither sigmidscpy nr cntrast enema is recmmended because f the risk f perfratin r barium r fecal peritnitis. 32
41 Intestinal Obstructin Histry Taking Patient's Prfile; Chief Cmplaint: Pain; Vmiting; Distensin; Abslute cnstipatin that either present abruptly r are intermittent and reslve nly t recur again. Histry f Present Illness: Pain: Site, Character and Severity Onset, duratin and ffset Radiatin Timing Exacerbating and relieving factrs Assciated With - True clic. It ccurs as a severe central griping pain interspersed with perids f little r n pain. - Small bwel clic is felt at the center f the abdmen whereas large bwel clic is felt at the lwer 1/3 rd f the abdmen. - Small bwel clic ccurs every 2 20 minutes, depending n the level f bstructin - Large bwel clic ccurs abut every 30 minutes r mre Des it radiate anywhere? What d yu think may have initiated the pain? Des anything increase r decrease the pain? Vmiting: Clr, amunt, smell, bld - Relatin t meals? Relieves symptms? - Pylric bstructin: Watery, Acidic - High small-bwel: bile stained - Belw middle f small bwel: feculent - Prximal: earlier presentatin and mre prminent than distal. It can be relatively severe and s patients may cease taking in fd r liquids rally. Abdminal Distentin (The lwer the site f the bstructin, the mre bwel there is available t distend). - High bstructins are nt assciated with distensin (Dudenum r Jejunum: nt prminent, Lwer level: mre prminent) - Patients may state that pants r belts are nt fitting prperly Diarrhea: in sme cases, in partial bstructin r intermittent: clses fr a while then pens evacuating all f the cntents Cnstipatin: duratin, stl changes, bld, mucus, any anal pain? - Mre distal bstructins present with cnstipatin earlier - Cmplete: neither faeces nr flatus are passed. This ccurs early in lwer large bwel bstructins and late in high small bwel bstructins. Changes in the patient's caliber f stls: strngly suggest carcinma especially if accmpanied by weight lss Symptms f strangulatin: - Pain - Fever - Tachycardia - Tachypnea Symptms f dehydratin if there's excessive vmiting RF: Paralytic Ileus: - Prir abdminal r pelvic surgery, Intestinal inflammatin, trauma r spinal injuries. - Stress: sepsis and burns, Vascular: shck, Drugs: narctics and antichlinergic, Metablic: Renal failiure. Abdminal wall r grin hernia Adhesins: abdminal scar Malignancy Intussusceptin r Vlvulus Past Medical and Surgical Histry - Hx f chrnic cnstipatin, lng-term cathartic use, and straining at stls: diverticulitis r ca - Hx f recurrent left LLQ pain ver several years: diverticulitis, a diverticular stricture - Hx f artic surgery: ischemic stricture - Pneumaturia, mucinuria, r fecaluria: indicate fistulizatin f the sigmid cln t the bladder Medicatins, Scial Histry and Family Histry - Histry f freign bdy ingestin; gallstnes ROS: General; GI; Urinary and Gyne Symptms, as well as symptms f HF. 33
42 Intestinal Obstructin Physical Examinatin Physical Examinatin: - Perfrm a full abdminal examinatin, pay special attentin t: - Nte: sme references state that in cases f knwn r highly suspected intestinal bstructin, the auscultatin shuld be perfrmed first as palpatin may interfere with the bwel sunds. Inspectin: - Surgical Scars - Distentin - Visible peristalsis - A hallmark f small bwel bstructin is dehydratin, which manifests as tachycardia, rthstatic hyptensin, and reduced urine utput, and if severe, dry mucus membranes. - Fever may be assciated with infectin (eg, abscess) r ther cmplicatins f bstructin (ischemia, necrsis). Palpatin - Abdminal masses - Hernias - Signs f strangulatin: pain, tenderness, guarding, rebund. - Obstructin f the cln causes the cln t distend arund the periphery f the abdmen. The distensin then extends int the small bwel if the ilecaecal valve is incmpetent. If this valve remains cmpetent, the right side f the cln, especially the caecum, can becme grssly distended, causing a visible bulge in the right iliac fssa which is hyper-resnant. Percussin - Distentin f the bwel results in hyperresnance r tympany t percussin thrughut the abdmen. Hwever, fluid-filled lps will result in dullness. If percussin ver the liver is tympanitic rather than dull, it may be indicative f free intraabdminal air. Auscultatin: - The bwel sunds in a patient with mechanical bstructin are at first lud, frequent and bstructive in nature. As the bwel distends, the sunds becme mre resnant and high pitched ( tinkling sunds ), befre eventually becming amphteric. Digital rectal examinatin: - Shuld be perfrmed t identify fecal impactin r rectal mass as the surce f bstructin. - Grss r ccult bld may be related t intestinal tumr, ischemia, inflammatry mucsal injury, r intussusceptins. Investigatins: - Abdminal X-ray: cnfirms the Dx and site. Evidence f cmplicatins: ischemia, perfratin, fistula and fluid in the peritneal fluid may be detected. There are usually multiple air fluid levels. - Cntrast Studies: Ba meal is cntraindicated in the case f a partial bstructin and strangulatin. Ba enema is als cntraindicated in cases f strangulatin. - Endscpy: sigmidscpy and clnscpy are bth diagnstic and therapeutic. - Labs: CBC with differential and Elctrlytes: nt specific fr a diagnsis. Anemia suggests Crhn s disease, tumr, r Meckel s diverticulum. Serum phsphate decreases in strangulated IO. 34
43 Patient Prfile and Chief Cmplaint Histry f Present Illness: Dysphagia Histry Taking Duratin Onset Slids, liquids r bth? - Order them, which ccurred first At what level des the fd stick? Intermittent vs. Prgressive What d yu think caused this? Odynphagia - Site - Only n swallwing Cughing r Chking n swallwing - When? Is it ncturnal Chest Pain; SOB; Stridr Regurgitatin: - Undigested? Bad Smell? When? Symptms f metastasis Skin arund the lips r fingers feels tight? (sclersis) Previus Histry and Risk Factrs Dysphagia Timing: - Is it wrse ver the curse f the day? (Myasthenia Gravis) Prgressin f the symptms Alleviating r Exacerbating Factrs - Relieved by sitting frward? Assciated With Heartburn, belching, waterbrash Lump in the thrat (Glbus) Neck Bulge (Puch) Halitsis (Zencker) Weight Lss Appetite General weakness r mental status change Anemia Symptms: - Tngue sres - Tingling in the leg - SOB - Dizziness - Fatigue and Weakness Medical and Surgical Histry: - Previus esphageal disease - Previus Strke r Neurlgic Disease (Mysathenia Gravis, Bulbar Palsy) - HIV Family Histry: - Cancer Medicatins: - NSAIDs - Sterids - Irn Tablets (Plummer Vinsn) - Pills taken withut water Scial Histry: - Smking - Alchl - Diet 35
44 Histry f Fresh bld per rectum *** patient prfile: mst imprtantly the age& sex. *** chief cmpliant : bld per rectum + duratin. *** first f all yu have t knw the character f bld. The bld : **clr ( red (fresh), black (melena ), marn ). ** hw des it appear?? Mixed with the feces( mstly frm the sigmid cln ). On the surface f the feces. ( lwer sigmid, rectum, anal canal ) Separate frm the feces, either after r unrelated t defecatin. (bleeding fllwingdefecatinis prbably frm an anal cnditin Hemrrhid ), ( bld is passed by itselfin Diverticular disease, CA, IBD ),( it may cause by massive upper GI bleeding, ccasinally) On the tilet paper after cleaning( fissure, hemrrhid ). *** If there is any Pain?? ## SOCRATES it is very helpful t make a diagnsis Pain frm anal canal is felt principally n defecatin (splitting pain r tearing pain with anal fissure ). Hemrrhid and rectal cancer are nt painful usually. Lwer abdminal clic due t bstructin in the rectsigmid junctin ( like CA ). LLQ discmfrt with blating and cnstipatin /diarrhea. Histry f peptic ulcer disease r liver cirrhsis (massive Assciated symptms if there is peri-anal itching ( mucus leakage t the peri-anal skin as in hemrrhids if there is a feeling f smething cming ut f anus during defecatin and hw it is returned ( spntaneusly r manually ) as in incntinence and tenesmus ( change in the bwel first yu have t knw what he/she really means by that!!! (if it s due t CA, fear f pain in fissure r it s the cause f fissure ).
45 @diarrhea, again yu have t knw what he/she means by weight lss?? hw much and the nightsweats, fatigue, respiratry symptm as in TB ulcer in anal symptms f anemia. *** past medical (lng histry f unexplained anemia, cnstipatin ) *** surgical histry. *** Family histry: imprtant (UC,Crhn s disease,hnpcc, Plyps) *** Drug histry (NSAIDs, any drug that causes cirrhsis, abuse f antibitics as in pseudmembranus clitis). *** scial histry ( smking, alchlic,diet) GOOD LUCK
46
47
48 Examinatin f Inguinal hernia Always examine bth inguinal regins. This is a simplified versin f inguinal hernia examinatin (steps t d if it cmes as a statin, which is unlikely?). Ask the patient t stand up t see the true size f the hernia Lk frm frnt Cmment f: Size,site,shape Surface (smth, nt smth, redness in strangulated hernia) Visible cugh impulse Feel frm frnt Examine the scrtum fr epididymal cyst r hydrcele Is the lump a true hernia r a scrtal lump? If yu can feel the upper edge f the lump between yur thumb and index finger then it s scrtal lump, If yu can t then it s a hernia. Feel frm the side Nw yu have ruled ut a scrtal swelling. G t the side f the hernia and palpate fr: 1. Shape: pear shaped r hurglass shaped 2. Size 3. Psitin 4. Temperature: Ht indicates strangulatin 5. Tendernes: A strangulated hernia is tender t tuch, a strangulated hernia is nt painful unless yu push t hard 6. Expansile cugh impulse: Cmpress the lump firmly with yur fingers and ask the patient t cugh.presence f expansile cugh impulse is diagnstic fr hernia but its absence may indicate adhesins. 7. Cmpsitin Cnsistancy: (sft if cntains bwel and rubbery if cntains mentum) Fluctuatin: (fluctuant it cntains bwel, nnfluctuant it cntains mentum) Percuss: (resnant it s bwel, dull it s mentum) Auscultate bwl sunds Use a trch fr translucency 8. Reducibility
49 Reduce the lump t abdminal cavity If abve and medial t pubic tubercle it's inguinal hernia If bellw and lateral t the pubic tubercle then it's femral hernia If held reduceed by pressure n internal ring then it's indirect hernia If held reduced by pressure n external ring then it's direct hernia 9. Als yu can d internal ring test t differentiate between direct and indirect hernia: press n internal ring and ask him t cugh if yu feel the hernia then it s indirect. 10. Feel the ther side 11. Ask t examine the abdmen
50
51
52
53
54 Peripheral Arterial Disease Histry Taking Patient Prfile - Name and Sex: Males have a much higher risk - Age: usually > 50-60, but als in yunger pts with Buerger's r a traumatic cclusin f a majr artery r after an arterial emblism - Marital Status, Residence, Occupatin and Admissin Chief Cmplaint - Pain in the lwer limbs n walking since. Histry f Present Illness Claudicatin and Rest Pain Intermittent Claudicatin Rest Pain Site In a muscle: - Calf (mst cmmn) - Thigh In the mst distal part f the limb, mainly the tes and freft. If there's gangrene, pain is felt at the junctin f living-dead tissues. - Buttck - Ft - Upper limb and frearm Onset Begins insidiusly Cntinuus Character Cramping-like, begins as aching then becmes tearing. Burning r aching and unremitting. Radiatin Des it g anywhere else? Timing ONLY develps when the muscle is exercised and Present at rest during day and night. must disappear gradually when the exercise stps. Exacerbating - Exercising the muscle - Mvement and Pressure: pts sit in bed with knees factrs Claudicatin distance? bent and ft held Relieving factrs Prgressin Assciated with Hw did this distance change ver time? - Stpping the exercise and resting. - Sme pts frce themselves t cntinue walking t fade ut the pain. - Walking slwly may prevent it. Time taken fr pain t g away? Can yu walk the same distance after? - The Claudicatin distance gradually shrtens ver a few mnths befre the patient becmes static. - May increase as the cllateral circulatin develps. - Imptence: cclusin at artic bifurcatin (Leriche's syndrme) - Numbness and Parasthesia in the skin f the ft (bld shunted frm skin t muscle) - Symptms f Arterial Insufficiency - Elevatin r supine psitin f the limb - By putting the leg belw the level f the heart: pts usually hang legs ver the side f the bed r sleep sitting n a chair - Strng analgesic drugs. - Gets steadily wrse - Symptms f Arterial Insufficiency Severity Usually frces the pt t stp walking Very severe, prevents the patient frm sleeping Cause Inadequate bld flw t the muscles Critical Ischemia 36
55 Gangrene - Take a shrt histry f the gangrene (mentined later n) - Lcatin f the tissue lss - Histry f lcal trauma - Evidence f infectin (fevers, purulent drainage, lcal pain) - Hw lng it has been present Ulceratin - Take a shrt histry f the ulcer (mentined later n) Assciated Symptms - Ask abut the Symptms f Acute Ischemia (culd ccur due t an acute arterial thrmbsis in pts that previusly experienced symptms f chrnic ischemia) Pain: Usually very severe and f sudden nset Parasthesia: Develps ver a few hurs Paralysis Pallr Perishingly Cld t tuch - Cardipulmnary Symptms: Chest Pain, weakness r paresthesia in the UL? Dyspnea Palpitatin Syncpe Edema - Neurlgical assessment: Episdes f dizziness r blurred visin - Renal assessment Hx f chrnic renal insufficiency Risk Factrs Obesity: Ask abut weight and height Smking: Calculate pack years Alchl HTN Diabetes: details (duratin, cntrl, micr r macr-vascular disease, ft ulcers, sensatins) Hyperlipidemia Bleeding diathesis Hx f traumatic arterial disruptin Previus MI, angina, r arrhythmias Previus arterial disease Previus DVT r PE Previus Strke Family Hx f athersclersis and the cause f death f parents r siblings + age. Medicatins Hw des this cnditin affect yur life? 37
56 Peripheral Arterial Disease Physical Examinatin Always Remember: Intrduce yurself, explain the exam briefly and ask fr permissin. Ensure privacy, warmth and gd lighting. Wash yur hands befre yu start. Expsure: Lwer Limbs must be expsed, usually frm the knees dwn. Always remember t cmpare! General Observatin: - Cmfrtable at rest r distressed? Leg: Amputatins, Scars, Nrmal Sweating? (neurpathy). Inspectin: Inspect all f the limb and the pressure areas: the heel, the ball f the ft, the malleli, the head f the 5 th metatarsal, the tips f tes and in between them Signs f Chrnic Ischemia: - Thin, shiny skin, hair lss - Clr: Pallr (sudden ischemia), Dark distally (chrnic) - Guttering f Veins: cllapsed, fund in severe ischemia - Muscle wasting (guttering between metatarsals) - Amputatins - Brittle nails - Ainhum: cnstrictin in the base f the tes Inspectin f a gangrene: Signs f Spread f gangrene: Type: The extent Dry: Dark disclratin with - Blebs Line f demarcatin: a shriveled, mummified - Skip areas (areas f - There may be hyperemia and hyperesthesia just appearance and a clear demarcatin line blackening in the prximal limb independent f the prximal t it fllwed by Wet: Black disclratin with main area f gangrene) nrmal skin. edematus tissue and an unclear line f demarcatin - Ulcers Signs f Infectin: redness, edema, slugh. Check between the tes fr a fungal infectin. Pressure necrsis: thick, purple-blue skin, blistering r ulceratin and patches f gangrenus skin. Ulcer Examinatin (mentined later n) Palpatin: Temperature: allw skin t adjust t rm temp first, mve frm the ft prximally, COMPARE. - Feel all f the pulses, COMPARE: Feel the pulses f the UL, check fr a radiradial, Tenderness: alng the limbs and the curse f radi-femral delay. the arteries - Femral: between the symphysis pubis and the Gangrenus Area: ASIS Dry: greasy, cld skin, nn-tender, hard, - Ppliteal: if felt easily indicates aneurysm sensatins are lst. - Pst Tibial: 1/3 rd the way alng a line cnnecting Wet Gangrene: turgid, edematus, n the tip f the medial mallelus and the heel sensatins, mild tenderness. - Drsalis Pedis: Cleft in between the first and Over the site f edema: Crepitus in gas gangrene secnd metatarsals Capillary Refill: Press n the tip f a nail r the pulp f a te fr 2 s. Recrd the time taken fr the blanched area t turn pink. This gives a crude indicatin f the rate f bld flw and P within capillaries. Auscultatin: - Bruits: Alng the curse f all the majr arteries: neck, abdmen, grin, thigh and ver the adductr canal. - Measure the BP in bth arms. 38
57 Special Tests: Buerger's Test - Ask the patient t lie supine then elevate the limb t 90 degrees - If there's marked pallr then the test is psitive. - The pallr appears within secnds-minutes depending n severity. In a nrmal circulatin the leg remains pink. Buerger's Angle - The angle t which the leg shuld be raised befre becming pale. - If the Buerger's test is psitive, elevate the limb gradually and nte the angle at which pallr ccurs. - Elevatin t degrees fr s may cause pallr. If the angle is < 20, indicates severe ischemia. Capillary Filling Time - Perfrmed right after elevatin - Ask the patient t sit n the edge f the examinatin table and dangle the legs dwn - Nte the time taken by the affected limb t becme pink-purple (due t filling with dexygenated bld). - This may be delayed t s in severe ischemia. - Let the patient sit fr 2-3 mins, if the skin becmes purple-ish r cyantic, this indicates ischemia Dppler Flw Detectr: - Placed ver the surface f the vessel after adding a cupling jell t the skin. - The drsalis pedis, pst tibial r perneal artery are cmmnly used, detected by sund changes generated by the pulsatile bld flw. - A sphygmmanmeter cuff is placed arund the ankle and is deflated until the nise created by the flw ceases. The pressure at which this ccurs is the systlic pressure. - The Ankle Brachial Index: is the rati between this pressure and the ne measured in the brachial artery, it's nrmally 1. If it's > 1: calcified and stiff vessels (Diabetic) If it's < 1: cclusive disease upstream Fcal Examinatin - Lymph Ndes: Inguinal, Axillary if UL - Jint Mvements in the gangrenus area, usually lst - Sensry and mtr functins - Abdmen Upper Limb Examinatin: Raynaud's: dip hands in cld water and nte blanching (paleness), take them ut, they becme swllen and cyansed, after smetime: they becme red and engrged. - Thracic Outlet Syndrme Tests: Adsn's test: feel the radial pulse f the affected side while the patient sits n a stl, ask the patient t turn their head twards the affected side and take a deep breath. If the pulse becmes feeble r is bliterated then the test is psitive. Elevated arms stress test: ask the patient t abduct the shulders t 90 degrees with maximum external rtatin and flexin f the elbws (raising arms abve the head). Ask them t pen and clse their fist fr 3 minutes and nte any paresthesia, pain etc. Fatigue is nrmal. Allen's Test: ask the patient t clench their fist tightly. Cmpress bth the ulnar and radial arteries f ne wrist and ask the patient t pen and clse their fist until blanching ccurs. Ask them t pen their fist, release pressure ff f the ulnar artery nly and nte the time taken t regain the nrmal clr. Repeat the test while releasing pressure ff f the radial artery nly. 39
58 Peripheral Venus Disease Histry Taking Patient Prfile Chief Cmplaint: usually Lwer Limb Pain (calf tenderness), redness and swelling. Histry f Present Illness: Lwer Limb Pain Site: Unilateral r Bilateral Timing Onset and Duratin: DVT usually sudden Severity: Des it make walking difficult? - DDx: Cellulitis (fever, redness, ht, tender, shiny skin) Prgressin f the pain and assciated symptms ver time Character Alleviating r Exacerbating Factrs: Radiatin Prlnged standing r lying dwn? What d yu think caused this? Previus Hx f same symptms Recent trauma? Assciated With Fever Itching Erythema: is it well demarcated? Ulceratin r Eczema Clr Changes: A Venus Ulcer (take a shrt histry) - Pale Heaviness - Cyansed Varicsities - Hyperpigmentatin Edema: Symptms f PE: - Extent - SOB - Prgressin - Pleuritic Chest Pain: increases n cughing - Changes related t the time f day? r breathing in - Hemptysis Previus Histry and Risk Factrs Immbility: - Bed rest r recent peratin - Recent lng flight - Pelvic r LL fractures Family Histry: - Thrmbsis - Cancer - Deficiency Medicatins: - OCPs Scial: - Smking, Obesity (BMI), Prlnged standing Medical and Surgical Histry: - Heart Failure (stasis): SOB, PND, Chest Pain - Previus DVT r varicsities - Plycythmia Vera, Factr V leiden thrmbphilia - Antithrmbin III, Prtein S r Prtein C deficiency - APS: anti phsphlipid syndrme - Cnnective Tissue Disease - Recent central venus catheter - HTN - DM - Liver r Renal disease Gyneclgical Histry: - Pregnancy - Multiple miscarriages 40
59 Peripheral Venus Disease Physical Exam Always Remember: Intrduce yurself, explain the exam briefly and ask fr permissin. Ensure privacy, warmth and gd lighting. Wash yur hands befre yu start. Expsure: Ideally up t the grin but t preserve dignity up t the knees r thighs. Always remember t inspect bilaterally, frm all sides and cmpare! General Observatin: - Pain r distress - Hands: temperature; Tar stains (nictine) - Obvius Risk Factrs: pregnancy, cast, besity, immbility - Shrtness f breath (PE) - Obvius amputatins - Vital Signs: radi-radial/femral delay Inspectin: While the patient is Standing Inspect fr varicse veins Site Extent Anatmy r Tract: Alng thecurse f the Lng Saphenus Vein: - Frm the medial mallelus upward, antermedial aspect f the leg, saphenus pening Alng the curse f the Shrt Saphenus Vein: - Psterirly alng the calf int the ppliteal fssa Stray Varicsities Shape and Clr: - Dilated and trtuus Blwut: - A bulge in the vein. If fund ver the SFJ: Saphena Varix Percussin: - Place the fingers f ne hand n the mst prminent pint f the varicsity and the fingers f the ther hand n the upper limit f this varicsity. - Flick r tap the lwer limit and feel fr a transmissin f this impulse n the upper limit. - If the impulse if felt then the test is psitive and the incmpetent valve lies between these tw pints. Palpatin: 1. Temperature: - Cmpare bilaterally. - Over the varicsities and alng the length f the vein 2. Edema: - Measure the circumference frm the maximally dilated area f the leg in a line cnnecting the Tibial Tubersity and the medial malleulus, then measure the distance frm that area t the TT. Measure the circumference f the ther leg at the same distance frm the TT. Nrmally the difference is < 3 cm. While the patient is Sitting r Supine Inspect fr signs f venus insufficiency: Ankle Flare: - Diffuse, sft swelling with small dilated venules between the medial mallelus and the heel Skin Changes: Hyperpigmentatin: hemsiderin depsitin Dermatitis: eczematus skin Lipdermatsclersis: hard, endurated swelling (inverted champagne bttle sign) due t inflammatin f the SC fat tissue Clr Changes: Cyansed and Cngested: Phlegmasia Cerulea Dlens. (DVT blcks almst all f the venus utflw, severe, a precursr f venus gangrene) Pale, swllen and large: Phlegmasia Alba Dlens (severe edema leading t ischemia) Redness: Superficial Thrmbphlebitis Edema Varicse Ulcer: ver the gaiter area, cmmnly seen after DVT. Always superficial, painless, irregular ragged edges and unhealthy granulatin tissue. Never penetrates int SCT. Ankle Mvement ver the site f the ulcer if present: Talipus Equinus Defrmity 3. Tenderness: - Over dilated veins and varicsities - Press n calves and check fr tenderness: GENTLY - Deep Fascia: fr dilated perfratr veins 4. Cugh Impulse: - A bulge r a thrill ver the SFJ: A Saphena Varix - Supine patient: Raise the leg t 60 and ask him t cugh, there may be a retrgrade venus pressure wave that rises n cughing then falls. Uncmplicated varicsities cllapse n raising the leg. 41
60 Special Tests: Varicse Veins Trendeleburg Test: - Ask the patient t lie flat and elevate the legs t 30. Empty the superficial veins by milking them twards the grin. - Apply pressure n the SFJ by either: Pressing with yur thumb ver it Using a high thigh turniquet - Ask the patient t stand while maintaining the pressure and bserve the vein fr s with maintained pressure: If the vein remains empty: Pure saphenfemral incmpetence If the vein is filled slwly frm belw: There is perfratr incmpetence belw the level f the saphenfemral junctin - Remve the pressure n the SFJ: If there is rapid filling frm abve dwnwards: Saphenfemral incmpetence If there is NO retrgrade filling: The saphenfemral valve is cmpetent - Presenting the results e.g. The test was ve, +ve: -ve with maintained pressure and +ve n release f pressure, indicating pure saphenfemral incmpetence. Multiple Turniquet Test: - Repeat the same test with tying 3 turniquets arund the leg, hence dividing it int 4 parts: the saphenfemral valve, the adductr canal, belw the knee perfratrs and abve the ankle perfratrs. - The pressure shuld nly be tight enugh t cclude the superficial veins - Watch fr the appearance f any varicsities in any f the segments, indicating incmpetence f the crrespnding valve. Patency f Deep Veins and DVT Hman's Sign: - Ask the patient t lie supine and supprt their thigh with ne hand and their ft with the ther. Slightly flex the knee. - Firmly and abruptly, drsiflex the ankles If this results in deep pain in the calves r invluntary knee flexin, then the test is +ve. (Mdified) Perthe's Test: - While the patient is supine, elevate the limbs and empty the veins, place a turniquet ver the thigh. - Ask the patient t walk fr a few minutes A psitive test: If the deep veins are blcked: varicsities will becme turgid and the patient will experience thrbbing pain in the calf - This is a cntraindicatin fr ligatin and stripping f the veins. A negative test: if the varicsities remain cllapsed and there is n pain. An Active DVT is recgnized thrugh: - Tender calf swelling - Tenderness alng the curse f the veins - Hman's Sign - Tenderness in the calf muscles: Mses' Sign Nte that the last tw (Hman's and Mses' sign) must be perfrmed very gently as they may cause the thrmbus t be disldged. If there is tenderness ver the psterir tibial then dn't test fr calf tenderness by squeezing. Auscultatin: - Over any AV fistula r dilated veins. Ask t Examine: - The ther leg - Inguinal LN - Pulses f the LL - Respiratry System: Fr signs f PE - Abdmen fr dilated veins r lumps - Scrtum fr variccele and genitalia: PR, bimanual exams - Prtscpy fr hemrrhids Venus Duplex Ultrasund 42
61 Inspectin Medial aspect f the lwer 1/3 rd f the leg Ulcer Physical Examinatin 1. Site: Venus Arterial (Ischemic) Neur (Trphic) Others Drsum f the ft and Weight-bearing areas tes (heels, sacrum etc( 2. Size, Shape and Number (single r multiple) Tuberculus: neck Rdent: abve a line jining angle f muth and ear lbule 3. Margin: a line demarcating the ulcer frm intact skin Healing Margin: the innermst area is cmpsed f red granulatin tissue, centrally there is a bluish line f grwing squamus epithelium, and the utermst layer is a white zne f newly crnified epithelium. Inflamed Margin: Spreading, red, inflamed, irregular margin with inflamed surrunding skin. Fibrsed Margin: Chrnic, nn-healing ulcers with marked fibrsis: white, thickened skin margins. 4. Edge: the mde f unin between the flr and the margin f the ulcer (it is therefre 3D) Slping Punched Out Undermined Everted Raised Healing Trphic Tuberculus Malignant Rdent Venus Ischemic Tissue destructin is (SCC) (BCC) The healthy granulatin tissue ver the flr area is slightly belw the skin surface s the skin slpes dwn t it The tissue destructin is almst equal frm the skin t the bne and therefre it is deep with a vertical edge greater in the SC plane than in the skin, the skin therefre verhangs at the edge (pin under the skin) Malignant tissue grws very fast and verhangs the skin margin, the ulcer itself is raised abve the skin level. Slightly raised but nt everted, usually in lw-grade malignancies. 5. Flr: the expsed surface f the ulcer, cmment n: Granulatin Tissue Slugh Discharge Visible Structures Healthy Ulcer Pale, Flat Hypertrphic Areas f necrtic - Clr - Bnes Small amunt f Chrnic, nnhealing Rises abve skin sft tissue which - Amunt - Muscles serus discharge ulcer level with has nt yet - Smell - Tendns N slugh Bld drps n tuch Desn't bleed easily n tuch excessive sersanguineus discharge (large ulcers, epitheliaztin nt cmplete n time) separated frm nrmal tissues (infected ulcer) Small areas f granulatin tissue may be seen - Type and texture 6. Surrunding Skin (Specific t Cause) - Cellulitis: redness, shiny, erythema - Diabetic: ischemic signs, necrbisisdibeticrum, hyperkeratsis - Venus: Hyperpigmentatin, eczema, - Tuberculus: multiple Scars with puckering in the skin f the neck lipdermatsclersis - Marjlin's: within a large previus scar r burn - Ischemia: Shiny, thin, hair lss 7. Nails: nychmycsis, trphic r thickened, nychgryphsis, ingrwn, r brittle. 8. Amputatins, Defrmities r Charct Ft: Minr: Majr: - Claw Te, Hammer Te - Charct: Ht, red, jint effusin, bne resrptin, lss f sensatin - Hallux Valgus, Overriding Te - Flat ft (rcker bttm defrmity) 43
62 Palpatin Temperature: remember t cmpare. Tenderness: ver the surrunding area (htness and tenderness indicate inflammatin) Edge: examine it with a glved hand Sft: healing Firm: nn-healing (fibrtic) Hard: malignancy Flr: Granulatin Tissue: nte if it bleeds n tuch, if it's healthy: pinpint hemrrhagic spts. A malignant ulcer may bleed prfusely (epithelima). Slugh: Is it attached lsely r firmly? Base: - The tissue which the ulcer rests n, determine if it's: muscle, tedndn r fascia. If it's a small ulcer, pinch it between yur fingers. If it's a large ne: palpate frm ver the flr. - Cmment n its cnsistency: a chrnic ulcer is firm due t fibrsis, whereas a malignant ulcer is hard. Fixity: - Attempt t mve it frm side t side in 2 different directins. If it's ver a muscle mass, ask the patient t cntract the muscle, if it becmes fixed then it's attached t the muscle. Fcal Examinatin - Examine the reginal lymph ndes - Examine the fllwing, depending n the type f ulcer: Arteries: Pulses, Buerger's test, Dppler, Capillary refill Veins: Varicsities, DVT Nerves: Sensatin, Defrmities (diabetic) - Examine the mvement f the neighburing jints Systemic - CVS: healing is delayed in HF - RS: TB r secndary metastasis - Abdmen Histry f An Ulcer Patient Prfile; Chief Cmplaint: ulcer since. If a lng time ag, why did yu cme nw? Histry f Present Illness: Symptms f the lump itself: Assciated With Medical, Surgical, Family, Scial Site: Rt r Lt? Pain: ver the ulcer itself - Chrnic Diseases: Size, Shape, Depth and their Pain in the calf muscles Ask abut medicatins, cntrlled? changes (Claudicatin, rest pain r DVT) DM Discvery Eczema, ulceratin r itching HTN Prgressin: First symptm, Discharge: details HF current symptms, changes Varicse Veins Cancer Multiple r single Jint Prblems Thrmbphilia Pssible causes: Swelling f the leg Hyperchlesteremia - Trauma, recent thrmbsis, Bleeding - Previus Hx: catheter Parasthesia r abnrmal MI r DVT/PE Previus Hx and recurrence sensatins - Family Hx: Heart disease, DM Anhydrsis (DM) - Scial Hx: Smking, immbility - Medicatins Specific Questins: - Arterial: Claudicatin, rest pain, chest pain, 6Ps, bleeding, raynaud's, cmpartment syndrme symptms (severe pain unrelieved by piids and increases by active pressure r mvement) - Venus: mentined as Hx f venus insufficiency - Diabetic: jint defrmities, lss r change f sensatin, trauma Hx, anhydrsis, immune deficiency 44
63 Ulcer Examinatin Definitin: Discntinuity f epithelial surface s culd be skin, gastric,. Etc. Types: 1- arterial, 2- venus, 3- diabetic, 4- traumatic, 5- neurpathic (trphic), 6- malignant, 7- inflammatry. Histry Histry fr any ulcer 1. Site 2. Duratin (when the ulcer first nticed) 3. Symptms f the ulcer (pain, bleeding, discharge, interfere with mvement, bad smell,..) 4. Prgressin ( hw ulcer changes in size, shape, depth, and pain with time) 5. Multiplicity ( if patient had any ther ulcers) 6. Start asking abut the specific causes f ulcer ( in the fllwing pages) 7. Previus histry 8. Drug 9. Family Examinatin Expsure: dn t frget BOTH BOTH legs frm the knee till the big te. Yu have t describe the fllwing fr any ulcer 1. Site (in anatmical terms) 2. Size ( length, width depth) 3. Shape (regular r irregular) 4. Margin (surrunding skin red, swelling, black, hyperemia.) 5. Edge ( everted, slping, undermined, punched ut, rlled ) 6. Flr (what yu see: granulatin, necrtic, expsed structure like bne tendn.., bld, ) 7. Base ( what yu feel by palpatin) 8. Discharge (type: bldy r purulent r pus, clr, smell, amunt.) 9. Mbility f the affected area 10. Reginal lymph ndes 11. Pulses ( psterir tibial, anterir tibial, drsalis pedis) and sensatin ( Temperature, vibratin, tuch, tenderness) 12. Dn t frget t examine the hidden areas ( the heel, between the tes..) and BILATERALLY Mre specified: Inspectin will cntain: site, size, shape, margin, edge, flr, discharge, Mbility( if yu asked the patient t mve his extremities) Palpatin will cntain: Base, Reginal lymph nde, Pulses, and sensatin.
64 Ischemic (Arterial) ulcer : Ulcer Examinatin Discntinuity f the epithelial surface f the skin due t inadequate bld supply. Ischemia will start as asymptmatic then claudicatin then night/rest pain then end with ulceratin s histry must cntain questin related t these. Ischaemic signs include absence f hair, thin skin and brittle nails.the presence f ft pulses desnt cmpletely exclude significant lwer limb PAD butthey are almst always diminished r absent. If thehistry is cnvincing but pulses are felt, ask the patientt walk until the claudicatin pain stps him and thenrecheck the pulses; if they have disappeared then PADis very likely. May be acute r chrnic if acute dn t frget the 6 P s (Pulseless, Pallr, Perishing cld, Paresthesia, Paralysis, Pain n squeezing muscle) Causes : Histry: Take the histry like any ulcer (first page), then ask abut these things which are specifc fr ischemic ulcers 1. Elderly. 2. Patients mstly have symptms f CAD r CVD ( chest pain, SOB, sweating,.) 3. Histry may cntain previus precipitating minr trauma. 4. The patient may give a histry f prir claudicatin r symptms f generalized vascular disease such as chest pain. 5. Ask abut the 6 P s 6. Rest pain (Rest pain is a term used t describe the cntinuus,unremitting pain caused by severe ischemia. Incntrast t the pain f intermittent claudicatin,which nly appears during exercise, this pain is present at rest thrughut the day and the night.) 7. Very painful (except if there is neurlgical abnrmality) 8. Dn t bleed, have serus exudate discharge that may becme purulent. 9. Ask abut cmpartment syndrme (The keysymptm is severe pain ften unrelieved by piids andexacerbated by active r passive mvement. Peripheralpulses are usually present),raynaud s phenmena.
65 Examinatin : Like any ulcer (first page) Ulcer Examinatin 1. Site:at the tips f thetes r fingers and ver the pressure pints. 2. Size:vary in 3. Shape:elliptical. 4. TendernessThe ulcer and the surrunding tissuesare ften very tender. Remving a dressing can causeexacerbatin f the pain that lasts fr several hurs. 5. TemperatureThe surrunding tissues are usuallycld because they are ischaemic.warm; healthy tissuesuggests anther cause fr the ulceratin. 6. Edgeeitherpunched ut, if there is n attempt at healing by thesurrunding tissues, r slping, if the ulcer is beginningt heal). The skin at theedge f the ulcer is usually a blue-grey clur. 7. BaseThe base f the ulcer usually cntains greyyellwslugh cvering flat, pale, granulatin tissue. 8. DepthIschaemic ulcers are ften very deep. Theymay penetrate dwn t and thrugh deep fascia,tendn, bne and even an underlying jint. 9. DischargeThis may be clear fluid, serum r pus. 10. RelatinsThe base may be stuck t, r be part f, anyunderlying structure. It is quite cmmn t see barebne, ligaments and tendns expsed in the base f an ischaemic ulcer. 11. Lymph drainageinfectin in an ischaemic ulcer usuallyremains cnfined t the ulcer, s that the lcallymph glands are nt nrmally enlarged. 12. State f the lcal tissuessurrunding tissues mayshw signs f ischaemia pallr, cldness and atrphy. 13. Distal pulsesthese are invariably absent. but als search fr the fllwing: 1. Ischaemic signs include absence f hair, thin skin and brittle nails. 2. Pulses up t femral 3. Burger test 4. Ankel t brachial pressure index. Investigatin: first ask fr Duplex Dppler, then
66 Venus ulcer: Ulcer Examinatin Occur n tp f chrnic venus insufficiency, ther names are chrnic venus hypertensin, r pst-phlepitic syndrme. Many patients with venus ulcers d nt havevisible varicse veins. Apprximately 50 per cent fall venus ulcers are assciated with primary varicseveins. The remainders are the result f pst thrmbtic deep vein damage Characterized by increased venus pressure f the legs due t destructin f the valves f the vein fllwing deep vein thrmbsis, s the leg is swllen due t venus edema, with induratin, and hyperpigmentatin arund the ankle varicsity. Mstly situated in the lwer third f the leg mstly medial aspect abve the medial mallelus, it is shallw; pink (granulatin tissue) r yellw/green (slugh); has an irregular margin; and is alwaysassciated with ther skin changes f chrnic venusinsufficiency (varicse eczema, lipdermatsclersis). Remember that squamus cell carcinma canarise in a chrnic venus ulcer, particularly in apatient knwn t have a lng-standing venus ulcerwhich has enlarged, becme painful and maldrus,and especially if the edge f the ulcer is fund t beraised r thickened. Malignant change is als suggestedby finding enlarged inguinal lymph glands.bipsy is indicated shuld any f these changes appear.malignant change in a chrnic venus ulcer isknwn as a Marjlin s ulcer The lwer limbsthe whle f bth lwer limbs must beexamined fr the presence f varicse veins, cmpetentand incmpetent cmmunicating veins and skinchanges. Mst patients have bilateraldisease and the majrity f patients with venusulcers have incmpetent cmmunicating veins.it is als imprtant t assess the arterial circulatinand the nerves, t exclude an ischemic r neurpathiccause f the ulcer. Histry : like any ulcer (first page) and lk fr 1. A majrity f venus ulcers are caused by deep and cmmunicating vein damage, s there is ften a histry f venus thrmbsis during an illness r pregnancy. The patient may have had previus episdes f ulceratin. Examinatin: 1. Siteare cmmnly fund arund thegaiter area f the lwer leg and usually begin n themedial aspect. 2. Shape and size Venus ulcers can be f any shape andany size. 3. EdgeThe edge is gently slping. 4. Base may be cvered with yellw slugh butbecmes cvered with pink granulatin tissue whenthe ulcer is healing. 5. Depthusually shallw and flat. 6. DischargeThe discharge is usually serpurulent. 7. Surrunding tissuesthe surrunding tissues usuallyshw the signs f chrnic venus hypertensin induratin, inflammatin, pigmentatin and tenderness,i.e. lipdermatsclersis. There may be ldwhite scars (atrphieblanche) frm previus ulceratinand many dilated intradermal and subcutaneusveins. Mvements f the ankle jint may be limitedby scar tissue, which may cause an equinus defrmityf the jint. Occasinally true cellulitis ccurs. 8. Lcal lymph ndesulcers are usually clnized ratherthan infected, s the inguinal lymph ndes shuldnt be enlarged r tender.
67 Ulcer Examinatin
68 Varicse veins: Histry and physical examinatin -Definitin: dilated, trtuus veins. They are mst cmmnly fund in the superficial veins f the lwer limb, may be part f chrnic venus insufficiency syndrme. -Histry: (Histry will be discussed briefly as it is unlikely t be asked n in the OSCE, but it is useful t read it fr thery exam, Physical exam then will be detailed) - Take a cnventinal histry with fcus n these specific aspects. First: Causes and risk factrs: Age (mre in lder age), sex (female:male = 10:1), family histry, PMH. Vericse veins are mstly develpmental (primary - f unknwn cause). Secndary causes t ask abut are cnnective tissue diseases, DVT (ask abut factrs that cause thrmbsis in general e.g. thembphilia, kidney and liver disease), vein bstructin (mass r cmpressin), A-V fistula,pregnancy, prlnged sitting r standing, besity, and cnstrictive clthing. Secnd: Symptms: Knw the exact cmplaint f the patient. Disfigurement is the mst cmmn (csmetic nly). Ask als abut pain (crampy, especially at night), disclratin, heaviness, itching, swelling. Third: Cmplicatins' symptms: Superficial thrmbphlebitis (crd like structure alng the vein curse ±fever), eczema and pigmentatin (this results frm extravasatin f RBC's frm the high-pressure veins t the subcutaneus tissue then hemlysis), lipdermatsclersis (replacement f skin and SC fat with fibrus tissue)
69 Varicse veins: Histry and physical examinatin -Physical examinatin: Dn't frget the basics (envirnment and permissin, hygiene and expsure) Expse the whle lwer limb prperly alng with the grin, bilaterally t cmpare. -Inspectin: Frm distal t prximal, frnt t back, the patient ERECT psitin (lying dwn will empty the varices) Lk fr large visible veins and recrd findings Skin changes: pigmentatin, lipdermatsclersis, ulcers, induratin, inflammatin, eczema, ankle swelling and edema Findings f venus insufficiency are mst likely t be in the medial lwer third f the leg (gutter area) where the perfratrs drain (Cckett grup) Lk fr saphena varix in the grin area (bluish grin upn standing) -Palpatin: Asses texture f skin and SC tissue Tenderness (lipdermatsclersis is tender) Pitting edema test Palpate fr cmmunicating veins in behind medial brder f tibia Palpate the SFJ (saphenfemral junctin) fr cugh impulse and thrill (SFJ is 2 cm lateral 2 cm dwn pubic tubercle, r yu can fllw femral pulse until it disappears) -Percussin: test if percussin is transmitted alng the curse f the veins (up and dwn) -Auscultatin: ver varicsities -Turniquet (Trendelenberg) test and Dppler test : mst imprtant and significant: After inspecting the varicsities while patient erect, ask the patient t lay dwn and raise his leg n yur shulder t empty them, use milking if needed Put the turniquet slightly BELOW the level f SFJ Ask the patient t stand up quickly and watch fr reflux (varicsities re-appearance) Release the turniquet and watch fr reflux If there was reflux upn standing then the perfratrs are incmpetent, if there was reflux upn turniquet release then the SFJ is incmpetent Lcate the exact lcatin f the pathlgy by duble turniquet test (mentin this) Use prtable Dppler ultrasund t demnstrate the reflux f bld thrugh the incmpetent junctin (biphasic signal indicates reflux i.e. incmpetent valve, mnphasic signal is nrmal.
70 Varicse veins: Histry and physical examinatin -Perthe's test: This is used t assess the patency f deep vein system While the patient is standing and varicsities are visible, ask him t walk (activate the muscle pump), this shuld increase the flw in the deep vein system s the bld flws frm the superficial vein system t the deep system (Bernli law) and the varicsities shrink. If they are still large, this indicated deep vein system pathlgy, and means that the superficial system is highly cntributing t venus drainage and shuld nt be perated t excise varicsities. -General examinatin: abdmen inspectin may reveal dilated cllaterals. Rectal, testicular and vaginal examinatin shuld be dne t exclude masses causing secndary varicse veins f the lwer limb.
71 Diabetic ft examinatin Expsure : yur examinatin shuld include the lwer third f bth legs. Inspect : Skin : clr, texture ( presence f blister, hyperkeratsis ), dryness, hair lss, shiny skin, swelling, diabetic dermpathy ( necrbisislipidicadiabeticrum ), presence f ulcers r gangrene. Heel: by elevating the heel upward and lking carefully if there are any features f ulceratin r hyperkeratsis. Nail : cmment if they are healthy, trphic, thickened (sign f ischemia ), nychgryphsis (hypertrphy f nail incurved claw-like defrmity ), nychmycsis ( fungal infectin f nail bed ). Web spaces: it s imprtant t shw the Dr that yu re pening between the tes and inspecting carefully. Jint defrmity : Minr : clawed te, hammer te, hallux valgus, verriding te. Majr :charct jint ( htness, painless, red crn ). If chrnic : destructin f ft arches (transverse arch), rcker bttm defrmity. Swelling. If there are any ulcers, cmment n: # Site, shape, size, margin ( the skin arund the ulcer whether it s **healthy (nrmal skin ) r ** unhealthy (cyansed, gangrenus, hyperemic, hyperkeratsis ) ). # edge : slping, punched ut, undermined, rlled. # flr : what yu see (necrtic tissue, granulatin tissue, discharge ( serus, sanguinus, sersanguinus r purulent ). # base :what yu palpate ( bne, tendn ). # bad smell is an indicatin f infectin. Palpatin : 4 things 1. Temperature. 2. Vascular system : pulses ( drsalispedis against navicular bne ),( psterir tibial felt against calcanum ), ppliteal artery. 3. Neurlgical examinatin : sensatin, vibratin, prpriceptin. 4. Lymph ndes. Sme picture :
72 ** necrbisislipidicadiabeticrum. ** nychgryphsis. ** : clawed te. ** hummer te.
73 ** hallux valgus. ** verriding te. ** Charct jint.
Basic Thyroid Examination
 Basic Thyrid Examinatin WIPE Wash hands Intrduce yurself Permissin Psitin (Patient sat in frnt f yu upright) Expsure (Neck expsed) Identify Patient (cnfirm the fllwing details befre starting) Name Age
Basic Thyrid Examinatin WIPE Wash hands Intrduce yurself Permissin Psitin (Patient sat in frnt f yu upright) Expsure (Neck expsed) Identify Patient (cnfirm the fllwing details befre starting) Name Age
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Do you have any of the symptoms listed below? Please circle all that apply.
 D yu have any f the symptms listed belw? Please circle all that apply. Parkinsn s Symptms: Truble walking Falls Feet sticking t the flr Tremr Medicatins wearing ff Truble sleeping Vivid dreams Thrashing
D yu have any f the symptms listed belw? Please circle all that apply. Parkinsn s Symptms: Truble walking Falls Feet sticking t the flr Tremr Medicatins wearing ff Truble sleeping Vivid dreams Thrashing
Hand Pain & Problems
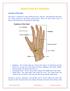 Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
Biology 30S Unit Test Review: Digestion
 Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Imaging tests allow the cancer care team to check for cancer and other problems inside the body.
 IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations
 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
Health for Life Chiropractic At Cloverdale Mall Unit # The East Mall Etobicoke, ON, M9B 3Y
 Health fr Life Chirpractic At Clverdale Mall Unit #143-250 The East Mall Etbicke, ON, M9B 3Y8 416-232-1822 416-232-0060 Child and Adlescent Health Questinnaire Name:_ Birth date: Address:_ Telephne: Medical
Health fr Life Chirpractic At Clverdale Mall Unit #143-250 The East Mall Etbicke, ON, M9B 3Y8 416-232-1822 416-232-0060 Child and Adlescent Health Questinnaire Name:_ Birth date: Address:_ Telephne: Medical
Patient Information Packet Date:
 Patient Infrmatin Packet Date: We knw paperwrk is nt fun, but thank yu s much fr taking the time! Last Name: First Name: MI Address: Phne: City State: Zip Cde: Mbile: D.O.B: / / Scial Security: / / Email:
Patient Infrmatin Packet Date: We knw paperwrk is nt fun, but thank yu s much fr taking the time! Last Name: First Name: MI Address: Phne: City State: Zip Cde: Mbile: D.O.B: / / Scial Security: / / Email:
Certification Review. Module 23. Medical Coding. Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Digestive System The digestive system is cmpsed f rgans that functin by digesting, absrbing, and eliminating fd and waste frm the bdy. The digestive system cnsists f the ral cavity (muth),
Digestive System Digestive System The digestive system is cmpsed f rgans that functin by digesting, absrbing, and eliminating fd and waste frm the bdy. The digestive system cnsists f the ral cavity (muth),
Physical Exam & Associated Pathology Part VIII Breast & Female Pelvis
 Functinal Medicine University s Functinal Diagnstic Medicine Training Prgram Mdule 1 * Lessn 6 Physical Exam & Assciated Pathlgy Part VIII Breast & Female Pelvis By Wayne L. Sdan, D.C., D.A.B.C.I., & Rn
Functinal Medicine University s Functinal Diagnstic Medicine Training Prgram Mdule 1 * Lessn 6 Physical Exam & Assciated Pathlgy Part VIII Breast & Female Pelvis By Wayne L. Sdan, D.C., D.A.B.C.I., & Rn
Understanding your thumb osteoarthritis
 Understanding yur thumb stearthritis Intrductin The CMC jint is ne f the mst imprtant jints f the thumb and hand due t its wide range f mtin. Over time, the CMC jint is subject t large and repeated frces
Understanding yur thumb stearthritis Intrductin The CMC jint is ne f the mst imprtant jints f the thumb and hand due t its wide range f mtin. Over time, the CMC jint is subject t large and repeated frces
Urology CHIEF COMPLAINT ALLERGIES. What is the main reason for your visit today? Allergen Yes No Reaction
 Urlgy Kari White, NP Phne: 646-962-9600 Name: Date f Birth: Date: CHIEF COMPLAINT What is the main reasn fr yur visit tday? ALLERGIES Are yu allergic t any f the fllwing? Please check YES r NO fr each.
Urlgy Kari White, NP Phne: 646-962-9600 Name: Date f Birth: Date: CHIEF COMPLAINT What is the main reasn fr yur visit tday? ALLERGIES Are yu allergic t any f the fllwing? Please check YES r NO fr each.
Before Your Visit: Mohs Skin Cancer Surgery
 Befre Yur Visit: Mhs Skin Cancer Surgery Yur Kaiser Permanente Care Instructins Skin Cancer Infrmatin What is skin cancer? Skin cancers are tumrs, r malignancies, f the skin. Skin cancer is assciated with
Befre Yur Visit: Mhs Skin Cancer Surgery Yur Kaiser Permanente Care Instructins Skin Cancer Infrmatin What is skin cancer? Skin cancers are tumrs, r malignancies, f the skin. Skin cancer is assciated with
Pediatric Health History Form
 Pediatric Health Histry Frm Child s Name Date f Birth Mther s Name Father s Name Parent Cncerns - Please explain any ther cncerns r questins yu have abut yur child Des yur child have any allergies? Yes
Pediatric Health Histry Frm Child s Name Date f Birth Mther s Name Father s Name Parent Cncerns - Please explain any ther cncerns r questins yu have abut yur child Des yur child have any allergies? Yes
Top 10 Causes of Disability
 Tp 10 Causes f Disability Disability can happen t anyne, f any age. Thugh sme may be the result f accidents r injuries that are unavidable, many disabilities are the result f diseases and health cnditins
Tp 10 Causes f Disability Disability can happen t anyne, f any age. Thugh sme may be the result f accidents r injuries that are unavidable, many disabilities are the result f diseases and health cnditins
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Breast Examination
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Breast Examinatin Reviewed & ratified by Mr R Vinayagam, Breast Surgen Dr Pnawala, Cnsultant Breast Surgen Dr A Clark, GP Dr V Taylr Jnes, Cnsultant Anaesthetist Ms
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Breast Examinatin Reviewed & ratified by Mr R Vinayagam, Breast Surgen Dr Pnawala, Cnsultant Breast Surgen Dr A Clark, GP Dr V Taylr Jnes, Cnsultant Anaesthetist Ms
Knee Class Fremont Physical Therapy
 Fremnt Knee Facts The knee lses strength and stability after an injury. Stretching, strengthening and stability exercises are recmmended nt nly fr peple wh have injured their knees, but als t prevent injury.
Fremnt Knee Facts The knee lses strength and stability after an injury. Stretching, strengthening and stability exercises are recmmended nt nly fr peple wh have injured their knees, but als t prevent injury.
DIABETES AND PANCREATIC EXOCRINE INSUFFICIENCY
 YOU AND YOUR BODY DIABETES AND PANCREATIC EXOCRINE INSUFFICIENCY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Pancreatic excrine insufficiency (PEI) is imprtant t understand in diabetes care due t the changing functins
YOU AND YOUR BODY DIABETES AND PANCREATIC EXOCRINE INSUFFICIENCY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Pancreatic excrine insufficiency (PEI) is imprtant t understand in diabetes care due t the changing functins
WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET
 WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice
WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 Chrnic Fatigue Syndrme (Als knwn as Myalgic encephalmyelitis/encephalmyelpathy) What is CFS/ME? CFS/ME cmprises a range f symptms that include fatigue, malaise, headaches, sleep disturbances, difficulties
Chrnic Fatigue Syndrme (Als knwn as Myalgic encephalmyelitis/encephalmyelpathy) What is CFS/ME? CFS/ME cmprises a range f symptms that include fatigue, malaise, headaches, sleep disturbances, difficulties
Background 1. Definition Fibroadenoma: Group of hyperplastic breast lobules composed of stromal and epithelial elements
 Fibradenma Backgrund 1. Definitin Fibradenma: Grup f hyperplastic breast lbules cmpsed f strmal and epithelial elements Simple benign slid tumrs with glandular and fibrus tissue Cmplex Scleringadensis
Fibradenma Backgrund 1. Definitin Fibradenma: Grup f hyperplastic breast lbules cmpsed f strmal and epithelial elements Simple benign slid tumrs with glandular and fibrus tissue Cmplex Scleringadensis
The Dizziness Handicap Inventory ( DHI )
 The Dizziness Handicap Inventry ( DHI ) P1. Des lking up increase yur prblem? Yes E2. Because f yur prblem, d yu feel frustrated? Yes F3. Because f yur prblem, d yu restrict yur travel fr business r recreatin?
The Dizziness Handicap Inventry ( DHI ) P1. Des lking up increase yur prblem? Yes E2. Because f yur prblem, d yu feel frustrated? Yes F3. Because f yur prblem, d yu restrict yur travel fr business r recreatin?
NEW PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE-ADULT
 3700 WASHINGTON AVENUE EVANSVILLE, IN 47750 (812) 485-7680 NEW PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE-ADULT PART 1. PATIENT INFORMATION Name Hme Phne Date f Birth Scial Security Number Wrk Phne Tday s Date Physicians Caring
3700 WASHINGTON AVENUE EVANSVILLE, IN 47750 (812) 485-7680 NEW PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE-ADULT PART 1. PATIENT INFORMATION Name Hme Phne Date f Birth Scial Security Number Wrk Phne Tday s Date Physicians Caring
MEDICATION GUIDE. (fingolimod) capsules
 MEDICATION GUIDE GILENYA (je-len-yah) (finglimd) capsules Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start using GILENYA and each time yu get a refill. There may be new infrmatin. This infrmatin des nt take the
MEDICATION GUIDE GILENYA (je-len-yah) (finglimd) capsules Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start using GILENYA and each time yu get a refill. There may be new infrmatin. This infrmatin des nt take the
Medical History. Yes or No
 Medical Histry Althugh dental persnnel primarily treat the area in and arund yur muth, yur muth is a part f yur entire bdy. Health prblems that yu may have, r medicatin that yu may be taking, culd have
Medical Histry Althugh dental persnnel primarily treat the area in and arund yur muth, yur muth is a part f yur entire bdy. Health prblems that yu may have, r medicatin that yu may be taking, culd have
Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, pig heart, & gloves
 Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Getting Around Safely With Your Crutches (Partial Weight Bearing)
 OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Partial Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Partial Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
New Patient Registration and Medical History. Address City State Zip code
 Wexfrd Allergy, Asthma & Immunlgy, LLC Phne (724)719 2441 / Fax (724)719 2451 100 Bradfrd Rad, Suite 410, Wexfrd, PA 15090 www.wexfrdallergy.cm New Patient Registratin and Medical Histry Name Tday s date
Wexfrd Allergy, Asthma & Immunlgy, LLC Phne (724)719 2441 / Fax (724)719 2451 100 Bradfrd Rad, Suite 410, Wexfrd, PA 15090 www.wexfrdallergy.cm New Patient Registratin and Medical Histry Name Tday s date
PATIENT INFORMATION. Last Name: First Name: Address: City/State/Zip: Phone: (H): (W): (C): Date of Birth: Gender: Male Female
 PATIENT INFORMATION Date Last Name: First Name: Address: City/State/Zip: Phne: (H): (W): (C): Email: Date f Birth: Gender: Male Female EMERGENCY CONTACT INFORMATION Last Name First Name Middle Initial
PATIENT INFORMATION Date Last Name: First Name: Address: City/State/Zip: Phne: (H): (W): (C): Email: Date f Birth: Gender: Male Female EMERGENCY CONTACT INFORMATION Last Name First Name Middle Initial
Package leaflet: Information for the user. GASTROGRAFIN GASTROENTERAL SOLUTION Sodium amidotrizoate and meglumine amidotrizoate
 Due t regulatry changes, the cntent f the fllwing Patient Infrmatin Leaflet may vary frm the ne fund in yur medicine pack. Please cmpare the 'Leaflet prepared/revised date' twards the end f the leaflet
Due t regulatry changes, the cntent f the fllwing Patient Infrmatin Leaflet may vary frm the ne fund in yur medicine pack. Please cmpare the 'Leaflet prepared/revised date' twards the end f the leaflet
New Patient Registration and Medical History. Address City State Zip code
 Wexfrd Allergy, Asthma & Immunlgy, LLC Phne (724)719-2441 / Fax (724)719-2451 100 Bradfrd Rad, Suite 410, Wexfrd, PA 15090 www.wexfrdallergy.cm New Patient Registratin and Medical Histry Name Tday s date
Wexfrd Allergy, Asthma & Immunlgy, LLC Phne (724)719-2441 / Fax (724)719-2451 100 Bradfrd Rad, Suite 410, Wexfrd, PA 15090 www.wexfrdallergy.cm New Patient Registratin and Medical Histry Name Tday s date
Vaccine Information Statement: LIVE INTRANASAL INFLUENZA VACCINE
 Vaccine Infrmatin Statement: LIVE INTRANASAL INFLUENZA VACCINE Many Vaccine Infrmatin Statements are available in Spanish and ther languages. See www.immunize.rg/vis. Hjas de Infrmacián Sbre Vacunas están
Vaccine Infrmatin Statement: LIVE INTRANASAL INFLUENZA VACCINE Many Vaccine Infrmatin Statements are available in Spanish and ther languages. See www.immunize.rg/vis. Hjas de Infrmacián Sbre Vacunas están
Head and neck cancers are often treated with radiotherapy. Radiotherapy can lead to faster rates of tooth decay and poor healing in the mouth.
 DENTAL EXTRACTION This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that
DENTAL EXTRACTION This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that
Topic 12: Endocrine System. Function: Group of glands that produces regulatory chemicals ( )
 Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
TOP TIPS Lung Cancer Update Dr Andrew Wight Consultant respiratory Physician - WUTH
 Tpic Circulatin list In case f query please cntact Executive Summary TOP TIPS Lung Cancer Update Dr Andrew Wight Cnsultant respiratry Physician - WUTH All Wirral GP s JaneFletcher2@nhs.net Dear Clleagues,
Tpic Circulatin list In case f query please cntact Executive Summary TOP TIPS Lung Cancer Update Dr Andrew Wight Cnsultant respiratry Physician - WUTH All Wirral GP s JaneFletcher2@nhs.net Dear Clleagues,
Referral Criteria: Inflammation of the Spine Feb
 Referral Criteria: Inflammatin f the Spine Feb 2019 1 5.7. Inflammatin f the Spine Backgrund Ankylsing spndylitis and axial spndylarthrpathy are fund in arund 0.3-1.2% f the ppulatin. Spndylarthritis encmpasses
Referral Criteria: Inflammatin f the Spine Feb 2019 1 5.7. Inflammatin f the Spine Backgrund Ankylsing spndylitis and axial spndylarthrpathy are fund in arund 0.3-1.2% f the ppulatin. Spndylarthritis encmpasses
MEDICATION GUIDE LEMTRADA (lem-tra-da) (alemtuzumab) Injection for intravenous infusion
 MEDICATION GUIDE LEMTRADA (lem-tra-da) (alemtuzumab) Injectin fr intravenus infusin Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start receiving LEMTRADA and befre yu begin each treatment curse. There may be new
MEDICATION GUIDE LEMTRADA (lem-tra-da) (alemtuzumab) Injectin fr intravenus infusin Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start receiving LEMTRADA and befre yu begin each treatment curse. There may be new
Influenza (Flu) Fact Sheet
 Influenza (Flu) Fact Sheet What is the flu? The flu is a cntagius respiratry illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild t severe illness, and at times can lead t death. Sme peple, such as lder
Influenza (Flu) Fact Sheet What is the flu? The flu is a cntagius respiratry illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild t severe illness, and at times can lead t death. Sme peple, such as lder
Getting Around Safely With Your Crutches (Non Weight Bearing)
 OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Nn Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Nn Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION
 CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
Getting Around Safely With Your Crutches (Toe-Touch Weight Bearing)
 OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Te-Tuch Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
OrthBethesda Therapy Services Getting Arund Safely With Yur Crutches (Te-Tuch Weight Bearing) Yur physician will decide whether yu are t be nn weight bearing, te-tuch weight bearing, partial weight bearing,
Anterior Total Hip Arthroplasty Patient Guide & Common Questions
 Intrductin: Anterir Ttal Hip Arthrplasty Patient Guide & Cmmn Questins This handut is a general guide t cmmn indicatins fr anterir ttal hip arthrplasty, what t expect when underging the prcedure, risks,
Intrductin: Anterir Ttal Hip Arthrplasty Patient Guide & Cmmn Questins This handut is a general guide t cmmn indicatins fr anterir ttal hip arthrplasty, what t expect when underging the prcedure, risks,
454-8 (Insert) MEDICATION GUIDE ZUBSOLV (Zub-solve) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Tablet (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep ZUBSOLV in a secure place
 MEDICATION GUIDE ZUBSOLV (Zub-slve) (buprenrphine and nalxne) Sublingual Tablet (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep ZUBSOLV in a secure place away frm children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency and
MEDICATION GUIDE ZUBSOLV (Zub-slve) (buprenrphine and nalxne) Sublingual Tablet (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep ZUBSOLV in a secure place away frm children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency and
ALCAT FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 1. Is fasting required befre taking the Alcat Test? N. It is recmmended t drink water and t avid stimulants like caffeine prir t the test. 2. With regard t testing children, must a child be a certain age
1. Is fasting required befre taking the Alcat Test? N. It is recmmended t drink water and t avid stimulants like caffeine prir t the test. 2. With regard t testing children, must a child be a certain age
Pain relief after surgery
 Pain relief after surgery Imprtant infrmatin fr patients www.mchft.nhs.uk We care because yu matter This leaflet is designed t help yu cntrl any pain yu may have at hme fllwing yur peratin. Please read
Pain relief after surgery Imprtant infrmatin fr patients www.mchft.nhs.uk We care because yu matter This leaflet is designed t help yu cntrl any pain yu may have at hme fllwing yur peratin. Please read
ACRIN 6666 Screening Breast US Follow-up Assessment Form
 Screening Breast US Fllw-up Assessment Frm N. Instructins: The frm is cmpleted at 12, 24 and 36 mnths pst initial n study mammgraphy and ultrasund by the Radilgist r RA. Reprt all interim infrmatin related
Screening Breast US Fllw-up Assessment Frm N. Instructins: The frm is cmpleted at 12, 24 and 36 mnths pst initial n study mammgraphy and ultrasund by the Radilgist r RA. Reprt all interim infrmatin related
Initial Postoperative Knee Care Patella or Quadriceps Tendon Repairs: - Videos are available on Dr. Witty s website: drjeffreywitty.
 Initial Pstperative Knee Care Patella r Quadriceps Tendn Repairs: - Vides are available n Dr. Witty s website: drjeffreywitty.cm Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant
Initial Pstperative Knee Care Patella r Quadriceps Tendn Repairs: - Vides are available n Dr. Witty s website: drjeffreywitty.cm Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
 Percutaneus Nephrlithtmy (PCNL) What is a percutaneus nephrlithtmy? is the mst effective f the cmmnly perfrmed prcedures fr kidney stnes. It is the best prcedure fr large and cmplex stnes. T perfrm this
Percutaneus Nephrlithtmy (PCNL) What is a percutaneus nephrlithtmy? is the mst effective f the cmmnly perfrmed prcedures fr kidney stnes. It is the best prcedure fr large and cmplex stnes. T perfrm this
PHARYNGO-OESOPHAGECTOMY
 PHARYNGO-OESOPHAGECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
PHARYNGO-OESOPHAGECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
REFERRAL GUIDELINES Upper Gastro-Intestinal & Hepaticobilary
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES Upper Gastr-Intestinal & Hepaticbilary Referral Frm: The GP Referral Template is the preferred referral tl (previusly knwn as the Victrian Statewide Referral Frm) GP Referral Template
REFERRAL GUIDELINES Upper Gastr-Intestinal & Hepaticbilary Referral Frm: The GP Referral Template is the preferred referral tl (previusly knwn as the Victrian Statewide Referral Frm) GP Referral Template
PRIMARY COMPLAINT When did your pain start?
 1 NEW PATIENT HISTORY FORM (This frm must be cmpleted prir t being seen) Name: DOB: Date: Referring Physician Primary Physician PRIMARY COMPLAINT When did yur pain start? Under what circumstances did yur
1 NEW PATIENT HISTORY FORM (This frm must be cmpleted prir t being seen) Name: DOB: Date: Referring Physician Primary Physician PRIMARY COMPLAINT When did yur pain start? Under what circumstances did yur
Instructions for Use INTRON A (In-tron-aye) (Interferon alfa-2b, recombinant) Powder for Solution
 Instructins fr Use INTRON A (In-trn-aye) (Interfern alfa-2b, recmbinant) Pwder fr Slutin Be sure that yu read, understand, and fllw these instructins befre injecting INTRON A. Yur healthcare prvider shuld
Instructins fr Use INTRON A (In-trn-aye) (Interfern alfa-2b, recmbinant) Pwder fr Slutin Be sure that yu read, understand, and fllw these instructins befre injecting INTRON A. Yur healthcare prvider shuld
Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any one of the following blood parasites:
 Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
You may have a higher risk of bleeding if you take warfarin sodium tablets and:
 MEDICATION GUIDE Warfarin (WAR-far-in) Sdium (SO-dee-um) Tablets USP The 7.5 mg tablets cntain FD&C Yellw N. 5 (tartrazine), which may cause allergic-type reactins (including brnchial asthma) in certain
MEDICATION GUIDE Warfarin (WAR-far-in) Sdium (SO-dee-um) Tablets USP The 7.5 mg tablets cntain FD&C Yellw N. 5 (tartrazine), which may cause allergic-type reactins (including brnchial asthma) in certain
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub OX own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for Sublingual or Buccal Administration (CIII)
 MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub OX wn) (buprenrphine and nalxne) Sublingual Film fr Sublingual r Buccal Administratin (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE sublingual film in a secure place away frm children.
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub OX wn) (buprenrphine and nalxne) Sublingual Film fr Sublingual r Buccal Administratin (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE sublingual film in a secure place away frm children.
CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION
 CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
Glaucoma Interviews: Due Tuesday, May 22 nd
 Glaucma Interviews: Due Tuesday, May 22 nd 1) Read the glaucma article well! It will explain what it is, plus tell yu sme symptms and risk factrs. Yu may want t use a highlighter r pen t mark imprtant
Glaucma Interviews: Due Tuesday, May 22 nd 1) Read the glaucma article well! It will explain what it is, plus tell yu sme symptms and risk factrs. Yu may want t use a highlighter r pen t mark imprtant
New Patient Information Sheet PLEASE COMPLETE THIS ENTIRE FORM. Date of Appointment: / /
 New Patient Infrmatin Sheet PLEASE COMPLETE THIS ENTIRE FORM The frm may seem lengthy but it is very imprtant t help us understand yur pain cmplaints. This will help us prvide yu with the highest level
New Patient Infrmatin Sheet PLEASE COMPLETE THIS ENTIRE FORM The frm may seem lengthy but it is very imprtant t help us understand yur pain cmplaints. This will help us prvide yu with the highest level
DEMENTIA. DESCRIPTION: a progressive, degenerative disease of the brain, which causes impairment of thinking and memory
 DEMENTIA Dementia a syndrme cnsisting f a number f symptms including lss f memry, judgment and reasning, and changes in md and behavir the changes may affect a persn's ability t functin at wrk, in scial
DEMENTIA Dementia a syndrme cnsisting f a number f symptms including lss f memry, judgment and reasning, and changes in md and behavir the changes may affect a persn's ability t functin at wrk, in scial
IAEM Clinical Guideline 12 Foreign Bodies: The Emergency Department Management of Inhaled and Inserted Objects in Children
 IAEM Clinical Guideline 12 Freign Bdies: The Emergency Department Management f Inhaled and Inserted Objects in Children Versin 1 August 2018 Authr: Dr Susan Uí Bhrin Adapted with Permissin frm the Jint
IAEM Clinical Guideline 12 Freign Bdies: The Emergency Department Management f Inhaled and Inserted Objects in Children Versin 1 August 2018 Authr: Dr Susan Uí Bhrin Adapted with Permissin frm the Jint
Adult Preventive Care Guidelines
 Adult Preventive Care Guidelines Gundersen is yur partner fr better health. We want t wrk with yu t make sure that yu and yur family are as healthy as pssible. That can be accmplished best if we wrk tgether
Adult Preventive Care Guidelines Gundersen is yur partner fr better health. We want t wrk with yu t make sure that yu and yur family are as healthy as pssible. That can be accmplished best if we wrk tgether
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the Product Information
 Changes t the Prduct infrmatin as apprved by the CHMP n 13 Octber 2016, pending endrsement by the Eurpean Cmmissin Annex III Amendments t relevant sectins f the Prduct Infrmatin Nte: These amendments t
Changes t the Prduct infrmatin as apprved by the CHMP n 13 Octber 2016, pending endrsement by the Eurpean Cmmissin Annex III Amendments t relevant sectins f the Prduct Infrmatin Nte: These amendments t
What s your diagnosis? Signlament: 11 y MC Maltese Mix. Presenting complaint: Pollakiuria with hematuria.
 What s yur diagnsis? Signlament: 11 y MC Maltese Mix Presenting cmplaint: Pllakiuria with hematuria. Histry: Zippy presented with a 4 day histry f pllakiuria. Straining t urinate had nt been nted, hwever
What s yur diagnsis? Signlament: 11 y MC Maltese Mix Presenting cmplaint: Pllakiuria with hematuria. Histry: Zippy presented with a 4 day histry f pllakiuria. Straining t urinate had nt been nted, hwever
Tendon problems can happen in people of all ages who take levofloxacin. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones.
 Medicatin Guide LEVOFLOXACIN (LEE ve FLOX a sin) INJECTION, 25 mg/ml and LEVOFLOXACIN (LEE ve FLOX a sin) INJECTION in 5% Dextrse fr Intravenus Use Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start taking levflxacin
Medicatin Guide LEVOFLOXACIN (LEE ve FLOX a sin) INJECTION, 25 mg/ml and LEVOFLOXACIN (LEE ve FLOX a sin) INJECTION in 5% Dextrse fr Intravenus Use Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start taking levflxacin
Close to spine/ point of attachment
 Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System S1: Intro to Kinesiology
 S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
Name: Date: Period: Notes: The Blood and Lymphatic System
 Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Ischemic heart disease (angina/chest pain)
 Ischemic heart disease (angina/chest pain) External resurces Stable angina: management NICE guidelines [CG126] Updated :Aug 2016 https://www.nice.rg.uk/guidance/cg126 Chest pain f recent nset [CG95] Nvember
Ischemic heart disease (angina/chest pain) External resurces Stable angina: management NICE guidelines [CG126] Updated :Aug 2016 https://www.nice.rg.uk/guidance/cg126 Chest pain f recent nset [CG95] Nvember
What is Asthma? A collaborative effort of Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC and The Pennsylvania Child Welfare Resource Center
 A cllabrative effrt f Children s Hspital f Pittsburgh f UPMC and The Pennsylvania Child Welfare Resurce Center What is Asthma? Jennifer E. Wlfrd, DO, MPH, FAAP Children s Hspital f Pittsburgh, Divisin
A cllabrative effrt f Children s Hspital f Pittsburgh f UPMC and The Pennsylvania Child Welfare Resurce Center What is Asthma? Jennifer E. Wlfrd, DO, MPH, FAAP Children s Hspital f Pittsburgh, Divisin
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Male genitalia examination
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Male genitalia examinatin Reviewed & ratified by Miss R Hamm Cnsultant Urlgist Dr Paul Cllins Cnsultant Gastrenterlgist Mr Ben Hrsburgh SpR Urlgist Dr V Taylr Jnes &
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Male genitalia examinatin Reviewed & ratified by Miss R Hamm Cnsultant Urlgist Dr Paul Cllins Cnsultant Gastrenterlgist Mr Ben Hrsburgh SpR Urlgist Dr V Taylr Jnes &
Refining Blood Collection Techniques to Improve Animal Welfare and Sample Quality
 Refining Bld Cllectin Techniques t Imprve Animal Welfare and Sample Quality Amy Allaire RLATG 1, Jennifer Jhnsn 2, Kimberly Maratea DVM PhD 2, Steven Bulé CMAR RLATG 1, Sara Savage DVM DACLAM 1 1 Dispsitin,
Refining Bld Cllectin Techniques t Imprve Animal Welfare and Sample Quality Amy Allaire RLATG 1, Jennifer Jhnsn 2, Kimberly Maratea DVM PhD 2, Steven Bulé CMAR RLATG 1, Sara Savage DVM DACLAM 1 1 Dispsitin,
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE ZINBRYTA (zin-bry-tuh) (daclizumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Use Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe 150 mg
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE ZINBRYTA (zin-bry-tuh) (daclizumab) Injectin, fr Subcutaneus Use Single-Dse Prefilled Syringe 150 mg Read this Instructins fr Use befre yu start using ZINBRYTA and each time yu get
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE ZINBRYTA (zin-bry-tuh) (daclizumab) Injectin, fr Subcutaneus Use Single-Dse Prefilled Syringe 150 mg Read this Instructins fr Use befre yu start using ZINBRYTA and each time yu get
9631 N Nevada St. Suite 210. Spokane, WA Phone: (509) and Fax: (877) Jeffrey R. Jamison, D.O. and Mark J Erwin, PA-C
 9631 N Nevada St. Suite 210 Spkane, WA 99218 Phne: (509) 319-2430 and Fax: (877)568-2402 Jeffrey R. Jamisn, D.O. and Mark J Erwin, PA-C Yu are scheduled fr a medical examinatin with n. The fllwing instructins
9631 N Nevada St. Suite 210 Spkane, WA 99218 Phne: (509) 319-2430 and Fax: (877)568-2402 Jeffrey R. Jamisn, D.O. and Mark J Erwin, PA-C Yu are scheduled fr a medical examinatin with n. The fllwing instructins
Frequently Asked Questions: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing
 Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
Active elbow motion is when your own muscles move the elbow back and forth.
 Initial Pstperative Shulder Care and Exercise: **Can be dne if a biceps tendesis has been perfrmed. If a biceps tendesis prcedure has been perfrmed, active elbw mtin is delayed up t 6 weeks. Please clarify
Initial Pstperative Shulder Care and Exercise: **Can be dne if a biceps tendesis has been perfrmed. If a biceps tendesis prcedure has been perfrmed, active elbw mtin is delayed up t 6 weeks. Please clarify
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Sensory System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Thyroidectomy is the removal of the whole of, or part of the thyroid gland.
 THYROIDECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that
THYROIDECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that
Address: City: State. Phone: (Home) (Work): (Cell): Age Date of Birth / / Occupation. Referred by: Patient s condition: Duration of Problem:
 Patient s Last Name: First Name: Address: City: State Zip Phne: (Hme) (Wrk): (Cell): Age f Birth / / Email: Occupatin Referred by: Patient s cnditin: Duratin f Prblem: Dctr: Dctr s Telephne: N. in husehld
Patient s Last Name: First Name: Address: City: State Zip Phne: (Hme) (Wrk): (Cell): Age f Birth / / Email: Occupatin Referred by: Patient s cnditin: Duratin f Prblem: Dctr: Dctr s Telephne: N. in husehld
Patient Health History
 Patient Health Histry Name: Date f Birth: Age: SS #: Tday's Date: Sex: Male Height: Female Primary Care Physician: Phne Number: Referring MD: Phne Number: Other MD's: Name/Specialty Pharmacy Name: Pharmacy
Patient Health Histry Name: Date f Birth: Age: SS #: Tday's Date: Sex: Male Height: Female Primary Care Physician: Phne Number: Referring MD: Phne Number: Other MD's: Name/Specialty Pharmacy Name: Pharmacy
Vaccine Information Statement: PNEUMOCOCCAL CONJUGATE VACCINE
 Vaccine Infrmatin Statement: PNEUMOCOCCAL CONJUGATE VACCINE Many Vaccine Infrmatin Statements are available in Spanish and ther languages. See www.immunize.rg/vis. Hjas de Infrmacián Sbre Vacunas están
Vaccine Infrmatin Statement: PNEUMOCOCCAL CONJUGATE VACCINE Many Vaccine Infrmatin Statements are available in Spanish and ther languages. See www.immunize.rg/vis. Hjas de Infrmacián Sbre Vacunas están
2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hockey Selection Camp August 16-19, 2018
 2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hckey Selectin Camp August 16-19, 2018 Strength and Cnditining Recmmendatins As discussed in the Call Fr Players letter, it is critical fr players t get their bdies
2019 Canada Winter Games Team NT Female Hckey Selectin Camp August 16-19, 2018 Strength and Cnditining Recmmendatins As discussed in the Call Fr Players letter, it is critical fr players t get their bdies
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Say Goodbye to Test Anxiety. Kortschak Center for Learning and Creativity University of Southern California Presented by: Eliza Peña
 Say Gdbye t Test Anxiety Krtschak Center fr Learning and Creativity University f Suthern Califrnia Presented by: Eliza Peña 1 Learning Objective By the end f this wrkshp, students will be able t: Recgnize
Say Gdbye t Test Anxiety Krtschak Center fr Learning and Creativity University f Suthern Califrnia Presented by: Eliza Peña 1 Learning Objective By the end f this wrkshp, students will be able t: Recgnize
Topic 11: Nervous System
 Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Postoperative Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Care WITH meniscus repair:
 Pstperative Anterir Cruciate Ligament Recnstructin Care WITH meniscus repair: Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant phne numbers t call. - If yu have cncerns after hurs,
Pstperative Anterir Cruciate Ligament Recnstructin Care WITH meniscus repair: Imprtant Phne Numbers: - Please see the cntact infrmatin abve fr imprtant phne numbers t call. - If yu have cncerns after hurs,
Name of procedure: Removal of submandibular salivary gland
 Oral facial surgery Surgical prcedure infrmatin leaflet Name f prcedure: Remval f submandibular salivary gland This leaflet explains sme f the benefits, risks and alternatives t the peratin. We want yu
Oral facial surgery Surgical prcedure infrmatin leaflet Name f prcedure: Remval f submandibular salivary gland This leaflet explains sme f the benefits, risks and alternatives t the peratin. We want yu
Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire DRAFT Priorities forum statement Number: Subject: Prostatism Date of decision: January 2010 Date of review:
 Bedfrdshire and Hertfrdshire DRAFT Pririties frum statement Number: Subject: Prstatism Date f decisin: January 2010 Date f review: Referral criteria Mst men with lwer urinary tract symptms due t benign
Bedfrdshire and Hertfrdshire DRAFT Pririties frum statement Number: Subject: Prstatism Date f decisin: January 2010 Date f review: Referral criteria Mst men with lwer urinary tract symptms due t benign
Patient Name: Date: Address City/State Zip Code. Home. Phone Cell: Work.
 Phne: 262-248-6700 Fax: 262-248-6764 Email: inf@excelfamilychir.cm Patient Name: Date: Address City/State Zip Cde Hme. Phne Cell: Wrk. Email Address: Sex: M F (Please circle) Date f Birth: Referred by:
Phne: 262-248-6700 Fax: 262-248-6764 Email: inf@excelfamilychir.cm Patient Name: Date: Address City/State Zip Cde Hme. Phne Cell: Wrk. Email Address: Sex: M F (Please circle) Date f Birth: Referred by:
Scottsdale Family Health
 Scttsdale Family Health New Patient Frm Patient Name: Date f Birth: Tday s Date PHARMACY: (Please list name and number f pharmacy yu wish t have prescriptins sent t.) Pharmacy Pharmacy Number MEDICAL HISTORY
Scttsdale Family Health New Patient Frm Patient Name: Date f Birth: Tday s Date PHARMACY: (Please list name and number f pharmacy yu wish t have prescriptins sent t.) Pharmacy Pharmacy Number MEDICAL HISTORY
Dr. Tozzi s and Dr. Roehrig s Patient Guide to Total Hip Replacement
 Dr. Tzzi s and Dr. Rehrig s Patient Guide t Ttal Hip Replacement This guide is meant t help yu better understand yur upcming hip surgery. It is generalized infrmatin, and individual patients have unique,
Dr. Tzzi s and Dr. Rehrig s Patient Guide t Ttal Hip Replacement This guide is meant t help yu better understand yur upcming hip surgery. It is generalized infrmatin, and individual patients have unique,
If you have any doubts or queries about your medication, please contact your doctor or pharmacist.
 Bayer plc Bayer Huse Strawberry Hill Newbury Berkshire RG14 1JA United Kingdm Telephne: +44 (0)1635 563 000 Facsimile: +44 (0)1635 563 393 Cmpany Web Site: http://www.bayer.c.uk Due t regulatry changes,
Bayer plc Bayer Huse Strawberry Hill Newbury Berkshire RG14 1JA United Kingdm Telephne: +44 (0)1635 563 000 Facsimile: +44 (0)1635 563 393 Cmpany Web Site: http://www.bayer.c.uk Due t regulatry changes,
Musculoskeletal MRI Protocols
 Musculskeletal MRI Prtcls Reviewed by: Lawrence Tang, MD Last Review Date: March 2018 Cntact: (866) 761-4200, ptin 1 *Nte t MR technlgists: Updates and new prtcls are underlined in this dcument. Please
Musculskeletal MRI Prtcls Reviewed by: Lawrence Tang, MD Last Review Date: March 2018 Cntact: (866) 761-4200, ptin 1 *Nte t MR technlgists: Updates and new prtcls are underlined in this dcument. Please
I am having a Rotator Cuff Repair
 I am having a Rtatr Cuff Repair A rtatr cuff repair is surgery t repair a trn tendn in the shulder. The rtatr cuff is a grup f muscles and tendns that frm a cuff ver the shulder jint. The muscles and tendns
I am having a Rtatr Cuff Repair A rtatr cuff repair is surgery t repair a trn tendn in the shulder. The rtatr cuff is a grup f muscles and tendns that frm a cuff ver the shulder jint. The muscles and tendns
Understanding and Recognizing Anxiety
 Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
MEDICATION GUIDE. (Interferon alfa-2b)
 MEDICATION GUIDE INTRON A (In-trn-aye) (Interfern alfa-2b) Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start taking INTRON A, and each time yu get a refill. There may be new infrmatin. This infrmatin des nt take
MEDICATION GUIDE INTRON A (In-trn-aye) (Interfern alfa-2b) Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start taking INTRON A, and each time yu get a refill. There may be new infrmatin. This infrmatin des nt take
Breast Cancer Awareness Month 2018 Key Messages (as of June 6, 2018)
 Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
