Flixweed vs. Polyethylene Glycol in the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial
|
|
|
- Julie Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iran J Pediatr April; 25(2):e425. Published online 2015 April 18. DOI: /ijp.425 Research Article Flixweed vs. Polyethylene Glycol in the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial Majid Nimrouzi 1, 2, * ; Omid Sadeghpour 1 ; Mohammad Hadi Imanieh 2 ; Mohammadreza Shams Ardekani 3 ; Alireza Salehi 3 ; Mohamad Bagher Minaei 4 ; Mohammad M. Zarshenas 5,6 1 Research Institute for Islamic and Complementary Medicine, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, IR Iran 2 Research Center for Traditional Medicine and History of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, IR Iran 3 Department of Traditional Pharmacy, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, IR Iran 4 School of Iranian Traditional Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, IR Iran 5 Department of Phytopharmaceuticals (Traditional Pharmacy), School of Pharmacy, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, IR Iran 6 Medicinal Plants Processing Research Center, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, IR Iran *Correspondence author: Majid Nimrouzi, Research Institute for Islamic and Complementary Medicine, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, IR Iran. Tel: , nimruzim@sums.ac.ir Received: February 5, 2015; Revised: February 13, 2015; Accepted: March 10, 2015 Background: Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is often considered as the first-line treatment for functional constipation in children. Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb et Berth (D. sophia) is a safe recommended medicine in Iranian folk and Traditional Persian Medicine for the treatment of constipation. Objectives: To clinically compare D. sophia with PEG 4000 (without electrolyte) in pediatric constipation and to assess its efficacy and side effects. Patients and Methods: 120 patients aged 2-12 years with constipation for at least 3 months were included in an 8 weeks lasting randomized controlled trial within two parallel-groups. Children received either PEG, 0.4 g/kg/day, or D. sophia seeds, 2 grams (for children aged 2-4 years) and 3 grams (for those aged > 4 years) per day. Results: A total of 109 patients completed the study (56 in D. sophia and 53 in PEG group). At the end of the study, 36 (64.3%) patients in D. sophia group and 29 (54.7%) in PEG group were out of Rome III criteria (P = 0.205). Median weekly stool frequency in 0, 1, 2, 3 weeks of the treatment was found to be 2, 5, 5, 5 in D. sophia and 3, 4, 4, 5 in PEG group (P = 0.139, 0.076, 0.844, 0.294), respectively. The number of patients who suffered flatulence was less (5, 8.9%) in D. sophia group as compared to PEG group (6, 11.3%) at the end of the trial (P = 0.461). D. sophia taste was less tolerated. Conclusions: D. sophia is introduced as a cheap and available medication which can be applied as a safe alternative to conventional PEG in the management of pediatric chronic functional constipation. Keywords: Children; Constipation; Polyethylene Glycol; Descurainia Sophia 1. Background Pediatric chronic constipation is often defined as having bowel movements less than three times per week and lasting for more than months (1). Constipation is one of the most common gastrointestinal (GI) complications, especially in the developed countries (2). The incidence of this disorder is about 15% in communities (3). Excluding neonatal period, the most common type of constipation is functional constipation (4). Chronic functional constipation (CFC) is an annoying disorder for both parents and children (5). Predisposing factors for childhood constipation may be discussed as genetic, psychological or organic (6). Common risk factors for functional constipation in children include low fiber diet, emotional stress, and positive family history in the first-degree relatives as well as painful defecation (7). Increased parental understanding and support as well as improving toileting habits and using laxatives warrant the control of this distressing condition in children (8). Single drug therapy hardly leads to control the symptoms in afflicted children. The treatment protocol should include lifestyle change via parental education, longterm maintenance therapy and fecal mass removal (9). Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is often mentioned as the firstline treatment for children with CFC (9). PEG is a non-toxic, hydrosoluble, high-molecular polymer which is safe for long-term application in children (10). Flixweed (Descurainia sophia L.) (D. sophia) is a known commonly-used medical herb in Traditional Persian Medicine. D. sophia is considered as a safe and mild laxative (11), and an anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antihelmetic herbal medicament (12). D. sophia is reported not toxic at the level of up to 2500 mg/kg of body weight Copyright 2015, Growth & Development Research Center. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non- Commercial 4.0 International License ( which permits copy and redistribute the material just in noncommercial usages, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 (13). About 15 aminoacids, 10 fatty acids, flavonoids and phenolic constituents have been isolated from D. sophia seed (11). A study showed that a combination of D. sophia and prune (Prunus domestica L.) could prevent adult Hajj pilgrims constipation (14). In Traditional Chinese Medicine, flixweed seeds are used to relieve cough and reduce edema. It has revealed cardiotonic effects and is also applied in some cancers. D. sophia has shown cytotoxic activity against cancer cells (15). 2. Objectives Current study aimed to compare the efficacy of D. sophia compared to PEG in the symptomatic alleviation of pediatric constipation. 3. Patients and Methods 3.1. Trial Design The study was conducted from January to August 2013 at Shahid Motahari Polyclinic in Shiraz. The study was approved by Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences; the trial enrollment started at January Before enrollment, informed consent was obtained from the parents. In this trial, patients were referred by a pediatric gastroenterologist who had done precise examination and confirmed the CFC Patients Patients were selected from 221 children referred to a pediatric gastroenterologist in Shahid Motahari Polyclinic. The inclusion criteria were children between 2 and 12 years who met the Rome III criteria for functional constipation, and were free of other medications. The inclusion criteria were based on the existence of 2 or more Rome III criteria for functional constipation for at least 3 months before diagnosis and lack of the Rome III criteria for IBS (Box 1) (16). Children having organic causes of defecation disorders such as Hirschsprung s disease, spina bifida occulta, hypothyroidism, cystic fibrosis, neurologic abnormalities, intestinal pseudo-obstruction, and diabetes mellitus were also excluded from the study (7). Box 1. Inclusion Criteria for Diagnosis of Functional Constipation in Children History of two or fewer defecations in the toilet per week At least one episode of fecal incontinence per week History of retentive posturing or excessive volitional stool retention History of painful or hard bowel movements Presence of a large fecal mass in the rectum History of large diameter stools that may obstruct the toilet 3.3. Study Procedure Through a block randomization, patients were divided into two parallel therapeutic groups (60 in each group). The sample size was determined based on similar studies (9). Totally, 120 children aged 2-12 years old who met the Rome III criteria were enrolled in the study. One group received an oral solution containing D. sophia seed and the other, PEG 40% without electrolyte. Due to the different tastes and appearance of both medications, the study was not blinded. However, the methodologist and the statistician who assessed and analyzed the data were blind to the protocol. At enrollment, a complete history was taken and physical examination done by a physician involved in the study. Stool frequency, fecal soiling (encopresis), stool consistency, retention posturing and abdominal pain, flatulence or rectal bleeding were recorded. Patients with fecal impaction were treated with bisacodyl suppositories at the first visit. Subsequently they were enrolled in the study. Medications were oral administration of PEG (40% solution without electrolytes), 0.4 g/kg (17), and D. sophia, two grams for 2-4 years old and three grams for 4-12 years old patients once daily for 8 weeks. Parents were requested to refer to the on call physician in case of seven days lack of bowel movement or confronting with any other complication. During the first three weeks, parents were asked to record a daily report of defecation frequency, stool consistency, soiling, painful defecation, retention and passing blood with defecation. Additionally, weekly reports were taken from by the interviewer. At the end of the first three weeks, parents were called to describe the condition of their children. Patients were also revisited and their charts were reviewed. The efficacy of the intervention in both groups was evaluated at three weeks and eight weeks of follow-up Behavior Modification According to conventional medicine and traditional medicine resources, behavior modifications and nutritional advices were the same in both groups. These points included toilet training, abstaining from junk foods and drinking adequate water, but not with the meals. The patients were asked to chew food morsels slowly (9, 18). Following termination of three weeks, patients were again visited and parents were assured to continue the behavior modifications. Medication was continued for further five weeks after the agreement Outcome Measures The primary outcome was determination of proportion of patients who had responded to treatment. Response to the treatment was defined as improvement of constipation for at least three bowel movements, soft stool and convenient defecation, no soiling and bloody stool per week as well as exiting the Rome III criteria for constipa- 2
3 tion after the third week. Patients were ruled out from the study if they had no bowel movement for seven days or developed fecal impaction, at any stage. Secondary outcomes were as follows: If the patients did not meet Rome III criteria at the end of the eighth week, the incidence and severity of gastrointestinal adverse effects including flatulence, abdominal pain and drug compliance were monitored at the end of the third and eighth week Statistical Analysis Quantitative data were presented as Mean ± SD and No. (%), or MED (IQR). Statistical analyses included the determination of Means ± SD, t test, Chi-square test, Fisher exact test and Mann-Whitney U-test with a significance level of 5%. 4. Results Among 221 referred patients, 120 cases who met the Rome III criteria for constipation were enrolled in the study. After receiving the written consents and block randomization, 11 patients withdrew the consent in the first week of treatment. The reason was doubts on the efficacy of treatment. On the other hand, 109 patients continued the recommended treatment (PEG: 53, and DS: 56). All patients were visited at the end of the third and eighth week. The participants age was between 2 and 12 (5.01 ± 2.38). The two groups were similar in demographic and Rome III criteria before starting treatment (Table 1). Duration of constipation was more than six months in 105 (96.3%) and 3-6 months in 4 (3.7%) patients. Fifty five (98.2%) children in D. sophia and 50 (94.3%) in PEG group had a history of constipation for more than six months. Thirty eight (67.9%) patients in D. sophia and 18 (34%) in PEG group had a history of receiving multiple none controlled- medications for over six months Treatment Success Based on Rome III criteria, both interventions demonstrated similar efficacies in relieving symptoms of constipation at the end of the third week (58.9% in the D. sophia group versus 54.7% in PEG group). However, 64.3% of patients in D. sophia group were out of criteria at the end of the eighth week as compared to those in PEG group (54.7%). No statistically significant difference was found between the efficacy of both interventions in the treatment of constipation at the end of third and eighth week of intervention (Table 2) Stool Frequency Median weekly stool frequency in the 0, 1, 2, 3 weeks of treatment was 2, 5, 5, 5 in D. sophia and 3, 4, 4, 5 in PEG group (P = 0.139, , 0.844, ), respectively. In regard of 6-12 year old children at the end of the first and second week of treatment, stool frequency was significantly improved in D. sophia group, as compared to the PEG group [D. sophia group: 7 (5.75-7), 7 (5.75-7); PEG group: 3 (3-4), 4 (3-6.5), P = ; P = ]. At the end of the third week, stool frequency in the PEG group was found better than that in the D. sophia group. However, the difference was not statistically significant [D. sophia group: 4.5 (5.75-7); PEG group: 6 (5.75-7); P = 0.203] (Table 3). Table 1. Baseline Characteristic in Descurainia sophia and PEG Group a, b Variable DS (n = 56) PEG (n = 53) P value Age, yr 4.86 ± ± Weight, kg ± ± Gender, male 26 (46) 22 (41.50) Percentile ± ± Frequency of Bowel movement/week 2 (1-3) 3 (2-3) Frequency of hard stool/week 2 (1-3) 2 (1-3) Frequency of painful defecation/week 2 (1-3) 3 (2-3) Frequency of retention/week 0 (0-0) 0 (0-0) Frequency of soiling/week 0 (0-1) 0 (0-1) a Abbreviations: DS: Descurainia sophia, PEG: Polyethylene glycol. b Data are presented as Mean ± SD, No. (%), or Med (IQR). Table 2. Efficacy of Treatment With PEG and Descurainia sophia Group According to Existing Rome III Criteria a, b Variables DS (n = 56) PEG (n = 53) P Value End of First week 1 (1.8) 3 (5.7) End of Second week 30 (53.6) 30 (56.6) 0.45 End of Third week 33 (58.9) 29 (54.7) End of Eighth week 36 (64.3) 29 (54.7) a Abbreviations: DS: Descurainia Sophia, PEG: Polyethylene glycol. b Data are presented as No. (%). 3
4 Table 3. Comparison of Stool Frequency, Hard Stool, Painful Defecation and Soiling in Descurainia Sophia and PEG Groups at Follow-up a, b Frequency, wk Before Intervention After First Week After Second Week After Third Week Stool frequency DS 2 (1-3) 5 (3-7) 5 (3-7) 5 (3-7) PEG 3 (2-3.5) 4 (3-6.5) 4 (3-7) 5 (4-7) P value Hard stool DS 2 (1-3) 2 (0-3) 2 (0-3) 1 (0-2.75) PEG 2 (1-3) 2 (1-3) 1 (0-3.5) 2 (0-3) P value Painful defecation DS 2 (1-3) 1 (0-2.75) 1 (0-2) 0.5 (0-2) PEG 3 (2-3) 2 (0-3) 1 (0-2) 0 (0-3) P value Soiling DS a 0 (0-1) 0 (0-0) 0 (0-0) 0 (0-0) PEG 0 (0-1) 0 (0-0) 0 (0-0) 0 (0-0) P value a Abbreviations: DS: Descurainia Sophia, PEG: Polyethylene glycol. b Data are presented as DS (n = 56) and PEG (n = 53) and as Med (IQR). Figure 1. Comparison of Retention Posturing in Descurainia Sophia and PEG Group in the Three Week Follow-up Enrolement 1-week follow-up 2-week follow-up 3-week follow-up DS PEG The differences between both groups were not significant (P values at weeks 0, 1, 2 and 3 were 0.156, 0.275, and respectively.). Table 4. Flatulence and Abdominal Pain in Descurainia sophia and PEG Group a, b Variables DS (n = 56) a PEG (n = 53) P value Baseline 22 (39.3) 20 (37.7) First week 14 (25.0) 20 (37.7) Second week 12 (21.4) 15 (28.3) Third week 10 (17.9) 11 (20.8) Eighth week 5 (8.9) 6 (11.3) a Abbreviations: DS: Descurainia Sophia, PEG: Polyethylene glycol. b Data are presented as No. (%) Pain and Retention Following three weeks of medication, hard stool frequency, painful defecation and stool retention decreased in both groups. However, the differences between groups were not statistically significant (Figure 1) Blood Stained Stool Median blood stained stool in baseline and weeks 1, 2 and 3 were 0 for both groups. Only one patient in D. sophia group and one in the PEG group reported a history of blood stained stool at the end of the third week [0 (0-0) in both groups; P = 0.365] Adverse Events During the first three weeks of treatment and despite of the dose increasing, 10 patients (18.9%) in PEG and 3 (5.4%) in D. sophia group needed bisacodyl suppositories after seven days of no bowel movement. The difference between two groups was significant (P = 0.03). At the beginning of the intervention, the number of patients who suffered from flatulence and abdominal pain in D. sophia group (22 = 39.3%) was more than that of the PEG group (20 = 37.7%). At the end of the eighth week, values of these parameters were less in the D. sophia group (5 = 8.9%) as compared to the PEG group (6 = 11.3%) (P = 0.461) (Table 4). The number of patients who disliked the taste of medication in the D. sophia group (17 = 30%) was significantly more than that of the PEG group (5 = 9.5%) (P = 0.004). 4
5 5. Discussion D. sophia is a cheap and available medication which can be introduced as a safe alternative for PEG in CFC. However, the taste may not be much acceptable. The D. sophia mechanism of action has not yet been elucidated. The seeds may act as a stool softener and bowel smooth muscle relaxant. D. sophia seeds oral solution produce mucilage that can absorb water from bowel lumen and thus may soften the stool. The compound, allyl disulfide in D. sophia seed may have relaxant effect on the smooth muscles and facilitate the defecation (19). As PEG is often mentioned as the first-line treatment for CFC, it was selected in the current study. Many studies have confirmed the related effects of PEG superiorities rather than the other laxatives in the treatment of CFC. Findings of the study conducted by Karami et al. showed the preference of PEG compared with liquid paraffin in treatment of CFC (20). Wang et al. found that two weeks treatment of CFC with PEG 4000 and lactulose is safe. But PEG revealed higher rates of success in the improvement of stool frequency than lactulose (21). In a meta-analysis, Lee-Robichaud et al. compared the efficacy of PEG and lactulose and showed the superiority of PEG over lactulose in treatment of functional constipation in both children and adults (22). Studies showed that PEG is very effective in the control of constipation. This medicament can rapidly stop the symptoms, even in patients with fecal impaction. Oral PEG can be used as a safe alternative of enema in patients with fecal impaction (23). Savino et al. found that enema and PEG are equally effective in treatment of fecal impaction in constipated children (24). A positive family history of constipation is found between 30 and 40 percent in different studies (24). In our study, 49 (45%) patients had positive family history of constipation. There was no relationship between positive family history and the result of treatment in both groups. A relationship between increasing body mass index and lower bowel movement frequency has been reported repeatedly in adults and children (25). Prevalence of obesity and overweight in Iranian children is 5.1% and 10.8%, respectively (26). The rates of overweight and obesity were 9.2% and 12.8% in our study. According to previous studies, the chance of recovery with PEG in CFC of children is about 56-90% (8). The less chance of recovery in our study may be due to the chronicity of disease in most of the patients. Considerably, history of receiving multiple drug and tolerance to many medications are additional parameters, especially in D. sophia group. Despite this fact, the recovery rate with D. sophia was found to be higher at the end of the eighth week than that with PEG. According to the relative supremacy of D. sophia versus PEG at the end of the eighth week, D. sophia was found to be more slowly-acting (64.3% vs. 54.7%) Strengths and Limitations Blinding was not possible regarding the differences in the appearance and dose of the applied medications. However, the methodologist and the statistician who assessed and analyzed the data were blind to the study. Taste of D. sophia was a limitation of consumption. The number of patients in D. sophia group who disliked the taste of medicine was more than that of the PEG group. Follow-ups were satisfactory and we missed no case to follow-up after starting the treatment. Data were collected from 100% of the parents by two follow up sessions at the end of the third and eighth week. D. sophia is a safe and cheap alternative for PEG. Efficacy of D. sophia is as much as PEG in the treatment of CFC. Compared to PEG, D. sophia showed better response in the control of annoying symptoms such as abdominal pain and flatulence. According to the outcomes of this trial, DS oral solution can be tastely modified to be applied for respective treatment in a long period. The longterm safety and efficacy of D. sophia should be evaluated by more comprehensive randomized clinical trials. References 1. What is chronic constipation? Definition and diagnosis. Gray JR. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011;25 Suppl B:7B 10B Colonic Transit Time In 64 Iranian Patients With Idiopathic Chronic Constipation. Ansari R, Sohrabi MR, Roohi S, Mikaeli J, Massarrat S, Tahaghoghi Mehrizi S, et al. Arch Iran Med. 2001;4(1): Clinical Manifestations of Hirschsprungâ s Disease: A Six Year Course Review of Admitted Patients in Gilan, Northern Iran. Izadi M, Mansour-Ghanaei F, Jafarshad R, Joukar F, Bagherzadeh AH, Tareh F. Middle East J Digest Dis. 2009;1(2): Constipation in infants and children: evaluation and treatment. A medical position statement of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. Baker SS, Liptak GS, Colletti RB, Croffie JM, Di Lorenzo C, Ector W, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;29(5): Systematic review: impact of constipation on quality of life in adults and children. Belsey J, Greenfield S, Candy D, Geraint M. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;31(9): Factors associated with childhood constipation. Inan M, Aydiner CY, Tokuc B, Aksu B, Ayvaz S, Ayhan S, et al. J Paediatr Child Health. 2007;43(10): Constipation in children: diagnosis and management. Rajindrajith S, Devanarayana NM. Sri Lanka J Child Health. 2009;38(4): Constipation in children. Afzal NA, Tighe MP, Thomson MA. Ital J Pediatr. 2011;37: A randomized, prospective, comparison study of a mixture of acacia fiber, psyllium fiber, and fructose vs polyethylene glycol 3350 with electrolytes for the treatment of chronic functional constipation in childhood. Quitadamo P, Coccorullo P, Giannetti E, Romano C, Chiaro A, Campanozzi A, et al. J Pediatr. 2012;161(4): Long-term safety of PEG 4000 in children with chronic functional constipation: A biochemical perspective. Bae SH. Korean J Pediatr. 2010;53(7): Determination of the volatile composition in essential oil of Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl (Flixweed) by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Li J, Liu X, Dong F, Xu J, Zheng Y, Shan W. Molecules. 2010;15(1): Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory constituents from the seeds of Descurainia sophia. Lee YJ, Kim NS, Kim H, Yi JM, Oh SM, Bang OS, et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2013;36(5): Chemical constituents of Descurainia sophia L. and its biological activity. Mohamed NH, Mahrous AE. Rec Nat Proc. 2009;3(1):58. 5
6 The effect of Descureania Sophia L. and Prunus Domestica L. in prevention of constipation among Iranian Hajj Pilgrims, Saudi Arabia. Pasalar M, Bagheri Lankarani K, Mehrabani D, Tolide H. Res J Pharmaceut Biol Chem Sci. 2013;4(2): Two new lactones and one new aryl-8-oxa-bicyclo[3,2,1]oct-3- en-2-one from Descurainia sophia. Sun K, Li X, Li W, Wang J, Liu J, Sha Y. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2004;52(12): Rome III: New standard for functional gastrointestinal disorders. Drossman DA, Dumitrascu DL. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2006;15(3): PEG3350 in the treatment of childhood constipation: a multicenter, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Nurko S, Youssef NN, Sabri M, Langseder A, McGowan J, Cleveland M, et al. J Pediatr. 2008;153(2):254. doi: /j.jpeds e Avicenna H. In: Ghanoon Dar Teb [The Canon of Medicine], Bulaq Edition. Sharafkandi A, editor. Vol Tehran: Uni of Tehran Pr; A novel sulphur glycoside from the seeds of Descurainia sophia (L.). Sun K, Li X, Liu JM, Wang JH, Li W, Sha Y. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2005;7(6): Polyethylene glycol versus paraffin for the treatment of childhood functional constipation. Karami H, Khademloo M, Niari P. Iran J Pediatr. 2009;19(3): Polyethylene glycol 4000 treatment for children with constipation: A randomized comparative multicenter study. Wang Y, Wang B, Jiang X, Jiang M, Xu C, Shao C, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2012;3(5): Lactulose versus Polyethylene Glycol for Chronic Constipation. Lee-Robichaud H, Thomas K, Morgan J, Nelson RL. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(7):e Rectal fecal impaction treatment in childhood constipation: enemas versus high doses oral PEG. Bekkali NL, van den Berg MM, Dijkgraaf MG, van Wijk MP, Bongers ME, Liem O, et al. Pediatrics. 2009;124(6):e Efficacy and tolerability of peg-only laxative on faecal impaction and chronic constipation in children. A controlled double blind randomized study vs a standard peg-electrolyte laxative. Savino F, Viola S, Erasmo M, Di Nardo G, Oliva S, Cucchiara S. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12: Functional constipation in children: a systematic review on prognosis and predictive factors. Pijpers MA, Bongers ME, Benninga MA, Berger MY. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010;50(3): Trend in the prevalence of obesity and overweight among Iranian children and adolescents: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Kelishadi R, Haghdoost AA, Sadeghirad B, Khajehkazemi R. Nutrition. 2014;30(4):393. 6
Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol. glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide, lactulose. treatment of functional constipation in children
 Original article Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulosein treatment of functional constipation in children Hossein Saneian 1, Neda Mostofizadeh 2 1 Assistant
Original article Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulosein treatment of functional constipation in children Hossein Saneian 1, Neda Mostofizadeh 2 1 Assistant
Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate.
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone. Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club
 Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
 Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children
 Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Constipation in childhood is characterized by a low defecation frequency in combination with either involuntary loss of
 USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
TREATMENT SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION
 SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
Constipation in children
 Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Constipation in children usually is functional (ie, constipation
 Efficacy and Complications of Polyethylene Glycols for Treatment of Constipation in Children A Meta-Analysis Si-Le Chen, MD, Shi-Rong Cai, MD, PhD, Liang Deng, MD, Xin-Hua Zhang, MD, PhD, Te-Dong Luo,
Efficacy and Complications of Polyethylene Glycols for Treatment of Constipation in Children A Meta-Analysis Si-Le Chen, MD, Shi-Rong Cai, MD, PhD, Liang Deng, MD, Xin-Hua Zhang, MD, PhD, Te-Dong Luo,
Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report
 Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report 1. Private practice, Quebec, Canada. Email: nathaelle@chirostmartin.com By Nathaëlle Martin-Marcotte,
Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report 1. Private practice, Quebec, Canada. Email: nathaelle@chirostmartin.com By Nathaëlle Martin-Marcotte,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
 Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Mohammed Y Hasosah 1*, Samer A Alamri 2, Faisal A Al-Husayni 2, Rakan M. Aljedaani 2, Mohammad A Zwawy
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Mohammed Y Hasosah 1*, Samer A Alamri 2, Faisal A Al-Husayni 2, Rakan M. Aljedaani 2, Mohammad A Zwawy
Gordon, Morris, Macdonald, John, Parker, Claire, Akobeng, Anthony and Thomas, Adrian
 Article Osmotic and stimulant laxatives for the management of childhood constipation Gordon, Morris, Macdonald, John, Parker, Claire, Akobeng, Anthony and Thomas, Adrian Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/15372/
Article Osmotic and stimulant laxatives for the management of childhood constipation Gordon, Morris, Macdonald, John, Parker, Claire, Akobeng, Anthony and Thomas, Adrian Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/15372/
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
Constipation in Children. Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG*
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation in childhood
 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014
 Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Authors and Disclosures
 Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Aging Persons with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD): Constipation KEYPOINTS OVERVIEW
 Aging Persons with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD): Constipation KEYPOINTS A major medical conditions that commonly is seen among persons with IDD and may lead to serious complications is constipation.
Aging Persons with Intellectual Developmental Disorders (IDD): Constipation KEYPOINTS A major medical conditions that commonly is seen among persons with IDD and may lead to serious complications is constipation.
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination
 Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
The involuntary loss of feces in the underwear after. Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence.
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
Paediatric constipation
 EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS constipation Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Best practice Paediatric constipation Diagnosis and treatment Dr Tim De Maayer Paediatric Gastroenterologist
EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS constipation Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Best practice Paediatric constipation Diagnosis and treatment Dr Tim De Maayer Paediatric Gastroenterologist
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences The Effect of Descureania Sophia L. and Prunus Domestica L. in Prevention of Constipation among Iranian Hajj Pilgrims, Saudi Arabia
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences The Effect of Descureania Sophia L. and Prunus Domestica L. in Prevention of Constipation among Iranian Hajj Pilgrims, Saudi Arabia
Original Article. Introduction
 Original Article A Randomized Clinical Trial on Treatment of Chronic Constipation by Traditional Persian Medicine Recommendations Compared to Allopathic Medicine: A Pilot Study Abstract Background: The
Original Article A Randomized Clinical Trial on Treatment of Chronic Constipation by Traditional Persian Medicine Recommendations Compared to Allopathic Medicine: A Pilot Study Abstract Background: The
IPS Childhood Constipation when we refer to Ped.Gastroenterologist? Dr.Muath Al Turaiki. Consultant of Pediatric Gastroenterology, K.S.
 Childhood Constipation when we refer to Ped.Gastroenterologist? Dr.Muath Al Turaiki Consultant of Pediatric Gastroenterology, K.S.H Dubai 22-24 Feb. 2018 Objectives: Why constipation?!!! Is it a burden
Childhood Constipation when we refer to Ped.Gastroenterologist? Dr.Muath Al Turaiki Consultant of Pediatric Gastroenterology, K.S.H Dubai 22-24 Feb. 2018 Objectives: Why constipation?!!! Is it a burden
Public Assessment Report Scientific discussion. Omnilax (macrogol) SE/H/1714/01/MR
 Public Assessment Report Scientific discussion Omnilax (macrogol) SE/H/1714/01/MR This module reflects the scientific discussion for the approval of Omnilax. The procedure was finalised on 2018-02-19.
Public Assessment Report Scientific discussion Omnilax (macrogol) SE/H/1714/01/MR This module reflects the scientific discussion for the approval of Omnilax. The procedure was finalised on 2018-02-19.
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation
 Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Chronic constipation in the elderly
 Chronic constipation in the elderly 1 Dec,2011 R 2 Natta Asanaleykha Epidemiology Definition Scope The impact of chronic constipation in the elderly Pathophysiology Evaluation the elderly patient with
Chronic constipation in the elderly 1 Dec,2011 R 2 Natta Asanaleykha Epidemiology Definition Scope The impact of chronic constipation in the elderly Pathophysiology Evaluation the elderly patient with
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines. Version 1 November 2016
 Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
Managing Defecation Disorders in Children
 A SUPPLEMENT TO Internal Medicine News Managing Defecation Disorders in Children Perspectives on Constipation and Encopresis: Current Issues and New Findings Infant Dyschezia and Functional Constipation
A SUPPLEMENT TO Internal Medicine News Managing Defecation Disorders in Children Perspectives on Constipation and Encopresis: Current Issues and New Findings Infant Dyschezia and Functional Constipation
Journal of American Science 2017;13(6) Celiac Disease in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Celiac Disease in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Ahmed Abdelmoaty Elnaggar, MD 1, Waleed El Nabawy, MD, Mohammed Ibrahim Atta, MD 1 Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University,
Celiac Disease in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Ahmed Abdelmoaty Elnaggar, MD 1, Waleed El Nabawy, MD, Mohammed Ibrahim Atta, MD 1 Internal Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University,
Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling
 Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS
 BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
Management of childhood constipation
 J Pediatr Rev. 2013;1(1)45-51 Management of childhood constipation Hassan Karami 1 Leila Shokohi 2* 1 Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Faculty of Medicine, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences,Sari,
J Pediatr Rev. 2013;1(1)45-51 Management of childhood constipation Hassan Karami 1 Leila Shokohi 2* 1 Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Faculty of Medicine, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences,Sari,
Managing functional constipation in children
 PRACTICE POINT Managing functional constipation in children A Rowan-Legg; Canadian Paediatric Society Community Paediatrics Committee Paediatr Child Health 2011;16(10):661-5 Posted: Dec 1 2011 Reaffirmed:
PRACTICE POINT Managing functional constipation in children A Rowan-Legg; Canadian Paediatric Society Community Paediatrics Committee Paediatr Child Health 2011;16(10):661-5 Posted: Dec 1 2011 Reaffirmed:
Usefulness of Assessment of Stool Form by the Modified Bristol Stool Form Scale in Primary Care Pediatrics
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 https://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2018.21.2.93 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2018 April 21(2):93-100 Original Article PGHN Usefulness of Assessment of Stool Form by the
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 https://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2018.21.2.93 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2018 April 21(2):93-100 Original Article PGHN Usefulness of Assessment of Stool Form by the
Constipation is a common and distressing pediatric problem, with a prevalence ranging from 7% to 30% in both western
 Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in Infants with Functional Chronic Constipation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Paola Coccorullo, MD, Caterina Strisciuglio, MD, Massimo Martinelli,
Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) in Infants with Functional Chronic Constipation: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Paola Coccorullo, MD, Caterina Strisciuglio, MD, Massimo Martinelli,
Constipation an Old Friend. Presented by Dr. Keith Harris
 Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka
 Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin
 Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
Go Back All Documents Expand Sections Collapse Sections Comment
 1 of 10 01/06/2014 09:10 AM Go Back All Documents Expand Sections Collapse Sections Comment Valid only on date printed: 2014-01-06 09:09. Discard immediately after use! Clinical Practice Guideline Issuing
1 of 10 01/06/2014 09:10 AM Go Back All Documents Expand Sections Collapse Sections Comment Valid only on date printed: 2014-01-06 09:09. Discard immediately after use! Clinical Practice Guideline Issuing
Identify electrolytes that should be monitored whenever prolonged or severe diarrhea is present
 Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
Constipation in childhood what is new for pediatricians and dietitians?
 Constipation in childhood what is new for pediatricians and dietitians? Jan Taminiau-Marc Benninga Emma Children s Hospital / AMC, Amsterdam / The Netherlands Approach of the child Complaints History Findings
Constipation in childhood what is new for pediatricians and dietitians? Jan Taminiau-Marc Benninga Emma Children s Hospital / AMC, Amsterdam / The Netherlands Approach of the child Complaints History Findings
Advancing gastroenterology, improving patient care
 American College of Gastroenterology Advancing gastroenterology, improving patient care Note to Visitors: A fully updated ACG Systematic Review on the Management of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation and
American College of Gastroenterology Advancing gastroenterology, improving patient care Note to Visitors: A fully updated ACG Systematic Review on the Management of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation and
CENTENE PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS DRUG REVIEW 2Q17 April May
 BRAND NAME Trulance GENERIC NAME Plecanatide MANUFACTURER Synergy Pharmaceuticals, Inc. DATE OF APPROVAL January 19, 2017 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE Anticipated in 1Q2017 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New
BRAND NAME Trulance GENERIC NAME Plecanatide MANUFACTURER Synergy Pharmaceuticals, Inc. DATE OF APPROVAL January 19, 2017 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE Anticipated in 1Q2017 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New
APDW 2016 Poster No. a90312
 APDW 2016 Poster No. a90312 SYN-010, a Proprietary Modified-Release Formulation of Lovastatin Lactone, Lowered Breath Methane and Improved Stool Frequency in Patients with IBS-C Results of a multi-center,
APDW 2016 Poster No. a90312 SYN-010, a Proprietary Modified-Release Formulation of Lovastatin Lactone, Lowered Breath Methane and Improved Stool Frequency in Patients with IBS-C Results of a multi-center,
A patient s guide to the. management of constipation following surgery
 A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
Xifaxan, Lotronex and Viberzi Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Lotronex (alosetron) a Indication For women with severe diarrheapredominant irritable
Hospital-Level Variation in Practice Patterns and Patient Outcomes for Pediatric Patients Hospitalized With Functional Constipation
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Hospital-Level Variation in Practice Patterns and Patient Outcomes for Pediatric Patients Hospitalized With Functional Constipation Jamie Librizzi, MD, MSHS, a Samuel Flores, MD, a Keith
RESEARCH ARTICLE Hospital-Level Variation in Practice Patterns and Patient Outcomes for Pediatric Patients Hospitalized With Functional Constipation Jamie Librizzi, MD, MSHS, a Samuel Flores, MD, a Keith
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
1. What evidence exists that prevention of constipation in the first year of life improves outcome of bowel management in later childhood?
 BOWEL FUNCTION AND CARE Overall Outcomes Primary Outcomes o Maintenance of social continence as appropriate for age level Secondary Outcomes o Maximization of independence with managing bowel program o
BOWEL FUNCTION AND CARE Overall Outcomes Primary Outcomes o Maintenance of social continence as appropriate for age level Secondary Outcomes o Maximization of independence with managing bowel program o
Disclosures. GI Motility Disorders. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Nursing Principles & Skills II. Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction
 Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Human Anatomy rectum
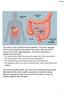 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Surveillance programme
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Surveillance programme Surveillance proposal consultation document Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Surveillance programme Surveillance proposal consultation document Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline
MANAGING CONSTIPATION
 MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
Does The Use Of Probiotics Treat Abdominal Pain In Children Between The Ages Of 4 And 18 With Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Does The Use Of Probiotics Treat Abdominal
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Does The Use Of Probiotics Treat Abdominal
Opioid-induced constipation a preventable problem
 www.veteransmates.net.au Opioid-induced a preventable problem One of the most common adverse effects of chronic opioid therapy is. 1-4 Up to 95% of patients prescribed an opioid report as a side effect,
www.veteransmates.net.au Opioid-induced a preventable problem One of the most common adverse effects of chronic opioid therapy is. 1-4 Up to 95% of patients prescribed an opioid report as a side effect,
Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation
 Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
Carminatives IBS C 11/12/10. Partial List of Carminatives and Secondary Benefits. Partial List of Carminatives and Secondary Benefits
 IBS C Individuals experience a range of symptoms in addition to constipation (straining and hard stools) but also report abdominal pain and bloating as particularly troubling. Carminatives Estimated average
IBS C Individuals experience a range of symptoms in addition to constipation (straining and hard stools) but also report abdominal pain and bloating as particularly troubling. Carminatives Estimated average
Research Article Opioid Use Is Not Associated with Incomplete Wireless Capsule Endoscopy for Inpatient or Outpatient Procedures
 Diagnostic and erapeutic Endoscopy, Article ID 651259, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/651259 Research Article Opioid Use Is Not Associated with Incomplete Wireless Capsule Endoscopy for Inpatient
Diagnostic and erapeutic Endoscopy, Article ID 651259, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/651259 Research Article Opioid Use Is Not Associated with Incomplete Wireless Capsule Endoscopy for Inpatient
Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider
 Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider Elizabeth Coss, MD General Gastroenterologist Audie Murphy Veterans Hospital UT Health This presentation does not
Diagnosis and Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) For the Primary Care Provider Elizabeth Coss, MD General Gastroenterologist Audie Murphy Veterans Hospital UT Health This presentation does not
Antidiarrheals Antidiarrheal
 Antidiarrheals Major factors in diarrhea Increased motility of the GI tract. Decreased absorption of fluid. Antidiarrheal drugs include: Antimotility agents. Adsorbents. Drugs that modify fluid and electrolyte
Antidiarrheals Major factors in diarrhea Increased motility of the GI tract. Decreased absorption of fluid. Antidiarrheal drugs include: Antimotility agents. Adsorbents. Drugs that modify fluid and electrolyte
Bowel Function and Care. Pat Beierwaltes, Chair Paige Church Lusine Ambartsumyan Sharon Braille Julie Dicker Tiffany Gordon Sue Liebold
 Bowel Function and Care Pat Beierwaltes, Chair Paige Church Lusine Ambartsumyan Sharon Braille Julie Dicker Tiffany Gordon Sue Liebold Outcomes Primary Outcomes Maintenance of social continence as appropriate
Bowel Function and Care Pat Beierwaltes, Chair Paige Church Lusine Ambartsumyan Sharon Braille Julie Dicker Tiffany Gordon Sue Liebold Outcomes Primary Outcomes Maintenance of social continence as appropriate
Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH
 Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, 2017 Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH Topic: Toileting: Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Learning Objectives: At the end of this
Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, 2017 Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH Topic: Toileting: Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Learning Objectives: At the end of this
Comparison of strategies and goals for treatment of chronic constipation among gastroenterologists and general practitioners
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (18) 31, 1-6 Comparison of strategies and goals for treatment of chronic constipation among gastroenterologists and general practitioners Dan Carter a,c, Eytan
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (18) 31, 1-6 Comparison of strategies and goals for treatment of chronic constipation among gastroenterologists and general practitioners Dan Carter a,c, Eytan
Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH
 Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, 2017 Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH Topic: Toileting: Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Learning Objectives: At the end of this
Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Continuity Clinic Curriculum Week of April 10, 2017 Nader Shaikh, MD, MPH Topic: Toileting: Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Learning Objectives: At the end of this
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
TITLE: Treatments for Constipation: A Review of Systematic Reviews
 TITLE: Treatments for Constipation: A Review of Systematic Reviews DATE: 17 November 2014 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Constipation has many definitions and is often described differently depending on the
TITLE: Treatments for Constipation: A Review of Systematic Reviews DATE: 17 November 2014 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Constipation has many definitions and is often described differently depending on the
Is Physical Activity Effective In Reducing The Gastrointestinal Symptoms Associated with Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Physical Activity Effective In Reducing
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Physical Activity Effective In Reducing
Constipation and bowel obstruction
 Constipation and bowel obstruction Constipation Infrequent or difficult defecation with reduced number of bowel movements, which may or may not be abnormally hard with increased difficulty or discomfort
Constipation and bowel obstruction Constipation Infrequent or difficult defecation with reduced number of bowel movements, which may or may not be abnormally hard with increased difficulty or discomfort
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 10 December 2008
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 10 December 2008 RELISTOR 12 mg/0.6 ml solution for injection 1 vial (CIP: 387 365-1) 2 vials + 2 sterile syringes
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 10 December 2008 RELISTOR 12 mg/0.6 ml solution for injection 1 vial (CIP: 387 365-1) 2 vials + 2 sterile syringes
WORKING PARTY ON HERBAL MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FINAL PROPOSAL FOR A CORE DATA FOR ISPAGHULA HUSK
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use 27 March 2003 EMEA/HMPWP/15/00 WORKING PARTY ON HERBAL MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FINAL PROPOSAL FOR A CORE DATA
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use 27 March 2003 EMEA/HMPWP/15/00 WORKING PARTY ON HERBAL MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FINAL PROPOSAL FOR A CORE DATA
Opioid Induced Constipation Lisa Clince Acute Pain CNS Palmerston North Hospital
 Opioid Induced Constipation Lisa Clince Acute Pain CNS Palmerston North Hospital 21-04-2016 MidCentral District Health Board 1 Overview Patient Experience Opioid Collaborative Constipation defined Opioid
Opioid Induced Constipation Lisa Clince Acute Pain CNS Palmerston North Hospital 21-04-2016 MidCentral District Health Board 1 Overview Patient Experience Opioid Collaborative Constipation defined Opioid
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT
 Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care
 Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Advances in Palliative Care
 Steven Pantilat, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Alan M. Kates and John M. Burnard Endowed Chair in Palliative Care Director, Palliative Care Program and Palliative Care Leadership Center Division of
Steven Pantilat, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Alan M. Kates and John M. Burnard Endowed Chair in Palliative Care Director, Palliative Care Program and Palliative Care Leadership Center Division of
Chronic constipation, often accompanied by encopresis. Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty. Patients and Methods
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
Approaching Childhood Constipation Anees Siddiqui, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology. Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Epidemiology.
 Approaching Childhood Constipation p Anees Siddiqui, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Disclosure Anees Siddiqui, MD, has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Specially for Children Dell
Approaching Childhood Constipation p Anees Siddiqui, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Disclosure Anees Siddiqui, MD, has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Specially for Children Dell
Research Article Efficacy of Adaptive Biofeedback Training in Treating Constipation-Related Symptoms
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 959734, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/959734 Research Article Efficacy of Adaptive Biofeedback Training in Treating
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 959734, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/959734 Research Article Efficacy of Adaptive Biofeedback Training in Treating
(minutes for web publishing)
 Gastrointestinal Subcommittee of the Pharmacology and Therapeutics Advisory Committee (PTAC) Meeting held on 28 March 2017 (minutes for web publishing) Gastrointestinal Subcommittee minutes are published
Gastrointestinal Subcommittee of the Pharmacology and Therapeutics Advisory Committee (PTAC) Meeting held on 28 March 2017 (minutes for web publishing) Gastrointestinal Subcommittee minutes are published
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Constipation. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Constipation. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
Non-pharmacological treatments for adult patients with functional constipation: a systematic review protocol
 Protocol Non-pharmacological treatments for adult patients with functional constipation: a systematic review protocol Min Chen, 1,2 Hui Zheng, 3 Juan Li, 3 Dequan Huang, 1,2 Qin Chen, 4 Jianqiao Fang 4
Protocol Non-pharmacological treatments for adult patients with functional constipation: a systematic review protocol Min Chen, 1,2 Hui Zheng, 3 Juan Li, 3 Dequan Huang, 1,2 Qin Chen, 4 Jianqiao Fang 4
Management of the Neurogenic Bowel. June st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota
 Management of the Neurogenic Bowel June 2016 41st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota DEPARTMENT OF NURSING Rhonda Bolin, BSN, RN, CPN Spina Bifida Nurse Texas Children s Hospital Spina Bifida
Management of the Neurogenic Bowel June 2016 41st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota DEPARTMENT OF NURSING Rhonda Bolin, BSN, RN, CPN Spina Bifida Nurse Texas Children s Hospital Spina Bifida
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Japan: Internet survey using Rome III criteria
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Japan: Internet survey using Rome III criteria Hiroto Miwa Division of Upper Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hyogo College
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Japan: Internet survey using Rome III criteria Hiroto Miwa Division of Upper Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hyogo College
Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up
 1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in Canada. A Special Report from the Canadian Digestive Health Foundation
 Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in Canada A Special Report from the Canadian Digestive Health Foundation February 2014 Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in
Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in Canada A Special Report from the Canadian Digestive Health Foundation February 2014 Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of Constipation in
Colon Hydrotherapy for defecation disorders
 Colon Hydrotherapy for defecation disorders Systematic Review Decision Support Document Nr. 032 ISSN online 1998-0469 Colon Hydrotherapy for defecation disorders Systematic Review Vienna, Mai 2009 Project
Colon Hydrotherapy for defecation disorders Systematic Review Decision Support Document Nr. 032 ISSN online 1998-0469 Colon Hydrotherapy for defecation disorders Systematic Review Vienna, Mai 2009 Project
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES
 OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
David Leff, DO. April 13, Disclosure. I have the following financial relationships to disclosure:
 David Leff, DO AOMA 94 th Annual Convention April 13, 2016 Disclosure I have the following financial relationships to disclosure: Speaker s Bureau: Allergan Labs, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Valeant Pharmaceutical
David Leff, DO AOMA 94 th Annual Convention April 13, 2016 Disclosure I have the following financial relationships to disclosure: Speaker s Bureau: Allergan Labs, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Valeant Pharmaceutical
