The Role of Botulinum Toxin A in the Establishment of Symmetry in Pediatric Paralysis of the Lower Lip
|
|
|
- Curtis Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Research Original Investigation The Role of Botulinum Toxin A in the Establishment of Symmetry in Pediatric Paralysis of the Lower Lip Siba Haykal, MD, PhD; Ehud Arad, MD; Shaghayegh Bagher, MSc; Carolyn Lai, MD; Marc Hohman, MD; Tessa Hadlock, MD; Ronald M. Zuker, MD, FRCSC; Gregory H. Borschel, MD IMPORTANCE Botulinum toxin A has been described as an effective adjunct treatment for achieving symmetry in adults with facial paralysis. Few investigators have described the use of botulinum toxin A in pediatric patients with facial paralysis. Author Audio Interview at jamafacialplasticsurgery.com OBJECTIVE To present our preliminary experience with botulinum toxin A in pediatric patients presenting with asymmetry of the lower lip. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS We performed a retrospective medical record review of all pediatric patients (age range, 4-17 years; mean [SD] age, 11.2 [4.7] years) with facial paralysis who were treated with botulinum toxin A injections from January 1, 2004, through December 31, Patients presented for treatment at The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, or the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Boston. MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES Using facial analysis software, we measured lower lip asymmetry in the patients photographs before and after treatment, at rest, and in a dynamic state. We performed analysis of variance to assess for improvement in symmetry. RESULTS We identified 18 patients with the following 3 primary indications for treatment: focal lip asymmetry (n = 11), extensive hemifacial asymmetry (n = 5), and focal synkinesis (n = 2). We found no complications related to botulinum toxin A treatment. The mean (SD) dynamic deviation before the injection was 3.5 (1.7) mm, whereas the mean dynamic deviation after the injection was 1.5 (0.8) mm. The mean (SD) deviation correction was evaluated at 61% (6%) and was statistically significant (P =.04). CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE Botulinum toxin A injection is a safe procedure for improving localized asymmetry in pediatric patients with facial paralysis. Preliminary results indicate that botulinum toxin A may be an effective treatment for lower lip asymmetry in children and adolescents. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE 4. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2015;17(3): doi: /jamafacial Published online March 5, Author Affiliations: Division of Plastic Surgery, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (Haykal, Bagher, Lai, Zuker, Borschel); Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (Haykal, Bagher, Lai, Zuker, Borschel); Department of Plastic Surgery, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel (Arad); Facial Nerve Center, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Boston (Hohman, Hadlock). Corresponding Author: Siba Haykal, MD, PhD, Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, 111 Elizabeth St, Toronto, ON M5G 1P7, Canada (siba.haykal@utoronto.ca). Facial paralysis results in variable degrees of functional deficits and aesthetic asymmetry. Severe cases of paralysis often require surgical reconstruction with nerve and muscle transfers, whereas milder cases can be treated with digastric muscle transfer, sling suspension, or orbicularis advancement, which are not uniformly successful, 1-3 or managed nonsurgically with physiotherapy and rehabilitation strategies. As an adjunct to physiotherapy, botulinum toxin A, a neurotoxin that prevents the release of acetylcholine, has been used for improvement of facial symmetry. Its purpose is the weakening of strong muscles on the nonparalyzed side of the face. The use of botulinum toxin A for facial paralysis has been described in adults 4-12 and more specifically for protective ptosis in the treatment of lagophthalmos 13 after iatrogenic nerve injury 14 and hyperlacrimation. 15 Use of botulinum toxin A in children is very limited, with one report of 11 pediatric patients treated for focal synkinesis after facial paralysis 16 and another report of treatment of lower lip asymmetry that included some pediatric patients. 17 The purpose of this study was to examine the use of botulinum toxin A in children with facial paralysis, focusing on indications, technique, and rate of complications. 174 JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery May/June 2015 Volume 17, Number 3 (Reprinted) jamafacialplasticsurgery.com
2 Original Investigation Research Methods Patient Selection We obtained approval from the research ethics boards of The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary (MEEI), Boston. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients or a family member. We performed a retrospective review of health records for all patients with facial paralysis who had been treated with botulinum toxin A in our institutions from January 1, 2004, through December 31, A multidisciplinary team approach was involved in the treatment of these patients. The team included a plastic surgeon (R.M.Z. and G.H.B.) or an earnose-throat surgeon (T.H.), a physiotherapist, and an occupational therapist. Table 1. Site and Amount of Botulinum Toxin A Injection Site of Injection Botulinum Toxin A Administered, U Orbicularis oculi Lip depressors Mentalis Platysma Figure 1. Demonstration of Botulinum Toxin A Injection Sites Data Collection The inclusion criteria consisted of all patients younger than 18 years with facial paralysis who were treated with botulinum toxin A and had a minimum of 2 years of follow-up after the last injection. Data included demographic information, characteristics of facial paralysis, surgical procedures, information pertaining to botulinum toxin A injections (doses, number of injections, and time intervals), and reported complications. Injection Technique Injection of botulinum toxin A was performed under deep sedation or general anesthesia in patients younger than 10 years and with no anesthesia for older patients. Injection sites were marked before administration of anesthesia, at locations best correlating with muscles causing the greatest degree of asymmetry. Depressor or levator muscles of the lip were injected at the points causing maximum depression or elevation of the lip. For treatment of focal synkinesis, injection points were marked over synkinetic muscles at areas with the most prominent synkinetic contractions and least risk for functional impairment. Injection sites were prepared with isopropyl alcohol. Doses of botulinum toxin A that were used for each muscle are summarized in Table 1, and injection sites are shown in Figure 1. Measurement of Facial Symmetry The facial analysis software developed by the MEEI has been validated for measuring facial symmetry. 18 We used the software to measure the difference in vertical aperture between the paralyzed and nonparalyzed sides of the lip, which was defined as the lip deviation in each photograph. For each patient, outcomes were determined by the change in lip deviation before and after botulinum toxin A injection (Figure 2). Statistical Analysis Values of lip deviation before and after botulinum toxin A injections (at rest and while smiling) were compared across evaluations by repeated-measures analysis of variance using commercially available software (PROC-Mixed SAS, version 9.3; SAS Institute Inc). Statistical significance was determined as P <.05. The location of injection of the superolateral and inferolateral orbicularis occuli is demonstrated as blue circles; the depressors (mainly depressor labii inferioris and anguli oris), orange circle; the mentalis, green circle; and the platysma, purple circles. The platysma is usually divided into anterosuperior, anteroinferior, superoposterior, and inferoposterior aspects. Results We included 18 patients in this study. Demographic patient data are summarized in Table 2. Patients ranged in age from 4 to 17 years (mean [SD] age, 11.2 [4.7] years). The 3 primary indications for treatment were focal lip asymmetry (n = 11), extensive hemifacial asymmetry (n = 5), and focal synkinesis (n = 2). Fourteen patients were female and 4 were male. Five patients had undergone reconstructive surgery for facial paralysis before botulinum toxin A treatment. Two of these patients had been treated with nerve cable grafts after trauma and tumor resection. Both patients had residual hemifacial asymmetry and focal synkinesis and were treated with botulinum toxin A injections to the orbicularis oculi, lip depressors, mentalis, and platysma. Three additional patients had been treated with a gracilis muscle transfer (as a 1-stage procedure with coaptation to the masseteric nerve in 1 patient and as a 2-stage procedure after facial nerve crossgraft in 2 patients). All 3 patients were treated with botulinum toxin A for focal lip asymmetry. The botulinum toxin A injection data by indication group is summarized in Table 3. The 11 patients treated for focal lip jamafacialplasticsurgery.com (Reprinted) JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery May/June 2015 Volume 17, Number 3 175
3 Research Original Investigation Figure 2. Representative Photographs of Lip Symmetry Analysis A Before Treatment B After Treatment C Before Treatment D After Treatment We used facial symmetry analysis software with repeated-measures analysis of variance. The lower lip difference was measured before (A and C) and after (B and D) botulinum toxin A treatment. Table 2. Summary of Patient Characteristics a Characteristic Data Age at presentation, mean (SD) [range], y 11.2 (4.7) [4-17] Sex Male 4 Female 14 Laterality of paralysis Right 7 Left 10 Bilateral 1 Cause of paralysis Acquired 11 Congenital 7 a Unless otherwise indicated, data are expressed as number of patients. asymmetry had a mean of 3.6 botulinum toxin A treatments compared with 8.4 for the 5 patients in the hemifacial group and 7.3 for the 2 patients in the focal synkinesis group. The median time between botulinum toxin A treatments was 4 months. Two of the patients treated for focal lip asymmetry underwent subsequent myectomy. During a minimum of 2 years from the last injection, no patients experienced complications attributed to botulinum toxin A. We used the MEEI facial analysis software for evaluation of the deviation correction before and after botulinum toxin A injection. The mean (SD) dynamic deviation before the injection was 3.5 (1.7) mm, whereas the mean (SD) dynamic deviation after the injection was 1.5 (0.8) mm. The deviation correction was evaluated at a mean (SD) of 61% (6%) and was statistically significant (P =.04). Discussion Asymmetry of the lower lip secondary to facial nerve dysfunction presents with challenging considerations. Several different techniques have been postulated to regain symmetry, including surgical and nonsurgical approaches. A standardized protocol has also been established to provide physicians with management techniques to improve patient satisfaction and to offer physicians and patients insight into the likely outcome. 17 Thus, multiple studies have shown that botulinum toxin A has a well-established objective benefit in 176 JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery May/June 2015 Volume 17, Number 3 (Reprinted) jamafacialplasticsurgery.com
4 Original Investigation Research Table 3. Botulinum Toxin A Injection Data by Indication Groups a Indication Patient Characteristic Lip Asymmetry (n = 11) Hemifacial Asymmetry (n=5) Focal Synkinesis (n=2) Reanimation procedure before injection, No. of patients No. of injections, mean (range) 3.6 (1-8) 8.4 (2-23) 7.3 (3-15) Time between injections, median (range), mo 4 (2-15) 4 (3-6) 4 (2-15) Subsequent myectomy, No. of patients a No patients experienced complications attributed to botulinum toxin A. the control of facial hyperkinesis in patients with facial nerve disorders. Studies have established the associated quality-of-life benefit and reaffirmed its important role in the multimodality management of facial nerve disorders. 19 Botulinum toxin A is injected to the normal side to weaken it, thus allowing the weaker affected side to overcome the effect of the contralateral normal muscle and provide a more symmetrical smile. Despite the numerous studies showing a benefit of botulinum toxin A in the adult population, very few studies have considered its role in the pediatric population. Terzis et al 16 studied 11 pediatric patients presenting with focal synkinesis after facial paralysis and compared facial nerve crossgrafting and secondary microcoaptations with direct muscle neurotization with or without botulinum toxin A injection. The authors concluded that facial nerve cross-grafting with botulinum toxin A injection was effective despite having only 2 patients treated in that group and a total of 4 pediatric patients receiving botulinum toxin A treatment. This study represents the largest pediatric population, to our knowledge, treated with botulinum toxin A. A total of 18 patients were included from The Hospital for Sick Children and the MEEI. Unlike those of previous studies, our patient population included 11 patients treated for focal lip asymmetry, 5 patients with extensive hemifacial asymmetry, and 2 patients with focal synkinesis. Moreover, we used the MEEI facial analysis software, which has been validated for measuring facial symmetry, 18 to quantify the difference in vertical aperture between the paralyzed and nonparalyzed sides of the lip and found significant differences before and after botulinum toxin A injections with a 61% correction. We have also shown that botulinum toxin A did not result in any complications during a minimum of 2 years from the last injection. Furthermore, our patients continued to show symmetrical results in follow-up, which gives insight into a potential mechanism of action and its important role in the pediatric population. As such, some investigators believe that botulinum toxin A, especially when used in conjunction with physiotherapy, 20 can promote better permanent symmetry 21 through the creation of new motor patterns as a result of central motor learning. 22 As such and knowing the potential for plasticity, the introduction of this treatment in the pediatric population can prove to be more beneficial. These patients will require long-term follow-up to determine permanency of the symmetry, which is a limitation of this study. Conclusions Botulinum toxin A injection represents an important adjunct therapy in the reestablishment of symmetry in the pediatric patient population with facial paralysis. We have shown that botulinum toxin A significantly improves symmetry of the lower lip, is safe, and has a potential for restoration of permanent symmetry. ARTICLE INFORMATION Accepted for Publication: December 30, Published Online: March 5, doi: /jamafacial Author Contributions: Drs Haykal and Borschel had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study concept and design: Arad, Bagher, Zuker, Borschel. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Haykal, Arad, Bagher, Lai, Hohman, Hadlock, Borschel. Drafting of the manuscript: Haykal, Arad, Borschel. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: All authors. Statistical analysis: Haykal, Arad, Bagher. Administrative, technical, or material support: Haykal, Arad, Hadlock, Borschel. Study supervision: Arad, Zuker, Borschel. Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None reported. REFERENCES 1. Terzis JK, Kalantarian B. Microsurgical strategies in 74 patients for restoration of dynamic depressor muscle mechanism: a neglected target in facial reanimation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;105(6): Hussain G, Manktelow RT, Tomat LR. Depressor labii inferioris resection: an effective treatment for marginal mandibular nerve paralysis. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57(6): Udagawa A, Arikawa K, Shimizu S, et al. A simple reconstruction for congenital unilateral lower lip palsy.plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120(1): Armstrong MW, Mountain RE, Murray JA. Treatment of facial synkinesis and facial asymmetry with botulinum toxin type A following facial nerve palsy.clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1996;21(1): Borodic G, Bartley M, Slattery W, et al. Botulinum toxin for aberrant facial nerve regeneration: double-blind, placebo-controlled trial using subjective endpoints. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116 (1): Sadiq S, Khwaja S, Saeed S. Botulinum toxin to improve lower facial symmetry in facial nerve palsy. Eye (Lond). 2012;73(11): de Maio M. Use of botulinum toxin in facial paralysis. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2003;5(3-4): Chen C-K, Tang Y-B. Myectomy and botulinum toxin for paralysis of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve: a series of 76 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120(7): de Maio M, Bento RF. Botulinum toxin in facial palsy: an effective treatment for contralateral hyperkinesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120(4): Bulstrode NW, Harrison DH. The phenomenon of the late recovered Bell s palsy: treatment options to improve facial symmetry. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115(6): jamafacialplasticsurgery.com (Reprinted) JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery May/June 2015 Volume 17, Number 3 177
5 Research Original Investigation 11. Choi KH, Rho SH, Lee JM, Jeon JH, Park SY, Kim J. Botulinum toxin injection of both sides of the face to treat post-paralytic facial synkinesis. JPlast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66(8): Kim J. Contralateral botulinum toxin injection to improve facial asymmetry after acute facial paralysis.otol Neurotol. 2013;34(2): Yücel OE, Artürk N. Botulinum toxin-a induced protective ptosis in the treatment of lagophthalmos associated with facial paralysis. Ophthalmol Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;28(4): Guyuron B, Huddleston SW. Aesthetic indications for botulinum toxin injection. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;93(5): Boroojerdi B, Ferbert A, Schwarz M, Herath H, Noth J. Botulinum toxin treatment of synkinesia and hyperlacrimation after facial palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998;65(1): Terzis JK, Karypidis D. Therapeutic strategies in post-facial paralysis synkinesis in pediatric patients. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65(8): Lindsay RW, Edwards C, Smitson C, Cheney ML, Hadlock T. A systematic algorithm for the management of lower lip asymmetry. Am J Otolaryngol. 2011;32(1): Hadlock TA, Urban LS. Toward a universal, automated facial measurement tool in facial reanimation. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2012;14(4): Mehta RP, Hadlock T. Botulinum toxin and quality of life in patients with facial paralysis. 2014;10(2): Monini S, De Carlo A, Biagini M, et al. Combined protocol for treatment of secondary effects from facial nerve palsy. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011;131(8): Lindsay RW, Robinson M, Hadlock TA. Comprehensive facial rehabilitation improves function in people with facial paralysis: a 5-year experience at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary.Phys Ther. 2010;90(3): Guntinas-Lichius O, Glowka TR, Angelov DN, Irintchev A, Neiss WF. Improved functional recovery after facial nerve reconstruction by temporary denervation of the contralateral mimic musculature with botulinum toxin in rats. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2011;25(1): JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery May/June 2015 Volume 17, Number 3 (Reprinted) jamafacialplasticsurgery.com
Management of Facial Synkinesis with a Combination of BTX-A and Biofeedback: A Randomized Trial
 Original Article Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Vol.27(6), Serial No.83, Nov 2015 Management of Facial Synkinesis with a Combination of BTX-A and Biofeedback: A Randomized Trial Abstract * Abbas
Original Article Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Vol.27(6), Serial No.83, Nov 2015 Management of Facial Synkinesis with a Combination of BTX-A and Biofeedback: A Randomized Trial Abstract * Abbas
CHAPTER 11 FACIAL PARALYSIS. Shailesh Agarwal, MD and Arash Momeni, MD
 CHAPTER 11 FACIAL PARALYSIS Shailesh Agarwal, MD and Arash Momeni, MD The facial nerve innervates a total of 23 paired muscles and the orbicularis oris muscle. The majority of muscles innervated by the
CHAPTER 11 FACIAL PARALYSIS Shailesh Agarwal, MD and Arash Momeni, MD The facial nerve innervates a total of 23 paired muscles and the orbicularis oris muscle. The majority of muscles innervated by the
Smile Restoration for Permanent Facial Paralysis
 Continuing Medical Education Smile Restoration for Permanent Facial Paralysis Jonathan Leckenby, Adriaan Grobbelaar Department of Plastic Surgery, The Royal Free Hospital, University of London, London,
Continuing Medical Education Smile Restoration for Permanent Facial Paralysis Jonathan Leckenby, Adriaan Grobbelaar Department of Plastic Surgery, The Royal Free Hospital, University of London, London,
jamafacialplasticsurgery.com JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery September/October 2014 Volume 16, Number 5 359
 Research Case Report/Case Series Salvage Procedures fter Failed Facial Reanimation Surgery Using the Masseteric Nerve as the Motor Nerve for Free Functional Gracilis Muscle Transfer Steffen U. Eisenhardt,
Research Case Report/Case Series Salvage Procedures fter Failed Facial Reanimation Surgery Using the Masseteric Nerve as the Motor Nerve for Free Functional Gracilis Muscle Transfer Steffen U. Eisenhardt,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences DYNAMIC REANIMATION FOR FACIAL PARALYSIS A REVIEW ABSTRACT
 Review Article Allied Sciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 DYNAMIC REANIMATION FOR FACIAL PARALYSIS A REVIEW RATHISHREE 1 AND DR. M.P.SANTHOSH KUMAR *2 1 Intern, saveetha
Review Article Allied Sciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 DYNAMIC REANIMATION FOR FACIAL PARALYSIS A REVIEW RATHISHREE 1 AND DR. M.P.SANTHOSH KUMAR *2 1 Intern, saveetha
Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed Face
 Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed Face Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Faculty Advisor: Karen H. Calhoun, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 30,
Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed Face Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Faculty Advisor: Karen H. Calhoun, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 30,
Facial Nerve Injury: Diagnosis and Repair
 Editor s Note: My thanks to the moderator, Julia K. Terzis, MD, PhD (board-certified plastic surgeon and ASAPS member, Norfolk, VA); and to panelists Ralph Manktelow, MD (board-certified plastic surgeon,
Editor s Note: My thanks to the moderator, Julia K. Terzis, MD, PhD (board-certified plastic surgeon and ASAPS member, Norfolk, VA); and to panelists Ralph Manktelow, MD (board-certified plastic surgeon,
Effect of Depressor Septi Resection in Rhinoplasty on Upper Lip Length
 Research Original Investigation Effect of Depressor Septi Resection in Rhinoplasty on Upper Lip Length Yan Ho, MD; Robert Deeb, MD; Richard Westreich, MD; William Lawson, MD, DDS IMPORTANCE Resection of
Research Original Investigation Effect of Depressor Septi Resection in Rhinoplasty on Upper Lip Length Yan Ho, MD; Robert Deeb, MD; Richard Westreich, MD; William Lawson, MD, DDS IMPORTANCE Resection of
Novel 3-D Video for Quantification of Facial Movement
 Novel 3-D Video for Quantification of Facial Movement Ritvik P. Mehta MD*, Song Zhang PhD, and Tessa A. Hadlock MD * Division of Otolaryngology, University of California San Diego, San Diego CA Harvard
Novel 3-D Video for Quantification of Facial Movement Ritvik P. Mehta MD*, Song Zhang PhD, and Tessa A. Hadlock MD * Division of Otolaryngology, University of California San Diego, San Diego CA Harvard
3D-Ultrasonography for evaluation of facial muscles in patients with chronic facial palsy or defective healing: a pilot study
 Volk et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2014, 14:4 TECHNICAL ADVANCE 3D-Ultrasonography for evaluation of facial muscles in patients with chronic facial palsy or defective healing: a pilot study
Volk et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2014, 14:4 TECHNICAL ADVANCE 3D-Ultrasonography for evaluation of facial muscles in patients with chronic facial palsy or defective healing: a pilot study
ORIGINAL RESEARCH FACIAL PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2008) 138, 468-472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH FACIAL PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY Novel 3-D video for quantification of facial movement Ritvik P. Mehta, MD, Song Zhang,
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2008) 138, 468-472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH FACIAL PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY Novel 3-D video for quantification of facial movement Ritvik P. Mehta, MD, Song Zhang,
Comparison of one-stage free gracilis muscle flap with two-stage method in chronic facial palsy*
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 21, No.2, August 2007. pp. 63-70 Comparison of one-stage free gracilis muscle flap with two-stage method in chronic facial palsy*
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 21, No.2, August 2007. pp. 63-70 Comparison of one-stage free gracilis muscle flap with two-stage method in chronic facial palsy*
REHABILITATION AND REANIMATION. Facial Plastic Surgery. University of Missouri Columbia, Missouri
 FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS: REHABILITATION AND REANIMATION Matthew A. Kienstra, MD, FACS Facial Plastic Surgery Mercy Health Care Springfield, Missouri University of Missouri Columbia, Missouri Incidence and
FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS: REHABILITATION AND REANIMATION Matthew A. Kienstra, MD, FACS Facial Plastic Surgery Mercy Health Care Springfield, Missouri University of Missouri Columbia, Missouri Incidence and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Electromyographic Differences Between Normal Upper and Lower Facial Muscles and the Influence of Onabotulinum Toxin A
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Electromyographic Differences Between Normal Upper and Lower Facial Muscles and the Influence of Onabotulinum Toxin A Bryan J. Winn, MD; Bryan S. Sires, MD, PhD Importance: Empirically
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Electromyographic Differences Between Normal Upper and Lower Facial Muscles and the Influence of Onabotulinum Toxin A Bryan J. Winn, MD; Bryan S. Sires, MD, PhD Importance: Empirically
Dynamic Facial Reanimation With Orthodromic Temporalis Tendon Transfer in Children
 Research Case Report/Case Series Dynamic Facial Reanimation With Orthodromic Temporalis Tendon Transfer in Children Rajanya S. Petersson, MD; Daniel E. Sampson, MD; James D. Sidman, MD IMPORTNCE To our
Research Case Report/Case Series Dynamic Facial Reanimation With Orthodromic Temporalis Tendon Transfer in Children Rajanya S. Petersson, MD; Daniel E. Sampson, MD; James D. Sidman, MD IMPORTNCE To our
Management of Facial Paralysis
 Section 3: Facial Surgery 6 Management of Facial Paralysis D Bray INTRODUCTION Significant functional, aesthetic and psychosocial sequelae accompany facial paralysis. Dysfunctional lacrimation, palpebral
Section 3: Facial Surgery 6 Management of Facial Paralysis D Bray INTRODUCTION Significant functional, aesthetic and psychosocial sequelae accompany facial paralysis. Dysfunctional lacrimation, palpebral
Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Facial Synkinesis and Hyperkinesis
 The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Facial Synkinesis and Hyperkinesis Roberto Filipo, MD; Irma Spahiu, MD;
The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Botulinum Toxin in the Treatment of Facial Synkinesis and Hyperkinesis Roberto Filipo, MD; Irma Spahiu, MD;
A new classification system of nasal contractures
 Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Microsurgical Strategies in 74 Patients for Restoration of Dynamic Depressor Muscle Mechanism: A Neglected Target in Facial Reanimation
 Microsurgical Strategies in 74 Patients for Restoration of Dynamic Depressor Muscle Mechanism: A Neglected Target in Facial Reanimation Julia K. Terzis, M.D., Ph.D., and Behrooz Kalantarian, M.D. Norfolk,
Microsurgical Strategies in 74 Patients for Restoration of Dynamic Depressor Muscle Mechanism: A Neglected Target in Facial Reanimation Julia K. Terzis, M.D., Ph.D., and Behrooz Kalantarian, M.D. Norfolk,
Botulinum toxin in the management of facial paralysis
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Botulinum toxin in the management of facial paralysis Jonathan A. Cabin a, Guy G. Massry b,c,d, and Babak Azizzadeh e,f Purpose of review Complete flaccid facial paralysis, as well
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Botulinum toxin in the management of facial paralysis Jonathan A. Cabin a, Guy G. Massry b,c,d, and Babak Azizzadeh e,f Purpose of review Complete flaccid facial paralysis, as well
Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current
 INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current Min-Hee Ryu, MD; David Kahng, MD; and Yongho Shin, MD, PhD Aesthetic Surgery Journal
INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Oculoplastic Surgery Surgical Correction of Crow s Feet Deformity With Radiofrequency Current Min-Hee Ryu, MD; David Kahng, MD; and Yongho Shin, MD, PhD Aesthetic Surgery Journal
Sierra Smith Bio 205 Extra Credit Essay. My Face. Growing up I was always told that it takes 43 muscles to frown but only 17
 Sierra Smith Bio 205 Extra Credit Essay My Face Growing up I was always told that it takes 43 muscles to frown but only 17 muscles to smile and I should just smile because it's easier. It wasn't until
Sierra Smith Bio 205 Extra Credit Essay My Face Growing up I was always told that it takes 43 muscles to frown but only 17 muscles to smile and I should just smile because it's easier. It wasn't until
Grading Facial Nerve Function Following Combined Static and Mimetic Surgical Techniques
 416 Original Article Grading Facial Nerve Function Following Combined Static and Mimetic Surgical Techniques John P. Leonetti 1 Sam J. Marzo 1 Douglas A. Anderson 2 Joshua M. Sappington 1 1 Department
416 Original Article Grading Facial Nerve Function Following Combined Static and Mimetic Surgical Techniques John P. Leonetti 1 Sam J. Marzo 1 Douglas A. Anderson 2 Joshua M. Sappington 1 1 Department
Effect of facial neuromuscular re-education on facial symmetry in patients with Bell s palsy: a randomized controlled trial
 Clinical Rehabilitation 2007; 21: 338343 Effect of facial neuromuscular re-education on facial symmetry in patients with Bell s palsy: a randomized controlled trial N Manikandan Department of Physiotherapy,
Clinical Rehabilitation 2007; 21: 338343 Effect of facial neuromuscular re-education on facial symmetry in patients with Bell s palsy: a randomized controlled trial N Manikandan Department of Physiotherapy,
SELECTIVE NEURECTOMIES TO ACHIEVE SYMMETRY IN PARTIAL AND COMPLETE FACIAL PARALYSIS
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (I976), 29, 43-52 SELECTIVE NEURECTOMIES TO ACHIEVE SYMMETRY IN PARTIAL AND COMPLETE FACIAL PARALYSIS By L. CLODIVS, M.D. Plastic Surgery Section, Second Surgical Department,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (I976), 29, 43-52 SELECTIVE NEURECTOMIES TO ACHIEVE SYMMETRY IN PARTIAL AND COMPLETE FACIAL PARALYSIS By L. CLODIVS, M.D. Plastic Surgery Section, Second Surgical Department,
FACIAL PARALYSIS ARISES FROM
 ONLINE FIRST ORIGINAL ARTICLE Toward a Universal, Automated Facial Measurement Tool in Facial Reanimation Tessa A. Hadlock, MD; Luke S. Urban, MS Objective: To describe a highly quantitative facial function
ONLINE FIRST ORIGINAL ARTICLE Toward a Universal, Automated Facial Measurement Tool in Facial Reanimation Tessa A. Hadlock, MD; Luke S. Urban, MS Objective: To describe a highly quantitative facial function
ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF FACIAL PALSY. Michael J. LaRouere, M.D. Michigan Ear Institute Farmington Hills, Michigan
 ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF FACIAL PALSY Michael J. LaRouere, M.D. Michigan Ear Institute Farmington Hills, Michigan FACIAL PARALYSIS - ETIOLOGY Bells Palsy Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Infection (Acute/Chronic)
ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF FACIAL PALSY Michael J. LaRouere, M.D. Michigan Ear Institute Farmington Hills, Michigan FACIAL PARALYSIS - ETIOLOGY Bells Palsy Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Infection (Acute/Chronic)
Facial Paralysis in Children
 117 Sashank Reddy, MD, PhD 1 Richard Redett, MD 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland Facial Plast Surg 2015;31:117 122. Address for
117 Sashank Reddy, MD, PhD 1 Richard Redett, MD 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland Facial Plast Surg 2015;31:117 122. Address for
Facial Palsy Management by the Multidisciplinary Team
 Facial Palsy Management by the Multidisciplinary Team Catriona Neville and Vanessa Venables Extended Scope Practitioner Therapists in Facial Palsy Queen Victoria Hospital East Grinstead 2013 MDT members
Facial Palsy Management by the Multidisciplinary Team Catriona Neville and Vanessa Venables Extended Scope Practitioner Therapists in Facial Palsy Queen Victoria Hospital East Grinstead 2013 MDT members
Treatment of gustatory hyperlacrimation (crocodile tears) with injection of botulinum toxin into the lacrimal gland
 (2002) 16, 705 709 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye Treatment of gustatory hyperlacrimation (crocodile tears) with injection of botulinum toxin into
(2002) 16, 705 709 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye Treatment of gustatory hyperlacrimation (crocodile tears) with injection of botulinum toxin into
It is now widely recognized that there is a critical. Dental Facial Aesthetics Aesthetic shaping of the neck/positive side effects on the gingiva
 Dental Facial Aesthetics Aesthetic shaping of the neck/positive side effects on the gingiva Warren Roberts, DMD This article discusses the relationship between Platysma, a large muscle of the face and
Dental Facial Aesthetics Aesthetic shaping of the neck/positive side effects on the gingiva Warren Roberts, DMD This article discusses the relationship between Platysma, a large muscle of the face and
Original Article Response to phenylephrine testing in upper eyelids with ptosis
 Original Article Response to phenylephrine testing in upper eyelids with ptosis Grace N. Lee, MD, a Li-Wei Lin, MD, b Sonia Mehta, MD, c and Suzanne K. Freitag, MD a Author affiliations: a Department of
Original Article Response to phenylephrine testing in upper eyelids with ptosis Grace N. Lee, MD, a Li-Wei Lin, MD, b Sonia Mehta, MD, c and Suzanne K. Freitag, MD a Author affiliations: a Department of
Use of Gastrointestinal Anastomosis Stapler for Harvest of Gracilis Muscle and Securing It in the Face for Facial Reanimation: A Novel Technique
 Use of Gastrointestinal Anastomosis Stapler for Harvest of Gracilis Muscle and Securing It in the Face for Facial Reanimation: A Novel Technique Sachin M. Shridharani, MD, Sahael M. Stapleton, BS, Richard
Use of Gastrointestinal Anastomosis Stapler for Harvest of Gracilis Muscle and Securing It in the Face for Facial Reanimation: A Novel Technique Sachin M. Shridharani, MD, Sahael M. Stapleton, BS, Richard
Lengthening Temporalis Myoplasty for Single-Stage Smile Reconstruction in Children with Facial Paralysis
 RECONSTRUCTIVE Lengthening Temporalis Myoplasty for Single-Stage Smile Reconstruction in Children with Facial Paralysis Andre Panossian, M.D. Los Angeles, Calif. Background: Free muscle transfer for dynamic
RECONSTRUCTIVE Lengthening Temporalis Myoplasty for Single-Stage Smile Reconstruction in Children with Facial Paralysis Andre Panossian, M.D. Los Angeles, Calif. Background: Free muscle transfer for dynamic
Unilateral Frontalis Sling for the Surgical Correction of Unilateral Poor-Function Ptosis
 Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Vol. 21, No. 6, pp 412 417 2005 The American Society of Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Inc. Unilateral Frontalis Sling for the Surgical Correction
Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Vol. 21, No. 6, pp 412 417 2005 The American Society of Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Inc. Unilateral Frontalis Sling for the Surgical Correction
The Beneficial Effects of Postrhinoplasty TapingFact or Fiction? Kyle A. Belek, MD, Ronald P. Gruber, MD
 The Beneficial Effects of Postrhinoplasty TapingFact or Fiction? Kyle A. Belek, MD, Ronald P. Gruber, MD Rhinoplasty The Beneficial Effects of Postrhinoplasty Taping: Fact or Fiction? Kyle A. Belek, MD;
The Beneficial Effects of Postrhinoplasty TapingFact or Fiction? Kyle A. Belek, MD, Ronald P. Gruber, MD Rhinoplasty The Beneficial Effects of Postrhinoplasty Taping: Fact or Fiction? Kyle A. Belek, MD;
Local Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Hemifacial Spasm
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 42, 245 249, 2002 Local Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Hemifacial Spasm Hirofumi OYAMA, AkiraIKEDA, Shigeo INOUE, Yasuhiro NAKASHIMA, and Masato SHIBUYA Department of Neurosurgery,
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 42, 245 249, 2002 Local Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Hemifacial Spasm Hirofumi OYAMA, AkiraIKEDA, Shigeo INOUE, Yasuhiro NAKASHIMA, and Masato SHIBUYA Department of Neurosurgery,
Static Suspension Technique with Fascia Lata for Facial Reanimation in Facial Palsy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. IV (April. 2017), PP 90-96 www.iosrjournals.org Static Suspension Technique with Fascia
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. IV (April. 2017), PP 90-96 www.iosrjournals.org Static Suspension Technique with Fascia
Apraxia of eyelid opening: Clinical features and therapy
 E u ropean Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 16 no. 2, 2006 / pp. 2 0 4-2 0 8 Apraxia of eyelid opening: Clinical features and therapy E. KERT Y 1, K. EIDAL 2 1 Department of Neuro l o g y, Rikshospitalet,
E u ropean Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 16 no. 2, 2006 / pp. 2 0 4-2 0 8 Apraxia of eyelid opening: Clinical features and therapy E. KERT Y 1, K. EIDAL 2 1 Department of Neuro l o g y, Rikshospitalet,
Lower motor cranial nerve dysfunction has an. Reconstructive
 Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Volumetry of Facial Muscles in Healthy Patients with Facial Palsy Gerd F. Volk, MD* Inna Karamyan, MD* Carsten M. Klingner, MD Jürgen R. Reichenbach, PhD Orlando
Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Volumetry of Facial Muscles in Healthy Patients with Facial Palsy Gerd F. Volk, MD* Inna Karamyan, MD* Carsten M. Klingner, MD Jürgen R. Reichenbach, PhD Orlando
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL
 What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Anatomy and Physiology app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
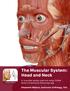 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Anatomy and Physiology app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES A. Watch the video 13.1 Muscular System Overview and observe
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Anatomy and Physiology app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES A. Watch the video 13.1 Muscular System Overview and observe
INTRAOPERATIVE NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL MONITORING FOR MICROVASCULAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH HEMIFACIAL SPASM
 INTRAOPERATIVE NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL MONITORING FOR MICROVASCULAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH HEMIFACIAL SPASM WILLIAM D. MUSTAIN, PH.D., CNIM, BCS-IOM DEPARTMENT OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY AND COMMUNICATIVE
INTRAOPERATIVE NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL MONITORING FOR MICROVASCULAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH HEMIFACIAL SPASM WILLIAM D. MUSTAIN, PH.D., CNIM, BCS-IOM DEPARTMENT OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY AND COMMUNICATIVE
INSTRUCTIONS INTRODUCTION RISKS OF BOTULINUM TOXIN / DERMAL FILLER INJECTIONS
 INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed consent document that has been prepared to help inform you concerning botulinum toxin / dermal filler injections and the risks involved. It is important that you read this
INSTRUCTIONS This is an informed consent document that has been prepared to help inform you concerning botulinum toxin / dermal filler injections and the risks involved. It is important that you read this
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Hemifacial spasm. Parkinson's Disease Center and Movement Disorders Clinic
 Parkinson's Disease Center and Movement Disorders Clinic 7200 Cambridge Street, 9th Floor, Suite 9A Houston, Texas 77030 713-798-2273 phone www.jankovic.org Hemifacial spasm Diagnosis Hemifacial spasm
Parkinson's Disease Center and Movement Disorders Clinic 7200 Cambridge Street, 9th Floor, Suite 9A Houston, Texas 77030 713-798-2273 phone www.jankovic.org Hemifacial spasm Diagnosis Hemifacial spasm
Superior Rectus Muscle Recession for Residual Head Tilt after Inferior Oblique Muscle Weakening in Superior Oblique Palsy
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(4):285-289 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.4.285 Original Article Superior Rectus Muscle Recession for Residual Head Tilt after Inferior
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(4):285-289 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.4.285 Original Article Superior Rectus Muscle Recession for Residual Head Tilt after Inferior
Botulinum Toxin Application
 Botulinum Toxin Application Clostridium botulinum: rod-shaped bacterium producing the neurotoxin botulin Gram-positive anaerobic bacterium Seven serotypes - A, B, C, D, E, F, G http://standeyo.com/news/08_health/081202.biological.weapons.html
Botulinum Toxin Application Clostridium botulinum: rod-shaped bacterium producing the neurotoxin botulin Gram-positive anaerobic bacterium Seven serotypes - A, B, C, D, E, F, G http://standeyo.com/news/08_health/081202.biological.weapons.html
Accepted 5 September 2008 Published online 3 March 2009 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: /21013
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE MARGINAL MANDIBULAR NERVE INJURY DURING NECK DISSECTION AND ITS IMPACT ON PATIENT PERCEPTION OF APPEARANCE Martin D. Batstone, MPhil(Surg), FRACDS(OMS), FRCS(OMFS), 1 Barry Scott, BSc,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MARGINAL MANDIBULAR NERVE INJURY DURING NECK DISSECTION AND ITS IMPACT ON PATIENT PERCEPTION OF APPEARANCE Martin D. Batstone, MPhil(Surg), FRACDS(OMS), FRCS(OMFS), 1 Barry Scott, BSc,
Long-term Efficacy of Botulinum Neurotoxin-A Treatment for Essential Blepharospasm
 pissn: 111-8942 eissn: 292-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 218;32(1):1-7 https://doi.org/1.3341/kjo.217.3 Original Article Long-term Efficacy of Botulinum Neurotoxin-A Treatment for Essential Blepharospasm Seunghyun
pissn: 111-8942 eissn: 292-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 218;32(1):1-7 https://doi.org/1.3341/kjo.217.3 Original Article Long-term Efficacy of Botulinum Neurotoxin-A Treatment for Essential Blepharospasm Seunghyun
Muscles of the Face, Head, and Neck
 Muscles of the Face, Head, and Neck 1 How Muscles Are Named Many muscles named using such features as Location Function Shape Direction of fibers Number of heads or divisions Points of attachment Size
Muscles of the Face, Head, and Neck 1 How Muscles Are Named Many muscles named using such features as Location Function Shape Direction of fibers Number of heads or divisions Points of attachment Size
A Clinical Analysis of Facial Nerve Paralysis due to Inflammatory Diseases of the Middle Ear and the Role of Early Decompression
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/311 A Clinical Analysis of Facial Nerve Paralysis due to Inflammatory Diseases of the Middle Ear and the Role of Early
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/311 A Clinical Analysis of Facial Nerve Paralysis due to Inflammatory Diseases of the Middle Ear and the Role of Early
Facial palsy is a well-known pathological condition. Masseteric facial nerve neurorrhaphy: results of a case series
 clinical article J Neurosurg 126:312 318, 2017 Masseteric facial nerve neurorrhaphy: results of a case series Federico Biglioli, MD, 1 Valeria Colombo, MD, 1 Dimitri Rabbiosi, MD, 1 Filippo Tarabbia, MD,
clinical article J Neurosurg 126:312 318, 2017 Masseteric facial nerve neurorrhaphy: results of a case series Federico Biglioli, MD, 1 Valeria Colombo, MD, 1 Dimitri Rabbiosi, MD, 1 Filippo Tarabbia, MD,
Lower Facial Reanimation Techniques Following Cancer Resection and Free Flap Reconstruction
 The Laryngoscope VC 2016 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Lower Facial Reanimation Techniques Following Cancer Resection and Free Flap Reconstruction Alexandra E.
The Laryngoscope VC 2016 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Lower Facial Reanimation Techniques Following Cancer Resection and Free Flap Reconstruction Alexandra E.
Facial Asymmetry Correction in Facial Palsy Patients with Silhouette Sutures
 International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2012, 3, 55-59 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijcm.2012.31012 Published Online January 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Facial Asymmetry Correction in Facial
International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2012, 3, 55-59 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijcm.2012.31012 Published Online January 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Facial Asymmetry Correction in Facial
Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Contouring of the Lower Face
 Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Contouring of the Lower Face SEONG WOOK CHOE, MD,* WAN IK CHO, MD,* CHANG KYUN LEE, MD, SEONG JUN SEO, MD* *Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang
Effects of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Contouring of the Lower Face SEONG WOOK CHOE, MD,* WAN IK CHO, MD,* CHANG KYUN LEE, MD, SEONG JUN SEO, MD* *Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang
cme Combined Eyelid and Strabismus Surgery: Examining Conventional Surgical Wisdom Educational Objectives
 Article Combined Eyelid and Strabismus Surgery: Examining Conventional Surgical Wisdom Michael S. McCracken, MD; Jonathan D. del Prado, MD; David B. Granet, MD; Leah Levi, MBBS; Don O. Kikkawa, MD Abstract
Article Combined Eyelid and Strabismus Surgery: Examining Conventional Surgical Wisdom Michael S. McCracken, MD; Jonathan D. del Prado, MD; David B. Granet, MD; Leah Levi, MBBS; Don O. Kikkawa, MD Abstract
Surgical treatment of bilateral paralytic lagophthalmos using scapha graft in a case of lepromatous leprosy
 Lepr Rev (2009) 80, 448 452 CASE REPORT Surgical treatment of bilateral paralytic lagophthalmos using scapha graft in a case of lepromatous leprosy LAURA LAVILLA, JESÚS CASTILLO, ÁNGEL M. DOMÍNGUEZ, NELSON
Lepr Rev (2009) 80, 448 452 CASE REPORT Surgical treatment of bilateral paralytic lagophthalmos using scapha graft in a case of lepromatous leprosy LAURA LAVILLA, JESÚS CASTILLO, ÁNGEL M. DOMÍNGUEZ, NELSON
Case Report. Physical Therapy for Facial Paralysis: A Tailored Treatment Approach. Key Words:
 Case Report Physical Therapy for Facial Paralysis: A Tailored Treatment Approach Background and Purpose. Bell palsy is an acute facial paralysis of unknown etiology. Although recovery from Bell palsy is
Case Report Physical Therapy for Facial Paralysis: A Tailored Treatment Approach Background and Purpose. Bell palsy is an acute facial paralysis of unknown etiology. Although recovery from Bell palsy is
Long-term facial improvement after repeated BoNT-A injections and mirror biofeedback exercises for chronic facial synkinesis: a case-series study
 2016 EDIZIONI MINERVA MEDICA Online version at http://www.minervamedica.it complication during the recovery phase of severe A facial palsy is the development of facial synkinesis, characterized by synchronous
2016 EDIZIONI MINERVA MEDICA Online version at http://www.minervamedica.it complication during the recovery phase of severe A facial palsy is the development of facial synkinesis, characterized by synchronous
Evaluation of the patient for cosmetic Botox injections
 Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 11 (2003) 349 358 Evaluation of the patient for cosmetic Botox injections Steven H. Dayan, MD, FACS*, Benjamin A. Bassichis, MD Department of Otolaryngology, Division of Facial
Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 11 (2003) 349 358 Evaluation of the patient for cosmetic Botox injections Steven H. Dayan, MD, FACS*, Benjamin A. Bassichis, MD Department of Otolaryngology, Division of Facial
An Algorithm to Guide Recipient Vessel Selection in Cases of Free Functional Muscle Transfer for Facial Reanimation
 An Algorithm to Guide Recipient Vessel Selection in Cases of Free Functional Muscle Transfer for Facial Reanimation Original Article Francis P Henry, Jonathan I Leckenby, Daniel P Butler, Adriaan O Grobbelaar
An Algorithm to Guide Recipient Vessel Selection in Cases of Free Functional Muscle Transfer for Facial Reanimation Original Article Francis P Henry, Jonathan I Leckenby, Daniel P Butler, Adriaan O Grobbelaar
RECONSTRUCTIVE.
 RECONSTRUCTIVE Intraoperative Muscle Electrical Stimulation for Accurate Positioning of the Temporalis Muscle Tendon during Dynamic, One-Stage Lengthening Temporalis Myoplasty for Facial and Lip Reanimation
RECONSTRUCTIVE Intraoperative Muscle Electrical Stimulation for Accurate Positioning of the Temporalis Muscle Tendon during Dynamic, One-Stage Lengthening Temporalis Myoplasty for Facial and Lip Reanimation
Occipital flattening in the infant skull
 Occipital flattening in the infant skull Kant Y. Lin, M.D., Richard S. Polin, M.D., Thomas Gampper, M.D., and John A. Jane, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of Plastic Surgery and Neurological Surgery, University
Occipital flattening in the infant skull Kant Y. Lin, M.D., Richard S. Polin, M.D., Thomas Gampper, M.D., and John A. Jane, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of Plastic Surgery and Neurological Surgery, University
Long-term functional recovery after facial nerve transection and repair in the rat
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2015 Long-term functional recovery after facial nerve transection and repair in the rat Caroline A. Banks Harvard
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2015 Long-term functional recovery after facial nerve transection and repair in the rat Caroline A. Banks Harvard
Features of Facial Asymmetry Following Incomplete Recovery from Facial Paralysis
 Original Article DOI.49/ymj..5.6.94 pissn: 5-5796, eissn: 976-47 Yonsei Med J 5(6):94-948, Features of Facial Asymmetry Following Incomplete Recovery from Facial Paralysis Jin Kim, Hyung Rok Lee, Jun Hui
Original Article DOI.49/ymj..5.6.94 pissn: 5-5796, eissn: 976-47 Yonsei Med J 5(6):94-948, Features of Facial Asymmetry Following Incomplete Recovery from Facial Paralysis Jin Kim, Hyung Rok Lee, Jun Hui
DO NOT DUPLICATE. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) has revolutionized the
 Original research WOUNDS 2013;25(4):89 93 From the Aesthetic and Plastic Surgery Institute, University of California Irvine, Orange, CA and Long Beach Memorial Medical Center, Long Beach, CA Address correspondence
Original research WOUNDS 2013;25(4):89 93 From the Aesthetic and Plastic Surgery Institute, University of California Irvine, Orange, CA and Long Beach Memorial Medical Center, Long Beach, CA Address correspondence
Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Facial Features
 Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Facial Features Vardan Papoian, Vartan Mardirossian 2, Donald Thomas Hess 2, Jeffrey H Spiegel 2 MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 2 Department of Surgery,
Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Facial Features Vardan Papoian, Vartan Mardirossian 2, Donald Thomas Hess 2, Jeffrey H Spiegel 2 MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 2 Department of Surgery,
Anticoagulant Complications in Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Research Original Investigation Anticoagulant Complications in Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Casey T. Kraft, BS; Emily Bellile, MS; Shan R. Baker, MD; Jennifer C. Kim, MD; Jeffrey S. Moyer,
Research Original Investigation Anticoagulant Complications in Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Casey T. Kraft, BS; Emily Bellile, MS; Shan R. Baker, MD; Jennifer C. Kim, MD; Jeffrey S. Moyer,
Cronicon EC DENTAL SCIENCE. Research Article. Facial Symmetry Improves After Treating Malocclusions with the Myobrace System
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Facial Symmetry Improves After Treating Malocclusions with the Myobrace System German O Ramirez-Yanez 1 * and John Flutter 2 1 College of Dentistry,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Facial Symmetry Improves After Treating Malocclusions with the Myobrace System German O Ramirez-Yanez 1 * and John Flutter 2 1 College of Dentistry,
Metadata of the chapter that will be visualized online
 Metadata of the chapter that will be visualized online ChapterTitle Chapter Sub-Title Periorbital Surgical Rehabilitation After Facial Nerve Paralysis Chapter CopyRight - Year Springer Science+Business
Metadata of the chapter that will be visualized online ChapterTitle Chapter Sub-Title Periorbital Surgical Rehabilitation After Facial Nerve Paralysis Chapter CopyRight - Year Springer Science+Business
Quantitative Determination of
 The Application of 3D Images for Quantitative Determination of Zygoma in an Asian Population Shih-Hsuan Mao, Yu-Hsuan Hsieh, Chih-Hao Chen, Chien-Tzung Chen Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
The Application of 3D Images for Quantitative Determination of Zygoma in an Asian Population Shih-Hsuan Mao, Yu-Hsuan Hsieh, Chih-Hao Chen, Chien-Tzung Chen Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
DOWNLOAD OR READ : REVERSING HEMIFACIAL SPASM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : REVERSING HEMIFACIAL SPASM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 reversing hemifacial spasm reversing hemifacial spasm pdf reversing hemifacial spasm reversing hemifacial spasm Smallpdf
DOWNLOAD OR READ : REVERSING HEMIFACIAL SPASM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 reversing hemifacial spasm reversing hemifacial spasm pdf reversing hemifacial spasm reversing hemifacial spasm Smallpdf
Surgical correction of unilateral and bilateral facial palsy
 562 REVIEW Surgical correction of unilateral and bilateral facial palsy D H Harrison... Unilateral and bilateral facial palsies are debilitating and depressing conditions for the patient. For the past
562 REVIEW Surgical correction of unilateral and bilateral facial palsy D H Harrison... Unilateral and bilateral facial palsies are debilitating and depressing conditions for the patient. For the past
Contralateral botulinum injections in patients with residual facial asymmetry and contralateral hyperkinesis after primary facial palsy surgery
 Contralateral botulinum injections in patients with residual facial asymmetry and contralateral hyperkinesis after primary facial palsy surgery Ann. Ital. Chir., 2015 86: 201-206 pii: S0003469X15023374
Contralateral botulinum injections in patients with residual facial asymmetry and contralateral hyperkinesis after primary facial palsy surgery Ann. Ital. Chir., 2015 86: 201-206 pii: S0003469X15023374
Double powered free gracilis muscle transfer for smile reanimation: A longitudinal optoelectronic study
 Accepted Manuscript Double powered free gracilis muscle transfer for smile reanimation: A longitudinal optoelectronic study Chiarella Sforza, Prof., Alice Frigerio, Andrea Mapelli, Filippo Tarabbia, Isabella
Accepted Manuscript Double powered free gracilis muscle transfer for smile reanimation: A longitudinal optoelectronic study Chiarella Sforza, Prof., Alice Frigerio, Andrea Mapelli, Filippo Tarabbia, Isabella
Survey of Methods of Facial Palsy Documentation in Use by Members of the Sir Charles Bell Society
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Survey of Methods of Facial Palsy Documentation in Use by Members of the Sir Charles Bell Society Adel Y.
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Survey of Methods of Facial Palsy Documentation in Use by Members of the Sir Charles Bell Society Adel Y.
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. The Role Of Plastic Surgery In Reducing A Patient s Disability Score A Reconstructive Approach. Peripheral Nerve Surgery
 Slide 1 The Role Of Plastic Surgery In Reducing A Patient s Disability Score A Reconstructive Approach Andrew I. Elkwood MD FACS Director of the Center for Treatment of Paralysis and Reconstructive Nerve
Slide 1 The Role Of Plastic Surgery In Reducing A Patient s Disability Score A Reconstructive Approach Andrew I. Elkwood MD FACS Director of the Center for Treatment of Paralysis and Reconstructive Nerve
MICRONEUROVASCULAR FREE MUSCLE TRANSFER WITH CROSS OVER NERVE GRAFTS IN FACIAL REANIMATION
 Department of Plastic Surgery Helsinki University Hospital University of Helsinki Finland MICRONEUROVASCULAR FREE MUSCLE TRANSFER WITH CROSS OVER NERVE GRAFTS IN FACIAL REANIMATION Tuija Ylä Kotola Academic
Department of Plastic Surgery Helsinki University Hospital University of Helsinki Finland MICRONEUROVASCULAR FREE MUSCLE TRANSFER WITH CROSS OVER NERVE GRAFTS IN FACIAL REANIMATION Tuija Ylä Kotola Academic
SOFT TISSUE SUPPORT IS AN
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstructive Application of the Endotine Suspension Devices James H. Boehmler IV, MD; Benjamin L. Judson, MD; Steven P. Davison, MD, DDS Objective: To illustrate the potential reconstructive
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstructive Application of the Endotine Suspension Devices James H. Boehmler IV, MD; Benjamin L. Judson, MD; Steven P. Davison, MD, DDS Objective: To illustrate the potential reconstructive
Device for Studying Reanimation of Unilateral Facial Paralysis
 Tampere University of Technology Device for Studying Reanimation of Unilateral Facial Paralysis Citation Rantanen, V., Vehkaoja, A. T., Verho, J. A., Veselý, P., Kontunen, A., Mattila, R.,... Lekkala,
Tampere University of Technology Device for Studying Reanimation of Unilateral Facial Paralysis Citation Rantanen, V., Vehkaoja, A. T., Verho, J. A., Veselý, P., Kontunen, A., Mattila, R.,... Lekkala,
Fibular Bone Graft for Nasal Septal Reconstruction: A Case Report
 220 Nasal septal reconstruction Case Report Fibular Bone Graft for Nasal Septal Reconstruction: A Case Report Yakup Cil1* Diyarbakır Military Hospital, Department of Plastic Surgery 21000 Diyarbakır, Turkey
220 Nasal septal reconstruction Case Report Fibular Bone Graft for Nasal Septal Reconstruction: A Case Report Yakup Cil1* Diyarbakır Military Hospital, Department of Plastic Surgery 21000 Diyarbakır, Turkey
Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed Face October 2002
 TITLE: Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed Face SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: October 30, 2002 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: Karen H.
TITLE: Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed Face SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: October 30, 2002 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: Karen H.
Management of ipsilateral ptosis with hypotropia
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1986, 70, 732-736 Management of ipsilateral ptosis with hypotropia L A FICKER, J R 0 COLLIN, AND J P LEE From Moorfields Eye Hospital, London SUMMARY Thirty-one patients
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1986, 70, 732-736 Management of ipsilateral ptosis with hypotropia L A FICKER, J R 0 COLLIN, AND J P LEE From Moorfields Eye Hospital, London SUMMARY Thirty-one patients
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Bell's Palsy
 Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Bell's Palsy Number: 0745 Policy *Pleasesee amendment forpennsylvaniamedicaidattheendofthiscpb. I. Aetna considers blink reflex testing medically necessary for the diagnosis
Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Bell's Palsy Number: 0745 Policy *Pleasesee amendment forpennsylvaniamedicaidattheendofthiscpb. I. Aetna considers blink reflex testing medically necessary for the diagnosis
Tarsal fixation of Fascia lata in Frontalis Sling Ptosis Surgery
 Original Article Tarsal fixation of Fascia lata in Frontalis Sling Ptosis Surgery Muhammad Moin Pak J Ophthalmol 2006, Vol. 22 No. 3.......................................................................................
Original Article Tarsal fixation of Fascia lata in Frontalis Sling Ptosis Surgery Muhammad Moin Pak J Ophthalmol 2006, Vol. 22 No. 3.......................................................................................
The Sublime Beauty of Normal
 Disclosures Basal Cell Carcinoma Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp The Sublime Beauty of Normal P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Director, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery UCSF Medical Center The
Disclosures Basal Cell Carcinoma Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp The Sublime Beauty of Normal P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Director, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery UCSF Medical Center The
Lateral Orbitotomy in the Management of Challenging Exotropia
 Lateral Orbitotomy in the Management of Challenging Exotropia Yahalom C (1, 2), Mc Nab A (3), Ben Simon G (3), Kowal L (1). 1- Centre for Eye Research Australia and Ocular Motility Clinic, Royal Victorian
Lateral Orbitotomy in the Management of Challenging Exotropia Yahalom C (1, 2), Mc Nab A (3), Ben Simon G (3), Kowal L (1). 1- Centre for Eye Research Australia and Ocular Motility Clinic, Royal Victorian
Irecall my first course on titanium
 Dental Facial Aesthetics Botox with Implants Warren Roberts, DMD and Janet Roberts, BSc, DMD Botulinum Toxin type A (BoNT-A) has been used extensively cosmetically treating facial lines & therapeutically
Dental Facial Aesthetics Botox with Implants Warren Roberts, DMD and Janet Roberts, BSc, DMD Botulinum Toxin type A (BoNT-A) has been used extensively cosmetically treating facial lines & therapeutically
Current considerations in the management of facial nerve palsy
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Current considerations in the management of facial nerve palsy Charles Kim and Gary J. Lelli Jr Purpose of review Facial nerve palsy is a potentially devastating condition that
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Current considerations in the management of facial nerve palsy Charles Kim and Gary J. Lelli Jr Purpose of review Facial nerve palsy is a potentially devastating condition that
Paradoxical Use of Frontalis Muscle and the Possible Role of Botulinum A Toxin in Permanent Motor Relearning
 Paradoxical Use of Frontalis Muscle and the Possible Role of Botulinum A Toxin in Permanent Motor Relearning Guy J. Ben Simon, MD, 1 Sean M. Blaydon, MD, 2 Robert M. Schwarcz, MD, 1 Tanuj Nakra, MD, 1
Paradoxical Use of Frontalis Muscle and the Possible Role of Botulinum A Toxin in Permanent Motor Relearning Guy J. Ben Simon, MD, 1 Sean M. Blaydon, MD, 2 Robert M. Schwarcz, MD, 1 Tanuj Nakra, MD, 1
The management of blepharoptosis is a complex issue. Many. Current Ptosis Management: A National Survey of ASOPRS Members ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Current Ptosis Management: A National Survey of ASOPRS Members Vinay K. Aakalu, M.D., M.P.H., and Pete Setabutr, M.D. Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Current Ptosis Management: A National Survey of ASOPRS Members Vinay K. Aakalu, M.D., M.P.H., and Pete Setabutr, M.D. Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University
Full Recovery of the Patient With Bell s Palsy Within Two to Six Weeks After Single Course of Pulsed Electromagnetic Therapy-Case Reports
 Case Report Full Recovery of the Patient With Bell s Palsy Within Two to Six Weeks After Single Course of Pulsed Electromagnetic Therapy-Case Reports Lauren Gorelick 1*, Ayala Rozano-Gorelick 2 1 Pain
Case Report Full Recovery of the Patient With Bell s Palsy Within Two to Six Weeks After Single Course of Pulsed Electromagnetic Therapy-Case Reports Lauren Gorelick 1*, Ayala Rozano-Gorelick 2 1 Pain
PREOPERATIVE COMPUTER
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Accuracy of Preoperative Computer Imaging in Rhinoplasty Umang Mehta, MD; Kashif Mazhar, MD; Andrew S. Frankel, MD Objective: To quantitatively measure the accuracy of preoperative computer
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Accuracy of Preoperative Computer Imaging in Rhinoplasty Umang Mehta, MD; Kashif Mazhar, MD; Andrew S. Frankel, MD Objective: To quantitatively measure the accuracy of preoperative computer
McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 12, NO 2 May 2011 27 McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mohamed A. Albadawy, MD and Bassem M.
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 12, NO 2 May 2011 27 McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mohamed A. Albadawy, MD and Bassem M.
