Surgical Treatment for Cervical Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis as a Cause of Dysphagia
|
|
|
- Bruno Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Surgical Treatment for Cervical Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis as a Cause of Dysphagia Katsuhito Yoshioka, Hideki Murakami, Satoru Demura, Satoshi Kato, Noritaka Yonezawa, Naoki Takahashi, Takaki Shimizu and Hiroyuki Tsuchiya Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan Abstract: Introduction: The majority of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) involving the anterior margin of the cervical vertebrae is asymptomatic, but it can cause dysphagia. Improvements in swallowing after surgical treatment have been reported in several case series. However, the appropriate amount of osteophyte for this disease in terms of the pathophysiology of dysphagia is still unknown. The current report describes the appropriate surgical procedure for dysphagia secondary to anterior cervical hyperostosis, and discusses the etiology of dysphagia. Methods: This is a retrospective review of four patients who presented with complaints of dysphagia secondary to anterior cervical hyperostosis. All patients underwent videofluoroscopic esophagrams (VFEs) to identify the specific region associated with the dysphagia. Esophageal obstruction was present at C3-4 in two patients and at C4-5 in two patients. Three patients underwent localized and limited of the anterior cervical. One patient underwent total of the anterior cervical, because re-ossification had occurred after a previous. Results: Postoperative VFE demonstrated an improvement in swallowing in the three patients who underwent limited of the. The patient who underwent total of the did not experience a full recovery of normal swallowing function. We concluded that the dysphagia was caused by both osteophyte obstruction and neuropathy resulting from the previous surgery or inflammation secondary to osteophyte irritation. Conclusions: Localized and limited of anterior cervical is recommended and should be considered for patients with dysphagia from anterior cervical hyperostosis. Keywords: Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), Ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament (OALL), Dysphagia Introduction Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) involving the cervical spine, also known as Forestier s disease 1),isa noninflammatory enthesopathy of unknown etiology. The diagnosis of DISH is established when the soft tissues of the anterolateral thoracolumbar spine are ossified in at least four contiguous segments, with flowing vertebral bony bridges and without obvious signs of intervertebral or apophyseal degenerative changes 2). The vast majority of patients with cervical are asymptomatic. In 1926, Mosher was the first to report a case of dysphagia due to a cervical spine osteophyte 3). In 1938, Lglauer reported the first surgical excision of a cervical spine osteophyte that was causing dysphagia 4). Dysphagia appears to be the most common presentation, though only a subset 0.1%-6% develops dysphagia due to cervical 5-7).However,acomprehensive discussion of the optimal surgical procedures according to pathogenesis is yet lacking. The aim of our study was to evaluate the appropriate extent of surgical of DISH-associated anterior causing dysphagia using preoperative and postoperative videofluoroscopic esophagram (VFE) findings. Subjects and Methods Four patients with DISH and anterior cervical presenting with the chief complaint of dysphagia are re- Corresponding author: Katsuhito Yoshioka, ortho0825yoshy@yahoo.co.jp Received: June 28, 2017, Accepted: October 20, 2017, Advance Publication: March 15, 2018 Copyright 2018 The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research 197
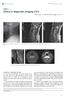
2 Table 1. Data of the Investigated Patients. Case Age Level of obstruction Disease duration Dysphagia Cough reflex Pharyngeal Epiglottic Videofluoroscopic assessment vallecula pyriform sinuses esophageal inlet Surgery 1 72 C3/4 2 years liquid/solid 2 68 C4/5 1 year liquid/solid decrease n.p. n.p. n.p. n.p. partial n.p. n.p. n.p. n.p. of the right side n.p. partial 3 68 C4/5 2 years solid n.p. n.p. n.p. n.p. n.p. partial 4 61 C3/4 8 months liquid/solid absence n.p. impaired of the right side extensive ported herein (Table 1). All four patients were men ranging in age from 61 to 72 years (mean age, 67.3 years). All patients complained of gradually progressing dysphagia for more than one year. Nonoperative management using a restricted diet of mainly soft foods and liquids was attempted in all patients; however, their complaints persisted. Patients were then referred to the authors institute for possible spinal surgical evaluation. All patients were also preoperatively assessed for gastroenterological or otolaryngological issues in order to exclude any intrinsic factors. In all four patients, lateral plain radiographs of the thoracic spine showed flowing ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament along the anterior vertebral bodies involving four or more contiguous levels, consistent with the diagnosis of DISH. Lateral plain radiographs of the cervical spine and sagittal computed tomography (CT) reconstruction showed protruding beaklike at C3/4 in one patient, and at C4/5 in two patients. Case 4 involved the postsurgical recurrence of an osteophyte, which was most protruding at C3/4. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) was identified by CT scans of the cervical spine in all patients. MR imaging demonstrated compression of the spinal canal in two patients. One of these patients (case 2) presented with mild clumsiness of the hands. VFE showed mechanical obstruction at the level of C3/4 in two patients (cases 1, 4), C4/5 in two patients (cases 2, 3). Although three cases revealed normal pharyngeal and normal laryngeal elevation, one case (case 4) demonstrated impaired laryngeal elevation. All four patients underwent surgical osteophyte. Results Three patients underwent localized and limited of the anterior beak-like at the level of the obstruction. Osteophytectomy was performed using a combination of osteotomes and diamond burs. The goal of reducing the mass was not to match the native anterior vertebral contour, but instead to match the level of the adjacent. Postoperative VFE at postoperative week two or three demonstrated remarkable improvement in swallowing function in these three patients. There were no complaints of obstruction in the transit of both solid and liquid es. Alternatively, one patient underwent total of the anterior cervical from C2 to T1 because of reossification subsequent to a previous partial. However, this patient did not experience a full recovery of normal swallowing function. Case 1 A 71-year-old male presented with a one-year history of slowly progressing dysphagia. He complained of difficulty in swallowing both liquid and solid diets with concomitant weight loss. Reduced mobility of the cervical spine was revealed on physical examination and X-ray. X-ray and CT reconstruction showed an anterior hyperostosis from C2 to C7 (Fig. 1a). The largest bony excrescences were 31 mm thick at the level of C3/4. VFE showed contrast medium residue in the valleculae at the level of C3/4 (Fig. 1b), but no in the pyriform sinuses or esophageal inlet. Pharyngeal and laryngeal elevation were normal. We concluded that the dysphagia was caused by mechanical obstruction due to the beak-like at the level of C3/ 4. The patient underwent localized and limited of the anterior beak-like from C3 to C4 (Fig. 1c). Postoperative VFE showed no remaining obstruction and he had no complaints of dysphagia during the swallowing of both solid and liquid es at follow-up (Fig. 1d). Case 4 A 62-year-old male presented with recurrence of dysphagia seven years after initial osteophyte. He complained of difficulty in swallowing both liquid and solid diets with concomitant weight loss for four months. Reduced mobility of the cervical spine was revealed on physical examination and X-ray. X-ray and CT reconstruction showed an anterior hyperostosis from C2 to T3, especially 198
3 Figure 1. Preoperative lateral radiograph of the cervical spine (a). Preoperative VFE shows obstruction at C3/4 (b). Postoperative lateral radiograph of the cervical spine (c). Postoperative VFE shows no obstruction (d). Figure 2. Preoperative axial cervical CT (a). Preoperative sagittal cervical CT (b). Preoperative VFE shows obstruction at C3/4 (c). Postoperative VFE revealed residue in the right side pyriform sinus, and esophageal inlet (d). on the right side (Fig. 2a, b). VFE showed contrast medium residue in the valleculae, right side pyriform sinus, and esophageal inlet (Fig. 2c). He had normal pharyngeal but impaired laryngeal elevation. We concluded that the dysphagia was caused by two pathologies: First, neuropathy induced by the previous surgery or inflammation secondary to osteophyte irritation; and second, mechanical obstruction due to regrowth of the osteophyte on the right side. Complete surgical removal of the was performed from C2 to T1 because of the recurrent nature of the case. VFE revealed no obstruction at the level of C3 to C4 (no contrast medium residue in the valleculae), and reduction in contrast medium residue in the right side pyriform sinus was observed three weeks postoperatively (Fig. 2d). However, a slight increasing of contrast medium residue in the esophageal inlet was identified. The patient achieved a slight improvement of the dysphagia one year after surgery. His dysphagia remained unchanged for the next year. Discussion The pathogenesis of dysphagia caused by anterior cervical hyperostosis is hypothesized to be the result of direct compression of the pharyngoesophageal segment. Seidler et al. 199
4 reported that larger than 10 mm thickness lead to symptoms 8). However, case 1 had no complaint until the size of progressed to 31 mm. This observation indicated that there is no direct correlation between the size of and the severity of symptoms. Rather, the osteophyte-size that causes dysphagia differs by site and individual. Furthermore, there are other mechanisms that cause dysphagia. Several possible explanations other than direct obstruction have been put forward: Several studies suggested neuropathy due to recurrent laryngeal nerve injury as a result of ongoing inflammation and fibrosis of the esophagus secondary to osteophyte irritation as a cause 9-14). One case report indicated a palsy of the left vocal cord due to pressure on the recurrent laryngeal nerve 15). Verlaan et al. analyzed 118 publications with a total of 204 patients between 1980 and ) and reported that swallowing dysfunction remained in only 13% of the patients after surgery. Likewise, in our case series, subjective symptoms showed complete improvement in three cases, with only case 4 showing persistent dysphagia following surgery. Preoperative VFE of case 4 revealed impaired laryngeal elevation. In postoperative VFE of case 4, impaired epiglottic was still observed, which suggested that pre-existing neuropathy was a cause of dysphagia. No contrast residue was observed in the valleculae and less contrast medium at the pyriform sinuses. This suggested that osteophyte was the mechanical cause of dysphagia. However, there was slight worsening of dysphagia in the esophageal inlet. Therefore, we hypothesized that extensive, total of the anterior cervical may increase the risk of damage to pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve, which, in our case, already had pre-existing neuropathy as a sequelae of the previous surgery that created prolonged inflammation and adhesion. Given the possibility that there is a factor other than mechanical compression that caused persistence of the symptoms even after surgical removal of the, careful preoperative evaluation of pharyngeal, laryngeal elevation, and other factors is essential, even in the case of large, evident. There is a controversy in the literature concerning the appropriate treatment of dysphagia due to Forestier s disease 10). The recommended first-line approach has been observation or diet modification and a regimen of anti-inflammatory medications 17). Resection of the offending anterior has represented the typical surgical intervention 16). However, previous reports did not address the extent of the osteophyte in detail 16,18). Some surgeons prefer the complete of all cervical spine 19-21). However, it was also reported that dysphagia persisted unchanged following surgery with extensive C3-6 osteophyte 20). We contend that extensive osteophyte is more disadvantageous than it is beneficial for the following two reasons: First, there is a possibility of neuropathy because the nerve is compressed for an extended period of time. Second, dysphagia tends to be more frequent in the C3 to C4 and 4 to C5 regions. Thus, we advocate for the localized and limited of based on VFE as the most appropriate treatment. Miyamoto et al. reported that patients with DISH who were treated with surgical of the anterior cervical without fusion developed radiological recurrence 12). However, only two patients became subsequently symptomatic, both with a minimum follow-up period of 10 years. On the other hand, Urrutia reported no radiological recurrence after anterior cervical osteophyte without fusion at one to nine years follow-ups 22) ;however,inthis previous study the cause and pathology of dysphagia was not discusses in detail. Several reports have insisted that appropriate management of this condition requires cervical fusion 12,23), as ligamentous ossification is believed to progress until rigidity is established. Nicolas H et al. also reported six cases of osteophytectomy and fusion 24). However, the possibility of adjacent segment osteophyte development after fusion surgery remains unclear. In the elderly population, tend to be slow growing, usually asymptomatic, and accompanied by dysphagia. It is necessary to accurately identify the site of mechanical obstruction using preoperative VFE if mechanical compression from anterior cervical osteophyte is the cause of dysphagia. Our first choice of strategy is partial osteophyte of the causative site without fusion. Osteophyte with fusion may be considered for younger patients with intervertebral mobility as a risk factor for recurrence. Conclusion We reported four cases of dysphagia secondary to anterior cervical hyperostosis. We recommend the localized and limited of anterior cervical according to pathogenesis. Wide surgical exposure and extensive anterior cervical osteophyte carry the risk of the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve damage due to the possibility of neuropathy from long term suppression. In such cases, VFE is necessary to accurately evaluate the cause of dysphagia. Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest. Author Contributions: Katsuhito Yoshioka wrote and prepared the manuscript, and all of the authors participated in the study design. All authors have read, reviewed, and approved the article. References 1. Forestier J, Rotes-Querol J. Senile ankylosing hyperostosis of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis. 1950;9(4): Resnick D, Shaul SR, Robins JM. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): Forestier s disease with extraspinal manifestations. Radiology. 1975;115(3): HP M. Exostoses of the cervical vertebrae as a cause for difficulty 200
5 in swallowing. Laryngoscope. 1926;36: SI. A case of dysphagia due to an osteochondroma of the cervical spine-osteotomy-recovery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1938;47: Kiss C, Szilagyi M, Paksy A, et al. Risk factors for diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: a case-control study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002;41(1): Aydin E, Akdogan V, Akkuzu B, et al. Six cases of Forestier syndrome, a rare cause of dysphagia. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006;126(7): Kmucha ST, Cravens RB, Jr. DISH syndrome and its role in dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994;110(4): Seidler TO, Perez Alvarez JC, Wonneberger K, et al. Dysphagia caused by ventral of the cervical spine: clinical and radiographic findings. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266(2): Masiero S, Padoan E, Bazzi M, et al. Dysphagia due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: an analysis of five cases. Rheumatol Int. 2010;30(5): Kos MP, van Royen BJ, David EF, et al. Anterior cervical resulting in severe dysphagia and aspiration: two case reports and literature review. J Laryngol Otol. 2009;123(10): McCafferty RR, Harrison MJ, Tamas LB, et al. Ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament and Forestier s disease: an analysis of seven cases. J Neurosurg. 1995;83(1): Miyamoto K, Sugiyama S, Hosoe H, et al. Postsurgical recurrence of causing dysphagia in patients with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(11): Stuart D. Dysphagia due to cervical. A description of five patients and a review of the literature. Int Orthop. 1989;13(2): Zerhouni EA, Bosma JF, Donner MW. Relationship of cervical spine disorders to dysphagia. Dysphagia. 1987;1: Fuerderer S, Eysel-Gosepath K, Schroder U, et al. Retro-pharyngeal obstruction in association with of the cervical spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(6): Verlaan JJ, Boswijk PF, de Ru JA, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine: an underestimated cause of dysphagia and airway obstruction. Spine J. 2011;11(11): Dutta S, Biswas KD, Mukherjee A, et al. Dysphagia due to forestier disease: three cases and systematic literature review. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;66(Suppl 1): Carlson ML, Archibald DJ, Graner DE, et al. Surgical management of dysphagia and airway obstruction in patients with prominent ventral cervical. Dysphagia. 2011;26(1): Egerter AC, Kim ES, Lee DJ, et al. Dysphagia Secondary to Anterior Osteophytes of the Cervical Spine. Global Spine J. 2015;5(5): e Fox TP, Desai MK, Cavenagh T, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: a rare cause of dysphagia and dysphonia. BMJ Case Rep. 2013; Zhang C, Ruan D, He Q, et al. Progressive dysphagia and neck pain due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine: a case report and literature review. Clin Interv Aging. 2014; 9: Urrutia J, Bono CM. Long-term results of surgical treatment of dysphagia secondary to cervical diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Spine J. 2009;9(9):e Suzuki K, Ishida Y, Ohmori K. Long term follow-up of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in the cervical spine. Analysis of progression of ossification. Neuroradiology. 1991;33(5): von der Hoeh NH, Voelker A, Jarvers JS, et al. Results after the surgical treatment of anterior cervical hyperostosis causing dysphagia. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(Suppl 4):S Spine Surgery and Related Research is an Open Access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view the details of this license, please visit ( mmons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/). 201
Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine
 Spine Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine A REPORT OF SEVEN CASES J. Mizuno, H. Nakagawa, J. Song From Aichi Medical University, Aichi-gun
Spine Symptomatic ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament with stenosis of the cervical spine A REPORT OF SEVEN CASES J. Mizuno, H. Nakagawa, J. Song From Aichi Medical University, Aichi-gun
A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis
 CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:614-618 A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis İlknur Albayrak 1, Sinan Bağcacı
CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:614-618 A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis İlknur Albayrak 1, Sinan Bağcacı
Case Report. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(6):865-870 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.6.865 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Kinematic Changes in Swallowing After Surgical
Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(6):865-870 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.6.865 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Kinematic Changes in Swallowing After Surgical
Prevalence of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Diagnosed by Whole Spine Computed Tomography: A Preliminary Study
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:41-46 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.41 Prevalence of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Diagnosed by Whole Spine Computed Tomography:
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:41-46 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.41 Prevalence of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Diagnosed by Whole Spine Computed Tomography:
Dysphagia Secondary to Anterior Osteophytes of the Cervical Spine
 e78 Case Report GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Dysphagia Secondary to Anterior Osteophytes of the Cervical Spine Alexander C. Egerter 1 Eric S. Kim 1 Darrin J. Lee 1 Jonathan J. Liu 1 Gilbert Cadena 1 Ripul
e78 Case Report GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Dysphagia Secondary to Anterior Osteophytes of the Cervical Spine Alexander C. Egerter 1 Eric S. Kim 1 Darrin J. Lee 1 Jonathan J. Liu 1 Gilbert Cadena 1 Ripul
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
ACDF. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. An introduction to
 An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
Frozen recapping laminoplasty: a new technique to treat spinal tumor
 EUROSPINE 2018 19-21 September, Barcelona, Spain Frozen recapping laminoplasty: a new technique to treat spinal tumor Noritaka Yonezawa, Hideki Murakami, Satoru Demura, Satoshi Kato, Katsuhito Yoshioka,
EUROSPINE 2018 19-21 September, Barcelona, Spain Frozen recapping laminoplasty: a new technique to treat spinal tumor Noritaka Yonezawa, Hideki Murakami, Satoru Demura, Satoshi Kato, Katsuhito Yoshioka,
Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion
 Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(6): 141-145 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160406.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C
Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(6): 141-145 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160406.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Disclosures: T. Yoshii: None. T. Yamada: None. T. Taniyama: None. S. Sotome: None. T. Kato: None. S. Kawabata: None. A. Okawa: None.
 Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
OSSIFIED ANTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT: A STUDY IN ADULT HUMAN DRY VERTEBRA IN CENTRAL INDIA
 Original Research Article OSSIFIED ANTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT: A STUDY IN ADULT HUMAN DRY VERTEBRA IN CENTRAL INDIA Ashita Kaore* 1, Ashish kamdi 2, M.P Fulpatil 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of
Original Research Article OSSIFIED ANTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT: A STUDY IN ADULT HUMAN DRY VERTEBRA IN CENTRAL INDIA Ashita Kaore* 1, Ashish kamdi 2, M.P Fulpatil 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of
Title. CitationSpine, 34(19): E709-E711. Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information.
 Title Cervical Myelopathy by C1 Posterior Tubercle Impinge Author(s)Kawabori, Masahito; Hida, Kazutoshi; Akino, Minoru; CitationSpine, 34(19): E709-E711 Issue Date 2009-09-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/70791
Title Cervical Myelopathy by C1 Posterior Tubercle Impinge Author(s)Kawabori, Masahito; Hida, Kazutoshi; Akino, Minoru; CitationSpine, 34(19): E709-E711 Issue Date 2009-09-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/70791
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy in 60 consecutive patients with cervical ossi cation of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
ASJ. Prevalence of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis in Patients with Spinal Disorders. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Prevalence Spine J 2017;11(1):63-70 of diffuse idiopathic https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.1.63 skeletal hyperostosis Prevalence of Diffuse
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Prevalence Spine J 2017;11(1):63-70 of diffuse idiopathic https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.1.63 skeletal hyperostosis Prevalence of Diffuse
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis versus Ankylosing Spondylitis: Brief Case Review
 Copyright 2006, Barrow Neurological Institute Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis versus Ankylosing Spondylitis: Brief Case Review Hamidreza Aliabadi, MD David Biglari, DO L. Fernando Gonzalez, MD
Copyright 2006, Barrow Neurological Institute Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis versus Ankylosing Spondylitis: Brief Case Review Hamidreza Aliabadi, MD David Biglari, DO L. Fernando Gonzalez, MD
CMEARTICLE * * * Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed
 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery,Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine,Nagoya,Japan 2
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 583 589, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.4.583 ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of sagittal alignment and range of motion of the cervical spine using multi-detector- row computed tomography
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 583 589, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.4.583 ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of sagittal alignment and range of motion of the cervical spine using multi-detector- row computed tomography
Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior Endplate Lesion after Recurrent Disc Herniation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Case Report Spontaneous Symptomatic Pseudoarthrosis at the L2-L3 Intervertebral Space with Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 497458, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/497458 Case Report Spontaneous Symptomatic Pseudoarthrosis at the L2-L3 Intervertebral Space with Diffuse
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 497458, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/497458 Case Report Spontaneous Symptomatic Pseudoarthrosis at the L2-L3 Intervertebral Space with Diffuse
ASJ. Surgical Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Stabilization for Spinal Fractures in Patients with Ankylosing Spinal Disorders
 Asian Spine Journal Clinical Study Asian Spine J 2018;12(3):434-441 https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2018.12.3.434 Surgical Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Stabilization for Spinal Fractures in Patients with
Asian Spine Journal Clinical Study Asian Spine J 2018;12(3):434-441 https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2018.12.3.434 Surgical Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Stabilization for Spinal Fractures in Patients with
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft. Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD
 Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis
 35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29800 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Moojen, Wouter Anton Title: Introducing new implants and imaging techniques for
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29800 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Moojen, Wouter Anton Title: Introducing new implants and imaging techniques for
One hospitalization with any of the defining diagnoses of spondylosis (see ICD9 and ICD10 code lists below) in any diagnostic position; or
 1 ORTHO 16 SPONDYLOSIS Includes spondylopathies due to asymptomatic and symptomatic degenerative changes of the bony spine (M47 and M48); Does not include ankylosing spondylitis (M45), other inflammatory
1 ORTHO 16 SPONDYLOSIS Includes spondylopathies due to asymptomatic and symptomatic degenerative changes of the bony spine (M47 and M48); Does not include ankylosing spondylitis (M45), other inflammatory
Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
 Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - A Multicenter Retrospective Study - Mitsumasa Hayashida,
Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - A Multicenter Retrospective Study - Mitsumasa Hayashida,
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation
 The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Ethn Dis. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 September 8.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Ethn Dis. 2008 ; 18(2 Suppl 2): S2 137-40. Dysphagia And Lung Aspiration Secondary To Anterior Cervical Osteophytes: A Case Report
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Ethn Dis. 2008 ; 18(2 Suppl 2): S2 137-40. Dysphagia And Lung Aspiration Secondary To Anterior Cervical Osteophytes: A Case Report
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Nagoya, Japan ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Key Primary CPT Codes: Refer to pages: 7-9 Last Review Date: October 2016 Medical Coverage Guideline Number:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA
 AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
Hehuan Xia, Yongsheng Lin, Zhihong Wang, Yipeng Yang, Bin Xu, Junming Cao
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(5):5039-5044 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0075161 Original Article Efficacy of posterior decompression and vertebral fusion for treatment of patients with unstable cervical
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(5):5039-5044 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0075161 Original Article Efficacy of posterior decompression and vertebral fusion for treatment of patients with unstable cervical
Pott s kyphosis. University Affiliated Sixth People s Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai , P.
 QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
Life expectancy after cervical laminoplasty Causes of the fatal prognosis at the early stage (within 5 years)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Life expectancy after cervical laminoplasty Causes of the fatal prognosis at the early stage (within 5 years) Yoshiharu Kawaguchi 1), Masato Nakano 1),
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Life expectancy after cervical laminoplasty Causes of the fatal prognosis at the early stage (within 5 years) Yoshiharu Kawaguchi 1), Masato Nakano 1),
Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki 3), Masatsune Yamagata 1), Yoshikazu Ikeda 1), Fumitake Nakajima 1)
 Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
CASE REPORT TOTAL EN BLOC SPONDYLECTOMY FOR L2 CHORDOMA: A CASE REPORT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 73. 197 ~ 203, 2011 CASE REPORT TOTAL EN BLOC SPONDYLECTOMY FOR L2 CHORDOMA: A CASE REPORT NORIMITSU WAKAO 1, SHIRO IMAGAMA 1, ZENYA ITO 1, KEI ANDO 1, KENICHI HIRANO 1, RYOJI TAUCHI
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 73. 197 ~ 203, 2011 CASE REPORT TOTAL EN BLOC SPONDYLECTOMY FOR L2 CHORDOMA: A CASE REPORT NORIMITSU WAKAO 1, SHIRO IMAGAMA 1, ZENYA ITO 1, KEI ANDO 1, KENICHI HIRANO 1, RYOJI TAUCHI
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome
 Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Cervical Osteophytes Impinging on the Pharynx: Importance of Size and Concurrent Disorders for Development of Aspiration
 G. Strasser 1 W. Schima 1 E. Schober 1 P. Pokieser 1 A. Kaider 2 D.-M. Denk 3 Received April 14, 1999; accepted after revision June 30, 1999. 1 Department of Radiology and Ludwig Boltzmann-Institute for
G. Strasser 1 W. Schima 1 E. Schober 1 P. Pokieser 1 A. Kaider 2 D.-M. Denk 3 Received April 14, 1999; accepted after revision June 30, 1999. 1 Department of Radiology and Ludwig Boltzmann-Institute for
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis with Cervical Spinal Cord Injury A Report of 3 Cases and a Literature Review
 Case Report 257 Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis with Cervical Spinal Cord Injury A Report of 3 Cases and a Literature Review S Sreedharan, 1 MBBS, YH Li, 2 FRCS (Glas, Edin), M Med (Surg), FAMS
Case Report 257 Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis with Cervical Spinal Cord Injury A Report of 3 Cases and a Literature Review S Sreedharan, 1 MBBS, YH Li, 2 FRCS (Glas, Edin), M Med (Surg), FAMS
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
Is OPLL-induced canal stenosis a risk factor of cord injury in cervical trauma?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 567-574 ORIGINAL STUDY Is OPLL-induced canal stenosis a risk factor of cord injury in cervical trauma? Kyung-Jin Song, Chan-Il Park, Do-Yeon Kim, Young-Ran Jung, Kwang-Bok
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 567-574 ORIGINAL STUDY Is OPLL-induced canal stenosis a risk factor of cord injury in cervical trauma? Kyung-Jin Song, Chan-Il Park, Do-Yeon Kim, Young-Ran Jung, Kwang-Bok
Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane
 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life
 Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
A Clicking Larynx: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges
 The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report A Clicking Larynx: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges Derrek A. Heuveling, MD, PhD ; Maarten
The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Case Report A Clicking Larynx: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges Derrek A. Heuveling, MD, PhD ; Maarten
Spondylolysis repair using a pedicle screw hook or claw-hook system. a comparison of bone fusion rates
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Spondylolysis repair using a pedicle screw hook or claw-hook system. a comparison of bone fusion rates Ko Ishida 1), Yoichi Aota 2), Naoto Mitsugi 1),
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Spondylolysis repair using a pedicle screw hook or claw-hook system. a comparison of bone fusion rates Ko Ishida 1), Yoichi Aota 2), Naoto Mitsugi 1),
Cervical myeloradiculopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament with versus without diffuse idiopathic spinal hyperostosis
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 Cervical myeloradiculopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament with versus without
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 Cervical myeloradiculopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament with versus without
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Prominent tibial tubercles
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Prominent tibial tubercles Michael Flannery, Damien Knudson, Yumeng Zhang ABSTRACT Abstract is not required for Clinical Images International
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Prominent tibial tubercles Michael Flannery, Damien Knudson, Yumeng Zhang ABSTRACT Abstract is not required for Clinical Images International
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS
 Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
SpineFAQs. Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
 SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
Association of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) and. Calcification and Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
 Association of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) and Calcification and Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament DONALD RESNICK,1 JOSE GUERRA, JR.,1 CHARLES A. ROBINSON,2 AND VINTON
Association of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) and Calcification and Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament DONALD RESNICK,1 JOSE GUERRA, JR.,1 CHARLES A. ROBINSON,2 AND VINTON
Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment of multi-segmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc disease: Is there a difference at 12 months?
 Original research ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc ( ) 51 51 56 ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc
Original research ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc ( ) 51 51 56 ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc
Abdominal Trunk Muscle Weakness is Associated with Chronic Low Back Pain and Locomotive Syndrome
 Abdominal Trunk Muscle Weakness is Associated with Chronic Low Back Pain and Locomotive Syndrome Norihiro Oku, Satoshi Kato, Hideki Murakami, Satoru Demura, Kazuya Shinmura, Noriaki Yokogawa, Takaki Shimizu,
Abdominal Trunk Muscle Weakness is Associated with Chronic Low Back Pain and Locomotive Syndrome Norihiro Oku, Satoshi Kato, Hideki Murakami, Satoru Demura, Kazuya Shinmura, Noriaki Yokogawa, Takaki Shimizu,
Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty
 CASE REPORT SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty Seiichi Odate, Jitsuhiko Shikata and Tsunemitsu
CASE REPORT SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty Seiichi Odate, Jitsuhiko Shikata and Tsunemitsu
ASJ. A Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
Idiopathic scoliosis Scoliosis Deformities I 06
 What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Spine Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Indiana University School of Medicine
 Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
ASJ. Anterior Herniation of Partially Calcified and Degenerated Cervical Disc Causing Dysphagia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 Asian Spine Journal 612 Cagatay Ozdol Case Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2015.9.4.612 Anterior Herniation of Partially Calcified and Degenerated Cervical Disc Causing Dysphagia Cagatay Ozdol
Asian Spine Journal 612 Cagatay Ozdol Case Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2015.9.4.612 Anterior Herniation of Partially Calcified and Degenerated Cervical Disc Causing Dysphagia Cagatay Ozdol
Imaging Characteristics of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis With an Emphasis on Acute Spinal Fractures: Review
 Imaging Characteristics of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis With an Emphasis on cute Spinal Fractures: Review Mihra S. Taljanovic 1, Tim. Hunter 1, Ronald J. Wisneski 2, Joachim F. Seeger 1, Christopher
Imaging Characteristics of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis With an Emphasis on cute Spinal Fractures: Review Mihra S. Taljanovic 1, Tim. Hunter 1, Ronald J. Wisneski 2, Joachim F. Seeger 1, Christopher
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Introduction SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Cervical Kyphotic Deformity after Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament with Normal Sagittal Spinal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Cervical Kyphotic Deformity after Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament with Normal Sagittal Spinal
RETROLISTHESIS. Retrolisthesis. is found mainly in the cervical spine and lumbar region but can also be often seen in the thoracic spine
 RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics
 Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
ASJ. Analysis of the Prevalence and Distribution of Cervical and Thoracic Compressive Lesions of the Spinal Cord in Lumbar Degenerative Disease
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia: A Case Series
 C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
Complex Spine Symposium January 12th, Balgrist University Hospital
 DEGENERATIVE CERVICAL MYELOPATHY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Prof. Dr. Mazda Farshad Chair of Orthopedic Surgery Chief of Spine Surgery Medical Director CERVICAL MYELOPATHY - CAUSES degenerative cervical
DEGENERATIVE CERVICAL MYELOPATHY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Prof. Dr. Mazda Farshad Chair of Orthopedic Surgery Chief of Spine Surgery Medical Director CERVICAL MYELOPATHY - CAUSES degenerative cervical
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
Prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) assessed with wholespine computed tomography in 1479 subjects
 Hiyama et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:178 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2108-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) assessed with
Hiyama et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:178 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2108-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) assessed with
Artificial Disc Replacement, Cervical
 Artificial Disc Replacement, Cervical Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.001 02/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 11/01/2011 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Artificial Disc Replacement, Cervical Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.001 02/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 11/01/2011 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Case report. Open Access. Abstract
 Open Access Case report Acute posterior neck pain in adult: a case series Yasuhiro Homma*, Akira Itoi, Tomoya Muta, Yoshio Shimamura, Kiyohito Naito, Atsuhiko Mogami, Osamu Obayashi, Colin G Murphy and
Open Access Case report Acute posterior neck pain in adult: a case series Yasuhiro Homma*, Akira Itoi, Tomoya Muta, Yoshio Shimamura, Kiyohito Naito, Atsuhiko Mogami, Osamu Obayashi, Colin G Murphy and
UPPER CERVICAL MYELOPATHY WITH METATROPIC DYSPLASIA
 UPPER CERVICAL MYELOPATHY WITH METATROPIC DYSPLASIA REPORT OF 4 SURGICAL CASES Yujiro Takeshita*, Kota Miyoshi**, Tomoaki Kitagawa** *Department of Orthopaedic and Spine Surgery, University of Tokyo, Japan
UPPER CERVICAL MYELOPATHY WITH METATROPIC DYSPLASIA REPORT OF 4 SURGICAL CASES Yujiro Takeshita*, Kota Miyoshi**, Tomoaki Kitagawa** *Department of Orthopaedic and Spine Surgery, University of Tokyo, Japan
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Forestier Disease: Single-Center Surgical Experience and Brief Literature Review
 Annals nfowtogy. Rhinolngy & Laryngology 119(9):602-608. 2010 Annals Publishing Company. All rights reserved. Forestier Disease: Single-Center Surgical Experience and Brief Literature Review Livio Presutti,
Annals nfowtogy. Rhinolngy & Laryngology 119(9):602-608. 2010 Annals Publishing Company. All rights reserved. Forestier Disease: Single-Center Surgical Experience and Brief Literature Review Livio Presutti,
Title. Author(s)Sudo, Hideki; Taneichi, H.; Kaneda, K. CitationSpinal Cord, 44(2): Issue Date Doc URL
 Title Secondary medulla oblongata involvement following mi instability in a patient with ossification of the po Author(s)Sudo, Hideki; Taneichi, H.; Kaneda, K. CitationSpinal Cord, 44(2): 126-129 Issue
Title Secondary medulla oblongata involvement following mi instability in a patient with ossification of the po Author(s)Sudo, Hideki; Taneichi, H.; Kaneda, K. CitationSpinal Cord, 44(2): 126-129 Issue
Retro-odontoid pseudotumors are mass lesions formed
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Microscopic Posterior Transdural Resection of Cervical Retro-Odontoid Pseudotumors Yasushi Fujiwara, MD, PhD,* Hideki Manabe,* Tadayoshi Sumida,w Nobuhiro Tanaka,z and Takahiko Hamasakiy
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Microscopic Posterior Transdural Resection of Cervical Retro-Odontoid Pseudotumors Yasushi Fujiwara, MD, PhD,* Hideki Manabe,* Tadayoshi Sumida,w Nobuhiro Tanaka,z and Takahiko Hamasakiy
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Anterior Cervical Fusion: What is the Effect on Swallow Function?
 Anterior Cervical Fusion: What is the Effect on Swallow Function? Rebecca L. Gould, MSC, CCC-SLP, BRS-S rebec26050@aol.com (561) 833-2090 www.med-speech.com STATE OF THE ART EVALUATION Anterior Cervical
Anterior Cervical Fusion: What is the Effect on Swallow Function? Rebecca L. Gould, MSC, CCC-SLP, BRS-S rebec26050@aol.com (561) 833-2090 www.med-speech.com STATE OF THE ART EVALUATION Anterior Cervical
Hoarseness. Evidence-based Key points for Approach
 Hoarseness Evidence-based Key points for Approach Sasan Dabiri, Assistant Professor Department of otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medial Sciences Definition:
Hoarseness Evidence-based Key points for Approach Sasan Dabiri, Assistant Professor Department of otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medial Sciences Definition:
Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI /s
 Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0515-1 TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Intraoperative evaluation using mobile computed tomography in anterior cervical
Yoshii et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:12 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0515-1 TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Intraoperative evaluation using mobile computed tomography in anterior cervical
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
PARADIGM SPINE. Patient Information. Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal
 PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
 283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
Pulmonary Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Pulmonary Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis PULMONARY MEDICINE. DR. R. ADITYAVADAN FINAL YEAR PG, DEPT. OF ETIOLOGY AS is a chronic multisystem disease characterized by inflammation of the spine,
Pulmonary Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis PULMONARY MEDICINE. DR. R. ADITYAVADAN FINAL YEAR PG, DEPT. OF ETIOLOGY AS is a chronic multisystem disease characterized by inflammation of the spine,
Case Report. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2013;37(3):438-442 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.3.438 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Traumatic Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation Presenting
Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2013;37(3):438-442 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.3.438 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Traumatic Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation Presenting
Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body lesions
 Eshra Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2019) 33:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0004-9 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body
Eshra Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2019) 33:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0004-9 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body
Risk factors of instrumentation failure after multilevel total en bloc spondylectomy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Risk factors of instrumentation failure after multilevel total en bloc spondylectomy Katsuhito Yoshioka 1), Hideki Murakami 1), Satoru Demura 1), Satoshi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Risk factors of instrumentation failure after multilevel total en bloc spondylectomy Katsuhito Yoshioka 1), Hideki Murakami 1), Satoru Demura 1), Satoshi
Applied physiology. 7- Apr- 15 Swallowing Course/ Anatomy and Physiology
 Applied physiology Temporal measures: Oral Transit Time (OTT) Pharyngeal Delay Time (PDT) Pharyngeal Transit Time (PTT) Oropharyngeal Swallowing Efficiency Score (OPSE score) 7- Apr- 15 Swallowing Course/
Applied physiology Temporal measures: Oral Transit Time (OTT) Pharyngeal Delay Time (PDT) Pharyngeal Transit Time (PTT) Oropharyngeal Swallowing Efficiency Score (OPSE score) 7- Apr- 15 Swallowing Course/
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Nara Medical University, Kashihara, Nara, Japan 2
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 1, pp 60~65, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.1.60 Posterior Fixation of a Cervical Fracture Using the RRS Loop Spine System and Polyethylene Tape in an Elderly
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 1, pp 60~65, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.1.60 Posterior Fixation of a Cervical Fracture Using the RRS Loop Spine System and Polyethylene Tape in an Elderly
Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients
 Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients Shota Takenaka* a, MD; Takashi Kaito b, MD; Noboru Hosono a, MD; Toshitada Miwa c, MD; Takenori Oda d, MD; Shinya Okuda d, MD; Tomoya
Neurological manifestations of thoracic myelopathy in 203 patients Shota Takenaka* a, MD; Takashi Kaito b, MD; Noboru Hosono a, MD; Toshitada Miwa c, MD; Takenori Oda d, MD; Shinya Okuda d, MD; Tomoya
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
