Digestive Health Tips:
|
|
|
- Madison Ward
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Digestive Health Tips: Adapted from the American College of Gastroenterology ( 10 Tips on Belching, Bloating, and Flatulence 1. Belching is caused by swallowed air from: o Eating or drinking too fast o Poorly fitting dentures; not chewing food completely o Carbonated beverages o Chewing gum or sucking on hard candies o Excessive swallowing due to nervous tension or postnasal drip o Forced belching to relieve abdominal discomfort 2. To prevent excessive belching, avoid: o Carbonated beverages o Chewing gum o Hard candies Activated charcoal and Simethicone may be helpful 3. Abdominal bloating and discomfort may be due to intestinal sensitivity or symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. To relieve symptoms, avoid: o Broccoli o Baked beans o Cabbage o Carbonated drinks o Cauliflower o Chewing gum o Hard candy 4. Abdominal distention resulting from weak abdominal muscles: o Is better in the morning o Gets worse as the day progresses o Is relieved by lying down 5. To prevent Abdominal distention: o Tighten abdominal muscles by pulling in your stomach several times during the day o So sit-up exercises if possible o Wear an abdominal support garment if exercise is too difficult 6. Flatulence is gas created through bacterial action in the bowel and passed rectally. Keep in mind that: o passages per day are normal o Primary gases are harmless and odorless o Noticeable smells are trace gases related to food intake
2 7. Foods that are likely to form gas include: o Milk, dairy products, and medications that contain lactose--if your body doesn't produce the enzyme (lactase) to break it down. o Certain vegetables--baked beans, cauliflower, broccoli, cabbage o Certain starches--wheat, oats, corn, potatoes. Rice is a good substitute. 8. If flatulence is a concern, see your doctor to determine if you are lactose intolerant. 9. Identify offending foods. Reduce or eliminate these gas-forming foods from your diet. 10. Activated Charcoal may provide some benefit. 8 Tips on Peptic Ulcer Disease 1. Ulcers are "sores" that frequently affect the stomach and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). 2. Bacterial infection is the most common cause of duodenal ulcers. 3. Stomach ulcers are often a side effect of pain killers and anti-inflammatory drugs used primarily to treat arthritis. 4. Alcohol ingestion, cigarette smoking, and emotional stress may also influence the development of an ulcer or interfere with its healing. 5. Upper abdominal pain is the most common symptom of ulcers, but many ulcers cause no symptoms at all. 6. Ulcers may hemorrhage (bleeding) into the gastrointestinal tract; this results in the passage of black ("tarry") stool. Very serious ulcer disease may also cause a blockage between the stomach and small intestine and this complication results in persistent vomiting. Severe pain results from the most urgent complication of ulcers - peritonitis caused by a tear through the wall of the stomach or duodenum. 7. Almost all ulcers can be treated successfully, usually without surgery. Many ulcers can be prevented. 8. Ulcer treatments include antibiotics, agents that neutralize gastric acid or reduce its secretion, and drugs that strengthen the resistance of the stomach and duodenum. 5 Tips on Swallowing and Heartburn 1. Abnormal swallowing is commonly perceived as food "sticking on the way down." If this complaint persists, it is sometimes due to a serious condition and should always prompt medical attention. 2. Swallowing difficulty may be caused by a number of different problems including: o Poor or incomplete chewing (possibly the result of dental problems, poorly fitted dentures, or eating too quickly) o Abnormal muscle contraction o Scar tissue from chronic inflammation o Infection o Cancer
3 3. Heartburn is a very common problem caused by regurgitation or reflux of gastric acid into the esophagus, which connects the mouth and the stomach. 4. Heartburn can often be eliminated by avoiding: o Smoking o Fatty food in the diet o Caffeine o Chocolate o Peppermint o Overeating o Bed-time snacks o Tight-fitting clothes that constrict the abdomen o Certain medications o Heavy lifting, straining 5. It is important to consider the possibility of heart disease before attributing any kind of chest pain to gastroesophageal reflux. 5 Tips on Nutrition and Aging 1. Nutrition plays a role in cardiovascular disease, some malignancies, adult-onset diabetes, osteoporosis, alcoholism, and recovery from major injury. 2. Malnutrition can weaken the immune system, impair healing following surgery or injury, lessen mobility, and reduce mental capabilities and function. It is common in older adults. 3. To maintain good health, total fat intake should be reduced to 30% or less of calories. Saturated fat intake should only account for 10% (one third of fat calories). Salt and alcohol intake also should be limited. 4. Dietary fat content composed primarily of monounsaturated fat (eg, olive oil) and polyunsaturated fat (eg, canola, corn and fish oils) may be associated with a lower incidence of cardiovascular disease. 5. Foods to be avoided include whole milk and dairy products (ice cream, cheese, butter); commercially baked goods (cookies and crackers); hot dogs, ham, and cold cuts; and oils, gravies, and salad dressing. 5 Tips on Gallstone Disease 1. Gallstones typically develop over many years, although they can form in months. Gallstones are present in about 20% of women and 10% of men over the age of There are two basic types of gallstones: cholesterol and pigment. Cholesterol gallstones are the most common type in the United States. 3. About 75% of gallstones do not cause symptoms. The most common symptom caused by gallbladder stones is episodic upper abdominal pain. 4. For healthy patients who have no symptoms, no therapy or change in diet is needed. Patients with uncomplicated symptomatic gallbladder stones should reduce dietary fat
4 and consider surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy). An alternate approach is oral bile acid therapy. For complicated disease, gallbladder removal is warranted. 5. Patients who undergo rapid weight loss are at risk for the development of small cholesterol gallstones and may benefit from bile acid therapy. Gallstones can seldom be prevented, although a low-fat diet may provide some protective benefit. 6 Tips on Hepatitis 1. Five different hepatitis viruses have been identified: type A; type B; type C; type D, or delta virus; and type E. Type A is probably the most prevalent type of viral hepatitis worldwide, followed by types B, E, C, and D. 2. Hepatitis A and E are transmitted through fecally contaminated food or water. Other modes of transmission include needle sharing among intravenous drug abusers; sexual contact; maternal transmission; and transmission by blood transfusion. 3. A simple blood test is used to determine that a person has one or more of the different types of hepatitis. 4. Acute hepatitis is typically characterized by flu-like symptoms (including fever, headaches, fatigue, nausea and vomiting) and jaundice. Chronic hepatitis is often asymptomatic. 5. Vaccines are available to protect against hepatitis A and B. Additionally, immune globulin for hepatitis A or hepatitis B is recommended when someone has been exposed to an infected person. 6. Among the ways to care for your liver are: limiting alcohol consumption; avoiding liverdamaging drugs; practicing safe sex; avoiding use of illegal drugs; avoiding high doses of vitamins unless prescribed; avoiding tattoos and the sharing of razors; not eating raw shellfish from questionable sources; and carefully following directions for use of toxic substances (e.g., cleaning products). 4 Tips on Circulatory Disorders of the GI Tract 1. The small intestine and the colon have a relatively restricted blood supply and are frequently affected by circulatory disorders, whereas the esophagus, stomach, and rectum are well supplied with blood and are only occasionally involved in circulatory disturbances. 2. The colon is commonly affected by ischemia (reduction of blood flow to a level not permitting normal function). In most cases, symptoms subside within days and healing is seen within 2 weeks. Antibiotics and bowel rest usually suffice. In complicated disease, damaged parts of the colon must be removed surgically. 3. Acute mesenteric ischemia results from inadequate circulation of blood to the small intestine. Treatment is aimed at dilating (opening) the blood vessels with drugs and/or surgery to restore intestinal blood flow and to remove any irreversibly damaged bowel.
5 4. Chronic mesenteric ischemia results when blood flow to the small intestine is reduced to an insufficient level. It causes pain associated with eating. Surgery is often warranted to correct the problem. 5 Tips on Use of Medications 1. Use of medications increases with age: 80% of older Americans who live independently receive 20 or more prescriptions per year Residents of nursing homes receive an average of 8-10 drugs per day 2. It is important to take medications as prescribed. Reasons for not following directions include: o Too many drugs o Error due to visual or mental impairment o Sharing drugs o Changing doctors o Use of over-the-counter drugs o Sparing expense o Drug side effects o Symptoms not improving 3. See your doctor regularly to check on medications and their effect (bring your medications with you for an office visit or to an emergency room): Drug effect changes with aging There is decreased absorption of drugs through the intestinal tract Decreased kidney function slows drug elimination Metabolism of drugs changes with age 4. The effect medications have on your body will change with aging. For example: Drug action may last longer Drugs may produce toxicity at a lower dose in mature adults than in younger adults 5. Remember that all changes you experience are not necessarily due to aging. For example, decrease in salivary flow is: Due to disease or medication not due to aging 5 Tips on Irritable Bowel Syndrome 1. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a digestive problem also known as "spastic colon" or "irritable colon." 2. IBS symptoms include: o Abdominal pain (colicky, periodic or continuous dull pain) o Erratic bowel activity; frequent constipation or diarrhea o Accompanying symptoms of bloating, nausea, headache, fatigue o Sensitivity to intestinal gas (cramping, flatulence) 3. The cause of IBS is unknown: o No evidence of specific disease o May be triggered by psychological factors or ingestion of food 4. IBS is a condition that:
6 o Is more common in women o Usually starts at an early age (20s and 30s) and recurs from time to time o Rarely starts past age Treatment of IBS includes: o Careful explanation of the syndrome, including what it is not o Better management of key triggers: stress and diet o Modification of diet to reduce or exclude foods that promote gas o Drug therapy to relieve symptoms (bulk fiber products, antispasmodics, antidiarrheals) o Occasionally, psychiatric therapy and medication 10 Tips on Hemorrhoids 1. Hemorrhoids are masses of swollen veins in the lower rectum (internal hemorrhoids) or at the anus (external hemorrhoids). 2. Symptoms of internal hemorrhoids include: o Bright red rectal bleeding o Staining of undergarments with mucus 3. Symptoms of external hemorrhoids include: o Pain and itching when irritated by constipation or diarrhea o Difficulty with hygiene 4. Hemorrhoids are caused by: o Straining o Work strain (lifting, etc.) o Straining while defecating o Chronic constipation o Passing hard, dry, small stools o Laxative abuse 5. Do not assume rectal bleeding is from hemorrhoids. See your doctor to rule out cancer or other disease. 6. To prevent or manage hemorrhoids, increase your fiber and fluid intake. Consider adding a fiber supplement. 7. Avoid straining at stool or sitting on the toilet for a long time. 8. Clean the external rectal area gently with soap and water following stool evacuation. 9. Try a topical cream or sitz baths to reduce inflammation. 10. See your doctor if you don't improve. 5 Tips on Inflammatory Bowel Disease 1. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an inflammation of the small or large intestine that may cause these symptoms: o Diarrhea
7 o Rectal bleeding o Sharp abdominal pain or cramping o Intestinal obstruction o Fever See your doctor if you have any of these symptoms 2. There are two types of IBD: o Ulcerative Colitis Starts in rectum and spreas upward Affects men more tham women o Crohn's Disease More patchy inflammation Can start anywhere in the digestive tract Affects women more than men 3. The cause of IBD is unknown. What is known about IBD includes the following: o IBD is not Contagious. o IBD is not caused by diet. o IBD is not a form of cancer. o IBD affects young and old alike. o IBD can usually be treated with medicine but sometimes requires surgery. 4. Diagnosis of IBD is based on: o Family history, travel history, current medications o Stool sample to rule out infection o Flexible sigmoidoscopy/colonoscopy and biopsy to rule out cancer and to identify o IBD o X-ray studies 5. Treatment of IBD may include: o Medications to reduce or eliminate inflammation o Special diet or elemental formula diet o Surgery Time is critical. If you suspect IBD, call your doctor. 10 Tips on Constipation and Incontinence of Stool 1. Despite widespread belief, constipation is not necessarily a part of growing older. 2. Bowel habits are similar in both younger and older healthy people. 3. Constipation is defined as stools that are: o Too small o Too hard o Too difficult to pass o Infrequent (less than 3 per week) 4. Constipation is caused by: o Not enough dietary fiber or fluids o Medication side effects
8 o Emotional or physical stress o Misconception about normal bowel habits o Lack of activity o Medical problems 5. How to manage mild-to-moderate constipation: o Gradually add dietary fiber from variou sources o Increase fluids (water, soup, broth, juices) o Eat meals on a regular schedule o Chew your food well o Gradually increase daily exercise o Respond to urges to move your bowels o Avoid straining See your doctor if these measures don't work 6. Dietary therapy (increased fiber and fluids) and fiber supplements are the preferred treatment for chronic constipation. 7. In some cases, your doctor may recommend the use of stool softeners. 8. Use of mineral oil or stimulant laxatives regularly, consult your doctor to make sure what you are using is right for you. 9. Incontinence of stool or fecal soiling is most often due to leakage around a fecal impaction. Removing the impaction will usually restore continence. 10. Incontinence of stool in healthy older people deserves full education and treatment. Treatment options include: o Adjustment in dietary fiber to reduce amount of stool o Medications to decrease stool frequency o Prescribed use of enemas (not soap enemas) o Biofeedback training o Surgery to restore anal function 10 Tips on Dietary Fiber 1. Keep in mind that a high-fiber diet may tend to improve: o Chronic constipation o Coronary heart disease o Hemorrhoids o Diabetes mellitus o Diverticular disease o Elevated cholesterol o Irritable bowel syndrome o Colorectal cancer 2. Try to double your daily fiber intake. o Average American intake: grams per day o Recommended intake: grams per day
9 3. Understand what fiber is, where it comes from: o Insoluble fiber Cereals Wheat/wheat bran Whole grains o Soluble fiber Brans Fruit Oatmeal/oat bran Psyllium Vegetables 4. Substitute high-fiber foods for high-fat and low-fiber foods. 5. Keep your daily fiber intake stable. Consider a fiber supplement if you: o Travel o Eat away from home often o Find it difficult to get enough fiber through food choices alone 6. Don't shock your system: Increase fiber levels in your diet gradually. 7. Always increase fluids (water, soup, broth, juices) when you increase fiber. 8. Add both soluble and insoluble fiber, from a variety of sources. 9. Compare fiber content of foods: Grams of Fiber 1 cup of Rice Krispies 1 1/3 cup of 100% Bran 9 1 slice of white bread slice of whole wheat bread 1.4 1/2 cup white rice 0.5 1/2cup brown rice 1.5 Bowl of chicken broth 0 Bowl of thick vegetable (minestrone) soup Choose foods high in fiber content. Fruits and Vegetables Highest in Fiber Per Serving Fruits Artichokes Apples, pears (with skin) Berries (blackberries, blueberries, raspberries) Dates Figs Prunes Vegetables Beans (baked, black, lima, pinto) Broccoli Chick-peas Lentils Parsnips Peas Pumpkin
10 Barley Other Good Fiber Choices Bread, Muffins (whole wheat, bran) Cereals (branflakes, bran, oatmeal, shredded wheat) Coconut Crackers (rye, whole wheat) Nuts (almonds, Brazil, peanuts, pecans, walnuts) Rice (brown) Seeds (pumpkin, sunflower) Rutabaga Squash (winter) Eating high-fiber foods is a healthy choice for most people. If you have ever received medical treatment for a digestive problem, however, it is very important that you check with your doctor to find out if a high-fiber diet is the right choice for you. 5 Tips on Diverticular Disease 1. Diverticulosis is a condition with pouch-like protrusions in the colon: o Rare before age 30 o Common after age 60 o Usually no symptoms 2. Complications of diverticulosis include: o Bright red rectal bleeding with clots o Diverticulitis 3. Ways to prevent and manage diverticular disease include: o Increasing dietary fiber to keep bowel movements soft o Avoiding stimulant laxatives 4. Diverticulitis is a serious complication in which pouches become inflamed or infected. Symptoms of diverticulitis include: o Pain in left lower abdomen o Fever o Sudden change in bowel habit See your doctor immediately if you have any of these symptoms. 5. Treatment of diverticulitis may include: o Antibiotics o Special feeding o Surgery
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems
 Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory
 Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation If you have bowel problems after radiation, you may feel embarrassed. Don t let this stop you from asking for help. Sometimes, radiation
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation If you have bowel problems after radiation, you may feel embarrassed. Don t let this stop you from asking for help. Sometimes, radiation
Nutritional Guidelines for Roux-en-Y and Duodenal Switch Gastric Restrictive Procedures. Phase III Regular Consistency
 Nutritional Guidelines for Roux-en-Y and Duodenal Switch Gastric Restrictive Procedures Phase III Regular Consistency The University of Chicago Hospitals Center for the Surgical Treatment of Obesity (March
Nutritional Guidelines for Roux-en-Y and Duodenal Switch Gastric Restrictive Procedures Phase III Regular Consistency The University of Chicago Hospitals Center for the Surgical Treatment of Obesity (March
F A M N O P R S ! D !
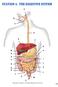 A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
Hemorrhoids. What are hemorrhoids? What is the cause? What are the symptoms?
 What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
What to eat when you have Short Bowel Syndrome
 What to eat when you have Short Bowel Syndrome What is Short Bowel Syndrome? Your bowel is an organ, shaped like a long tube, and is made up of the small and large bowel. The small bowel is about 15 to
What to eat when you have Short Bowel Syndrome What is Short Bowel Syndrome? Your bowel is an organ, shaped like a long tube, and is made up of the small and large bowel. The small bowel is about 15 to
Chapter 5: Common Digestive Problems from The Kansas State University Human Nutrition (HN 400) Flexbook by Brian Lindshield is in the public domain
 Chapter 5: Common Digestive Problems from The Kansas State University Human Nutrition (HN 400) Flexbook by Brian Lindshield is in the public domain in the United States. 5 Common Digestive Problems Before
Chapter 5: Common Digestive Problems from The Kansas State University Human Nutrition (HN 400) Flexbook by Brian Lindshield is in the public domain in the United States. 5 Common Digestive Problems Before
The Aging Digestive System
 The Aging Digestive System shows significant senescence in old age: less saliva food less flavorful, harder swallowing ~half of those over 65 yrs wear dentures gastric mucosa secretes less acid reduces
The Aging Digestive System shows significant senescence in old age: less saliva food less flavorful, harder swallowing ~half of those over 65 yrs wear dentures gastric mucosa secretes less acid reduces
Unconsciously gulping air as they talk, especially when they are upset, excited or nervous
 Topic Page: Flatulence Definition: flatulence from Stedman's Medical Dictionary (flat yū-lents). Presence of an excessive amount of gas in the stomach and intestines. [Mod. L. flatulentus, fr. L. flatus,
Topic Page: Flatulence Definition: flatulence from Stedman's Medical Dictionary (flat yū-lents). Presence of an excessive amount of gas in the stomach and intestines. [Mod. L. flatulentus, fr. L. flatus,
Gas in the Digestive Tract
 Gas in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Everyone has gas and eliminates it by burping
Gas in the Digestive Tract National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Everyone has gas and eliminates it by burping
Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea www.nscancercare.ca What is diarrhea? Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea Diarrhea
Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea www.nscancercare.ca What is diarrhea? Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea Diarrhea
Nutrition and Dietetics Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Diverticular disease Nutrition and Dietetics Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have diverticular disease. It contains information about the disease and
Diverticular disease Nutrition and Dietetics Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have diverticular disease. It contains information about the disease and
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Heart Healthy Nutrition. Mary Cassio, RD Cardiac Rehabilitation Program
 Heart Healthy Nutrition Mary Cassio, RD Cardiac Rehabilitation Program Today s Topics Healthy Eating Guidelines Eating Well with Canada s Food Guide Balanced Eating Heart Healthy Nutrition Increased blood
Heart Healthy Nutrition Mary Cassio, RD Cardiac Rehabilitation Program Today s Topics Healthy Eating Guidelines Eating Well with Canada s Food Guide Balanced Eating Heart Healthy Nutrition Increased blood
Fiber: What Is It and What Does It Do? By James L. Holly, MD. Your Life Your Health. The Examiner. May 5, 2005
 Fiber: What Is It and What Does It Do? By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner May 5, 2005 I don t know about you, but fiber has always been a mystery to me. Soluble fiber, insoluble fiber?
Fiber: What Is It and What Does It Do? By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner May 5, 2005 I don t know about you, but fiber has always been a mystery to me. Soluble fiber, insoluble fiber?
Fiber In Your Diet. Provided by Hemorrhoid Centers of America Version Fiber
 In Your Diet The lack of dietary fiber and fluids is a contributing factor to the development of hemorrhoids and anal fissures. We recommend consuming 25-35 grams of fiber and drinking 7 glasses of fluids
In Your Diet The lack of dietary fiber and fluids is a contributing factor to the development of hemorrhoids and anal fissures. We recommend consuming 25-35 grams of fiber and drinking 7 glasses of fluids
Goals for Eating Well, Living Well
 Goals for Eating Well, Living Well Fruit/Vegetable servings per day (rainbow of colors) Dairy/Calcium-rich foods per day (1300 mg/day) Large servings of water per day Hours of screen time (texting, computer,
Goals for Eating Well, Living Well Fruit/Vegetable servings per day (rainbow of colors) Dairy/Calcium-rich foods per day (1300 mg/day) Large servings of water per day Hours of screen time (texting, computer,
Basic Review of Digestion
 Basic Review of Digestion In the mouth, food is broken down, mixed with saliva, and formed into a bolus. Wave like muscle movements, called peristalsis, push the food throughout the rest of the digestive
Basic Review of Digestion In the mouth, food is broken down, mixed with saliva, and formed into a bolus. Wave like muscle movements, called peristalsis, push the food throughout the rest of the digestive
High Fiber Diet for Children
 High Fiber Diet for Children How much fiber does my child need? General Guidelines: Age + 5 = Recommended Grams of Fiber Per Day Example: Your child is 5 years old. 5 years + 5 = 10 grams of fiber needed
High Fiber Diet for Children How much fiber does my child need? General Guidelines: Age + 5 = Recommended Grams of Fiber Per Day Example: Your child is 5 years old. 5 years + 5 = 10 grams of fiber needed
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Dietary advice for people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Dietary advice for people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohn s disease and Ulcerative colitis Information for patients Name Your Dietitian Dietitian contact number: 0118 322 7116 What is Inflammatory
Dietary advice for people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohn s disease and Ulcerative colitis Information for patients Name Your Dietitian Dietitian contact number: 0118 322 7116 What is Inflammatory
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a variety of symptoms, most commonly cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Symptoms can vary from person to person,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has a variety of symptoms, most commonly cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Symptoms can vary from person to person,
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
What is Fiber? Non-digestible part of plant foods. Important for maintaining good health. Most Americans only eat about half of the fiber they need!
 Fill Up On Fiber! Project Sponsors USDA project funded through the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program School District of Philadelphia Department of Nutrition Sciences, Drexel University What is
Fill Up On Fiber! Project Sponsors USDA project funded through the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program School District of Philadelphia Department of Nutrition Sciences, Drexel University What is
Bowel Problems and Radiation Therapy
 Bowel Problems and Radiation Therapy (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) 1 Table of Contents What Will I
Bowel Problems and Radiation Therapy (The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different.) 1 Table of Contents What Will I
Carbohydrates and Weight Loss
 Carbohydrates and Weight Loss A Macronutrient Our Body Uses for Energy Provides energy for the body to function properly by every cell in the body, even the brain. Carbohydrate: Calories of Macronutrients:
Carbohydrates and Weight Loss A Macronutrient Our Body Uses for Energy Provides energy for the body to function properly by every cell in the body, even the brain. Carbohydrate: Calories of Macronutrients:
COLONOSCOPY CHECKLIST
 COLONOSCOPY CHECKLIST Instructions: Attached are detailed instructions to help you prepare for your colonoscopy. Here s a checklist of things to do as you prepare for your colonoscopy. As you do each one,
COLONOSCOPY CHECKLIST Instructions: Attached are detailed instructions to help you prepare for your colonoscopy. Here s a checklist of things to do as you prepare for your colonoscopy. As you do each one,
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse
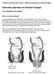 Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment
 Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment Information for cancer survivors Read this pamphlet to learn: What bowel problems are What causes bowel problems What you can do to manage your bowel problems
Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment Information for cancer survivors Read this pamphlet to learn: What bowel problems are What causes bowel problems What you can do to manage your bowel problems
Nutrition Tips to Build a Healthy GI Tract with Parkinson s Disease
 Nutrition Tips to Build a Healthy GI Tract with Parkinson s Disease Meghann Featherstun MS RD LD Meghann.Featherstun@UHHospitals.org Clinical Dietitian & Wellness Coach University Hospitals Accountable
Nutrition Tips to Build a Healthy GI Tract with Parkinson s Disease Meghann Featherstun MS RD LD Meghann.Featherstun@UHHospitals.org Clinical Dietitian & Wellness Coach University Hospitals Accountable
General Surgery. Haemorrhoids
 General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
General Surgery Haemorrhoids Hemorrhoids_PRINT.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:50:45 PM A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn
Be a Food Label Detective!
 Be a Food Label Detective! Elyse Kontra Kara Kelly Total Fat Type of fat is more important than total fat Limit total fat intake to 25-35% of your total calories Fat-free Caloriefree http://www.diabetes.org/food-and-fitness/food/what-can-ieat/taking-a-closer-look-at-labels.html
Be a Food Label Detective! Elyse Kontra Kara Kelly Total Fat Type of fat is more important than total fat Limit total fat intake to 25-35% of your total calories Fat-free Caloriefree http://www.diabetes.org/food-and-fitness/food/what-can-ieat/taking-a-closer-look-at-labels.html
 Page 1 of 7 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Patient education: High-fiber diet (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is fiber? Fiber is a substance
Page 1 of 7 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Patient education: High-fiber diet (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is fiber? Fiber is a substance
Patient Information Leaflet. Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation
 Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
APPLIED KINESIOLOGY INTAKE FORM. Patient Name: Date: Date of Birth: Referred by: address: Day time phone number. Address CHIEF COMPLAINT:
 APPLIED KINESIOLOGY INTAKE FORM Patient Name: Date: Age: Date of Birth: Referred by: Email address: Day time phone number Address CHIEF COMPLAINT: Describe other methods used to relieve discomfort (other
APPLIED KINESIOLOGY INTAKE FORM Patient Name: Date: Age: Date of Birth: Referred by: Email address: Day time phone number Address CHIEF COMPLAINT: Describe other methods used to relieve discomfort (other
Nutrition after your pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure)
 Nutrition after your pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) People who have had a Whipple procedure may have different nutritional problems. This handout will help you identify and manage common nutrition
Nutrition after your pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) People who have had a Whipple procedure may have different nutritional problems. This handout will help you identify and manage common nutrition
COLONOSCOPY CHECKLIST
 COLONOSCOPY CHECKLIST Instructions: Attached are detailed instructions to help you prepare for your colonoscopy. Here s a checklist of things to do as you prepare for your colonoscopy. As you do each one,
COLONOSCOPY CHECKLIST Instructions: Attached are detailed instructions to help you prepare for your colonoscopy. Here s a checklist of things to do as you prepare for your colonoscopy. As you do each one,
Gas and Flatulence Prevention Diet
 Gas and Flatulence Prevention Diet Purpose Intestinal gas means different things to different people. Patients may complain of excessive bloating after eating, belching, or rectal gas (flatulence), or
Gas and Flatulence Prevention Diet Purpose Intestinal gas means different things to different people. Patients may complain of excessive bloating after eating, belching, or rectal gas (flatulence), or
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
Dietary advice for people with colostomies
 Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
Principles of the DASH Diet
 DASH Diet Lower your blood pressure by changing your eating habits. The DASH diet is based on findings from the "Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension" clinical study that found that high blood pressure
DASH Diet Lower your blood pressure by changing your eating habits. The DASH diet is based on findings from the "Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension" clinical study that found that high blood pressure
FACTS ABOUT FIBER Dietary fiber is the part of a plant that provides and maintains the plant's structure. Cellulose, hemicellulose, polysaccharides,
 FACTS ABOUT FIBER Dietary fiber is the part of a plant that provides and maintains the plant's structure. Cellulose, hemicellulose, polysaccharides, pectins, gums, mucilages, and lignins are dietary fibers.
FACTS ABOUT FIBER Dietary fiber is the part of a plant that provides and maintains the plant's structure. Cellulose, hemicellulose, polysaccharides, pectins, gums, mucilages, and lignins are dietary fibers.
Constipation in Toddlers 1-3 Years
 Constipation in Toddlers 1-3 Years Description Content Review Date: August 2005 Printable Version / View Related Services Constipation is stool that is dry, hard and difficult or painful to pass. The number
Constipation in Toddlers 1-3 Years Description Content Review Date: August 2005 Printable Version / View Related Services Constipation is stool that is dry, hard and difficult or painful to pass. The number
My Diabetic Meal Plan during Pregnancy
 My Diabetic Meal Plan during Pregnancy When you have diabetes and are pregnant, you need to eat small meals and s throughout the day to help control your blood sugar. This also helps you get in enough
My Diabetic Meal Plan during Pregnancy When you have diabetes and are pregnant, you need to eat small meals and s throughout the day to help control your blood sugar. This also helps you get in enough
Diverticula (including Diverticulosis, Diverticular Disease and Diverticulitis)
 Diverticula (including Diverticulosis, Diverticular Disease and Diverticulitis) Page 1 of 5 Diverticula of the colon are common in older people. They commonly cause no symptoms, and in most cases no treatment
Diverticula (including Diverticulosis, Diverticular Disease and Diverticulitis) Page 1 of 5 Diverticula of the colon are common in older people. They commonly cause no symptoms, and in most cases no treatment
Bowel Health in Adults
 Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Keepin It Regular tips and tricks for resolving intestinal issues
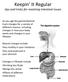 Keepin It Regular tips and tricks for resolving intestinal issues As you age the gastrointestinal track changes for a variety of different reasons, including changes in how your body works and changes
Keepin It Regular tips and tricks for resolving intestinal issues As you age the gastrointestinal track changes for a variety of different reasons, including changes in how your body works and changes
ABLE TO READ THE LABEL?
 ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
COLONOSCOPY CHECKLIST
 COLONOSCOPY CHECKLIST Instructions: Attached are detailed instructions to help you prepare for your colonoscopy. Here s a checklist of things to do as you prepare for your colonoscopy. As you do each one,
COLONOSCOPY CHECKLIST Instructions: Attached are detailed instructions to help you prepare for your colonoscopy. Here s a checklist of things to do as you prepare for your colonoscopy. As you do each one,
How to Fight Diabetes and Win. Meal. Planning NUTURNA. Advance Diabetic Support
 How to Fight Diabetes and Win Meal Planning NUTURNA TM Advance Diabetic Support Meal Planning Well-balanced and portion-controlled meals are vital to the control of blood sugar levels and management of
How to Fight Diabetes and Win Meal Planning NUTURNA TM Advance Diabetic Support Meal Planning Well-balanced and portion-controlled meals are vital to the control of blood sugar levels and management of
Foreword. Bowel Management
 2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
What to eat and drink after gastrointestinal (GI) surgery
 What to eat and drink after gastrointestinal (GI) surgery For patients who have had surgery on their gastrointestinal tract (stomach and intestines) Read this resource to learn: What should I eat and drink
What to eat and drink after gastrointestinal (GI) surgery For patients who have had surgery on their gastrointestinal tract (stomach and intestines) Read this resource to learn: What should I eat and drink
Patient information - Constipation
 Preventing constipation Constipation is a common problem. It means either going to the toilet to empty the bowels less often than usual, or passing hard or painful stools. Constipation may be caused by
Preventing constipation Constipation is a common problem. It means either going to the toilet to empty the bowels less often than usual, or passing hard or painful stools. Constipation may be caused by
Nutrition Essentials Improving your PKU diet through balanced nutrition
 Nutrition Essentials Improving your PKU diet through balanced nutrition Sharon L Ernst, MPH, RD, CSP, FAND Associate Professor Chief Metabolic Dietitian Division of Medical Genetics Department of Pediatrics
Nutrition Essentials Improving your PKU diet through balanced nutrition Sharon L Ernst, MPH, RD, CSP, FAND Associate Professor Chief Metabolic Dietitian Division of Medical Genetics Department of Pediatrics
Valley Gastroenterology E Mission Ste 102 Spokane WA
 Gastric Bypass Diet www.gicare.com Purpose Gastric bypass is a type of surgery in which the stomach is reduced in size by one of several methods. This smaller stomach is then reconnected or bypassed to
Gastric Bypass Diet www.gicare.com Purpose Gastric bypass is a type of surgery in which the stomach is reduced in size by one of several methods. This smaller stomach is then reconnected or bypassed to
Digestion and Aging. Janice M. Joneja Ph.D. RD
 Digestion and Aging Janice M. Joneja Ph.D. RD DIGESTION Food enters the mouth and exits at the anus Digestion starts as soon as food enters the mouth and ends when it exits at the anus Food is moved on
Digestion and Aging Janice M. Joneja Ph.D. RD DIGESTION Food enters the mouth and exits at the anus Digestion starts as soon as food enters the mouth and ends when it exits at the anus Food is moved on
Patients First. Preventing Constipation. Often, constipation is relieved by choosing highfiber. increasing fluids, and exercising.
 Patient Education HEALTH AND WELLNESS Often, constipation is relieved by choosing highfiber foods, increasing fluids, and exercising. Preventing Constipation Signs of constipation are bowel movements that
Patient Education HEALTH AND WELLNESS Often, constipation is relieved by choosing highfiber foods, increasing fluids, and exercising. Preventing Constipation Signs of constipation are bowel movements that
The Top 25 Food Choices in the Performance Diet
 The Top 25 Food Choices in the Performance Diet # Name Information Picture 1 Water The single most essential component that represents 80% of your body and 65% of your weight 2 Beans Top ranked carbohydrates
The Top 25 Food Choices in the Performance Diet # Name Information Picture 1 Water The single most essential component that represents 80% of your body and 65% of your weight 2 Beans Top ranked carbohydrates
What Is the Low-FODMAP Diet?
 LOW-FODMAP DIET What Is the Low-FODMAP Diet? FODMAP refers to a group of five sugars found in certain foods. These sugars are lactose, fructose (in excess), fructans, galactans and polyols. Specifically,
LOW-FODMAP DIET What Is the Low-FODMAP Diet? FODMAP refers to a group of five sugars found in certain foods. These sugars are lactose, fructose (in excess), fructans, galactans and polyols. Specifically,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 ROBERT M. SELIG, M.D., FAAP JOANN C. COZZA, D.O., FAAP DANIEL S. SELIG, M.D., FAAP ANDORRA PEDIATRICS 8945 RIDGE AVENUE SUITE 3-4-5 PHILADELPHIA, PA 19128 215-483-8558 Irritable Bowel Syndrome What Is
ROBERT M. SELIG, M.D., FAAP JOANN C. COZZA, D.O., FAAP DANIEL S. SELIG, M.D., FAAP ANDORRA PEDIATRICS 8945 RIDGE AVENUE SUITE 3-4-5 PHILADELPHIA, PA 19128 215-483-8558 Irritable Bowel Syndrome What Is
Causes Of Flatulence. How to Stop Farting Fast by Using Natural Remedies for Gas
 How to Stop Farting Fast by Using Natural Remedies for Gas 4.5 (90.23%) 43 votes Gases are a taboo subject and farting is something very personal and quite embarrassing when it happens in a public place
How to Stop Farting Fast by Using Natural Remedies for Gas 4.5 (90.23%) 43 votes Gases are a taboo subject and farting is something very personal and quite embarrassing when it happens in a public place
A painful problem. Symptoms of haemorrhoids. Causes of haemorrhoids. Your evaluation
 A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn t be they re a very common problem that affects all kinds of people, including
A painful problem Haemorrhoids, cushions of swollen veins in the anal canal, are often a source of embarrassment. They shouldn t be they re a very common problem that affects all kinds of people, including
Chapter 34. Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Copyright The Food Intolerance Testing Group. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
 Copyright 2018 The Food Intolerance Testing Group All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording,
Copyright 2018 The Food Intolerance Testing Group All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording,
 Page 1 of 7 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Page 1 of 7 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
MANAGING CONSTIPATION
 MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
MANAGING CONSTIPATION INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Constipation is. The Symptoms of Constipation. How to Help Manage Constipation. WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
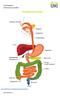 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Nutrition Wars: Choosing Better Carbohydrates
 Nutrition Wars: Choosing Better Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? There are 2 main types of carbohydrates: Simple carbohydrates include sugars found naturally in fruit, some vegetables, milk and milk
Nutrition Wars: Choosing Better Carbohydrates What are carbohydrates? There are 2 main types of carbohydrates: Simple carbohydrates include sugars found naturally in fruit, some vegetables, milk and milk
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Laura Kim, MGH Dietetic Intern March 17, 2015
 Laura Kim, MGH Dietetic Intern March 17, 2015 Introduction Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Understand basic functions of each nutrient Identify food sources of carbohydrates, fats, proteins Create balanced
Laura Kim, MGH Dietetic Intern March 17, 2015 Introduction Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Understand basic functions of each nutrient Identify food sources of carbohydrates, fats, proteins Create balanced
What does heart healthy eating mean to me?
 Healthy eating for your heart This handout will help you choose heart healthy foods to include as part of a healthy diet. What does heart healthy eating mean to me? Heart healthy eating, along with an
Healthy eating for your heart This handout will help you choose heart healthy foods to include as part of a healthy diet. What does heart healthy eating mean to me? Heart healthy eating, along with an
Juvenile Arthritis & Nutrition: Understanding the Facts, Demystifying Trends. Laura Gibofsky, MS, RD, CSP, CDN July 25, 2015
 Juvenile Arthritis & Nutrition: Understanding the Facts, Demystifying Trends Laura Gibofsky, MS, RD, CSP, CDN July 25, 2015 Overview There are no foods that cause Juvenile Arthritis (JA) or that can cure
Juvenile Arthritis & Nutrition: Understanding the Facts, Demystifying Trends Laura Gibofsky, MS, RD, CSP, CDN July 25, 2015 Overview There are no foods that cause Juvenile Arthritis (JA) or that can cure
eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH
 eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH It may seem like information on diet changes daily, BUT THERE IS ACTUALLY A LOT WE KNOW ABOUT HOW TO EAT WELL. Eating well can help you improve your overall
eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH It may seem like information on diet changes daily, BUT THERE IS ACTUALLY A LOT WE KNOW ABOUT HOW TO EAT WELL. Eating well can help you improve your overall
Crohn's Disease. What causes Crohn s disease? What are the symptoms?
 Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Diverticular Disease Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
Medical Nutrition Therapy Goals
 Jeannine B. Mills MS,RD,CSO,LD Norris Cotton Cancer Center Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center Medical Nutrition Therapy Goals Prevent or reverse poor nutrition Maintain dose and schedule of cancer treatments
Jeannine B. Mills MS,RD,CSO,LD Norris Cotton Cancer Center Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center Medical Nutrition Therapy Goals Prevent or reverse poor nutrition Maintain dose and schedule of cancer treatments
Eat Well, Live Well Nutritional Guidelines for those 50+ April 10, 2014 Laura Vandervet, Registered Dietitian
 Eat Well, Live Well Nutritional Guidelines for those 50+ April 10, 2014 Laura Vandervet, Registered Dietitian Outline Benefits of healthy eating Meeting your nutritional requirements Using Canada s Food
Eat Well, Live Well Nutritional Guidelines for those 50+ April 10, 2014 Laura Vandervet, Registered Dietitian Outline Benefits of healthy eating Meeting your nutritional requirements Using Canada s Food
than 7%) can help protect your heart, kidneys, blood vessels, feet and eyes from the damage high blood glucose levels. October November 2014
 October November 2014 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Be Heart Smart: Know Your ABCs of Diabetes There is a strong
October November 2014 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Be Heart Smart: Know Your ABCs of Diabetes There is a strong
FIBER Healthy Eating Tip of the Month February
 FIBER Healthy Eating Tip of the Month February 2018 1 2 What is Fiber? Fiber is a carbohydrate found in plant foods that your body cannot digest. Soluble fiber: attracts water and turns to gel during digestion.
FIBER Healthy Eating Tip of the Month February 2018 1 2 What is Fiber? Fiber is a carbohydrate found in plant foods that your body cannot digest. Soluble fiber: attracts water and turns to gel during digestion.
JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD
 GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
GASTROENTEROLOGY JOHN MICHAEL ROACH, MD 520 N. 4 TH AVE. PASCO, WA 99301 Phone: (509) 546-8383 Name: Date of Birth: First Middle (full) Last m/d/yr Primary care provider: Referring physician: Local Pharmacy:
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
SSM Weight Loss Institute. Pre-Operative Nutrition Class
 SSM Weight Loss Institute Pre-Operative Nutrition Class Key Principles: liquids No carbonated beverages Do not drink 15 min before and 30 min after eating Caffeine: limit to 16 ounces/day No alcohol for
SSM Weight Loss Institute Pre-Operative Nutrition Class Key Principles: liquids No carbonated beverages Do not drink 15 min before and 30 min after eating Caffeine: limit to 16 ounces/day No alcohol for
Irritable Bowel. Syndrome. Health Promotion Service
 The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
Saratoga Schenectady Endoscopy Center, LLC Burnt Hills, N.Y Hemorrhoids. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Hemorrhoids National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins
Hemorrhoids National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins
HEALTH TIP #15 ALL NATURAL FIBRE FOOD & DRINK MIX
 HEALTH TIP #15 ALL NATURAL FIBRE FOOD & DRINK MIX WHY YOU MAY NEED THIS PRODUCT: When the colon doesn t do its job all organs suffer. Un-eliminated waste materials soaks back through the colon wall into
HEALTH TIP #15 ALL NATURAL FIBRE FOOD & DRINK MIX WHY YOU MAY NEED THIS PRODUCT: When the colon doesn t do its job all organs suffer. Un-eliminated waste materials soaks back through the colon wall into
P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K
 PATIENT HANDBOOK Heal Your Gut, Heal Your Body The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is one of the most sophisticated systems of the human body. We often think of the GI tract for its primary role in digesting
PATIENT HANDBOOK Heal Your Gut, Heal Your Body The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is one of the most sophisticated systems of the human body. We often think of the GI tract for its primary role in digesting
WHY DO WE NEED FOOD? FOOD AND DIET
 WHY DO WE NEED FOOD? FOOD AND DIET Food gives us the energy required for chemical reaction to keep us alive Energy also required for many activities and to maintain body temperature Food also gives us
WHY DO WE NEED FOOD? FOOD AND DIET Food gives us the energy required for chemical reaction to keep us alive Energy also required for many activities and to maintain body temperature Food also gives us
WHAT EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW ABOUT GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS IN WOMEN. By Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., FACG
 WHAT EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW ABOUT GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS IN WOMEN By Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., FACG Originally published in October 2002. Updated by Dr. Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., MACG in April 2007.
WHAT EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW ABOUT GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS IN WOMEN By Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., FACG Originally published in October 2002. Updated by Dr. Robyn G. Karlstadt, M.D., MACG in April 2007.
IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME
 IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents Here are some questions to ask your doctor. WHAT IS IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME? 4
IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents Here are some questions to ask your doctor. WHAT IS IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME? 4
Nutrition for the heart. Geoffrey Axiak Nutritionist
 Nutrition for the heart Geoffrey Axiak Nutritionist The Food Pyramid Dairy 2-3 servings Vegetables 3-5 servings Breads/Grains 6-11 servings Fats & Oils Use Sparingly Proteins 2-3 servings Fruits 2-4 servings
Nutrition for the heart Geoffrey Axiak Nutritionist The Food Pyramid Dairy 2-3 servings Vegetables 3-5 servings Breads/Grains 6-11 servings Fats & Oils Use Sparingly Proteins 2-3 servings Fruits 2-4 servings
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
What I need to know about Irritable Bowel Syndrome NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know
Nutrients. The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning.
 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
HEALTH TIPS FOR THE MONTH OF SEPTEMBER HEALTHY EATING IS IN YOUR MIND Continuous
 HEALTH TIPS FOR THE MONTH OF SEPTEMBER 2017 HEALTHY EATING IS IN YOUR MIND Continuous 5. Eat more healthy carbs and whole grains Choose healthy carbohydrates and fiber sources, especially whole grains,
HEALTH TIPS FOR THE MONTH OF SEPTEMBER 2017 HEALTHY EATING IS IN YOUR MIND Continuous 5. Eat more healthy carbs and whole grains Choose healthy carbohydrates and fiber sources, especially whole grains,
ENERGY NUTRIENTS: THE BIG PICTURE WHY WE EAT FUNCTIONS FATS FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN
 ENERGY NUTRIENTS: FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN Angeline B. David, DRPH, MHS NAD Health Summit March 14, 2013 The science of cooking is not a small matter.... This art should be regarded as the most valuable of
ENERGY NUTRIENTS: FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN Angeline B. David, DRPH, MHS NAD Health Summit March 14, 2013 The science of cooking is not a small matter.... This art should be regarded as the most valuable of
Nutrition Tips to Manage Your Diabetes
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu As part of your diabetes treatment plan, it is important to eat healthy, stay active and maintain a healthy body weight. This can help keep your blood sugar
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu As part of your diabetes treatment plan, it is important to eat healthy, stay active and maintain a healthy body weight. This can help keep your blood sugar
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
 Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
Low Copper Diet For Wilson's Disease
 Low Copper Diet For Wilson's Disease www.gicare.com Purpose Wilson's disease is a hereditary disorder in which the body retains too much copper. Copper is a trace mineral in the body. This means it is
Low Copper Diet For Wilson's Disease www.gicare.com Purpose Wilson's disease is a hereditary disorder in which the body retains too much copper. Copper is a trace mineral in the body. This means it is
