Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Visceral Nervous System. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
|
|
|
- Martin Nash
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Visceral Nervous System Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) zhanghq58@126.com Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University 1
2 The Visceral Nervous System 2
3 The Visceral nervous system Function: It control the visceral functions. And also helps control blood pressure, gastrointestinal motility & secretion, urinary bladder emptying, sweating,body tempreature & many other activities. Composition Visceral motor (efferent) nerves (autonomic nervous system) Sympathetic part Parasympathetic part Visceral sensory (afferent) nerves Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Glands 3
4 Visceral motor (efferent) nerves (Autonomic nervous system) Sympathetic part Parasympathetic part 4
5 Somatic and Autonomic Nervous System 5
6 Comparison of somatic & visceral efferent pathway acetylcholine Acetylcholine Norepinephrine acetylcholine 6
7 Main Differences Between Somatic Motor and Visceral Motor Nerve Somatic Visceral Effectors Skeletal muscles Cardiac, smooth muscles and glands Control From lower center to effector to require Voluntary (consciousness) Single neuron Involuntary (unconsciousness ) Two neurons: Preganglionic neuron, Postganglionic neuron Kind of fibers One Two: sympathetic & parasympathetic Fibers Thick myelinated Preganglionic: thin myelinated postganglionic: unmyelinated Distributive form Nerve trunk Nerve plexuses Transmitter Acetylcholine Preganglionic: acetylcholine postganglionic: Ach or NE Ach-acetylcholine. NE-nonepinephrine 7
8 Neurotransmitters-Learn by yourself Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic ACh ACh NE Striated muscle Heart Sm. mus. Glands ACh ACh Sweat glands ACh Parasympathetic ACh E, NE ACh Heart Sm. mus. Glands Ach- acetylcholine; E-epinephrin; NE-norepinephrine 8
9 Institution Sympathetic Nerve Lower center Peripheral part Lateral horn in gray matter of T1~L3 Sympathetic trunk Sympathetic ganglia Branches from sympathetic ganglia Sympathetic plexus 9
10 Sympathetic Part Lower center: located in intermediolateral nucleus (lateral gray horn) of spinal cord segments T1~L2 or L3 Sympathetic ganglia Paravertebral ganglia Prevertebral ganglia Transverse section of upper lumbar segment 10
11 Arranged on either side of vertebral column Consist of 19~24 of ovalshaped ganglia 3 in cervical part 11~12 in thoracic part 4-5 in lumbar part 3~4 in sacral part Ganglion impar unpaired on the anterior Paravertebral Ganglia surface of coccyx 11
12 Paravertebral Ganglia in the neck 1-Sup. cervical ganglion: largest, situated in front of transverse processes of C1~C3 vertebra 2-Mid. cervical ganglion: smallest, is at level of transverse processes of C6 vertebra 3-Inf.cervical ganglion: situated at level of C7 vertebra, and may be fused with first thoracic ganglion to form cervicothoracic ganglion
13 Paravertebral ganglia in the thorax & lumbar Thoracic paravertebral ganglia lumbar paravertebral ganglia 13
14 Sympathetic Trunk Formed by paravertebral ganglia & interganglionic branches Lie on either side of vertebral column from base of skull to coccyx The trunks of two side unite in front of the coccyx at a small swelling, the ganglion impar Sympathetic trunk in thorax 14
15 Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University Mediastinum-lateral view (from left & right side) Sympathetic trunk Lateral view (left) Lateral view (right) Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University
16 Prevertebral Ganglia 1 Lie anteriorly to vertebral column and near the arteries for which they are named 1-Celiac ganglia (2) 2-Aorticorenal ganglia(2) 3-Sup.mesenteric ganglion 4-Inf. mesenteric ganglion
17 Communicating branches Concept : communicating branches is the nerve between sympathetic trunk and ant.branches of spinal nerves. White communicating branches: myelinated preganglionic fiber looks like white in fresh. Gray communicating branches: unmyelinated postganglionic fiber looks like gray in fresh. Grey communicating branch White communicating branch 17
18 Preganglionic Fibers Preganglionic fibers 15 pairs white communicating branches Sympathetic trunk (only spinal levels T1~L3 have white communicating branch) 18
19 Three Fates of Preganglionic Fibers 1. Relay in corresponding ganglion 2. Ascend or descend in sympathetic trunk and relay in higher or lower ganglion 3. Pass without synapse to a prevertebral ganglion for relay
20 Comparison of somatic & visceral efferent pathway 20
21 Preganglionic Fibers 1-Greater splanchnic nerve formed by preganglionic fibers from T5~T9 ganglia, and relay in celiac ganglion. 2-Lesser splanchnic nerve formed by preganglionic fibers from T10~T12 ganglia, and relay in aorticorenal ganglion. Their postganglionic fibers supply the liver, spleen, kidney and alimentary tract as far as the left colic flexure
22 Right view of thoracic cavity 22
23 Preganglionic Fibers Lumbar splanchnic nerve Formed by preganglionic fibers from L1~L4 ganglia, and relay in prevertebral ganglia. The postganglionic fibers supply descending and sigmoid colon, rectum, pelvic viscera and lower limbs. 23
24 Three Fates of Postganglionic Fibers Back to a spinal nerve along gray communicating branches to terminate in blood vessels, arrectores pilorum m. & sweat glands of head, neck, trunk and limbs The fibers form their network around blood vessels passing to visceral end organs Terminate directly in certain organs
25 Distribution of Sympathetic Nerve Preganglionic fibers T1~T5 T5~T12 L1~L3 Postganglionic fibers Head, neck, upper limb and thoracic viscera Abdominal viscera Pelvic viscera and lower limb 25
26 General description of sympathetic system Postganglionic fiber: Skin Sweat gland Arrectores pilorum Blood vessel Arrectores pilorum 1celiac ganglion 2sup.mesenteric ganglion 3inf.mesenteric ganglion Preganglionic fiber-red Postganglionic fiber-black: 26
27 Parasympathetic portion 27
28 Parasympathetic Part Lower center located in four pairs parasympathetic nuclei in brain stem and the sacral parasympathetic nucleus in segments S2~S4 of spinal cord Parasympathetic ganglia: terminal ganglia are near or within the wall of a visceral organ Para-organ ganglia Ciliary ganglion Pterygopalatine ganglion Submandibular ganglion Otic ganglion Intra-organ ganglia 28
29 General description of parasympathatic nerve Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University 29 Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University
30 Cranial portion of parasympathetic nerve 1 Ⅲ ciliary ganglion sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles Ⅸ Ⅶ pterygopalatine ganglion submandibular ganglion lacrimal gland sublingual gland submandibular gland Ⅹ 1 Accessory n of Ⅲ 2 Sup.solivatory n. 3 Inf.solivatory n. 4 Dorsal n.of Ⅹ otic ganglion terminal ganglia In or near the target organs parotid gland heart, lungs, liver, spleen kidneys,alimentary tract as far as left colic flexure 30
31 (a) The abdominal componets of sympathetic nervous system (a)collateral ganglia and the abdominal aortic plexus(b)the adrenal gland,frontal section showing the sympathetic adrenal medulla. (b) 31
32 Sacral Portion of Parasympathetic Nerve Preganglionic fibers from sacral parasympathetic nucleus leave spinal cord with ant.roots of the spinal n. S 2 ~S 4, Then leave sacral n. & form pelvic splanchnic n. & travel by way of pelvic plexus to terminal ganglia in pelvic cavity Postganglionic fibers terminate in descending & sigmoid colon, rectum (below the left colic flexure) & pelvic viscera 32
33 Main differences between sympathetic & parasympathetic nerve Content Sympathetic n. Parasympathetic n. Location of lower center Intermediolateral nucleus (lateral gray horn) of spinal cord segments T1~L3 Four pairs parasympathetic nuclei and sacral parasympathetic nucleus Ganglia position Paravertebral, prevertebral Para-organ or intra-organ ganglia Length of preganglionic fiber. Length of postganglionic fiber. Ratio of Pre. to postganglionic neuron Distributions Different effects to visceral organs Shorter Longer Longer Shorter 1 to many 1 to a few Wider. throughout the body viscera of head. thorax, abdomen, and pelvis Prepares for emergency situation (expends energy) Limited.No in blood vessel.sweat glands, arrectores pilorum, medullary part of suprerenal gland. Conserve and restore body energy (conserves energy) 33
34 General description of parasympathatic nerve 34
35 Main differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve The location of ganglia 35
36 Functional differences between sympathetic & parasympathetic nerve Content Sympathetic n. Parasympathetic n. Different action Prepares for emergency situation ( Fight or flight ) Conserve and restore body energy (Silence and sleep) Pupil Dilates Constricts Heart contraction Increases Decreases force Heart rate Become more rapid Become slow Respiration rate Increase Decrease Blood pressure Increase Decrease Bronchi Dilates Constricts 36
37 Functions of the iris Dim light:-iris dilates Sympathetic neurone Normal light Dilator pupillae Sphincter pupillae Pupil Parasympathetic neurone Ganglion Bright light:-iris constricts 37
38 Sympathetic and vasomotor tone 38
39 Blood pressure reflex regulation 39
40 Visceral plexus The plexus are aggregations of the sympathetic & parasympathetic & visceral sensory nerve. Cardiac plexuses Superficial plexus below aortic arch Deep plexus Ant. to bifurcation of trachea Pulmonary plexus Ant. Pulmonary plexus in front of pulmonary root Post.pulmonary plexus in rear of pulmonary root 40
41 Visceral Plexuses Celiac plexus Largest plexus Located around the root celiac a. & Sup.mesenteric a. Abdominal aortic plexus Located below celiac plexus Hypogastric plexus Celiac plexus Superior hypogastric plexus lie between common iliac aa. Inferior hypogastric plexus (pelvic plexus) Lie in both side of rectum 41
42 Functions of the Autonomic NS Sympathetic nerve Parasympathetic nerve 3-F 3-S Fight Silence Flight Sleep Fright Sex -42-
43 Visceral Sensory (afferent) n. Conduct the impulses from enteroceptors of the viscera to the CNS. The CNS adjusts the visceral action by the visceral motor nerve. Three conductive pathway. 1.Synapse with the visceral efferent neuron to form the viscero-visceral reflex. 2,Synapse with the somatomotor neurons to form the viscero-somatic reflex. 3.Conduct the impulse to the cortex through a complex pathway to give birth to the visceral sensation. 43
44 Feature of Visceral Sensory n. With higher pain threshold: Contrast to the somatosensory fibers, the number of the visceral sensory fibers is less,and most fibers is thinner & have a higher pain threshold. Not sensitive to pain,but sensitive to hungry, dialation (bladder,rectum) Not sensitive to cutting but sensitive to temperature,ischemia & stretch 44
45 Feature of Visceral Sensory n. Diffusive visceral pain: The afferent pathway of the visceral sensation is more diffusive than the somatosensory ones. e.g.the sensory fibers from a visceral organ pass through several segments of spinal n.to the central centres.& a spinal n.may contain the sensory fibers from several organ.so the visceral pain is diffusive and can not be orientated preferably. 45
46 Visceral Sensory Nerves Nucleus of solitary tract Enteroceptors Ⅶ,Ⅸ, Ⅹ Thalamus Cerebral cortex Posterior horn Hypothalamus Sympathetic nerve Pelvic splanchnic nerve Somatic motor neurons visceral motor neuclei Effectors 46
47 Centers of Visceral Sensory Nerves There are a few representative motor areas in the limbic lobe of the cerebrum: Respiration; Blood pressure ;Gastrointestine; Bladder pupil etc. Hypothalamus also regulate visceral activity: low center of sympathetic and parasympathetic n. Brain stem and cerebellum: Brain stem directly regulate the functions of the respiration and cardiovascular activities. 47
48 Referred Pain Sometimes,when a viscera is in phthological conditions or received excessive stimulation,a certain region innervated by somatic n.will feel pain. The phenomena is called the referred pain. Pain originating from organs perceived as coming from skin.site of pain may be distant from organ For example: When patient suffers from heart discease may feel pain in on the medial side of the left arm. patient suffering from hepatic or cystic disease may feel pain in the right shoulder. 48
49 Mechanism of referred Pain The mechanism of the referred pain is thought that same spinal segment controls both the diseased viscera and the surface region,and the impulse from the diseased viscera can pervade to the adjacent somatic sensory neurons & produce pain. 49
50 From the viscera is often felt in specific areas of the skin When some viscera suffer from disease,related referred pain area 50
51 Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University 体重达 550 公斤的曼努埃尔 Weight 465kg,lose weight 272kg Within five years Weight 550kg 据英国 每日邮报 11 月 20 日报道, 来自美国德克萨斯州的梅拉 罗萨莱斯 (Mayra Rosales) 体重 460kg 在五年内成功减掉 272 公斤 Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University
52 The end 6.1kg newborn The fattest person family Whose name is liang yong (210kg) 52
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY
 Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni
 Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.)
 Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Organisation of the nervous system
 Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Part 1. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Stimulatory
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: DIVISIONS AND STRUCTURE The Autonomic Nervous System and its Divisions: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) controls
!! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: DIVISIONS AND STRUCTURE The Autonomic Nervous System and its Divisions: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) controls
Fig Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata. Integrating center. Receptor. Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
 Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 14 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 14 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Autonomic Nervous System. Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24
 Autonomic Nervous System Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24 OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS PNS BRAIN SPINAL CORD SOMATIC ANS SYMPATHEIC PARASYMPATHEIC LOCATION OF GANGLIA IN THE ANS Short post-ganglionic
Autonomic Nervous System Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24 OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS PNS BRAIN SPINAL CORD SOMATIC ANS SYMPATHEIC PARASYMPATHEIC LOCATION OF GANGLIA IN THE ANS Short post-ganglionic
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors. Chapter 9. Autonomic Motor Nerves. Autonomic Neurons. Autonomic Ganglia. Autonomic Neurons 9/19/11
 Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
4/8/2015. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS. Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013
![[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013 [ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013](/thumbs/86/93473883.jpg) Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
4/9/2019. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
The Autonomic Nervous
 Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Divisions of ANS. Divisions of ANS 2 Divisions dualing innervate most organs. Autonomic Nervous System (Chapter 9)
 Autonomic Nervous System (Chapter 9) Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) general properties anatomy Autonomic Effects on Target Organs Subs of Nervous System Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral
Autonomic Nervous System (Chapter 9) Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) general properties anatomy Autonomic Effects on Target Organs Subs of Nervous System Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall
 Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
Chapter 16. Autonomic nervous system. AP2 Chapter 16: ANS
 Chapter 16 Autonomic nervous system AP2 Chapter 16: ANS 1 Quick Review Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Division Motor Division Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous
Chapter 16 Autonomic nervous system AP2 Chapter 16: ANS 1 Quick Review Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Division Motor Division Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous
Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions
 16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
Introduction to The Autonomic Nervous System. Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic Divisions. Adrenergic and Cholinergic Fibers. ANS Neurotransmitters
 Chapter 15 Introduction to The Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic Divisions Adrenergic and Cholinergic Fibers ANS Neurotransmitters Autonomic Nervous System Portion of the nervous
Chapter 15 Introduction to The Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic Divisions Adrenergic and Cholinergic Fibers ANS Neurotransmitters Autonomic Nervous System Portion of the nervous
Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System
 Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Why This Matters Understanding the autonomic
Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Why This Matters Understanding the autonomic
Group of students. - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e
 - 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
- 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D.
 Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
cardiac plexus is continuous with the coronary and no named branches pain from the heart and lungs
 Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System Responsible for control of visceral effectors and visceral reflexes: smooth muscle, glands, the heart. e.g. blood pressure, cardiac output, plasma glucose The autonomic system
The Autonomic Nervous System Responsible for control of visceral effectors and visceral reflexes: smooth muscle, glands, the heart. e.g. blood pressure, cardiac output, plasma glucose The autonomic system
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Objectives 1. Describe the CNS components of the ANS 2. Understand the peripheral pathways that connect the ANS with targets in the body. 3. Understand the classes of disorders
Autonomic Nervous System Objectives 1. Describe the CNS components of the ANS 2. Understand the peripheral pathways that connect the ANS with targets in the body. 3. Understand the classes of disorders
Autonomic Division of NS
 Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs. János Hanics M.D.
 Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs János Hanics M.D. Vegetative (autonomic) nervous system General function: to keep the homeostasis of
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs János Hanics M.D. Vegetative (autonomic) nervous system General function: to keep the homeostasis of
The Nervous System PART D. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
Introduction. Autonomic means self-governed ; the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will
 Introduction Autonomic means self-governed ; the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will It regulates fundamental states and life processes such as heart rate, BP, and body temperature
Introduction Autonomic means self-governed ; the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will It regulates fundamental states and life processes such as heart rate, BP, and body temperature
Neuropsychiatry Block
 Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system
 Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Autonomic nervous system
 Autonomic nervous system 1. Autonomic nervous system (ANS) nomenclature 2. Topographic organization and structural features of ANS 3. Main subdivisions of the ANS: sympathetic nervous system parasympathetic
Autonomic nervous system 1. Autonomic nervous system (ANS) nomenclature 2. Topographic organization and structural features of ANS 3. Main subdivisions of the ANS: sympathetic nervous system parasympathetic
Autonomic nervous system
 Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56161 1 Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System * Stephanie Fretham Based on Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
OpenStax-CNX module: m56161 1 Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System * Stephanie Fretham Based on Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Autonomic Nervous System. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Introduction to Autonomic
 Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamus
 Lu Chen LSA room 201 Phone: (510) 643-8163 Email: luchen@berkeley.edu Office hours: M,W,F, 10-11 am 1 Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamus Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 2 Hypothalamus Brain stem
Lu Chen LSA room 201 Phone: (510) 643-8163 Email: luchen@berkeley.edu Office hours: M,W,F, 10-11 am 1 Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamus Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 2 Hypothalamus Brain stem
Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System. Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition. Martini & Ober
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Spinal nerves. Aygul Shafigullina. Department of Morphology and General Pathology
 Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
The Nervous System. Autonomic Division. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the portion of the nervous system which innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & glands, & controls the visceral functions of the
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the portion of the nervous system which innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & glands, & controls the visceral functions of the
T. Laitinen Departments of Physiology and Clinical Physiology, University of Kuopio and Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland
 AUTONOMOUS NEURAL REGULATION T. Laitinen Departments of Physiology and Clinical Physiology, University of Kuopio and Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland Keywords: Autonomic nervous system, sympathetic
AUTONOMOUS NEURAL REGULATION T. Laitinen Departments of Physiology and Clinical Physiology, University of Kuopio and Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland Keywords: Autonomic nervous system, sympathetic
Do Now pg What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in.
 Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
The Autonomic Nervous System
 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully integrate text
14 The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully integrate text
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology
 The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Lesson 33. Objectives: References: Chapter 16: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 16:
 Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System(ANS)
 Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System(ANS) ANS Pharmacology Lecture 1 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy, University of Sulaimani 2018-2019 AUTOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS) The ANS is the major
Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System(ANS) ANS Pharmacology Lecture 1 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy, University of Sulaimani 2018-2019 AUTOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS) The ANS is the major
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS):
 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical 1 st year students, 2017/2018. ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Textbook of Medical Physiology,
University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical 1 st year students, 2017/2018. ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Textbook of Medical Physiology,
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 13 Done by Tamara Wahbeh Corrected by Doctor Omar Shaheen In this sheet the following concepts will be covered: 1. Divisions of the nervous system 2. Anatomy of the ANS. 3. ANS innervations. 4.
number 13 Done by Tamara Wahbeh Corrected by Doctor Omar Shaheen In this sheet the following concepts will be covered: 1. Divisions of the nervous system 2. Anatomy of the ANS. 3. ANS innervations. 4.
Organization of Nervous System: Comparison of Somatic vs. Autonomic: Nervous system. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS)
 NS Parasympathetic Somatic NS Organization of Nervous System: Nervous system Comparison of Somatic vs. : Cell body location NTs organs Marieb & Hoehn Figure 14.2 Ganglion: A group of cell bodies located
NS Parasympathetic Somatic NS Organization of Nervous System: Nervous system Comparison of Somatic vs. : Cell body location NTs organs Marieb & Hoehn Figure 14.2 Ganglion: A group of cell bodies located
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Academic Resource Center. Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
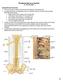 Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Mohd.Khatatbeh
 10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
Physiologic Anatomy and Nervous Connections of the Bladder
 Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
Overview of the autonomic (vegetative) nervous system
 Overview of the autonomic (vegetative) nervous system 1 The nervous system for topographic indication is divided into two divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) i peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Overview of the autonomic (vegetative) nervous system 1 The nervous system for topographic indication is divided into two divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) i peripheral nervous system (PNS).
When motor nervous severed (cut, damaged), SK. Ms enter state of paralysis & atrophy
 11/25/2012 1 Somatic NS have their cell bodies within CNS Conduct impulses along single axon from spinal cord to neuromuscular junction Send axon to SK.M Muscles consciously induced to contract or relax
11/25/2012 1 Somatic NS have their cell bodies within CNS Conduct impulses along single axon from spinal cord to neuromuscular junction Send axon to SK.M Muscles consciously induced to contract or relax
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System 6 th March, 2015 & 19 th March, 2015 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Autonomic Nervous System Role
Autonomic Nervous System 6 th March, 2015 & 19 th March, 2015 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Autonomic Nervous System Role
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
